中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (15): 1825-1832.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0055
所属专题: 营养最新文章合集
郭文超1,2, 秦寒枝2,*( ), 滕娇1,2, 金魁3, 孙建3, 王忠丽4, 蒋燕2
), 滕娇1,2, 金魁3, 孙建3, 王忠丽4, 蒋燕2
收稿日期:2021-11-19
修回日期:2022-02-27
出版日期:2022-03-17
发布日期:2022-04-07
通讯作者:
秦寒枝
基金资助:
Wenchao GUO1,2, Hanzhi QIN2,*( ), Jiao TENG1,2, Kui JIN3, Jian SUN3, Zhongli WANG4, Yan JIANG2
), Jiao TENG1,2, Kui JIN3, Jian SUN3, Zhongli WANG4, Yan JIANG2
Received:2021-11-19
Revised:2022-02-27
Published:2022-03-17
Online:2022-04-07
Contact:
Hanzhi QIN
About author:摘要: 背景 肠内营养支持可有效改善重型颅脑损伤患者的营养状况,有利于患者的预后,但国内外相关文献缺乏针对此类患者的系统的营养管理方案,少见肠内营养支持最佳证据总结。 目的 检索并总结成人重型颅脑损伤患者肠内营养支持的最佳证据,为临床中该类患者的营养管理提供循证依据。 方法 计算机检索BMJ Best Practice、Up To Date、国际指南协作网(GIN)、英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所(NICE)、美国国立指南库(NGC)、加拿大安大略护理学会网站(RNAO)、医脉通、欧洲肠内肠外营养学会(ESPEN)、美国肠内肠外营养学会(ASPEN)、美国重症医学会(SCCM)、欧洲重症医学会(ESICM)、JBI循证卫生保健数据库、Cochrane Library、PubMed、EMBase、CINAHL、中国生物医学文献服务系统(CBM)、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普网中与成人重型颅脑损伤患者肠内营养相关的所有证据,包括指南、证据总结、最佳实践、专家共识、系统评价及Meta分析,检索时间为2011年4月至2021年4月。采用相应的质量评价标准对纳入的文献进行质量评价,采用JBI循证卫生保健中心证据预分级系统(2014版)和JBI证据推荐级别系统(2014版)对证据进行描述及汇总。 结果 共纳入18篇文献,其中临床指南5篇,证据总结3篇,专家共识3篇,系统评价2篇,Meta分析5篇。纳入文献总体质量高,并从营养筛查、营养评估、启动肠内营养时机、能量及蛋白质需求量、肠内营养成分、喂养途径、输注方式及并发症管理8个方面最终形成了25条最佳证据。 结论 在给予成人重型颅脑损伤患者肠内营养时,医护人员需要依据最佳证据实施,同时也应结合我国目前的医疗现状及具体治疗目标来制定个体化的肠内营养支持方案,提高营养支持效果,从而改善患者临床结局。
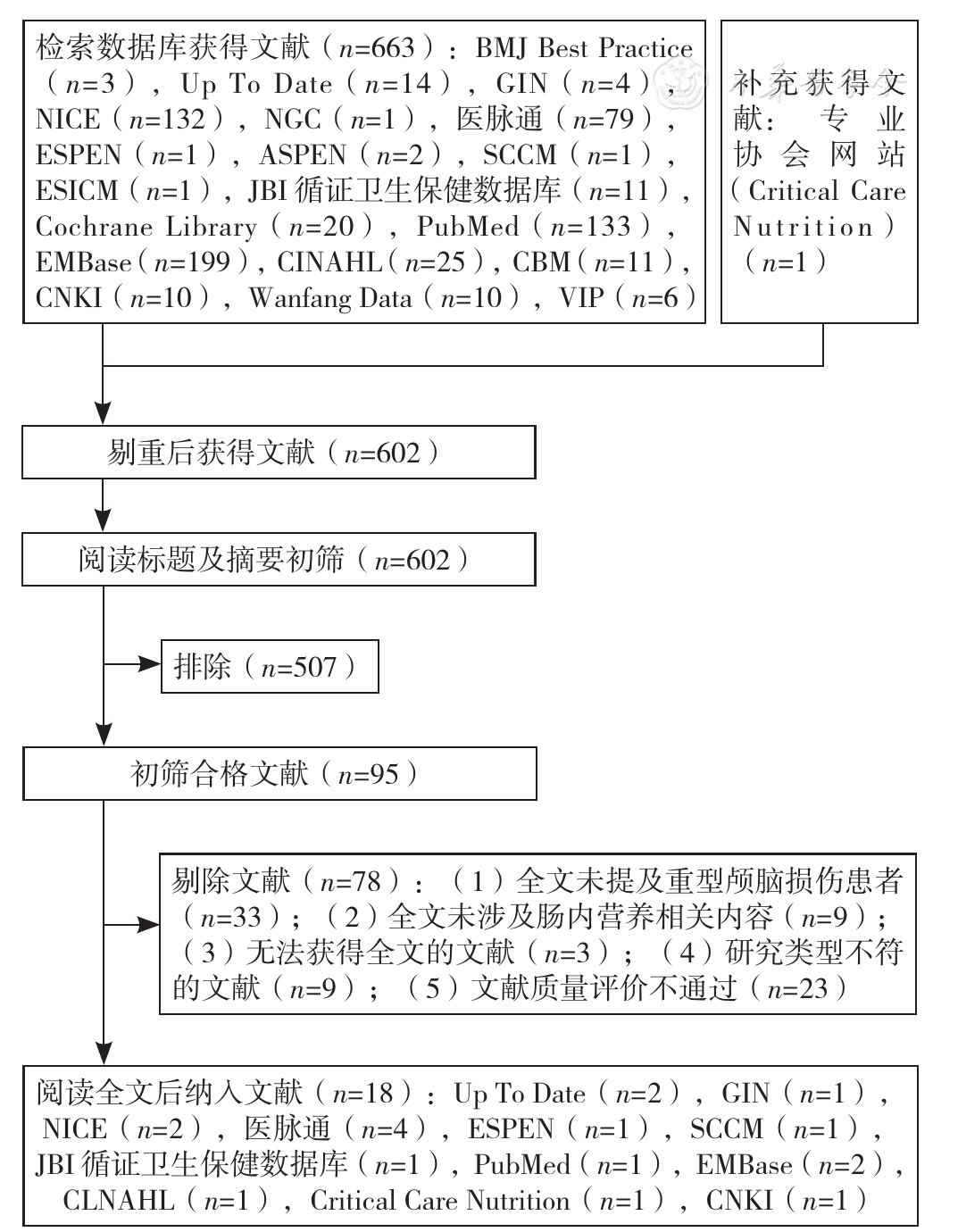
图1 文献检索流程注:GIN=国际指南协作网,NICE=英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所,NGC=美国国立指南库,ESPEN=欧洲肠内肠外营养学会,ASPEN=美国肠内肠外营养学会,SCCM=美国重症医学会,ESICM=欧洲重症医学会,CBM=中国生物医学文献服务系统,CNKI=中国知网,Wanfang Data=万方数据知识服务平台,VIP=维普网
Figure 1 Literature screening strategy
| 第一作者 | 证据来源 | 证据类型 | 文献主题 | 发表年份(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCCS[ | Critical Care Nutrition | 临床指南 | 加拿大临床实践指南 | 2015 |
| ACS[ | GIN | 临床指南 | ACS:创伤性脑损伤治疗的最佳实践指南 | 2015 |
