中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 3200-3208.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0377
牛奔1, 朱晓倩2, 杨辰3, 梁万年4,*( ), 刘珏5,*(
), 刘珏5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-15
修回日期:2024-09-10
出版日期:2025-09-05
发布日期:2025-07-24
通讯作者:
梁万年, 刘珏
作者贡献:
牛奔负责确定论文选题、文献筛选核对、论文撰写及修改、经费支持;朱晓倩、杨辰负责文献检索、筛选和去重,以及文献数据分析;刘珏负责图表制作、论文修改及质控、经费支持;梁万年负责论文选题、质控、指导及修改,并对文章整体负责。
基金资助:
NIU Ben1, ZHU Xiaoqian2, YANG Chen3, LIANG Wannian4,*( ), LIU Jue5,*(
), LIU Jue5,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-15
Revised:2024-09-10
Published:2025-09-05
Online:2025-07-24
Contact:
LIANG Wannian, LIU Jue
摘要: 背景 由于其强大的语言处理能力和广泛的应用潜力,以ChatGPT为代表的大语言模型引领了医疗领域自然语言处理的新趋势。 目的 本研究通过文献计量分析揭示2017年以来医疗大语言模型的研究热点、主题分布及未来发展方向。 方法 通过Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台和维普网数据库,系统检索和筛选2017年1月—2024年6月关于医疗大语言模型的文献。利用CiteSpace软件提取文献中的主题关键词等信息,分析并对比国内外研究的演进、热点和趋势。 结果 共纳入1 071篇相关文献,结果显示国外研究集中于人工智能、大语言模型、深度学习、知识图谱等技术在医学中的应用,而国内研究则相对较少,侧重于中文医学问答系统构建和医疗数据非结构化问题处理。 结论 深化医疗数据挖掘,拓展多场景应用,并借鉴国际大语言模型的微调和应用评估经验,促进我国医疗大语言模型技术的发展和医学领域应用。
中图分类号:
| 检索类型 | 检索词 |
|---|---|
| 英文检索式 | (TS=("medical" O R "medical treatment" O R "medicine" O R "health care" O R "medical service" O R "medicare" O R "medical cure" O R "health" O R "treatment" O R "treat" O R "medical activities" O R "medicine art" O R "medical practice" O R "medical services" O R "medical system" O R "medical enterprise" O R "medical management" O R "medication" O R "medical history" O R "health services" O R "medical process" O R "medical organization" O R "medical therapy" O R "medical health" O R "medical science" O R "medical institution" O R "medicine treatment" O R "clinical care" O R "medical service care" O R "medical activity" O R "medical contingent" O R "medical institutions" O R "healing" O R "medical problems" O R "medical enterprises" O R "medical technology" O R "health & medical care" O R "medical service practice" O R "medical insurance" O R "medical assistance" O R "medical care" O R "pharmacy" O R "medicinal" O R "clinical" )AND TS=("large language model" O R "language model" O R "linguistic model" O R "language models" O R "language modeling" O R "language module" O R "language mode" O R "chinese language model" O R "language level")) |
| 中文检索式 | (TS=("医疗+医学+医疗卫生")AND TS=("大语言模型+生成式语言模型+GPT模型+BERT模型+超级语言模型")) |
表1 中英文文献检索词
Table 1 Search terms for large language models in the field of medical in English and Chinese
| 检索类型 | 检索词 |
|---|---|
| 英文检索式 | (TS=("medical" O R "medical treatment" O R "medicine" O R "health care" O R "medical service" O R "medicare" O R "medical cure" O R "health" O R "treatment" O R "treat" O R "medical activities" O R "medicine art" O R "medical practice" O R "medical services" O R "medical system" O R "medical enterprise" O R "medical management" O R "medication" O R "medical history" O R "health services" O R "medical process" O R "medical organization" O R "medical therapy" O R "medical health" O R "medical science" O R "medical institution" O R "medicine treatment" O R "clinical care" O R "medical service care" O R "medical activity" O R "medical contingent" O R "medical institutions" O R "healing" O R "medical problems" O R "medical enterprises" O R "medical technology" O R "health & medical care" O R "medical service practice" O R "medical insurance" O R "medical assistance" O R "medical care" O R "pharmacy" O R "medicinal" O R "clinical" )AND TS=("large language model" O R "language model" O R "linguistic model" O R "language models" O R "language modeling" O R "language module" O R "language mode" O R "chinese language model" O R "language level")) |
| 中文检索式 | (TS=("医疗+医学+医疗卫生")AND TS=("大语言模型+生成式语言模型+GPT模型+BERT模型+超级语言模型")) |
