中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 1568-1576.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0753
所属专题: 社区卫生服务最新研究合辑; 神经退行性病变最新文章合辑; 营养最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
刘晓, 张巾英, 彭滟, 王黎, 陈晓梅, 刘佳, 邓梦惠, 杨燕妮*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-14
修回日期:2023-01-27
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-02-23
通讯作者:
杨燕妮
基金资助:
LIU Xiao, ZHANG Jinying, PENG Yan, WANG Li, CHEN Xiaomei, LIU Jia, DENG Menghui, YANG Yanni*( )
)
Received:2022-10-14
Revised:2023-01-27
Published:2023-05-05
Online:2023-02-23
Contact:
YANG Yanni
摘要: 背景 保持脑健康是健康老龄化的高阶目标,合理膳食营养被认为是有望降低痴呆风险的重要途径之一,但目前临床上缺乏具体化、全面性的促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理方案,导致医务人员对社区居民的相关健康指导缺失或不足。 目的 检索、评价并总结促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理相关证据,为临床开展旨在促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理工作提供依据。 方法 于2022年3月,计算机检索UpToDate、BMJ最佳临床实践、乔安娜布里格斯研究所(JBI)循证卫生保健中心数据库、美国国立老化研究所(NIA)网站、加拿大安大略省注册护士协会(RNAO)网站、the Cochrane Library、PubMed、中国知网、医脉通等数据库和网站,获取促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理相关文献,文献类型包括临床决策、推荐实践、指南、证据总结、专家共识、系统评价,检索时限均为2017-01-01至2022-03-29。由2名接受过系统循证医学培训的研究者独立筛选文献、提取资料并对纳入的文献进行质量评价后,从符合质量标准的文献中提取证据,并对证据进行质量分级,总结促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理最佳证据。 结果 共纳入28篇文献,包括3篇指南,5篇专家共识,1篇临床决策,19篇系统评价;纳入文献总体质量较高。从干预时机、膳食营养评估和筛查、膳食模式及成分、特定营养素、咖啡摄入、体质量管理、健康教育及指导7个方面共汇总23条最佳证据。 结论 合理膳食营养对居民保持脑健康有促进作用,社区医务人员应结合临床情境、居民膳食营养现状与选择偏好、最佳证据,为居民制定个体化、促进其脑健康的膳食营养管理方案。
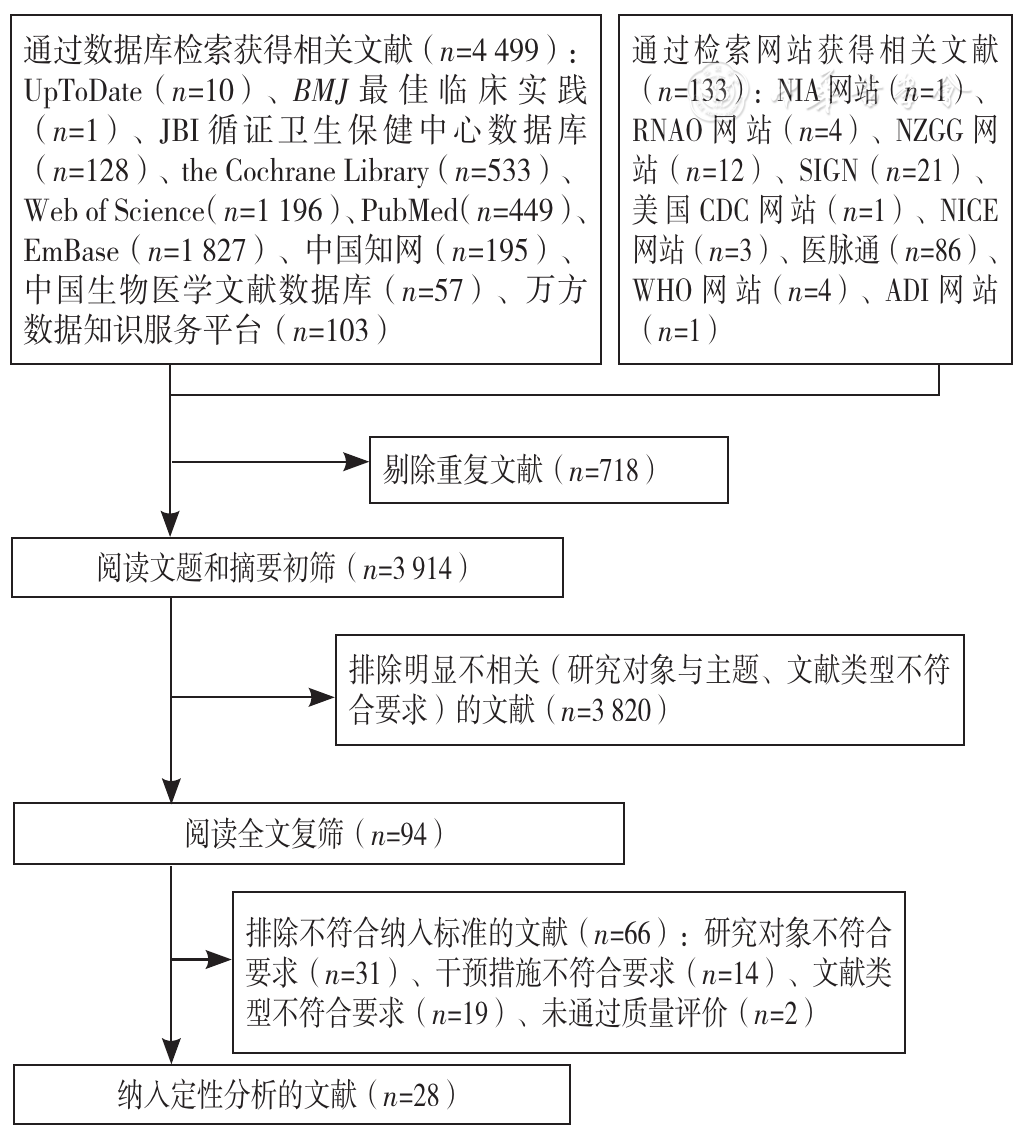
图1 文献检索和筛选流程注:JBI=乔安娜布里格斯研究所,NIA=美国国立老化研究所,RNAO=加拿大安大略省注册护士协会,NZGG=新西兰指南协作组,SIGN=苏格兰院际指南协作网,CDC=疾病控制与预防中心,NICE=英国国家卫生与照护优化研究所,WHO=世界卫生组织,ADI=国际阿尔茨海默病协会
Figure 1 Flow chart of literature searching and screening
| 作者 | 发表年份(年) | 文献来源 | 文献性质 | 文献主题 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 2020 | 中国知网 | 指南 | 中国AD一级预防指南 |
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 2018 | 中国知网 | 指南 | AD的危险因素及其干预 |
| WHO[ | 2019 | WHO网站 | 指南 | 降低认知衰退和痴呆风险 |
| LIVINGSTON等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 专家共识 | 痴呆预防、干预和护理 |
| ROCKWOOD等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 专家共识 | 降低晚年罹患痴呆的风险 |
| SMITH等[ | 2018 | Web of Science | 专家共识 | 同型半胱氨酸与痴呆 |
| SABBAGH等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 专家共识 | 降低认知功能衰退风险的一级预防建议 |
| 中华医学会肠外肠内营养学分会脑健康营养协作组等[ | 2021 | 中国知网 | 专家共识 | AD脑健康营养干预专家共识 |