| CARNEY[ | 医脉通 | 临床指南 | 重型颅脑损伤救治指南第4版 | 2017 |
| MCCLAVE[ | SCCM | 临床指南 | SCCM和ASPEN:成人危重病患者的营养支持治疗指南 | 2016 |
| SINGER[ | ESPEN | 临床指南 | ESPEN:重症监护室临床营养指南 | 2019 |
| SERES[ | Up To Date | 证据总结 | 危重患者的营养支持:综述 | 2020 |
| SERES[ | Up To Date | 证据总结 | 危重患者的营养支持:肠内营养 | 2021 |
| JAYASEKARA[ | JBI循证卫生保健数据库 | 证据总结 | 颅脑损伤:营养支持 | 2020 |
| 中华医学会神经外科学分会[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 中国神经外科重症患者气道管理专家共识(2016) | 2016 |
| 孙仁华[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 重症患者早期肠内营养临床实践专家共识 | 2018 |
| 中华医学会创伤学分会神经创伤专业学组[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 颅脑创伤患者肠内营养管理流程中国专家共识(2019) | 2019 |
| WANG[ | EMBase | Meta分析 | 创伤性脑损伤患者的营养支持:前瞻性研究的系统评价和荟萃分析 | 2013 |
| WANG[ | EMBase | Meta分析 | 严重创伤性脑损伤中小肠和胃喂养的比较:随机对照试验的系统评价和荟萃分析 | 2015 |
| 郑丽娜[ | 中国知网 | Meta分析 | 不同肠内营养管饲方式的重型颅脑损伤患者并发症发生情况的Meta分析 | 2019 |
| DU[ | PubMed | Meta分析 | 肠内营养联合益生菌治疗重型颅脑损伤的系统评价及Meta分析 | 2020 |
| OJO[ | NICE | Meta分析 | 混合肠内营养配方的营养价值和物理性质评价:系统评价和Meta分析 | 2020 |
| LOTTES STEWART[ | NICE | 系统评价 | 营养支持方案及其对肠内营养输送的影响:系统评价 | 2014 |
| SHARMA[ | CLNAHL | 系统评价 | BCAA和创伤性脑损伤:系统评价 | 2018 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of included literature
| 第一作者 | 证据来源 | 证据类型 | 文献主题 | 发表年份(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCCS[ | Critical Care Nutrition | 临床指南 | 加拿大临床实践指南 | 2015 |
| ACS[ | GIN | 临床指南 | ACS:创伤性脑损伤治疗的最佳实践指南 | 2015 |
| CARNEY[ | 医脉通 | 临床指南 | 重型颅脑损伤救治指南第4版 | 2017 |
| MCCLAVE[ | SCCM | 临床指南 | SCCM和ASPEN:成人危重病患者的营养支持治疗指南 | 2016 |
| SINGER[ | ESPEN | 临床指南 | ESPEN:重症监护室临床营养指南 | 2019 |
| SERES[ | Up To Date | 证据总结 | 危重患者的营养支持:综述 | 2020 |
| SERES[ | Up To Date | 证据总结 | 危重患者的营养支持:肠内营养 | 2021 |
| JAYASEKARA[ | JBI循证卫生保健数据库 | 证据总结 | 颅脑损伤:营养支持 | 2020 |
| 中华医学会神经外科学分会[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 中国神经外科重症患者气道管理专家共识(2016) | 2016 |
| 孙仁华[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 重症患者早期肠内营养临床实践专家共识 | 2018 |
