中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2126-2134.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.007
所属专题: 社区卫生服务最新研究合集; 消化系统疾病最新文章合集
收稿日期:2021-05-23
修回日期:2021-10-27
出版日期:2022-04-22
发布日期:2022-04-22
通讯作者:
马纪林
Received:2021-05-23
Revised:2021-10-27
Published:2022-04-22
Online:2022-04-22
Contact:
Jilin MA
About author:摘要: 背景 非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)早期难以发现,常在出现代谢性疾病时才能被发现,但目前关于非侵入性指标对NAFLD合并代谢综合征预测价值的研究报道较少见。 目的 探讨非侵入性指标单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值(MHR)对NAFLD合并代谢综合征的预测价值,并进行多因素Logistic决策树分析。 方法 2020年6—12月,共有9 812例年龄>45周岁的社区常住居民在上海市松江区泗泾镇社区卫生服务中心进行健康体检,其中符合纳入与排除标准的目标代谢性疾病(包括代谢综合征、糖尿病、高血压、血脂异常等)患者4 652例,无代谢性疾病患者1 075例(健康对照组);4 652例目标代谢性疾病患者中无NAFLD及代谢综合征者1 948例(对照组),仅有NAFLD者1 248例(NAFLD组),NAFLD合并代谢综合征者1 456例(MAFLD组)。比较四组受试者一般资料、人体测量学指标、血压、生化指标及血常规检查结果;MHR、脂质蓄积指数(LAP)与分组的相关性分析采用Spearman秩相关分析。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线以确定非侵入性指标中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)、血小板与淋巴细胞比值(PLR)、淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值(LMR)、MHR预测社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征的最佳截断值,并进行多因素Logistic决策树分析。 结果 本研究在9 812例进行健康体检的年龄>45周岁的社区常住居民中共发现目标代谢性疾病患者7 517例、NAFLD患者2 704例,目标代谢性疾病、NAFLD患病率分别为76.61%(7 517/9 812)、27.59%(2 704/9 812)。四组受试者女性比例、年龄、体质指数(BMI)、腰围、臀围、腰臀比、收缩压、舒张压、空腹血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、总胆红素、血尿酸、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、ALT/AST、γ-谷氨酰转肽酶(GGT)、估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR)、白细胞计数、中性粒细胞计数、单核细胞计数、淋巴细胞计数、血小板计数、NLR、PLR、LMR、MHR、酒精性脂肪性肝病/非酒精性脂肪性肝病指数(ANI)、LAP、血浆致动脉硬化指数(AIP)、腰围分类、BMI分类、高血压及血脂异常发生情况比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。Spearman秩相关分析结果显示,MHR、LAP与研究对象分组均呈正相关(rs值分别为0.342、0.580,P<0.001)。ROC曲线分析结果显示,非侵入性指标NLR、PLR、LMR、MHR预测社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.528〔95%CI(0.511,0.545)〕、0.581〔95%CI(0.564,0.598)〕、0.546〔95%CI(0.529,0.563)〕、0.695〔95%CI(0.679,0.711)〕,灵敏度分别为74.66%、59.82%、51.79%、69.51%,特异度分别为31.52%、53.95%、56.62%、60.63%,最佳截断值分别为2.192、115.470、0.193、0.292。多因素Logistic决策树分析结果显示,性别、BMI分类、腰围分类、三酰甘油、空腹血糖对MHR预测社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征有影响。 结论 MHR对社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征的预测价值较高,而性别、BMI分类、腰围分类、三酰甘油、空腹血糖是影响MHR预测社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征准确性的重要变量。
