中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (06): 760-768.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0461
所属专题: 肿瘤最新文章合辑; 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑; 数智医疗最新文章合辑
涂嘉欣1, 叶惠清1, 张小强2, 林雪婷1, 杨善岚1, 邓莉芳1, 吴磊1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-20
修回日期:2022-08-21
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-08-25
通讯作者:
吴磊
基金资助:
TU Jiaxin1, YE Huiqing1, ZHANG Xiaoqiang2, LIN Xueting1, YANG Shanlan1, DENG Lifang1, WU Lei1,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-20
Revised:2022-08-21
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-08-25
Contact:
WU Lei
About author:摘要: 背景 随着近20余年人工智能(AI)在食管癌领域应用研究的骤增,出现了许多关于该研究的系统、荟萃分析等,但其仅针对AI在该领域应用的单一方面的总结研究,研究人员难以全面了解领域最新发展与研究热点。 目的 通过文献计量分析总结AI在食管癌领域的应用,阐明AI在食管癌领域相关研究的进展、热点和新兴趋势。 方法 检索Web of Science Core Collection(WoSCC)的Science Citation Index Expanded(SCI-E)数据库收录的AI应用于食管癌领域的所有英文文献,检索时间2000-01-01至2022-04-06。应用Microsoft Excel 2019、CiteSpace(5.8R3-64bit)和VOSviewer(1.6.18)对文献进行发文量、国家、作者、机构、共被引和关键词分析。 结果 2000—2022年共检索到AI应用于食管癌领域的文献918篇,共计引用文献总量23 490篇。发文趋势:2000—2016年为迟缓期,发文量从6篇增至40篇;2017—2022年为快速增长期,发文量从62篇突增至216篇。60个国家、118家机构、5 979位作者参与了AI在食管癌领域应用的研究,发文量排名前3位的国家分别是中国(306篇)、美国(238篇)、英国(113篇),机构合作强度排名前3位的分别是阿姆斯特丹大学〔连线粗细(TLS)=72〕、凯瑟琳娜医院(TLS=64)、埃因霍芬大学(TLS=53),发文量排名前3位的作者是荷兰的作者Jacques J G H M Bergman(16篇)、日本的作者Tomohiro Tada(12篇)、荷兰的作者Fons Van Der Sommen(12篇)。共被引作者39 962位,共被引文献42 992篇。AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究的突现关键词共33个,早期(2001—2008年):突现关键词以p53、突变为主;中期(2013—2018年):以食管癌分类、检查新技术(断层扫描)以及食管癌和不同癌症之间区分、鉴别和比较为主;近期(2019—2022年):以深度学习、卷积神经网络、机器学习在食管癌检查、诊断应用为最新前沿,且深度学习一词突现强度排在33个突现关键词首位(突现强度为13.89)。 结论 AI在食管癌领域的相关研究已迈入新阶段,从基因、突变逐步朝精准检查、诊断和治疗方向发展,深度学习、卷积神经网络、机器学习在食管癌检查、诊断应用为近期(2019—2022年)AI应用于食管癌领域的最新前沿。未来AI应用于食管癌的挑战可能主要集中在食管癌个体化数据收集、数据质量、数据处理规范、AI代码复现、辅助诊断可信度决策上。
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 | 文献数量(篇) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | esophag* (Topic) or oesophag* (Topic) or gullet (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 103 423 |
| 2# | cancer* (Topic) or tumour* (Topic) or tumor* (Topic) or neoplas* (Topic) or onco* (Topic) or carcinoma* (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 3 272 272 |
| 3# | 1# AND 2# | 54 077 |
