| [1] |
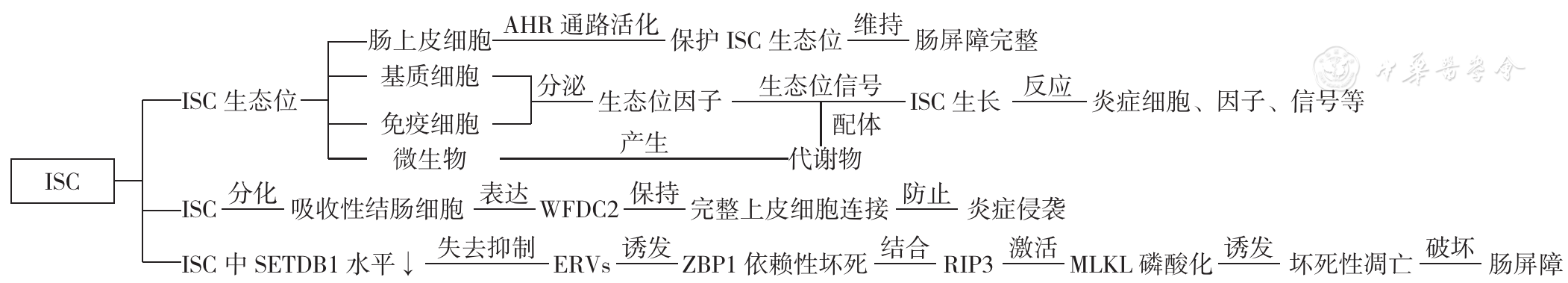
SCHEWE M, FRANKEN P F, SACCHETTI A,et al. Secreted phospholipases A2 are intestinal stem cell niche factors with distinct roles in homeostasis,inflammation,and cancer[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2016, 19(1):38-51. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.05.023.
|
| [2] |
PARIKH K, ANTANAVICIUTE A, FAWKNER-CORBETT D,et al. Colonic epithelial cell diversity in health and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7746):49-55. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0992-y.
|
| [3] |
WANG R C, LI H D, WU J F,et al. Gut stem cell necroptosis by genome instability triggers bowel inflammation[J]. Nature, 2020, 580(7803):386-390. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2127-x.
|
| [4] |
TAKEDA N, JAIN R, LEBOEUF M R,et al. Interconversion between intestinal stem cell populations in distinct niches[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6061):1420-1424. DOI: 10.1126/science.1213214.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
GERSEMANN M, STANGE E F, WEHKAMP J. From intestinal stem cells to inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17(27):3198-3203. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3198.
|
| [7] |
METIDJI A, OMENETTI S, CROTTA S,et al. The environmental sensor AHR protects from inflammatory damage by maintaining intestinal stem cell homeostasis and barrier integrity[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(6):1542. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.05.024.
|
| [8] |
CHEN Y, YE Z H, SEIDLER U,et al. Microenvironmental regulation of intestinal stem cells in the inflamed intestine[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 273:119298. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119298.
|
| [9] |
PETERSON L W, ARTIS D. Intestinal epithelial cells:regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2014, 14(3):141-153. DOI: 10.1038/nri3608.