| 组别 | 例数 | 女性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄( | BMI(kg/m2) | 腰围( | 臀围( | 腰臀比( | 收缩压( | 舒张压( | 空腹血糖( | 总胆固醇( | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 健康对照组 | 1 075 | 737(68.56) | 59.5±9.2 | 22.2±2.6 | 74.5±7.6 | 88.5±5.1 | 0.84±0.06 | 118±11 | 77±7 | 5.3±0.5 | 4.70±0.70 | |
| 对照组 | 1 948 | 1 083(55.60)a | 64.7±9.0a | 23.4±2.6a | 79.1±7.8a | 90.6±5.4 | 0.87±0.06a | 140±17a | 86±10a | 6.0±1.6a | 4.94±1.04 | |
| NAFLD组 | 1 248 | 1 045(83.73)ab | 63.2±7.8ab | 26.1±3.0ab | 83.7±7.6ab | 94.0±5.8 | 0.89±0.05ab | 139±17a | 85±9a | 6.0±1.4a | 5.21±1.05 | |
| MAFLD组 | 1 456 | 995(68.34)bc | 64.7±8.3ac | 27.9±3.0abc | 90.2±7.8abc | 97.3±6.3 | 0.93±0.05abc | 142±18abc | 86±10a | 7.4±2.5abc | 5.18±1.13 | |
| 检验统计量值 | 96.707 | 98.774 | 1 137.694 | 1 005.658 | 631.238 | 573.261 | 557.742 | 255.693 | 357.480 | 65.384 | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 组别 | 三酰甘油( | LDL-C( | HLD-C( | 总胆红素( | 血尿酸( | ALT( | AST( | ALT/AST( | GGT〔M(QR),U/L〕 | eGFR〔 | 白细胞计数( | |
| 健康对照组 | 1.10±0.40 | 2.96±0.63 | 1.60±0.34 | 12.33±6.10 | 281.73±68.59 | 16±13 | 21±8 | 0.74±0.25 | 14.95(22.56) | 90.91±13.05 | 5.5±1.3 | |
| 对照组 | 1.44±0.96a | 3.18±0.96 | 1.48±0.38a | 12.47±5.38 | 310.08±81.23a | 17±11a | 21±8 | 0.79±0.27a | 18.67(28.44) | 85.60±14.81a | 5.9±1.5a | |
| NAFLD组 | 1.76±0.92ab | 3.46±0.96 | 1.38±0.28ab | 12.02±5.04 | 327.10±76.86ab | 26±19ab | 24±12ab | 1.03±0.34ab | 24.55(37.01) | 88.62±12.45ab | 6.1±1.4ab | |
| MAFLD组 | 2.66±1.72abc | 3.29±1.03 | 1.17±0.27abc | 11.99±4.78 | 351.50±84.15abc | 31±23abc | 26±14abc | 1.14±0.36abc | 30.40(46.71) | 86.25±14.62ac | 6.6±1.6abc | |
| 检验统计量值 | 479.960 | 59.596 | 411.073 | 3.136 | 175.232 | 268.532 | 83.674 | 541.209 | 78.484e | 39.971 | 141.461 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.024 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 中性粒细胞计数( | 单核细胞计数( | 淋巴细胞计数( | 血小板计数( | NLR( | PLR( | LMR( | MHR( | ANI〔M(QR)〕 | LAP( | AIP( | |
| 健康对照组 | 3.2±1.1 | 0.3±0.1 | 1.8±0.5 | 220.1±59.0 | 0.23±0.10 | 130.06±44.65 | 1.90±0.94 | 0.20±0.09 | 130.06±44.65 | 16.24±10.96 | -0.18±0.21 | |
| 对照组 | 3.5±1.2a | 0.4±0.2a | 1.9±0.6a | 222.7±62.9 | 0.29±0.15a | 125.62±46.16a | 1.99±1.04a | 0.22±0.09a | 125.62±46.16a | 26.75±21.82a | -0.05±0.28a | |
| NAFLD组 | 3.5±1.1a | 0.4±0.1ab | 2.1±0.6ab | 236.5±58.7ab | 0.29±0.11a | 120.35±40.29ab | 1.79±0.70ab | 0.20±0.07ab | 120.35±40.29ab | 41.70±21.28ab | 0.07±0.23ab | |
| MAFLD组 | 3.8±1.1abc | 0.4±0.1abc | 2.2±0.7abc | 234.8±64.3ab | 0.39±0.16abc | 113.80±40.36abc | 1.86±0.76bc | 0.21±0.08bc | 113.80±40.36abc | 77.62±49.89abc | 0.31±0.27abc | |
