中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (02): 225-232.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0427
金子开1, 王旭1, 孙凯1,2, 王艳国3, 师彬4, 罗杰1,2, 朱立国1,2, 魏戌1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-20
修回日期:2022-06-28
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2022-08-05
通讯作者:
魏戌
基金资助:
JIN Zikai1, WANG Xu1, SUN Kai1,2, WANG Yanguo3, SHI Bin4, LUO Jie1,2, ZHU Liguo1,2, WEI Xu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-20
Revised:2022-06-28
Published:2023-01-15
Online:2022-08-05
Contact:
WEI Xu
About author:摘要: 颈椎病是常见的脊柱退行性疾病,手法治疗是治疗颈椎病的临床常用方法之一,有研究表明手法治疗在改善颈椎病患者疼痛方面疗效显著,但其具体机制尚不明确。随着神经影像学的发展,临床对颈椎病患者脑结构及脑功能的可视化分析成为可能,从中枢角度提出的体感重塑学说成为研究颈椎病发病机制的新热点,基于中枢效应探究不同类型手法治疗颈椎病是手法研究的新方向。本文从调控大脑区域活动、改变默认模式网络、调节交感神经功能三方面阐述不同类型手法治疗颈椎病的中枢镇痛机制,发现手法治疗可通过加强中枢门控作用调节感觉运动整合过程的方式;或通过增强默认模式网络中感觉皮质和执行功能皮质的连接强度加快局部神经重塑,进而减弱负性记忆、情绪相关区域之间的白质纤维连接的方式;或通过调节交感神经功能,恢复脑疼痛抑制机制和中枢敏化作用的方式来达到镇痛效果。本研究总结的疼痛激活相关脑区、脑功能网络及各种生物标志物与观察指标为今后研究提供方向。未来应用基础研究应循序渐进设计研究方案,注重研究人群的广泛性,多时点观测手法疗效机制,进一步丰富手法的科学内涵。
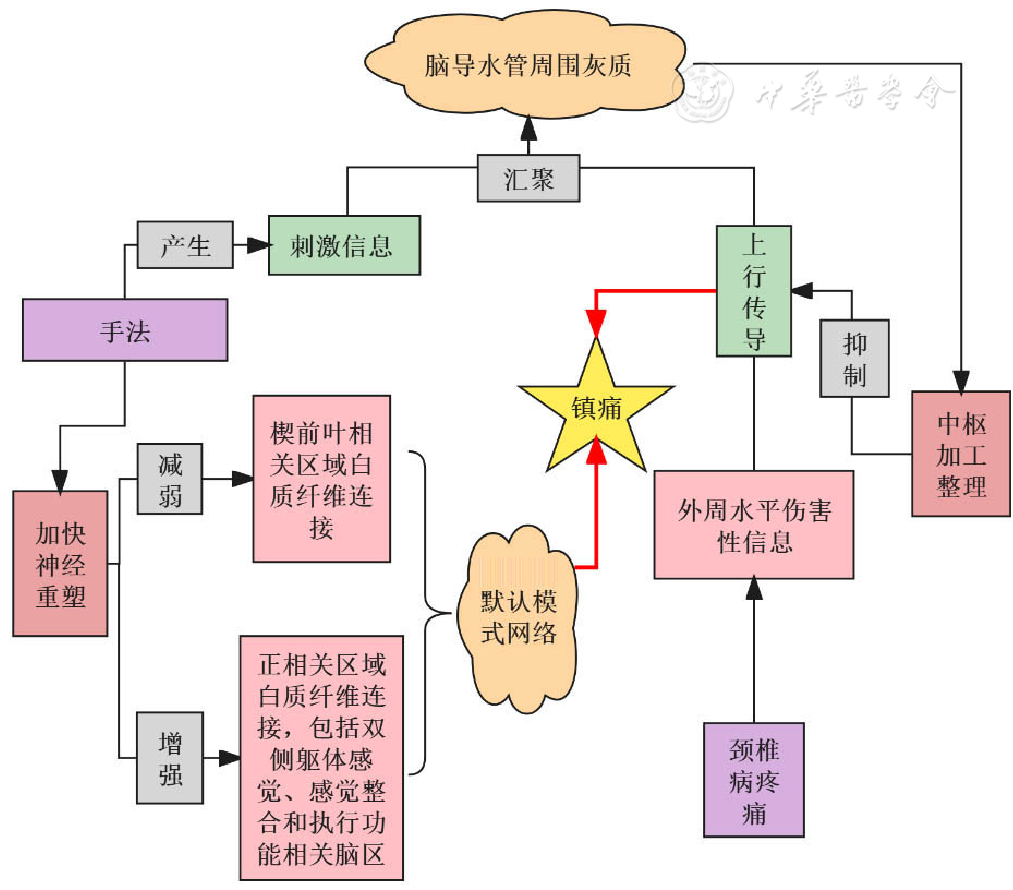
图1 软组织放松手法为主的调节颈椎病患者默认模式网络镇痛机制示意图
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the analgesic mechanism oof default mode network in cervical spondylosis patients with soft tissue relaxation manipulation
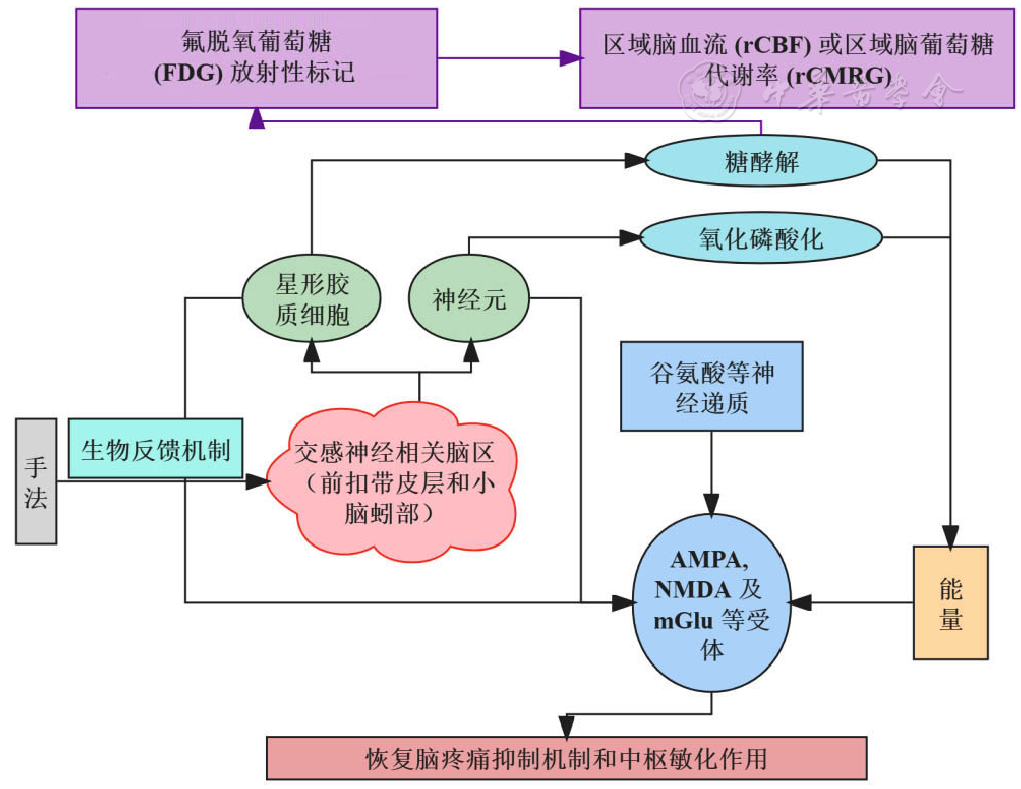
图2 针对颈部节段的关节松动手法干预颈椎病患者交感神经脑区葡萄糖代谢镇痛机制图注:AMPA=α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基-4-异恶唑丙酸受体,NMDA=N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体,mGlu=代谢型谷氨酸受体
Figure 2 Joint release manipulation of cervical segments as an analgesic mechanism for sympathetic brain region glucose metabolism in patients with cervical spondylosis
| 发表年份(年) | 第一作者 | 涉及区域 | 检测方法 | 具体改变 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | WANG[ | 大脑白质 | DSI | 整个大脑的广义各向异性较低,胼胝体和辐射冠QA增加 |
