中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (02): 233-240.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0579
所属专题: 心力衰竭最新文章合辑; 心血管最新文章合辑; 用药最新文章合辑; 老年问题最新文章合辑
高燕, 梁堃, 栾明亚, 张舰心, 徐宁, 刘娜娜, 张晓苹, 尚葛础, 刘科卫*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-08
修回日期:2022-08-26
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
刘科卫
基金资助:
GAO Yan, LIANG Kun, LUAN Mingya, ZHANG Jianxin, XU Ning, LIU Nana, ZHANG Xiaoping, SHANG Gechu, LIU Kewei*( )
)
Received:2022-08-08
Revised:2022-08-26
Published:2023-01-15
Online:2022-08-31
Contact:
LIU Kewei
About author:摘要: 背景 托伐普坦在老年慢性心力衰竭(CHF)患者中应用广泛,但不同剂量的托伐普坦对老年CHF患者预后的影响尚不明确。 目的 探讨7.5 mg/d和15.0 mg/d两种常用剂量的托伐普坦对高龄老年CHF患者预后的影响。 方法 回顾性分析2016年2月至2022年2月于中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九六〇医院保健病房采用托伐普坦药物治疗CHF的高龄(年龄≥80岁)老年患者的临床资料,按照托伐普坦应用剂量分为7.5 mg/d组和15.0 mg/d组。以全因死亡、心血管死亡出现或至随访结束为随访终点。绘制Kaplan-Meier生存曲线,分析两组患者全因死亡与心血管死亡的差异。采用Cox比例风险回归模型分析两种剂量托伐普坦对老年CHF患者全因死亡和心血管死亡的影响。 结果 共纳入高龄老年CHF患者212例,随访374.5(155.5,940.5)d,随访期间共124例(58.5%)患者发生全因死亡,54例(25.5%)患者发生心血管死亡。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线比较显示,托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组全因死亡率和心血管死亡率均高于托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组(P=0.004 3,P=0.001 2)。多因素Cox比例风险回归模型分析显示,在校正了年龄、纽约心脏协会(NYHA)心功能分级、慢性肾脏病(CKD)、糖尿病、高血压、冠心病、利尿剂、白蛋白(ALB)、血清N末端脑钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)与估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR)后,与7.5 mg/d组相比,15.0 mg/d组患者全因死亡和心血管死亡风险分别增加1.03倍〔HR=2.03,95%CI(1.34,2.99)〕和1.51倍〔HR=2.51,95%CI(1.40,4.50)〕。对eGFR、年龄、ALB、NT-proBNP进行分层分析结果显示,托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组全因死亡和心血管死亡的风险仍增加。 结论 在高龄(年龄≥80岁)老年CHF患者中,托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组比托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组全因死亡和心血管死亡风险增加,推荐使用7.5 mg/d托伐普坦。
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别(男/女) | 体质量(kg) | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | NYHA心功能分级〔n(%)〕 | 糖尿病〔n(%)〕 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCAD | ACS | Ⅱ级 | Ⅲ级 | Ⅳ级 | ||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 112 | 91.0±4.6 | 110/2 | 64.8±8.6 | 107(95.5) | 5(4.5) | 44(39.3) | 47(42.0) | 21(18.8) | 42(37.5) |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 100 | 91.1±3.4 | 97/3 | 65.0±10.7 | 96(96.0) | 4(4.0) | 44(44.0) | 33(33.0) | 23(23.0) | 41(41.0) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.013a | — | 0.013a | — | 1.868 | 0.145 | ||||
| P值 | 0.911 | 0.668 | 0.908 | 1.000 | 0.393 | 0.704 | ||||