| 检验统计量值 | 72.693 | 84.465 | 119.124 | 24.379 | 298.825 | 35.014 | 13.422 | 29.055 | 35.014e | 1 094.515 | 914.337 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 腰围分类〔n(%)〕 | BMI分类〔n(%)〕 | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | 血脂异常〔n(%)〕 | ||||||||
| ≥90 cm(男)或≥85 cm(女) | <90 cm(男)或<85 cm(女) | 正常 | 超重 | 肥胖 | 无 | 有 | 无 | 高胆固醇血症 | 高三酰甘油血症 | 混合性高脂血症 | 低高密度脂蛋白血症 | |
| 健康对照组 | 58(5.40) | 1 017(94.60) | 741(68.93) | 220(20.47) | 114(10.60) | 1 075(100.00) | 0 | 1 075(100.00) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 对照组 | 264(13.55) | 1 684(86.45) | 1 087(55.80) | 690(35.42) | 171(8.78) | 146(7.49) | 1 802(92.51) | 1 475(75.72) | 173(8.88) | 172(8.83) | 35(1.80) | 93(4.77) |
| NAFLD组 | 380(30.45) | 868(69.55) | 267(21.39) | 666(53.37) | 315(25.24) | 211(16.91) | 1 037(83.09) | 850(68.11) | 131(10.50) | 178(14.26) | 66(5.29) | 23(1.84) |
| MAFLD组 | 1 104(75.82) | 352(24.18) | 122(8.38) | 653(44.85) | 681(46.77) | 153(10.51) | 1 303(89.49) | 545(37.43) | 109(7.49) | 524(35.99) | 136(9.34) | 142(9.75) |
| 检验统计量值 | 1 955.472d | 1 975.670d | 3 492.297d | 1 435.230d | ||||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
表1 四组受试者一般资料、人体测量学指标、血压、生化指标及血常规检查结果比较
Table 1 Comparison of general information,anthropometric indicators,blood pressure,biochemical indicators and routine blood test results between physical examinees without metabolic disorders,those with other metabolic disorders except nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome,those with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,and those with both nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome
| 组别 | 例数 | 女性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄( | BMI(kg/m2) | 腰围( | 臀围( | 腰臀比( | 收缩压( | 舒张压( | 空腹血糖( | 总胆固醇( | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 健康对照组 | 1 075 | 737(68.56) | 59.5±9.2 | 22.2±2.6 | 74.5±7.6 | 88.5±5.1 | 0.84±0.06 | 118±11 | 77±7 | 5.3±0.5 | 4.70±0.70 | |
| 对照组 | 1 948 | 1 083(55.60)a | 64.7±9.0a | 23.4±2.6a | 79.1±7.8a | 90.6±5.4 | 0.87±0.06a | 140±17a | 86±10a | 6.0±1.6a | 4.94±1.04 | |
| NAFLD组 | 1 248 | 1 045(83.73)ab | 63.2±7.8ab | 26.1±3.0ab | 83.7±7.6ab | 94.0±5.8 | 0.89±0.05ab | 139±17a | 85±9a | 6.0±1.4a | 5.21±1.05 | |
| MAFLD组 | 1 456 | 995(68.34)bc | 64.7±8.3ac | 27.9±3.0abc | 90.2±7.8abc | 97.3±6.3 | 0.93±0.05abc | 142±18abc | 86±10a | 7.4±2.5abc | 5.18±1.13 | |