| 2019 | DE PAUW[ | 楔前叶、前扣带回、顶上回、颞上回、中央前回 | VBM、SBM | 存在左顶上回和楔前叶灰质体积选择性增加,中央前回和颞上回灰质体积选择性减少 |
| 2015 | TAN[ | 左侧初级感觉运动皮质、右侧感觉关联皮质 | RS-fMRI | 左侧初级感觉和运动皮质中Reho显著较低,右侧感觉关联皮质中Reho较高;术后3个月,左侧PostG/PreG Reho增加 |
| 2015 | 张华[ | 扣带前回,顶下回、楔前叶、岛叶、顶上回、中央前回,额叶执行功能区域 | 独立成分分析、SVM算法 | DMN本身主要区域、运动感觉区、额叶执行功能区域的DMN连接增强 |
| 2014 | ZHOU[ | 感觉运动皮质 | RS-fMRI | 右侧中央前回、右侧中央后回和左侧补充运动区皮质低频振荡振幅(ALFF/LFO)增加 |
| 2013 | SPARKS[ | 小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、岛叶、中央前回 | 血氧水平依赖性功能磁共振成像 | 左右小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、中脑导水管周围灰质、岛叶皮质、前扣带皮质、体感皮质、辅助运动区和运动前区显著激活 |
表1 颈椎病患者脑结构、脑功能网络连接改变
Table 1 Altered brain structure and functional brain network connectivity in patients with cervical spondylosis
| 发表年份(年) | 第一作者 | 涉及区域 | 检测方法 | 具体改变 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | WANG[ | 大脑白质 | DSI | 整个大脑的广义各向异性较低,胼胝体和辐射冠QA增加 |
| 2019 | DE PAUW[ | 楔前叶、前扣带回、顶上回、颞上回、中央前回 | VBM、SBM | 存在左顶上回和楔前叶灰质体积选择性增加,中央前回和颞上回灰质体积选择性减少 |
| 2015 | TAN[ | 左侧初级感觉运动皮质、右侧感觉关联皮质 | RS-fMRI | 左侧初级感觉和运动皮质中Reho显著较低,右侧感觉关联皮质中Reho较高;术后3个月,左侧PostG/PreG Reho增加 |
| 2015 | 张华[ | 扣带前回,顶下回、楔前叶、岛叶、顶上回、中央前回,额叶执行功能区域 | 独立成分分析、SVM算法 | DMN本身主要区域、运动感觉区、额叶执行功能区域的DMN连接增强 |
| 2014 | ZHOU[ | 感觉运动皮质 | RS-fMRI | 右侧中央前回、右侧中央后回和左侧补充运动区皮质低频振荡振幅(ALFF/LFO)增加 |
| 2013 | SPARKS[ | 小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、岛叶、中央前回 | 血氧水平依赖性功能磁共振成像 | 左右小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、中脑导水管周围灰质、岛叶皮质、前扣带皮质、体感皮质、辅助运动区和运动前区显著激活 |
| 发表年份(年) | 第一作者 | 观察指标及生物标志物 | 主要区域 | 手法机制 | 手法类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 刘钰[ | FA | 大脑左侧扣带海马束 | 促进局部神经的形成与重塑,调节脑功能网络连接,且能减弱负性记忆及情绪相关区域白质纤维连接,从而改善疼痛及相关不良记忆与情绪 | 软组织放松手法联合关节松动手法 |
| 2019 | WEBER[ | NPS | 次级体感皮质、前扣带皮质、枕叶复合体 | 改变处理身体疼痛的特定脑区内与疼痛有关的大脑活动 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2017 | HAAVIK[ | SEP | 中央后回 | 加强中枢对过度感觉信息的门控作用,调节感觉运动整合过程 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2015 | 张华[ | DMN | 左中央后回,右侧顶上、下回、右侧额中回 | 增强中枢水平DMN中感觉皮质和执行功能皮质的连接强度 | 软组织放松手法 |