| LARSON[ | 2019 | UpToDate | 临床决策 | 认知功能障碍和痴呆评估 |
| JIANG等[ | 2017 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 增加水果和蔬菜摄入量对降低认知障碍和痴呆风险的影响 |
| GOODWILL等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 低水平维生素D对认知功能的影响 |
| WU等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 咖啡摄入量与认知障碍的发病风险 |
| LOUGHREY等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 地中海饮食对健康老年人认知功能的影响 |
| WU等[ | 2017 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 水果和蔬菜摄入量与认知障碍的发病风险 |
| KNIGHT等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 地中海饮食对年龄相关性认知功能的影响 |
| ZENG等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 以鱼为主的饮食模式对降低认知衰退的影响 |
| RUTJES等[ | 2018 | the Cochrane Library | 系统评价 | 补充维生素和矿物质对健康中老年人认知功能的影响 |
| CAO等[ | 2019 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 膳食脂肪摄入对认知功能的影响 |
| AMMAR等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 多酚干预对健康老年人认知功能的影响 |
| WHITTY等[ | 2020 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 生活方式和社会心理干预对降低认知衰退的影响 |
| BEHRENS等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 维生素B对认知功能的影响 |
| LIU等[ | 2020 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 膳食模式、饮食质量与痴呆的发病风险 |
| YU等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | AD的循证预防 |
| KOSTI等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 鱼类摄入量、n-3脂肪酸对认知功能的影响 |
| KHEIROURI等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | MIND对老年人认知功能的影响 |
| ZHANG等[ | 2021 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 叶酸对AD的影响 |
| MCGRATTAN等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 营养干预对预防认知障碍和痴呆的影响 |
| WANG等[ | 2022 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 维生素B对降低认知功能衰退和痴呆发病风险的影响 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1 General characteristics of the included literature
| 作者 | 发表年份(年) | 文献来源 | 文献性质 | 文献主题 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 2020 | 中国知网 | 指南 | 中国AD一级预防指南 |
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 2018 | 中国知网 | 指南 | AD的危险因素及其干预 |
| WHO[ | 2019 | WHO网站 | 指南 | 降低认知衰退和痴呆风险 |
| LIVINGSTON等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 专家共识 | 痴呆预防、干预和护理 |
| ROCKWOOD等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 专家共识 | 降低晚年罹患痴呆的风险 |
| SMITH等[ | 2018 | Web of Science | 专家共识 | 同型半胱氨酸与痴呆 |
| SABBAGH等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 专家共识 | 降低认知功能衰退风险的一级预防建议 |
| 中华医学会肠外肠内营养学分会脑健康营养协作组等[ | 2021 | 中国知网 | 专家共识 | AD脑健康营养干预专家共识 |
