中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (21): 2651-2660.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0203
所属专题: 泌尿系统疾病最新文章合辑; 神经退行性病变最新文章合辑; 阿尔茨海默病最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
收稿日期:2022-02-19
修回日期:2022-05-08
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-05-25
通讯作者:
邹海欧
Hui ZHANG1, Wei YANG2, Dan WEI1, Zijuan ZHOU2, Haiou ZOU1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-19
Revised:2022-05-08
Published:2022-07-20
Online:2022-05-25
Contact:
Haiou ZOU
About author:摘要: 背景 认知障碍(CI)在终末期肾病(ESRD)患者中发病率较高,且严重影响患者的预后。及早识别其发生的影响因素具有重要意义,但现有研究结论尚存争议,且国内尚无相关系统综述。 目的 系统评价中国ESRD患者CI的影响因素。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、EMBase、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普网和中国生物医学文献数据库,搜集有关我国ESRD患者CI影响因素的研究,检索时限均为建库至2021年10月。采用主题词与自由词相结合的方式进行检索,并根据各数据库特点进行调整。研究类型为横断面研究、队列研究或病例对照研究;研究对象为满足2002年肾脏病预后质量指南(K/DOQI)标准慢性肾脏疾病(CKD)5期的ESRD患者,或已经接受腹膜透析(PD)或者血液透析(HD)治疗的患者,且为中国人群。由2名研究者独立筛选文献,提取资料并评价纳入研究的质量后,使用Stata 15.0软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入44篇文献,包括42 172例患者。纳入的队列研究和病例对照研究均为高质量研究,横断面研究质量均在中等及以上。Meta分析结果显示,年龄高〔OR=1.17,95%CI(1.13,1.22),P<0.001〕、透析龄长〔OR=1.02,95%CI(1.00,1.03),P=0.008〕、高血压〔OR=2.02,95%CI(1.06,3.86),P=0.032〕、脑卒中〔OR=1.93,95%CI(1.33,2.80),P=0.001〕、糖尿病〔OR=1.99,95%CI(1.62,2.44),P<0.001〕、Charlson合并症指数高〔OR=5.28,95%CI(1.48,18.82),P=0.010〕、抑郁〔OR=2.46,95%CI(1.61,3.77),P<0.001〕、高甲状旁腺激素(PTH)〔OR=1.02,95%CI(1.00,1.04),P=0.034〕、高C反应蛋白(CRP)〔OR=1.20,95%CI(1.01,1.42),P=0.040〕、高同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)〔OR=3.34,95%CI(2.06,5.42),P<0.001〕均是我国ESRD患者CI的危险因素。男性〔OR=0.55,95%CI(0.37,0.82),P=0.003〕、教育程度高〔OR=0.45,95%CI(0.37,0.55),P<0.001〕、高血红蛋白(Hb)〔OR=0.91,95%CI(0.86,0.95),P<0.001〕、高血清白蛋白(ALB)〔OR=0.77,95%CI(0.63,0.94),P=0.009〕、高血清肌酐(Cr)〔OR=0.997,95%CI(0.995,0.999),P=0.003〕均是我国ESRD患者CI的保护因素。 结论 当前证据证明,年龄高、透析龄长、高血压、脑卒中、糖尿病、Charlson合并症指数高、抑郁、高PTH、高CRP、高Hcy是ESRD患者CI的危险因素,男性、教育程度高、高Hb、高ALB、高Cr是ESRD患者CI的保护因素。受纳入研究的数量和质量的限制,上述结论尚需要更多高质量研究予以验证。

图1 中国知网检索策略
Figure 1 Strategy for searching literature about associated factors of cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with end-stage renal disease in CNKI database
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 人群来源 | 样本量(T/C) | 平均年龄(岁) | 所研究的影响因素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郭一丹[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 496/117 | 63.82±7.14 | ①③④⑦ |
| 姜玲[ | 2017 | 山东省青岛市 | 62/25 | 41.03±4.16 | ①④ |
| 赵洁[ | 2020 | 陕西省西安市 | 84/36 | 60.12±10.89 | ①⑧ |
| 田茹[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 57/29 | — | ①②③ |
| 程琼[ | 2015 | 广东省广州市 | 142/97 | 60.61±5.99 | ③⑧ |
| 李荣娜[ | 2021 | 河北省秦皇岛市 | 68/52 | — | ①④⑧ |
| 陈管洁[ | 2021 | 江苏省连云港市 | 93/359 | 54.05±14.37 | ①②③ |
| 陈管洁(1)[ | 2021 | 江苏省连云港市 | 134/333 | — | ①③ |
| 钟馨[ | 2015 | 广东省深圳市 | 80/60 | — | ① |
| 侯娟[ | 2019 | 江苏省南京市 | 59/26 | 65.75 | ①④ |
| 胡延毅[ | 2015 | 四川省南充市 | 62/23 | 58.4±11.5 | ①④⑧ |
| 吴雷云[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 51/39 | — | ① |
| 吴雷云(1)[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 105/75 | 62.48±8.55 | |
| 董莉萍[ | 2018 | 湖北省武汉市 | 87/66 | 60.05±14.18 | ①④ |
| 高丽华[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 138/74 | 53.7±14.6 | ①④ |
| 李芬[ | 2020 | 江苏省徐州市 | 85/115 | 63.1±7.2 | ①③⑧ |
| 钱玉珺[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 127/62 | 56.4±14.2 | ⑤ |
| 蒋婷婷[ | 2020 | 河南省郑州市 | 46/189 | 72.27±5.70 | ①② |
| 钟成[ | 2018 | 江苏省南京市 | 55/50 | 77.5±7.3 | ⑨ |
| 张春霞[ | 2019 | 北京市 | 79/40 | 72.6±11.9 | ①③ |
| 张倩[ | 2021 | 河北省保定市 | 189/98 | 60.15±10.79 | ④⑤⑦ |
