中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (04): 453-460.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.281
所属专题: 肥胖最新文章合集
杨媛1, 周光清2,*, 李宛霖1, 赵创艺1, 袁空军1
收稿日期:2021-05-08
修回日期:2021-07-21
出版日期:2022-02-05
发布日期:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
周光清
基金资助:Values of Different Obesity Indicators in Predicting the Risk of Hyperuricemia:a Comparative Study
YANG Yuan1,ZHOU Guangqing2*,LI Wanlin1,ZHAO Chuangyi1,Yuan Kongjun1
1.School of Health Management,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China
2.Health Management Center,Nanfang Hospital,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China
*Corresponding author:ZHOU Guangqing,Professor,Master supervisor;E-mail:13318898668@189.cn
Received:2021-05-08
Revised:2021-07-21
Published:2022-02-05
Online:2022-01-29
摘要: 背景高尿酸血症(HUA)已经超过糖尿病成为我国第二大代谢性疾病,其患病率呈逐年攀升态势且常伴发多系统疾病,如何有效预防其发生并控制其流行已成为我国亟待解决的重要公共卫生问题。目的明确不同肥胖指标〔腰围(WC)、体质指数(BMI)、腰高比(WHtR)、身体形态指数(ABSI)、身体圆度指数(BRI)、内脏脂肪指数(VAI)和脂质聚集指数(LAP)〕对HUA发生的影响,分析并比较不同肥胖指标对HUA发生风险的预测价值,旨在为HUA的早期预防及筛查提供参考与依据。方法采用整群抽样方法,选取2020年1—12月在广东省某三级甲等医院健康管理中心接受健康体检的体检者为研究对象。通过查阅健康管理中心的电子病历收集体检者的一般人口学、既往史、体格检查和实验室检查指标等资料,并计算BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP。采用二元Logistic回归探讨不同肥胖指标对HUA发生的影响,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价不同肥胖指标对HUA的预测价值并计算切点。结果共纳入32 374例健康体检者,检出HUA 13 546例,HUA检出率为41.84%,其中,男性和女性体检者HUA检出率分别为54.11%(10 026/18 530)和25.43%(3 520/13 844),男性HUA检出率高于女性(P<0.001)。男性HUA体检者WC、BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP均高于女性HUA体检者(P<0.001)。二元Logistic回归结果显示,在校正混杂变量后,WC、BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP均是男性和女性HUA发生的影响因素(P<0.001)。男性WC、BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP预测HUA发生风险的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.612、0.626、0.602、0.512、0.602、0.617和0.642,切点分别为80.5 cm、24.3 kg/m2、0.48、0.072、3.8、1.4和26.7;女性WC、BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP预测HUA发生风险的AUC分别为0.637、0.636、0.637、0.555、0.638、0.583和0.660,切点分别为72.5cm、22.7 kg/m2、0.47、0.074、4.2、1.3和15.3。无论在男性体检人群还是女性体检人群中,LAP预测HUA的AUC高于其他6项肥胖指标(P均<0.05),ABSI预测HUA的AUC低于其他6项肥胖指标(P均<0.05)。结论WC、BMI、WHtR、ABSI、BRI、VAI和LAP均是影响男性和女性HUA发生的因素,但不同肥胖指标对HUA的预测能力存在差异。无论对于男性还是女性,LAP均是预测HUA发生风险的最佳肥胖指标。
中图分类号:
YANG Yuan, ZHOU Guangqing, LI Wanlin, ZHAO Chuangyi, Yuan Kongjun.
Values of Different Obesity Indicators in Predicting the Risk of Hyperuricemia:a Comparative Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(04): 453-460.