| LARSON[ | 2019 | UpToDate | 临床决策 | 认知功能障碍和痴呆评估 |
| JIANG等[ | 2017 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 增加水果和蔬菜摄入量对降低认知障碍和痴呆风险的影响 |
| GOODWILL等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 低水平维生素D对认知功能的影响 |
| WU等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 咖啡摄入量与认知障碍的发病风险 |
| LOUGHREY等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 地中海饮食对健康老年人认知功能的影响 |
| WU等[ | 2017 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 水果和蔬菜摄入量与认知障碍的发病风险 |
| KNIGHT等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 地中海饮食对年龄相关性认知功能的影响 |
| ZENG等[ | 2017 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 以鱼为主的饮食模式对降低认知衰退的影响 |
| RUTJES等[ | 2018 | the Cochrane Library | 系统评价 | 补充维生素和矿物质对健康中老年人认知功能的影响 |
| CAO等[ | 2019 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 膳食脂肪摄入对认知功能的影响 |
| AMMAR等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 多酚干预对健康老年人认知功能的影响 |
| WHITTY等[ | 2020 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 生活方式和社会心理干预对降低认知衰退的影响 |
| BEHRENS等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 维生素B对认知功能的影响 |
| LIU等[ | 2020 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 膳食模式、饮食质量与痴呆的发病风险 |
| YU等[ | 2020 | PubMed | 系统评价 | AD的循证预防 |
| KOSTI等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 鱼类摄入量、n-3脂肪酸对认知功能的影响 |
| KHEIROURI等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | MIND对老年人认知功能的影响 |
| ZHANG等[ | 2021 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 叶酸对AD的影响 |
| MCGRATTAN等[ | 2022 | Web of Science | 系统评价 | 营养干预对预防认知障碍和痴呆的影响 |
| WANG等[ | 2022 | PubMed | 系统评价 | 维生素B对降低认知功能衰退和痴呆发病风险的影响 |
| 作者 | 标准化百分比(%) | 标准化百分比≥60%的领域数(个) | 标准化百分比≥30%的领域数(个) | 推荐级别 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围和目的 | 参与人员 | 制定严谨性 | 表达清晰性 | 适用性 | 编辑独立性 | ||||
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 83.3 | 66.7 | 57.3 | 94.4 | 39.6 | 91.7 | 4 | 6 | B |
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 72.2 | 58.3 | 56.2 | 88.9 | 41.7 | 91.7 | 3 | 6 | B |
| WHO[ | 100.0 | 97.2 | 97.9 | 100.0 | 95.8 | 91.7 | 6 | 6 | A |
表2 纳入指南的质量评价结果
Table 2 Methodological quality assessment for included guidelines
| 作者 | 标准化百分比(%) | 标准化百分比≥60%的领域数(个) | 标准化百分比≥30%的领域数(个) | 推荐级别 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围和目的 | 参与人员 | 制定严谨性 | 表达清晰性 | 适用性 | 编辑独立性 | ||||
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 83.3 | 66.7 | 57.3 | 94.4 | 39.6 | 91.7 | 4 | 6 | B |