| 检验统计量值 | 96.707 | 98.774 | 1 137.694 | 1 005.658 | 631.238 | 573.261 | 557.742 | 255.693 | 357.480 | 65.384 | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 组别 | 三酰甘油( | LDL-C( | HLD-C( | 总胆红素( | 血尿酸( | ALT( | AST( | ALT/AST( | GGT〔M(QR),U/L〕 | eGFR〔 | 白细胞计数( | |
| 健康对照组 | 1.10±0.40 | 2.96±0.63 | 1.60±0.34 | 12.33±6.10 | 281.73±68.59 | 16±13 | 21±8 | 0.74±0.25 | 14.95(22.56) | 90.91±13.05 | 5.5±1.3 | |
| 对照组 | 1.44±0.96a | 3.18±0.96 | 1.48±0.38a | 12.47±5.38 | 310.08±81.23a | 17±11a | 21±8 | 0.79±0.27a | 18.67(28.44) | 85.60±14.81a | 5.9±1.5a | |
| NAFLD组 | 1.76±0.92ab | 3.46±0.96 | 1.38±0.28ab | 12.02±5.04 | 327.10±76.86ab | 26±19ab | 24±12ab | 1.03±0.34ab | 24.55(37.01) | 88.62±12.45ab | 6.1±1.4ab | |
| MAFLD组 | 2.66±1.72abc | 3.29±1.03 | 1.17±0.27abc | 11.99±4.78 | 351.50±84.15abc | 31±23abc | 26±14abc | 1.14±0.36abc | 30.40(46.71) | 86.25±14.62ac | 6.6±1.6abc | |
| 检验统计量值 | 479.960 | 59.596 | 411.073 | 3.136 | 175.232 | 268.532 | 83.674 | 541.209 | 78.484e | 39.971 | 141.461 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.024 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 中性粒细胞计数( | 单核细胞计数( | 淋巴细胞计数( | 血小板计数( | NLR( | PLR( | LMR( | MHR( | ANI〔M(QR)〕 | LAP( | AIP( | |
| 健康对照组 | 3.2±1.1 | 0.3±0.1 | 1.8±0.5 | 220.1±59.0 | 0.23±0.10 | 130.06±44.65 | 1.90±0.94 | 0.20±0.09 | 130.06±44.65 | 16.24±10.96 | -0.18±0.21 | |
| 对照组 | 3.5±1.2a | 0.4±0.2a | 1.9±0.6a | 222.7±62.9 | 0.29±0.15a | 125.62±46.16a | 1.99±1.04a | 0.22±0.09a | 125.62±46.16a | 26.75±21.82a | -0.05±0.28a | |
| NAFLD组 | 3.5±1.1a | 0.4±0.1ab | 2.1±0.6ab | 236.5±58.7ab | 0.29±0.11a | 120.35±40.29ab | 1.79±0.70ab | 0.20±0.07ab | 120.35±40.29ab | 41.70±21.28ab | 0.07±0.23ab | |
| MAFLD组 | 3.8±1.1abc | 0.4±0.1abc | 2.2±0.7abc | 234.8±64.3ab | 0.39±0.16abc | 113.80±40.36abc | 1.86±0.76bc | 0.21±0.08bc | 113.80±40.36abc | 77.62±49.89abc | 0.31±0.27abc | |
| 检验统计量值 | 72.693 | 84.465 | 119.124 | 24.379 | 298.825 | 35.014 | 13.422 | 29.055 | 35.014e | 1 094.515 | 914.337 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 腰围分类〔n(%)〕 | BMI分类〔n(%)〕 | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | 血脂异常〔n(%)〕 | ||||||||
| ≥90 cm(男)或≥85 cm(女) | <90 cm(男)或<85 cm(女) | 正常 | 超重 | 肥胖 | 无 | 有 | 无 | 高胆固醇血症 | 高三酰甘油血症 | 混合性高脂血症 | 低高密度脂蛋白血症 | |
| 健康对照组 | 58(5.40) | 1 017(94.60) | 741(68.93) | 220(20.47) | 114(10.60) | 1 075(100.00) | 0 | 1 075(100.00) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 对照组 | 264(13.55) | 1 684(86.45) | 1 087(55.80) | 690(35.42) | 171(8.78) | 146(7.49) | 1 802(92.51) | 1 475(75.72) | 173(8.88) | 172(8.83) | 35(1.80) | 93(4.77) |