| 组别 | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | CKD〔n(%)〕 | 硝酸类药物〔n(%)〕 | 抗血小板药物〔n(%)〕 | β受体阻滞剂〔n(%)〕 | RAS抑制剂〔n(%)〕 | 钙通道阻滞剂〔n(%)〕 | 曲美他嗪〔n(%)〕 | ||
| ACEI | ARB | |||||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 85(75.9) | 28(25.0) | 44(39.3) | 70(62.5) | 75(67.0) | 17(15.2) | 26(23.2) | 35(31.2) | 63(56.2) | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 77(77.0) | 38(38.0) | 32(32.0) | 63(63.0) | 65(65.0) | 18(18.0) | 24(24.0) | 34(34.0) | 47(47.0) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.001 | 3.580 | 0.923 | 0 | 0.024 | 0.380 | 0.078 | 1.459 | ||
| P值 | 0.978 | 0.058 | 0.337 | 1.000 | 0.876 | 0.826 | 0.780 | 0.227 | ||
| 组别 | 口服利尿剂〔n(%)〕 | 呋塞米剂量〔n(%)〕 | 螺内酯剂量〔n(%)〕 | 静脉注射利尿剂〔n(%)〕 | 随访时间〔M(P25,P75),d〕 | |||||
| 呋塞米 | 螺内酯 | 呋塞米+螺内酯 | ≤20 mg/d | >20 mg/d | ≤20 mg/d | >20 mg/d | ||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 18(16.1) | 26(23.2) | 43(38.4) | 51(45.5) | 10(8.9) | 59(52.7) | 10(8.9) | 50(44.6) | 383.0(168.5,1 108.0) | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 13(13.0) | 25(25.0) | 34(34.0) | 41(41.0) | 6(6.0) | 42(42.0) | 17(17.0) | 53(53.0) | 362.5(142.8,787.8) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 1.373 | 1.451 | 4.058 | 1.161 | 2.864b | |||||
| P值 | 0.712 | 0.484 | 0.131 | 0.281 | 0.091 | |||||
| 组别 | 托伐普坦应用时间〔M(P25,P75),d〕 | 托伐普坦应用时间〔n(%)〕 | 用药前24 h尿量(ml) | LVEF(%) | 左心室后壁厚度(mm) | 左心室舒张末内径(mm) | 左心房内径(mm) | |||
| 7~13 d | 14~29 d | ≥30 d | ||||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 85.0(36.5,275.8) | 10(8.9) | 17(15.2) | 85(75.9) | 1 809.5±652.4 | 56.7±5.2 | 10.1±0.7 | 44.6±4.1 | 38.1±6.6 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 126.0(56.2,361.5) | 10(10.0) | 10(10.0) | 80(80.0) | 1 621.7±555.4 | 55.4±4.3 | 10.0±0.5 | 44.1±4.7 | 37.2±8.0 | |
| 检验统计量值 | 2.006b | 1.291 | 4.948a | 2.845a | 0.130a | 0.606a | 0.596a | |||
| P值 | 0.064 | 0.524 | 0.027 | 0.088 | 0.719 | 0.437 | 0.441 | |||
表1 两组患者基线资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of baseline data between two groups of patients
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别(男/女) | 体质量(kg) | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | NYHA心功能分级〔n(%)〕 | 糖尿病〔n(%)〕 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCAD | ACS | Ⅱ级 | Ⅲ级 | Ⅳ级 | ||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 112 | 91.0±4.6 | 110/2 | 64.8±8.6 | 107(95.5) | 5(4.5) | 44(39.3) | 47(42.0) | 21(18.8) | 42(37.5) |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 100 | 91.1±3.4 | 97/3 | 65.0±10.7 | 96(96.0) | 4(4.0) | 44(44.0) | 33(33.0) | 23(23.0) | 41(41.0) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.013a | — | 0.013a | — | 1.868 | 0.145 | ||||