| 英文关键词 | 中文关键词 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 序号 | 频次(次) | 关键词 | 中心性 | 年份(年) | 序号 | 频次(次) | 关键词 | 中心性 | 年份(年) |
| 1 | 435 | artificial intelligence | 0.10 | 2023 | 1 | 18 | 深度学习 | 0.27 | 2019 |
| 2 | 262 | large language models | 0.13 | 2023 | 2 | 12 | 人工智能 | 0.13 | 2021 |
| 3 | 163 | large language model | 0 | 2023 | 3 | 8 | 知识图谱 | 0.01 | 2021 |
| 4 | 115 | natural language processing | 0.14 | 2023 | 4 | 4 | 实体识别 | 0.06 | 2023 |
| 5 | 81 | machine learning | 0 | 2023 | 5 | 4 | 电子病历 | 0.05 | 2021 |
| 6 | 60 | medical education | 0.04 | 2023 | 6 | 4 | 循证医学 | 0.03 | 2021 |
| 7 | 40 | generative ai | 0.01 | 2023 | 7 | 4 | 医疗问答 | 0.01 | 2022 |
| 8 | 35 | chatgpt | 0.02 | 2023 | 8 | 4 | 文献分类 | 0 | 2020 |
| 9 | 32 | language model | 0.18 | 2019 | 9 | 3 | 机器学习 | 0.05 | 2018 |
| 10 | 32 | deep learning | 0.01 | 2023 | 10 | 3 | 医疗领域 | 0.01 | 2023 |
表2 国内外医疗大语言模型前10关键词词频分布
Table 2 Top 10 high-frequency keywords in the field of medical large language models
| 英文关键词 | 中文关键词 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 序号 | 频次(次) | 关键词 | 中心性 | 年份(年) | 序号 | 频次(次) | 关键词 | 中心性 | 年份(年) |
| 1 | 435 | artificial intelligence | 0.10 | 2023 | 1 | 18 | 深度学习 | 0.27 | 2019 |
| 2 | 262 | large language models | 0.13 | 2023 | 2 | 12 | 人工智能 | 0.13 | 2021 |
| 3 | 163 | large language model | 0 | 2023 | 3 | 8 | 知识图谱 | 0.01 | 2021 |
| 4 | 115 | natural language processing | 0.14 | 2023 | 4 | 4 | 实体识别 | 0.06 | 2023 |
| 5 | 81 | machine learning | 0 | 2023 | 5 | 4 | 电子病历 | 0.05 | 2021 |
| 6 | 60 | medical education | 0.04 | 2023 | 6 | 4 | 循证医学 | 0.03 | 2021 |
| 7 | 40 | generative ai | 0.01 | 2023 | 7 | 4 | 医疗问答 | 0.01 | 2022 |
| 8 | 35 | chatgpt | 0.02 | 2023 | 8 | 4 | 文献分类 | 0 | 2020 |
| 9 | 32 | language model | 0.18 | 2019 | 9 | 3 | 机器学习 | 0.05 | 2018 |
| 10 | 32 | deep learning | 0.01 | 2023 | 10 | 3 | 医疗领域 | 0.01 | 2023 |
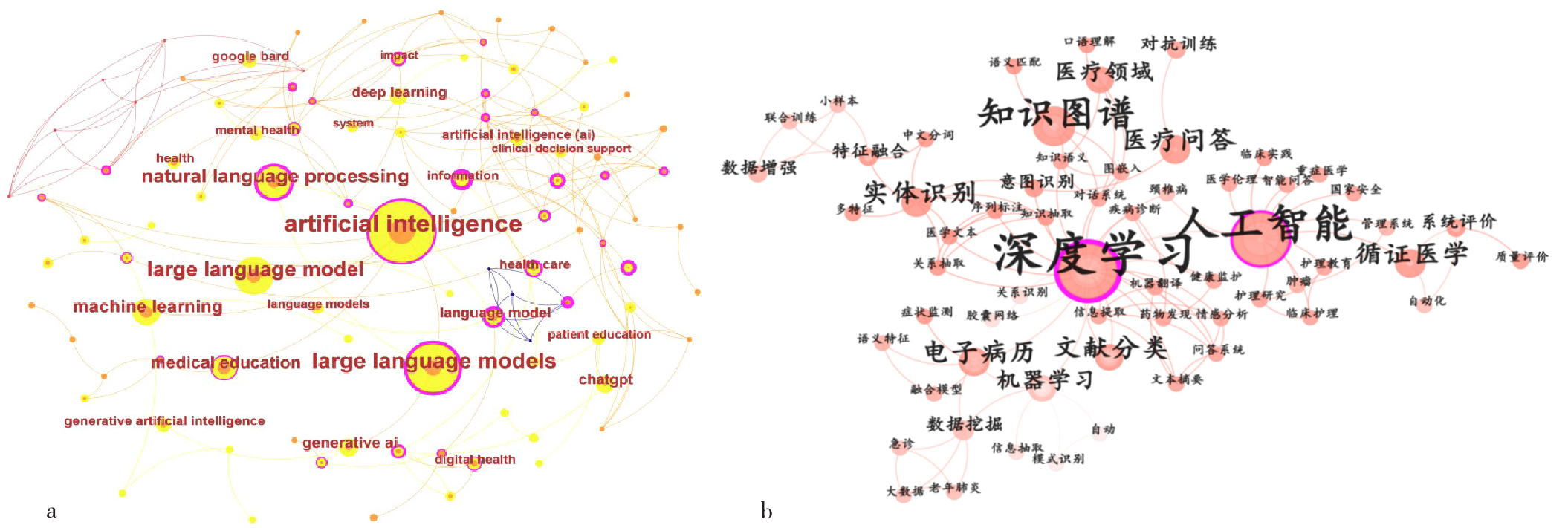
图3 医疗大语言模型研究关键词共现图谱 注:a为国际医疗大语言模型研究关键词共现图谱,b为国内医疗大语言模型研究关键词共现图谱。
Figure 3 Keyword co-occurrence network of researches in medical large language models
| 聚类 | 国际 | 聚类 | 国内 |
|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | care | #0 | 人工智能 |
| #1 | models | #1 | 实体识别 |
| #2 | large language models(llms) | #2 | 深度学习 |
| #3 | electronic health record | #3 | 模式识别 |
| #4 | evidence-based medicine | #4 | 知识图谱 |
| #5 | large language model | ||
| #6 | deep learning | ||
| #7 | language models | ||
| #8 | forensic ai | ||
| #9 | chatbots | ||
| #10 | ethics-medical | ||
| #11 | medical question answering | ||
| #12 | artificial intelligence | ||
| #13 | Llama 2 | ||
| #14 | decision support systems |
表3 国内外关键词聚类
Table 3 Keyword clustering in the field of medical large language models at home and abroad
| 聚类 | 国际 | 聚类 | 国内 |
|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | care | #0 | 人工智能 |
| #1 | models | #1 | 实体识别 |
| #2 | large language models(llms) | #2 | 深度学习 |
| #3 | electronic health record | #3 | 模式识别 |
| #4 | evidence-based medicine | #4 | 知识图谱 |
| #5 | large language model | ||
| #6 | deep learning | ||
| #7 | language models | ||
| #8 | forensic ai | ||
| #9 | chatbots | ||
| #10 | ethics-medical | ||
| #11 | medical question answering | ||
| #12 | artificial intelligence | ||
| #13 | Llama 2 | ||
| #14 | decision support systems |