| 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组等[ | 72.2 | 58.3 | 56.2 | 88.9 | 41.7 | 91.7 | 3 | 6 | B |
| WHO[ | 100.0 | 97.2 | 97.9 | 100.0 | 95.8 | 91.7 | 6 | 6 | A |
| 作者 | ① | ②a | ③ | ④a | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦a | ⑧ | ⑨a | ⑩ | ⑪a | ⑫ | ⑬a | ⑭ | ⑮a | ⑯ | 质量等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIANG等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| GOODWILL等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| LOUGHREY等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| KNIGHT等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 中 |
| ZENG等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| RUTJES等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| CAO等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| AMMAR等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WHITTY等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 高 |
| BEHRENS等[ | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 中 |
| LIU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| KOSTI等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| KHEIROURI等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 高 |
| ZHANG等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 中 |
| MCGRATTAN等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| YU等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| WANG等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
表3 纳入系统评价的质量评价结果
Table 3 Quality evaluation of included systematic reviews
| 作者 | ① | ②a | ③ | ④a | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦a | ⑧ | ⑨a | ⑩ | ⑪a | ⑫ | ⑬a | ⑭ | ⑮a | ⑯ | 质量等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIANG等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| GOODWILL等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| LOUGHREY等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| KNIGHT等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 中 |
| ZENG等[ | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| RUTJES等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| CAO等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| AMMAR等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| WHITTY等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 高 |
| BEHRENS等[ | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 中 |
