中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 2540-2547.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0853
所属专题: 肿瘤最新文章合辑; 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑; 营养最新文章合辑
薛珊1, 李来有1,*( ), 梁军利1, 靳英辉2, 魏淑艳3
), 梁军利1, 靳英辉2, 魏淑艳3
收稿日期:2022-10-24
修回日期:2023-01-26
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-03-28
通讯作者:
李来有
XUE Shan1, LI Laiyou1,*( ), LIANG Junli1, JIN Yinghui2, WEI Shuyan3
), LIANG Junli1, JIN Yinghui2, WEI Shuyan3
Received:2022-10-24
Revised:2023-01-26
Published:2023-07-15
Online:2023-03-28
Contact:
LI Laiyou
摘要: 背景 食管癌患者常发生营养不良,国内外研究显示,营养不良严重影响患者的恢复。目前居家期间接受家庭肠内营养(HEN)的患者越来越多,但HEN对食管癌患者的有效性和安全性并不明确。 目的 通过Meta分析评价HEN对食管癌患者的有效性和安全性。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、Cochrane Library、Embase、Web of Science、CINAHL、Scopus、万方数据知识服务平台、中国知网、维普网及中国生物医学文献数据库,搜集有关食管癌患者接受HEN的随机对照试验,检索时限从建库至2021年12月。试验组患者接受HEN支持〔肠内管饲(ETF)和口服营养补充(ONS)均可〕,对照组仅接受常规口服饮食。由2名研究者独立筛选文献、提取资料,并采用Cochrane协作网推荐的RoB 2.0工具对文献进行质量评价。采用RevMan 5.4.1软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入14篇文献,包括1 040例食管癌患者。Meta分析结果显示,试验组患者体质量增长值、BMI增长值、血红蛋白增长值、血清总蛋白增长值、血清前白蛋白增长值、血清转铁蛋白增长值均高于对照组〔SMD=0.63,95%CI(0.40,0.85),P<0.000 01;SMD=0.60,95%CI(0.44,0.76),P<0.000 01;SMD=1.58,95%CI(1.37,1.79),P<0.000 01;SMD=1.19,95%CI(0.79,1.58),P<0.000 01;SMD=0.97,95%CI(0.79,1.14),P<0.000 01;SMD=1.12,95%CI(0.45,1.79),P=0.001〕。在ETF亚组和ONS亚组分析中,试验组血清白蛋白增长值均高于对照组〔SMD=1.25,95%CI(0.82,1.68),P<0.000 01;SMD=0.61,95%CI(0.26,0.97),P<0.000 01〕。试验组营养不良发生率低于对照组〔OR=0.47,95%CI(0.33,0.67),P<0.000 1〕。两组胃肠道并发症发生率比较,差异无统计学意义〔RR=1.33,95%CI(1.00,1.77),P=0.05〕。试验组和对照组生活质量评分比较,差异无统计学意义〔MD=4.97,95%CI(0.06,9.87),P=0.05〕;试验组躯体功能评分高于对照组〔MD=6.67,95%CI(2.86,10.48),P=0.000 6〕,疲劳症状评分低于对照组〔MD=-7.31,95%CI(-11.85,-2.77),P=0.002〕。敏感性分析结果显示,合并结果稳定可靠。 结论 HEN能够改善食管癌术后出院患者的营养状况和躯体功能,并减轻患者的疲劳症状,且并未增加胃肠道并发症的发生率,但暂未发现能够改善患者总体生活质量。
| 步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| #1 | "Esophageal Neoplasms" [MeSH] OR "esophageal neoplasm" [Title] OR "esophageal neoplasms" [Title] OR "cancer of esophagus" [Title] OR "cancer of the esophagus" [Title] OR "esophagus cancer" [Title] OR "esophagus cancers" [Title] OR "esophageal cancer" [Title] OR "esophageal cancers" [Title] OR "esophageal carcinoma" [Title] OR "esophagus carcinoma" [Title] OR "esophagectomy" [Title] OR "esophagus resection" [Title] OR "postesophagectomy" [Title] |
| #2 | "Enteral Nutrition" [MeSH] OR "home enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "family enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral nutritional" [Title/Abstract] OR "nasogastric gavage" [Title/Abstract] OR "tube feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteric feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "jejunostomy" [Title/Abstract] OR "oral nutritional supplements" [Title/Abstract] OR "ONS" [Title/Abstract] |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 |
| #4 | "aftercare" [All Fields] OR "discharge" [All Fields] OR "home" [All Fields] OR "family" [All Fields] OR "community" [All Fields] |