|
| [10] |
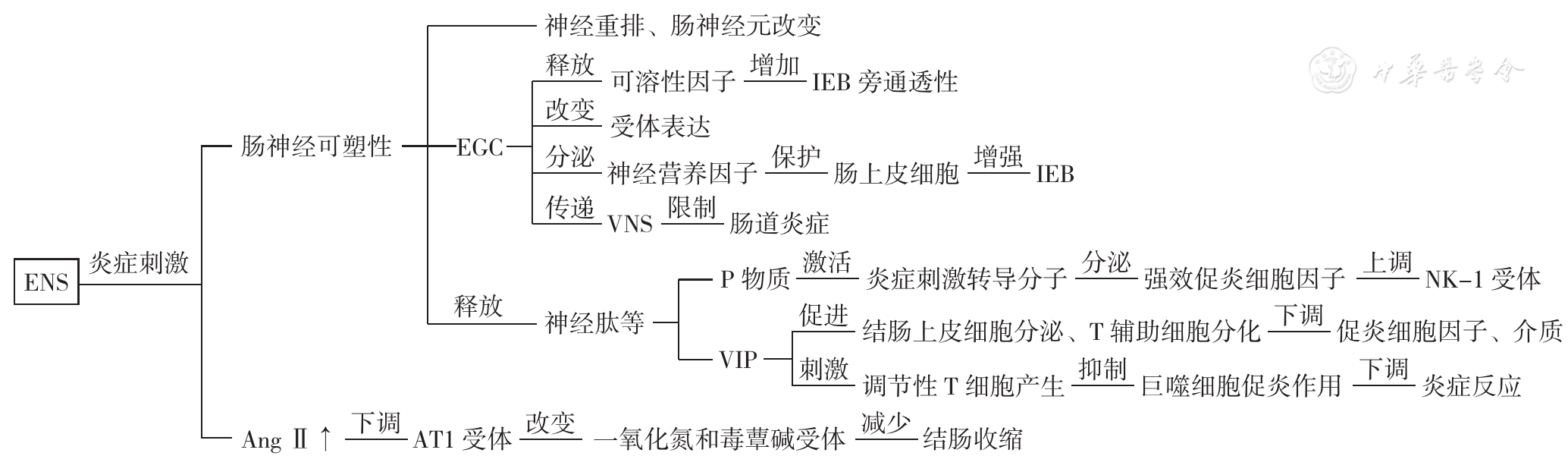
VASINA V, BARBARA G, TALAMONTI L,et al. Enteric neuroplasticity evoked by inflammation[J]. Auton Neurosci, 2006, 126/127:264-272. DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.02.025.
|
| [11] |
MAWE G M. Colitis-induced neuroplasticity disrupts motility in the inflamed and post-inflamed colon[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(3):949-955. DOI: 10.1172/JCI76306.
|
| [12] |
DVORAK A M, ONDERDONK A B, MCLEOD R S,et al. Axonal necrosis of enteric autonomic nerves in continent ileal pouches. Possible implications for pathogenesis of Crohn's disease[J]. Ann Surg, 1993, 217(3):260-271. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199303000-00008.
|
| [13] |
UYTTEBROEK L, PYPE C, HUBENS G,et al. Effect of TNBS-induced colitis on enteric neuronal subpopulations in adult zebrafish[J]. Eur J Histochem, 2020, 64(3):3161. DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2020.3161.
|
| [14] |
BERNARDINI N, SEGNANI C, IPPOLITO C,et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of myenteric ganglia and interstitial cells of Cajal in ulcerative colitis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2012, 16(2):318-327. DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01298.x.
|
| [15] |
COSTANTINI T W, BANSAL V, KRZYZANIAK M,et al. Vagal nerve stimulation protects against burn-induced intestinal injury through activation of enteric glia cells[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2010, 299(6):G1308-1318. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00156.2010.
|
| [16] |
VAN LANDEGHEM L, CHEVALIER J, MAHÉ M M,et al. Enteric glia promote intestinal mucosal healing via activation of focal adhesion kinase and release of proEGF[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2011, 300(6):G976-987. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00427.2010.
|
| [17] |
STEINKAMP M, GEERLING I, SEUFFERLEIN T,et al. Glial-derived neurotrophic factor regulates apoptosis in colonic epithelial cells[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 124(7):1748-1757. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00404-9.
|
| [18] |
VON BOYEN G B, STEINKAMP M, REINSHAGEN M,et al. Nerve growth factor secretion in cultured enteric glia cells is modulated by proinflammatory cytokines[J]. J Neuroendocrinol, 2006, 18(11):820-825. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2006.01478.x.