| LIU等[ | Y | N | Y | PY | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 低 |
| KOSTI等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| KHEIROURI等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | X | X | Y | Y | X | Y | 高 |
| ZHANG等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | PY | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 中 |
| MCGRATTAN等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| YU等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| WANG等[ | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 高 |
| 证据内容 | 证据等级 | 推荐级别 |
|---|---|---|
| 干预时机 | ||
| 1.对居民AD相关危险因素,如不健康饮食、肥胖、高同型半胱氨酸血症等进行早期识别和干预[ | 5b | A |
| 膳食营养评估和筛查 | ||
| 2.建议医务人员每年至少评估1次>45岁居民的膳食模式和习惯[ | 5b | A |
| 3.建议定期对居民进行血液检查,以评估其同型半胱氨酸水平;应对高同型半胱氨酸血症患者进行维生素B和/或叶酸治疗,并关注其认知功能[ | 1a | A |
| 4.推荐对接受痴呆评估的居民进行维生素B12缺乏症和甲状腺功能减退症筛查[ | 2a | B |
| 5.建议使用MNA-SF、NRS-2002对≥65岁老年人、认知障碍科就诊的人群进行常规营养风险筛查[ | 5b | A |
| 6.完善对高营养不良风险人群的营养评估工作,包括病史采集、人体测量、实验室检查、功能状态评估,以明确其营养不良的原因;做出营养不良的诊断和分级诊断,并制订营养治疗计划[ | 5b | A |
| 膳食模式及成分 | ||
| 7.向居民推荐健康、均衡的膳食模式,鼓励居民遵循"五谷为养、五畜为益、五菜为充、五果为助"的平衡膳食原则,倡导饮食多样化[ | 3a | A |
| 8.建议居民高度依从MeDi或MIND,以便降低痴呆患病风险并延缓认知功能下降[ | 3a | A |
| 9.建议居民增加富含单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA)和多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)的豆类、高纤维坚果和全谷物,以及鸡肉等非红肉的摄入量,减少富含饱和脂肪酸(SFA)的高脂乳制品(如黄油、奶酪)、红肉、油炸食品和加工食品摄入量,以降低认知功能下降的风险[ | 5b | A |
| 10.建议居民增加水果和蔬菜的摄入量,每日增加100 g水果和蔬菜摄入可使认知障碍和痴呆风险降低约13%[ | 3b | A |
| 11.建议居民每周摄入2份鱼(250 g),以降低全因痴呆和AD的风险[ | 3a | A |
| 特定营养素 | ||
| 12.富含多酚的补充剂对认知功能有潜在益处,但至少中等剂量(≥500 mg)的具有中等生物利用度(≈9%)至高生物利用度(43%)的多酚(例如:异黄酮类、没食子酸、儿茶素和黄烷酮)才能发挥作用[ | 1a | B |
| 13.叶酸缺乏(<13.5 nmol/L)会增加罹患AD和认知功能下降的风险,每日摄入足够的叶酸(≥400 g/d)对认知功能有益[ | 3b | A |
| 14.食物中含有的维生素C或将维生素C作为补充剂服用对居民认知功能有一定的积极作用[ | 1a | A |
| 15.低水平维生素D与较差的认知功能相关[ | 3b | B |
| 16.来源于鱼类的二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)对执行功能有积极影响,但对整体认知功能没有明显影响[ | 3a | B |
| 17.营养素缺乏可能与AD认知功能改变有关,但不推荐单独补充某种营养素,或限制某种营养素及其化合物的摄入,以改善认知功能或预防和延缓AD的发生和发展[ | 5b | A |
| 咖啡摄入 | ||
| 18.咖啡摄入量和患认知障碍的风险呈"J"形关系,每日饮用1~2杯咖啡的情况下,认知障碍发病风险最低[ | 3a | A |
| 体质量管理 | ||
| 19. 65岁以下的成年人应通过减少热量摄入、适当运动来维持或减轻体质量,以维持BMI在18.5~24.9 kg/m2,>65岁的成年人BMI不宜过低[ | 3a | A |
| 20.应密切监测年龄>65岁且体质量有减轻趋势的成年人的认知状况[ | 3a | A |
| 健康教育及指导 | ||
| 21.医务人员应为居民提供MIND、DASH、MeDi模式相关知识的教育和指导[ | 5b | A |
| 22.对于饮食不太健康的居民,医务人员应该就健康膳食对脑健康的重要性进行健康指导,并在每次年度会面时向其提出可接受的脑健康相关膳食营养干预措施,通过共同决策帮助其改变不良饮食行为习惯,促进其健康膳食行为习惯的养成[ | 5b | A |