| #5 | #3 AND #4 |
表1 PubMed数据库检索策略
Table 1 Searching strategy of PubMed database
| 步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| #1 | "Esophageal Neoplasms" [MeSH] OR "esophageal neoplasm" [Title] OR "esophageal neoplasms" [Title] OR "cancer of esophagus" [Title] OR "cancer of the esophagus" [Title] OR "esophagus cancer" [Title] OR "esophagus cancers" [Title] OR "esophageal cancer" [Title] OR "esophageal cancers" [Title] OR "esophageal carcinoma" [Title] OR "esophagus carcinoma" [Title] OR "esophagectomy" [Title] OR "esophagus resection" [Title] OR "postesophagectomy" [Title] |
| #2 | "Enteral Nutrition" [MeSH] OR "home enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "family enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral nutrition" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral nutritional" [Title/Abstract] OR "nasogastric gavage" [Title/Abstract] OR "tube feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteral feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "enteric feeding" [Title/Abstract] OR "jejunostomy" [Title/Abstract] OR "oral nutritional supplements" [Title/Abstract] OR "ONS" [Title/Abstract] |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 |
| #4 | "aftercare" [All Fields] OR "discharge" [All Fields] OR "home" [All Fields] OR "family" [All Fields] OR "community" [All Fields] |
| #5 | #3 AND #4 |
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 样本量(E/C) | 年龄(E/C) | 病理分期(Ⅰ/Ⅱ /Ⅲ/Ⅳ) | 干预措施及持续时间(E/C) | 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIU[ | 2020 | 26/24 | 62.04±5.12/64.58±5.87 | 24/16/10/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养或ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①②④⑧⑨ |
| BOWREY[ | 2015 | 20/21 | 64.6±8.0/63.1±8.7 | 6/12/22/1 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养6周/常规口服饮食6周 | ①⑧⑨ |
| XIE[ | 2021 | 42/35 | 61.57±8.45/63.06±5.79 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ⑧⑨ | |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 53/53 | 67.83±7.17/67.79±7.24 | 49/57/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑦⑨⑩ |
| LI[ | 2020 | 30/32 | 63.25±5.23/63.61±5.64 | 11/23/21/7 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①② |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 30/30 | 70.37±7.58/69.53±9.4 | 9/27/24/0 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑥⑩ |
| ZENG[ | 2017 | 30/30 | 61.7±8.4/59.3±10.4 | 1/28/31/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ⑧⑨⑩ |
| 范富翠[ | 2020 | 40/40 | 62.58±6.64/60.88±6.86 | Ⅰ~Ⅲ | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ③④⑤⑥⑦⑩ |
| 曹子昂[ | 2013 | 40/40 | 65.8/67.4 | 1/36/42/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养2个月/常规口服饮食2个月 | ④⑤⑥⑦⑨ |
| 童雅萍[ | 2018 | 44/41 | 62.07±7.06/60.85±8.08 | 32/53/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑦⑩ |
| 刘秀娟[ | 2021 | 46/48 | 59.03±7.79/57.52±7.88 | 21/51/22/0 | 十二指肠营养管喂养2个月/常规口服饮食2个月 | ②③④⑤⑩ |