| 4# | "artificial intelligen*" (Topic) or computational NEAR/5 intelligence (Topic) or expert* system* (Topic) or intelligent learning (Topic) or feature* extraction (Topic) or feature* mining (Topic) or feature* learning (Topic) or machine learning (Topic) or feature* selection (Topic) or unsupervised clustering (Topic) or image* segmentation (Topic) or supervised learning (Topic) or semantic segmentation (Topic) or deep network* (Topic) or bayes* network (Topic) or deep learning (Topic) or neural network* (Topic) or neural learning (Topic) or neural nets model (Topic) or artificial neural network (Topic) or data mining (Topic) or graph mining (Topic) or data clustering (Topic) or big data (Topic) or knowledge graph (Topic) or AI (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 1 068 667 |
| 5# | 3# AND 4# | 1 074 |
表1 2000—2022年AI在食管癌领域研究文献检索策略
Table 1 List of esophageal cancer studies using AI published from 2000 to 2022
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 | 文献数量(篇) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | esophag* (Topic) or oesophag* (Topic) or gullet (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 103 423 |
| 2# | cancer* (Topic) or tumour* (Topic) or tumor* (Topic) or neoplas* (Topic) or onco* (Topic) or carcinoma* (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 3 272 272 |
| 3# | 1# AND 2# | 54 077 |
| 4# | "artificial intelligen*" (Topic) or computational NEAR/5 intelligence (Topic) or expert* system* (Topic) or intelligent learning (Topic) or feature* extraction (Topic) or feature* mining (Topic) or feature* learning (Topic) or machine learning (Topic) or feature* selection (Topic) or unsupervised clustering (Topic) or image* segmentation (Topic) or supervised learning (Topic) or semantic segmentation (Topic) or deep network* (Topic) or bayes* network (Topic) or deep learning (Topic) or neural network* (Topic) or neural learning (Topic) or neural nets model (Topic) or artificial neural network (Topic) or data mining (Topic) or graph mining (Topic) or data clustering (Topic) or big data (Topic) or knowledge graph (Topic) or AI (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 1 068 667 |
| 5# | 3# AND 4# | 1 074 |
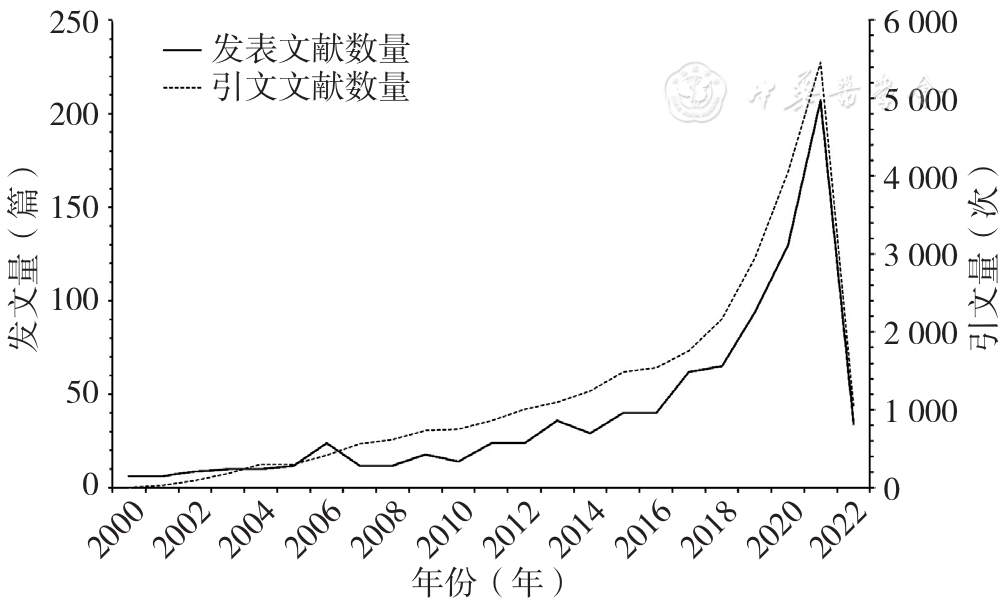
图1 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究的年发文、引文数量