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 强度 | 开始年份(年) | 结束年份(年) | 2019—2024年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chat generative pre-trained transformer | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| transfer learning | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| efficacy | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| prevalence | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| ai chatbot | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| cancer | 2023 | 1.28 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| conversational agents | 2023 | 1.28 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| privacy | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| interventions | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| health communication | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| anxiety | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| people | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| united states | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| medical ethics | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| algorithms | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| knowledge | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| medical information | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| natural language processing(nlp) | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| conversational agent | 2023 | 0.92 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| academic integrity | 2023 | 0.67 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
表4 英文文献前20个关键词突现结果
Table 4 Top 20 keywords with bursts in studies regarding medical large language models in English
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 强度 | 开始年份(年) | 结束年份(年) | 2019—2024年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chat generative pre-trained transformer | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| transfer learning | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| efficacy | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| prevalence | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| ai chatbot | 2023 | 1.34 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| cancer | 2023 | 1.28 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| conversational agents | 2023 | 1.28 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| privacy | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| interventions | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| health communication | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| anxiety | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| people | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| united states | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| medical ethics | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| algorithms | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| knowledge | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| medical information | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| natural language processing(nlp) | 2023 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| conversational agent | 2023 | 0.92 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| academic integrity | 2023 | 0.67 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 强度 | 开始年份(年) | 结束年份(年) | 2017—2024年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对抗训练 | 2022 | 0.48 | 2022 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