| 栾凤武[ | 2021 | 广西壮族自治区宁夏市 | 30/24 | 46.2±11.7 | ①②③④ |
| 姜璐[ | 2015 | 江苏省扬州市 | 23/49 | 59.2±11.8 | |
| 庞娇阳[ | 2021 | 上海市 | 38/55 | 61.62±11.90 | ①② |
| 赵媛[ | 2021 | 山西省太原市 | 49/57 | — | ①③④ |
| 朱亚南[ | 2018 | 山东省青岛市 | 99/127 | 57.45±12.60 | ①③ |
| 田晓琳[ | 2019 | 天津市 | 69/30 | 61.50±9.19 | |
| 杨杰[ | 2017 | 安徽省巢湖市 | 62/39 | 65.81±8.083 | ①③ |
| 刘娇娜[ | 2016 | 辽宁省沈阳市 | 99/117 | 51.05±12.67 | ①③⑦ |
| 李庆根[ | 2020 | 安徽省合肥市 | 57/64 | 50.25±12.14 | |
| 梁丽珍[ | 2014 | 广东省深圳市 | 71/24 | 50.7±5.6 | ①③④ |
| YI[ | 2021 | 广东省广州市 | 321/322 | 45.0(37.0,57.4) | ⑨ |
| SHEA[ | 2015 | 香港 | 21/130 | 60.0±15.0 | ①②③⑦⑩ |
| SHEA[ | 2016 | 香港 | 33/81 | 59.0±15.0 | ①③⑧ |
| XIAO[ | 2021 | 湖北省武汉市 | 168/56 | 58±14 | ①③⑥ |
| LU[ | 2018 | 上海市 | 113/106 | 60.07±12.44 | ③⑦ |
| LUO[ | 2020 | 香港 | 26/55 | 71.59±4.23 | ①②③④⑦⑧ |
| CHOU[ | 2014 | 台湾 | 414/1203 | 63.3±13.0 | ①②③④⑥⑦ |
| LING[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2 940/29 248 | — | ①⑧⑩ |
| LI[ | 2004 | 安徽省合肥市、北京市 | 61/212 | 53.58±14.06 | ①②③ |
| LIAO[ | 2017 | 多中心 | 113/311 | 52.7±4.3 | |
| ZHU[ | 2021 | 浙江省金华市 | 75/35 | — | ①②④ |
| DONG[ | 2016 | 多中心 | 130/328 | 52.1±14.2 | |
| CUI[ | 2020 | 江苏省南京市 | 167/36 | 54.83±13.61 |
表1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the studies included
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 人群来源 | 样本量(T/C) | 平均年龄(岁) | 所研究的影响因素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郭一丹[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 496/117 | 63.82±7.14 | ①③④⑦ |
| 姜玲[ | 2017 | 山东省青岛市 | 62/25 | 41.03±4.16 | ①④ |
| 赵洁[ | 2020 | 陕西省西安市 | 84/36 | 60.12±10.89 | ①⑧ |
| 田茹[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 57/29 | — | ①②③ |
| 程琼[ | 2015 | 广东省广州市 | 142/97 | 60.61±5.99 | ③⑧ |
| 李荣娜[ | 2021 | 河北省秦皇岛市 | 68/52 | — | ①④⑧ |
| 陈管洁[ | 2021 | 江苏省连云港市 | 93/359 | 54.05±14.37 | ①②③ |
| 陈管洁(1)[ | 2021 | 江苏省连云港市 | 134/333 | — | ①③ |
| 钟馨[ | 2015 | 广东省深圳市 | 80/60 | — | ① |
| 侯娟[ | 2019 | 江苏省南京市 | 59/26 | 65.75 | ①④ |
| 胡延毅[ | 2015 | 四川省南充市 | 62/23 | 58.4±11.5 | ①④⑧ |
| 吴雷云[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 51/39 | — | ① |
| 吴雷云(1)[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 105/75 | 62.48±8.55 | |
| 董莉萍[ | 2018 | 湖北省武汉市 | 87/66 | 60.05±14.18 | ①④ |
| 高丽华[ | 2021 | 北京市 | 138/74 | 53.7±14.6 | ①④ |
| 李芬[ | 2020 | 江苏省徐州市 | 85/115 | 63.1±7.2 | ①③⑧ |
| 钱玉珺[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 127/62 | 56.4±14.2 | ⑤ |
| 蒋婷婷[ | 2020 | 河南省郑州市 | 46/189 | 72.27±5.70 | ①② |
| 钟成[ | 2018 | 江苏省南京市 | 55/50 | 77.5±7.3 | ⑨ |
| 张春霞[ | 2019 | 北京市 | 79/40 | 72.6±11.9 | ①③ |
| 张倩[ | 2021 | 河北省保定市 | 189/98 | 60.15±10.79 | ④⑤⑦ |
| 栾凤武[ | 2021 | 广西壮族自治区宁夏市 | 30/24 | 46.2±11.7 | ①②③④ |
| 姜璐[ | 2015 | 江苏省扬州市 | 23/49 | 59.2±11.8 | |
| 庞娇阳[ | 2021 | 上海市 | 38/55 | 61.62±11.90 | ①② |
| 赵媛[ | 2021 | 山西省太原市 | 49/57 | — | ①③④ |
| 朱亚南[ | 2018 | 山东省青岛市 | 99/127 | 57.45±12.60 | ①③ |
| 田晓琳[ | 2019 | 天津市 | 69/30 | 61.50±9.19 | |
| 杨杰[ | 2017 | 安徽省巢湖市 | 62/39 | 65.81±8.083 | ①③ |
| 刘娇娜[ | 2016 | 辽宁省沈阳市 | 99/117 | 51.05±12.67 | ①③⑦ |
| 李庆根[ | 2020 | 安徽省合肥市 | 57/64 | 50.25±12.14 | |
| 梁丽珍[ | 2014 | 广东省深圳市 | 71/24 | 50.7±5.6 | ①③④ |
| YI[ | 2021 | 广东省广州市 | 321/322 | 45.0(37.0,57.4) | ⑨ |
| SHEA[ | 2015 | 香港 | 21/130 | 60.0±15.0 | ①②③⑦⑩ |
| SHEA[ | 2016 | 香港 | 33/81 | 59.0±15.0 | ①③⑧ |
| XIAO[ | 2021 | 湖北省武汉市 | 168/56 | 58±14 | ①③⑥ |
| LU[ | 2018 | 上海市 | 113/106 | 60.07±12.44 | ③⑦ |
| LUO[ | 2020 | 香港 | 26/55 | 71.59±4.23 | ①②③④⑦⑧ |
| CHOU[ | 2014 | 台湾 | 414/1203 | 63.3±13.0 | ①②③④⑥⑦ |
| LING[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2 940/29 248 | — | ①⑧⑩ |
