中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (08): 995-1006.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.046
所属专题: 高血压最新文章合辑
张平*, 邹婧, 高存州, 吴爱萍, 李蓉山
收稿日期:2021-07-12
修回日期:2021-11-25
出版日期:2022-03-15
发布日期:2022-03-02
通讯作者:
张平
基金资助:Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension:a Meta-analysis
ZHANG Ping*,ZOU Jing,GAO Cunzhou,WU Aiping,LI Rongshan
Department of Basic Medicine,Guizhou Health Vocational College,Tongren 554300,China
*Corresponding author:ZHANG Ping,Lecturer;E-mail:545077638@qq.com
Received:2021-07-12
Revised:2021-11-25
Published:2022-03-15
Online:2022-03-02
摘要: 背景难治性高血压是一种特殊类型的高血压,病因复杂,治疗难度大,更易引起靶器官损害。近年研究发现,在难治性高血压患者三联常用降压药物治疗基础上添加小剂量螺内酯能有效控制血压。但这些研究规模普遍较小,其有效性与安全性尚需进一步验证。目的系统评价螺内酯治疗难治性高血压的疗效及安全性。方法计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、The Cochrane Library、中国知网、维普网、万方数据知识服务平台,筛选螺内酯治疗难治性高血压的随机对照研究,检索时间为建库至2021-05-03。由2名研究员独立筛选文献、提取资料并评价纳入研究的偏倚风险后,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。结果共纳入20项研究。9项研究未报告随机化分组方法,1项研究按纳入顺序编号奇偶分配(错误的随机化方法),7项研究未描述是否采用盲法,4项研究为开放标签,3项研究描述了分配隐藏,1项研究结果数据不完整、未报告对照组治疗后的安全性指标。Meta分析结果显示,疗效方面:与安慰剂和空白对照相比,螺内酯降低诊室血压、24 h动态血压、日间血压及夜间血压的效果好(P<0.05);与其他降压药物总体相比,螺内酯降低诊室收缩压、24 h动态血压、日间收缩压、夜间收缩压及家庭自测收缩压的效果好(P<0.05);与肾脏去交感神经术相比,螺内酯降低日间血压及夜间收缩压的效果好(P<0.05)。安全性方面:与安慰剂相比,应用螺内酯患者的血钾及血肌酐水平高(P<0.05);与其他降压药物总体相比,应用螺内酯患者的血钾水平升高(P<0.05);与肾脏去交感神经术相比,应用螺内酯患者的血肌酐水平升高(P<0.05)。结论螺内酯治疗难治性高血压是相对有效及安全的,但受纳入研究数量和质量的限制,该结论尚需更多高质量研究予以证实。
中图分类号:
ZHANG Ping, ZOU Jing, GAO Cunzhou, WU Aiping, LI Rongshan.
Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(08): 995-1006.
| 第一作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 病例数(T/C) | 研究类型 | 平均年龄(T/C,岁) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | 随访时间(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||||
| ABOLGHASMI [ | 2011 | 伊朗 | 19/22 | RCT | (49±13.2)/(50±10.1) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2011 | 捷克 | 55/56 | RCT | (61.4±9.6)/(60.1±9.4) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 郭鑫[ | 2012 | 中国 | 57/58 | RCT | (61.8±11.5)/(59.0±11.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ②⑥ | 8 |
| 马彬[ | 2012 | 中国 | 56/56 | RCT | - | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+卡维地洛12.5~50.0 mg/d | ①⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 张俊松[ | 2012 | 中国 | 58/66 | RCT | (63.4±14.3)/(63.8±13.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 24 |
| OXLUND [ | 2013 | 丹麦 | 61/58 | RCT | (62.9±7.1)/(63.9±6.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 16 |
| NI [ | 2014 | 中国 | 40/36 | RCT | (55.7±12.3)/(54.9±14.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②⑦ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2014 | 捷克 | 74/76 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 8 |
| WILLIAMS [ | 2015 | 英国 | 285/274 /282/285 | RCT | 61.4±9.6 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂基础降压治疗+多沙唑嗪4~8 mg/d基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5~10 mg/d | ①⑤ | 12 |
| 盖延红[ | 2015 | 中国 | 73/71 | RCT | 61.5±9.7 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③④⑥ | 12 |
| DJOUMESSI [ | 2016 | 喀麦隆 | 9/8 | RCT | (64.6±9.6)/(61.0±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+坎地沙坦8 mg/d,阿替洛尔100 mg/d或甲基多巴750 mg/d | ①⑤ | 4 |
