中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (03): 354-362.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.086
廖桂彬1, 龚嘉倩1, 赵利娜2, 侯江涛2, 郑鸿铭1, 李逸婷1, 吴苑1, 陈斌2,*
收稿日期:2021-07-02
修回日期:2021-09-28
出版日期:2022-01-20
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
陈斌
基金资助:Urease Breath Test and Stool Antigen Test Diagnose Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Patients with Bleeding Peptic Ulcer:a Meta-analysis
LIAO Guibin1,GONG Jiaqian1,ZHAO Lina2,HOU Jiangtao2,ZHENG Hongming1,LI Yiting1,WU Yuan1,CHEN Bin2*
1.Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510405,China
2.The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510405,China
*Corresponding author:CHEN Bin,Professor,Chief physician;E-mail:ddwchen@qq.com
LIAO Guibin and GONG Jiaqian are co-first authors
Received:2021-07-02
Revised:2021-09-28
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-12-29
摘要: 背景在消化性溃疡出血(PUB)患者中,抑酸药物的使用以及出血状态等会对幽门螺杆菌(H.pylori)感染的诊断造成干扰,关于尿素呼气试验(UBT)和粪便抗原检测(SAT)应用于出血患者的诊断准确性报道并不一致。目的明确UBT和SAT用于PUB患者H.pylori感染的准确性。方法计算机检索PubMed、EMBase、the Cochrane Library、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、中国生物医学文献服务系统(CBM),收集有关PUB患者运用UBT和/或SAT诊断H.pylori感染的诊断准确性试验,检索时间为建库至2021-03-31。提取资料并应用QUADAS-2工具进行文献质量评价;运用双变量混合效应模型和网络Meta分析模型(NMA)合并诊断试验效应量;采用Meta回归和亚组分析的方法探究异质性的来源。结果共纳入18篇文献,总计25项研究,包含1 105例患者。Meta分析结果显示,UBT、SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并灵敏度为0.90〔95%CI(0.79,0.95)〕、0.89〔95%CI(0.81,0.94)〕,合并特异度为0.91〔95%CI(0.86,0.95)〕、0.75〔95%CI(0.59,0.87)〕,合并诊断比值比为88.89〔95%CI(31.01,254.82)〕、24.35〔95%CI(13.76,43.09)〕,合并阳性似然比为10.07〔95%CI(6.07,16.71)〕、3.60〔95%CI(2.11,6.12)〕,合并阴性似然比为0.11〔95%CI(0.05,0.24)〕、0.15〔95%CI(0.09,0.24)〕,综合受试者工作特征(SROC)曲线下面积为0.93〔95%CI(0.90,0.95)〕、0.91〔95%CI(0.88,0.93)〕。Meta回归提示,取样时间对UBT和SAT的灵敏度异质性存在影响,取样时间和H.pylori感染判定标准对UBT的合并特异度异质性存在影响。Deek漏斗图提示纳入研究间不存在潜在发表偏倚(PUBT=0.53,PSAT=0.64)。结论UBT具有更好地发现PUB患者H.pylori感染的能力,对疾病诊断的帮助优于SAT。鉴于SAT的假阳性结果,针对PUB患者不推荐单独使用SAT,同时依据取样时间与诊断效能的负相关性,为尽量避免质子泵抑制剂对检测结果的影响,推荐血流动力学稳定条件下尽早完善H.pylori相关检测。
中图分类号:
LIAO Guibin, GONG Jiaqian, ZHAO Lina, HOU Jiangtao, ZHENG Hongming, LI Yiting, WU Yuan, CHEN Bin.
Urease Breath Test and Stool Antigen Test Diagnose Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Patients with Bleeding Peptic Ulcer:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(03): 354-362.
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU[ | 1999 | 中国 | 77 | 0 | ①阳性或②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 77(100.0) | 93.5 | - |