| 组别 | 例数 | 男性 | BMI分级 | 腹型肥胖 | 高血压 | 糖尿病 | 高脂血症 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体质量过低 | 正常体质量 | 超重 | 肥胖 | |||||||
| 非HUA组 | 18 828 | 8 504(45.17) | 1 707(9.07) | 11 713(62.21) | 4 553(24.18) | 855(4.54) | 3 897(20.70) | 1 837(9.76) | 421(2.24) | 4 412(23.43) |
| HUA组 | 13 546 | 10 026(74.01) | 395(2.91) | 5 802(42.83) | 5 453(40.26) | 1 896(14.00) | 5 694(42.03) | 2 287(16.88) | 360(2.66) | 5 703(42.10) |
| χ2值 | 2 678.532 | 2 493.220 | 1 720.241 | 359.934 | 5.947 | 1 277.987 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.015 | <0.001 | ||||
表1 HUA组与非HUA组健康体检者的临床资料比较〔计数资料,n(%)〕
Table 1 Comparison of the clinical conditions of adult physical examinees with and without hyperuricemia(enumeration data)
| 组别 | 例数 | 男性 | BMI分级 | 腹型肥胖 | 高血压 | 糖尿病 | 高脂血症 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体质量过低 | 正常体质量 | 超重 | 肥胖 | |||||||
| 非HUA组 | 18 828 | 8 504(45.17) | 1 707(9.07) | 11 713(62.21) | 4 553(24.18) | 855(4.54) | 3 897(20.70) | 1 837(9.76) | 421(2.24) | 4 412(23.43) |
| HUA组 | 13 546 | 10 026(74.01) | 395(2.91) | 5 802(42.83) | 5 453(40.26) | 1 896(14.00) | 5 694(42.03) | 2 287(16.88) | 360(2.66) | 5 703(42.10) |
| χ2值 | 2 678.532 | 2 493.220 | 1 720.241 | 359.934 | 5.947 | 1 277.987 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.015 | <0.001 | ||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(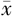 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 收缩压(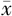 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 舒张压(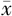 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | FBG (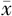 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TC (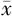 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TG (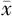 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C (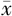 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非HUA组 | 18 828 | 39.9±12.1 | 119±15 | 72±11 | 5.2±1.1 | 5.09±1.00 | 1.25±0.97 | 3.16±0.76 |
| HUA组 | 13 546 | 40.5±12.4 | 125±15 | 76±11 | 5.3±1.0 | 5.35±1.06 | 1.80±1.46 | 3.39±0.79 |
| 检验统计量值 | -4.616a | -35.358a | -33.933a | -8.002a | -22.211a | -38.044b | -26.335a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表2 HUA组与非HUA组健康体检者的临床资料比较(计量资料)
Table 2 Comparison of the clinical conditions of adult physical examinees with and without hyperuricemia(measurement data)
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(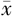 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 收缩压(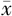 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 舒张压(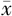 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | FBG (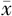 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TC (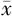 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TG (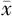 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C (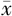 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非HUA组 | 18 828 | 39.9±12.1 | 119±15 | 72±11 | 5.2±1.1 | 5.09±1.00 | 1.25±0.97 | 3.16±0.76 |
| HUA组 | 13 546 | 40.5±12.4 | 125±15 | 76±11 | 5.3±1.0 | 5.35±1.06 | 1.80±1.46 | 3.39±0.79 |
| 检验统计量值 | -4.616a | -35.358a | -33.933a | -8.002a | -22.211a | -38.044b | -26.335a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 性别 | 例数 | WC(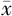 ±s,cm) ±s,cm) | BMI(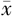 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | WHtR(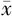 ±s) ±s) | ABSI(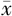 ±s) ±s) | BRI(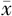 ±s) ±s) | VAI〔M(QR)〕 | LAP〔M(QR)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 10 026 | 84.2±8.9 | 25.1±3.2 | 0.49±0.05 | 0.075±0.004 | 3.3±1.0 | 1.6(1.5) | 29.8(34.1) |
| 女 | 3 520 | 74.3±9.1 | 22.9±3.5 | 0.47±0.06 | 0.073±0.005 | 2.9±1.1 | 1.2(1.2) | 16.8(24.4) |
