中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 3180-3186.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0183
收稿日期:2024-06-28
修回日期:2025-04-28
出版日期:2025-09-05
发布日期:2025-07-24
通讯作者:
赵亚利
作者贡献:
焦姝婷负责文章的构思与设计,文献的查询与数据的收集、整理、分析及文章撰写;赵亚利负责文章构思及设计,指导文章撰写,负责文章的质量控制及审校,并对文章整体负责、监督管理。
基金资助:Received:2024-06-28
Revised:2025-04-28
Published:2025-09-05
Online:2025-07-24
Contact:
ZHAO Yali
摘要: 背景 随着国家对医学教育创新发展的重视,本科教学作为医学教育的启蒙阶段也备受关注。 目的 运用Kano模型,探索本科《全科医学概论》课程质量改革的关键要素并构建课程质量优化策略。 方法 采用目的抽样法,于2023年11—12月选取220名完成2023年秋季学期《全科医学概论》课程学习的医学生(首都医科大学2021级临床医学、儿科学及眼视光医学专业的5年制及长学制学生)作为调查对象,采用《全科医学概论》课程内容需求问卷调查学生对该课程的需求现状,并进行属性归类、Better-Worse系数分析和平均满意系数(ASC)值分析。 结果 全部学生有3项必备因素,20项期望因素,4项魅力因素。临床医学学生特有需求中必备因素7项,期望因素1项,魅力因素5项;儿科学和眼视光医学学生特有需求中,必备因素5项,期望因素3项,魅力因素3项。5年制学生特有需求中必备因素1项,期望因素2项,魅力因素3项;长学制学生特有需求中,必备因素4项,期望因素2项,魅力因素3项。 结论 遵循"务必满足必备因素,优先满足期望因素,有选择性满足魅力因素,适当精简和调整无差异因素"的原则,构建出提升高校全科医学课程质量优化的建议。
| 维度 | 需求内容 |
|---|---|
| 课程内容 | |
| 1.全科医学、全科医疗、全科医生概念和学科特点 | |
| 2.全科医学产生与发展历史背景 | |
| 3.全科医生角色和历史使命 | |
| 4.全科医生/全科医疗与其他专科医生/专科医疗之间区别 | |
| 5.全科医疗基本特征与原则 | |
| 6.全科医学在中国内地发展情况 | |
| 7."以人为中心"基本理念 | |
| 8.四种医学模式变化与临床关注中心转移 | |
| 9."以人为中心"照顾原则 | |
| 10.全科医生应诊主要任务 | |
| 11.家庭的定义、结构与功能、家庭生活周期、家庭资源、生活压力事件 | |
| 12.家庭对健康影响 | |
| 13.家庭评估常用技术(如家系图、家庭圈等) | |
| 14.家庭照顾 | |
| 15.社区定义、要素、分类及社区资源等内容 | |
| 16.社区常见健康问题、社区卫生服务机构功能及提供以社区为基础照顾的意义 | |
| 17.以社区为导向的基层医疗(COPC)的定义、要素、发展阶段及实施步骤 | |
| 18.社区诊断的概念、目的、原则、主要内容及实施步骤 | |
| 19.三级预防策略及全科医生预防医学优势 | |
| 20.临床预防概念、产生背景、特点 | |
| 21.临床预防常用方法(如免疫接种、筛检等)及临床预防服务指南 | |
| 22.医患关系定义、模式及沟通类型 | |
| 23.全科医疗中医患沟通技巧及影响因素 | |
| 24.全科医疗中常见患者类型及相应沟通技巧 | |
| 25.妇女儿童保健概述 | |
| 26.妇女全生命周期分期及各期保健 | |
| 27.儿童年龄分期、生长发育规律、各期主要健康问题及保健重点 | |
| 28.老年保健概述 | |
| 29.老年人特殊状态及常见健康问题 | |
| 30.社区老年保健体系、老年保健服务内容及重点 | |
| 31.社区老年人临终关怀 | |
| 32.高血压概述的内容(包括诊断、流行、危险因素、分级、并发症等) | |
| 33.高血压社区管理 | |
| 34. 2型糖尿病概述(包括诊断、流行、危险因素、并发症等) | |
| 35. 2型糖尿病社区管理 | |
| 36.社区卫生服务中心的优势及特色内容 | |
| 37.多病共患老年患者接诊的观摩机会 | |
| 38.全科医生与困难患者(不配合患者、心理问题患者等)沟通的接诊技巧展示 | |
| 教学模式 | |
| 39.采取情境教学 | |
| 40.采取以问题为导向的教学(PBL) | |
| 41.采取案例教学(CBD) | |
| 42.采取团队小组讨论教学(TBL) | |
| 43.增加社区见习学时 | |
| 44.设置课后答疑助教 | |
表1 《全科医学概论》课程需求内容
Table 1 Content of requirements for Introduction to General Practice
| 维度 | 需求内容 |
|---|---|
| 课程内容 | |
| 1.全科医学、全科医疗、全科医生概念和学科特点 | |
| 2.全科医学产生与发展历史背景 | |
| 3.全科医生角色和历史使命 | |
| 4.全科医生/全科医疗与其他专科医生/专科医疗之间区别 | |
| 5.全科医疗基本特征与原则 | |
| 6.全科医学在中国内地发展情况 | |
| 7."以人为中心"基本理念 | |
| 8.四种医学模式变化与临床关注中心转移 | |
| 9."以人为中心"照顾原则 | |
| 10.全科医生应诊主要任务 | |
| 11.家庭的定义、结构与功能、家庭生活周期、家庭资源、生活压力事件 | |
| 12.家庭对健康影响 | |
| 13.家庭评估常用技术(如家系图、家庭圈等) | |
| 14.家庭照顾 | |
| 15.社区定义、要素、分类及社区资源等内容 | |
| 16.社区常见健康问题、社区卫生服务机构功能及提供以社区为基础照顾的意义 | |