| 王倩[ | 2019 | 48/48 | 53±6.75/55±7.25 | 41/55/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4个月/常规口服饮食4个月 | ①②③④⑤ |
| 谷金玲[ | 2020 | 41/40 | 54±8.0/52±7.9 | 30/42/9/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑩ |
| 石海燕[ | 2021 | 34/34 | 67.3±8.1/68.4±8.5 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①④⑤⑥ |
表2 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 样本量(E/C) | 年龄(E/C) | 病理分期(Ⅰ/Ⅱ /Ⅲ/Ⅳ) | 干预措施及持续时间(E/C) | 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIU[ | 2020 | 26/24 | 62.04±5.12/64.58±5.87 | 24/16/10/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养或ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①②④⑧⑨ |
| BOWREY[ | 2015 | 20/21 | 64.6±8.0/63.1±8.7 | 6/12/22/1 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养6周/常规口服饮食6周 | ①⑧⑨ |
| XIE[ | 2021 | 42/35 | 61.57±8.45/63.06±5.79 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ⑧⑨ | |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 53/53 | 67.83±7.17/67.79±7.24 | 49/57/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑦⑨⑩ |
| LI[ | 2020 | 30/32 | 63.25±5.23/63.61±5.64 | 11/23/21/7 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①② |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 30/30 | 70.37±7.58/69.53±9.4 | 9/27/24/0 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑥⑩ |
| ZENG[ | 2017 | 30/30 | 61.7±8.4/59.3±10.4 | 1/28/31/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ⑧⑨⑩ |
| 范富翠[ | 2020 | 40/40 | 62.58±6.64/60.88±6.86 | Ⅰ~Ⅲ | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ③④⑤⑥⑦⑩ |
| 曹子昂[ | 2013 | 40/40 | 65.8/67.4 | 1/36/42/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养2个月/常规口服饮食2个月 | ④⑤⑥⑦⑨ |
| 童雅萍[ | 2018 | 44/41 | 62.07±7.06/60.85±8.08 | 32/53/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑦⑩ |
| 刘秀娟[ | 2021 | 46/48 | 59.03±7.79/57.52±7.88 | 21/51/22/0 | 十二指肠营养管喂养2个月/常规口服饮食2个月 | ②③④⑤⑩ |
| 王倩[ | 2019 | 48/48 | 53±6.75/55±7.25 | 41/55/0/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4个月/常规口服饮食4个月 | ①②③④⑤ |
| 谷金玲[ | 2020 | 41/40 | 54±8.0/52±7.9 | 30/42/9/0 | 空肠造瘘管饲喂养4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ②③④⑤⑥⑩ |
| 石海燕[ | 2021 | 34/34 | 67.3±8.1/68.4±8.5 | ONS 4周/常规口服饮食4周 | ①④⑤⑥ |
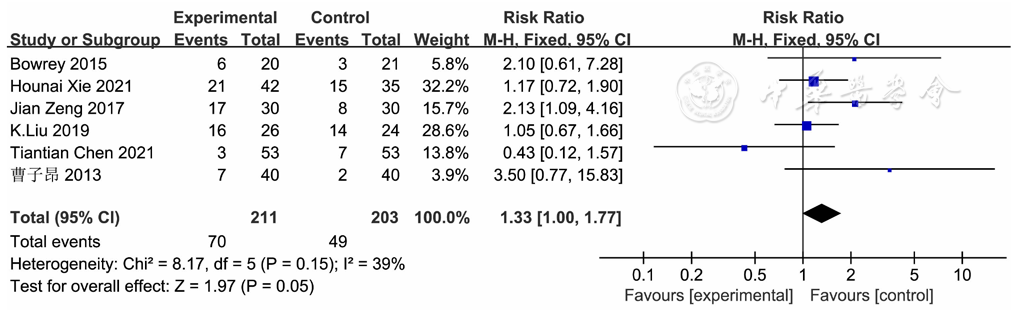
图11 干预组与对照组胃肠道并发症比较的森林图
Figure 11 Forest plot of comparison the prevalence of gastrointestinal complications between the experimental and control groups
| [1] | |
| [2] |
|
| [3] | |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
陈静儒,张振香,郭瑾,等. 照顾者对食管癌患者营养照护的质性研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志,2018,34(2):126-130. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1672-7088.2018.02.011.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
医学名词审定委员会.肠外肠内营养学名词[M].北京:科学出版社,2019:11.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
范富翠,童雅萍,梁冠冕,等. NRS2002结合营养指标评价食管癌术后出院患者的营养状况[J]. 广东医学,2020,41(19):1970-1974. DOI:10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20200938.