| t(Z)值 | 55.667 | 31.932 | 21.310 | 23.042 | 20.031 | -17.003a | -27.685a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表3 不同性别HUA体检者肥胖指标比较
Table 3 Comparison of obesity indices among adult physical examinees with hyperuricemia by sex
| 性别 | 例数 | WC(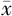 ±s,cm) ±s,cm) | BMI(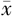 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | WHtR(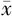 ±s) ±s) | ABSI(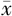 ±s) ±s) | BRI(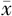 ±s) ±s) | VAI〔M(QR)〕 | LAP〔M(QR)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 10 026 | 84.2±8.9 | 25.1±3.2 | 0.49±0.05 | 0.075±0.004 | 3.3±1.0 | 1.6(1.5) | 29.8(34.1) |
| 女 | 3 520 | 74.3±9.1 | 22.9±3.5 | 0.47±0.06 | 0.073±0.005 | 2.9±1.1 | 1.2(1.2) | 16.8(24.4) |
| t(Z)值 | 55.667 | 31.932 | 21.310 | 23.042 | 20.031 | -17.003a | -27.685a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 自变量 | 男 | 女 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 原值进入 | 原值进入 |
| 高血压 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 糖尿病 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 高脂血症 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| WC(cm) | <76.0=1,76.0~81.0=2,>81.0~87.0=3,>87.0=4 | <65.0=1,65.0~69.0=2,>69.0~75.0=3,>75.0=4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | <22.3=1,22.3~24.2=2,>24.2~26.2=3,>26.2=4 | <19.6=1,19.6~21.2=2,>21.2~23.4=3,>23.4=4 |
| WHtR | <0.45=1,0.45~0.47=2,>0.47~0.51=3,>0.51=4 | <0.41=1,0.41~0.43=2,>0.43~0.47=3,>0.47=4 |
| ABSI | <0.072=1,0.072~0.074=2,>0.074~0.077=3,>0.077=4 | <0.070=1,0.070~0.071=2,>0.071~0.074=3,>0.074=4 |
| BRI | <3.6=1,3.6~3.9=2,>3.9~4.3=3,>4.3=4 | <3.4=1,3.4~3.8=2,>3.8~4.3=3,>4.3=4 |
| VAI | <0.9=1,0.9~1.3=2,>1.3~2.1=3,>2.1=4 | <0.8=1,0.8~1.0=2,>1.0~1.5=3,>1.5=4 |
| LAP | <12.8=1,12.8~24.2=2,>24.2~42.6=3,>42.6=4 | <5.7=1,5.7~10.8=2,>10.8~20.4=3,>20.4=4 |
表4 不同肥胖指标对HUA影响的二元Logistic回归分析变量赋值
Table 4 Assignment of each obesity variable in the binary logistic regression analysis
| 自变量 | 男 | 女 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 原值进入 | 原值进入 |
| 高血压 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 糖尿病 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 高脂血症 | 无=0,有=1 | 无=0,有=1 |
| WC(cm) | <76.0=1,76.0~81.0=2,>81.0~87.0=3,>87.0=4 | <65.0=1,65.0~69.0=2,>69.0~75.0=3,>75.0=4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | <22.3=1,22.3~24.2=2,>24.2~26.2=3,>26.2=4 | <19.6=1,19.6~21.2=2,>21.2~23.4=3,>23.4=4 |
| WHtR | <0.45=1,0.45~0.47=2,>0.47~0.51=3,>0.51=4 | <0.41=1,0.41~0.43=2,>0.43~0.47=3,>0.47=4 |
| ABSI | <0.072=1,0.072~0.074=2,>0.074~0.077=3,>0.077=4 | <0.070=1,0.070~0.071=2,>0.071~0.074=3,>0.074=4 |
| BRI | <3.6=1,3.6~3.9=2,>3.9~4.3=3,>4.3=4 | <3.4=1,3.4~3.8=2,>3.8~4.3=3,>4.3=4 |
| VAI | <0.9=1,0.9~1.3=2,>1.3~2.1=3,>2.1=4 | <0.8=1,0.8~1.0=2,>1.0~1.5=3,>1.5=4 |
| LAP | <12.8=1,12.8~24.2=2,>24.2~42.6=3,>42.6=4 | <5.7=1,5.7~10.8=2,>10.8~20.4=3,>20.4=4 |
| 自变量 | b | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.418 | 0.043 | 95.160 | 1.519(1.397,1.653) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.685 | 0.044 | 242.224 | 1.984(1.820,2.162) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.000 | 0.046 | 467.377 | 2.719(2.483,2.977) | <0.001 | |
| BMI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.498 | 0.043 | 135.011 | 1.646(1.513,1.790) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.719 | 0.044 | 269.891 | 2.053(1.884,2.237) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.107 | 0.046 | 576.701 | 3.024(2.763,3.310) | <0.001 | |
| WHtR(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.404 | 0.043 | 87.593 | 1.498(1.377,1.631) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.675 | 0.042 | 257.745 | 1.965(1.809,2.134) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.013 | 0.048 | 441.825 | 2.754(2.506,3.027) | <0.001 | |
| ABSI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.138 | 0.042 | 10.577 | 1.148(1.056,1.248) | 0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.199 | 0.043 | 21.333 | 1.220(1.121,1.327) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.206 | 0.045 | 20.855 | 1.228(1.124,1.341) | <0.001 | |