Figure 1 Annual number of publications and citations of global esophageal cancer research using AI from 2000 to 2022
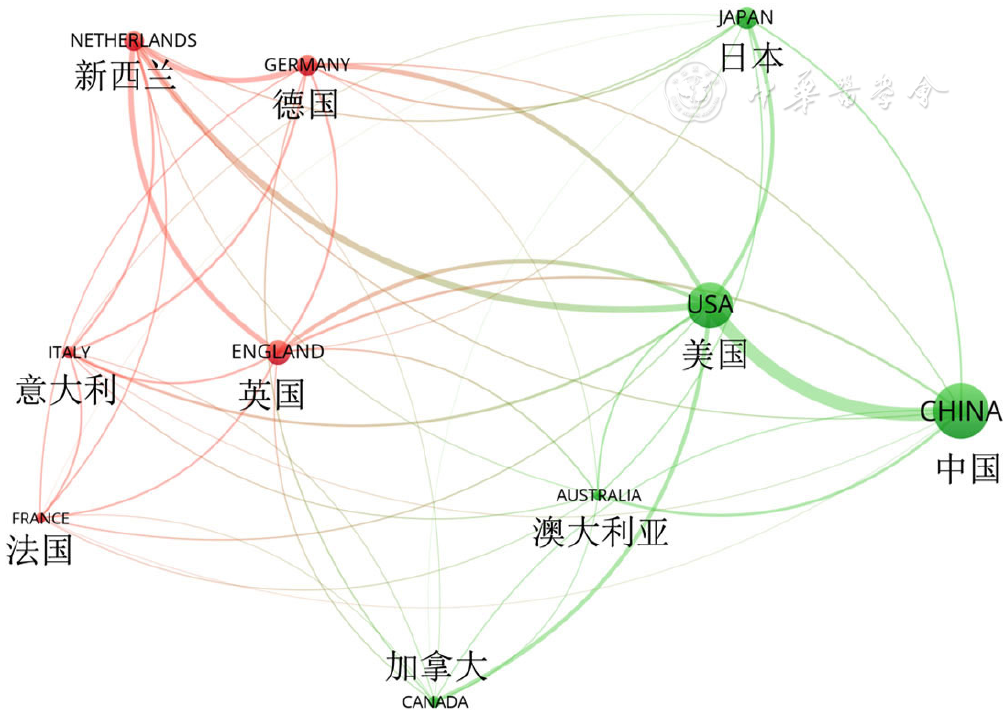
图2 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究国家合作VOSviewer可视化图(前10位)
Figure 2 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of top 10 research countries related to esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
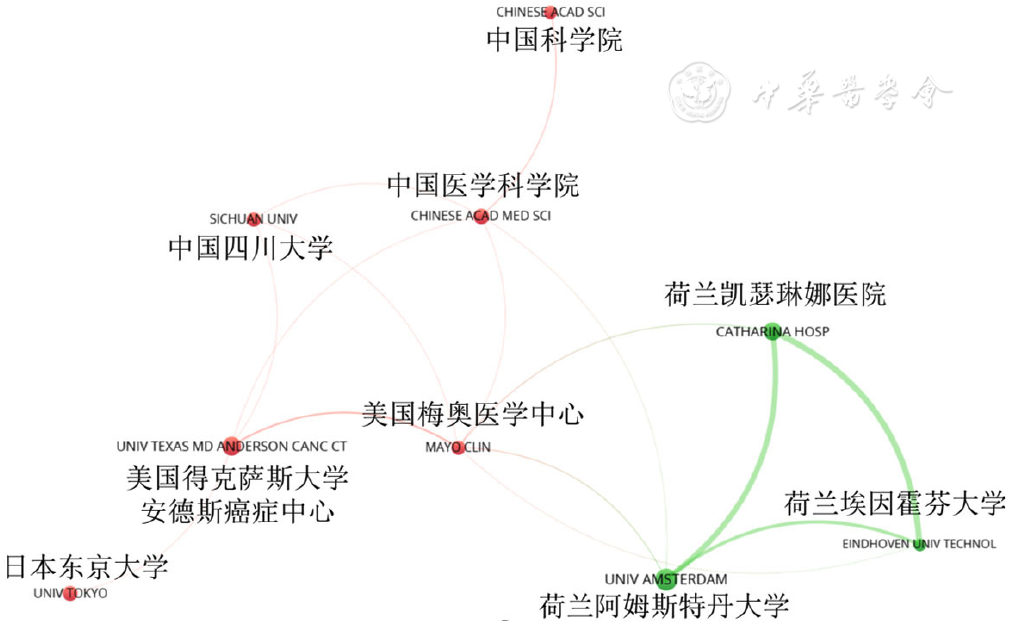
图3 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究机构合作VOSviewer可视化图(发文量>15篇)
Figure 3 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of institutions published more than 15 esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
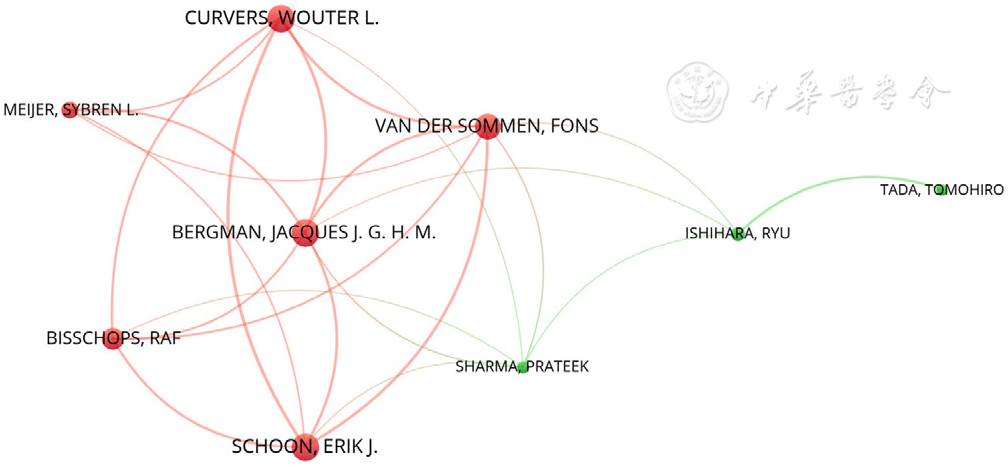
图4 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究作者合作VOSviewer可视化图(发文量>10篇)
Figure 4 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of authors published more than 10 esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
| 序号 | 共被引作者 | 地区 | 共被引次数(次) | 总被引次数(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Freddie Ian Bray | 法国 | 89 | 304 | 0 |
| 2 | Prateek Sharma | 美国 | 87 | 1 907 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Yoshimasa Horie | 日本 | 56 | 691 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Jacques Ferlay | 法国 | 53 | 748 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jesper Lagergren | 瑞典 | 52 | 1 591 | 0.15 |
| 6 | Lambin Philippe | 比利时 | 46 | 562 | 0.04 |
| 7 | Rebecca L Siegel | 美国 | 46 | 417 | 0 |
| 8 | Hirasawa Toshiaki | 日本 | 45 | 1 025 | 0.06 |
| 9 | Nicholas James Shaheen | 美国 | 45 | 136 | 0.04 |
| 10 | Thomas William Rice | 美国 | 43 | 1 107 | 0.12 |
表2 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究作者共被引次数(前10位)
Table 2 Total co-citations of esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022 by author (top 10)
| 序号 | 共被引作者 | 地区 | 共被引次数(次) | 总被引次数(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Freddie Ian Bray | 法国 | 89 | 304 | 0 |
| 2 | Prateek Sharma | 美国 | 87 | 1 907 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Yoshimasa Horie | 日本 | 56 | 691 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Jacques Ferlay | 法国 | 53 | 748 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jesper Lagergren | 瑞典 | 52 | 1 591 | 0.15 |