| 17.以社区为导向的基层医疗(COPC)的定义、要素、发展阶段及实施步骤 | |
| 18.社区诊断的概念、目的、原则、主要内容及实施步骤 | |
| 19.三级预防策略及全科医生预防医学优势 | |
| 20.临床预防概念、产生背景、特点 | |
| 21.临床预防常用方法(如免疫接种、筛检等)及临床预防服务指南 | |
| 22.医患关系定义、模式及沟通类型 | |
| 23.全科医疗中医患沟通技巧及影响因素 | |
| 24.全科医疗中常见患者类型及相应沟通技巧 | |
| 25.妇女儿童保健概述 | |
| 26.妇女全生命周期分期及各期保健 | |
| 27.儿童年龄分期、生长发育规律、各期主要健康问题及保健重点 | |
| 28.老年保健概述 | |
| 29.老年人特殊状态及常见健康问题 | |
| 30.社区老年保健体系、老年保健服务内容及重点 | |
| 31.社区老年人临终关怀 | |
| 32.高血压概述的内容(包括诊断、流行、危险因素、分级、并发症等) | |
| 33.高血压社区管理 | |
| 34. 2型糖尿病概述(包括诊断、流行、危险因素、并发症等) | |
| 35. 2型糖尿病社区管理 | |
| 36.社区卫生服务中心的优势及特色内容 | |
| 37.多病共患老年患者接诊的观摩机会 | |
| 38.全科医生与困难患者(不配合患者、心理问题患者等)沟通的接诊技巧展示 | |
| 教学模式 | |
| 39.采取情境教学 | |
| 40.采取以问题为导向的教学(PBL) | |
| 41.采取案例教学(CBD) | |
| 42.采取团队小组讨论教学(TBL) | |
| 43.增加社区见习学时 | |
| 44.设置课后答疑助教 | |
| 需求内容 | 全部学生(n=176) | 临床医学(n=141) | 儿科学+眼视光学(n=35) | 5年制(n=109) | 长学制(n=67) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | |
| 1 | I | 0.520/-0.349 | 0.434 | I | 0.504/-0.369 | 0.436 | A | 0.588/-0.265 | 0.426 | I | 0.532/-0.321 | 0.427 | I | 0.500/-0.394 | 0.447 |
| 2 | I | 0.425/-0.207 | 0.316 | I | 0.407/-0.214 | 0.311 | I | 0.500/-0.177 | 0.338 | I | 0.422/-0.193 | 0.307 | I | 0.431/-0.231 | 0.331 |
| 3 | I | 0.457/-0.263 | 0.360 | I | 0.450/-0.271 | 0.361 | I | 0.486/-0.229 | 0.357 | I | 0.486/-0.275 | 0.381 | I | 0.409/-0.242 | 0.326 |
| 4 | I | 0.528/-0.369 | 0.449 | I | 0.524/-0.369 | 0.447 | I | 0.543/-0.371 | 0.457 | I | 0.569/-0.385 | 0.477 | I | 0.463/-0.343 | 0.403 |
| 5 | I | 0.497/-0.354 | 0.426 | I | 0.497/-0.376 | 0.436 | I | 0.500/-0.265 | 0.382 | I | 0.532/-0.349 | 0.44 | I | 0.439/-0.364 | 0.402 |
| 6 | I | 0.506/-0.304 | 0.405 | I | 0.514/-0.307 | 0.411 | I | 0.471/-0.294 | 0.382 | I | 0.523/-0.294 | 0.408 | I | 0.477/-0.323 | 0.400 |
| 7 | O | 0.625/-0.415 | 0.520 | O | 0.600/-0.421 | 0.511 | A | 0.571/-0.371 | 0.471 | O | 0.624/-0.450 | 0.537 | A | 0.627/-0.358 | 0.493 |
| 8 | I | 0.472/-0.341 | 0.406 | I | 0.539/-0.340 | 0.440 | I | 0.429/-0.343 | 0.386 | I | 0.495/-0.349 | 0.422 | I | 0.433/-0.328 | 0.381 |
| 9 | I | 0.563/-0.392 | 0.477 | O | 0.638/-0.411 | 0.525 | I | 0.514/-0.314 | 0.414 | O | 0.606/-0.422 | 0.514 | I | 0.493/-0.343 | 0.418 |
| 10 | O | 0.591/-0.466 | 0.528 | I | 0.518/-0.475 | 0.496 | I | 0.571/-0.429 | 0.500 | O | 0.606/-0.477 | 0.541 | O | 0.567/-0.448 | 0.508 |
| 11 | I | 0.531/-0.309 | 0.420 | I | 0.486/-0.314 | 0.400 | I | 0.571/-0.286 | 0.429 | I | 0.556/-0.315 | 0.435 | I | 0.493/-0.299 | 0.396 |
| 12 | I | 0.537/-0.314 | 0.426 | I | 0.575/-0.319 | 0.447 | A | 0.571/-0.286 | 0.429 | I | 0.574/-0.343 | 0.458 | I | 0.478/-0.269 | 0.373 |
