中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (35): 4404-4411.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0378
所属专题: 老年人群健康最新文章合辑; 用药最新文章合辑; 老年人合理用药专题研究; 老年问题最新文章合辑
钟萍萍1, 南亚昀1,2, 彭琳琳1, 周宇婷1, 陈琼1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-07
修回日期:2023-07-09
出版日期:2023-12-15
发布日期:2023-07-17
通讯作者:
陈琼
基金资助:
ZHONG Pingping1, NAN Yayun1,2, PENG Linlin1, ZHOU Yuting1, CHEN Qiong1,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-07
Revised:2023-07-09
Published:2023-12-15
Online:2023-07-17
Contact:
CHEN Qiong
摘要: 背景 近年来,随着多重用药在老年人群中日益常见,相关研究数量也明显上升,需要对其发展态势进行阶段性分析。 目的 分析2003—2022年老年人多重用药领域的研究趋势及前沿热点。 方法 检索Web of Science核心合集数据库的Science Citation Index Expanded(SCI-E)和Social Sciences Citation Index(SSCI)子集数据库,将文献类型限制为Article或Review,纳入发表时间为2003—2022年有关老年人多重用药的英文文献。使用VOSviewer(v.1.6.18)和CiteSpace(v.6.1.R6)进行文献计量学分析。 结果 共得到3 987篇文献,其中Article 3 208篇,Review 779篇。近20年全球发文量快速增长,美国(1 097篇,27.51%)在该领域发表的文献最多。University of Sydney(156篇,3.91%)的发文量最大,该机构的Hilmer,Sarah N.(67篇,1.68%)是成果产出最多的作者。Drugs & Aging(181篇,4.54%)是收录老年人多重用药相关文献最多的期刊。该领域高频关键词主要是elderly、polypharmacy、prevalence和risk,目前的新热点是老年人多重用药相关临床后果和公共卫生问题。 结论 近20年,老年人多重用药领域取得了飞速发展,发文量不断增长,其中美国是贡献最大的国家。研究热点主要集中在老年人多重用药的发生率及风险方面,未来的研究可能更多地围绕相关临床后果和公共卫生问题展开。
| 排序 | 国家 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 美国 | 1 097(27.51) | 531 |
| 2 | 澳大利亚 | 400(10.03) | 403 |
| 3 | 英国 | 344(8.63) | 532 |
| 4 | 意大利 | 304(7.62) | 461 |
| 5 | 加拿大 | 267(6.70) | 299 |
| 6 | 荷兰 | 248(6.22) | 419 |
| 7 | 西班牙 | 246(6.17) | 347 |
| 8 | 德国 | 234(5.87) | 347 |
| 9 | 中国 | 192(4.82) | 104 |
| 10 | 法国 | 175(4.39) | 252 |
表1 2003—2022年老年人多重用药方面发文量排名前十的主要国家分布情况
Table 1 Ranking of the top ten major countries of polypharmacy publications in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 国家 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 美国 | 1 097(27.51) | 531 |
| 2 | 澳大利亚 | 400(10.03) | 403 |
| 3 | 英国 | 344(8.63) | 532 |
| 4 | 意大利 | 304(7.62) | 461 |
| 5 | 加拿大 | 267(6.70) | 299 |
| 6 | 荷兰 | 248(6.22) | 419 |
| 7 | 西班牙 | 246(6.17) | 347 |
| 8 | 德国 | 234(5.87) | 347 |
| 9 | 中国 | 192(4.82) | 104 |
| 10 | 法国 | 175(4.39) | 252 |
| 排序 | 作者 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hilmer,Sarah N. | 67(1.68) | 127 |
| 2 | Reeve,Emily | 48(1.20) | 105 |
| 3 | Johnell,Kristina | 44(1.10) | 91 |
| 4 | Gnjidic,Danijela | 41(1.03) | 92 |
| 5 | Fastbom,Johan | 36(0.90) | 66 |
| 6 | Bell,J. Simon | 35(0.88) | 80 |
| 7 | Hughes,Carmel M. | 31(0.78) | 59 |
| 8 | Onder,Graziano | 31(0.78) | 101 |
| 9 | O'Mahony,Denis | 30(0.75) | 74 |
| 10 | Petrovic,Mirko | 26(0.65) | 65 |
表2 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究发文量排名前十的主要作者分布情况
Table 2 Ranking of the top ten major authors of polypharmacy researches in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 作者 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hilmer,Sarah N. | 67(1.68) | 127 |
| 2 | Reeve,Emily | 48(1.20) | 105 |
| 3 | Johnell,Kristina | 44(1.10) | 91 |
| 4 | Gnjidic,Danijela | 41(1.03) | 92 |
| 5 | Fastbom,Johan | 36(0.90) | 66 |
| 6 | Bell,J. Simon | 35(0.88) | 80 |
| 7 | Hughes,Carmel M. | 31(0.78) | 59 |
| 8 | Onder,Graziano | 31(0.78) | 101 |