| 6 | Lambin Philippe | 比利时 | 46 | 562 | 0.04 |
| 7 | Rebecca L Siegel | 美国 | 46 | 417 | 0 |
| 8 | Hirasawa Toshiaki | 日本 | 45 | 1 025 | 0.06 |
| 9 | Nicholas James Shaheen | 美国 | 45 | 136 | 0.04 |
| 10 | Thomas William Rice | 美国 | 43 | 1 107 | 0.12 |
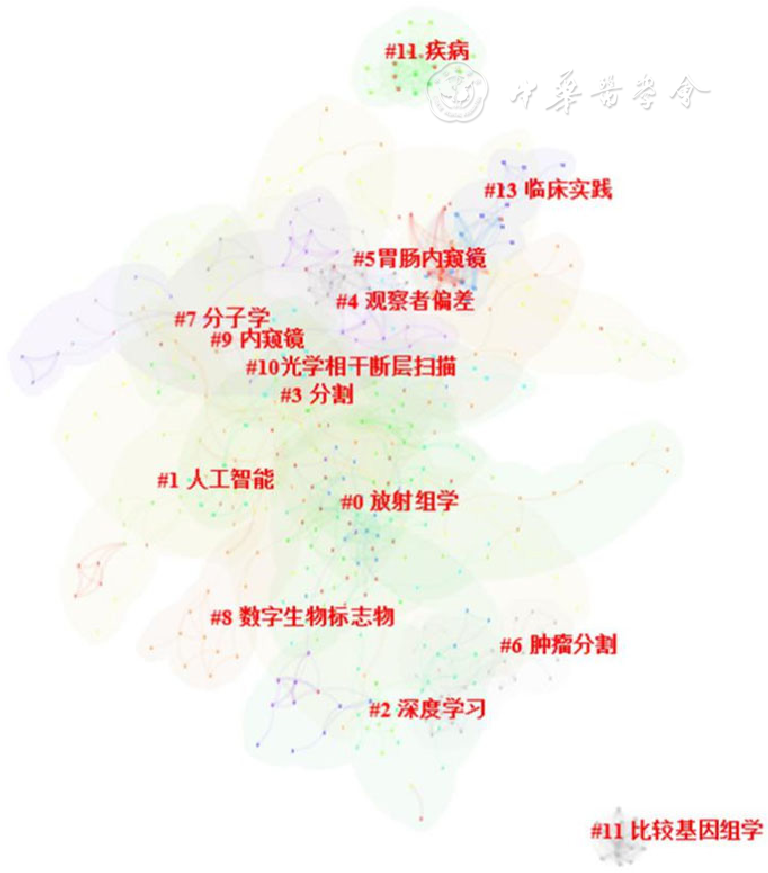
图5 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究共被引文献聚类分析图谱(前14位聚类团)
Figure 5 The cluster analysis map of co-cited esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022(top 14 clusters)
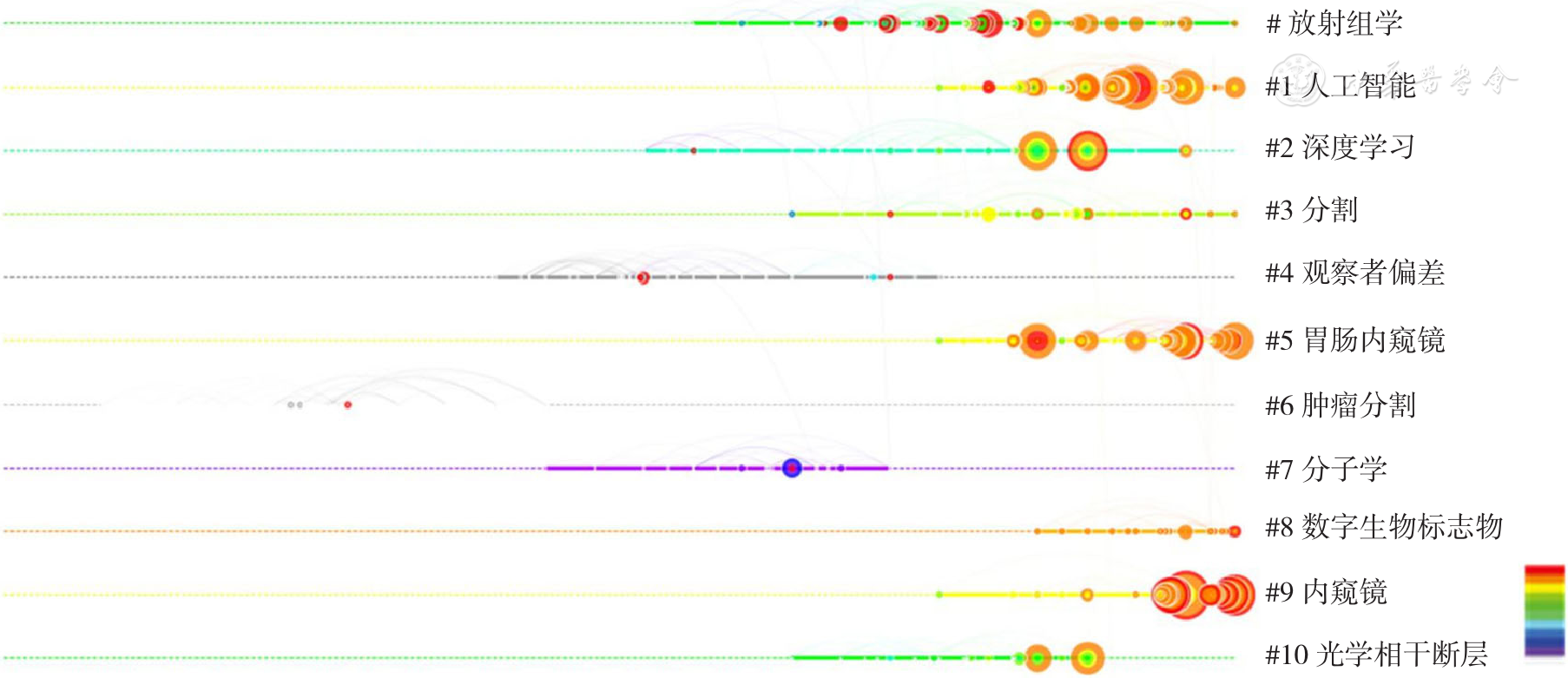
图6 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究共被引文献主要聚类团共被引文献出现时间演变规律注:时间演变以颜色变化表示,表示从下往上时间为2000—2022年
Figure 6 The co-citation cluster analysis of time evolution about co-cited documents in main clusters from 2000 to 2022
| 序号 | 文章题目 | 期刊名称 | 第一作者 | 出版年份(年) | 共被引次数(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global cancer statistics 2018:Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | BRAY | 2018 | 87 |
| 2 | Diagnostic outcomes of esophageal cancer by artificial intelligence using convolutional neural networks | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | HORIE | 2019 | 56 |
| 3 | Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images | Gastric Cancer | HIRASAWA | 2018 | 43 |
| 4 | Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | GUO | 2019 | 37 |
| 5 | Deep-learning system detects neoplasia in patients with barrett's esophagus with higher accuracy than endoscopists in a multistep training and validation study with benchmarking | Gastroenterology | DE GROOF | 2020 | 32 |
| 6 | Endoscopic detection and differentiation of esophageal lesions using a deep neural network | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | OHMORI | 2020 | 32 |
| 7 | Using a deep learning system in endoscopy for screening of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (with video) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | CAI | 2019 | 31 |
| 8 | Computer-assisted diagnosis of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using narrow-band imaging magnifying endoscopy | Endoscopy | ZHAO | 2019 | 30 |
| 9 | Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma | Nature | KIM | 2017 | 30 |
| 10 | Cancer statistics in China,2015 | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | CHEN | 2016 | 30 |