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 23(71.9) | 87.0 | 100.0 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 78 | 44(56.4) | ②阳性或④和⑥均阳性 | 是 | <24 h | 68(87.2) | 91.3 | 77.8 |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 32(100.0) | 100.0 | - |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第7天 | 32(100.0) | 90.6 | - |
| WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN[ | 2002 | 丹麦 | 95 | 70(73.7) | ②阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 44(46.3) | 86.4 | 96.1 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | - | 59(86.8) | 93.1 | 87.5 |
| WINIARSKI[ | 2003 | 波兰 | 81 | - | ⑥阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 64(79.0) | 98.4 | 100.0 |
| LIAO[ | 2003 | 中国 | 57 | 0 | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 46(80.7) | 100.0 | 81.8 |
| LO[ | 2005 | 中国 | 55 | 26(47.3) | ①阳性或②③④⑥中至少有3项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 35(63.6) | 94.3 | 85.0 |
| 张厚德[ | 1997 | 中国 | 51 | - | ②和④均阳性 | - | <96 h | 42(82.4) | 73.8 | 100.0 |
| 林勇[ | 2004 | 中国 | 40 | - | ③和⑥均阳性 | 否 | - | 24(60.0) | 37.5 | 87.5 |
| 李舜[ | 2005 | 中国 | 31 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | - | 31(100.0) | 61.3 | - |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 56(48.3) | 51.8 | 86.7 |
表1 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染研究的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU[ | 1999 | 中国 | 77 | 0 | ①阳性或②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 77(100.0) | 93.5 | - |
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 23(71.9) | 87.0 | 100.0 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 78 | 44(56.4) | ②阳性或④和⑥均阳性 | 是 | <24 h | 68(87.2) | 91.3 | 77.8 |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 32(100.0) | 100.0 | - |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第7天 | 32(100.0) | 90.6 | - |
| WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN[ | 2002 | 丹麦 | 95 | 70(73.7) | ②阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 44(46.3) | 86.4 | 96.1 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | - | 59(86.8) | 93.1 | 87.5 |
| WINIARSKI[ | 2003 | 波兰 | 81 | - | ⑥阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 64(79.0) | 98.4 | 100.0 |
| LIAO[ | 2003 | 中国 | 57 | 0 | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 46(80.7) | 100.0 | 81.8 |
| LO[ | 2005 | 中国 | 55 | 26(47.3) | ①阳性或②③④⑥中至少有3项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 35(63.6) | 94.3 | 85.0 |
| 张厚德[ | 1997 | 中国 | 51 | - | ②和④均阳性 | - | <96 h | 42(82.4) | 73.8 | 100.0 |
| 林勇[ | 2004 | 中国 | 40 | - | ③和⑥均阳性 | 否 | - | 24(60.0) | 37.5 | 87.5 |