| 人工智能 | 2021 | 0.72 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 医疗领域 | 2023 | 0.52 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 药物发现 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 中文医学 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 问答系统 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 疾病诊断 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 预训练 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 模块分解 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 复杂系统 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 应用 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 机器翻译 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 护理研究 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 智能问答 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| chip-cdn 2021 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 重症医学 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 特征提取 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 医学伦理 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 信息提取 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 居家健康 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
表5 中文文献前20个关键词突现结果
Table 5 Top 20 keywords with bursts in studies regarding medical large language models in Chinese
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 强度 | 开始年份(年) | 结束年份(年) | 2017—2024年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对抗训练 | 2022 | 0.48 | 2022 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
| 人工智能 | 2021 | 0.72 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 医疗领域 | 2023 | 0.52 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 药物发现 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 中文医学 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 问答系统 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 疾病诊断 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 预训练 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 模块分解 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 复杂系统 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 应用 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 机器翻译 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 护理研究 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 智能问答 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| chip-cdn 2021 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 重症医学 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 特征提取 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 医学伦理 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 信息提取 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| 居家健康 | 2023 | 0.41 | 2023 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
管立本,李实. 融合多粒度语义信息和知识图谱的中文医疗问答匹配模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2024,60(14):152-161. DOI:10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2305-0453.
|
| [6] |
乔凯,陈可佳,陈景强. 基于知识图谱与关键词注意机制的中文医疗问答匹配方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2021,34(8):733-741. DOI:10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.202108006.
|
| [7] |
王润周,张新生. 基于混合动态掩码与多策略融合的医疗知识图谱问答[J]. 计算机科学与探索,2024 ,18 (10):2770-2786. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3982.2021.11.001.
|
| [8] |
吴宗友,白昆龙,杨林蕊,等. 电子病历文本挖掘研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2021,58(3):513-527. DOI:10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200402.
|
| [9] | |
| [10] |
梁立荣,李长伟,沈晔,等. 基于层叠条件随机场模型的电子病历文本信息抽取[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2019,36(10):47-54,112. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.10.009.
|
| [11] |
吕学强,张剑,穆天杨,等. 嵌入知识语义的医疗领域对话系统[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2023,44(12):3794-3799. DOI:10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2023.12.037.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
罗华宇,许敏,曾朝蓉,等. ChatGPT在护理领域中应用的前景与挑战[J]. 中华护理教育,2023,20(12):1520-1523. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.1672-9234.2023.12.019.
|
| [28] |
施强慧,张子凡,胡博,等. 深度学习与人工智能在颈腰椎退变性疾病诊断及治疗中的应用研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2021,46(10):1034-1039. DOI:10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.10.13.