| OLIVERAS [ | 2016 | 西班牙 | 13/11 | RCT | (64.9±8.2)/(61.9±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 24 |
| ROSA [ | 2016 | 捷克 | 50/51 | RCT | (59±9) /(56±12) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②⑦⑧ | 48 |
| YANG [ | 2016 | 中国 | 15/15 | RCT | (44.7±10.8) /(43.4±15.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 曾潇[ | 2016 | 中国 | 78/82 | RCT | (60.7±7.7)/(61.0±8.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑥⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 卢旭[ | 2017 | 中国 | 41/38 | RCT | (73.45±5.88) /(71.11±7.15) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 48 |
| KRIEGER[ | 2018 | 巴西 | 84/78 | RCT | (54±11.1)/(56.3±9.7) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯12.5~50.0 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+可乐定0.1~0.3 mg/d | ①②③④⑧ | 12 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 2018 | 多国 | 191/212 | RCT | 74(65,80) /71(63,78) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯23 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ① | 32 |
| 杨晶敏[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40/40/40 | RCT | (54.7±10.7)/(54.7±8.5) / (57.9±11.3) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5 mg基础降压治疗+特拉唑嗪2 mg/d | ②⑦ | 12 |
| 黄娟[ | 2020 | 中国 | 45/49 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+倍他乐克50 mg/d | ① ③④ | 8 |
表1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of included studies
| 第一作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 病例数(T/C) | 研究类型 | 平均年龄(T/C,岁) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | 随访时间(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||||
| ABOLGHASMI [ | 2011 | 伊朗 | 19/22 | RCT | (49±13.2)/(50±10.1) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2011 | 捷克 | 55/56 | RCT | (61.4±9.6)/(60.1±9.4) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 郭鑫[ | 2012 | 中国 | 57/58 | RCT | (61.8±11.5)/(59.0±11.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ②⑥ | 8 |
| 马彬[ | 2012 | 中国 | 56/56 | RCT | - | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+卡维地洛12.5~50.0 mg/d | ①⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 张俊松[ | 2012 | 中国 | 58/66 | RCT | (63.4±14.3)/(63.8±13.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 24 |
| OXLUND [ | 2013 | 丹麦 | 61/58 | RCT | (62.9±7.1)/(63.9±6.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 16 |
| NI [ | 2014 | 中国 | 40/36 | RCT | (55.7±12.3)/(54.9±14.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②⑦ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2014 | 捷克 | 74/76 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 8 |
| WILLIAMS [ | 2015 | 英国 | 285/274 /282/285 | RCT | 61.4±9.6 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂基础降压治疗+多沙唑嗪4~8 mg/d基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5~10 mg/d | ①⑤ | 12 |
| 盖延红[ | 2015 | 中国 | 73/71 | RCT | 61.5±9.7 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③④⑥ | 12 |
| DJOUMESSI [ | 2016 | 喀麦隆 | 9/8 | RCT | (64.6±9.6)/(61.0±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+坎地沙坦8 mg/d,阿替洛尔100 mg/d或甲基多巴750 mg/d | ①⑤ | 4 |