| 中华医学会创伤学分会神经创伤专业学组[ | 医脉通 | 专家共识 | 颅脑创伤患者肠内营养管理流程中国专家共识(2019) | 2019 |
| WANG[ | EMBase | Meta分析 | 创伤性脑损伤患者的营养支持:前瞻性研究的系统评价和荟萃分析 | 2013 |
| WANG[ | EMBase | Meta分析 | 严重创伤性脑损伤中小肠和胃喂养的比较:随机对照试验的系统评价和荟萃分析 | 2015 |
| 郑丽娜[ | 中国知网 | Meta分析 | 不同肠内营养管饲方式的重型颅脑损伤患者并发症发生情况的Meta分析 | 2019 |
| DU[ | PubMed | Meta分析 | 肠内营养联合益生菌治疗重型颅脑损伤的系统评价及Meta分析 | 2020 |
| OJO[ | NICE | Meta分析 | 混合肠内营养配方的营养价值和物理性质评价:系统评价和Meta分析 | 2020 |
| LOTTES STEWART[ | NICE | 系统评价 | 营养支持方案及其对肠内营养输送的影响:系统评价 | 2014 |
| SHARMA[ | CLNAHL | 系统评价 | BCAA和创伤性脑损伤:系统评价 | 2018 |
| 第一作者 | 各领域标准化百分比(%) | ≥60%的领域数(个) | ≤30%的领域数(个) | 推荐级别(级) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围和目的 | 参与人员 | 指南制定的严谨性 | 指南呈现的清晰性 | 指南的适用性 | 指南编辑的独立性 | ||||
| CCCS[ | 88.9 | 86.1 | 72.2 | 79.2 | 45.8 | 83.3 | 5 | 0 | B |
| ACS[ | 88.9 | 44.4 | 57.3 | 94.4 | 79.2 | 16.7 | 3 | 1 | B |
| CARNEY[ | 100.0 | 66.7 | 94.8 | 80.6 | 66.7 | 100.0 | 6 | 0 | A |
| MCCLAVE[ | 100.0 | 69.4 | 93.8 | 97.2 | 68.8 | 100.0 | 6 | 0 | A |
| SINGER[ | 100.0 | 58.7 | 86.5 | 91.7 | 70.8 | 100.0 | 5 | 0 | B |
表2 AGREEⅡ临床指南质量评价结果
Table 2 AGREEⅡ clinical guidelines quality evaluation results
| 第一作者 | 各领域标准化百分比(%) | ≥60%的领域数(个) | ≤30%的领域数(个) | 推荐级别(级) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围和目的 | 参与人员 | 指南制定的严谨性 | 指南呈现的清晰性 | 指南的适用性 | 指南编辑的独立性 | ||||
| CCCS[ | 88.9 | 86.1 | 72.2 | 79.2 | 45.8 | 83.3 | 5 | 0 | B |
| ACS[ | 88.9 | 44.4 | 57.3 | 94.4 | 79.2 | 16.7 | 3 | 1 | B |
| CARNEY[ | 100.0 | 66.7 | 94.8 | 80.6 | 66.7 | 100.0 | 6 | 0 | A |
| MCCLAVE[ | 100.0 | 69.4 | 93.8 | 97.2 | 68.8 | 100.0 | 6 | 0 | A |
| SINGER[ | 100.0 | 58.7 | 86.5 | 91.7 | 70.8 | 100.0 | 5 | 0 | B |
| 第一作者 | 是否明确标注了观点的来源? | 观点是否来源于该领域有影响力的专家? | 所提出的观点是否以研究相关的人群利益为中心? | 陈述的结论是不是基于分析的结果?观点的表达是否具有逻辑性? | 是否参考了现有的其他文献? | 所提出的观点与以往文献是否有不一致的地方? | 是否纳入? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中华医学会神经外科学分会[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 纳入 |