| 李舜[ | 2005 | 中国 | 31 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | - | 31(100.0) | 61.3 | - |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 56(48.3) | 51.8 | 86.7 |
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | 试剂盒 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 23(71.9) | 95.7 | 33.3 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | <48 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 59(86.8) | 96.6 | 33.3 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 114 | 55(48.2) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | <24h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 56(49.1) | 83.9 | 89.7 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 109 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | 第2天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 53(48.6) | 79.2 | 87.5 |
| VAN LEERDAM[ | 2003 | 荷兰 | 36 | 20(55.6) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | - | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 15(41.7) | 100.0 | 52.4 |
| LIN[ | 2004 | 中国 | 93 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | <72 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 47(50.5) | 81.6 | 68.2 |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 单克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 94.1 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 73.5 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 34(100.0) | 58.8 | - |
| 于涛[ | 2006 | 中国 | 15 | - | ②③⑤中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 10(66.7) | 100.0 | 80.0 |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 单克隆免疫层析试验 | 56(48.3) | 91.1 | 83.3 |
表2 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染研究的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | 试剂盒 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 23(71.9) | 95.7 | 33.3 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | <48 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 59(86.8) | 96.6 | 33.3 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 114 | 55(48.2) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | <24h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 56(49.1) | 83.9 | 89.7 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 109 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | 第2天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 53(48.6) | 79.2 | 87.5 |
| VAN LEERDAM[ | 2003 | 荷兰 | 36 | 20(55.6) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | - | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 15(41.7) | 100.0 | 52.4 |