| BRI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.432 | 0.043 | 100.176 | 1.540(1.415,1.676) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.693 | 0.045 | 240.956 | 2.000(1.832,2.183) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.039 | 0.048 | 469.027 | 2.825(2.572,3.104) | <0.001 | |
| VAI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.356 | 0.042 | 70.202 | 1.427(1.313,1.551) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.718 | 0.044 | 271.485 | 2.051(1.883,2.234) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.990 | 0.051 | 380.463 | 2.692(2.437,2.973) | <0.001 | |
| LAP(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.515 | 0.043 | 144.697 | 1.674(1.539,1.821) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.909 | 0.045 | 414.750 | 2.483(2.275,2.710) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.387 | 0.052 | 724.426 | 4.004(3.619,44.429) | <0.001 | |
表5 不同肥胖指标对男性体检人群发生HUA影响的二元Logistic回归分析
Table 5 Results of binary Logistic regression analysis of the association of different obesity indices with hyperuricemia in adult male physical examinees
| 自变量 | b | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.418 | 0.043 | 95.160 | 1.519(1.397,1.653) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.685 | 0.044 | 242.224 | 1.984(1.820,2.162) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.000 | 0.046 | 467.377 | 2.719(2.483,2.977) | <0.001 | |
| BMI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.498 | 0.043 | 135.011 | 1.646(1.513,1.790) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.719 | 0.044 | 269.891 | 2.053(1.884,2.237) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.107 | 0.046 | 576.701 | 3.024(2.763,3.310) | <0.001 | |
| WHtR(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.404 | 0.043 | 87.593 | 1.498(1.377,1.631) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.675 | 0.042 | 257.745 | 1.965(1.809,2.134) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.013 | 0.048 | 441.825 | 2.754(2.506,3.027) | <0.001 | |
| ABSI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.138 | 0.042 | 10.577 | 1.148(1.056,1.248) | 0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.199 | 0.043 | 21.333 | 1.220(1.121,1.327) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.206 | 0.045 | 20.855 | 1.228(1.124,1.341) | <0.001 | |
| BRI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.432 | 0.043 | 100.176 | 1.540(1.415,1.676) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.693 | 0.045 | 240.956 | 2.000(1.832,2.183) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.039 | 0.048 | 469.027 | 2.825(2.572,3.104) | <0.001 | |
| VAI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.356 | 0.042 | 70.202 | 1.427(1.313,1.551) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.718 | 0.044 | 271.485 | 2.051(1.883,2.234) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.990 | 0.051 | 380.463 | 2.692(2.437,2.973) | <0.001 | |
| LAP(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.515 | 0.043 | 144.697 | 1.674(1.539,1.821) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.909 | 0.045 | 414.750 | 2.483(2.275,2.710) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.387 | 0.052 | 724.426 | 4.004(3.619,44.429) | <0.001 | |
| 自变量 | b | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.198 | 0.062 | 10.074 | 1.218(1.079,1.377) | 0.002 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.537 | 0.061 | 76.644 | 1.710(1.517,1.929) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.171 | 0.064 | 334.771 | 3.225(2.845,3.656) | <0.001 | |
| BMI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.161 | 0.063 | 6.606 | 1.175(1.039,1.329) | 0.010 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.404 | 0.062 | 42.952 | 1.498(1.327,1.690) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.030 | 0.061 | 286.866 | 2.802(2.487,3.157) | <0.001 | |
| WHtR(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.269 | 0.061 | 19.715 | 1.309(1.162,1.474) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.558 | 0.060 | 87.540 | 1.747(1.554,1.936) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.186 | 0.064 | 338.740 | 3.274(2.885,3.715) | <0.001 | |