| 孙仁华[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 纳入 |
| 中华医学会创伤学分会神经创伤专业学组[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 纳入 |
表3 专家共识质量评价结果
Table 3 Expert consensus quality evaluation results
| 第一作者 | 是否明确标注了观点的来源? | 观点是否来源于该领域有影响力的专家? | 所提出的观点是否以研究相关的人群利益为中心? | 陈述的结论是不是基于分析的结果?观点的表达是否具有逻辑性? | 是否参考了现有的其他文献? | 所提出的观点与以往文献是否有不一致的地方? | 是否纳入? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中华医学会神经外科学分会[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 纳入 |
| 孙仁华[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 纳入 |
| 中华医学会创伤学分会神经创伤专业学组[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 纳入 |
| 第一作者 | 是否提供了前期设计方案? | 研究的选择和资料的提取是否具有可重复性? | 检索策略是否全面? | 纳入标准是否包括文献的发表状态,如灰色文献? | 是否提供了纳入与排除研究的列表? | 是否描述了纳入研究的基本特征? | 是否评价和报告了纳入研究的方法学质量? | 所得结论是否合理考虑到纳入研究的方法学质量? | 结果合并的方法是否恰当? | 是否评估了发表偏倚的可能性? | 是否说明了相关的利益冲突? | 是否纳入? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| 郑丽娜[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| DU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| OJO[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 纳入 |
| LOTTES STEWART[ | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 纳入 |
| SHARMA[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
表4 AMSTAR系统评价质量评价结果
Table 4 AMSTAR systematic reviews quality evaluation results
| 第一作者 | 是否提供了前期设计方案? | 研究的选择和资料的提取是否具有可重复性? | 检索策略是否全面? | 纳入标准是否包括文献的发表状态,如灰色文献? | 是否提供了纳入与排除研究的列表? | 是否描述了纳入研究的基本特征? | 是否评价和报告了纳入研究的方法学质量? | 所得结论是否合理考虑到纳入研究的方法学质量? | 结果合并的方法是否恰当? | 是否评估了发表偏倚的可能性? | 是否说明了相关的利益冲突? | 是否纳入? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| 郑丽娜[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| DU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| OJO[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 纳入 |
| LOTTES STEWART[ | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 纳入 |
| SHARMA[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 纳入 |