| NAFLD组 | 380(30.45) | 868(69.55) | 267(21.39) | 666(53.37) | 315(25.24) | 211(16.91) | 1 037(83.09) | 850(68.11) | 131(10.50) | 178(14.26) | 66(5.29) | 23(1.84) |
| MAFLD组 | 1 104(75.82) | 352(24.18) | 122(8.38) | 653(44.85) | 681(46.77) | 153(10.51) | 1 303(89.49) | 545(37.43) | 109(7.49) | 524(35.99) | 136(9.34) | 142(9.75) |
| 检验统计量值 | 1 955.472d | 1 975.670d | 3 492.297d | 1 435.230d | ||||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
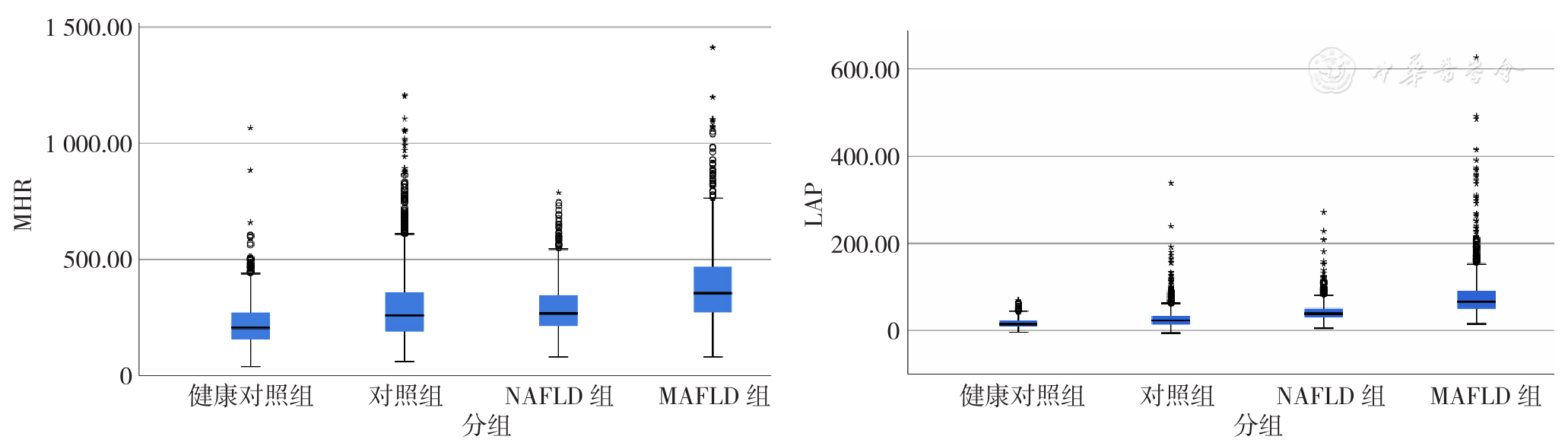
图2 MHR、LAP与研究对象分组的相关性分析注:A为单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值(MHR),B为脂质蓄积指数(LAP)
Figure 2 Correlations of monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and lipid accumulation product index with the grouping
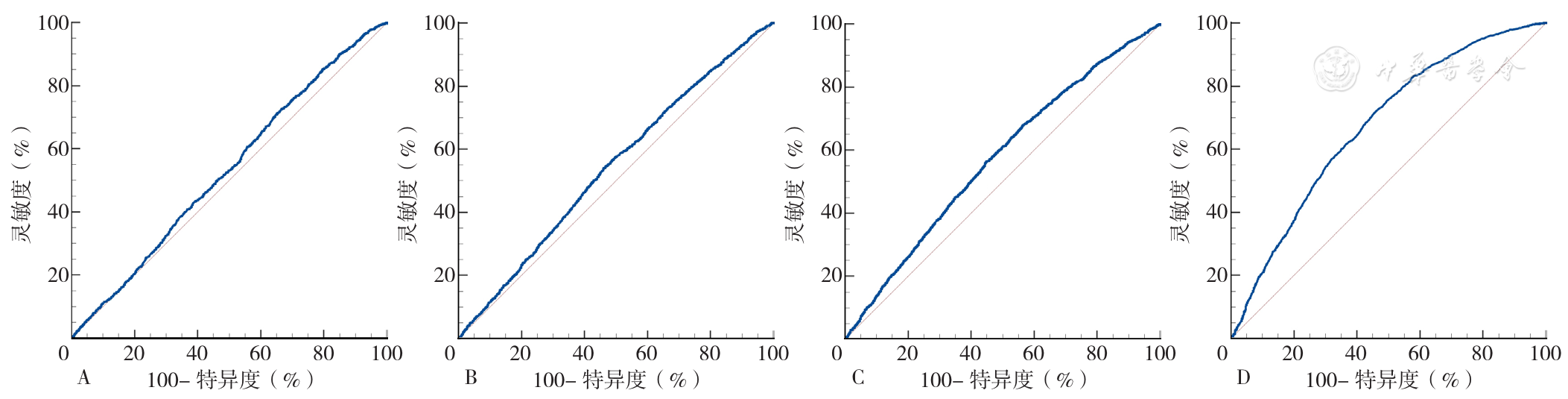
图3 非侵入性指标NLR、PLR、LMR、MHR对社区居民NAFLD合并代谢综合征预测价值的ROC曲线注:A为中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR),B为血小板与淋巴细胞比值(PLR),C为淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值(LMR),D为MHR
Figure 3 ROC analysis for noninvasive indicators(including neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio,platelet to lymphocyte ratio,lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio)in predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with metabolic syndrome in physical examinees in the community
| 项目 | MHR≤0.292(n=2 350) | MHR>0.292(n=2 302) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | 项目 | MHR≤0.292(n=2 350) | MHR>0.292(n=2 302) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 455/1 905 | 1 084/1 218 | 417.727a | <0.001 | PLR( | 126.88±43.84 | 114.00±41.44 | 105.961 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄( | 63.5±8.2 | 65.1±8.7 | 6.504 | <0.001 | LMR( | 0.18±0.06 | 0.24±0.09 | 657.565 | <0.001 | |
| BMI( | 24.8±3.4 | 26.2±3.4 | 14.623 | <0.001 | ANI〔M(QR)〕 | -2.94(0.22) | -2.45(0.97) | 1.351b | 0.245 | |
| 腰围( | 81.0±8.5 | 86.7±8.7 | 22.600 | <0.001 | LAP( | 35.75±26.48 | 57.86±47.07 | 19.792 | <0.001 | |
| 臀围( | 92.1±6.2 | 95.1±6.4 | 253.068 | <0.001 | AIP( | -0.03±0.27 | 0.22±0.29 | 30.217 | <0.001 | |
| 腰臀比( | 0.88±0.06 | 0.91±0.06 | 20.016 | <0.001 | 腰围分类〔n(%)〕 | 169.495 | <0.001 | |||
| 收缩压( | 141±17 | 140±18 | 1.837 | 0.066 | ≥90 cm(男)或≥85 cm(女) | 668(28.43) | 1 080(46.92) | |||
| 舒张压( | 86±9 | 86±10 | 1.152 | 0.249 | <90 cm(男)或<85 cm(女) | 1 682(71.57) | 1 222(53.08) | |||