表3 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究共被引文献(前10位)
Table 3 The analysis of co-cited esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022(top 10)
| 序号 | 文章题目 | 期刊名称 | 第一作者 | 出版年份(年) | 共被引次数(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global cancer statistics 2018:Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | BRAY | 2018 | 87 |
| 2 | Diagnostic outcomes of esophageal cancer by artificial intelligence using convolutional neural networks | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | HORIE | 2019 | 56 |
| 3 | Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images | Gastric Cancer | HIRASAWA | 2018 | 43 |
| 4 | Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | GUO | 2019 | 37 |
| 5 | Deep-learning system detects neoplasia in patients with barrett's esophagus with higher accuracy than endoscopists in a multistep training and validation study with benchmarking | Gastroenterology | DE GROOF | 2020 | 32 |
| 6 | Endoscopic detection and differentiation of esophageal lesions using a deep neural network | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | OHMORI | 2020 | 32 |
| 7 | Using a deep learning system in endoscopy for screening of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (with video) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | CAI | 2019 | 31 |
| 8 | Computer-assisted diagnosis of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using narrow-band imaging magnifying endoscopy | Endoscopy | ZHAO | 2019 | 30 |
| 9 | Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma | Nature | KIM | 2017 | 30 |
| 10 | Cancer statistics in China,2015 | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | CHEN | 2016 | 30 |
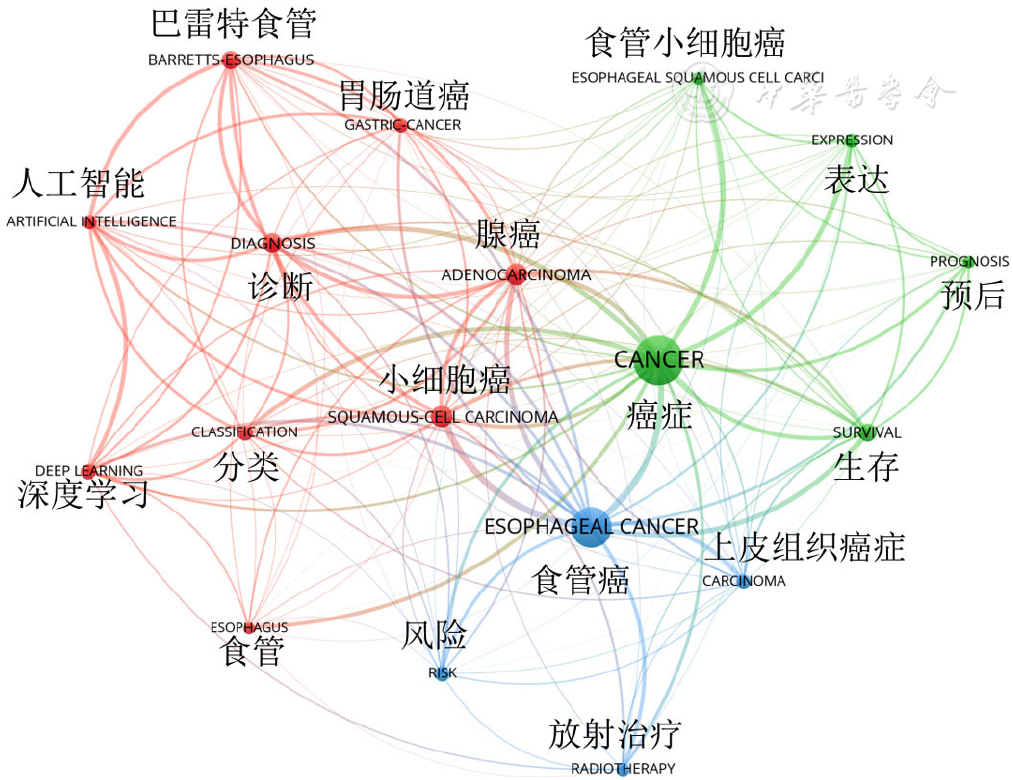
图7 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究关键词共线图谱VOSviewer可视化图(出现频率≥50次)
Figure 7 VOSviewer network visualization of the collinear map of keywords (frequency ≥ 50) in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
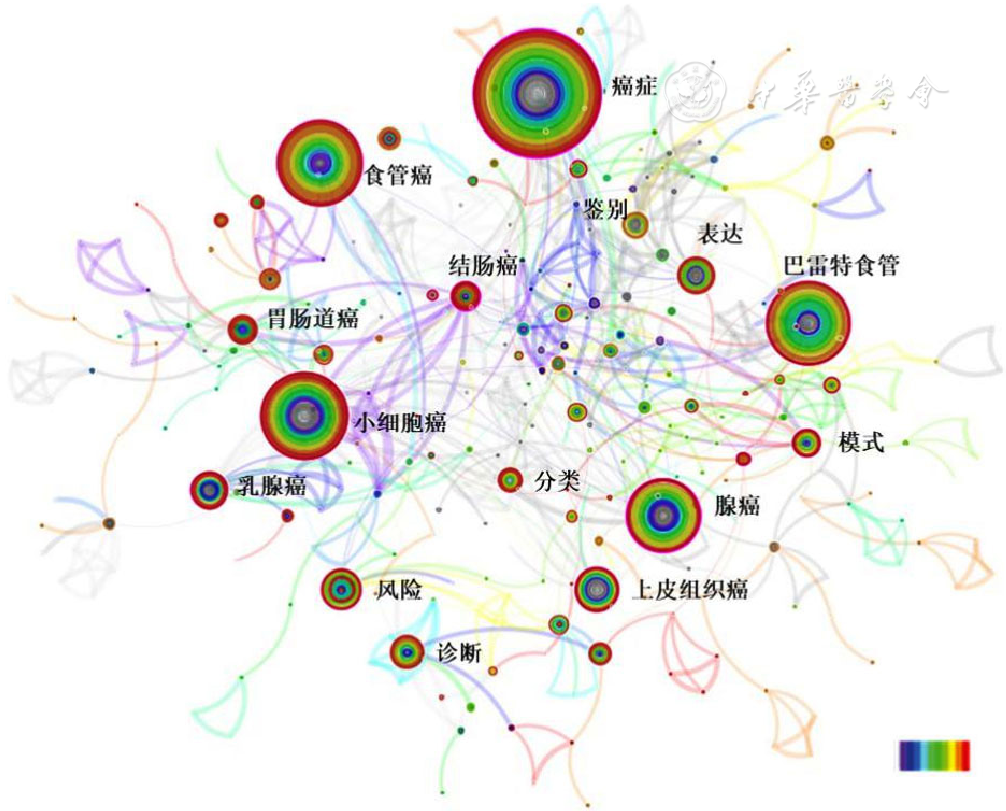
图8 2000—2016年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究关键词CiteSpace可视化共现图谱注:时间演变以颜色变化表示,表示从左往右时间为2000—2016年;圆圈大小代表关键词频率高低,连线粗细代表共线关系强弱