| 项目 | 证据内容 | 证据等级(级) | 推荐级别(级) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 营养筛查 | 1.每个在ICU停留超过48 h的危重患者应该被认为有营养不良的风险[ | 5b | B |
| 2.应对重型颅脑损伤患者进行营养风险筛查,可根据NRS-2002评分和NUTRIC评分进行评估[ | 2c | A | |
| 3.NUTRIC评分≥5分,或NRS-2002评分≥5分被认为是高风险患者。营养风险高的患者更有可能从早期肠内营养中受益[ | 2c | A | |
| 营养评估 | 4.应结合一般临床评估、常用实验室检查指标、疾病严重程度、胃肠道功能及误吸风险等对患者进行综合性营养评估[ | 5b | A |
| 启动肠内营养时机 | 5.早期肠内营养优于早期肠外营养,重型颅脑损伤患者应优先接受早期肠内营养[ | 1a | A |
| 6.当患者血流动力学稳定后,在创伤后24~48 h开始早期肠内营养[ | 1a | A | |
| 能量及蛋白质需求量 | 7.建议具备监测条件的单位,使用IC法监测重型颅脑损伤并使用机械通气支持患者的EE;如没有条件,则使用来自肺动脉导管的VO2或者呼吸机的VCO2来评估EE[ | 5b | B |
| 8.至少在创伤后第5天,最多第7天,给患者进行营养支持以达到基础的热量替代,以降低死亡率[ | 1c | A | |
| 9.重症患者目标喂养量为25~30 kcal·kg-1·d-1,重型颅脑损伤且有呼吸机支持的患者在早期应达到目标喂养量的80%,同时要注意监测再喂养综合征[ | 1c | A | |
| 10.重型颅脑损伤患者的蛋白质供应可增加至1.5~2.5 g·kg(真实体质量)-1·d-1[ | 5b | A | |
| 肠内营养成分 | 11.对于重型颅脑损伤患者,在胃肠功能正常的情况下,常规推荐高蛋白含量的整蛋白型制剂;如胃肠功能障碍,则推荐使用氨基酸和短肽型制剂[ | 5b | B |
| 12.建议在重型颅脑损伤且机械通气支持的患者中使用含精氨酸的免疫调节制剂或标准肠内配方的EPA/DHA补充剂[ | 2a | A | |
| 13.建议在重型颅脑损伤患者的肠内营养中添加益生菌制剂[ | 1a | A | |
| 14.对于重型颅脑损伤患者推荐含有BCAA的肠内营养配方[ | 1b | B | |
| 15.与混合肠内营养配方相比,商业型营养配方含有更多的能量、碳水化合物、矿物质及维生素,且黏度和渗透压相对较低[ | 4a | B | |
| 16.对于重型颅脑损伤且机械通气支持的患者,含有抗氧化维生素和微量矿物质的肠内营养配方可有效改善患者的预后[ | 2b | B | |
| 喂养途径 | 17.推荐对重型颅脑损伤患者使用鼻肠管喂养[ | 1a | A |
| 18.若患者采用鼻胃管喂养,建议将床头抬高至30°~45°,除非有医学禁忌证[ | 1c | A | |
| 输注方式 | 19.建议使用可控性肠内营养泵进行持续输注肠内营养[ | 2b | A |
| 并发症管理 | 20.对于重型颅脑损伤的患者,应制定由ICU护士推动的肠内喂养方案[ | 2b | B |
| 21.胃潴留或误吸:初始阶段建议每4 h监测GRV,如GRV>250 ml应暂停肠内喂养[ | 5b | B | |
| 22.胃潴留或误吸:建议进行幽门后喂养;在无禁忌证的情况下,使用促胃肠动力药物;调换含MCT高的肠内营养配方制剂[ | 5b | A | |
| 23.喂养性腹泻:建议将营养液的温度调节至接近体温,减慢输注速度,并考虑使用富含膳食纤维的配方。如果患者存在持续性的腹泻、对纤维耐受不佳考虑应用短肽型制剂[ | 5b | A | |
| 24.血糖异常波动:建议常规监测血糖,肠内营养开始前2 d至少每隔4 h测量1次[ | 5b | B | |
| 25.血糖异动:血糖水平保持在7.8~10.0 mmol/L,当超过10.0 mmol/L时,建议更换糖尿病配方制剂或给予胰岛素[ | 5b | A |
表5 成人重型颅脑损伤患者肠内营养支持的最佳证据总结
Table 5 Evidence summary for enteral nutrition support in adults with severe head injury
| 项目 | 证据内容 | 证据等级(级) | 推荐级别(级) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 营养筛查 | 1.每个在ICU停留超过48 h的危重患者应该被认为有营养不良的风险[ | 5b | B |