| LI[ | 2004 | 安徽省合肥市、北京市 | 61/212 | 53.58±14.06 | ①②③ |
| LIAO[ | 2017 | 多中心 | 113/311 | 52.7±4.3 | |
| ZHU[ | 2021 | 浙江省金华市 | 75/35 | — | ①②④ |
| DONG[ | 2016 | 多中心 | 130/328 | 52.1±14.2 | |
| CUI[ | 2020 | 江苏省南京市 | 167/36 | 54.83±13.61 |
| 纳入研究 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | ⑨ | ⑩ | 最终得分 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郭一丹[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
| 姜玲[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 赵洁[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 田茹[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 李荣娜[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 陈管洁[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 陈管洁(1)[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 钟馨[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 侯娟[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 胡延毅[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 吴雷云[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| 吴雷云(1)[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 董莉萍[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 高丽华[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 李芬[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 钱玉珺[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 蒋婷婷[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 钟成[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 张春霞[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 张倩[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 栾凤武[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 姜璐[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 庞娇阳[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 赵媛[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 朱亚南[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 田晓琳[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 杨杰[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 刘娇娜[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 李庆根[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 梁丽珍[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| YI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| XIAO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| LU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| LUO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| CHOU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| LI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| LIAO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| ZHU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| DONG[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| CUI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
表2 横断面研究的质量评价结果(分)
Table 2 Results of methodological quality evaluation of the included cross-sectional studies
| 纳入研究 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | ⑨ | ⑩ | 最终得分 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郭一丹[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