| P值 | 0.911 | 0.668 | 0.908 | 1.000 | 0.393 | 0.704 | ||||
| 组别 | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | CKD〔n(%)〕 | 硝酸类药物〔n(%)〕 | 抗血小板药物〔n(%)〕 | β受体阻滞剂〔n(%)〕 | RAS抑制剂〔n(%)〕 | 钙通道阻滞剂〔n(%)〕 | 曲美他嗪〔n(%)〕 | ||
| ACEI | ARB | |||||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 85(75.9) | 28(25.0) | 44(39.3) | 70(62.5) | 75(67.0) | 17(15.2) | 26(23.2) | 35(31.2) | 63(56.2) | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 77(77.0) | 38(38.0) | 32(32.0) | 63(63.0) | 65(65.0) | 18(18.0) | 24(24.0) | 34(34.0) | 47(47.0) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.001 | 3.580 | 0.923 | 0 | 0.024 | 0.380 | 0.078 | 1.459 | ||
| P值 | 0.978 | 0.058 | 0.337 | 1.000 | 0.876 | 0.826 | 0.780 | 0.227 | ||
| 组别 | 口服利尿剂〔n(%)〕 | 呋塞米剂量〔n(%)〕 | 螺内酯剂量〔n(%)〕 | 静脉注射利尿剂〔n(%)〕 | 随访时间〔M(P25,P75),d〕 | |||||
| 呋塞米 | 螺内酯 | 呋塞米+螺内酯 | ≤20 mg/d | >20 mg/d | ≤20 mg/d | >20 mg/d | ||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 18(16.1) | 26(23.2) | 43(38.4) | 51(45.5) | 10(8.9) | 59(52.7) | 10(8.9) | 50(44.6) | 383.0(168.5,1 108.0) | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 13(13.0) | 25(25.0) | 34(34.0) | 41(41.0) | 6(6.0) | 42(42.0) | 17(17.0) | 53(53.0) | 362.5(142.8,787.8) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 1.373 | 1.451 | 4.058 | 1.161 | 2.864b | |||||
| P值 | 0.712 | 0.484 | 0.131 | 0.281 | 0.091 | |||||
| 组别 | 托伐普坦应用时间〔M(P25,P75),d〕 | 托伐普坦应用时间〔n(%)〕 | 用药前24 h尿量(ml) | LVEF(%) | 左心室后壁厚度(mm) | 左心室舒张末内径(mm) | 左心房内径(mm) | |||
| 7~13 d | 14~29 d | ≥30 d | ||||||||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 85.0(36.5,275.8) | 10(8.9) | 17(15.2) | 85(75.9) | 1 809.5±652.4 | 56.7±5.2 | 10.1±0.7 | 44.6±4.1 | 38.1±6.6 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 126.0(56.2,361.5) | 10(10.0) | 10(10.0) | 80(80.0) | 1 621.7±555.4 | 55.4±4.3 | 10.0±0.5 | 44.1±4.7 | 37.2±8.0 | |
| 检验统计量值 | 2.006b | 1.291 | 4.948a | 2.845a | 0.130a | 0.606a | 0.596a | |||
| P值 | 0.064 | 0.524 | 0.027 | 0.088 | 0.719 | 0.437 | 0.441 | |||
| 组别 | 例数 | BUN(mmol/L) | Cr(μmol/L) | eGFR〔ml·min-1(1.73 m2) -1〕 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 112 | 8.5±5.3 | 8.9±5.2 | 0.784 | 0.441 | 106.6±57.7 | 106.5±50.3 | 1.960 | 0.052 | 35.4±13.5 | 35.6±12.9 | 2.183 | 0.330 |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 100 | 8.6±5.2 | 10.3±6.4 | 3.320 | 0.001 | 111.0±54.9 | 121.4±61.6 | 4.700 | <0.001 | 34.9±12.1 | 33.8±12.7 | -1.961 | 0.050 |
| t(Z)值 | 0.441 | 0.037 | 0.110 | 1.730 | 0.047 | 0.012 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.597 | 0.848 | 2.582 | 0.190 | 0.828 | 0.914 | |||||||