| LIN[ | 2004 | 中国 | 93 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | <72 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 47(50.5) | 81.6 | 68.2 |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 单克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 94.1 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 73.5 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 34(100.0) | 58.8 | - |
| 于涛[ | 2006 | 中国 | 15 | - | ②③⑤中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 10(66.7) | 100.0 | 80.0 |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 单克隆免疫层析试验 | 56(48.3) | 91.1 | 83.3 |
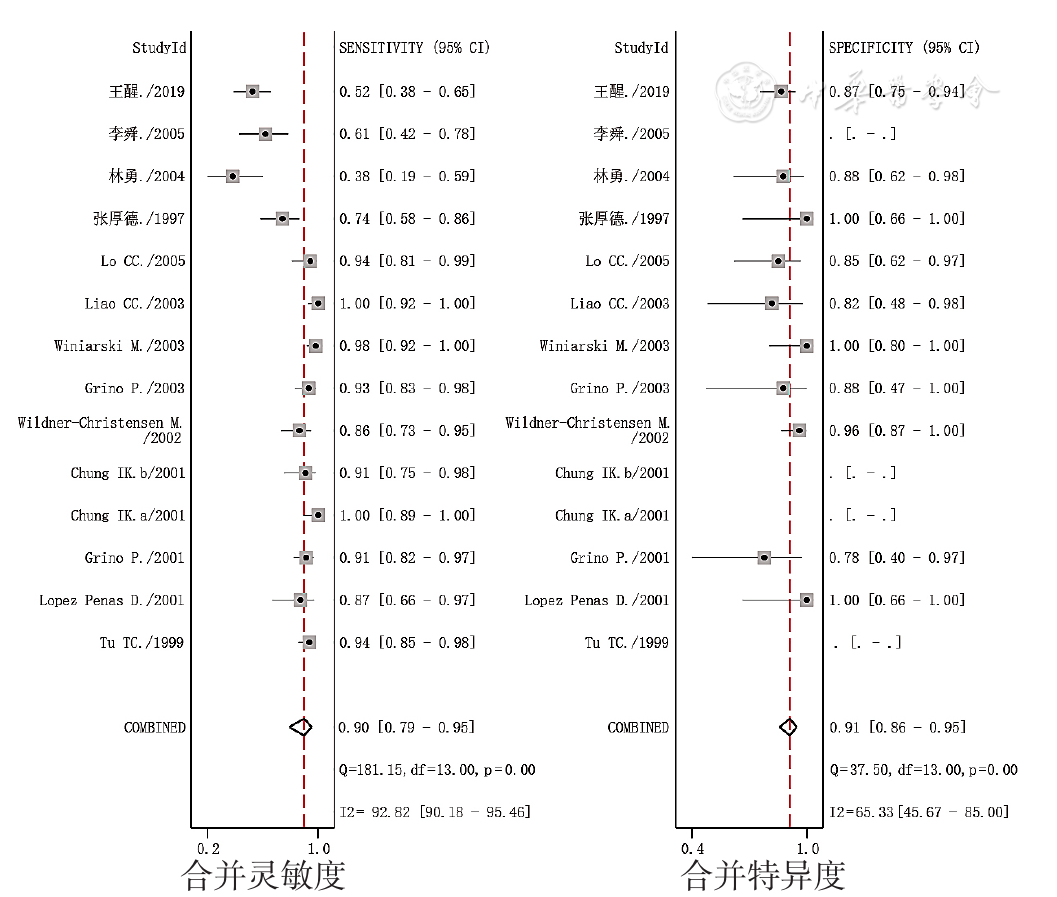
图3 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并灵敏度和合并特异度的森林图
Figure 3 Forest plots of pooled sensitivity and specificity of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
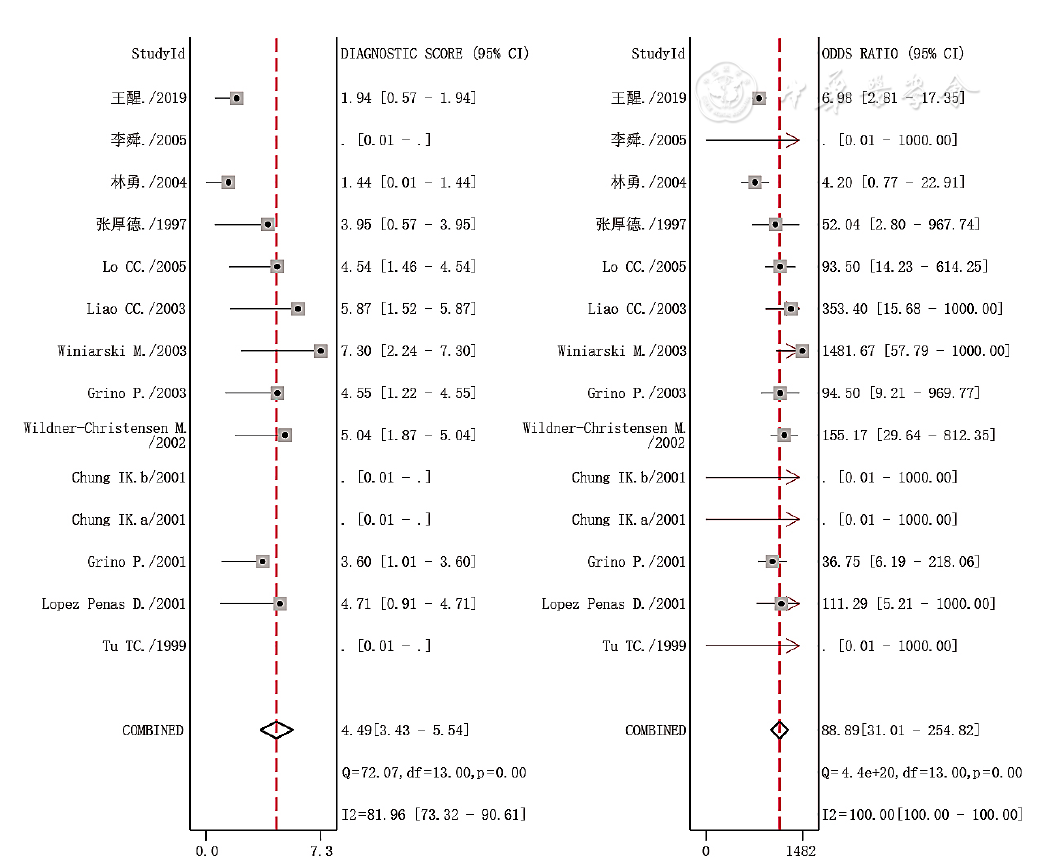
图4 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并诊断比值比的森林图
Figure 4 Forest plots of diagnostic odds ratio of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
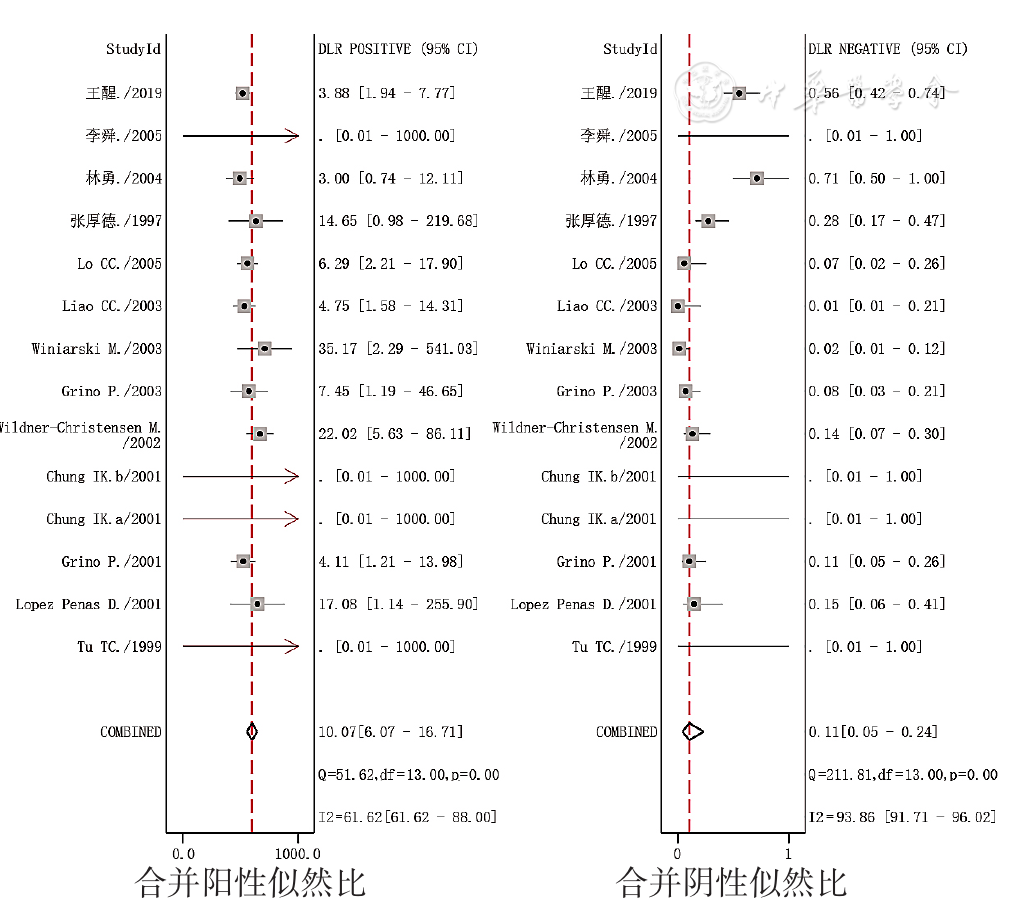
图5 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并似然比的森林图
Figure 5 Forest plots of likelihood ratio of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
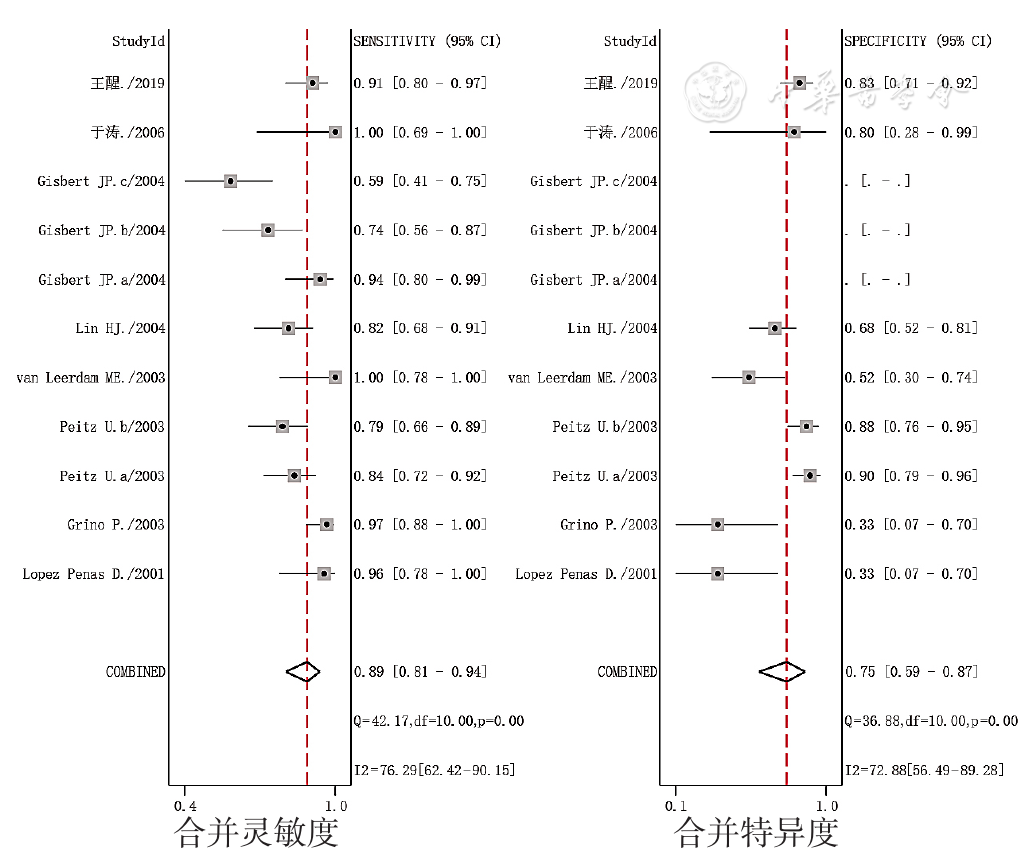
图6 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并灵敏度和合并特异度的森林图
Figure 6 Forest plots of pooled sensitivity and specificity of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
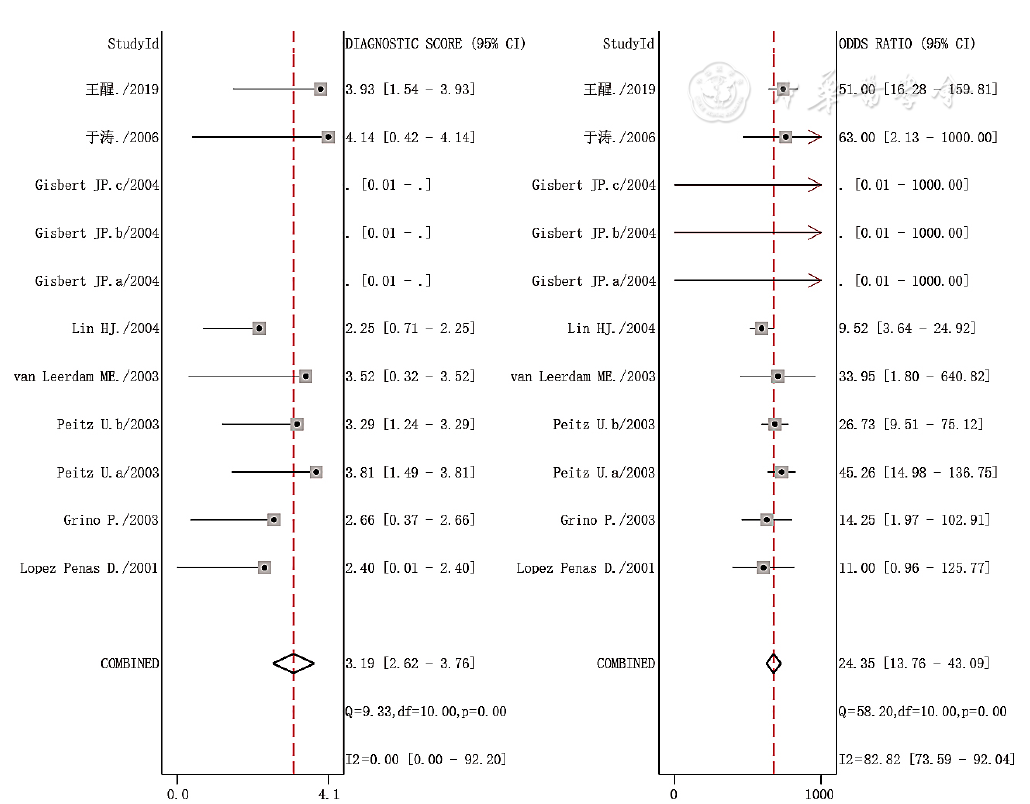
图7 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并诊断比值比的森林图
Figure 7 Forest plots of diagnostic odds ratio of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
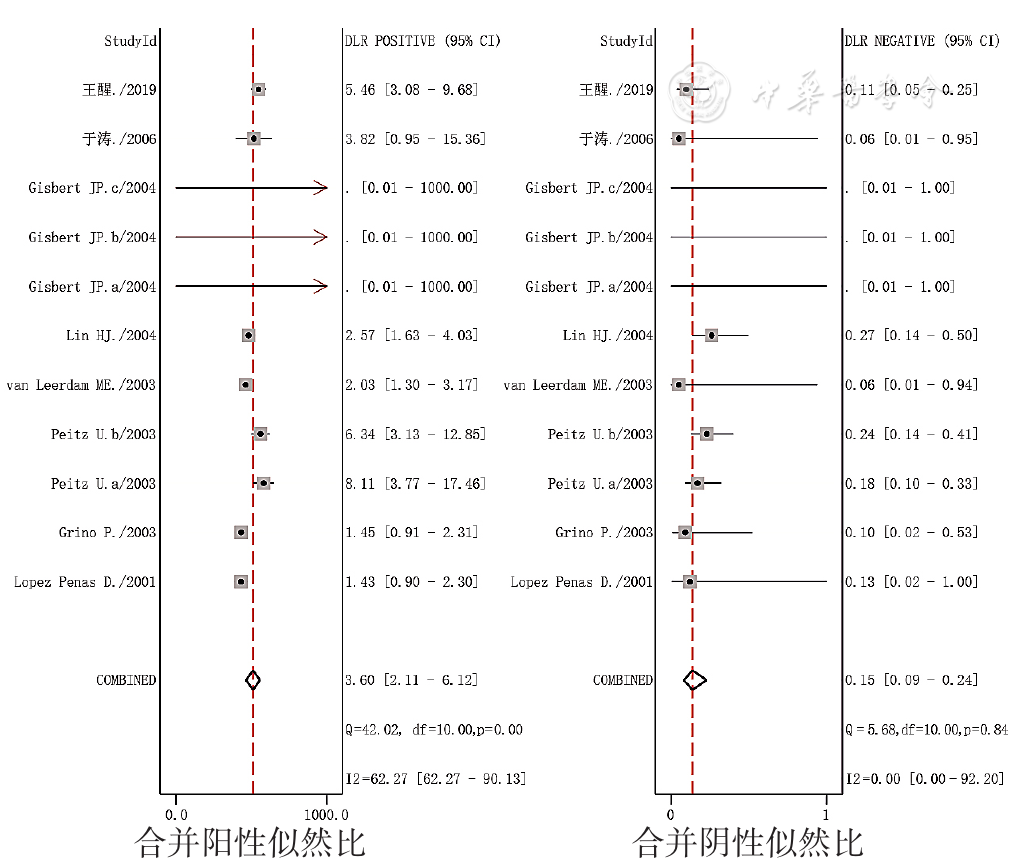
图8 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并似然比的森林图
Figure 8 Forest plots of likelihood ratio of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
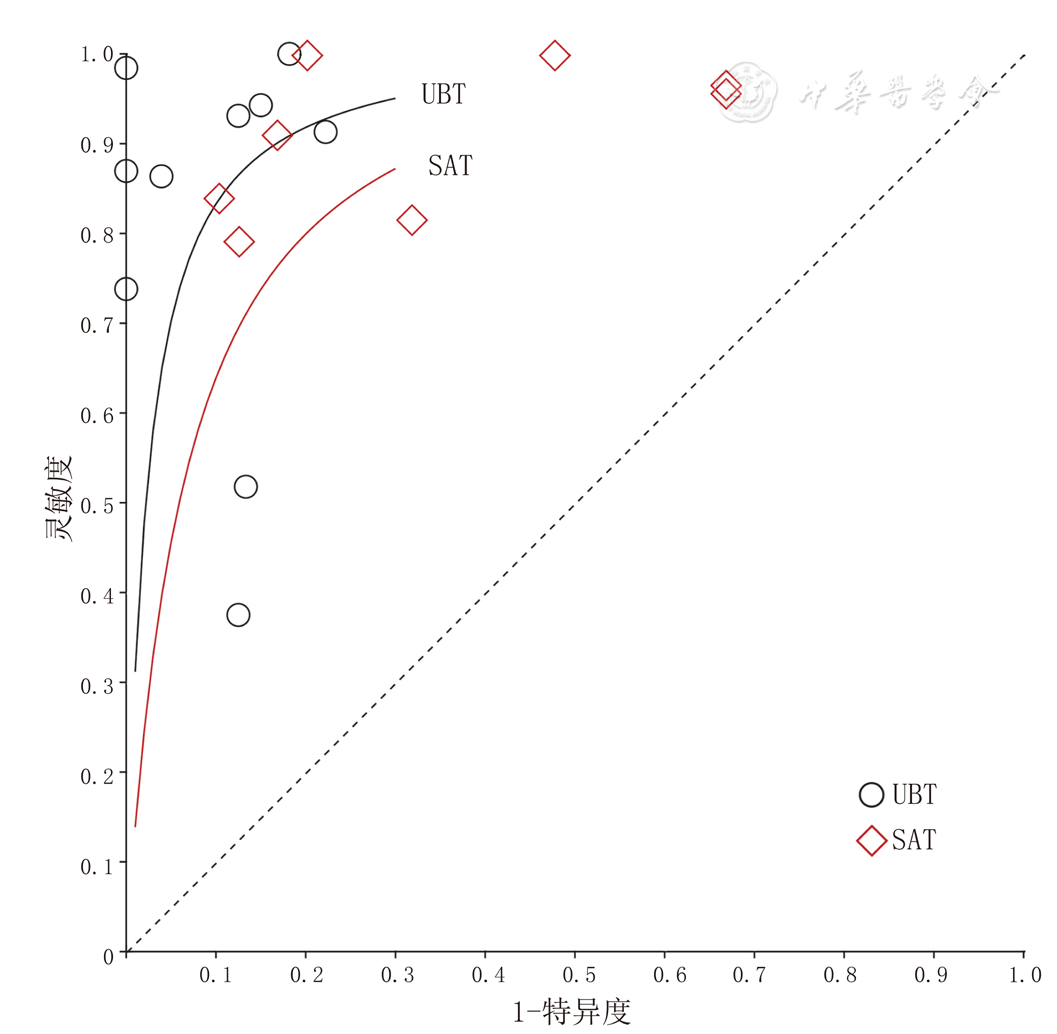
图9 UBT和SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的综合受试者工作特征曲线
Figure 9 Comprehensive receiver operating characteristic curve of the UBT and SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
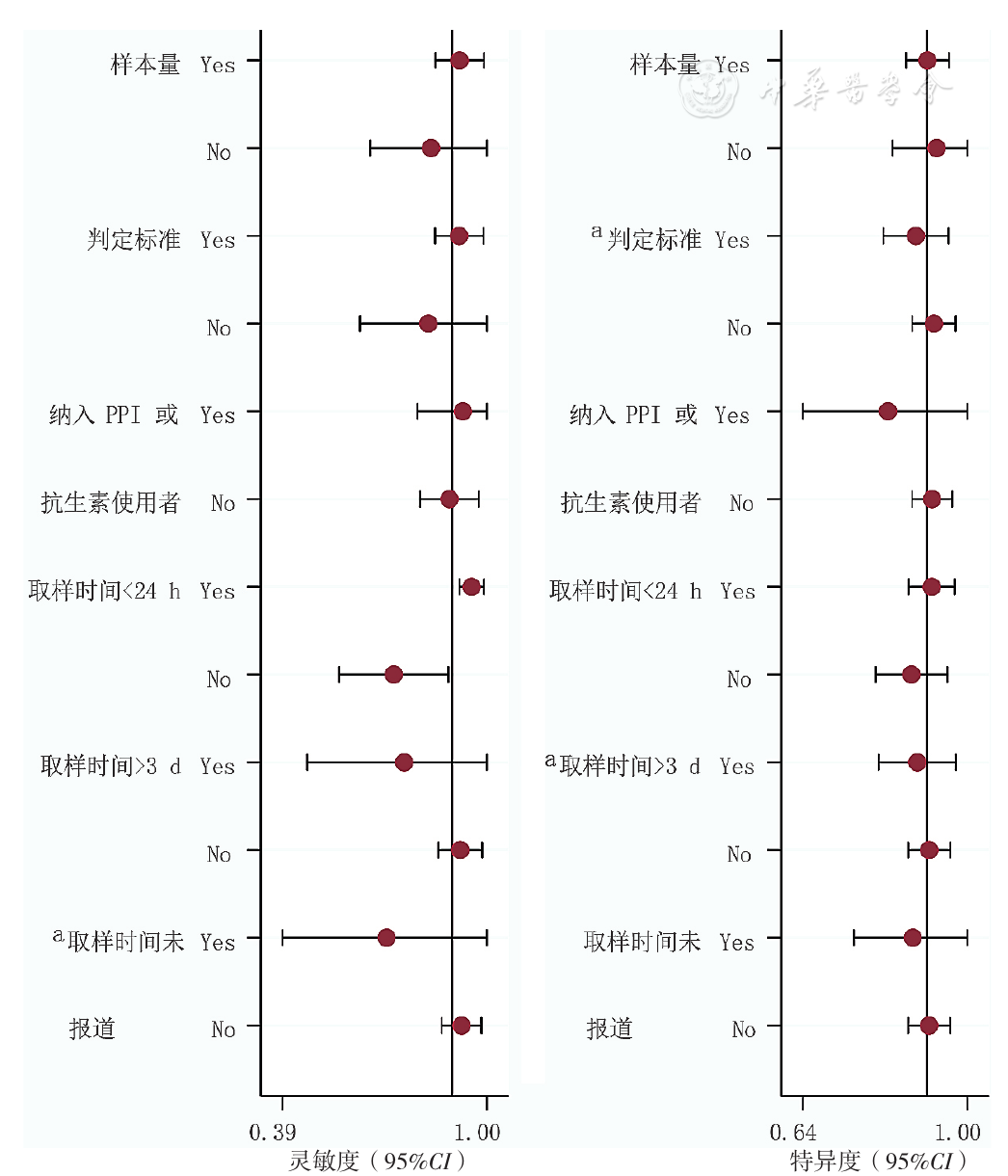
图10 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的Meta回归结果
Figure 10 Meta-regression results of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
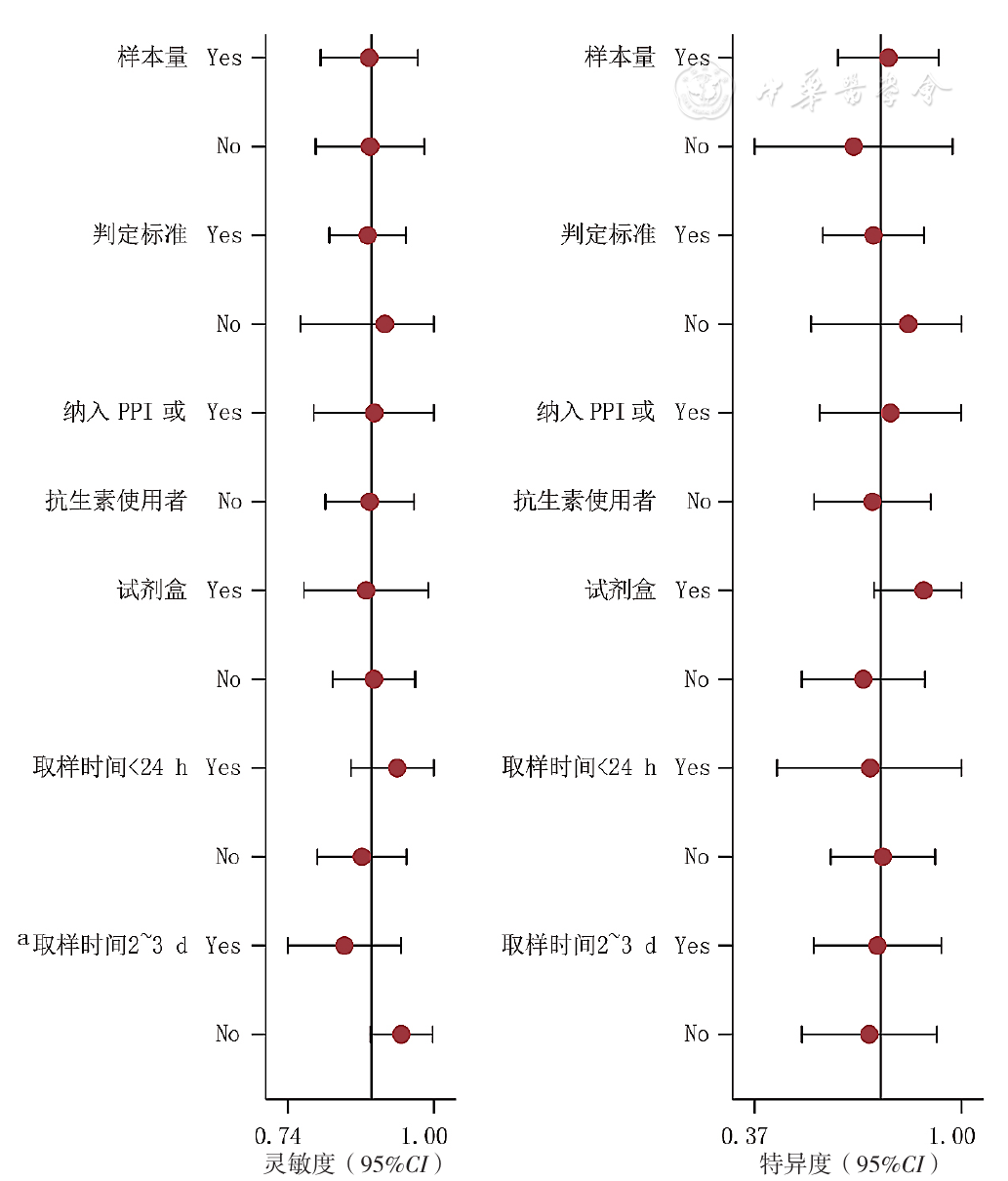
图11 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的Meta回归结果