|
| [24] |
曹子昂,潘文标,梁而慷,等. 穿刺导管空肠造口术对食管癌患者术后肠内营养支持的临床意义[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(14):6355-6357. DOI:10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2013.14.033.
|
| [25] |
童雅萍,谢玲女,沈祝苹,等. 家庭肠内营养对食管癌根治术后患者营养状况的影响研究[J]. 护士进修杂志,2018,33(6):493-496. DOI:10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2018.06.005.
|
| [26] |
刘秀娟. 家庭肠内营养对微创食管癌根治术后患者营养状况的影响[J]. 中国临床护理,2021,13(3):158-161,164. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3768.2021.03.006.
|
| [27] |
王倩,王振华,王萍,等. 家庭肠内营养支持治疗对食管癌切除术后患者营养状况的影响[J]. 医学临床研究,2019,36(8):1651-1652. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2019.08.077.
|
| [28] |
谷金玲,龚太乾,宋伟安,等. 家庭肠内营养治疗对微创食管癌根治术后营养状况的影响[J]. 武警医学,2020,31(8):657-660. DOI:10.14010/j.cnki.wjyx.2020.08.004.
|
| [29] |
石海燕,陈宏林,吴超,等. 口服营养补充对食管癌根治术后出院患者营养状况影响的研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2021,59(11):176-179.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
郭敏,殷秀敏,王翠,等. 食管癌患者术后3个月症状群的调查[J]. 中华护理杂志,2019,54(8):1189-1193. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.08.014.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [3] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [4] | 韩笑, 李奇遇, 葛蒲, 范思园, 刘迪玥, 吴一波, 张清霜. 高血压患者行为生活方式对生命质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [5] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [6] | 聂丹宁, 史曙生, 陶昱如. 本体感觉神经肌肉促进技术联合螺旋稳定肌肉链训练治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的临床效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3032-3042. |
| [7] | 吴越, 王雪彤, 柯碧莲. 近视性黄斑病变低视力患者视觉相关生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [8] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [9] | 王笑林, 李秋月, 周彦君, 张金辉, 梁涛. 转移性结直肠癌患者呋喹替尼治疗相关心血管毒性发生率和风险的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [10] | 文敏, 周永玲, 刘静静, 蒋苛晴, 刘娟, 朱晓丹. 基于移动医疗APP的认知补偿训练对稳定期精神分裂症患者的干预效果与机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2819-2825. |
| [11] | 杨涵单, 乔雯, 何姝, 陈易, 童云梅. 接纳承诺疗法联合舍曲林对抑郁症青少年抑郁情绪、自杀意念及睡眠质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2813-2818. |
| [12] | 马盼盼, 王思静, 游娜, 丁大法, 鲁一兵. Danuglipron与Orforglipron治疗2型糖尿病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [13] | 阿迪力·吐尔孙, 程刚. 非奈利酮治疗2型糖尿病肾病有效性和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2686-2691. |
| [14] | 胡婉琴, 余深艳, 曹学华, 向凤, 贾钰. 中国儿童性早熟影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2661-2671. |
| [15] | 王颖, 颜轶隽, 刘蕾, 胡毓敏, 张扬, 刘凯, 姜博仁. 抗阻力运动联合营养干预对老年2型糖尿病合并肌少症患者血糖稳定性影响的临床研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2604-2610. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