|
| [29] |
徐璐璐,洪贇,叶鹰. ChatGPT及GPT类技术的医学信息学应用前景探讨[J]. 情报理论与实践,2023,46(6):38-42. DOI:10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2023.06.006.
|
| [30] |
丁文婧. "助手"还是"杀手":用ChatGPT求医问药的风险分析[J]. 医学与哲学,2023,44(23):22-25. DOI:10.12014/j.issn.1002-0772.2023.23.05.
|
| [31] |
张忆汝,汤永,朱敏,等. 基于自然语言处理和深度学习的急性呼吸道传染病早期识别模型的构建[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2024(15):2394-2400. DOI:11.3436.r.20240722.1302.062.
|
| [32] |
梁文桐,朱艳辉,詹飞,等. 基于深度学习多模型融合的医疗命名实体识别[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2022,39(10):162-168,229. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2022.10.025.
|
| [33] |
席运江,李曼,邓雨珊,等. 中文在线医疗社区问答内容知识图谱构建研究[J]. 图书情报工作,2024,68(4):124-136. DOI:10.13266/j.issn.0252-3116.2023.24.010.
|
| [34] |
| [1] | 王慧, 胡银环, 冯显东, 刘莎, 汪洋帆. 人工智能在心理干预中的应用:效果、挑战与前景[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3209-3216. |
| [2] | 潘琦, 任菁菁, 马方晖, 胡梦杰. 全科医师对AI辅助诊疗系统的认知与需求调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [3] | 石佳瑞, 王梓力, 张薛晴, 宋玉磊, 徐桂华, 柏亚妹. 南京市社区认知症服务中心认知初步筛查服务开展现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [4] | 赵亚利, 路孝琴, 刘珏, 张艺帆, 朱祖懿, 陈开元, 刘民, 梁万年. 智能全科医生评估指标体系构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2705-2711. |
| [5] | 王松柱, 姚易, 周伊恒, 赵茄茜, 杨荣, 赵茜, 张瑞, 代华, 李东泽, 廖晓阳, 杨辉. 近五年全科医学研究热点及发展趋势分析:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [6] | 闫温馨, 刘珏, 梁万年. DeepSeek赋能全科医学:潜在应用与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2065-2069. |
| [7] | 曾泳添, 陈日玲, 农雪艳, 刘洲, 梁力中, 朱子健. 数字疗法在自闭症筛查到干预的临床研究进展与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1702-1708. |
| [8] | 李伊婷, 徒文静, 尹婷婷, 梅紫琦, 张苏闽, 王萌, 徐桂华. 人工智能在炎症性肠病患者营养管理中应用的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1709-1716. |
| [9] | 戈琼, 胡佳康, 俞玉琪, 赖文文, 罗时文, 卢曲琴. RNA测序技术应用于肝癌的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1473-1478. |
| [10] | 张小娟, 刘阳, 彭博, 曹晓琳, 叶媛, 朱坤. 基层医疗卫生机构儿科建设与服务提供研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1228-1235. |
| [11] | 王甘红, 张子豪, 奚美娟, 夏开建, 周燕婷, 陈健. 基于卷积神经网络建立中药材自动识别的人工智能模型及应用程序[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(09): 1128-1136. |
| [12] | 程琦, 于文兵, 李科科, 左右, 焦乾鑫, 刘新浩, 高丽丽. 基于CiteSpace的中学生心理健康研究的热点与前沿趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(07): 853-862. |
| [13] | 清华大学万科公共卫生与健康学院, 北京大学公共卫生学院, 中国医师协会全科医师分会. 智能全科医生中国专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 135-142. |
| [14] | 张璇, 张飞, 李铭麟, 王佳贺. 智能机器人在基层慢性病管理中的应用与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 7-12. |
| [15] | 闫温馨, 胡健, 曾华堂, 刘民, 梁万年. 人工智能大语言模型在基层医疗卫生服务中的应用与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 1-6. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





