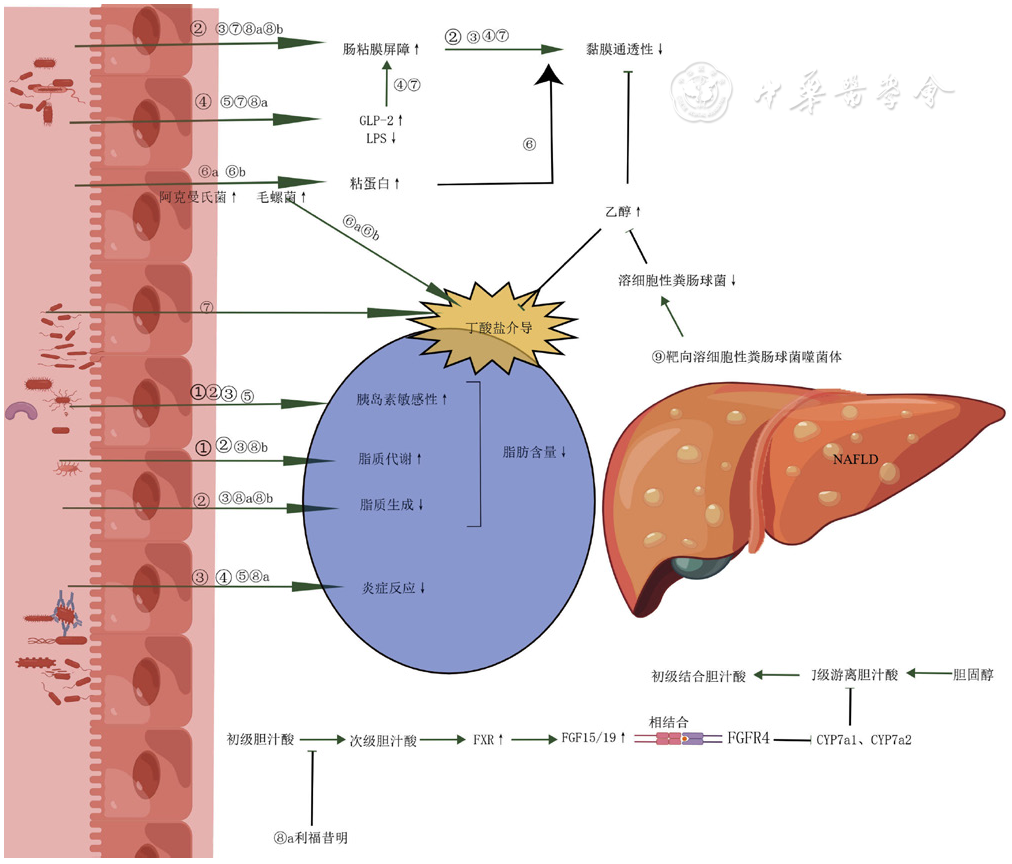
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
CARIOU B, BYRNE C D, LOOMBA R,et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a metabolic disease in humans:a literature review[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2021, 23(5):1069-1083. DOI: 10.1111/dom.14322.
|
| [3] |
MÉNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ N, DÍAZ-OROZCO L E. Editorial:international consensus recommendations to replace the terminology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2021, 27:e933860. DOI: 10.12659/MSM.933860.
|
| [4] |
GE X J, ZHENG L M, WANG M,et al. Prevalence trends in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease at the global,regional and national levels,1990-2017:a population-based observational study[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(8):e036663. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-036663.
|
| [5] |
AHMAD M I, KHAN M U, KODALI S,et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma due to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:current concepts and future challenges[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9:477-496. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S344559.
|
| [6] |
NOUREDDIN M, SANYAL A J. Pathogenesis of NASH:the impact of multiple pathways[J]. Curr Hepatol Rep, 2018, 17(4):350-360. DOI: 10.1007/s11901-018-0425-7.
|
| [7] |
KIM W, KIM B G, LEE J S,et al. Randomised clinical trial:the efficacy and safety of oltipraz,a liver X receptor alpha-inhibitory dithiolethione in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 45(8):1073-1083. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13981.