| 空腹血糖( | 6.2±1.7 | 6.7±2.2 | 9.522 | <0.001 | BMI分类 | 161.870a | <0.001 | |||
| 总胆固醇( | 5.22±1.05 | 4.94±1.09 | 8.854 | <0.001 | 正常 | 913(38.85) | 563(24.46) | |||
| 三酰甘油( | 1.58±0.87 | 2.24±1.63 | 17.348 | <0.001 | 超重 | 961(40.89) | 1 048(45.53) | |||
| LDL-C( | 3.39±0.99 | 3.18±0.97 | 7.223 | <0.001 | 肥胖 | 476(20.26) | 691(30.01) | |||
| HDL-C( | 1.53±0.34 | 1.18±0.25 | 40.574 | <0.001 | 高血压 | 5.788a | <0.001 | |||
| 总胆红素( | 12.16±5.22 | 12.24±5.01 | 0.234 | 0.629 | 无 | 232(9.87) | 278(12.08) | |||
| 血尿酸( | 304.45±73.32 | 351.25±85.38 | 20.072 | <0.001 | 有 | 2 118(90.13) | 2 024(87.92) | |||
| ALT( | 21±16 | 27±20 | 10.371 | <0.001 | 血脂异常〔n(%)〕 | 457.264a | <0.001 | |||
| AST( | 23±11 | 25±12 | 5.240 | <0.001 | 无 | 1 687(71.79) | 1 183(51.39) | |||
| ALT/AST | 0.88±0.32 | 1.04±0.37 | 15.191 | <0.001 | 高胆固醇血症 | 285(12.13) | 128(5.56) | |||
| GGT〔M(QR),U/L〕 | 20.17(31.60) | 24.47(41.19) | 56.332b | <0.001 | 高三酰甘油血症 | 256(10.89) | 618(26.85) | |||
| eGFR〔 | 88.35±13.13 | 84.84±15.02 | 8.494 | <0.001 | 混合性高脂血症 | 90(3.83) | 147(6.39) | |||
| 白细胞计数( | 5.5±1.1 | 6.9±1.5 | 35.590 | <0.001 | 低高密度脂蛋白血症 | 32(1.36) | 226(9.81) | |||
| 中性粒细胞计数( | 3.2±0.9 | 4.0±1.2 | 25.921 | <0.001 | 分组〔n(%)〕 | 341.805a | <0.001 | |||
| 单核细胞计数( | 0.3±0.1 | 0.5±0.1 | 55.544 | <0.001 | 对照组 | 1 181(50.26) | 767(33.32) | |||
| 淋巴细胞计数( | 1.9±0.6 | 2.2±0.7 | 19.815 | <0.001 | NAFLD组 | 725(30.85) | 523(22.72) | |||
| 血小板计数( | 223.2±59.4 | 237.3±64.9 | 7.740 | <0.001 | MAFLD组 | 444(18.89) | 1 012(43.96) | |||
| NLR( | 1.84±0.75 | 1.95±0.99 | 20.166 | <0.001 | ||||||
表2 不同MHR的目标代谢性疾病患者一般资料、人体测量学指标、血压、生化指标、血常规检查结果及分组情况比较
Table 2 Comparison of general information,anthropometric indicators,blood pressure,biochemical indicators,routine blood test results in physical examinees with target metabolic disorders by monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio
| 项目 | MHR≤0.292(n=2 350) | MHR>0.292(n=2 302) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | 项目 | MHR≤0.292(n=2 350) | MHR>0.292(n=2 302) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 455/1 905 | 1 084/1 218 | 417.727a | <0.001 | PLR( | 126.88±43.84 | 114.00±41.44 | 105.961 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄( | 63.5±8.2 | 65.1±8.7 | 6.504 | <0.001 | LMR( | 0.18±0.06 | 0.24±0.09 | 657.565 | <0.001 | |
| BMI( | 24.8±3.4 | 26.2±3.4 | 14.623 | <0.001 | ANI〔M(QR)〕 | -2.94(0.22) | -2.45(0.97) | 1.351b | 0.245 | |
| 腰围( | 81.0±8.5 | 86.7±8.7 | 22.600 | <0.001 | LAP( | 35.75±26.48 | 57.86±47.07 | 19.792 | <0.001 | |