| 9 | O'Mahony,Denis | 30(0.75) | 74 |
| 10 | Petrovic,Mirko | 26(0.65) | 65 |
| 排序 | 机构 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Sydney | 156(3.91) | 364 |
| 2 | Karolinska Institute | 100(2.51) | 182 |
| 3 | Monash University | 93(2.33) | 237 |
| 4 | University of Pittsburgh | 61(1.53) | 134 |
| 5 | University of Toronto | 59(1.48) | 133 |
| 6 | Dalhousie University | 54(1.35) | 215 |
| 7 | Stockholm University | 53(1.33) | 126 |
| 8 | University of South Australia | 52(1.30) | 125 |
| 9 | University of Queensland | 52(1.30) | 198 |
| 10 | University of Calif San Francisco | 52(1.30) | 138 |
表3 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究发文量排名前十的主要机构分布情况
Table 3 Ranking of the top ten major institutions of polypharmacy publications in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 机构 | 发文量〔篇(%),n=3 987〕 | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Sydney | 156(3.91) | 364 |
| 2 | Karolinska Institute | 100(2.51) | 182 |
| 3 | Monash University | 93(2.33) | 237 |
| 4 | University of Pittsburgh | 61(1.53) | 134 |
| 5 | University of Toronto | 59(1.48) | 133 |
| 6 | Dalhousie University | 54(1.35) | 215 |
| 7 | Stockholm University | 53(1.33) | 126 |
| 8 | University of South Australia | 52(1.30) | 125 |
| 9 | University of Queensland | 52(1.30) | 198 |
| 10 | University of Calif San Francisco | 52(1.30) | 138 |
| 排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次(次) | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | elderly | 2 593 | 10 884 |
| 2 | polypharmacy | 2 140 | 9 804 |
| 3 | prevalence | 732 | 3 714 |
| 4 | risk | 712 | 3 537 |
| 5 | people | 583 | 3 023 |
| 6 | adults | 515 | 2 653 |
| 7 | mortality | 460 | 2 240 |
| 8 | care | 444 | 2 158 |
| 9 | frailty | 412 | 1 932 |
| 10 | population | 389 | 2 073 |
表4 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究排名前十的主要关键词分布情况
Table 4 Ranking of the top ten major keywords of polypharmacy researches in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次(次) | 总连线强度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | elderly | 2 593 | 10 884 |
| 2 | polypharmacy | 2 140 | 9 804 |
| 3 | prevalence | 732 | 3 714 |
| 4 | risk | 712 | 3 537 |
| 5 | people | 583 | 3 023 |
| 6 | adults | 515 | 2 653 |
| 7 | mortality | 460 | 2 240 |
| 8 | care | 444 | 2 158 |
| 9 | frailty | 412 | 1 932 |
| 10 | population | 389 | 2 073 |
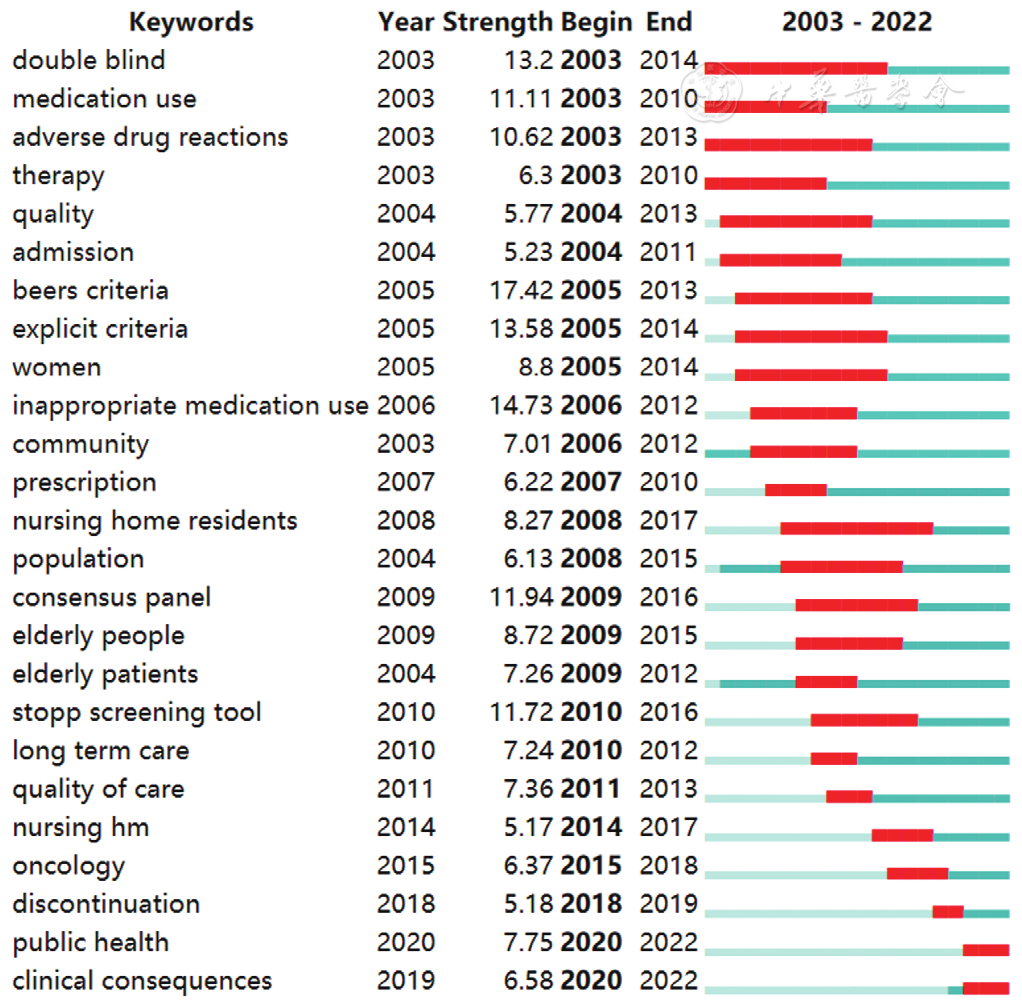
图6 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究突现强度排名前25的关键词
Figure 6 Top 25 keywords with strongest citation bursts for polypharmacy researches in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 期刊 | 发文量(篇) | 影响因子 | JCR分区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Drugs & Aging | 181 | 2.8 | Q3 |
| 2 | BMC Geriatrics | 148 | 4.1 | Q1 |
| 3 | Journal of the American Geriatrics Society | 141 | 6.3 | Q1 |
| 4 | BMJ Open | 87 | 2.9 | Q2 |
| 5 | Journal of Geriatric Oncology | 84 | 3.0 | Q3 |
| 6 | PLOS ONE | 81 | 3.7 | Q2 |
| 7 | Journal of the American Medical Directors Association | 80 | 7.6 | Q1 |
| 8 | European Geriatric Medicine | 79 | 3.8 | Q3 |
| 9 | International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy | 78 | 2.4 | Q3 |