Figure 11 Meta-regression results of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 检查方式 | 亚组 | 研究数量(项) | 合并灵敏度 | 合并特异度 | 合并诊断比值比 | 合并阳性似然比 | 合并阴性似然比 | SROC曲线下面积 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBT | 取样时间<24 h | 8[ | 0.94(0.91,0.96) | 0.92(0.85,0.96) | 119.27(49.06,289.94) | 7.78(4.04,14.97) | 0.09(0.05,0.17) | 0.97(0.96,0.98) |
| 取样时间>3 d | 3[ | 0.69(0.60,0.76) | 0.88(0.78,0.94) | 11.84(2.01,69.85) | 4.37(1.93,9.89) | 0.41(0.21,0.80) | 0.81(0.78,0.83) | |
| 复合标准 | 10[ | 0.89(0.86,0.92) | 0.87(0.77,0.93) | 46.65(14.98,145.29) | 5.30(3.10,9.06) | 0.15(0.06,0.37) | 0.92(0.89,0.94) | |
| 单一标准 | 4[ | 0.76(0.70,0.82) | 0.92(0.86,0.96) | 87.63(4.42,173.31) | 11.53(2.09,63.66) | 0.14(0.02,0.81) | 0.94(0.92,0.96) | |
| SAT | 取样时间<24 h | 3[ | 0.89(0.80,0.95) | 0.82(0.71,0.90) | 37.24(14.19,97.76) | 3.47(0.74,16.14) | 0.17(0.09,0.30) | 0.93(0.90,0.95) |
| 取样时间2~3 d | 6[ | 0.82(0.77,0.87) | 0.75(0.66,0.82) | 15.26(7.76,30.01) | 2.77(1.23,6.24) | 0.24(0.16,0.35) | 0.87(0.80,0.95) |
表3 UBT和SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的亚组分析结果(点估计及95%CI)
Table 3 Subgroup analysis results of the UBT and SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 检查方式 | 亚组 | 研究数量(项) | 合并灵敏度 | 合并特异度 | 合并诊断比值比 | 合并阳性似然比 | 合并阴性似然比 | SROC曲线下面积 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBT | 取样时间<24 h | 8[ | 0.94(0.91,0.96) | 0.92(0.85,0.96) | 119.27(49.06,289.94) | 7.78(4.04,14.97) | 0.09(0.05,0.17) | 0.97(0.96,0.98) |
| 取样时间>3 d | 3[ | 0.69(0.60,0.76) | 0.88(0.78,0.94) | 11.84(2.01,69.85) | 4.37(1.93,9.89) | 0.41(0.21,0.80) | 0.81(0.78,0.83) | |
| 复合标准 | 10[ | 0.89(0.86,0.92) | 0.87(0.77,0.93) | 46.65(14.98,145.29) | 5.30(3.10,9.06) | 0.15(0.06,0.37) | 0.92(0.89,0.94) | |
| 单一标准 | 4[ | 0.76(0.70,0.82) | 0.92(0.86,0.96) | 87.63(4.42,173.31) | 11.53(2.09,63.66) | 0.14(0.02,0.81) | 0.94(0.92,0.96) | |
| SAT | 取样时间<24 h | 3[ | 0.89(0.80,0.95) | 0.82(0.71,0.90) | 37.24(14.19,97.76) | 3.47(0.74,16.14) | 0.17(0.09,0.30) | 0.93(0.90,0.95) |
| 取样时间2~3 d | 6[ | 0.82(0.77,0.87) | 0.75(0.66,0.82) | 15.26(7.76,30.01) | 2.77(1.23,6.24) | 0.24(0.16,0.35) | 0.87(0.80,0.95) |
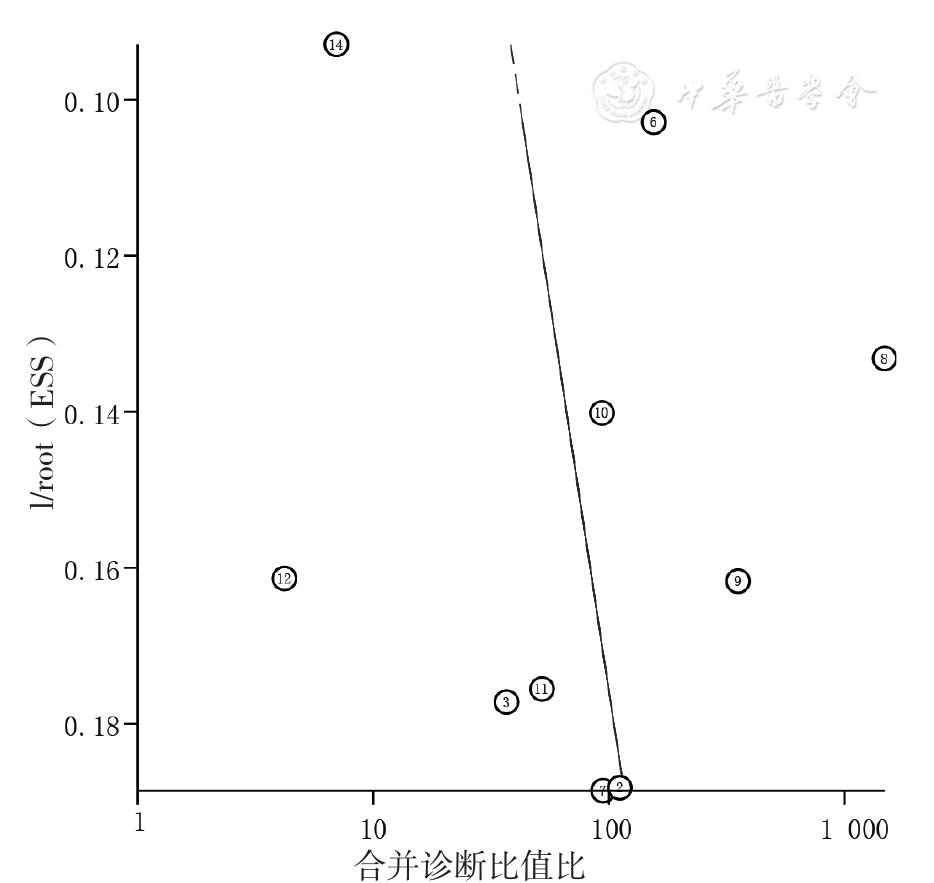
图12 UBT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并诊断比值比的发表偏倚的Deeks漏斗图
Figure 12 Deeks funnel plot for evaluating publication bias among the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
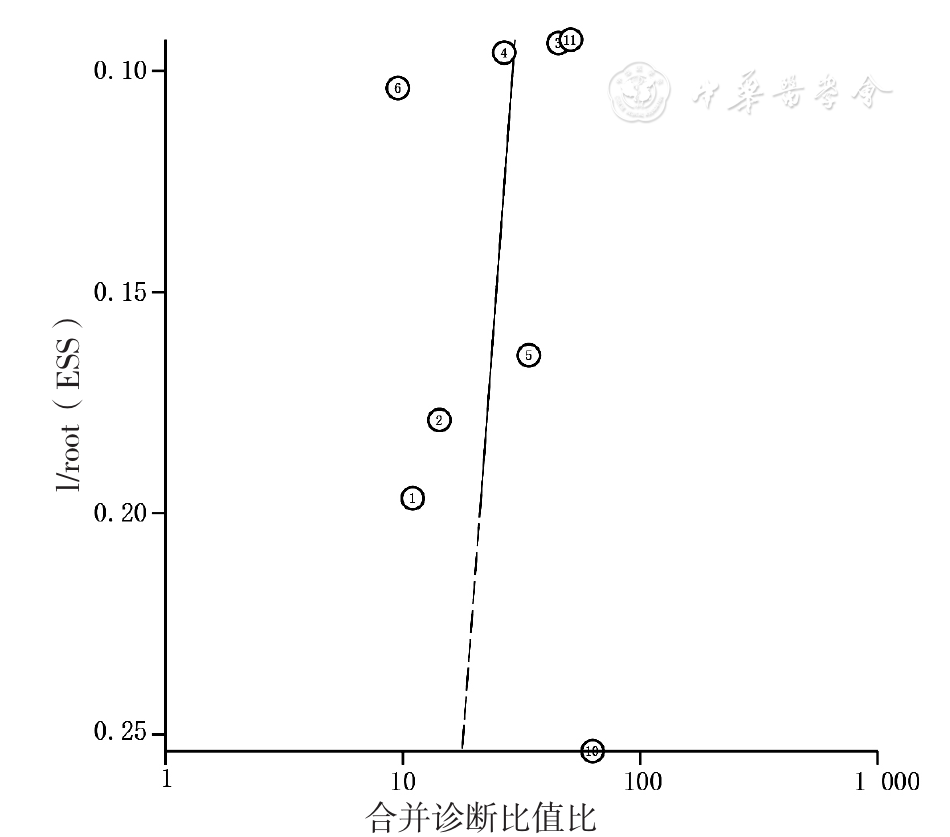
图13 SAT诊断PUB患者H.pylori感染的合并诊断比值比的发表偏倚的Deeks漏斗图