| 臀围( | 92.1±6.2 | 95.1±6.4 | 253.068 | <0.001 | AIP( | -0.03±0.27 | 0.22±0.29 | 30.217 | <0.001 | |
| 腰臀比( | 0.88±0.06 | 0.91±0.06 | 20.016 | <0.001 | 腰围分类〔n(%)〕 | 169.495 | <0.001 | |||
| 收缩压( | 141±17 | 140±18 | 1.837 | 0.066 | ≥90 cm(男)或≥85 cm(女) | 668(28.43) | 1 080(46.92) | |||
| 舒张压( | 86±9 | 86±10 | 1.152 | 0.249 | <90 cm(男)或<85 cm(女) | 1 682(71.57) | 1 222(53.08) | |||
| 空腹血糖( | 6.2±1.7 | 6.7±2.2 | 9.522 | <0.001 | BMI分类 | 161.870a | <0.001 | |||
| 总胆固醇( | 5.22±1.05 | 4.94±1.09 | 8.854 | <0.001 | 正常 | 913(38.85) | 563(24.46) | |||
| 三酰甘油( | 1.58±0.87 | 2.24±1.63 | 17.348 | <0.001 | 超重 | 961(40.89) | 1 048(45.53) | |||
| LDL-C( | 3.39±0.99 | 3.18±0.97 | 7.223 | <0.001 | 肥胖 | 476(20.26) | 691(30.01) | |||
| HDL-C( | 1.53±0.34 | 1.18±0.25 | 40.574 | <0.001 | 高血压 | 5.788a | <0.001 | |||
| 总胆红素( | 12.16±5.22 | 12.24±5.01 | 0.234 | 0.629 | 无 | 232(9.87) | 278(12.08) | |||
| 血尿酸( | 304.45±73.32 | 351.25±85.38 | 20.072 | <0.001 | 有 | 2 118(90.13) | 2 024(87.92) | |||
| ALT( | 21±16 | 27±20 | 10.371 | <0.001 | 血脂异常〔n(%)〕 | 457.264a | <0.001 | |||
| AST( | 23±11 | 25±12 | 5.240 | <0.001 | 无 | 1 687(71.79) | 1 183(51.39) | |||
| ALT/AST | 0.88±0.32 | 1.04±0.37 | 15.191 | <0.001 | 高胆固醇血症 | 285(12.13) | 128(5.56) | |||
| GGT〔M(QR),U/L〕 | 20.17(31.60) | 24.47(41.19) | 56.332b | <0.001 | 高三酰甘油血症 | 256(10.89) | 618(26.85) | |||
| eGFR〔 | 88.35±13.13 | 84.84±15.02 | 8.494 | <0.001 | 混合性高脂血症 | 90(3.83) | 147(6.39) | |||
| 白细胞计数( | 5.5±1.1 | 6.9±1.5 | 35.590 | <0.001 | 低高密度脂蛋白血症 | 32(1.36) | 226(9.81) | |||
| 中性粒细胞计数( | 3.2±0.9 | 4.0±1.2 | 25.921 | <0.001 | 分组〔n(%)〕 | 341.805a | <0.001 | |||
| 单核细胞计数( | 0.3±0.1 | 0.5±0.1 | 55.544 | <0.001 | 对照组 | 1 181(50.26) | 767(33.32) | |||
| 淋巴细胞计数( | 1.9±0.6 | 2.2±0.7 | 19.815 | <0.001 | NAFLD组 | 725(30.85) | 523(22.72) | |||
| 血小板计数( | 223.2±59.4 | 237.3±64.9 | 7.740 | <0.001 | MAFLD组 | 444(18.89) | 1 012(43.96) | |||
| NLR( | 1.84±0.75 | 1.95±0.99 | 20.166 | <0.001 | ||||||
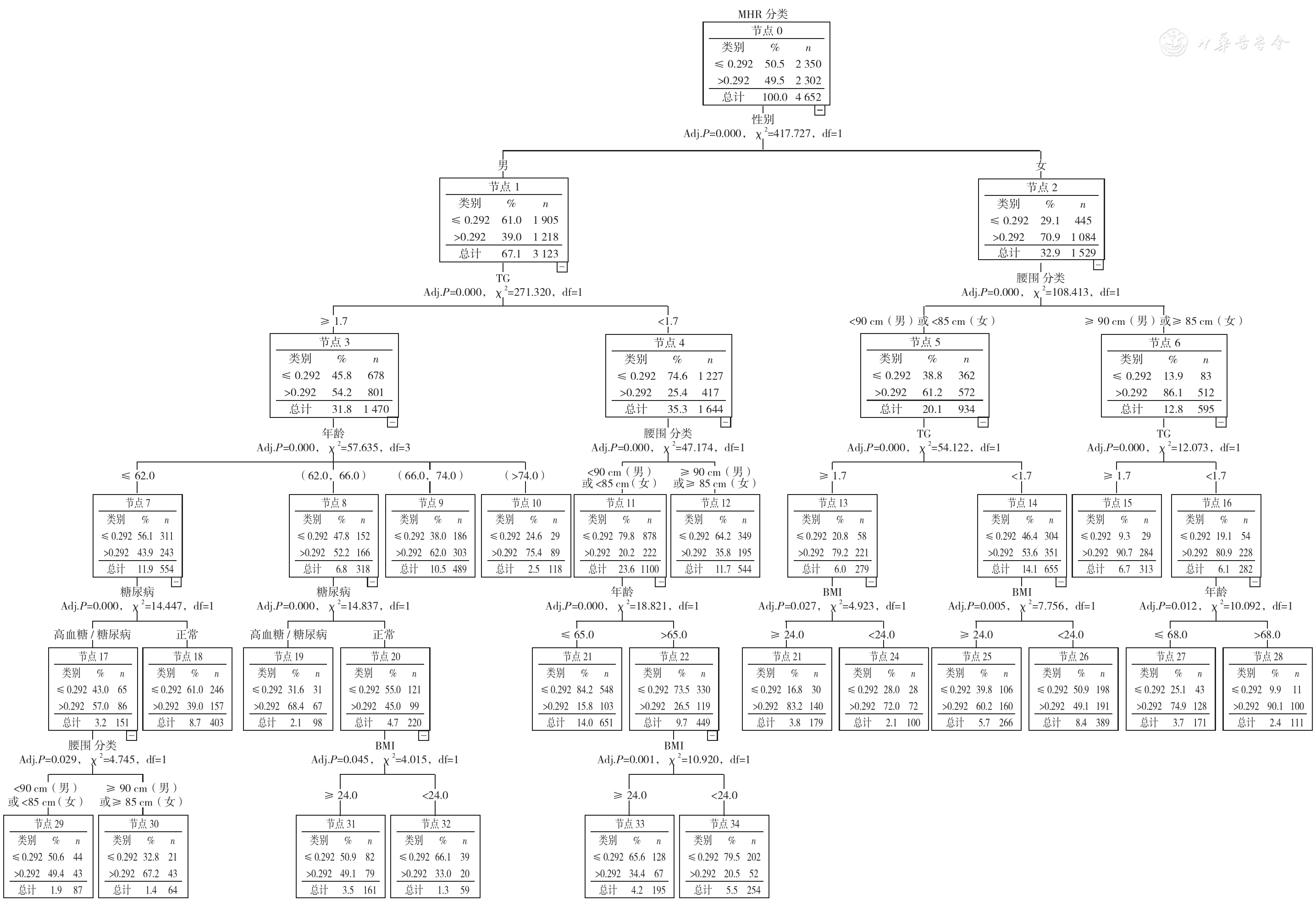
图4 性别、BMI分类、腰围分类、三酰甘油和空腹血糖对MHR影响的多因素Logistic决策树分析注:TG=三酰甘油,BMI=体质指数
Figure 4 Multivariate regression tree analysis of the association of sex,BMI,triacylglycerol,and fasting blood glucose with monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
中华人民共和国卫生部疾病控制司. 血吸虫病防治手册[M]. 3版. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,2000.
|
| [5] |
李岳生. 血吸虫病诊断与治疗[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2006.