| 2013 | SPARKS[ | BOLD | 小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、岛叶、中央前回 | 降低疼痛基质相关区域脑血流量,并减少岛叶皮质的激活 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2013 | JULIAN[ | CBI | 小脑 | 通过减轻小脑抑制运动皮质的程度,保持小脑正常运动整合、输出过程 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2011 | OGURA[ | FDG | 小脑蚓部后端、前扣带皮质 | 激活前扣带皮质,提高葡萄糖代谢,调节交感神经活动恢复脑疼痛抑制机制和中枢敏化作用 | 关节松动手法 |
表2 不同类型手法治疗颈椎病的中枢镇痛机制
Table 2 Central analgesic mechanisms in different types of manipulation for cervical spondylosis
| 发表年份(年) | 第一作者 | 观察指标及生物标志物 | 主要区域 | 手法机制 | 手法类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 刘钰[ | FA | 大脑左侧扣带海马束 | 促进局部神经的形成与重塑,调节脑功能网络连接,且能减弱负性记忆及情绪相关区域白质纤维连接,从而改善疼痛及相关不良记忆与情绪 | 软组织放松手法联合关节松动手法 |
| 2019 | WEBER[ | NPS | 次级体感皮质、前扣带皮质、枕叶复合体 | 改变处理身体疼痛的特定脑区内与疼痛有关的大脑活动 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2017 | HAAVIK[ | SEP | 中央后回 | 加强中枢对过度感觉信息的门控作用,调节感觉运动整合过程 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2015 | 张华[ | DMN | 左中央后回,右侧顶上、下回、右侧额中回 | 增强中枢水平DMN中感觉皮质和执行功能皮质的连接强度 | 软组织放松手法 |
| 2013 | SPARKS[ | BOLD | 小脑、杏仁核、丘脑、岛叶、中央前回 | 降低疼痛基质相关区域脑血流量,并减少岛叶皮质的激活 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2013 | JULIAN[ | CBI | 小脑 | 通过减轻小脑抑制运动皮质的程度,保持小脑正常运动整合、输出过程 | 关节松动手法 |
| 2011 | OGURA[ | FDG | 小脑蚓部后端、前扣带皮质 | 激活前扣带皮质,提高葡萄糖代谢,调节交感神经活动恢复脑疼痛抑制机制和中枢敏化作用 | 关节松动手法 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
魏戌,王旭,孙凯,等. 中医手法治疗颈椎病的研究现状与展望[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(10):4781-4784.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] | |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
张华,王昊,李多多,等. 颈椎病慢性疼痛患者的默认网络研究[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2015,21(1):69-73. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2015.01.018.