| OLIVERAS [ | 2016 | 西班牙 | 13/11 | RCT | (64.9±8.2)/(61.9±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 24 |
| ROSA [ | 2016 | 捷克 | 50/51 | RCT | (59±9) /(56±12) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②⑦⑧ | 48 |
| YANG [ | 2016 | 中国 | 15/15 | RCT | (44.7±10.8) /(43.4±15.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 曾潇[ | 2016 | 中国 | 78/82 | RCT | (60.7±7.7)/(61.0±8.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑥⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 卢旭[ | 2017 | 中国 | 41/38 | RCT | (73.45±5.88) /(71.11±7.15) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 48 |
| KRIEGER[ | 2018 | 巴西 | 84/78 | RCT | (54±11.1)/(56.3±9.7) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯12.5~50.0 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+可乐定0.1~0.3 mg/d | ①②③④⑧ | 12 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 2018 | 多国 | 191/212 | RCT | 74(65,80) /71(63,78) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯23 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ① | 32 |
| 杨晶敏[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40/40/40 | RCT | (54.7±10.7)/(54.7±8.5) / (57.9±11.3) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5 mg基础降压治疗+特拉唑嗪2 mg/d | ②⑦ | 12 |
| 黄娟[ | 2020 | 中国 | 45/49 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+倍他乐克50 mg/d | ① ③④ | 8 |
| 第一作者 | 随机方法 | 盲法 | 分配隐藏 | 结果数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABOLGHASMI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 郭鑫[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 马彬[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 张俊松[ | 纳入顺序编号奇偶分配 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OXLUND[ | 网站生成的随机化方案 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| NI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| WILLIAMS[ | 计算机随机数字发生器 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 盖延红[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| DJOUMESSI[ | 未报告 | 单盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OLIVERAS[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSA[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| YANG[ | SPSS 19.0软件 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 曾潇[ | SPSS软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 卢旭[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| KRIEGER[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 杨晶敏[ | RandA1.0随机化软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 黄娟[ | 未报告 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 不完整 | 是,未报告对照组治疗后安全性指标 | 不清楚 |
表2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评估
Table 2 Results of bias risk assessment of included studies
| 第一作者 | 随机方法 | 盲法 | 分配隐藏 | 结果数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABOLGHASMI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 郭鑫[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 马彬[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 张俊松[ | 纳入顺序编号奇偶分配 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OXLUND[ | 网站生成的随机化方案 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| NI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| WILLIAMS[ | 计算机随机数字发生器 