| 13 | I | 0.480/-0.286 | 0.383 | I | 0.593/-0.307 | 0.450 | I | 0.457/-0.200 | 0.329 | I | 0.519/-0.324 | 0.421 | I | 0.418/-0.224 | 0.321 |
| 14 | I | 0.494/-0.290 | 0.392 | I | 0.518/-0.291 | 0.404 | I | 0.543/-0.286 | 0.414 | I | 0.532/-0.294 | 0.413 | I | 0.433/-0.284 | 0.358 |
| 15 | I | 0.471/-0.305 | 0.388 | I | 0.529/-0.300 | 0.414 | I | 0.514/-0.314 | 0.414 | I | 0.472/-0.287 | 0.38 | I | 0.470/-0.333 | 0.402 |
| 16 | I | 0.506/-0.364 | 0.435 | I | 0.486/-0.371 | 0.429 | I | 0.543/-0.343 | 0.443 | I | 0.495/-0.376 | 0.436 | I | 0.522/-0.343 | 0.433 |
| 17 | I | 0.554/-0.377 | 0.466 | I | 0.482/-0.397 | 0.440 | I | 0.559/-0.294 | 0.426 | I | 0.551/-0.376 | 0.463 | I | 0.561/-0.379 | 0.470 |
| 18 | I | 0.580/-0.403 | 0.491 | I | 0.460/-0.417 | 0.439 | A | 0.629/-0.343 | 0.486 | I | 0.587/-0.413 | 0.500 | I | 0.567/-0.388 | 0.478 |
| 19 | I | 0.574/-0.369 | 0.472 | I | 0.497/-0.369 | 0.433 | I | 0.571/-0.371 | 0.471 | I | 0.615/-0.385 | 0.500 | I | 0.508/-0.343 | 0.425 |
| 20 | I | 0.497/-0.291 | 0.394 | I | 0.550/-0.300 | 0.425 | I | 0.457/-0.257 | 0.357 | I | 0.532/-0.303 | 0.417 | I | 0.439/-0.273 | 0.356 |
| 21 | I | 0.557/-0.352 | 0.455 | I | 0.567/-0.362 | 0.465 | I | 0.571/-0.314 | 0.443 | I | 0.569/-0.339 | 0.454 | I | 0.537/-0.373 | 0.455 |
| 22 | I | 0.597/-0.398 | 0.497 | I | 0.575/-0.397 | 0.486 | O | 0.629/-0.400 | 0.514 | O | 0.651/-0.413 | 0.532 | I | 0.508/-0.373 | 0.440 |
| 23 | I | 0.592/-0.402 | 0.497 | I | 0.504/-0.417 | 0.460 | I | 0.571/-0.343 | 0.457 | O | 0.639/-0.435 | 0.537 | I | 0.515/-0.349 | 0.432 |
| 24 | O | 0.640/-0.440 | 0.540 | O | 0.557/-0.457 | 0.507 | O | 0.686/-0.371 | 0.529 | O | 0.661/-0.468 | 0.564 | I | 0.606/-0.394 | 0.500 |
| 25 | I | 0.577/-0.406 | 0.491 | A | 0.593/-0.393 | 0.493 | O | 0.686/-0.457 | 0.571 | O | 0.611/-0.435 | 0.523 | I | 0.522/-0.358 | 0.440 |
| 26 | O | 0.611/-0.434 | 0.523 | O | 0.597/-0.425 | 0.511 | O | 0.657/-0.457 | 0.557 | O | 0.657/-0.463 | 0.560 | I | 0.537/-0.388 | 0.463 |
| 27 | I | 0.571/-0.360 | 0.466 | A | 0.633/-0.353 | 0.493 | A | 0.657/-0.400 | 0.529 | I | 0.574/-0.352 | 0.463 | I | 0.567/-0.373 | 0.470 |
| 28 | I | 0.572/-0.376 | 0.474 | I | 0.554/-0.367 | 0.460 | I | 0.571/-0.400 | 0.486 | O | 0.630/-0.398 | 0.514 | I | 0.477/-0.339 | 0.408 |
| 29 | I | 0.546/-0.369 | 0.457 | I | 0.600/-0.379 | 0.489 | A | 0.571/-0.343 | 0.457 | I | 0.596/-0.385 | 0.491 | I | 0.463/-0.343 | 0.403 |
| 30 | I | 0.535/-0.356 | 0.445 | I | 0.550/-0.350 | 0.450 | A | 0.600/-0.371 | 0.486 | I | 0.589/-0.383 | 0.486 | I | 0.448/-0.313 | 0.381 |
| 31 | O | 0.603/-0.425 | 0.514 | I | 0.577/-0.402 | 0.489 | O | 0.600/-0.514 | 0.557 | O | 0.667/-0.444 | 0.556 | I | 0.500/-0.394 | 0.447 |