| ABSI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | -0.118 | 0.058 | 4.061 | 0.889(0.793,0.997) | 0.044 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.012 | 0.058 | 0.041 | 1.012(0.903,1.133) | 0.839 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.249 | 0.059 | 17.802 | 1.283(1.143,1.441) | <0.001 | |
| BRI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.238 | 0.063 | 14.245 | 1.269(1.121,1.436) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.545 | 0.062 | 75.971 | 1.724(1.525,1.949) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.127 | 0.065 | 299.524 | 3.086(2.717,3.507) | <0.001 | |
| VAI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | -0.007 | 0.059 | 0.013 | 0.993(0.884,1.116) | 0.908 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.143 | 0.058 | 6.067 | 1.154(1.030,1.294) | 0.014 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.490 | 0.058 | 71.780 | 1.632(1.457,1.828) | <0.001 | |
| LAP(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.197 | 0.063 | 9.838 | 1.218(1.077,1.378) | 0.002 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.601 | 0.062 | 93.166 | 1.824(1.614,2.061) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.367 | 0.066 | 434.460 | 3.922(3.449,4.460) | <0.001 | |
表6 不同肥胖指标对女性体检人群发生HUA影响的二元Logistic回归分析
Table 6 Results of binary Logistic regression analysis of the association of different obesity indices with hyperuricemia in adult female physical examinees
| 自变量 | b | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.198 | 0.062 | 10.074 | 1.218(1.079,1.377) | 0.002 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.537 | 0.061 | 76.644 | 1.710(1.517,1.929) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.171 | 0.064 | 334.771 | 3.225(2.845,3.656) | <0.001 | |
| BMI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.161 | 0.063 | 6.606 | 1.175(1.039,1.329) | 0.010 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.404 | 0.062 | 42.952 | 1.498(1.327,1.690) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.030 | 0.061 | 286.866 | 2.802(2.487,3.157) | <0.001 | |
| WHtR(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.269 | 0.061 | 19.715 | 1.309(1.162,1.474) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.558 | 0.060 | 87.540 | 1.747(1.554,1.936) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.186 | 0.064 | 338.740 | 3.274(2.885,3.715) | <0.001 | |
| ABSI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | -0.118 | 0.058 | 4.061 | 0.889(0.793,0.997) | 0.044 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.012 | 0.058 | 0.041 | 1.012(0.903,1.133) | 0.839 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.249 | 0.059 | 17.802 | 1.283(1.143,1.441) | <0.001 | |
| BRI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.238 | 0.063 | 14.245 | 1.269(1.121,1.436) | <0.001 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.545 | 0.062 | 75.971 | 1.724(1.525,1.949) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.127 | 0.065 | 299.524 | 3.086(2.717,3.507) | <0.001 | |
| VAI(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | -0.007 | 0.059 | 0.013 | 0.993(0.884,1.116) | 0.908 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.143 | 0.058 | 6.067 | 1.154(1.030,1.294) | 0.014 | |
| 第4分位组 | 0.490 | 0.058 | 71.780 | 1.632(1.457,1.828) | <0.001 | |
| LAP(以第1分位组为参照) | ||||||
| 第2分位组 | 0.197 | 0.063 | 9.838 | 1.218(1.077,1.378) | 0.002 | |
| 第3分位组 | 0.601 | 0.062 | 93.166 | 1.824(1.614,2.061) | <0.001 | |
| 第4分位组 | 1.367 | 0.066 | 434.460 | 3.922(3.449,4.460) | <0.001 | |
| 指标 | 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC(95%CI) | P值 | 切点 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | AUC(95%CI) | P值 | 切点 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | |
| WC | 0.612(0.605,0.619) | <0.001 | 80.5 cm | 0.66 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.637(0.629,0.645) | <0.001 | 72.5 cm | 0.54 | 0.67 | 0.21 |
| BMI | 0.626(0.619,0.633) | <0.001 | 24.3 kg/m2 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.636(0.628,0.644) | <0.001 | 22.7 kg/m2 | 0.48 | 0.72 | 0.21 |
| WHtR | 0.602(0.594,0.609) | <0.001 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.637(0.629,0.646) | <0.001 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.73 | 0.21 |