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 盖延红[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| DJOUMESSI[ | 未报告 | 单盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OLIVERAS[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSA[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| YANG[ | SPSS 19.0软件 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 曾潇[ | SPSS软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 卢旭[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| KRIEGER[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 杨晶敏[ | RandA1.0随机化软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 黄娟[ | 未报告 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 不完整 | 是,未报告对照组治疗后安全性指标 | 不清楚 |
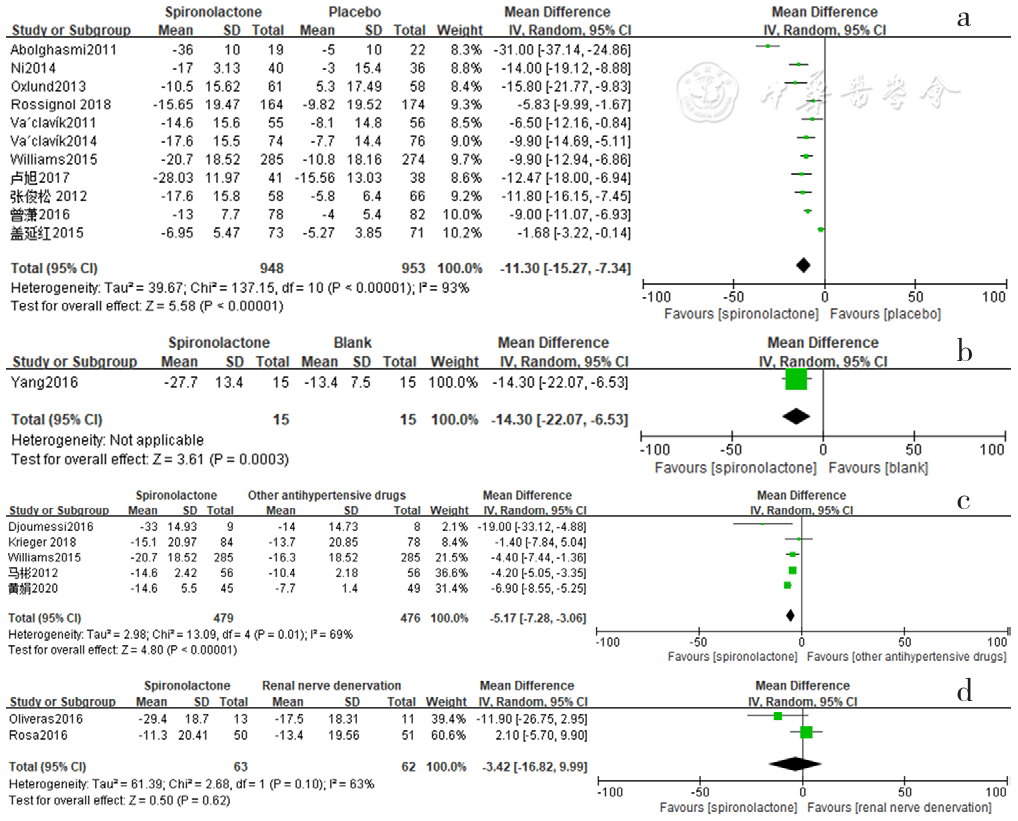
图2 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比诊室收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 2 Forest plot of the effect of reducing clinic systolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
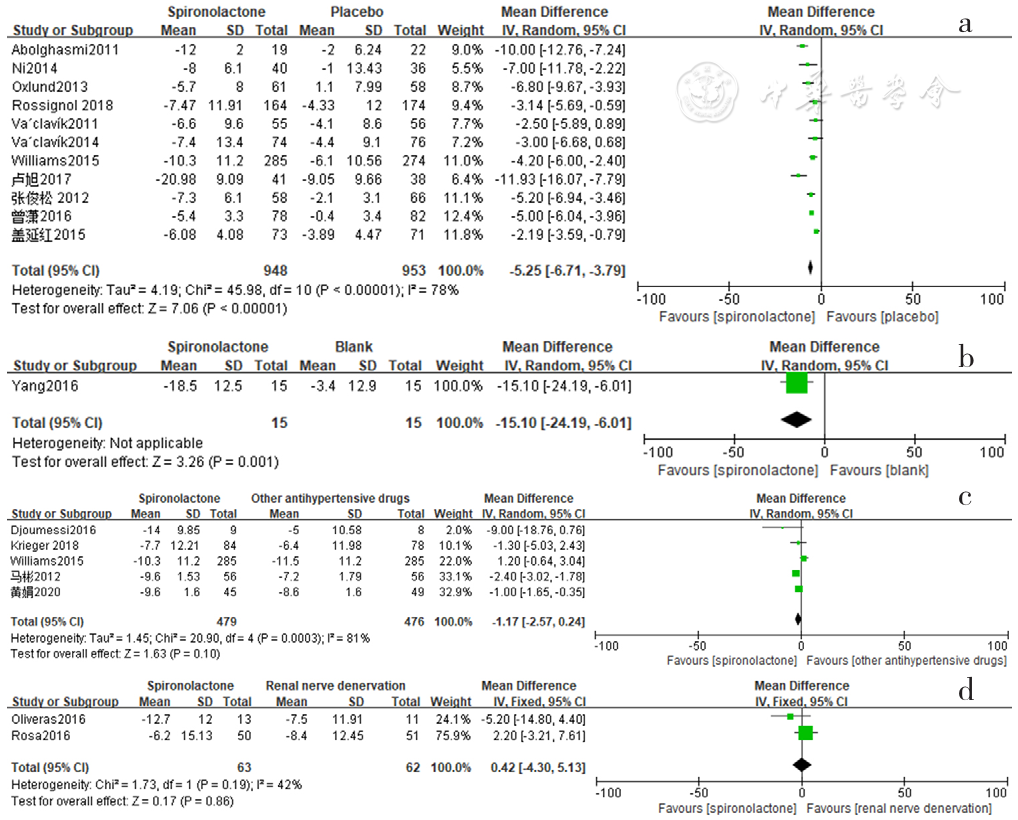
图3 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比诊室舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 3 Forest plot of the effect of reducing clinic diastolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
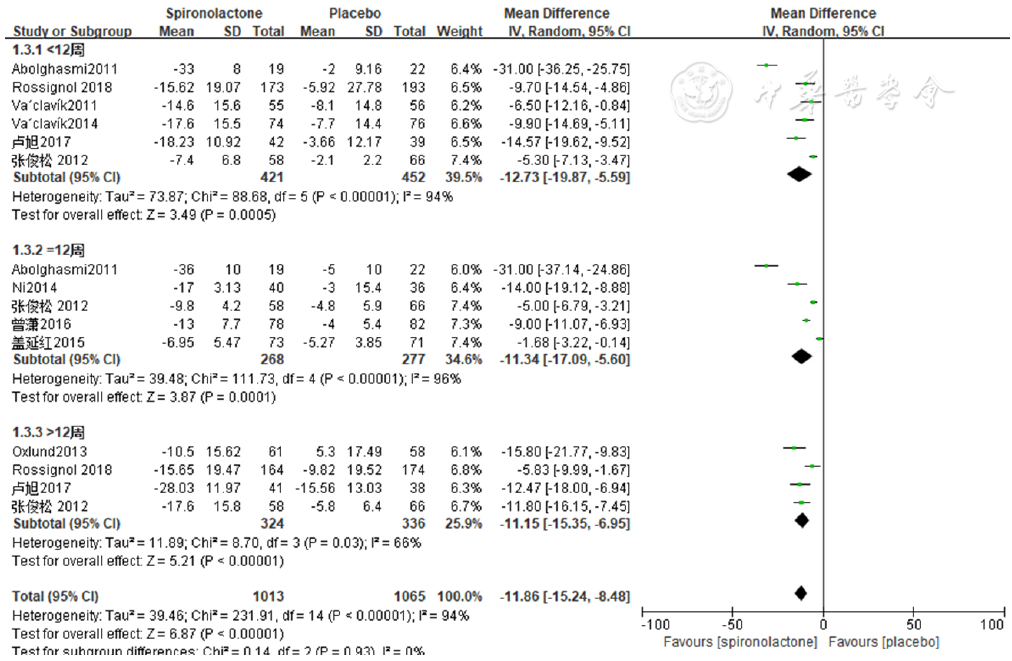
图4 依干预时间行亚组分析诊室收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 4 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone versus placebo on reducing clinic systolic blood pressure by the duration of intervention
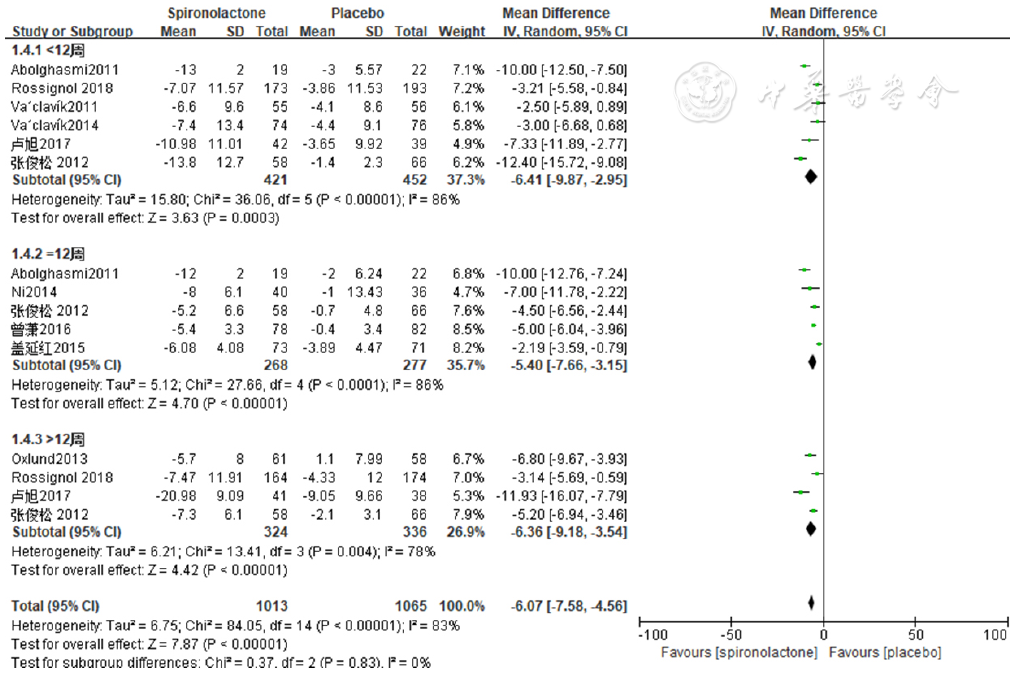
图5 依干预时间行亚组分析诊室舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 5 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone versus placebo on reducing clinic diastolic blood pressure by the duration of intervention
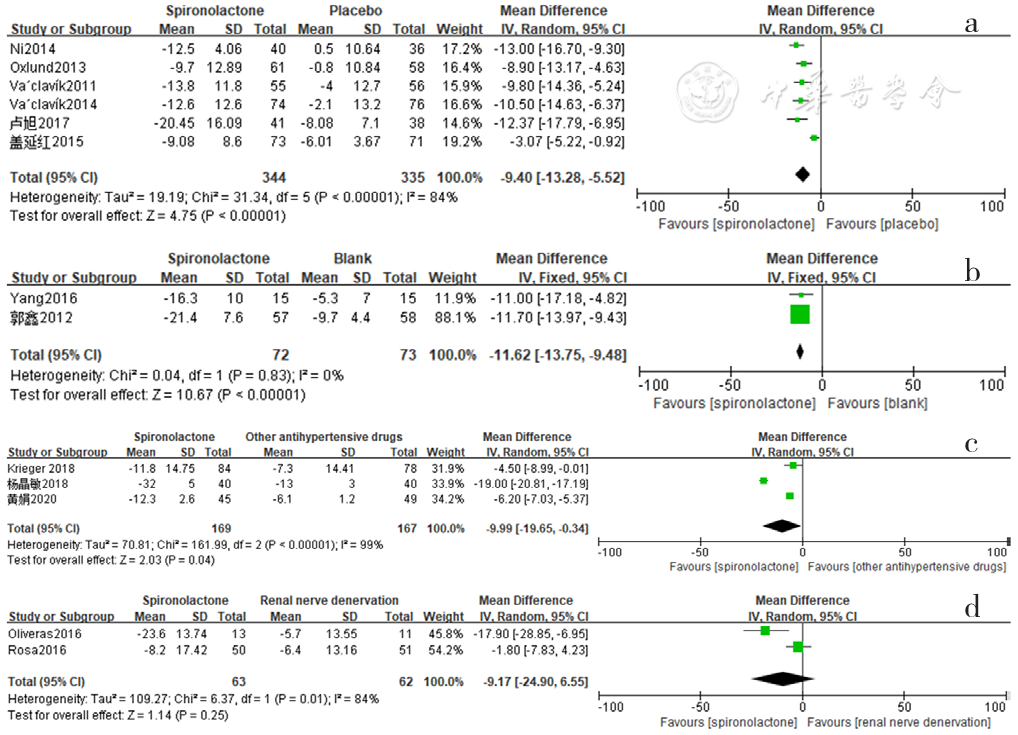
图6 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比24 h动态收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 6 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
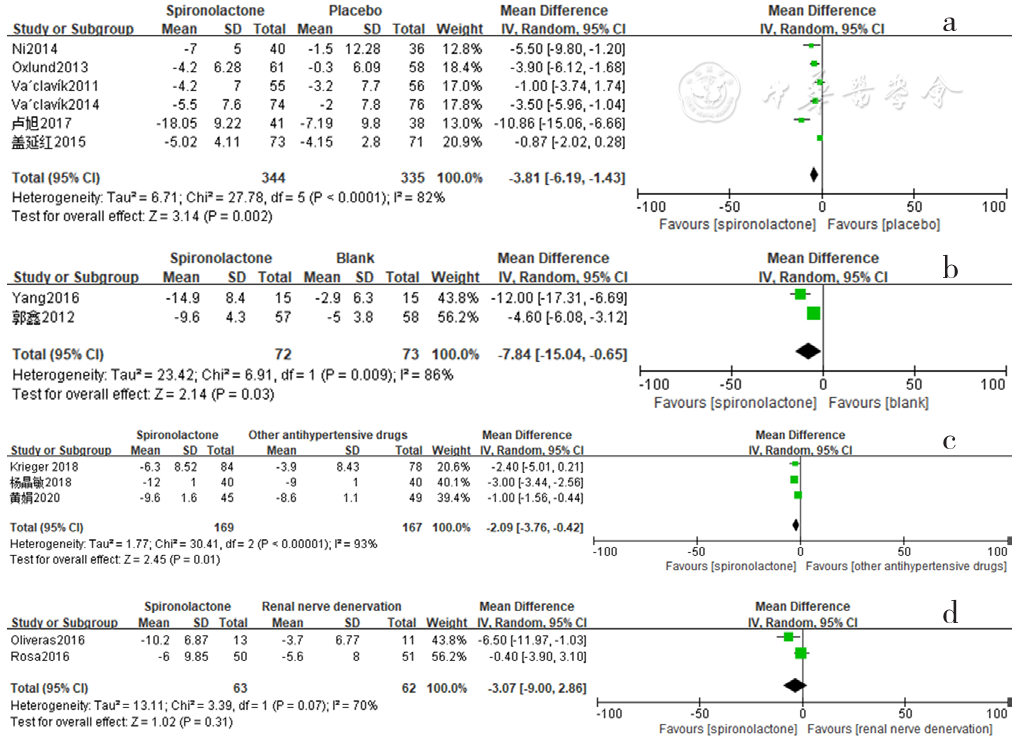
图7 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比24 h动态舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 7 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
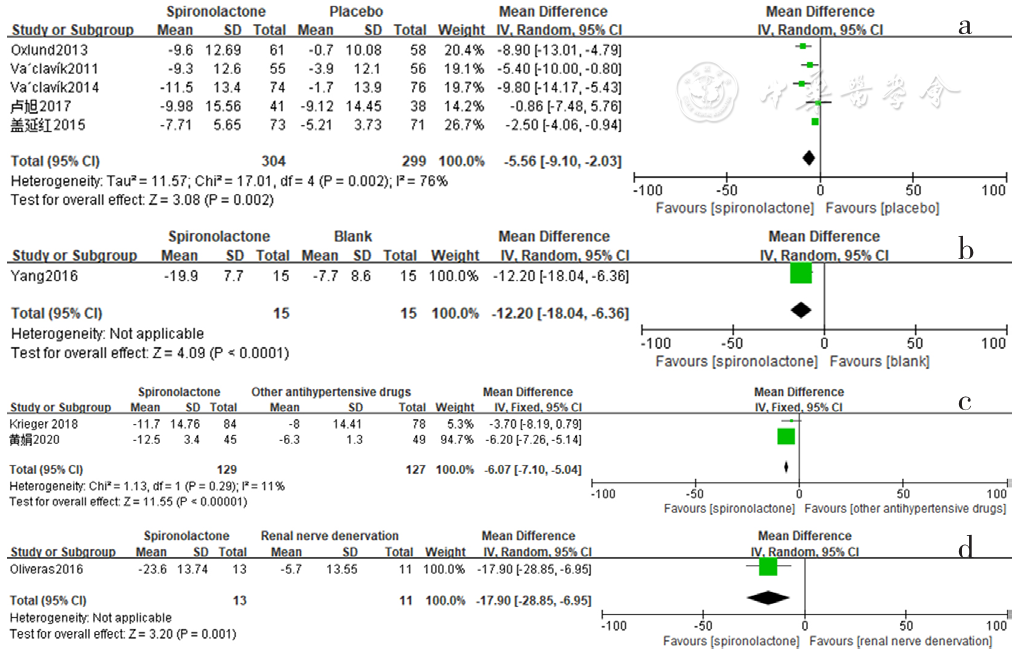
图8 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比日间收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 8 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing daytime systolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
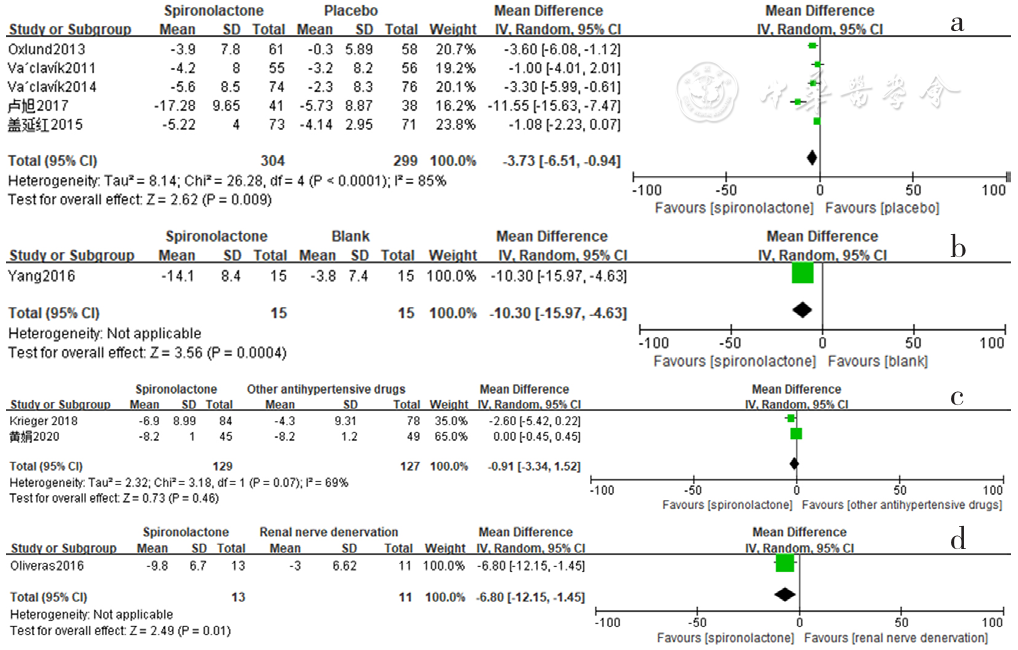
图9 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比日间舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 9 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing daytime diastolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
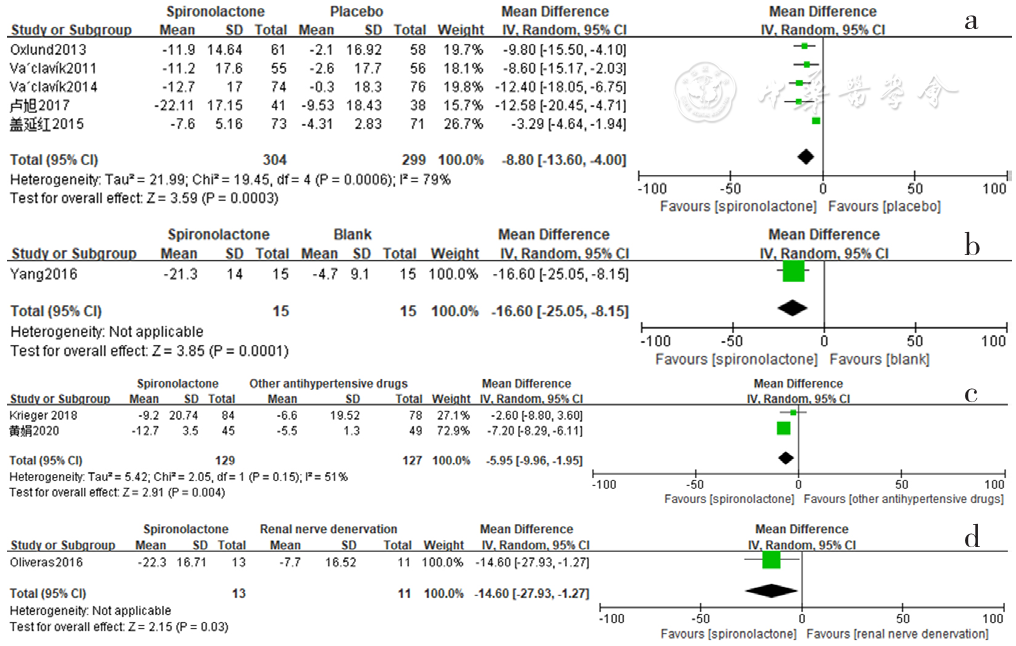
图10 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比夜间收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 10 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing nighttime systolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
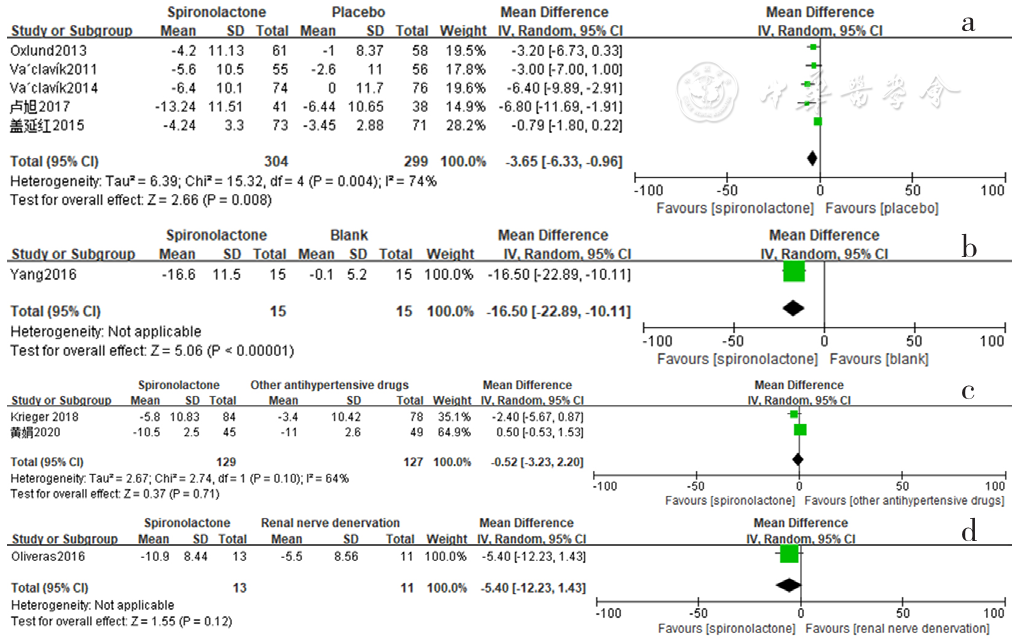