| 组别 | NT-proBNP〔M(P25,P75),ng/L〕 | cTnI〔M(P25,P75),μg/L〕 | 血钠(mmol/L) | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1 082.0(396.7,2 832.0) | 890.3(321.6,1 764.0) | -1.759 | 0.081 | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 1.273 | 0.206 | 132.2±5.8 | 137.6±4.3 | 7.947 | <0.001 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 992.8(457.5,3 552.0) | 969.9(310.5,2 529.0) | -2.024 | 0.046 | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 0.01(0.01,0.05) | 1.083 | <0.001 | 133.2±5.5 | 137.8±5.2 | 8.994 | <0.001 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.906a | 2.391a | 0.314a | 0.950a | 2.912 | 0.269 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.341 | 0.122 | 0.576 | 0.330 | 0.090 | 0.605 | |||||||
| 组别 | 血钾(mmol/L) | 24 h尿量(ml) | ALT〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 4.2±0.6 | 4.1±0.5 | -0.190 | 0.846 | 1 809.5±652.4 | 2 082.9±589.1 | 4.093 | <0.001 | 16.0(12.0,29.5) | 14.0(9.5,24.5) | -1.756 | 0.177 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 4.1±0.6 | 4.1±0.5 | 0.390 | 0.715 | 1 621.7±555.4 | 2 034.6±665.8 | 6.852 | <0.001 | 17.0(11.0,25.0) | 14.0(8.0,22.2) | -1.413 | 0.162 | |
| t(Z)值 | 1.055 | 0.518 | 4.948 | 3.863 | 1.295a | 1.42a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.306 | 0.473 | 0.027 | 0.051 | 0.255 | 0.233 | |||||||
| 组别 | AST〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | AKP〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | γ-GT〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 16.0(12.0,29.5) | 14.0(9.5,24.5) | -1.417 | 0.251 | 73.0(57.0,91.0) | 72.0(59.0,92.5) | -0.266 | 0.807 | 28.0(22.0,41.0) | 30.0(19.0,47.0) | 0.210 | 0.847 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 21.0(16.0,31.0) | 20.0(16.5,29.0) | -0.650 | 0.510 | 111.0±54.9 | 121.4±61.6 | 4.700 | 0.812 | 30.0(21.0,50.0) | 34.0(19.8,51.5) | 1.472 | 0.142 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.094a | 0.091a | 3.771 | 0.06 | 0.147a | 0.937a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.759 | 0.763 | 0.052 | 0.806 | 0.702 | 0.333 | |||||||
| 组别 | TBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | DBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | IBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 9.8(7.5,13.4) | 9.8(7.6,14.2) | 1.477 | 0.236 | 3.1(2.3,4.0) | 3.0(2.2,4.6) | 0.678 | 0.547 | 7.0(5.1,9.9) | 6.4(4.9,9.1) | 2.611 | 0.080 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 10.3(7.8,14.7) | 10.8(8.0,15.8) | 1.812 | 0.072 | 3.1(2.1,4.5) | 3.8(2.5,6.1) | 1.773 | 0.084 | 7.2(5.4,9.8) | 6.7(4.7,9.5) | -0.670 | 0.493 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.547a | 1.171a | 0.150a | 4.819a | 0.047a | 0.035a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.459 | 0.279 | 0.699 | 0.058 | 0.829 | 0.852 | |||||||