| 23.确定居民潜在的饮食动机和障碍[ | 5b | A |
表4 促进社区居民脑健康的膳食营养管理最佳证据总结
Table 4 Evidence summary of dietary nutrients management for brain health promotion in community-dwelling people
| 证据内容 | 证据等级 | 推荐级别 |
|---|---|---|
| 干预时机 | ||
| 1.对居民AD相关危险因素,如不健康饮食、肥胖、高同型半胱氨酸血症等进行早期识别和干预[ | 5b | A |
| 膳食营养评估和筛查 | ||
| 2.建议医务人员每年至少评估1次>45岁居民的膳食模式和习惯[ | 5b | A |
| 3.建议定期对居民进行血液检查,以评估其同型半胱氨酸水平;应对高同型半胱氨酸血症患者进行维生素B和/或叶酸治疗,并关注其认知功能[ | 1a | A |
| 4.推荐对接受痴呆评估的居民进行维生素B12缺乏症和甲状腺功能减退症筛查[ | 2a | B |
| 5.建议使用MNA-SF、NRS-2002对≥65岁老年人、认知障碍科就诊的人群进行常规营养风险筛查[ | 5b | A |
| 6.完善对高营养不良风险人群的营养评估工作,包括病史采集、人体测量、实验室检查、功能状态评估,以明确其营养不良的原因;做出营养不良的诊断和分级诊断,并制订营养治疗计划[ | 5b | A |
| 膳食模式及成分 | ||
| 7.向居民推荐健康、均衡的膳食模式,鼓励居民遵循"五谷为养、五畜为益、五菜为充、五果为助"的平衡膳食原则,倡导饮食多样化[ | 3a | A |
| 8.建议居民高度依从MeDi或MIND,以便降低痴呆患病风险并延缓认知功能下降[ | 3a | A |
| 9.建议居民增加富含单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA)和多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)的豆类、高纤维坚果和全谷物,以及鸡肉等非红肉的摄入量,减少富含饱和脂肪酸(SFA)的高脂乳制品(如黄油、奶酪)、红肉、油炸食品和加工食品摄入量,以降低认知功能下降的风险[ | 5b | A |
| 10.建议居民增加水果和蔬菜的摄入量,每日增加100 g水果和蔬菜摄入可使认知障碍和痴呆风险降低约13%[ | 3b | A |
| 11.建议居民每周摄入2份鱼(250 g),以降低全因痴呆和AD的风险[ | 3a | A |
| 特定营养素 | ||
| 12.富含多酚的补充剂对认知功能有潜在益处,但至少中等剂量(≥500 mg)的具有中等生物利用度(≈9%)至高生物利用度(43%)的多酚(例如:异黄酮类、没食子酸、儿茶素和黄烷酮)才能发挥作用[ | 1a | B |
| 13.叶酸缺乏(<13.5 nmol/L)会增加罹患AD和认知功能下降的风险,每日摄入足够的叶酸(≥400 g/d)对认知功能有益[ | 3b | A |
| 14.食物中含有的维生素C或将维生素C作为补充剂服用对居民认知功能有一定的积极作用[ | 1a | A |
| 15.低水平维生素D与较差的认知功能相关[ | 3b | B |
| 16.来源于鱼类的二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)对执行功能有积极影响,但对整体认知功能没有明显影响[ | 3a | B |
| 17.营养素缺乏可能与AD认知功能改变有关,但不推荐单独补充某种营养素,或限制某种营养素及其化合物的摄入,以改善认知功能或预防和延缓AD的发生和发展[ | 5b | A |
| 咖啡摄入 | ||
| 18.咖啡摄入量和患认知障碍的风险呈"J"形关系,每日饮用1~2杯咖啡的情况下,认知障碍发病风险最低[ | 3a | A |
| 体质量管理 | ||
| 19. 65岁以下的成年人应通过减少热量摄入、适当运动来维持或减轻体质量,以维持BMI在18.5~24.9 kg/m2,>65岁的成年人BMI不宜过低[ | 3a | A |
| 20.应密切监测年龄>65岁且体质量有减轻趋势的成年人的认知状况[ | 3a | A |
| 健康教育及指导 | ||
| 21.医务人员应为居民提供MIND、DASH、MeDi模式相关知识的教育和指导[ | 5b | A |
| 22.对于饮食不太健康的居民,医务人员应该就健康膳食对脑健康的重要性进行健康指导,并在每次年度会面时向其提出可接受的脑健康相关膳食营养干预措施,通过共同决策帮助其改变不良饮食行为习惯,促进其健康膳食行为习惯的养成[ | 5b | A |
| 23.确定居民潜在的饮食动机和障碍[ | 5b | A |
| [1] |
徐俊,郑华光,洪音. 主动脑健康 提高认知储备[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志,2021,15(2):113-116. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115624-20201130-00833.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2018. The state of the art of dementia research:new frontiers[EB/OL]. (2018-09-21)[2022-03-29].