图11 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比夜间舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 11 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing nighttime diastolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
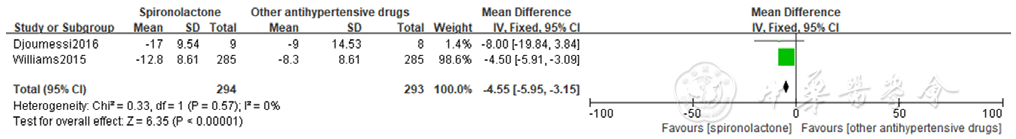
图12 螺内酯组与其他降压药物组相比家庭自测收缩压降低效果的森林图
Figure 12 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing self-measured home systolic blood pressure compared with that of other antihypertensive drugs
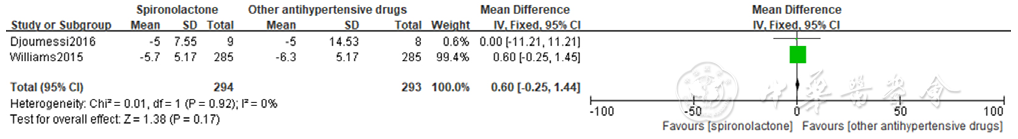
图13 螺内酯组与其他降压药物组相比家庭自测舒张压降低效果的森林图
Figure 13 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone versus other antihypertensive drugs on reducing self-measured home diastolic blood pressure
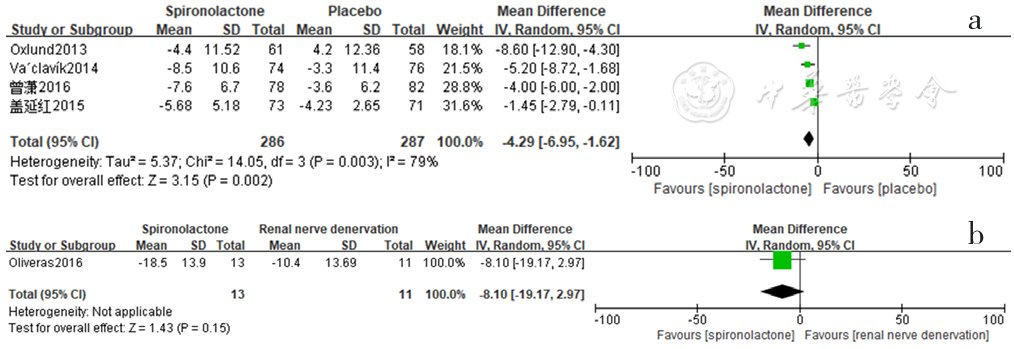
图14 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比诊室脉压降低效果的森林图
Figure 14 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone versus placebo and renal sympathetic denervation on reducing clinical pulse pressure
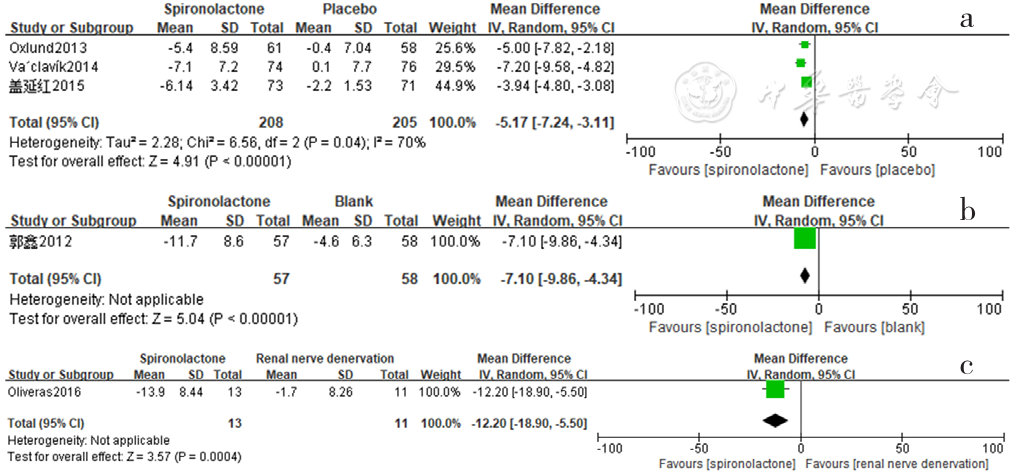
图15 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比24 h脉压降低效果的森林图
Figure 15 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour pulse pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank) and renal sympathetic denervation
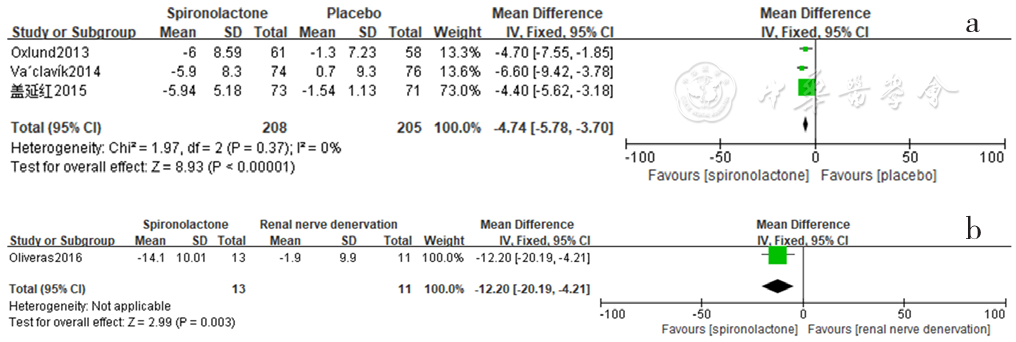
图16 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比日间脉压降低效果的森林图
Figure 16 Forest plot of the effect of reducing daytime pulse pressure of spironolactone compared with that of placebo and renal sympathetic denervation
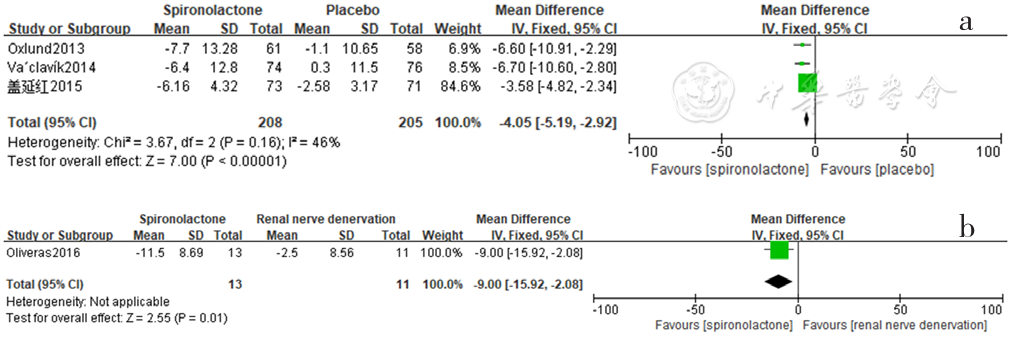
图17 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比夜间脉压降低效果的森林图
Figure 17 Forest plot of the effect of reducing nighttime pulse pressure of spironolactone versus placebo and renal sympathetic denervation
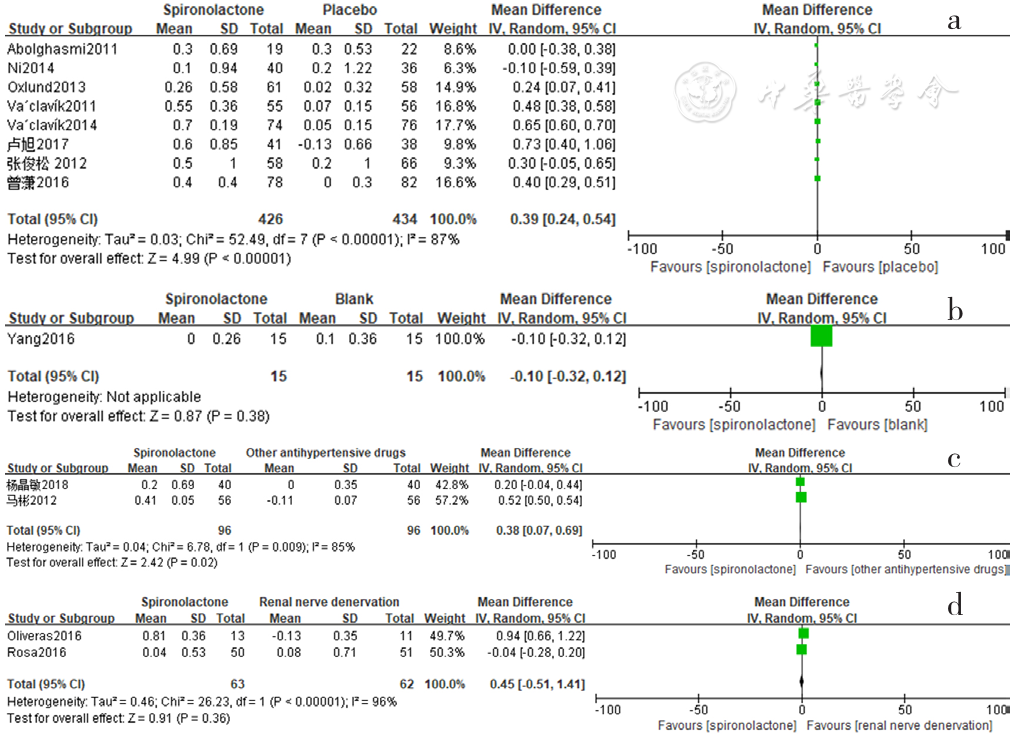
图18 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比血钾水平变化的森林图
Figure 18 Forest plot of the changes in serum potassium levels of spironolactone-treated group compared with those of placebo,blank,other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation groups
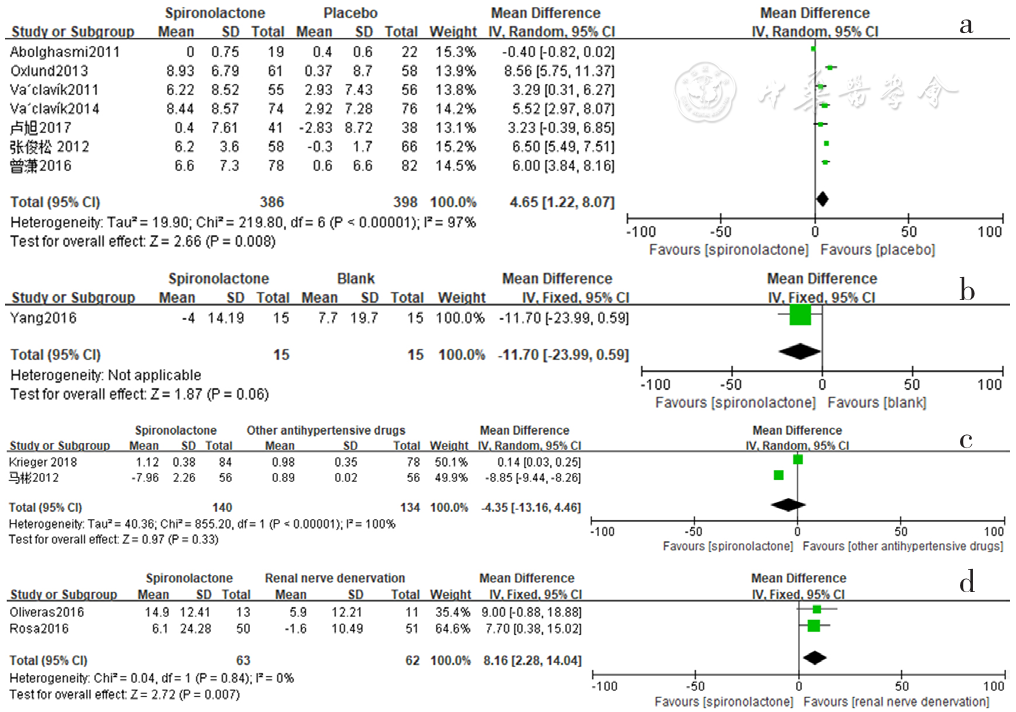
图19 螺内酯组与安慰剂组、空白组、其他降压药物组、肾脏去交感神经术组相比血肌酐水平变化的森林图
Figure 19 Forest plot of the changes in serum creatinine levels of spironolactone-treated group compared with those of placebo,blank,other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation groups
| [1] | CAREY R M, CALHOUN D A, BAKRIS G L,et al. Resistant hypertension:detection,evaluation,and management:a scientific statement from the American heart association[J]. Hypertension,2018,72(5):e53-90. DOI:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084. |
| [2] | TSUJIMOTO T, KAJIO H. Spironolactone use and improved outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with resistant hypertension[J]. J Am Heart Assoc,2020,9(23):e018827. DOI:10.1161/jaha.120.018827. |
| [3] | HIGGINS J, GREEN S.Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (version 5.1.0),2011[EB/OL].[2021-04-11].. |
| [4] | ABOLGHASMI R, TAZIKI O. Efficacy of low dose spironolactone in chronic kidney disease with resistant hypertension[J]. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl,2011,22(1):75-78. |