Figure 13 Deeks funnel plot for evaluating publication bias among the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| [1] | LAINE L, BARKUN A N, SALTZMAN J R,et al. ACG clinical guideline:upper gastrointestinal and ulcer bleeding[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2021,116(5):899-917. DOI:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001245. |
| [2] | 王锦萍,崔毅,王锦辉,等. 上消化道出血15年临床流行病学变化趋势[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志,2017,20(4):425-431. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2017.04.012. |
| [3] | 中华消化杂志编辑委员会,中华消化外科杂志编辑委员会. 急性非静脉曲张性上消化道出血多学科防治共识[J]. 中华消化杂志,2019,39(12):793-799. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2019.12.001. |
| [4] | 邬兰,张永,曾宪涛. QUADAS-2在诊断准确性研究的质量评价工具中的应用[J]. 湖北医药学院学报,2013,32(3):201-208. |
| [5] | 曾宪涛,何明武. 诊断准确性试验Meta分析软件一本通[M]. 北京:军事医学科学出版社,2014. |
| [6] | 周支瑞,胡志德. 疯狂统计学[M]. 长沙:中南大学出版社,2018. |
| [7] | 吴景玲,葛龙,张俊华,等. 多个诊断性试验准确性的比较:网状Meta分析方法介绍[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2017,17(8):987-992. DOI:10.7507/1672-2531.201706041. |
| [8] | 高亚,孙凤,武珊珊,等. 网络Meta分析研究进展系列(五):诊断试验准确性网络Meta分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2020,12(10):1161-1165. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2020.10.03. |
| [9] | TU T C, LEE C L, WU C H,et al. Comparison of invasive and noninvasive tests for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. Gastrointest Endosc,1999,49(3 Pt 1):302-306. DOI:10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70005-2. |
| [10] | LóPEZ PEÑAS D, NARANJO RODRíGUEZ A, MUÑOZ MOLINERO J,et al. Efficacy of fecal detection of Helicobacter pylori with the HpSA technique in patients with upper digestive hemorrhage[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol,2001,24(1):5-8. |
| [11] | GRIÑó P, PASCUAL S, SUCH J,et al. Comparison of diagnostic methods for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol,2001,36(12):1254-1258. DOI:10.1080/003655201317097083. |
| [12] | CHUNG I K, HONG S J, KIM E J,et al. What is the best method to diagnose Helicobacter infection in bleeding peptic ulcers?:a prospective trial[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2001,16(3):147-152. DOI:10.3904/kjim.2001.16.3.147. |
| [13] | WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN M, TOUBORG LASSEN A, LINDEBJERG J,et al. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in bleeding peptic ulcer patients,evaluation of urea-based tests[J]. Digestion,2002,66(1):9-13. DOI:10.1159/000064421. |
| [14] | GRIÑó P, PASCUAL S, SUCH J,et al. Comparison of stool immunoassay with standard methods for detection of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper-gastrointestinal bleeding of peptic origin[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2003,15(5):525-529. DOI:10.1097/01.meg.0000059114.41030.a9. |