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global,regional,and national burden of neurological disorders,1990—2016:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet Neurol,2019,18(5):459-480. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
World Health Organization. Risk reduction of cognitive decline and dementia:WHO guidelines[EB/OL]. (2019-05-14)[2022-03-29].
|
| [13] | |
| [14] |
|
| [15] | |
| [16] |
张方圆,沈傲梅,曾宪涛,等. 系统评价方法学质量评价工具AMSTAR 2解读[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2018,10(1):14-18. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2018.01.03.
|
| [17] |
The Joanna Briggs Institute(JBI). The Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools[EB/OL]. [2022-03-29].
|
| [18] |
王春青,胡雁. JBI证据预分级及证据推荐级别系统(2014版)[J]. 护士进修杂志,2015,30(11):964-967. DOI:10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2015.11.002.
|
| [19] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 中国阿尔茨海默病一级预防指南[J]. 中华医学杂志,2020,100(35):2721-2735. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200702-02017.
|
| [20] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(七):阿尔茨海默病的危险因素及其干预[J]. 中华医学杂志,2018,98(19):1461-1466. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.19.002.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
中华医学会肠外肠内营养学分会脑健康营养协作组,阿尔茨海默病脑健康营养干预专家共识撰写组,徐俊,等. 阿尔茨海默病脑健康营养干预专家共识[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2021,51(12):1762-1788. DOI:10.1360/SSV-2021-0196.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Practice parameter for diagnosis and evaluation of dementia. (summary statement)Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology[J]. Neurology,1994,44(11):2203-2206. DOI:10.1212/wnl.44.11.2203.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
李华. 成年人改变生活方式以降低痴呆风险的信念与健康行为的关系研究[D]. 重庆:陆军军医大学,2021.
|
| [57] |
|
| [1] | 纪冰, 姜嘟嘟, 陈晨, 郑艳玲, 石建伟, 方力争, 杜雪平. 分级诊疗背景下带状疱疹社区全科诊疗路径构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3110-3118. |
| [2] | 石佳瑞, 王梓力, 张薛晴, 宋玉磊, 徐桂华, 柏亚妹. 南京市社区认知症服务中心认知初步筛查服务开展现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [3] | 陈友兰, 蓝彦琦, 吴阿华, 张海霞, 黄健康, 郭志南. "三师共管"家庭医生签约服务对老年高血压患者的健康管理效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2769-2775. |
| [4] | 马盼盼, 王思静, 游娜, 丁大法, 鲁一兵. Danuglipron与Orforglipron治疗2型糖尿病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [5] | 刘洪亚, 于德华. 上海市社区全专结合临床诊疗技术建设实践[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2390-2397. |
| [6] | 刘青芳, 韦有仕, 肖斐, 周春香, 刘群, 袁慧, 曹天然. 麦角硫因激活核因子E2相关因子2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路改善血管性痴呆大鼠认知功能障碍研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2156-2162. |
| [7] | 李杰, 杜汋, 邵屾, 潘东, 张雅欣. 基于数据包络分析和随机前沿分析的天津市基层医疗卫生机构中医诊疗服务运营效率研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 1980-1986. |
| [8] | 叶青, 陈明敏, 任菁菁. 基层全科医师发展精神卫生亚专长的必要性及路径探索[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 1950-1954. |
| [9] | 何梅亮, 刘修良, 赵梅桂, 郭艳芳, 徐英. 社区电子健康档案使用情况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1628-1634. |
| [10] | 赵琳琳, 罗琪, 胡清华, 陈小垒, 杜娟, 邵爽. 家庭医生团队开展慢性病医防融合服务现状及阻碍的定性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1661-1667. |
| [11] | 于德华. 基于全专结合的社区专病诊疗技术发展策略[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1256-1258. |
| [12] | 张含之, 于德华. 基于全科医学思维的全专协作慢病管理实证探讨[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1259-1264. |
| [13] | 石建军, 金花, 陆媛, 于德华. 社区全专结合门诊建设模式及优化策略[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1249-1255. |
| [14] | 张小娟, 刘阳, 彭博, 曹晓琳, 叶媛, 朱坤. 基层医疗卫生机构儿科建设与服务提供研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1228-1235. |
| [15] | 首都医科大学肿瘤学系妇科肿瘤学组. 妇科常见恶性肿瘤全专结合管理专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(08): 911-922. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