| [5] | VÁCLAVÍK J, SEDLÁK R, PLACHÝ M,et al. Addition of spironolactone in patients with resistant arterial hypertension (ASPIRANT)[J]. Hypertension,2011,57(6):1069-1075. DOI:10.1161/hypertensionaha.111.169961. |
| [6] | 郭鑫. 醛固酮受体拮抗剂—螺内酯治疗难治性高血压的疗效观察[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2012. |
| [7] | 马彬. 小剂量安体舒通治疗顽固性高血压疗效分析[J]. 中国实用医药,2012,7(23):35-37. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2012.23.098. |
| [8] | 张俊松,邓节喜,郭寿贵,等. 螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的随机、单盲、对照试验[J]. 海南医学院学报,2012,18(6):788-790,793. DOI:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.2012.06.013. |
| [9] | OXLUND C S, HENRIKSEN J E, TARNOW L,et al. Low dose spironolactone reduces blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus:a double blind randomized clinical trial[J]. J Hypertens,2013,31(10):2094-2102. DOI:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283638b1a. |
| [10] | NI X Y, ZHANG J S, ZHANG P,et al. Effects of spironolactone on dialysis patients with refractory hypertension:a randomized controlled study[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich),2014,16(9):658-663. DOI:10.1111/jch.12374. |
| [11] | VÁCLAVÍK J, SEDLÁK R, JARKOVSKÝ J,et al. Effect of spironolactone in resistant arterial hypertension:a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled trial (ASPIRANT-EXT)[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2014,93(27):e162. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000000162. |
| [12] | WILLIAMS B, MACDONALD T M, MORANT S,et al. Spironolactone versus placebo,bisoprolol,and doxazosin to determine the optimal treatment for drug-resistant hypertension (PATHWAY-2):a randomised,double-blind,crossover trial[J]. Lancet,2015,386(10008):2059-2068. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00257-3. |
| [13] | 盖延红,栾晓东,朱为勇,等. 螺内酯治疗不同年龄难治性高血压的疗效差别[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2015,7(4):537-538,541. DOI:10.3969/j.1674-4055.2015.04.33. |
| [14] | DJOUMESSI R N, NOUBIAP J J, KAZE F F,et al. Effect of low-dose spironolactone on resistant hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus:a randomized controlled trial in a sub-Saharan African population[J]. BMC Res Notes,2016,9:187. DOI:10.1186/s13104-016-1987-5. |
| [15] | OLIVERAS A, ARMARIO P, CLARÀ A,et al. Spironolactone versus sympathetic renal denervation to treat true resistant hypertension:results from the DENERVHTA study-a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hypertens,2016,34(9):1863-1871. DOI:10.1097/hjh.0000000000001025. |
| [16] | ROSA J, WIDIMSKÝ P, WALDAUF P,et al. Role of adding spironolactone and renal denervation in true resistant hypertension:one-year outcomes of randomized PRAGUE-15 study[J]. Hypertension,2016,67(2):397-403. DOI:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06526. |
| [17] | YANG L R, ZHANG H M, CAI M,et al. Effect of spironolactone on patients with resistant hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens,2016,38(5):464-468. DOI:10.3109/10641963.2015.1131290. |
| [18] | 曾潇,周宁,曹少雄,等. 小剂量螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的临床研究[J]. 江西医药,2016,51(8):742-745. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2016.08.006. |