| 姜玲[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 赵洁[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 田茹[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 李荣娜[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 陈管洁[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 陈管洁(1)[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 钟馨[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 侯娟[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 胡延毅[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 吴雷云[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| 吴雷云(1)[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 董莉萍[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 高丽华[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 李芬[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 钱玉珺[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 蒋婷婷[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 钟成[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 张春霞[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 张倩[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 栾凤武[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 姜璐[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 庞娇阳[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 赵媛[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 朱亚南[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 田晓琳[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 杨杰[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 刘娇娜[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 李庆根[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 梁丽珍[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| YI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| XIAO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| LU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| LUO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| CHOU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| LI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| LIAO[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| ZHU[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| DONG[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| CUI[ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 纳入研究 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露或结果评价 | 最终得分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHEA[ | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| SHEA[ | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
表3 队列研究的质量评价结果(分)
Table 3 Methodological quality evaluation results of the includedcohort studies
| 纳入研究 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露或结果评价 | 最终得分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHEA[ | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| SHEA[ | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| 纳入研究 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露或结果评价 | 最终得分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 程琼[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| LING[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
表4 病例对照研究的质量评价结果(分)
Table 4 Methodological quality evaluation results of the included case-control studies
| 纳入研究 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露或结果评价 | 最终得分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 程琼[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| LING[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 影响因素 | 纳入研究 | 患者例数 | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | 效应量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||||
| 年龄(高) | 31[ | 38 933 | 88.6 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.17(1.13,1.22) | <0.001 |
| 性别(男性) | 10[ | 3 172 | 69.2 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.55(0.37,0.82) | 0.003 |
| 教育程度(高) | 20[ | 5 653 | 82.3 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.45(0.37,0.55) | <0.001 |
| 透析龄(长) | 14[ | 3 705 | 81.1 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.03) | 0.008 |