| 32 | O | 0.603/-0.437 | 0.520 | O | 0.576/-0.439 | 0.507 | O | 0.714/-0.429 | 0.571 | O | 0.630/-0.463 | 0.546 | I | 0.561/-0.394 | 0.477 |
| 33 | I | 0.574/-0.403 | 0.489 | I | 0.567/-0.418 | 0.493 | I | 0.600/-0.343 | 0.471 | O | 0.606/-0.440 | 0.523 | I | 0.522/-0.343 | 0.433 |
| 34 | O | 0.638/-0.471 | 0.555 | O | 0.619/-0.468 | 0.543 | O | 0.714/-0.486 | 0.600 | O | 0.657/-0.519 | 0.588 | I | 0.606/-0.394 | 0.500 |
| 35 | I | 0.574/-0.398 | 0.486 | I | 0.567/-0.404 | 0.486 | I | 0.600/-0.371 | 0.486 | O | 0.587/-0.431 | 0.509 | I | 0.552/-0.343 | 0.448 |
| 36 | I | 0.577/-0.337 | 0.457 | I | 0.550/-0.307 | 0.429 | O | 0.686/-0.457 | 0.571 | I | 0.569/-0.349 | 0.459 | I | 0.591/-0.318 | 0.455 |
| 37 | O | 0.657/-0.361 | 0.509 | I | 0.630/-0.341 | 0.486 | O | 0.765/-0.441 | 0.603 | A | 0.648/-0.333 | 0.491 | O | 0.672/-0.406 | 0.539 |
| 38 | O | 0.644/-0.397 | 0.520 | O | 0.626/-0.381 | 0.504 | O | 0.714/-0.457 | 0.586 | I | 0.633/-0.358 | 0.495 | O | 0.662/-0.462 | 0.562 |
| 39 | I | 0.626/-0.345 | 0.485 | I | 0.591/-0.336 | 0.464 | O | 0.765/-0.382 | 0.574 | A | 0.638/-0.295 | 0.467 | O | 0.606/-0.424 | 0.515 |
| 40 | I | 0.449/-0.261 | 0.355 | I | 0.429/-0.241 | 0.335 | I | 0.531/-0.344 | 0.438 | I | 0.398/-0.223 | 0.311 | I | 0.532/-0.323 | 0.427 |
| 41 | I | 0.595/-0.364 | 0.480 | I | 0.590/-0.345 | 0.468 | O | 0.618/-0.441 | 0.529 | I | 0.608/-0.346 | 0.477 | I | 0.576/-0.394 | 0.485 |
| 42 | I | 0.362/-0.215 | 0.289 | I | 0.366/-0.211 | 0.289 | I | 0.346/-0.231 | 0.289 | I | 0.344/-0.189 | 0.267 | I | 0.390/-0.254 | 0.322 |
| 43 | I | 0.512/-0.310 | 0.411 | I | 0.500/-0.284 | 0.392 | I | 0.559/-0.412 | 0.485 | I | 0.451/-0.265 | 0.358 | I | 0.606/-0.379 | 0.492 |
| 44 | I | 0.520/-0.349 | 0.434 | I | 0.396/-0.252 | 0.324 | I | 0.429/-0.343 | 0.386 | I | 0.389/-0.250 | 0.319 | I | 0.424/-0.303 | 0.364 |
表2 学生需求属性归类表
Table 2 Attribute category of students' needs
| 需求内容 | 全部学生(n=176) | 临床医学(n=141) | 儿科学+眼视光学(n=35) | 5年制(n=109) | 长学制(n=67) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | 归类 | Better/Worse系数 | ASC值 | |
| 1 | I | 0.520/-0.349 | 0.434 | I | 0.504/-0.369 | 0.436 | A | 0.588/-0.265 | 0.426 | I | 0.532/-0.321 | 0.427 | I | 0.500/-0.394 | 0.447 |
| 2 | I | 0.425/-0.207 | 0.316 | I | 0.407/-0.214 | 0.311 | I | 0.500/-0.177 | 0.338 | I | 0.422/-0.193 | 0.307 | I | 0.431/-0.231 | 0.331 |
| 3 | I | 0.457/-0.263 | 0.360 | I | 0.450/-0.271 | 0.361 | I | 0.486/-0.229 | 0.357 | I | 0.486/-0.275 | 0.381 | I | 0.409/-0.242 | 0.326 |
| 4 | I | 0.528/-0.369 | 0.449 | I | 0.524/-0.369 | 0.447 | I | 0.543/-0.371 | 0.457 | I | 0.569/-0.385 | 0.477 | I | 0.463/-0.343 | 0.403 |