|
| [8] |
HOOZEMANS J, DE BRAUW M, NIEUWDORP M,et al. Gut microbiome and metabolites in patients with NAFLD and after bariatric surgery:a comprehensive review[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11(6):353. DOI: 10.3390/metabo11060353.
|
| [9] |
VALLIANOU N, STRATIGOU T, CHRISTODOULATOS G S,et al. Understanding the role of the gut microbiome and microbial metabolites in obesity and obesity-associated metabolic disorders:current evidence and perspectives[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2019, 8(3):317-332. DOI: 10.1007/s13679-019-00352-2.
|
| [10] |
NOGACKA A M, GÓMEZ-MARTÍN M, SUÁREZ A,et al. Xenobiotics formed during food processing:their relation with the intestinal microbiota and colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(8):E2051. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20082051.
|
| [11] |
WAN M L Y, LING K H, EL-NEZAMI H,et al. Influence of functional food components on gut health[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 59(12):1927-1936. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1433629.
|
| [12] |
OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome:major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7(1):91. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-019-0704-8.
|
| [13] |
YAN X F, JIN J J, SU X H,et al. Intestinal flora modulates blood pressure by regulating the synthesis of intestinal-derived corticosterone in high salt-induced hypertension[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126(7):839-853. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316394.
|
| [14] |
ZHAO Y Z, ZHOU J L, LIU J Q,et al. Metagenome of gut microbiota of children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Pediatr, 2019, 7:518. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2019.00518.
|
| [15] |
HOYLES L, FERNÁNDEZ-REAL J M, FEDERICI M,et al. Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic steatosis in non-diabetic obese women[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24(7):1070-1080. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0061-3.
|
| [16] |
YUAN J, CHEN C, CUI J H,et al. Fatty liver disease caused by high-alcohol-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 30(6):1172. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.006.
|
| [17] |
SHARPTON S R, AJMERA V, LOOMBA R. Emerging role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:from composition to function[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(2):296-306. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.08.065.
|
| [18] |
DE MUNCK T J I, XU P, VERWIJS H J A,et al. Intestinal permeability in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40(12):2906-2916. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14696
|
| [19] |
CHEN J, ZHENG M H, LIU J,et al. Ratio of conjugated chenodeoxycholic to muricholic acids is associated with severity of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2019, 27(12):2055-2066. DOI: 10.1002/oby.22627.
|
| [20] |
JI Y, YIN Y, SUN L J,et al. The molecular and mechanistic insights based on gut-liver axis:nutritional target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) improvement[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(9):E3066. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21093066.
|
| [21] |
ZHAO S, JANG C, LIU J,et al. Dietary fructose feeds hepatic lipogenesis via microbiota-derived acetate[J]. Nature, 2020, 579(7800):586-591. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2101-7.
|
| [22] |
VIVEIROS K. The role of life style modifications in comprehensive non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment[J]. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken), 2021, 17(1):11-14. DOI: 10.1002/cld.1007.
|
| [23] |
BARTON W, PENNEY N C, CRONIN O,et al. The microbiome of professional athletes differs from that of more sedentary subjects in composition and particularly at the functional metabolic level[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(4):625-633. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313627.
|
| [24] |
VALLIANOU N, DALAMAGA M, STRATIGOU T,et al. Do antibiotics cause obesity through long-term alterations in the gut microbiome? A review of current evidence[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2021, 10(3):244-262. DOI: 10.1007/s13679-021-00438-w.
|
| [25] |
CARBAJO-PESCADOR S, PORRAS D, GARCÍA-MEDIAVILLA M V,et al. Beneficial effects of exercise on gut microbiota functionality and barrier integrity,and gut-liver crosstalk in an in vivo model of early obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2019, 12(5):dmm039206. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.039206.
|
| [26] |
CHENG R T, WANG L, LE S L,et al. A randomized controlled trial for response of microbiome network to exercise and diet intervention in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):2555. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29968-0.
|
| [27] |
VILAR-GOMEZ E, MARTINEZ-PEREZ Y, CALZADILLA-BERTOT L,et al. Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 149(2):367-378.e5;quize14-15. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005.
|
| [28] |
SAVARD C, TARTAGLIONE E V, KUVER R,et al. Synergistic interaction of dietary cholesterol and dietary fat in inducing experimental steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57(1):81-92. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25789.