| 透析方式(腹透) | 2[ | 476 | 94.2 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.080(0.001,9.170) | 0.301 |
| 透析频率(高) | 2[ | 1 841 | 77.5 | 0.012 | 随机 | 0.53(0.19,1.44) | 0.212 |
| Kt/V(高) | 7[ | 3 184 | 99.4 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.12(0.01,1.01) | 0.051 |
| 高血压 | 8[ | 33 147 | 90.5 | <0.001 | 随机 | 2.02(1.06,3.86) | 0.032 |
| 收缩压(高) | 2[ | 748 | 75.3 | 0.044 | 随机 | 1.17(0.95,1.44) | 0.144 |
| 高血脂 | 2[ | 32 339 | 52.0 | 0.149 | 随机 | 0.82(0.35,1.90) | 0.645 |
| 心血管病史 | 2[ | 1 727 | 37.7 | 0.205 | 固定 | 1.16(0.89,1.51) | 0.271 |
| 脑卒中 | 5[ | 34 652 | 66.8 | 0.010 | 随机 | 1.93(1.33,2.80) | 0.001 |
| 糖尿病 | 13[ | 36 387 | 52.1 | 0.012 | 随机 | 1.99(1.62,2.44) | <0.001 |
| 胰岛素抵抗指数(高) | 2[ | 177 | 85.4 | 0.009 | 随机 | 1.68(0.15,18.27) | 0.672 |
| 合并症指数(高) | 2[ | 406 | 60.8 | 0.110 | 随机 | 5.28(1.48,18.82) | 0.010 |
| 睡眠情况(失眠) | 2[ | 32 427 | 52.7 | 0.146 | 随机 | 1.40(0.92,2.12) | 0.112 |
| 抑郁 | 4[ | 33 183 | 76.2 | 0.002 | 随机 | 2.46(1.61,3.77) | <0.001 |
| 营养不良 | 2[ | 573 | 59.5 | 0.116 | 随机 | 2.52(0.91,7.01) | 0.076 |
| 贫血 | 2[ | 32 308 | 94.0 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.91(0.58,6.31) | 0.291 |
| 瘦体组织质量(高) | 2[ | 301 | 70.0 | 0.068 | 随机 | 0.51(0.12,2.12) | 0.353 |
| Hb(高) | 16[ | 3 862 | 86.8 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.91(0.86,0.95) | <0.001 |
| ALB(高) | 5[ | 2 279 | 85.4 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.77(0.63,0.94) | 0.009 |
| Cr(高) | 2[ | 2 069 | 0 | 0.928 | 固定 | 0.997(0.995,0.999) | 0.003 |
| PTH(高) | 4[ | 1 030 | 62.0 | 0.048 | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.04) | 0.034 |
| iPTH(高) | 3[ | 584 | 83.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.000(0.996,1.010) | 0.359 |
| UA(高) | 2[ | 219 | 99.9 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.31(0.03,3.20) | 0.322 |
| CRP(高) | 4[ | 327 | 90.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.20(1.01,1.42) | 0.040 |
| hs-CRP(高) | 3[ | 379 | 89.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 2.30(0.88,6.00) | 0.089 |
| P(高) | 2[ | 1 904 | 59.8 | 0.115 | 随机 | 0.52(0.07,3.59) | 0.505 |
| 25(OH)D3(高) | 3[ | 604 | 84.6 | 0.002 | 随机 | 0.94(0.85,1.05) | 0.300 |
| Hcy(高) | 2[ | 260 | 0 | 0.968 | 固定 | 3.34(2.06,5.42) | <0.001 |
表5 中国ESRD患者CI影响因素的Meta分析结果
Table 5 Meta-analysis of influencing factors of cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with end-stage renal disease
| 影响因素 | 纳入研究 | 患者例数 | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | 效应量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||||
| 年龄(高) | 31[ | 38 933 | 88.6 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.17(1.13,1.22) | <0.001 |
| 性别(男性) | 10[ | 3 172 | 69.2 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.55(0.37,0.82) | 0.003 |
| 教育程度(高) | 20[ | 5 653 | 82.3 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.45(0.37,0.55) | <0.001 |
| 透析龄(长) | 14[ | 3 705 | 81.1 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.03) | 0.008 |
| 透析方式(腹透) | 2[ | 476 | 94.2 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.080(0.001,9.170) | 0.301 |
| 透析频率(高) | 2[ | 1 841 | 77.5 | 0.012 | 随机 | 0.53(0.19,1.44) | 0.212 |
| Kt/V(高) | 7[ | 3 184 | 99.4 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.12(0.01,1.01) | 0.051 |
| 高血压 | 8[ | 33 147 | 90.5 | <0.001 | 随机 | 2.02(1.06,3.86) | 0.032 |
| 收缩压(高) | 2[ | 748 | 75.3 | 0.044 | 随机 | 1.17(0.95,1.44) | 0.144 |
| 高血脂 | 2[ | 32 339 | 52.0 | 0.149 | 随机 | 0.82(0.35,1.90) | 0.645 |
| 心血管病史 | 2[ | 1 727 | 37.7 | 0.205 | 固定 | 1.16(0.89,1.51) | 0.271 |
| 脑卒中 | 5[ | 34 652 | 66.8 | 0.010 | 随机 | 1.93(1.33,2.80) | 0.001 |