|
| [19] |
VON BOYEN GEORG B T,NADINE D,CHRISTOPH H,et al. The endothelin axis influences enteric glia cell functions[J]. Med Sci Monit,2010,16(6):BR161-167.
|
| [20] |
LANGNESS S, KOJIMA M, COIMBRA R,et al. Enteric glia cells are critical to limiting the intestinal inflammatory response after injury[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2017, 312(3):G274-282. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00371.2016.
|
| [21] |
SURRENTI C, RENZI D, GARCEA M R,et al. Colonic vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in ulcerative colitis[J]. J Physiol Paris, 1993, 87(5):307-311. DOI: 10.1016/0928-4257(93)90037-T.
|
| [22] |
GROSS K J, POTHOULAKIS C. Role of neuropeptides in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2007, 13(7):918-932. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.20129.
|
| [23] |
GONZALEZ-REY E, FERNANDEZ-MARTIN A, CHORNY A,et al. Therapeutic effect of urocortin and adrenomedullin in a murine model of Crohn's disease[J]. Gut, 2006, 55(6):824-832. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.084525.
|
| [24] |
KOKKOTOU E, TORRES D, MOSS A C,et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 2-deficient mice have reduced intestinal inflammatory responses[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 177(5):3355-3361. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.5.3355.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
EYSSELEIN V E,NAST C C. Neuropeptides and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Z Gastroenterol Verh,1991,26:253-257.
|
| [27] |
DELGADO M, LECETA J, GANEA D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators by activated microglia[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2003, 73(1):155-164. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0702372.
|
| [28] |
LECETA J, GOMARIZ R P, MARTINEZ C,et al. Receptors and transcriptional factors involved in the anti-inflammatory activity of VIP and PACAP[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2000, 921:92-102. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06954.x.
|
| [29] |
DELGADO M, GANEA D. Cutting edge:is vasoactive intestinal peptide a type 2 cytokine?[J]. J Immunol, 2001, 166(5):2907-2912. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.2907.
|
| [30] |
CHANDRASEKHARAN B, NEZAMI B G, SRINIVASAN S. Emerging neuropeptide targets in inflammation:NPY and VIP[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2013, 304(11):G949-957. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00493.2012.
|
| [31] |
CAPETTINI L S, MONTECUCCO F, MACH F,et al. Role of renin-angiotensin system in inflammation,immunity and aging[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2012, 18(7):963-970. DOI: 10.2174/138161212799436593.
|
| [32] |
SHI Y Y, LIU T J, HE L,et al. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system promotes colitis development[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:27552. DOI: 10.1038/srep27552.
|
| [33] |
GARG M, ANGUS P W, BURRELL L M,et al. Review article:the pathophysiological roles of the renin-angiotensin system in the gastrointestinal tract[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2012, 35(4):414-428. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04971.x.
|
| [34] |
ZIZZO M G, AUTERI M, AMATO A,et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ type Ⅱ receptors and colonic dysmotility in 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2017, 29(6):10.1111/nmo.13019. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13019.
|
| [35] |
FERREIRA-DUARTE M, RODRIGUES-PINTO T, SOUSA T,et al. Interaction between the renin-angiotensin system and enteric neurotransmission contributes to colonic dysmotility in the TNBS-induced model of colitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(9):4836. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094836.
|
| [36] |
LUNDGREN O, JODAL M, JANSSON M,et al. Intestinal epithelial stem/progenitor cells are controlled by mucosal afferent nerves[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2):e16295. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016295.
|
| [37] |
BAGHDADI M B, AYYAZ A, COQUENLORGE S,et al. Enteric glial cell heterogeneity regulates intestinal stem cell niches[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(1):86-100.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.10.004
|
| [38] |
TAKAHASHI T, SHIRAISHI A, MURATA J. The coordinated activities of nAChR and Wnt signaling regulate intestinal stem cell function in mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(3):738. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030738.