Figure 8 CiteSpace-generated visualized co-occurrence map of keywords in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2016
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.31 | 16 | 2000 | 结直肠癌 |
| 2 | 0.23 | 71 | 2000 | 癌症 |
| 3 | 0.23 | 41 | 2000 | 上皮小细胞癌 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 49 | 2000 | 小细胞癌 |
| 5 | 0.19 | 6 | 2005 | 突变 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 47 | 2003 | 巴雷特食管癌 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 48 | 2000 | 食管癌 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 21 | 2001 | 乳腺癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 6 | 2001 | p53 |
| 10 | 0.13 | 25 | 2001 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 11 | 0.12 | 10 | 2003 | 肿瘤 |
| 12 | 0.11 | 23 | 2007 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.11 | 8 | 2015 | 食管腺癌 |
表4 2000—2016年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究中心性>0.10关键词信息表
Table 4 Keywords with centrality greater than 0.10 in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2016
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.31 | 16 | 2000 | 结直肠癌 |
| 2 | 0.23 | 71 | 2000 | 癌症 |
| 3 | 0.23 | 41 | 2000 | 上皮小细胞癌 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 49 | 2000 | 小细胞癌 |
| 5 | 0.19 | 6 | 2005 | 突变 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 47 | 2003 | 巴雷特食管癌 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 48 | 2000 | 食管癌 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 21 | 2001 | 乳腺癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 6 | 2001 | p53 |
| 10 | 0.13 | 25 | 2001 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 11 | 0.12 | 10 | 2003 | 肿瘤 |
| 12 | 0.11 | 23 | 2007 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.11 | 8 | 2015 | 食管腺癌 |
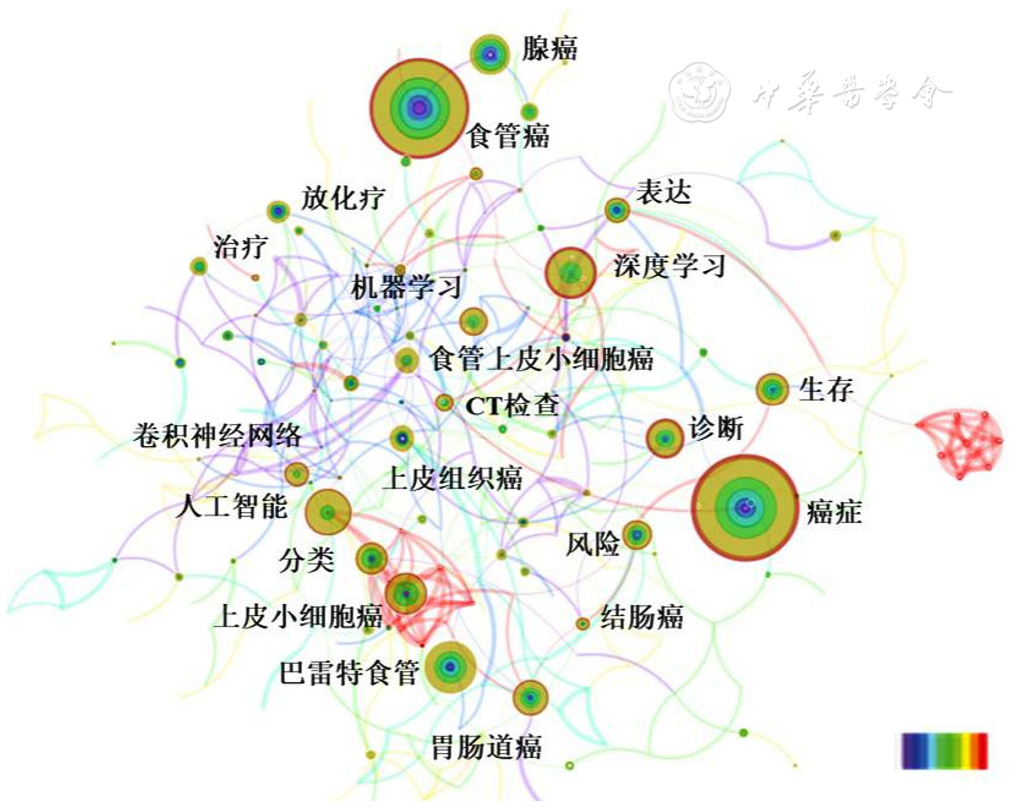
图9 2017—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究关键词CiteSpace可视化共现图谱注:时间演变以颜色变化表示,表示从左往右时间为2017—2022年;圆圈大小代表关键词频率高低,连线粗细代表共线关系强弱
Figure 9 CiteSpace-generated visualized co-occurrence map of keywords in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2017 to 2022
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 | 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.24 | 11 | 2017 | 生物学标志物 | 14 | 0.14 | 20 | 2017 | 验证 |