| 糖尿病 | 13[ | 36 387 | 52.1 | 0.012 | 随机 | 1.99(1.62,2.44) | <0.001 |
| 胰岛素抵抗指数(高) | 2[ | 177 | 85.4 | 0.009 | 随机 | 1.68(0.15,18.27) | 0.672 |
| 合并症指数(高) | 2[ | 406 | 60.8 | 0.110 | 随机 | 5.28(1.48,18.82) | 0.010 |
| 睡眠情况(失眠) | 2[ | 32 427 | 52.7 | 0.146 | 随机 | 1.40(0.92,2.12) | 0.112 |
| 抑郁 | 4[ | 33 183 | 76.2 | 0.002 | 随机 | 2.46(1.61,3.77) | <0.001 |
| 营养不良 | 2[ | 573 | 59.5 | 0.116 | 随机 | 2.52(0.91,7.01) | 0.076 |
| 贫血 | 2[ | 32 308 | 94.0 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.91(0.58,6.31) | 0.291 |
| 瘦体组织质量(高) | 2[ | 301 | 70.0 | 0.068 | 随机 | 0.51(0.12,2.12) | 0.353 |
| Hb(高) | 16[ | 3 862 | 86.8 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.91(0.86,0.95) | <0.001 |
| ALB(高) | 5[ | 2 279 | 85.4 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.77(0.63,0.94) | 0.009 |
| Cr(高) | 2[ | 2 069 | 0 | 0.928 | 固定 | 0.997(0.995,0.999) | 0.003 |
| PTH(高) | 4[ | 1 030 | 62.0 | 0.048 | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.04) | 0.034 |
| iPTH(高) | 3[ | 584 | 83.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.000(0.996,1.010) | 0.359 |
| UA(高) | 2[ | 219 | 99.9 | <0.001 | 随机 | 0.31(0.03,3.20) | 0.322 |
| CRP(高) | 4[ | 327 | 90.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 1.20(1.01,1.42) | 0.040 |
| hs-CRP(高) | 3[ | 379 | 89.7 | <0.001 | 随机 | 2.30(0.88,6.00) | 0.089 |
| P(高) | 2[ | 1 904 | 59.8 | 0.115 | 随机 | 0.52(0.07,3.59) | 0.505 |
| 25(OH)D3(高) | 3[ | 604 | 84.6 | 0.002 | 随机 | 0.94(0.85,1.05) | 0.300 |
| Hcy(高) | 2[ | 260 | 0 | 0.968 | 固定 | 3.34(2.06,5.42) | <0.001 |
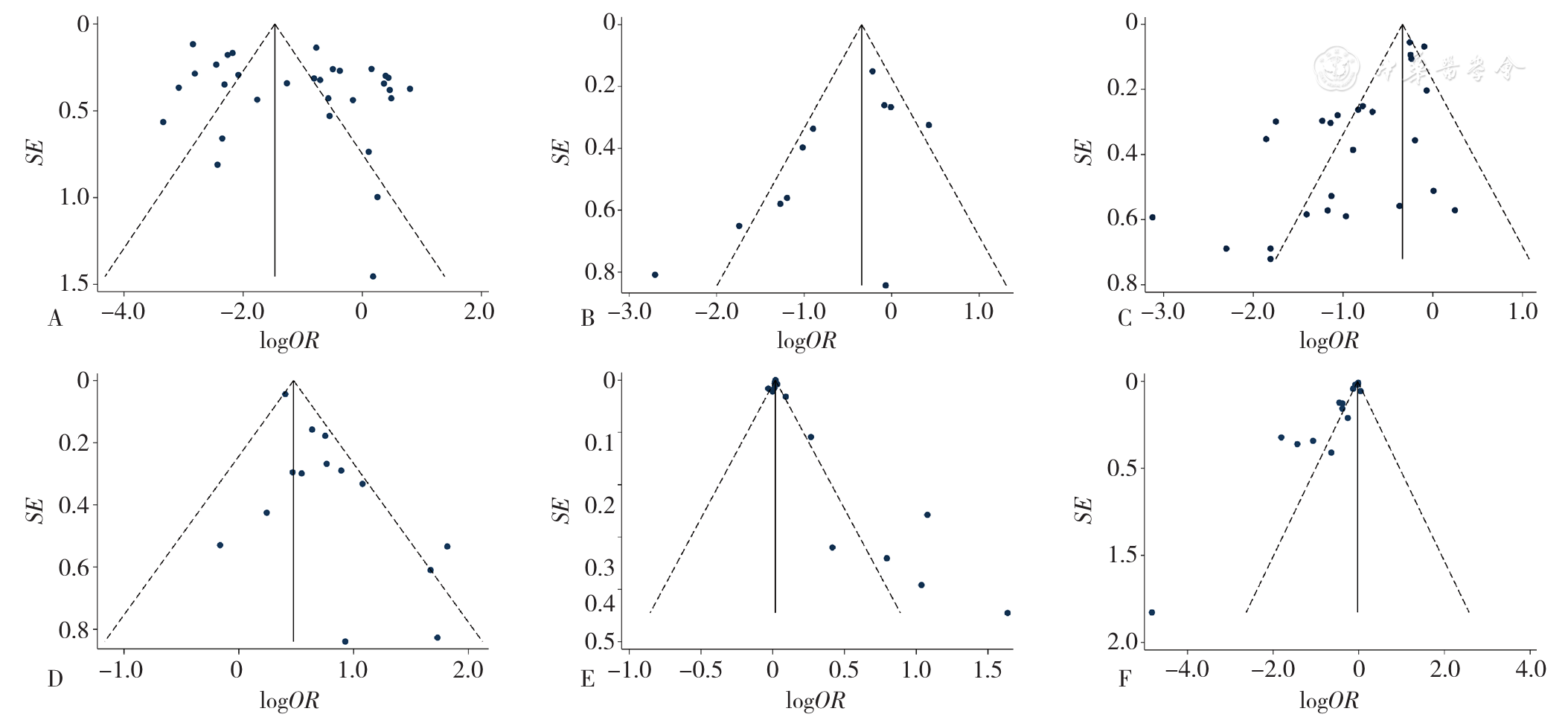
图3 对ESRD患者CI影响的漏斗图注:A为年龄,B为性别,C为教育程度,D为糖尿病,E为透析龄,F为血红蛋白
Figure 3 Funnel plot assessing the publication bias in studies of cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with end-stage renal disease
| 影响因素 | 剔除后纳入文献 | 剔除文献 | 剔除前 | 剔除后 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 偏倚风险P值 | 模型 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 偏倚风险P值 | |||
| 性别 | 9[ | 1[ | 随机 | 0.55(0.37,0.82) | 0.003 | 0.037 | 随机 | 0.63(0.44,0.90) | 0.011 | 0.109 |
| 透析龄 | 12[ | 2[ | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.03) | 0.008 | 0.022 | 随机 | 1.02(1.01,1.03) | 0.004 | 0.116 |
| 糖尿病 | 10[ | 3[ | 随机 | 1.99(1.62,2.44) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 固定 | 1.79(1.52,2.10) | <0.001 | 0.084 |
表6 相关因素敏感性分析结果
Table 6 Results of sensitivity analysis of cognitive impairment-related factors inChinese patients with end-stage renal disease
| 影响因素 | 剔除后纳入文献 | 剔除文献 | 剔除前 | 剔除后 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 偏倚风险P值 | 模型 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 偏倚风险P值 | |||
| 性别 | 9[ | 1[ | 随机 | 0.55(0.37,0.82) | 0.003 | 0.037 | 随机 | 0.63(0.44,0.90) | 0.011 | 0.109 |
| 透析龄 | 12[ | 2[ | 随机 | 1.02(1.00,1.03) | 0.008 | 0.022 | 随机 | 1.02(1.01,1.03) | 0.004 | 0.116 |
| 糖尿病 | 10[ | 3[ | 随机 | 1.99(1.62,2.44) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 固定 | 1.79(1.52,2.10) | <0.001 | 0.084 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
王善志,朱永俊,李国铨,等. 中国成人慢性肾脏病患病率的Meta分析结果及对比[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2018,34(8):579-586. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-7097.2018.08.004.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
席海玲,陈赟敏,周婷婷,等. 腹膜透析联合血液透析治疗终末期肾病的研究进展[J]. 中国血液净化,2020,19(8):550-553. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2020.08.012.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] | |
| [7] |