| 2.应对重型颅脑损伤患者进行营养风险筛查,可根据NRS-2002评分和NUTRIC评分进行评估[ | 2c | A | |
| 3.NUTRIC评分≥5分,或NRS-2002评分≥5分被认为是高风险患者。营养风险高的患者更有可能从早期肠内营养中受益[ | 2c | A | |
| 营养评估 | 4.应结合一般临床评估、常用实验室检查指标、疾病严重程度、胃肠道功能及误吸风险等对患者进行综合性营养评估[ | 5b | A |
| 启动肠内营养时机 | 5.早期肠内营养优于早期肠外营养,重型颅脑损伤患者应优先接受早期肠内营养[ | 1a | A |
| 6.当患者血流动力学稳定后,在创伤后24~48 h开始早期肠内营养[ | 1a | A | |
| 能量及蛋白质需求量 | 7.建议具备监测条件的单位,使用IC法监测重型颅脑损伤并使用机械通气支持患者的EE;如没有条件,则使用来自肺动脉导管的VO2或者呼吸机的VCO2来评估EE[ | 5b | B |
| 8.至少在创伤后第5天,最多第7天,给患者进行营养支持以达到基础的热量替代,以降低死亡率[ | 1c | A | |
| 9.重症患者目标喂养量为25~30 kcal·kg-1·d-1,重型颅脑损伤且有呼吸机支持的患者在早期应达到目标喂养量的80%,同时要注意监测再喂养综合征[ | 1c | A | |
| 10.重型颅脑损伤患者的蛋白质供应可增加至1.5~2.5 g·kg(真实体质量)-1·d-1[ | 5b | A | |
| 肠内营养成分 | 11.对于重型颅脑损伤患者,在胃肠功能正常的情况下,常规推荐高蛋白含量的整蛋白型制剂;如胃肠功能障碍,则推荐使用氨基酸和短肽型制剂[ | 5b | B |
| 12.建议在重型颅脑损伤且机械通气支持的患者中使用含精氨酸的免疫调节制剂或标准肠内配方的EPA/DHA补充剂[ | 2a | A | |
| 13.建议在重型颅脑损伤患者的肠内营养中添加益生菌制剂[ | 1a | A | |
| 14.对于重型颅脑损伤患者推荐含有BCAA的肠内营养配方[ | 1b | B | |
| 15.与混合肠内营养配方相比,商业型营养配方含有更多的能量、碳水化合物、矿物质及维生素,且黏度和渗透压相对较低[ | 4a | B | |
| 16.对于重型颅脑损伤且机械通气支持的患者,含有抗氧化维生素和微量矿物质的肠内营养配方可有效改善患者的预后[ | 2b | B | |
| 喂养途径 | 17.推荐对重型颅脑损伤患者使用鼻肠管喂养[ | 1a | A |
| 18.若患者采用鼻胃管喂养,建议将床头抬高至30°~45°,除非有医学禁忌证[ | 1c | A | |
| 输注方式 | 19.建议使用可控性肠内营养泵进行持续输注肠内营养[ | 2b | A |
| 并发症管理 | 20.对于重型颅脑损伤的患者,应制定由ICU护士推动的肠内喂养方案[ | 2b | B |
| 21.胃潴留或误吸:初始阶段建议每4 h监测GRV,如GRV>250 ml应暂停肠内喂养[ | 5b | B | |
| 22.胃潴留或误吸:建议进行幽门后喂养;在无禁忌证的情况下,使用促胃肠动力药物;调换含MCT高的肠内营养配方制剂[ | 5b | A | |
| 23.喂养性腹泻:建议将营养液的温度调节至接近体温,减慢输注速度,并考虑使用富含膳食纤维的配方。如果患者存在持续性的腹泻、对纤维耐受不佳考虑应用短肽型制剂[ | 5b | A | |
| 24.血糖异常波动:建议常规监测血糖,肠内营养开始前2 d至少每隔4 h测量1次[ | 5b | B | |
| 25.血糖异动:血糖水平保持在7.8~10.0 mmol/L,当超过10.0 mmol/L时,建议更换糖尿病配方制剂或给予胰岛素[ | 5b | A |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
中华医学会神经外科学分会,中国神经外科重症管理协作组. 中国神经外科重症患者气道管理专家共识(2016)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2016,96(21):1639-1642. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.021.004.