| 5 | I | 0.497/-0.354 | 0.426 | I | 0.497/-0.376 | 0.436 | I | 0.500/-0.265 | 0.382 | I | 0.532/-0.349 | 0.44 | I | 0.439/-0.364 | 0.402 |
| 6 | I | 0.506/-0.304 | 0.405 | I | 0.514/-0.307 | 0.411 | I | 0.471/-0.294 | 0.382 | I | 0.523/-0.294 | 0.408 | I | 0.477/-0.323 | 0.400 |
| 7 | O | 0.625/-0.415 | 0.520 | O | 0.600/-0.421 | 0.511 | A | 0.571/-0.371 | 0.471 | O | 0.624/-0.450 | 0.537 | A | 0.627/-0.358 | 0.493 |
| 8 | I | 0.472/-0.341 | 0.406 | I | 0.539/-0.340 | 0.440 | I | 0.429/-0.343 | 0.386 | I | 0.495/-0.349 | 0.422 | I | 0.433/-0.328 | 0.381 |
| 9 | I | 0.563/-0.392 | 0.477 | O | 0.638/-0.411 | 0.525 | I | 0.514/-0.314 | 0.414 | O | 0.606/-0.422 | 0.514 | I | 0.493/-0.343 | 0.418 |
| 10 | O | 0.591/-0.466 | 0.528 | I | 0.518/-0.475 | 0.496 | I | 0.571/-0.429 | 0.500 | O | 0.606/-0.477 | 0.541 | O | 0.567/-0.448 | 0.508 |
| 11 | I | 0.531/-0.309 | 0.420 | I | 0.486/-0.314 | 0.400 | I | 0.571/-0.286 | 0.429 | I | 0.556/-0.315 | 0.435 | I | 0.493/-0.299 | 0.396 |
| 12 | I | 0.537/-0.314 | 0.426 | I | 0.575/-0.319 | 0.447 | A | 0.571/-0.286 | 0.429 | I | 0.574/-0.343 | 0.458 | I | 0.478/-0.269 | 0.373 |
| 13 | I | 0.480/-0.286 | 0.383 | I | 0.593/-0.307 | 0.450 | I | 0.457/-0.200 | 0.329 | I | 0.519/-0.324 | 0.421 | I | 0.418/-0.224 | 0.321 |
| 14 | I | 0.494/-0.290 | 0.392 | I | 0.518/-0.291 | 0.404 | I | 0.543/-0.286 | 0.414 | I | 0.532/-0.294 | 0.413 | I | 0.433/-0.284 | 0.358 |
| 15 | I | 0.471/-0.305 | 0.388 | I | 0.529/-0.300 | 0.414 | I | 0.514/-0.314 | 0.414 | I | 0.472/-0.287 | 0.38 | I | 0.470/-0.333 | 0.402 |
| 16 | I | 0.506/-0.364 | 0.435 | I | 0.486/-0.371 | 0.429 | I | 0.543/-0.343 | 0.443 | I | 0.495/-0.376 | 0.436 | I | 0.522/-0.343 | 0.433 |
| 17 | I | 0.554/-0.377 | 0.466 | I | 0.482/-0.397 | 0.440 | I | 0.559/-0.294 | 0.426 | I | 0.551/-0.376 | 0.463 | I | 0.561/-0.379 | 0.470 |
| 18 | I | 0.580/-0.403 | 0.491 | I | 0.460/-0.417 | 0.439 | A | 0.629/-0.343 | 0.486 | I | 0.587/-0.413 | 0.500 | I | 0.567/-0.388 | 0.478 |
| 19 | I | 0.574/-0.369 | 0.472 | I | 0.497/-0.369 | 0.433 | I | 0.571/-0.371 | 0.471 | I | 0.615/-0.385 | 0.500 | I | 0.508/-0.343 | 0.425 |
| 20 | I | 0.497/-0.291 | 0.394 | I | 0.550/-0.300 | 0.425 | I | 0.457/-0.257 | 0.357 | I | 0.532/-0.303 | 0.417 | I | 0.439/-0.273 | 0.356 |
| 21 | I | 0.557/-0.352 | 0.455 | I | 0.567/-0.362 | 0.465 | I | 0.571/-0.314 | 0.443 | I | 0.569/-0.339 | 0.454 | I | 0.537/-0.373 | 0.455 |
| 22 | I | 0.597/-0.398 | 0.497 | I | 0.575/-0.397 | 0.486 | O | 0.629/-0.400 | 0.514 | O | 0.651/-0.413 | 0.532 | I | 0.508/-0.373 | 0.440 |