表2 两组患者托伐普坦治疗前后实验室检查指标比较
Table 2 Comparison of laboratory indices before and after tolvaptan treatment in two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | BUN(mmol/L) | Cr(μmol/L) | eGFR〔ml·min-1(1.73 m2) -1〕 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 112 | 8.5±5.3 | 8.9±5.2 | 0.784 | 0.441 | 106.6±57.7 | 106.5±50.3 | 1.960 | 0.052 | 35.4±13.5 | 35.6±12.9 | 2.183 | 0.330 |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 100 | 8.6±5.2 | 10.3±6.4 | 3.320 | 0.001 | 111.0±54.9 | 121.4±61.6 | 4.700 | <0.001 | 34.9±12.1 | 33.8±12.7 | -1.961 | 0.050 |
| t(Z)值 | 0.441 | 0.037 | 0.110 | 1.730 | 0.047 | 0.012 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.597 | 0.848 | 2.582 | 0.190 | 0.828 | 0.914 | |||||||
| 组别 | NT-proBNP〔M(P25,P75),ng/L〕 | cTnI〔M(P25,P75),μg/L〕 | 血钠(mmol/L) | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1 082.0(396.7,2 832.0) | 890.3(321.6,1 764.0) | -1.759 | 0.081 | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 1.273 | 0.206 | 132.2±5.8 | 137.6±4.3 | 7.947 | <0.001 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 992.8(457.5,3 552.0) | 969.9(310.5,2 529.0) | -2.024 | 0.046 | 0.01(0.01,0.04) | 0.01(0.01,0.05) | 1.083 | <0.001 | 133.2±5.5 | 137.8±5.2 | 8.994 | <0.001 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.906a | 2.391a | 0.314a | 0.950a | 2.912 | 0.269 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.341 | 0.122 | 0.576 | 0.330 | 0.090 | 0.605 | |||||||
| 组别 | 血钾(mmol/L) | 24 h尿量(ml) | ALT〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | t配对值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 4.2±0.6 | 4.1±0.5 | -0.190 | 0.846 | 1 809.5±652.4 | 2 082.9±589.1 | 4.093 | <0.001 | 16.0(12.0,29.5) | 14.0(9.5,24.5) | -1.756 | 0.177 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 4.1±0.6 | 4.1±0.5 | 0.390 | 0.715 | 1 621.7±555.4 | 2 034.6±665.8 | 6.852 | <0.001 | 17.0(11.0,25.0) | 14.0(8.0,22.2) | -1.413 | 0.162 | |
| t(Z)值 | 1.055 | 0.518 | 4.948 | 3.863 | 1.295a | 1.42a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.306 | 0.473 | 0.027 | 0.051 | 0.255 | 0.233 | |||||||