|
| [5] | |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
史颜梅,张全城,赵红乐,等. 早期肠内营养支持对颅脑损伤患者营养状况及感染并发症影响的Meta分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2019,25(29):3765-3770. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2907.2019.29.012.
|
| [9] | |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
胡雁,郝玉芳. 循证护理学[M]. 2版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2018.
|
| [13] |
CCCS. Canadian clinical practice guidelines 2015[EB/OL]. (2015-09-14)[2021-07-11].
|
| [14] |
American College of Surgeons. ACS TQIP:best practices in the management of traumatic brain injury[EB/OL]. [2021-07-11].
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
孙仁华,江荣林,黄曼,等. 重症患者早期肠内营养临床实践专家共识[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2018,30(8):715-721. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.08.001.
|
| [22] |
中华医学会创伤学分会神经创伤专业学组. 颅脑创伤患者肠内营养管理流程中国专家共识(2019)[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2019,35(3):193-198. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-8050.2019.03.001.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
郑丽娜,刘巧. 不同肠内营养管饲方式的重型颅脑损伤患者并发症发生情况的Meta分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2019,25(19):2462-2466. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2907.2019.19.020.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [1] | 郑思婷, 何春渝, 周均, 孔叶, 杨薪瑶, 周海英, 魏晓霏. 脑卒中运动功能障碍患者自我管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3230-3237. |
| [2] | 薛珊, 李来有, 梁军利, 靳英辉, 魏淑艳. 家庭肠内营养在食管癌患者中有效性和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2540-2547. |
| [3] | 刘晓, 张巾英, 彭滟, 王黎, 陈晓梅, 刘佳, 邓梦惠, 杨燕妮. 促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(13): 1568-1576. |
| [4] | 刘晓, 彭滟, 张巾英, 邓梦惠, 龚德, 陈晓梅, 李洁, 杨燕妮. 促进社区居民脑健康的运动干预方案的构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(13): 1590-1597. |
| [5] | 王茜茜, 沈睿, 王俊杰, 徐霓影. 绝经后骨质疏松症患者运动干预的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(09): 1151-1158. |
| [6] | 王若冰, 王留根, 李和平, 曾西. 脑卒中住院患者不同时间点营养状况影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(06): 665-671. |
| [7] | 陈欢, 侯朝铭, 高静, 柏丁兮, 吴晨曦, 王浩, 游倩, 鲜圆圆. 糖尿病患者甲病管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(32): 3984-3990. |
| [8] | 王秋爽, 安欣, 史新慧, 张丹, 马京华. 成人阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征无创正压通气治疗管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(27): 3429-3434. |
| [9] | 赵镇雪, 王欣, 谭凯文, 赵春善. 含糖饮料摄入与高血压发病风险剂量反应的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(26): 3324-3330. |
| [10] | 王倩倩, 周健, 江志伟, 龚冠闻. 入院24小时内肠内营养治疗重症急性胰腺炎疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(24): 3057-3064. |
| [11] | 任斌, 杨雷方, 丁新民, 梁继芳. 重型颅脑损伤患者血清可溶性α-Klotho蛋白水平动态变化及临床意义研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(20): 2493-2497. |
| [12] | 何聪聪, 孟利敏, 刘慧珍, 郭秀芳, 王菲菲, 林栋美. 非药物干预措施对癌症患者症状群干预效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(19): 2414-2420. |
| [13] | 王湾湾,李园园,石小天,马清. 营养对衰弱影响的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(6): 673-677. |
| [14] | 黄雨滟,黄厚强,陈佩云,彭博,陈颖异,郑思琳. 预防和控制流感在养老院暴发管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(15): 1867-1873. |
| [15] | 胡月,蒋运兰,楚鑫,杨淑艳,沈音丽,唐欣. 一例非小细胞肺癌患者癌因性疲乏杵针疗法的循证护理[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(35): 4514-4518. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