|
| [6] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病与相关代谢紊乱诊疗共识(第二版)[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2018,34(7):549-554. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2018.07.004.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
中华医学会,中华医学会杂志社,中华医学会消化病学分会,等. 酒精性肝病基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2020,19(11):990-996. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200812-00898.
|
| [9] | |
| [10] |
中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国),中华医学会心血管病学分会,等.中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002.
|
| [11] |
中华医学会,中华医学会杂志社,中华医学会全科医学分会,等. 血脂异常基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2019,18(5):406-416. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2019.05.003.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
张玄娥,顾蕾,张晓燕,等. 上海杨浦中老年社区人群内脏脂肪指数和脂质蓄积指数与血尿酸的相关性[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2020,41(2):185-191. DOI:10.16118/j.1008-0392.2020.02.008.
|
| [14] |
李礼,王凤荣. 冠状动脉Gensini评分、血浆致动脉硬化指数与不稳定型心绞痛中医证型相关性的研究进展[J]. 中国民间疗法,2020,28(24):113-115. DOI:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2020.2445.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
唐任宽. 慢性炎症状态下脂质代谢紊乱及肝脏、主动脉损害的分子机制[D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学,2008.
|
| [20] |
顾伟根,冯静亚. 超重和肥胖人群非酒精性脂肪肝的流行现状及相关危险因素分析[J]. 甘肃医药,2015,34(2):112-115.
|
| [21] |
赵波,胡来明,李小莉. 血脂及炎症指标在非酒精性脂肪肝合并颈动脉粥样硬化患者中的改变[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2017,26(12):1406-1408. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2017.12.020.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] | 杨慧, 胡汝为, 刘汝青, 卢俊峰, 吴兢兰. 糖尿病患者社区卫生服务体验与血糖控制效果的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4290-4295. |
| [2] | 王丽娜, 高鹏飞, 曹帆, 葛莹, 颜维, 何岱昆. 不同性别人群非酒精性脂肪性肝病患病现况及影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4143-4151. |
| [3] | 马艳艳, 任付先, 王宇, 高登峰. (中性粒细胞+单核细胞)/淋巴细胞比值对心力衰竭患者住院死亡的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3791-3796. |
| [4] | 周小琦, 刘新会, 张微, 李长风, 严亚琼. 老年人丙氨酸氨基转移酶和天冬氨酸氨基转移酶/丙氨酸氨基转移酶与2型糖尿病及代谢综合征的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3645-3649. |
| [5] | 程晓冉, 张笑天, 李明月, 程昊哲, 汤皓晴, 郑汇娴, 张柏松, 刘晓云. 医防融合背景下慢性病随访对高血压和糖尿病患者健康行为及血压/血糖控制的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3482-3488. |
| [6] | 费思杰, 张强, 刘方方, 白璐, 孙彩红, 信彩凤. 糖化血红蛋白变异性与2型糖尿病合并射血分数保留心力衰竭患者新发心房颤动的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3246-3251. |
| [7] | 顾蕴杰, 宋静, 殷峻. 低碳饮食治疗内源性胰岛素缺乏糖尿病患者的临床研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3308-3313. |
| [8] | 孔德先, 邢煜玲, 孙文文, 张智敏, 周霏, 马慧娟. 预估葡萄糖处理率与2型糖尿病合并代谢相关脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3252-3258. |
| [9] | 何荣, 张丽, 李鹏, 张晓玲, 张国, 臧懿然, 吴寿岭, 孙丽霞. 有氧运动对不同血糖水平男性人群动脉僵硬度的即时影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 2997-3004. |
| [10] | 袁仙仙, 王佳, 张可欣, 杨蕊华, 郑薇, 李光辉. 妊娠前不同体质指数孕妇妊娠期血脂水平与巨大儿的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 2973-2979. |
| [11] | 周诗宇, 谌绍林, 邓仁丽, 代米, 刘涛, 田坤明. 脂质比值与代谢综合征的关联及预测价值评价:基于多阶段横断面研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2589-2596. |
| [12] | 丁晓云, 金菊珍, 杨瑾, 周静, 胡瑾, 蒙玥, 梁晓仙, 盖云, 汪俊华, 王子云. 腰围和空腹血糖对40~65岁人群阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征与动脉硬化关联的中介效应研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2597-2602. |
| [13] | 高哲, 段凯欣, 吕秀芹, 马慧娟, 张志梅, 宋光耀. 胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂改善高果糖饮食诱导的胰岛素抵抗大鼠肝脏脂质沉积机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2639-2646. |
| [14] | 张卓然, 于长禾, 安易, 何新, 郭一, 邓金燕, 李悦, 韩登, 皮珊珊, 贺俊芝, 陈玥, 叶永安, 杜宏波. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病临床指南和共识的质量评价及推荐意见比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2439-2446. |
| [15] | 苏阿芳, 朱国玲, 张云水, 陈朔华, 赵秀娟, 杨文浩, 王银洁, 王凤飞, 辛英瑛, 吴寿岭, 张杰, 蒋晓忠. 非肥胖人群基线空腹血糖水平与急性胰腺炎发病风险的关系:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(18): 2203-2208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||