| 组别 | AST〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | AKP〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | γ-GT〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 16.0(12.0,29.5) | 14.0(9.5,24.5) | -1.417 | 0.251 | 73.0(57.0,91.0) | 72.0(59.0,92.5) | -0.266 | 0.807 | 28.0(22.0,41.0) | 30.0(19.0,47.0) | 0.210 | 0.847 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 21.0(16.0,31.0) | 20.0(16.5,29.0) | -0.650 | 0.510 | 111.0±54.9 | 121.4±61.6 | 4.700 | 0.812 | 30.0(21.0,50.0) | 34.0(19.8,51.5) | 1.472 | 0.142 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.094a | 0.091a | 3.771 | 0.06 | 0.147a | 0.937a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.759 | 0.763 | 0.052 | 0.806 | 0.702 | 0.333 | |||||||
| 组别 | TBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | DBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | IBIL〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | ||||||||||
| 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | 基线水平 | 治疗后 | Z值 | P值 | ||
| 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 9.8(7.5,13.4) | 9.8(7.6,14.2) | 1.477 | 0.236 | 3.1(2.3,4.0) | 3.0(2.2,4.6) | 0.678 | 0.547 | 7.0(5.1,9.9) | 6.4(4.9,9.1) | 2.611 | 0.080 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 10.3(7.8,14.7) | 10.8(8.0,15.8) | 1.812 | 0.072 | 3.1(2.1,4.5) | 3.8(2.5,6.1) | 1.773 | 0.084 | 7.2(5.4,9.8) | 6.7(4.7,9.5) | -0.670 | 0.493 | |
| t(Z)值 | 0.547a | 1.171a | 0.150a | 4.819a | 0.047a | 0.035a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.459 | 0.279 | 0.699 | 0.058 | 0.829 | 0.852 | |||||||
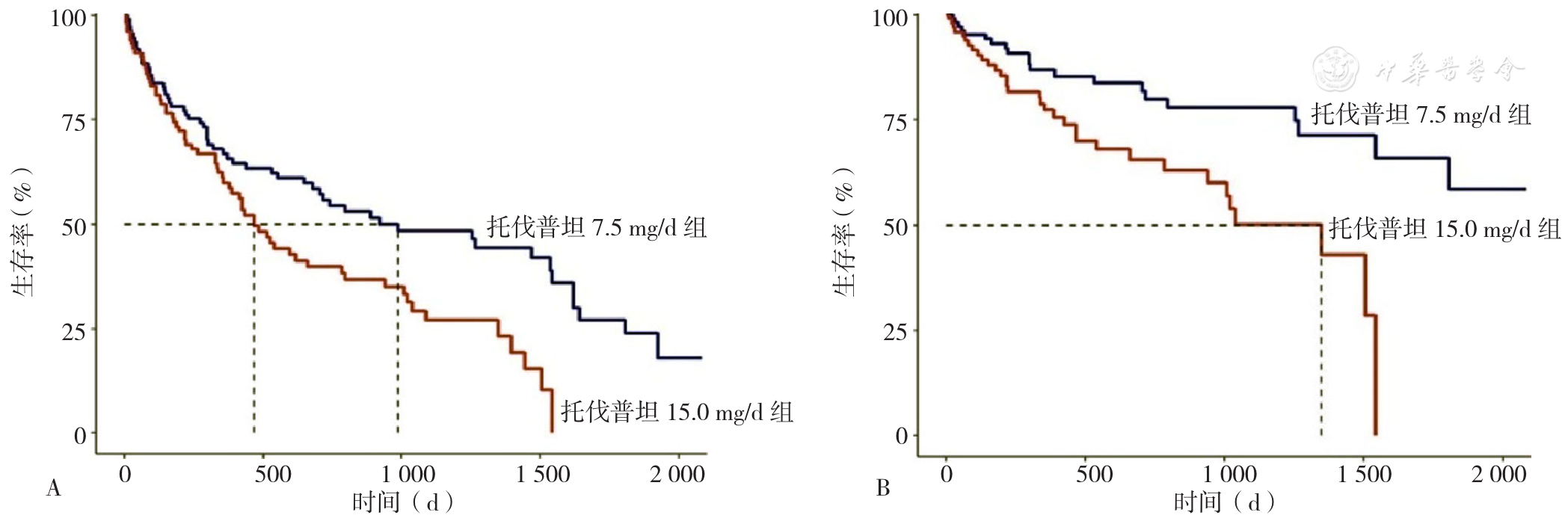
图1 两组患者全因死亡和心血管死亡的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线注:A为全因死亡,B为心血管死亡
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for all-cause death and cardiovascular death in two groups of patients
| 变量 | 单因素分析 | 多因素分析 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 1.70(1.18,2.46) | 0.005 | 2.04(1.38,3.01) | 0.001 |
| 年龄 | 1.03(0.99,1.07) | 0.195 | 1.02(0.97,1.07) | 0.523 |
| NYHA(Ⅲ级) | 1.23(0.81,1.85) | 0.336 | 1.16(0.73,1.85) | 0.536 |
| NYHA(Ⅳ级) | 2.13(1.36,3.35) | 0.001 | 2.15(1.21,3.83) | 0.009 |
| CKD | 1.06(0.71,1.57) | 0.784 | 1.02(0.61,1.69) | 0.954 |
| β受体阻滞剂 | 0.92(0.63,1.33) | 0.644 | 0.89(0.6,1.31) | 0.562 |
| RAS抑制剂 | 0.64(0.43,0.93) | 0.021 | 0.72(0.48,1.07) | 0.105 |
| 口服呋塞米 | 1.91(1.05,3.48) | 0.034 | 2.27(1.08,4.76) | 0.030 |
| 螺内酯 | 1.19(0.68,2.07) | 0.552 | 1.72(0.93,3.19) | 0.086 |
| 呋塞米+螺内酯 | 1.82(1.11,3.00) | 0.018 | 2.05(1.15,3.66) | 0.015 |
| ALB | 0.94(0.9,0.98) | 0.002 | 0.95(0.90,1.00) | 0.035 |
| lgNTproBNP | 1.55(1.15,2.08) | 0.004 | 1.26(0.83,1.92) | 0.285 |
| eGFR | 0.87(0.85,1.08) | 0.348 | 0.99(0.97,1.02) | 0.564 |
表3 两种剂量托伐普坦与高龄老年HF患者全因死亡的Cox比例风险回归分析