| 23 | I | 0.592/-0.402 | 0.497 | I | 0.504/-0.417 | 0.460 | I | 0.571/-0.343 | 0.457 | O | 0.639/-0.435 | 0.537 | I | 0.515/-0.349 | 0.432 |
| 24 | O | 0.640/-0.440 | 0.540 | O | 0.557/-0.457 | 0.507 | O | 0.686/-0.371 | 0.529 | O | 0.661/-0.468 | 0.564 | I | 0.606/-0.394 | 0.500 |
| 25 | I | 0.577/-0.406 | 0.491 | A | 0.593/-0.393 | 0.493 | O | 0.686/-0.457 | 0.571 | O | 0.611/-0.435 | 0.523 | I | 0.522/-0.358 | 0.440 |
| 26 | O | 0.611/-0.434 | 0.523 | O | 0.597/-0.425 | 0.511 | O | 0.657/-0.457 | 0.557 | O | 0.657/-0.463 | 0.560 | I | 0.537/-0.388 | 0.463 |
| 27 | I | 0.571/-0.360 | 0.466 | A | 0.633/-0.353 | 0.493 | A | 0.657/-0.400 | 0.529 | I | 0.574/-0.352 | 0.463 | I | 0.567/-0.373 | 0.470 |
| 28 | I | 0.572/-0.376 | 0.474 | I | 0.554/-0.367 | 0.460 | I | 0.571/-0.400 | 0.486 | O | 0.630/-0.398 | 0.514 | I | 0.477/-0.339 | 0.408 |
| 29 | I | 0.546/-0.369 | 0.457 | I | 0.600/-0.379 | 0.489 | A | 0.571/-0.343 | 0.457 | I | 0.596/-0.385 | 0.491 | I | 0.463/-0.343 | 0.403 |
| 30 | I | 0.535/-0.356 | 0.445 | I | 0.550/-0.350 | 0.450 | A | 0.600/-0.371 | 0.486 | I | 0.589/-0.383 | 0.486 | I | 0.448/-0.313 | 0.381 |
| 31 | O | 0.603/-0.425 | 0.514 | I | 0.577/-0.402 | 0.489 | O | 0.600/-0.514 | 0.557 | O | 0.667/-0.444 | 0.556 | I | 0.500/-0.394 | 0.447 |
| 32 | O | 0.603/-0.437 | 0.520 | O | 0.576/-0.439 | 0.507 | O | 0.714/-0.429 | 0.571 | O | 0.630/-0.463 | 0.546 | I | 0.561/-0.394 | 0.477 |
| 33 | I | 0.574/-0.403 | 0.489 | I | 0.567/-0.418 | 0.493 | I | 0.600/-0.343 | 0.471 | O | 0.606/-0.440 | 0.523 | I | 0.522/-0.343 | 0.433 |
| 34 | O | 0.638/-0.471 | 0.555 | O | 0.619/-0.468 | 0.543 | O | 0.714/-0.486 | 0.600 | O | 0.657/-0.519 | 0.588 | I | 0.606/-0.394 | 0.500 |
| 35 | I | 0.574/-0.398 | 0.486 | I | 0.567/-0.404 | 0.486 | I | 0.600/-0.371 | 0.486 | O | 0.587/-0.431 | 0.509 | I | 0.552/-0.343 | 0.448 |
| 36 | I | 0.577/-0.337 | 0.457 | I | 0.550/-0.307 | 0.429 | O | 0.686/-0.457 | 0.571 | I | 0.569/-0.349 | 0.459 | I | 0.591/-0.318 | 0.455 |
| 37 | O | 0.657/-0.361 | 0.509 | I | 0.630/-0.341 | 0.486 | O | 0.765/-0.441 | 0.603 | A | 0.648/-0.333 | 0.491 | O | 0.672/-0.406 | 0.539 |
| 38 | O | 0.644/-0.397 | 0.520 | O | 0.626/-0.381 | 0.504 | O | 0.714/-0.457 | 0.586 | I | 0.633/-0.358 | 0.495 | O | 0.662/-0.462 | 0.562 |
| 39 | I | 0.626/-0.345 | 0.485 | I | 0.591/-0.336 | 0.464 | O | 0.765/-0.382 | 0.574 | A | 0.638/-0.295 | 0.467 | O | 0.606/-0.424 | 0.515 |
| 40 | I | 0.449/-0.261 | 0.355 | I | 0.429/-0.241 | 0.335 | I | 0.531/-0.344 | 0.438 | I | 0.398/-0.223 | 0.311 | I | 0.532/-0.323 | 0.427 |
| 41 | I | 0.595/-0.364 | 0.480 | I | 0.590/-0.345 | 0.468 | O | 0.618/-0.441 | 0.529 | I | 0.608/-0.346 | 0.477 | I | 0.576/-0.394 | 0.485 |