| ABSI | 0.512(0.505,0.520) | <0.001 | 0.072 | 0.80 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.555(0.547,0.564) | <0.001 | 0.074 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 0.10 |
| BRI | 0.602(0.595,0.609) | <0.001 | 3.8 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 0.638(0.630,0.646) | <0.001 | 4.2 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.20 |
| VAI | 0.617(0.610,0.625) | <0.001 | 1.4 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.583(0.575,0.591) | <0.001 | 1.3 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.13 |
| LAP | 0.642(0.634,0.649) | <0.001 | 26.7 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.21 | 0.660(0.652,0.668) | <0.001 | 15.3 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.25 |
表7 不同性别体检人群不同肥胖指标预测HUA的价值比较
Table 7 The AUC with optimal cut point values of different obesity indices for predicting hyperuricemia in adult physical examinees by sex
| 指标 | 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC(95%CI) | P值 | 切点 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | AUC(95%CI) | P值 | 切点 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | |
| WC | 0.612(0.605,0.619) | <0.001 | 80.5 cm | 0.66 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.637(0.629,0.645) | <0.001 | 72.5 cm | 0.54 | 0.67 | 0.21 |
| BMI | 0.626(0.619,0.633) | <0.001 | 24.3 kg/m2 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.636(0.628,0.644) | <0.001 | 22.7 kg/m2 | 0.48 | 0.72 | 0.21 |
| WHtR | 0.602(0.594,0.609) | <0.001 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.637(0.629,0.646) | <0.001 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.73 | 0.21 |
| ABSI | 0.512(0.505,0.520) | <0.001 | 0.072 | 0.80 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.555(0.547,0.564) | <0.001 | 0.074 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 0.10 |
| BRI | 0.602(0.595,0.609) | <0.001 | 3.8 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 0.638(0.630,0.646) | <0.001 | 4.2 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.20 |
| VAI | 0.617(0.610,0.625) | <0.001 | 1.4 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.583(0.575,0.591) | <0.001 | 1.3 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.13 |
| LAP | 0.642(0.634,0.649) | <0.001 | 26.7 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.21 | 0.660(0.652,0.668) | <0.001 | 15.3 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.25 |
| 指标 | 男 | 女 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC | BMI | WHtR | ABSI | BRI | VAI | LAP | WC | BMI | WHtR | ABSI | BRI | VAI | LAP | |
| WC | 1 | 5.657a | 6.757a | 26.213a | 6.516a | 1.275 | 11.766a | 1 | 0.376 | 0.029 | 15.924a | 0.170 | 8.362a | 9.177a |
| BMI | - | 1 | 9.723a | 20.229a | 9.550a | 1.947 | 4.917a | - | 1 | 0.406 | 10.614a | 0.481 | 7.897a | 6.061a |
| WHtR | - | - | 1 | 23.284a | 2.004a | 3.597a | 14.818a | - | - | 1 | 15.664a | 0.733 | 8.403a | 18.129a |
| ABSI | - | - | - | 1 | 23.426a | 20.383a | 29.756a | - | - | - | 1 | 15.703a | 3.877a | 18.903a |
| BRI | - | - | - | - | 1 | 3.482a | 14.657a | - | - | - | - | 1 | 8.443a | 8.072a |
| VAI | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 9.397a | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 13.049a |
| LAP | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
表8 不同性别体检人群肥胖指标预测HUA的AUC比较(Z值)
Table 8 Pairwise comparisons of the AUC of obesity indices in predicting hyperuricemia in adult physical examinees by gender (Z values)
| 指标 | 男 | 女 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC | BMI | WHtR | ABSI | BRI | VAI | LAP | WC | BMI | WHtR | ABSI | BRI | VAI | LAP | |
| WC | 1 | 5.657a | 6.757a | 26.213a | 6.516a | 1.275 | 11.766a | 1 | 0.376 | 0.029 | 15.924a | 0.170 | 8.362a | 9.177a |
| BMI | - | 1 | 9.723a | 20.229a | 9.550a | 1.947 | 4.917a | - | 1 | 0.406 | 10.614a | 0.481 | 7.897a | 6.061a |
| WHtR | - | - | 1 | 23.284a | 2.004a | 3.597a | 14.818a | - | - | 1 | 15.664a | 0.733 | 8.403a | 18.129a |
| ABSI | - | - | - | 1 | 23.426a | 20.383a | 29.756a | - | - | - | 1 | 15.703a | 3.877a | 18.903a |
| BRI | - | - | - | - | 1 | 3.482a | 14.657a | - | - | - | - | 1 | 8.443a | 8.072a |
| VAI | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 9.397a | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 13.049a |