Table 3 Cox risk regression analysis of two doses of tolvaptan and all-cause mortality in elderly patients with heart failure
| 变量 | 单因素分析 | 多因素分析 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 1.70(1.18,2.46) | 0.005 | 2.04(1.38,3.01) | 0.001 |
| 年龄 | 1.03(0.99,1.07) | 0.195 | 1.02(0.97,1.07) | 0.523 |
| NYHA(Ⅲ级) | 1.23(0.81,1.85) | 0.336 | 1.16(0.73,1.85) | 0.536 |
| NYHA(Ⅳ级) | 2.13(1.36,3.35) | 0.001 | 2.15(1.21,3.83) | 0.009 |
| CKD | 1.06(0.71,1.57) | 0.784 | 1.02(0.61,1.69) | 0.954 |
| β受体阻滞剂 | 0.92(0.63,1.33) | 0.644 | 0.89(0.6,1.31) | 0.562 |
| RAS抑制剂 | 0.64(0.43,0.93) | 0.021 | 0.72(0.48,1.07) | 0.105 |
| 口服呋塞米 | 1.91(1.05,3.48) | 0.034 | 2.27(1.08,4.76) | 0.030 |
| 螺内酯 | 1.19(0.68,2.07) | 0.552 | 1.72(0.93,3.19) | 0.086 |
| 呋塞米+螺内酯 | 1.82(1.11,3.00) | 0.018 | 2.05(1.15,3.66) | 0.015 |
| ALB | 0.94(0.9,0.98) | 0.002 | 0.95(0.90,1.00) | 0.035 |
| lgNTproBNP | 1.55(1.15,2.08) | 0.004 | 1.26(0.83,1.92) | 0.285 |
| eGFR | 0.87(0.85,1.08) | 0.348 | 0.99(0.97,1.02) | 0.564 |
| 因变量 | 自变量 | 未调整模型 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 全因死亡 | 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1.00 | — | 1.00 | 1.00 | — | 1 | — | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 1.70(1.18,2.46) | 0.005 | 1.73(1.19,2.50) | 0.004 | 1.76(1.22,2.60) | 0.003 | 2.03(1.34,2.99) | 0.001 | |
| 心血管死亡 | 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1.00 | — | 1.00 | 1.00 | — | 1 | — | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 2.48(1.40,4.39) | 0.002 | 2.50(1.41,4.45) | 0.002 | 2.75(1.52,4.96) | 0.001 | 2.51(1.40,4.50) | 0.002 | |
表4 两种剂量托伐普坦对全因死亡和心血管死亡事件影响的Cox比例风险回归模型
Table 4 Cox proportional risk regression models for the effect of two doses of tolvaptan on all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality
| 因变量 | 自变量 | 未调整模型 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 全因死亡 | 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1.00 | — | 1.00 | 1.00 | — | 1 | — | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 1.70(1.18,2.46) | 0.005 | 1.73(1.19,2.50) | 0.004 | 1.76(1.22,2.60) | 0.003 | 2.03(1.34,2.99) | 0.001 | |
| 心血管死亡 | 托伐普坦7.5 mg/d组 | 1.00 | — | 1.00 | 1.00 | — | 1 | — | |
| 托伐普坦15.0 mg/d组 | 2.48(1.40,4.39) | 0.002 | 2.50(1.41,4.45) | 0.002 | 2.75(1.52,4.96) | 0.001 | 2.51(1.40,4.50) | 0.002 | |
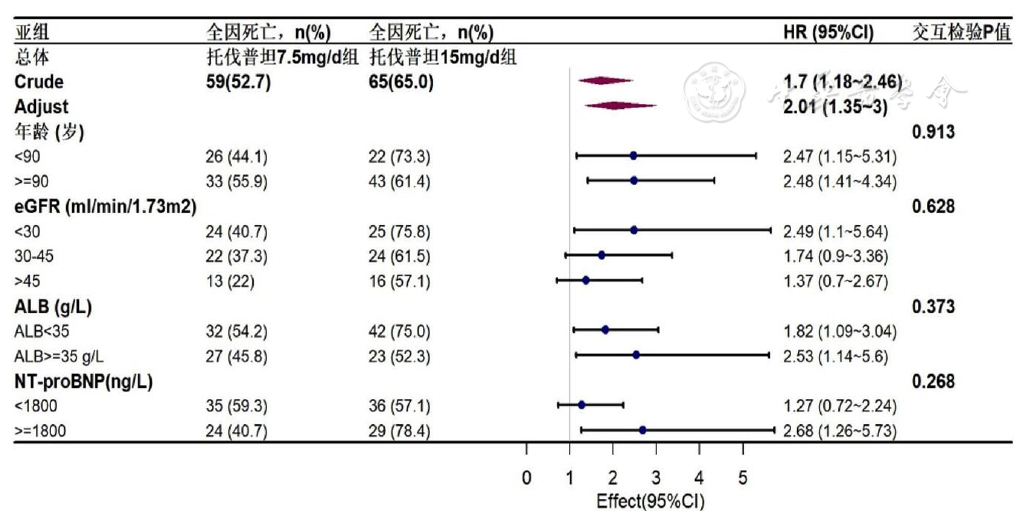
图2 两种剂量托伐普坦与全因死亡风险的Cox回归亚组分析
Figure 2 Subgroup analysis of the association between two doses of tolvaptan and the risk of all-cause mortality by Cox regression analysis
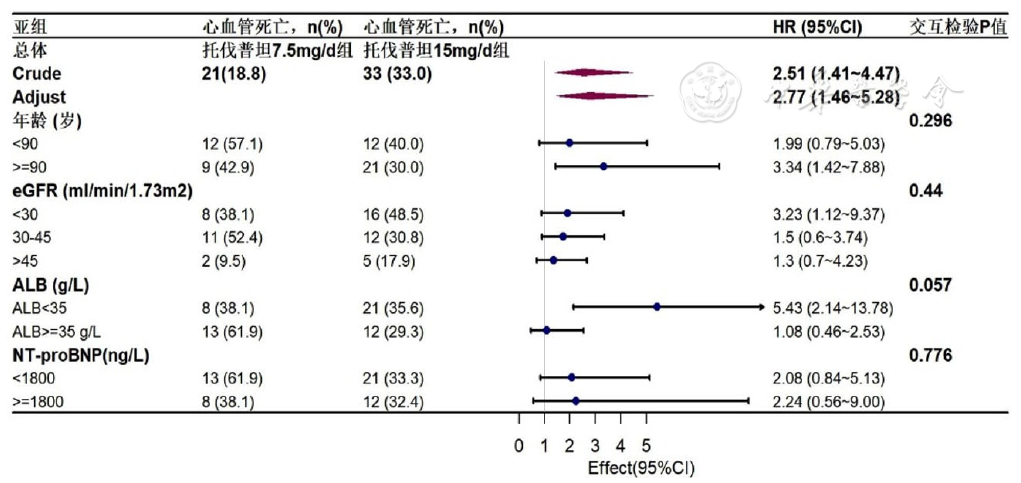
图3 两种剂量托伐普坦与心血管死亡风险的Cox回归亚组析