| 2 | 0.22 | 18 | 2017 | 基因 | 15 | 0.13 | 36 | 2017 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 38 | 2017 | 表达 | 16 | 0.13 | 4 | 2020 | 计算机辅助诊断 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 19 | 2017 | 发育不良 | 17 | 0.13 | 26 | 2017 | 肺癌 |
| 5 | 0.18 | 15 | 2017 | 协助 | 18 | 0.13 | 13 | 2017 | 食管癌 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 6 | 2020 | 计算机辅助检测 | 19 | 0.13 | 2 | 2020 | CPR |
| 7 | 0.17 | 8 | 2019 | 准确度 | 20 | 0.13 | 4 | 2018 | 术前放化疗 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 10 | 2017 | 氟-18FDG断层扫描 | 21 | 0.12 | 4 | 2020 | 食管上皮小细胞癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 4 | 2017 | 肿瘤抑制因子 | 22 | 0.11 | 5 | 2021 | 生物信息学分析 |
| 10 | 0.16 | 11 | 2017 | 数据 | 23 | 0.11 | 42 | 2017 | CT检查 |
| 11 | 0.15 | 22 | 2017 | 结肠癌 | 24 | 0.11 | 4 | 2018 | 标志物 |
| 12 | 0.14 | 6 | 2017 | FDG断层扫描 | 25 | 0.11 | 41 | 2017 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.14 | 11 | 2017 | 鉴别 | 26 | 0.11 | 2 | 2017 | 纹理特征 |
表5 2017—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究中心性>0.10关键词信息表
Table 5 Keywords with centrality over 0.10 in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2017 to 2022
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 | 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.24 | 11 | 2017 | 生物学标志物 | 14 | 0.14 | 20 | 2017 | 验证 |
| 2 | 0.22 | 18 | 2017 | 基因 | 15 | 0.13 | 36 | 2017 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 38 | 2017 | 表达 | 16 | 0.13 | 4 | 2020 | 计算机辅助诊断 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 19 | 2017 | 发育不良 | 17 | 0.13 | 26 | 2017 | 肺癌 |
| 5 | 0.18 | 15 | 2017 | 协助 | 18 | 0.13 | 13 | 2017 | 食管癌 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 6 | 2020 | 计算机辅助检测 | 19 | 0.13 | 2 | 2020 | CPR |
| 7 | 0.17 | 8 | 2019 | 准确度 | 20 | 0.13 | 4 | 2018 | 术前放化疗 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 10 | 2017 | 氟-18FDG断层扫描 | 21 | 0.12 | 4 | 2020 | 食管上皮小细胞癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 4 | 2017 | 肿瘤抑制因子 | 22 | 0.11 | 5 | 2021 | 生物信息学分析 |
| 10 | 0.16 | 11 | 2017 | 数据 | 23 | 0.11 | 42 | 2017 | CT检查 |
| 11 | 0.15 | 22 | 2017 | 结肠癌 | 24 | 0.11 | 4 | 2018 | 标志物 |
| 12 | 0.14 | 6 | 2017 | FDG断层扫描 | 25 | 0.11 | 41 | 2017 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.14 | 11 | 2017 | 鉴别 | 26 | 0.11 | 2 | 2017 | 纹理特征 |
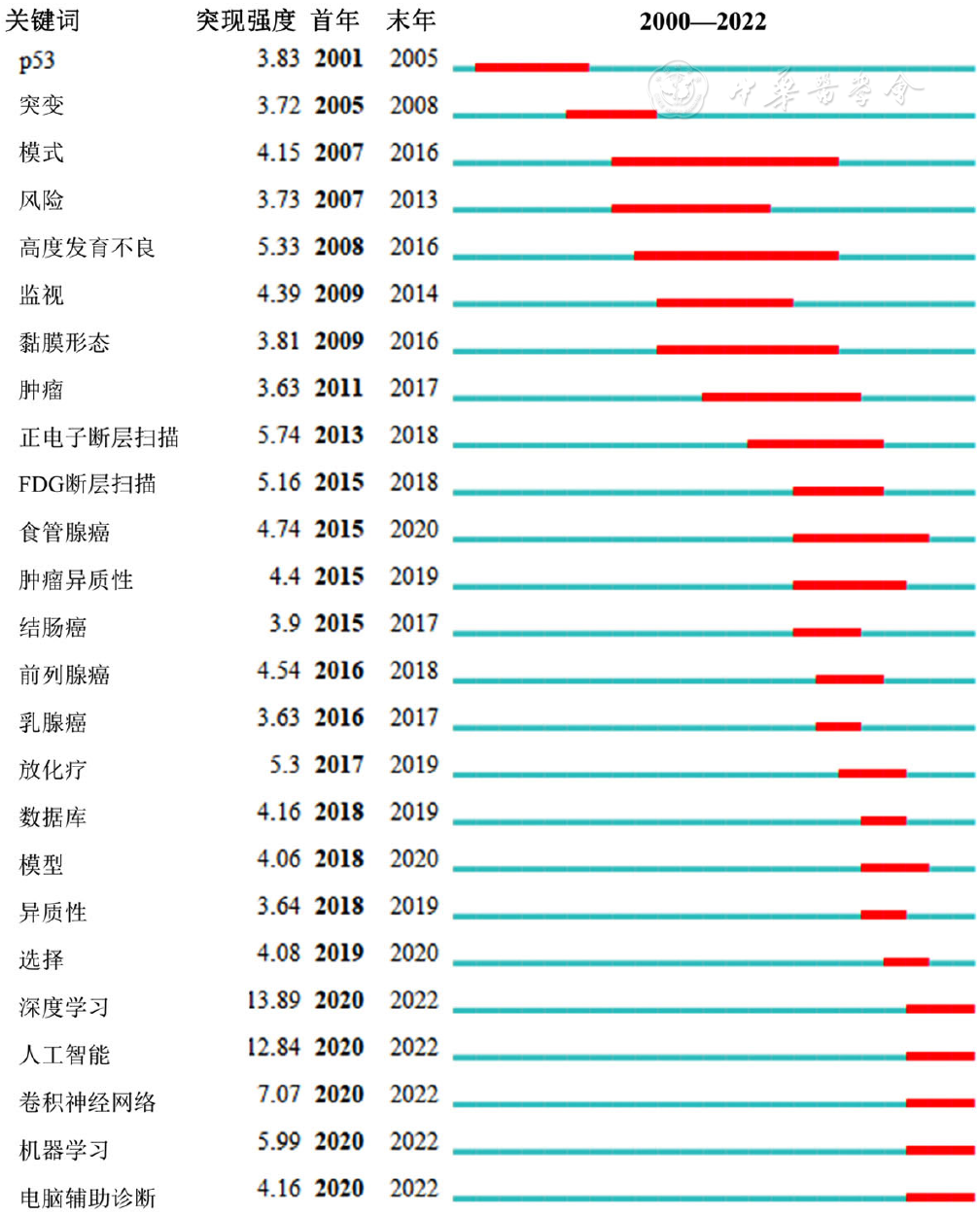