| [15] | WINIARSKI M, BIELANSKI W, PLONKA M,et al. The usefulness of capsulated 13C-urea breath test in diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol,2003,37(1):34-38. DOI:10.1097/00004836-200307000-00010. |
| [16] | LIAO C C, LEE C L, LAI Y C,et al. Accuracy of three diagnostic tests used alone and in combination for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with bleeding gastric ulcers[J]. Chin Med J (Engl),2003,116(12):1821-1826. |
| [17] | LO C C, LAI K H, PENG N J,et al. Polymerase chain reaction:a sensitive method for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2005,11(25):3909-3914. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v11.i25.3909. |
| [18] | 张厚德,杜冀晖,苏卓娃,等. 上消化道出血对14C-尿素呼气试验准确性影响[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,1997,6(2):66-67. |
| [19] | 林勇,李荣洲,郑超秀,等. 14C-尿素呼气试验在消化性溃疡并出血病人假阴性原因分析[J]. 浙江临床医学,2004,6(7):577. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7664.2004.07.023. |
| [20] | 李舜,张家云,邓咏梅. 14C-尿素呼气试验在不同胃黏膜病变中的诊断价值及影响因素分析[J]. 实用医学杂志,2005,21(5):477-478. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2005.05.015. |
| [21] | 王醒,高广周,石峥,等. 粪便幽门螺杆菌检测在上消化道溃疡出血患者中的价值[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(25):165-166. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.25.123. |
| [22] | PEITZ U, LEODOLTER A, KAHL S,et al. Antigen stool test for assessment of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2003,17(8):1075-1084. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01548.x. |
| [23] | VAN LEERDAM M E, VAN DER ENDE A, TEN KATE F J,et al. Lack of accuracy of the noninvasive Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test in patients with gastroduodenal ulcer bleeding[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2003,98(4):798-801. DOI:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07387.x. |
| [24] | LIN H J, LO W C, PERNG C L,et al. Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test in patients with bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. Helicobacter,2004,9(6):663-668. DOI:10.1111/j.1083-4389.2004.00276.x. |
| [25] | GISBERT J P, TRAPERO M, CALVET X,et al. Evaluation of three different tests for the detection of stool antigens to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2004,19(8):923-929. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01932.x. |
| [26] | 于涛. 幽门螺杆菌粪便抗原检测卡的应用及质子泵抑制剂对其结果的影响[D]. 广州:中山大学,2006. |