| LAP | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| [1] | WU J, QIU L, CHENG X Q,et al. Hyperuricemia and clustering of cardiovascular risk factors in the Chinese adult population[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):5456. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-05751-w. |
| [2] | 李静. 高尿酸血症的流行病学研究[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2016,21(2):83-86. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2016.02.001. |
| [3] | 刘敏,孟娟. 基于全科医生视角的《2020年美国风湿病学会痛风治疗指南》解读[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(25):3148-3153. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.133. |
| [4] | 于宏杰,钟培松,袁红,等. 肥胖指标预测高尿酸血症风险研究[J]. 预防医学,2020,32(8):846-850. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2020.08.022. |
| [5] | 苏健,吕淑荣,杨婕,等. 江苏省成人脂质蓄积指数与高血压和糖尿病患病风险关系的研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2018,22(3):217-221. DOI:10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.03.002. |
| [6] | ZHANG J, FANG L, QIU L,et al. Comparison of the ability to identify arterial stiffness between two new anthropometric indices and classical obesity indices in Chinese adults[J]. Atherosclerosis,2017,263(1):263-271. DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.06.031. |
| [7] | KOULI G M, PANAGIOTAKOS D B, KYROU I,et al. Visceral adiposity index and 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence:the ATTICA study[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovas,2017,27(10):881-889. DOI:10.1016/j.numecd.2017.06.015. |
| [8] | 黄俊轩,张晓霞,彭欣,等. 脂质蓄积指数对珠三角社区人群2型糖尿病患病风险的预测价值[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(24):3012-3017. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.017. |
| [9] | KRAKAUER N Y, KRAKAUER J C. A new body shape index predicts mortality hazard independently of body mass index[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(7):e39504. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0039504. |
| [10] | THOMAS D M, BREDLAU C, WESTPHAL A B,et al. Relationships between body roundness with body fat and visceral adipose tissue emerging from a new geometrical model[J]. Obesity,2013,21(11):2264-2271. DOI:10.1002/oby.20408. |
| [11] | AMATO M C, CARLA G, MASSIMO G,et al. Visceral adiposity index:a reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk[J]. Diabetes Care,2010,33(4):920-922. DOI:10.2337/dc09-1825. |
| [12] | KAHN H S. "The lipid accumulation product" performs better than the body mass index for recognizing cardiovascular risk:a population-based comparison[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disor,2005,5(1):87-97. DOI:10.1186/1471-2261-5-26. |
| [13] | 中华医学会内分泌学分会. 高尿酸血症和痛风治疗的中国专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2013,29(11):913-920. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2013.11.001. |
| [14] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2018,38(4):292-344. DOI:10.19538/j.nk2018040108. |
| [15] | 《中国高血压防治指南》修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南2018年修订版[J]. 心脑血管病防治,2019,19(1):1-44. |
| [16] | 中国成人血脂异常防治指南制订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2007,35(5):390-419. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0253-3758.2007.05.003. |
| [17] | 中华医学会内分泌学分会肥胖学组. 中国成人肥胖症防治专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2011,27(9):711-717. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2011.09.003. |
| [18] | 宇传华. ROC分析方法及其在医学研究中的应用[D]. 西安:第四军医大学,2000. |
| [19] | 于亮,王宗站. 青岛市市南区老年人高尿酸血症与代谢综合征的关系分析[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2019,21(10):1092-1093. DOI:10.3969/ji.ssn.1009-0126.2019.10.021. |
| [20] | 黄佳乐,王新月,李红卫. 厦门市居民高尿酸血症与膳食嘌呤摄入的相关性研究[J]. 营养学报,2019,41(1):20-23. DOI:10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.2019.01.006. |
| [21] | 陈少雄,覃壮丽,李晓敏,等. 广东佛山市高尿酸血症与血清肌酐、血糖及高血压的分析[J]. 新医学,2016,47(3):175-178. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2016.03.010. |
| [22] | 宋康,姚勇利,魏兰,等. 青海省汉族居民高尿酸血症的患病情况分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2018,45(22):4094-4096. |
| [23] | 妥娅,任晓岚,李国菊,等. 甘肃地区城镇汉族成年人高尿酸血症现状及影响因素[J]. 中国公共卫生,2018,34(6):808-811. DOI:10.11847/zgggws1117951. |
| [24] | 韩尚廷,许梅花. 膳食营养素与高尿酸血症关系的研究进展[J]. 现代预防医学,2019,46(22):4070-4072. |