图10 2000—2022年全球AI应用于食管癌领域相关研究突现关键词信息(前25位)注:突现强度大小表示该关键词出现的强弱,突现持续时间用红色色块宽度表示,首次年份、末次年份标识该关键词成为研究前沿开始和结束时间。
Figure 10 Top 25 burst keywords in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中共中央办公厅 国务院办公厅印发《关于进一步加强科研诚信建设的若干意见》[EB/OL].(2018-05-30)[2022-04-30].
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
科技部办公厅. 科技部办公厅关于加强新型冠状病毒肺炎科技攻关项目管理有关事项的通知[J]. 现代养生,2020,20(S1):6.
|
| [1] | 牛奔, 朱晓倩, 杨辰, 梁万年, 刘珏. 基于CiteSpace的国内外医疗大语言模型研究热点演进及趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3200-3208. |
| [2] | 王慧, 胡银环, 冯显东, 刘莎, 汪洋帆. 人工智能在心理干预中的应用:效果、挑战与前景[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3209-3216. |
| [3] | 潘琦, 任菁菁, 马方晖, 胡梦杰. 全科医师对AI辅助诊疗系统的认知与需求调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [4] | 赵亚利, 路孝琴, 刘珏, 张艺帆, 朱祖懿, 陈开元, 刘民, 梁万年. 智能全科医生评估指标体系构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2705-2711. |
| [5] | 王松柱, 姚易, 周伊恒, 赵茄茜, 杨荣, 赵茜, 张瑞, 代华, 李东泽, 廖晓阳, 杨辉. 近五年全科医学研究热点及发展趋势分析:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [6] | 闫温馨, 刘珏, 梁万年. DeepSeek赋能全科医学:潜在应用与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2065-2069. |
| [7] | 李伊婷, 徒文静, 尹婷婷, 梅紫琦, 张苏闽, 王萌, 徐桂华. 人工智能在炎症性肠病患者营养管理中应用的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1709-1716. |
| [8] | 戈琼, 胡佳康, 俞玉琪, 赖文文, 罗时文, 卢曲琴. RNA测序技术应用于肝癌的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1473-1478. |
| [9] | 王甘红, 张子豪, 奚美娟, 夏开建, 周燕婷, 陈健. 基于卷积神经网络建立中药材自动识别的人工智能模型及应用程序[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(09): 1128-1136. |
| [10] | 程琦, 于文兵, 李科科, 左右, 焦乾鑫, 刘新浩, 高丽丽. 基于CiteSpace的中学生心理健康研究的热点与前沿趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(07): 853-862. |
| [11] | 宋芬芬, 李胜棉. 基于卡瑞利珠单抗的方案治疗局部晚期及转移性食管癌的真实世界研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(07): 844-852. |
| [12] | 清华大学万科公共卫生与健康学院, 北京大学公共卫生学院, 中国医师协会全科医师分会. 智能全科医生中国专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 135-142. |
| [13] | 张璇, 张飞, 李铭麟, 王佳贺. 智能机器人在基层慢性病管理中的应用与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 7-12. |
| [14] | 王珍妮, 须月萍, 夏开建, 徐晓丹, 顾丽华. 基于YOLO神经网络构建压力性损伤自动检测和分期的人工智能模型[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4582-4590. |
| [15] | 周伊恒, 杨梓钰, 吕垚, 刘力滴, 沈灿, 廖晓阳, 贾禹. 《人工智能在心血管疾病中的应用科学声明》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4353-4357. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