| [27] | 田金徽,陈杰峰. 诊断试验系统评价/Meta分析指导手册[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社,2015. |
| [28] | MALFERTHEINER P, MEGRAUD F, O'MORAIN C A,et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the maastricht V/Florence consensus report[J]. Gut,2017,66(1):6-30. DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312288. |
| [29] | 中华医学会,中华医学会杂志社,中华医学会全科医学分会,等. 幽门螺杆菌感染基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2020,19(5):397-402. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200223-00158. |
| [30] | 《中华内科杂志》编辑委员会,《中华医学杂志》编辑委员会,《中华消化杂志》编辑委员会,等. 急性非静脉曲张性上消化道出血诊治指南(2018年,杭州)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2019,58(3):173-180. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.03.005. |
| [1] | 王喆, 董志浩, 郑好, 孔文程, 张玉宽, 张秋月, 韩晶. 针刺干预偏头痛优势方案构建研究:基于熵权TOPSIS法[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4336-4342. |
| [2] | 王越, 陈晴, 刘鲁蓉. 中国老年人抑郁检出率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [3] | 蹇秋枫, 徐荣华, 姚倩, 周媛媛. 中国老年脑卒中患者认知障碍患病率和影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [4] | 贾钰, 周紫彤, 曹学华, 胡婉琴, 向凤, 熊浪宇, 王晓霞. 中国40~65岁女性围绝经期综合征发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4080-4088. |
| [5] | 李纪新, 邱林杰, 任燕, 王文茹, 李美洁, 张晋. 膳食炎症指数与超重和肥胖及腹型肥胖关系的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4089-4097. |
| [6] | 何静漪, 王芳, 税晓玲, 李玲, 梁倩. 非药物干预改善围绝经期失眠症状疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3963-3974. |
| [7] | 张懂理, 沈冲, 张卫川, 陈海滨, 赵建军. 程序性死亡因子1/程序性死亡因子1配体抑制剂治疗肾细胞癌有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3815-3822. |
| [8] | 朱琳, 郭闫葵, 高琛, 陈学志, 王法帅. 单纯西药、中成药及其联合治疗卒中后失眠疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3823-3832. |
| [9] | 何莉, 张逸凡, 沈雪纯, 孙燕, 赵洋. 中国大陆地区居民慢性病共病的流行趋势:一项Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3599-3607. |
| [10] | 胡婧伊, 洪景, 郭晓冬, 张晓红, 莫宁, 周小翠, 余钦, 周敏华, 孙艳, 倪柳, 石晓丽, 苏小青, 李玉倩. 社区参与安宁疗护对临终期肿瘤患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3573-3584. |
| [11] | 林洋, 王芳, 王寒, 武蓉, 王瑶, 徐子尧, 王旭, 王彦丁. 老年共病患者衰弱患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3185-3193. |
| [12] | 郭银宁, 缪雪怡, 蒋小曼, 徐婷, 许勤. 蛋白质补充对衰弱/衰弱前期老年人肌肉质量和肌肉力量以及身体功能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(23): 2854-2863. |
| [13] | 王雪岩, 田金徽, 张莉, 翟巾帼. 不同干预措施对胎儿臀位/横位孕妇母婴结局影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2647-2658. |
| [14] | 何满兰, 袁萍, 何磊, 陈璐. 神经源性膀胱患者尿路感染危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2659-2665. |
| [15] | 薛珊, 李来有, 梁军利, 靳英辉, 魏淑艳. 家庭肠内营养在食管癌患者中有效性和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2540-2547. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