| [19] | 卢旭.小剂量螺内酯在老年难治性高血压患者中疗效及安全性分析[D].北京:解放军总医院(北京301医院)&军医进修学院,2017. |
| [20] | KRIEGER E M, DRAGER L F, GIORGI D M A,et al. Spironolactone versus clonidine as a fourth-drug therapy for resistant hypertension:the ReHOT randomized study (resistant hypertension optimal treatment)[J]. Hypertension,2018,71(4):681-690. DOI:10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10662. |
| [21] | ROSSIGNOL P, CLAGGETT B L, LIU J,et al. Spironolactone and resistant hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Am J Hypertens,2018,31(4):407-414. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpx210. |
| [22] | 杨晶敏,杨文,刘洁云. 螺内酯、特拉唑嗪、比索洛尔对难治性高血压患者的治疗效果及安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2018,21(31):3845-3849. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.31.014. |
| [23] | 黄娟.螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的疗效及安全性[J].当代医药论丛,2020,18(15):126-128. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2020.15.090. |
| [24] | LOTUFO P A, PEREIRA A C, VASCONCELLOS P S,et al. Resistant hypertension:risk factors,subclinical atherosclerosis,and comorbidities among adults-the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil)[J]. J Clin Hypertens:Greenwich,2015,17(1):74-80. DOI:10.1111/jch.12433. |
| [25] | CAO G Z, CHEN C, LIN Q S,et al. Prevalence,clinical characteristics and echocardiography parameters of non-resistant,resistant and refractory hypertension in Chinese[J]. Postgrad Med,2017,129(2):187-192. DOI:10.1080/00325481.2017.1272398. |
| [26] | HWANG A Y, DIETRICH E, PEPINE C J,et al. Resistant hypertension:mechanisms and treatment[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep,2017,19(7):1-11. DOI:10.1007/s11906-017-0754-x. |
| [27] | SIDDIQUI M, CALHOUN D A. Refractory versus resistant hypertension[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens,2017,26(1):14-19. DOI:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000286. |
| [28] | SALLES G F, RIBEIRO F M, GUIMARÃES G M,et al. A reduced heart rate variability is independently associated with a blunted nocturnal blood pressure fall in patients with resistant hypertension[J]. J Hypertens,2014,32(3):644-651. DOI:10.1097/HJH.0000000000000068. |
| [29] | DAUGHERTY S L, POWERS J D, MAGID D J,et al. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients[J]. Circulation,2012,125(13):1635-1642. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.068064. |
| [30] | 那开宪.应重视醛固酮受体拮抗剂在心血管疾病中的应用[J].中国临床医生杂志,2016,44(11):1-3. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2016.11.001. |
| [31] | ROSSIGNOL P, CLAGGETT B L, LIU J,et al. Spironolactone and resistant hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Am J Hypertens,2018,31(4):407-414. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpx210. |
| [32] | TSUJIMOTO T, KAJIO H. Spironolactone use and improved outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with resistant hypertension[J]. J Am Heart Assoc,2020,9(23):e018827. DOI:10.1161/jaha.120.018827. |