| [25] | 曲建昌,窦京涛,王安平,等. 社区老年人群尿酸与代谢综合征关系的研究[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2020,22(9):900-903. DOI:10.3969/ji.ssn1009-0126.2020.09.002. |
| [26] | 李林,朱小霞,戴宇翔,等. 中国高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(3):235-248. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.03.021. |
| [27] | 吴珊珊,叶山东,邢燕,等. 高尿酸血症与体质量指数和脂代谢紊乱关系的临床研究[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2016,19(3):232-235. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6790.2016.03.003. |
| [28] | REILLY J J, EL-HAMDOUCHI A, DIOUF A,et al. Determining the worldwide prevalence of obesity[J]. Lancet,2018,391(10132):1773-1774. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30794-3. |
| [29] | ZHANG N, CHANG Y, GUO X,et al. A body shape index and body roundness index:two new body indices for detecting association between obesity and hyperuricemia in rural area of China[J]. Eur J Intern Med,2016,29(6):32-36. DOI:10.1016/j.ejim.2016.01.019. |
| [30] | HUANG Z P, HUANG B X, ZHANG H,et al. Waist-to-height ratio is a better predictor of hyperuricemia than body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese[J]. Ann Nutr Metab,2019,75(3):187-194. DOI:10.1159/000504282. |
| [31] | 马玲,于飞,王莉,等. 肥胖指标在研究高尿酸血症危险因素中的意义[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2013,36(2):204-207. |
| [32] | 周艾婧,潘庆,李爱玲,等. 肥胖及代谢相关指标对凉山彝族农村居民高尿酸血症预测价值[J]. 中国公共卫生,2015,31(12):1646-1650. DOI:10.11847/zgggws2015-31-12-36. |
| [33] | 张玄娥,顾蕾,张晓燕,等. 上海杨浦中老年社区人群内脏脂肪指数和脂质蓄积指数与血尿酸的相关性[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2020,41(2):185-191. DOI:10.16118/j.1008-0392.2020.02.008 |
| [34] | 刘晨,张黎军. 新型体脂指数脂质蓄积指数和内脏脂肪指数的相关研究进展[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2016,24(11):1032-1035. DOI:10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-6187.2016.11.16. |
| [35] | 金昕晔,邹大进. 国内外肥胖症相关指南评介[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2012,32(10):757-760. |
| [36] | ZHEN L X, HUA L H, SHAN H,et al. Association between hyperuricemia and nontraditional adiposity indices[J]. Clin Rheumatol,2019,38(4):1055-1062. |
| [1] | 王秋实, 李虹伟. CHA2DS2-VASc卒中风险评分对冠心病三支血管或左主干病变患者主要不良心血管事件的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4130-4136. |
| [2] | 张鹏, 高鹰, 杨洪喜, 万春晓. 中国长寿地区老年人血尿酸水平与慢性肾脏病发病风险研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3884-3889. |
| [3] | 王珍, 申国旗, 李亚南, 朱英华, 仇航, 郑迪, 徐通达, 李文华. 急性心肌梗死患者行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后发生对比剂急性肾损伤风险预测模型的建立与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3650-3656. |
| [4] | 何应梅, 贾雪, 朱国军, 刘冰. 血清尿酸纵向轨迹对新发高三酰甘油血症的影响:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3636-3639. |
| [5] | 李梓盟, 王荣, 陈帅, 赵彩丽, 王晓聪, 温雅璐, 刘龙. 基于metaPRS与APOEε4优化轻度认知障碍遗传风险统计建模策略的应用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3104-3111. |
| [6] | 沈傲梅, 路潜, 符鑫, 韦小夏, 卞静如, 张丽媛, 强万敏, 庞冬. 基于前瞻性队列研究的Meta分析构建乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿风险预测模型研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(17): 2078-2088. |
| [7] | 宋华隆, 高鹰. 血尿酸水平与2型糖尿病发病风险的关联队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(15): 1831-1839. |
| [8] | 辛家东, 周嘉宝, 吴志远, 张栩铭, 高建东. 尿酸排泄及其相关转运蛋白在高尿酸血症中的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(15): 1916-1922. |
| [9] | 陈一佳, 戚圣香, 杜金玲, 王琛琛, 周海茸, 叶青, 秦真真, 苏健, 武鸣, 洪忻. 心脏代谢指数对体质量正常人群代谢异常表型的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(14): 1716-1725. |
| [10] | 陈颖, 王子涵, 薛崇祥, 陶诗怡, 孙梓宜, 黄力. 踝肱指数和肱踝动脉脉搏波速度与血管舒张功能联合载脂蛋白B与载脂蛋白A-1比值对中青年冠心病血瘀证的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(14): 1726-1732. |
| [11] | 赵伟, 杨珊珊, 唐荣杰, 杨芳, 孙锋, 廉秋芳. 甲状腺功能正常的高血压患者血清甲状腺激素水平与高尿酸血症的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(35): 4394-4398,4405. |
| [12] | 秦克, 李同林, 宫帅, 江美芳. 血清miR-210、miR-181a表达水平与慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期患者糖皮质激素治疗效果的关系及其预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(24): 3013-3017. |
| [13] | 饶艳, 姚梅琪, 江大为, 毛翠. 脑卒中后发生急性肾损伤风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(23): 2885-2891. |
| [14] | 桂晶晶, 金阿全, 万瑜, 赵轩, 朱琳杰, 赵逸东, 姚嘉琦, 张力文, 黄志英. 血栓弹力图在肺炎支原体肺炎患儿病情评估中的应用价值[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(21): 2624-2628. |
| [15] | 刘振宇, 王江敏, 魏云鹏, 应华清. 社区居民睡眠时间和高尿酸血症的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(14): 1681-1686. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