| 10 | European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology | 72 | 2.9 | Q3 |
表5 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究发文量排名前十的主要期刊分布情况
Table 5 Ranking of the top ten major journals of polypharmacy publications in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 期刊 | 发文量(篇) | 影响因子 | JCR分区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Drugs & Aging | 181 | 2.8 | Q3 |
| 2 | BMC Geriatrics | 148 | 4.1 | Q1 |
| 3 | Journal of the American Geriatrics Society | 141 | 6.3 | Q1 |
| 4 | BMJ Open | 87 | 2.9 | Q2 |
| 5 | Journal of Geriatric Oncology | 84 | 3.0 | Q3 |
| 6 | PLOS ONE | 81 | 3.7 | Q2 |
| 7 | Journal of the American Medical Directors Association | 80 | 7.6 | Q1 |
| 8 | European Geriatric Medicine | 79 | 3.8 | Q3 |
| 9 | International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy | 78 | 2.4 | Q3 |
| 10 | European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology | 72 | 2.9 | Q3 |
| 排序 | 被引次数(次) | 中心性 | 标题 | 作者 | 发表时间(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 347 | 0.03 | What is polypharmacy?A systematic review of definitions | Masnoon N | 2017 |
| 2 | 309 | 0 | American Geriatrics Society 2015 Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Radcliff S | 2015 |
| 3 | 280 | 0.19 | STOPP/START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people:version 2 | O'Mahony D | 2015 |
| 4 | 211 | 0.01 | American Geriatrics Society Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Fick D | 2012 |
| 5 | 203 | 0.02 | Reducing Inappropriate Polypharmacy The Process of Deprescribing | Scott IA | 2015 |
| 6 | 191 | 0 | American Geriatrics Society 2019 Updated AGS Beers Criteria(R) for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Fick DM | 2019 |
| 7 | 170 | 0 | Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly | Maher RL | 2014 |
| 8 | 109 | 0.01 | Health Outcomes Associated with Polypharmacy in Community-Dwelling Older Adults:a Systematic Review | Fried TR | 2014 |
| 9 | 106 | 0 | Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes:five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes | Gnjidic D | 2012 |
| 10 | 86 | 0.06 | The feasibility and effect of deprescribing in older adults on mortality and health:a systematic review and meta-analysis | Page AT | 2016 |
表6 2003—2022年老年人多重用药研究排名前十的被引文献分布情况
Table 6 Ranking of the top ten major citations of polypharmacy researches in the elderly from 2003 to 2022
| 排序 | 被引次数(次) | 中心性 | 标题 | 作者 | 发表时间(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 347 | 0.03 | What is polypharmacy?A systematic review of definitions | Masnoon N | 2017 |
| 2 | 309 | 0 | American Geriatrics Society 2015 Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Radcliff S | 2015 |
| 3 | 280 | 0.19 | STOPP/START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people:version 2 | O'Mahony D | 2015 |
| 4 | 211 | 0.01 | American Geriatrics Society Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Fick D | 2012 |
| 5 | 203 | 0.02 | Reducing Inappropriate Polypharmacy The Process of Deprescribing | Scott IA | 2015 |