| [33] | CHEN C, ZHU X Y, LI D,et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of spironolactone in patients with resistant hypertension:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2020,99(34):e21694. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000021694. |
| [34] | MUXFELDT E S, CHEDIER B, RODRIGUES C I S. Resistant and refractory hypertension:two sides of the same disease?[J]. J Bras Nefrol,2019,41(2):266-274. DOI:10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2018-0108. |
| [35] | CAREY R M, CALHOUN D A, BAKRIS G L,et al. Resistant hypertension:detection,evaluation,and management:a scientific statement from the American heart association[J]. Hypertension,2018,72(5):e53-90. DOI:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084. |
| [36] | ACELAJADO M C, HUGHES Z H, OPARIL S,et al. Treatment of resistant and refractory hypertension[J]. Circ Res,2019,124(7):1061-1070. DOI:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312156. |
| [37] | 赵林蔚,朱利杰,张优,等. 肾动脉射频消融去交感神经术研究进展[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2017,31(2):194-196. DOI:10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2017.02.029. |
| [38] | TOUYZ R M. Reactive oxygen species,vascular oxidative stress,and redox signaling in hypertension:what is the clinical significance?[J]. Hypertension,2004,44(3):248-252. DOI:10.1161/01.HYP.0000138070.47616.9d. |
| [39] | KHOSLA N, KALAITZIDIS R, BAKRIS G L. Predictors of hyperkalemia risk following hypertension control with aldosterone blockade[J]. Am J Nephrol,2009,30(5):418-424. DOI:10.1159/000237742. |
| [1] | 吴文俊, 卫靖靖, 李雪, 任红杰, 于瑞, 彭广操, 朱明军. 基于隐结构模型结合关联规则分析冠心病合并高血压的方药规律[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3787-3795. |
| [2] | 白佳欣, 程玉, 周伊恒, 刘力滴, 杨荣, 姚易, 袁波, 张永刚, 雷弋, 曾锐, 贾禹, 廖晓阳. 《早发性高血压的评估与治疗:英国和爱尔兰高血压协会立场声明》对中国早发性高血压临床管理的建议[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3741-3746. |
| [3] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [4] | 秦邦国, 孙瑾, 李曼, 邱娇娇, 程柏凯, 朱平, 王曙霞. 农村高血压人群非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与左心室肥厚的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3753-3760. |
| [5] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [6] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [7] | 韩笑, 李奇遇, 葛蒲, 范思园, 刘迪玥, 吴一波, 张清霜. 高血压患者行为生活方式对生命质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [8] | 余孜孜, 刘杜丽, 李熙敏, 阮春怡, 尹向阳, 蔡乐. 农村高血压患病和自我管理现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [9] | 唐尚锋, 黄阳珍, 潘阳阳, 郑妍惜, 熊忠宝, 张康康, 宋佳, 魏艺琳, 王春盈, 董衡, 陈蔓维, 卿华. 高血压基层医防融合服务规范[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3089-3095. |
| [10] | 魏云鸿, 杨莉, 王玉路, 叶秋芳, 代安妮, 何燕. 肥胖相关性高血压患者不同运动阶段心肺功能的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2972-2978. |
| [11] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [12] | 何金玉, 朱丽都孜·解思思别克, 张宁, 刘民, 梁万年. 我国规范化管理高血压患者血压控制及影响因素研究的现状、挑战与未来展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2968-2971. |
| [13] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [14] | 王笑林, 李秋月, 周彦君, 张金辉, 梁涛. 转移性结直肠癌患者呋喹替尼治疗相关心血管毒性发生率和风险的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [15] | 陈友兰, 蓝彦琦, 吴阿华, 张海霞, 黄健康, 郭志南. "三师共管"家庭医生签约服务对老年高血压患者的健康管理效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2769-2775. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