李云生,王文龙,戴再友,等. 高压氧对腹膜透析患者认知功能障碍和脑源性神经营养因子的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2016,17(8):705-707.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
郭一丹,张春霞,田茹,等. 中老年维持性血液透析患者认知功能损伤特征的横断面研究[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2021,37(8):632-638. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20201118-00094.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
王宇,汤嘉敏,潘燕彬,等. 认知功能及躯体功能与血液透析患者负性情绪的相关性[J]. 国际护理学杂志,2021,40(4):607-609. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn221370-20191231-00176.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
刘敏,关思博,闵旭,等. 腹膜透析患者认知功能障碍的研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2018,19(2):182-185. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2018.02.033.
|
| [15] |
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2003,42(4 Suppl 3):S1-201.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等. Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(4):297-299. DOI:10.3969/j.1674-4055.2012.04.004.
|
| [18] |
姜玲,孔慧,张洁,等. 中青年终末期肾脏病维持性血液透析患者认知功能改变及相关影响因素分析[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2017,9(2):150-153. DOI:10.12037/YXQY.2017.02-32.
|
| [19] |
赵洁,蒙军平,王华,等. 影响血液透析患者认知功能的相关因素分析[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2020,5(22):15-16,25. DOI:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202022005.
|
| [20] |
田茹,冯兴中,罗洋. 血液透析患者中医证型与认知功能障碍的相关性研究[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2020,15(11):2086-2089,2093. DOI:10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.201125.
|
| [21] | |
| [22] |
李荣娜,胡秋霞,周大敏. 维持性血液透析患者血清同型半胱氨酸、胱抑素C、超敏C反应蛋白水平变化及其与认知功能障碍的相关性分析[J]. 中国医刊,2021,56(4):416-419. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-1070.2021.04.017.
|
| [23] |
陈管洁,张海林,尹丽霞,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知衰弱的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理,2021,21(8):1179-1185. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2021.08.013.
|
| [24] |
陈管洁,张海林,尹丽霞,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍与衰弱的相关性[J]. 护理学杂志,2021,36(6):27-31. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.06.027.
|
| [25] |
钟馨,李朝晖,陈瑞娟,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍相关因素分析[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2015,15(3):175-179. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2015.03.010.
|
| [26] |
侯娟,陆鹏,张勇,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍及相关危险因素分析[J]. 现代医学,2019,47(11):1387-1390. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7562.2019.11.022.
|
| [27] |
胡延毅,邓红梅,龙红英,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍的相关因素分析及防治体会[J]. 中华全科医学,2015,13(2):320-322. DOI:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2015.02.013.
|
| [28] |
吴雷云,邓英辉,张爱华. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍的特点及其与预后的关系[J]. 中国临床医生杂志,2021,49(7):806-810. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2021.07.016.
|
| [29] |
吴雷云,秦雅婧,张爱华. 维持性血液透析患者人体成分与认知功能障碍的关系[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2021,42(4):522-527. DOI:10.12289/j.issn.1008-0392.21159.
|
| [30] |
董莉萍,吴玮聪,位红兰,等. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能与全因死亡及心脑血管病死亡关系的分析[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2018,18(2):2430-2432. DOI:10.16563/j.cnki.1671-6272.2018.04.010.
|
| [31] |
高丽华,邓春颖,孙妍,等. 维持性血液透析的终末期肾病患者认知障碍及相关因素分析[J]. 中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2021,24(3):307-311. DOI:10.11723/mtgyyx1007-9564202103018.
|
| [32] |
李芬. 慢性肾脏病腹膜透析病人认知功能障碍现状及影响因素分析[J]. 全科护理,2020,18(35):4905-4907. DOI:10.12104/j.issn.1674-4748.2020.35.011.