| 42 | I | 0.362/-0.215 | 0.289 | I | 0.366/-0.211 | 0.289 | I | 0.346/-0.231 | 0.289 | I | 0.344/-0.189 | 0.267 | I | 0.390/-0.254 | 0.322 |
| 43 | I | 0.512/-0.310 | 0.411 | I | 0.500/-0.284 | 0.392 | I | 0.559/-0.412 | 0.485 | I | 0.451/-0.265 | 0.358 | I | 0.606/-0.379 | 0.492 |
| 44 | I | 0.520/-0.349 | 0.434 | I | 0.396/-0.252 | 0.324 | I | 0.429/-0.343 | 0.386 | I | 0.389/-0.250 | 0.319 | I | 0.424/-0.303 | 0.364 |
| 项目 | 全部学生 | 不同专业 | 不同学制 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临床医学 | 儿科学+眼视光学 | 5年制 | 长学制 | ||
| M | 29、4、16 | 30、13、4、5、1、16、20、15、14 | 10、28、43、7、19、4 | 4、17、16 | 1、31、22、5 |
| O | 34、24、10、26、38、32、31、37、22、23、18、25、33、35、41、9、28、19、17、7 | 34、26、7、32、38、25、33、31、22、35、21、23、28、18、19 | 37、34、38、39、32、25、36、31、26、41、24、27、30、35、22 | 34、24、26、31、32、10、23、7、22、25、33、28、9、35、18、19、29、30 | 38、37、39、10、24、34、7、43、41、18、32、27、17、26、21、25 |
| A | 39、27、36、21 | 9、24、10、27、37、42、39、17、36 | 18、33、1 | 38、37、41、39、27、12 | 36、35、16、33、40 |
| I | 30、1、44、12、5、11、43、8、6、20、14、15、13、3、40、2、42 | 29、12、8、6、 11、43、3、40、 2、44、42 | 23、29、16、21、40、11、12、17、9、14、15、8、44、6、5、3、20、2、13、42 | 36、21、5、11、1、8、13、20、14、6、3、15、43、44、40、2、42 | 23、19、9、28、4、29、15、6、11、8、30、12、44、14、20、2、3、42、13 |
表3 不同特征学生需求分布情况及重要度排序
Table 3 Distribution of needs of students with different characteristics and ranking of their importance
| 项目 | 全部学生 | 不同专业 | 不同学制 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临床医学 | 儿科学+眼视光学 | 5年制 | 长学制 | ||
| M | 29、4、16 | 30、13、4、5、1、16、20、15、14 | 10、28、43、7、19、4 | 4、17、16 | 1、31、22、5 |
| O | 34、24、10、26、38、32、31、37、22、23、18、25、33、35、41、9、28、19、17、7 | 34、26、7、32、38、25、33、31、22、35、21、23、28、18、19 | 37、34、38、39、32、25、36、31、26、41、24、27、30、35、22 | 34、24、26、31、32、10、23、7、22、25、33、28、9、35、18、19、29、30 | 38、37、39、10、24、34、7、43、41、18、32、27、17、26、21、25 |
| A | 39、27、36、21 | 9、24、10、27、37、42、39、17、36 | 18、33、1 | 38、37、41、39、27、12 | 36、35、16、33、40 |
| I | 30、1、44、12、5、11、43、8、6、20、14、15、13、3、40、2、42 | 29、12、8、6、 11、43、3、40、 2、44、42 | 23、29、16、21、40、11、12、17、9、14、15、8、44、6、5、3、20、2、13、42 | 36、21、5、11、1、8、13、20、14、6、3、15、43、44、40、2、42 | 23、19、9、28、4、29、15、6、11、8、30、12、44、14、20、2、3、42、13 |
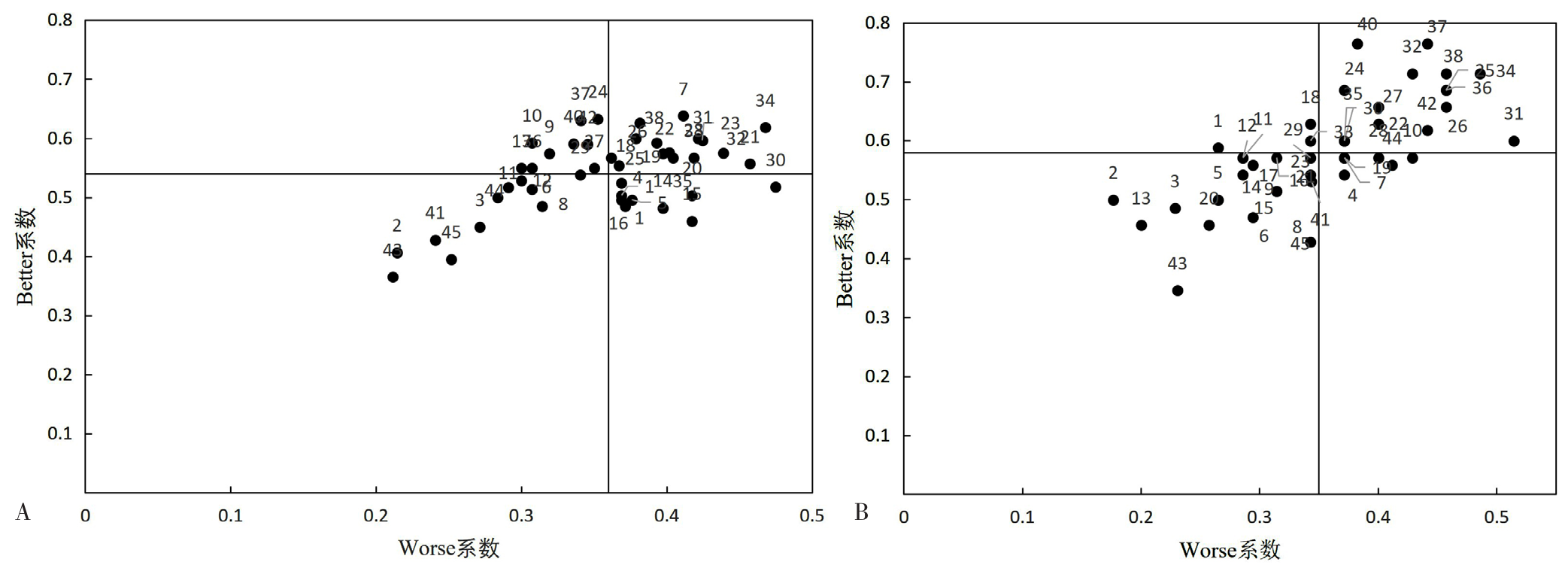
图2 临床医学和儿科学+眼视光学学生需求Better-Worse象限图 注:A和B分别为临床医学和儿科学+眼视光学学生需求Better-Worse象限图。
Figure 2 Better-Worse quadrant diagram of needs for clinical medicine and pediatrics + optometry students
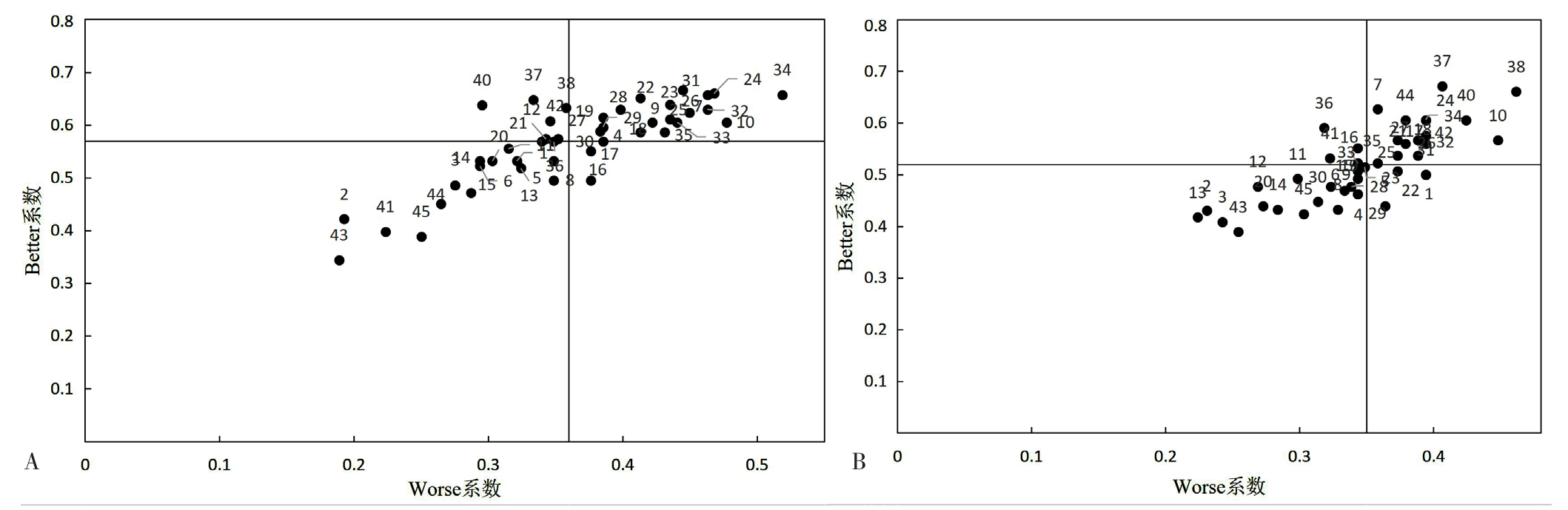
图3 5年制学生与长学制学生需求Better-Worse象限图 注:A和B分别为5年制和长学制学生需求Better-Worse象限图。
Figure 3 Better-Worse quadrant diagram of needs for 5-year vs. longer-term students
| [1] |
国务院办公厅.国务院办公厅关于加快医学教育创新发展的指导意见[A/OL]. (2020-09-23)[2025-04-27].