| 6 | 191 | 0 | American Geriatrics Society 2019 Updated AGS Beers Criteria(R) for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults | Fick DM | 2019 |
| 7 | 170 | 0 | Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly | Maher RL | 2014 |
| 8 | 109 | 0.01 | Health Outcomes Associated with Polypharmacy in Community-Dwelling Older Adults:a Systematic Review | Fried TR | 2014 |
| 9 | 106 | 0 | Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes:five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes | Gnjidic D | 2012 |
| 10 | 86 | 0.06 | The feasibility and effect of deprescribing in older adults on mortality and health:a systematic review and meta-analysis | Page AT | 2016 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
孙飞,李倩倩,颜庭法,等. 国内老年人多重用药的文献计量学分析[J]. 泰山医学院学报,2018,39(2):124-127. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7115.2018.02.002.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
渠吉皊,沈易静,周婷,等. 老年多重用药研究现状与热点前沿的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国药房,2020,31(21):2664-2671.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
姚泽麟. 政府职能与分级诊疗——"制度嵌入性"视角的历史总结[J]. 公共管理学报,2016,13(3):61-70,155. DOI:10.16149/j.cnki.23-1523.2016.03.006.
|
| [24] |
周婷婷,谢莉玲,孙文静,等. 社区慢性病病人安全用药管理研究进展[J]. 护理研究,2021,35(20):3673-3676. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2021.20.020.
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 崔宇阳, 程桂荣, 曾燕, 黄招兰, 谭伟. 社区老年人婚姻状况和社会支持及生活习惯与认知障碍的关联:基于湖北老年记忆队列基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3240-3247. |
| [4] | 牛奔, 朱晓倩, 杨辰, 梁万年, 刘珏. 基于CiteSpace的国内外医疗大语言模型研究热点演进及趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3200-3208. |
| [5] | 燕芳红, 彭国恬, 张国莉, 孙瑞仪, 马玉霞, 韩琳. 医联体内老年慢性病管理内容的匹配分析:基于"指南-实践-需求"视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3119-3126. |
| [6] | 于文华, 李建国, 段文燕, 高旭妍, 李夏夏, 张子龙, 张丽, 马丽娜. 老年人功能受损评估量表在社区老年人中的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [7] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [8] | 李嘉欣, 刘钟桧, 谢硕, 付志方, 孙丹, 焦红梅. 分解代谢及炎症状态的生物标志物变化趋势对老年患者慢性危重症的早期预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2993-2999. |
| [9] | 赵晓晴, 郭桐桐, 张欣怡, 李林虹, 张亚, 嵇丽红, 董志伟, 高倩倩, 蔡伟芹, 郑文贵, 井淇. 社区老年人认知障碍风险预测模型的构建与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [10] | 石小天, 王珊, 杨华昱, 杨一帆, 李旭, 马清. 中国老年人体重指数和死亡的相关性:一项队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2791-2797. |
| [11] | 刘美霞, 尹金念, 吴玫, 杨星, 周全湘, 杨敬源. 体重指数对三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与认知功能关联的影响:一项贵州农村老年人群的现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| [12] | 李丽清, 杨苏乐, 曾传美. 我国慢性病管理研究热点的演进路径与发展趋势预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2321-2329. |
| [13] | 王松柱, 姚易, 周伊恒, 赵茄茜, 杨荣, 赵茜, 张瑞, 代华, 李东泽, 廖晓阳, 杨辉. 近五年全科医学研究热点及发展趋势分析:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [14] | 郝爱华, 曾子莹, 金爱琼, 唐玲玲, 郑梓悫, 马景泰, 赵建国, 曾韦霖, 肖建鹏, 聂辉, 杨颖. 老年高血压患者可避免住院的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [15] | 陈巧巧, 苏萍, 赵颖颖, 逄锦宏, 施婕, 王雅倩, 李秋春, 何蕊言, 王玥, 陈学禹, 乔俊鹏, 迟蔚蔚. 三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与老年人群新发心脏代谢性共病的相关性:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2270-2277. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