|
| [33] |
钱玉珺,杨建萍,侯波,等. 维持性血液透析与腹膜透析患者认知功能障碍的比较[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2020,36(9):657-665. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20200303-00119.
|
| [34] |
蒋婷婷,单岩,杜理平,等. 老年血液透析患者认知衰弱现状及其与跌倒恐惧的相关性研究[J]. 中国护理管理,2020,20(7):1005-1009. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2020.07.010.
|
| [35] |
钟成,赵亚亚,赵卫红. 老年维持性血液透析合并认知功能障碍相关危险因素研究[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志:电子版,2018,10(6):135-138. DOI:10.12037/YXQY.2018.06-03.
|
| [36] |
张春霞,郭一丹,罗洋. 老年透析患者血清超敏C反应蛋白与认知功能的关系[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2019,29(16):85-89. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2019.16.016.
|
| [37] |
张倩,李璐,文诗伟,等. 继发性甲状旁腺功能亢进症与终末期肾病轻度认知障碍的关系研究[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2021,21(1):15-21. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.y20-071.
|
| [38] |
栾凤武,彭佳楠,冯晓楠,等. 腹膜透析患者认知障碍及其危险因素的研究[J]. 宁夏医学杂志,2021,43(8):684-686. DOI:10.13621/j.1001-5949.2021.08.0684.
|
| [39] |
姜璐,韩年华. 非透析慢性肾衰竭患者认知功能障碍与胰岛素抵抗关系的研究[J]. 哈尔滨医药,2015,35(2):87-89.
|
| [40] |
庞娇阳,张炜晨,黄碧红,等. 残余肾功能与维持性血液透析患者认知功能关系的研究[J]. 中国血液净化,2021,20(2):90-94. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2021.02.005.
|
| [41] |
赵媛. 维持性血液透析患者认知障碍与左室射血分数的关系[D]. 太原:山西医科大学,2021.
|
| [42] |
朱亚南. 血液透析患者认知功能障碍的危险因素分析及预测模型的构建[D]. 青岛:青岛大学,2018.
|
| [43] |
田晓琳. 维持性血液透析的ESRD患者的认知障碍及其与脑小血管病的关系[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2019.
|
| [44] |
杨杰. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能障碍及其危险因素分析[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2020.
|
| [45] |
刘娇娜. 维持性血液透析患者认知功能损害危险因素分析及中医证型特点[D]. 沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2016.
|
| [46] |
李庆根. 维持性腹膜透析患者认知功能障碍与营养不良之间的关系研究[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2020.
|
| [47] |
梁丽珍. 非血管性因素对慢性肾衰竭血液透析病人认知功能的影响研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2014,35(13):2025-2026.
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(五):轻度认知障碍的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华医学杂志,2018,98(17):1294-1301. DOI:10.3760/cma,j.issn.0376-2491.2018.17.003.
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
李艳青,吴红霞,孙建萍,等. 老年2型糖尿病患者轻度认知障碍危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2021,48(9):1715-1720.
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
张兰,孙超,程艳娇,等. 维持性血液透析患者心理和认知功能调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国血液净化,2019,18(2):107-109. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2019.02.007.
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [4] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [5] | 张睿敏, 董哲毅, 李爽, 王倩, 陈香美. 基于肾活检病理诊断的糖尿病肾病中医相关因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3307-3313. |
| [6] | 胡洁蔓, 谭斐翔, 袁安新, 陈世宇, 唐楚蕾, 殷月姮, 巴磊, 许勤. 结直肠癌患者术后衰弱变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [7] | 丑欣彤, 彭瀚瑜, 马慧, 张珍, 苏先, 邱红燕. 产妇对避孕决策的偏好及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [8] | 魏姣花, 彭慧如, 彭建业, 谭文婷, 黄金娥, 方立. MOTS-c在心房颤动患者血清中的表达及其与心房重构的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [9] | 崔宇阳, 程桂荣, 曾燕, 黄招兰, 谭伟. 社区老年人婚姻状况和社会支持及生活习惯与认知障碍的关联:基于湖北老年记忆队列基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3240-3247. |
| [10] | 褚艺婧, 严雨格, 顾杰, 席彪, 祝墡珠, 黄蛟灵. 中国基层医务人员留用意愿影响因素分析:基于城乡差异比较[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3161-3168. |
| [11] | 余孜孜, 刘杜丽, 李熙敏, 阮春怡, 尹向阳, 蔡乐. 农村高血压患病和自我管理现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [12] | 范博阳, 张玉, 孙雯宁, 张慧芳, 王英杰, 张奥, 赵洋, 王海鹏. 基层医生慢性病医防融合服务行为意向及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [13] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [14] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [15] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