|
| [29] |
CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE J E,et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1):328-357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29367.
|
| [30] |
ALLER R, BURGUEÑO GOMEZ B, SIGÜENZA R,et al. Comparative study of overweight and obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2019, 111(4):256-263. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.5926/2018.
|
| [31] |
CALABRESE F M, DISCIGLIO V, FRANCO I,et al. A low glycemic index Mediterranean diet combined with aerobic physical activity rearranges the gut microbiota signature in NAFLD patients[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(9):1773. DOI: 10.3390/nu14091773.
|
| [32] |
HILL C, GUARNER F, REID G,et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 11(8):506-514. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66.
|
| [33] |
MOHAMAD NOR M H, AYOB N, MOKHTAR N M,et al. The effect of probiotics (MCP® BCMC® strains) on hepatic steatosis,small intestinal mucosal immune function,and intestinal barrier in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(9):3192. DOI: 10.3390/nu13093192.
|
| [34] |
LUO M M, YAN J B, WU L Y,et al. Probiotics alleviated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-fed rats via gut microbiota/FXR/FGF15 signaling pathway[J]. J Immunol Res, 2021, 2021:2264737. DOI: 10.1155/2021/2264737.
|
| [35] |
PARK E J, LEE Y S, KIM S M,et al. Beneficial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum strains on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high fat/high fructose diet-fed rats[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2):E542. DOI: 10.3390/nu12020542.
|
| [36] |
AHN S B, JUN D W, KANG B K,et al. Randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled study of a multi species probiotic mixture in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1):5688. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42059-3.
|
| [37] |
DUSEJA A, ACHARYA S K, MEHTA M,et al. High potency multistrain probiotic improves liver histology in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):a randomised,double-blind,proof of concept study[J]. BMJ Open Gastroenterol, 2019, 6(1):e000315. DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2019-000315.
|
| [38] |
LAVEKAR A S, V RAJE D, MANOHAR T,et al. Role of probiotics in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:a meta-analysis[J]. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol, 2017, 7(2):130-137. DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1233.
|
| [39] |
HOLSCHER H D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota[J]. Gut Microbes, 2017, 8(2):172-184. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1290756.
|
| [40] |
PLOVIER H, EVERARD A, DRUART C,et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice[J]. Nat Med, 2017, 23(1):107-113. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4236.
|
| [41] |
SINGH D P, KHARE P, ZHU J,et al. A novel cobiotic-based preventive approach against high-fat diet-induced adiposity,nonalcoholic fatty liver and gut derangement in mice[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2016, 40(3):487-496. DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2015.197.
|
| [42] |
BOMHOF M R, PARNELL J A, RAMAY H R,et al. Histological improvement of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with a prebiotic:a pilot clinical trial[J]. Eur J Nutr, 2019, 58(4):1735-1745. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1721-2.
|
| [43] |
CHONG P L, LAIGHT D, ASPINALL R J,et al. A randomised placebo controlled trial of VSL#3® probiotic on biomarkers of cardiovascular risk and liver injury in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1):144. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01660-5.
|
| [44] |
KOBYLIAK N, ABENAVOLI L, MYKHALCHYSHYN G,et al. A multi-strain probiotic reduces the fatty liver index,cytokines and aminotransferase levels in NAFLD patients:evidence from a randomized clinical trial[J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2018, 27(1):41-49. DOI: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.271.kby.
|
| [45] |
MOFIDI F, POUSTCHI H, YARI Z,et al. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:a pilot,randomised,double-blind,placebo-controlled,clinical trial[J]. Br J Nutr, 2017, 117(5):662-668. DOI: 10.1017/S0007114517000204.
|
| [46] |
SCORLETTI E, AFOLABI P R, MILES E A,et al. Synbiotics alter fecal microbiomes,but not liver fat or fibrosis,in a randomized trial of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(6):1597-1610.e7. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.031.
|
| [47] |
FEROLLA S M, COUTO C A, COSTA-SILVA L,et al. Beneficial effect of synbiotic supplementation on hepatic steatosis and anthropometric parameters,but not on gut permeability in a population with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(7):397. DOI: 10.3390/nu8070397.