|
| [39] |
BOROVIKOVA L V, IVANOVA S, ZHANG M,et al. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin[J]. Nature, 2000, 405(6785):458-462. DOI: 10.1038/35013070.
|
| [40] |
ZHU P P, LU T K, WU J Y,et al. Gut microbiota drives macrophage-dependent self-renewal of intestinal stem cells via niche enteric serotonergic neurons[J]. Cell Res, 2022, 32(6):555-569. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-022-00645-7.
|
| [41] |
SAVIDGE T C, NEWMAN P, POTHOULAKIS C,et al. Enteric glia regulate intestinal barrier function and inflammation via release of S-nitrosoglutathione[J]. Gastroenterology, 2007, 132(4):1344-1358. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.01.051.
|
| [42] |
CABARROCAS J, SAVIDGE T C, LIBLAU R S. Role of enteric glial cells in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Glia, 2003, 41(1):81-93. DOI: 10.1002/glia.10169.
|
| [43] |
SCHMITT M, SCHEWE M, SACCHETTI A,et al. Paneth cells respond to inflammation and contribute to tissue regeneration by acquiring stem-like features through SCF/c-kit signaling[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 24(9):2312-2328.e7. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.085.
|
| [44] |
KAWAGUCHI J, NICHOLS J, GIERL M S,et al. Isolation and propagation of enteric neural crest progenitor cells from mouse embryonic stem cells and embryos[J]. Development, 2010, 137(5):693-704. DOI: 10.1242/dev.046896.
|
| [45] |
METZGER M, CALDWELL C, BARLOW A J,et al. Enteric nervous system stem cells derived from human gut mucosa for the treatment of aganglionic gut disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 136(7):2214-2225.e1-3. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.048.
|
| [46] |
LINDLEY R M, HAWCUTT D B, CONNELL M G,et al. Human and mouse enteric nervous system neurosphere transplants regulate the function of aganglionic embryonic distal colon[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 135(1):205-216.e6. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.035.
|
| [47] |
HOTTA R, CHENG L S, GRAHAM H K,et al. Isogenic enteric neural progenitor cells can replace missing neurons and glia in mice with Hirschsprung disease[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2016, 28(4):498-512. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12744.
|
| [48] |
CHANG D F, ZUBER S M, GILLIAM E A,et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived enteric neural crest cells repopulate human aganglionic tissue-engineered intestine to form key components of the enteric nervous system[J]. J Tissue Eng, 2020, 11:2041731420905701. DOI: 10.1177/2041731420905701.
|
| [49] |
GAO H Y,WEI M F,WANG Y,et al. Differentiation of GDNF and NT-3 dual gene-modified rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into enteric neuron-like cells[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci,2012,32(1):87-91.
|
| [50] |
LIN R, DING Z, MA H,et al. In vitro conditioned bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote de novo functional enteric nerve regeneration,but not through direct-transdifferentiation[J]. Stem Cells, 2015, 33(12):3545-3557. DOI: 10.1002/stem.2197.
|
| [51] |
ROBINSON A M, SAKKAL S, PARK A,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and conditioned medium avert enteric neuropathy and colon dysfunction in guinea pig TNBS-induced colitis[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2014, 307(11):G1115-1129. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00174.2014.
|
| [52] |
STAVELY R, ROBINSON A M, MILLER S,et al. Allogeneic guinea pig mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate neurological changes in experimental colitis[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2015, 6:263. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-015-0254-3.
|
| [53] |
BOYER L, GHOREISHI M, TEMPLEMAN V,et al. Myenteric plexus injury and apoptosis in experimental colitis[J]. Auton Neurosci, 2005, 117(1):41-53. DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2004.10.006.
|
| [54] |
FURNESS J B. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 9(5):286-294. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.32.
|
| [55] |
HOU Q H, HUANG J X, AYANSOLA H,et al. Intestinal stem cells and immune cell relationships:potential therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11:623691. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.623691.
|
 )
)
 )
)