|
| [33] |
张华,王昊,李多多,等. 中医推拿对颈椎病慢性疼痛患者静息态脑功能默认网络的影响[J]. 北京中医药大学学报,2014,37(12):845-850,. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2014.12.012.
|
| [34] |
王昊,左伟斌,张慧,等. 推拿对慢性神经根型颈椎病疼痛相关脑区的影响[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2017,23(6):854-857,860.
|
| [35] |
刘钰,陈红,王昊,等. 推拿对颈椎病疼痛患者脑白质微观结构影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(2):167-171. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2021.02.037.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
梁龙,于杰,魏戌,等. 基于筋束骨理论建立慢性劳损型上颈椎失稳尸体模型及评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3152-3156. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2610.
|
| [59] |
魏戌,朱立国,高景华,等. 旋提手法对椎动脉型颈椎病患者经颅多普勒相关指标的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2017,58(18):1573-1576. DOI:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2017.18.012
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
魏戌,韩涛,孙凯,等. 中医药防治骨与关节退行性疾病的优势、关键问题及研究策略[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(35):4421-4426. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.032.
|
| [1] | 王婷婷, 唐勇, 张文轲, 李志刚. 高尿酸血症运动干预的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3841-3846. |
| [2] | 周晟, 邓长生, 邹冠炀, 宋健平. 疟疾心血管疾病并发症发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3466-3472. |
| [3] | 黄雨琳, 王浩云, 李燕梅, 萧雪英. 胃癌患者化疗期间症状群的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3338-3344. |
| [4] | 刘银银, 隋鸿平, 李婷婷, 姜桐桐, 史铁英, 夏云龙. 乳腺癌治疗相关心脏毒性风险预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3072-3078. |
| [5] | 李苗秀, 朱博文, 孔令军, 房敏. 青少年脊柱侧弯保守治疗临床评估工具研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3079-3088. |
| [6] | 肖瑶, 万钧. 直接口服抗凝药在静脉血栓栓塞特殊人群中的临床应用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3066-3071. |
| [7] | 阮万百, 李俊峰, 尹艳梅, 彭磊, 朱克祥. 胰腺癌靶向治疗及免疫治疗的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2950-2960. |
| [8] | 周连鹏, 李伟峰, 董新刚, 王晓元. 铜稳态调节机制在认知障碍中的作用探析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2941-2949. |
| [9] | 董浩铖, 郝潇, 安东, 李浩翰, 李树仁. 射血分数超常的心力衰竭的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2692-2696. |
| [10] | 杜琼靓, 林白浪, 郭洪花. 群组育儿保健模式的研究进展及启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2672-2678. |
| [11] | 褚田雨, 顾艳. 颈动脉钙化特征在评估斑块稳定性及临床事件中的作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2247-2252. |
| [12] | 朱子一, 何贵新, 秦伟彬, 宋惠, 张利文, 唐伟智, 杨斐斐, 刘凌云, 欧阳彬. 线粒体自噬改善心肌梗死后心肌纤维化及其中医药干预的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2294-2300. |
| [13] | 谭文彬, 李佳, 刘明玉, 路永欣, 程雅欣. 神经系统疾病及相关治疗药物对骨质疏松症影响的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2092-2100. |
| [14] | 隋鸿平, 李婷婷, 姜桐桐, 夏云龙, 史铁英. 血管内皮生长因子信号通路抑制剂相关高血压的血压管理研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(15): 1932-1936. |
| [15] | 李伊婷, 徒文静, 尹婷婷, 梅紫琦, 张苏闽, 王萌, 徐桂华. 人工智能在炎症性肠病患者营养管理中应用的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1709-1716. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