|
| [48] |
VALLIANOU N, STRATIGOU T, CHRISTODOULATOS G S,et al. Probiotics,prebiotics,synbiotics,postbiotics,and obesity:current evidence,controversies,and perspectives[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2020, 9(3):179-192. DOI: 10.1007/s13679-020-00379-w.
|
| [49] |
VALLEJO-CORDOBA B, CASTRO-LÓPEZ C, GARCÍA H S,et al. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics:a review of current evidence and emerging trends[J]. Adv Food Nutr Res, 2020, 94:1-34. DOI: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2020.06.001.
|
| [50] |
PELUZIO M D C G, MARTINEZ J A, MILAGRO F I. Postbiotics:metabolites and mechanisms involved in microbiota-host interactions[J]. Trends Food Sci Technol, 2021, 108:11-26. DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.004.
|
| [51] |
WANG S H, AHMADI S, NAGPAL R,et al. Lipoteichoic acid from the cell wall of a heat killed Lactobacillus paracasei D3-5 ameliorates aging-related leaky gut,inflammation and improves physical and cognitive functions:from C. elegans to mice[J]. Geroscience, 2020, 42(1):333-352. DOI: 10.1007/s11357-019-00137-4.
|
| [52] |
MA L Y, NI Y H, WANG Z,et al. Spermidine improves gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese mice[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 12(1):1-19. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1832857.
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
ZHOU D, PAN Q, SHEN F,et al. Total fecal microbiota transplantation alleviates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice via beneficial regulation of gut microbiota[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):1529. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01751-y.
|
| [55] |
VRIEZE A, VAN NOOD E, HOLLEMAN F,et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 143(4):913-916.e7. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031.
|
| [56] |
WITJES J J, SMITS L P, PEKMEZ C T,et al. Donor fecal microbiota transplantation alters gut microbiota and metabolites in obese individuals with steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2020, 4(11):1578-1590. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1601.
|
| [57] |
CRAVEN L, RAHMAN A, NAIR PARVATHY S,et al. Allogenic fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease improves abnormal small intestinal permeability:a randomized control trial[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(7):1055-1065. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000661.
|
| [58] |
KAJI K, TAKAYA H, SAIKAWA S,et al. Rifaximin ameliorates hepatic encephalopathy and endotoxemia without affecting the gut microbiome diversity[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(47):8355-8366. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8355.
|
| [59] |
JIAN J, NIE M T, XIANG B Y,et al. Rifaximin ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice through regulating gut microbiome-related bile acids[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13:841132. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.841132.
|
| [60] |
FUJINAGA Y, KAWARATANI H, KAYA D,et al. Effective combination therapy of angiotensin-Ⅱ receptor blocker and rifaximin for hepatic fibrosis in rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15):E5589. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155589.
|
| [61] |
GANGARAPU V, INCE A T, BAYSAL B,et al. Efficacy of rifaximin on circulating endotoxins and cytokines in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 27(7):840-845. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000348.
|
| [62] |
COBBOLD J F L, ATKINSON S, MARCHESI J R,et al. Rifaximin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis:an open-label pilot study[J]. Hepatol Res, 2018, 48(1):69-77. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12904.
|
| [63] |
SUN D L, ZUO C, HUANG W,et al. Triclosan targeting of gut microbiome ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-fed mice[J]. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 2022, 75(6):341-353. DOI: 10.1038/s41429-022-00522-w.
|
| [64] |
MAHANA D, TRENT C M, KURTZ Z D,et al. Antibiotic perturbation of the murine gut microbiome enhances the adiposity,insulin resistance,and liver disease associated with high-fat diet[J]. Genome Med, 2016, 8(1):48. DOI: 10.1186/s13073-016-0297-9.
|
| [65] |
GÓRSKI A, BOLLYKY P L, PRZYBYLSKI M,et al. Perspectives of phage therapy in non-bacterial infections[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9:3306. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03306.
|
| [66] |
DUAN Y, LLORENTE C, LANG S,et al. Bacteriophage targeting of gut bacterium attenuates alcoholic liver disease[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7783):505-511. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1742-x.
|
 )
)