|
| [2] |
吴岩. 建设中国"金课" [J]. 中国大学教学,2018(12):4-9.
|
| [3] |
冯仁蔚,李小明,付玉,等. "双一流"建设背景下高校本科教育质量保障的新要求[J]. 教育现代化,2019,6(51):99-103. DOI:10.16541/j.cnki.2095-8420.2019.51.036.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
奉小斌,张群祥. 大学管理类专业课堂教学互动需求研究——以《卓越质量管理与实践》课程为例[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(社会科学版),2016,42(2):207-214.
|
| [6] |
王锐,王锦萱,罗仙平. 学习评论视域下基于KANO模型的在线课程质量影响因素分析[J]. 黑龙江高教研究,2021,39(10):155-160. DOI:10.19903/j.cnki.cn23-1074/g.2021.10.026.
|
| [7] |
齐殿君,江南,于晓松. 我国本科生全科医学教育教学情况调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(7):789-793.
|
| [8] |
李惠英,涂彩霞,任丹阳,等. 基于Kano模型的儿科药学教学质量提升的关键要素[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(1):156-162.
|
| [9] |
窦蓓,刘扣英,许勤,等. 基于Kano模型的护理硕士生循证护理课程需求分析[J]. 华西医学,2022,37(11):1705-1710.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
钟凯颖. 基于Kano模型对不同程度失能老人长期照护需求的调查研究[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学,2022.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
曲玉新. 基于KANO模型的宫颈癌患者支持性照顾需求调查分析[D]. 济南:山东大学,2021.
|
| [15] |
李秋实,李雯,费康月,等. 协同视角下高校图书馆大学生数字素养教育的需求分析及路径优化研究[J]. 图书馆学研究,2023(3):67-82.
|
| [16] |
刘振天,吴秋怡. "'以’学生为中心"抑或"学生为中心":一个本体论的新认知[J]. 教育发展研究,2023,43(9):1-9.
|
| [17] |
刘建清,赵红霞,陈洪友. 我国高校个性化教育的理论、政策进展与实践反思[J]. 国家教育行政学院学报,2024(1):89-95.
|
| [18] |
祁祯楠,董爱梅,韩晓宁,等. 本科生阶段全科医学教学模式研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(7):839-842.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
战京燕,娄景秋,王少坤,等. 我国全科住院医师规范化培训教学模式及应用效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(19):2401-2407.
|
| [23] |
刘畅. 我国全科医学人才培养存在的问题与解决路径[J]. 高等教育研究,2020,41(3):94-99.
|
| [24] |
金花,易春涛,倪衡如,等. 社区卫生服务中心全科医学临床质量状况及存在问题分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(1):35-42.
|
| [25] |
江笑笑,李惠萍,张婷,等. 护理专业整合校外教育资源的模式研究[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2018,35(2):137-139.
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] | 赵稳稳, 李诺雅, 张雅丽, 张金佳, 张敏, 刘华雷, 席彪, 王荣英. 临床住培基地(综合医院)全科医学师资质量评价指标体系构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3187-3192. |
| [2] | 翟佳燚, 陆媛, 潘莹, 于德华. 全科临床诊疗思维课程引进程序性评价课程体验的质性研究——基于建构主义视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3193-3199. |
| [3] | 潘琦, 任菁菁, 马方晖, 胡梦杰. 全科医师对AI辅助诊疗系统的认知与需求调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [4] | 杨辉. 全科医学研究脑洞:经济、健康、基本医疗服务的提供和利用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 0-C6. |
| [5] | 李金宏, 王宇, 徐耀铭, 刘洋, 侯静晖. 探讨全科-专科-基层实践基地联合门诊教学在全科住院医师规范化培训中的应用效果[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2726-2730. |
| [6] | 崔珑严, 代高岚歆, 陶红兵. 全科医生亚专长培养模式的国际经验及对中国的启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2720-2725. |
| [7] | 杨信, 王宏, 韩建军, 梁万年, 胡丙杰. 2023年世界家庭医生组织欧洲分会修订全科医学/家庭医学定义的主要内容及其意义[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2712-2719. |
| [8] | 杨辉. 探讨基本医疗与住院服务供应和利用的关系[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2449-2456. |
| [9] | 刘洪亚, 于德华. 上海市社区全专结合临床诊疗技术建设实践[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2390-2397. |
| [10] | 王松柱, 姚易, 周伊恒, 赵茄茜, 杨荣, 赵茜, 张瑞, 代华, 李东泽, 廖晓阳, 杨辉. 近五年全科医学研究热点及发展趋势分析:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [11] | 闫温馨, 刘珏, 梁万年. DeepSeek赋能全科医学:潜在应用与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2065-2069. |
| [12] | 陈怡翔, 唐尚锋. 华中地区家庭医生团队内部互动网络对工作满意度的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 1961-1965. |
| [13] | 张雪原, 谢晨妹, 李若凡, 张婉雪, 贾金忠. 全科医学博士专业学位研究生招生现状与思考[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1583-1589. |
| [14] | 赵铁夫, 张彬, 韩红亚, 罗鸿池, 马涵英. 全科医学硕士研究生医患沟通能力现状及导师对其的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1590-1594. |
| [15] | 杨辉. 倡导全科医学的质性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1421-1426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||