Figure 3 Subgroup analysis of the association between two doses of tolvaptan and the risk of cardiovascular death by Cox regression analysis
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
中国医师协会心力衰竭专业委员会,中华心力衰竭和心肌病杂志编辑委员会. 心力衰竭容量管理中国专家建议[J]. 中华心力衰竭和心肌病杂志(中英文),2018,2(1):8-16.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
中华医学会心血管病学分会心力衰竭学组,中国医师协会心力衰竭专业委员会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2018 [J] . 中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(10):760-789. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.10.004.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
徐先静,黄改荣,刘雪亚,等. 托伐普坦治疗75岁及以上难治性心力衰竭患者的临床疗效观察[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(9):1038-1041.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 程雨欣, 方嘉敏, 梁好, 汪志玲, 魏琳, 廖惠莲, 徐明明, 陈玉梅, 李燕芬, 董丽娟, 郭银桂. 老年择期手术患者术前血小板计数/白蛋白比值与术后新发衰弱的相关性分析:一项多中心研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3359-3367. |
| [4] | 徐艳朋, 黄佩, 张平平, 罗艳, 施晓琪, 吴柳松, 陈艳, 何志旭. 急性T淋巴细胞白血病β-肾上腺素受体的表达情况及临床意义研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3391-3398. |
| [5] | 崔宇阳, 程桂荣, 曾燕, 黄招兰, 谭伟. 社区老年人婚姻状况和社会支持及生活习惯与认知障碍的关联:基于湖北老年记忆队列基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3240-3247. |
| [6] | 燕芳红, 彭国恬, 张国莉, 孙瑞仪, 马玉霞, 韩琳. 医联体内老年慢性病管理内容的匹配分析:基于"指南-实践-需求"视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3119-3126. |
| [7] | 丁香, 刘健, 陈晓露, 张先恒. 中草药降低类风湿关节炎合并链球菌感染患者再入院的风险:一项匹配队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3005-3012. |
| [8] | 于文华, 李建国, 段文燕, 高旭妍, 李夏夏, 张子龙, 张丽, 马丽娜. 老年人功能受损评估量表在社区老年人中的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [9] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [10] | 李嘉欣, 刘钟桧, 谢硕, 付志方, 孙丹, 焦红梅. 分解代谢及炎症状态的生物标志物变化趋势对老年患者慢性危重症的早期预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2993-2999. |
| [11] | 陈飞, 王金英, 于海搏, 李新, 张佳佳, 申曼, 詹晓凯, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 张天宇, 黄仲夏. 中性粒细胞明胶酶相关运载蛋白、T细胞免疫球蛋白粘蛋白受体1、血管细胞黏附分子-1和激活素A升高在新诊断多发性骨髓瘤患者中的意义研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2740-2749. |
| [12] | 杨继, 张垚, 赵英强, 张秋月. 中医三级防控模式对冠心病与脑卒中患者的管理效能评价:一项单中心前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2750-2761. |
| [13] | 赵晓晴, 郭桐桐, 张欣怡, 李林虹, 张亚, 嵇丽红, 董志伟, 高倩倩, 蔡伟芹, 郑文贵, 井淇. 社区老年人认知障碍风险预测模型的构建与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [14] | 石小天, 王珊, 杨华昱, 杨一帆, 李旭, 马清. 中国老年人体重指数和死亡的相关性:一项队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2791-2797. |
| [15] | 刘美霞, 尹金念, 吴玫, 杨星, 周全湘, 杨敬源. 体重指数对三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与认知功能关联的影响:一项贵州农村老年人群的现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





