中国全科医学 ›› 2026, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (09): 1217-1224.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0675
• 综述与专论 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-12-10
修回日期:2025-04-06
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-28
通讯作者:
高曦
作者贡献:
杨阳、高曦进行文章的构思与设计;杨阳进行文献、资料收集及整理,撰写论文;高曦进行文章的可行性分析,论文的修订,负责文章的质量控制及审校,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:Received:2024-12-10
Revised:2025-04-06
Published:2026-03-20
Online:2026-01-28
Contact:
GAO Xi
摘要: 骨质疏松是一种临床常见的骨骼疾病,由多种因素引发,其主要机制是改变机体炎性微环境,促使破骨细胞生成增多,进而导致骨吸收增加、骨量减少。反常骨形成则是一种通过调控部分成骨细胞凋亡,进而影响巨噬细胞胞葬以促进成骨细胞分化,调节骨形成并增加骨量的过程。成骨细胞主要参与骨形成,破骨细胞参与骨吸收,二者共同介导骨稳态的调节。在正常稳态下,发生骨重塑的成骨细胞中约有50%会发生凋亡。当促成骨细胞部分凋亡引发反常骨形成时,巨噬细胞被募集并发挥胞葬作用。在胞葬作用下,巨噬细胞极化为M2型。M2巨噬细胞通过调节成骨细胞分化并抑制破骨细胞生成,在发挥骨吸收抑制作用的同时,使新鲜成骨细胞迅速占据原陈旧成骨细胞的位置继续参与骨形成。由于新鲜成骨细胞的骨形成量高于陈旧成骨细胞,所以会出现骨量较凋亡前显著增加。对出现骨质疏松的机体促进部分成骨细胞凋亡或许能够反向增加骨量,反常骨形成有望成为治疗骨质疏松的新方向。因此,本文提出通过"反常骨形成"治疗骨质疏松,并分析其相关机制,以期为骨质疏松相关研究及治疗提供新的思路。
中图分类号:
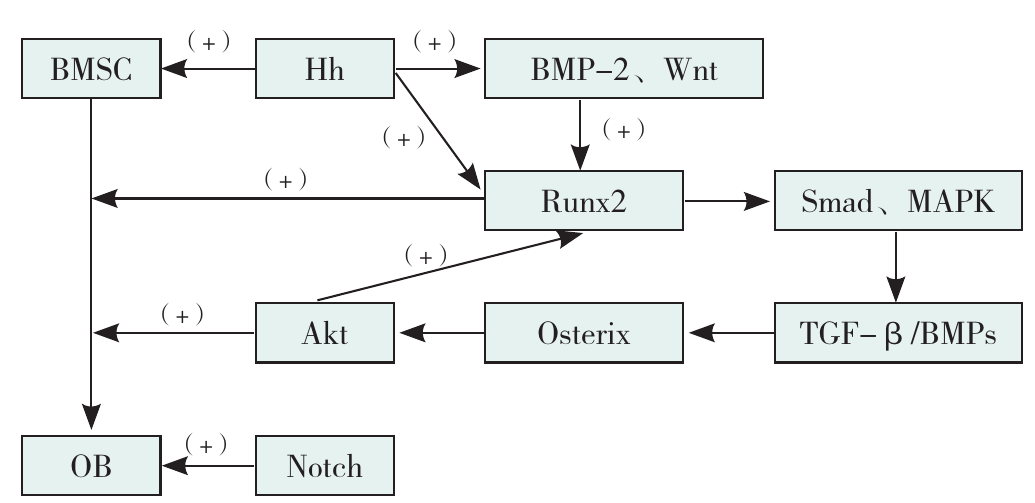
图1 BMSC分化为OB的相关机制注:BMSC=骨髓间充质干细胞,OB=成骨细胞,Hh=Hedgehog信号通路,BMP-2=骨形态发生蛋白2,Akt=蛋白激酶B,Wnt=经典Wnt信号通路,Smad=经典Smad依赖信号通路,MAPK=p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路,TGF-β/BMPs=转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白。
Figure 1 Mechanisms involved in the differentiation of BMSC into OB
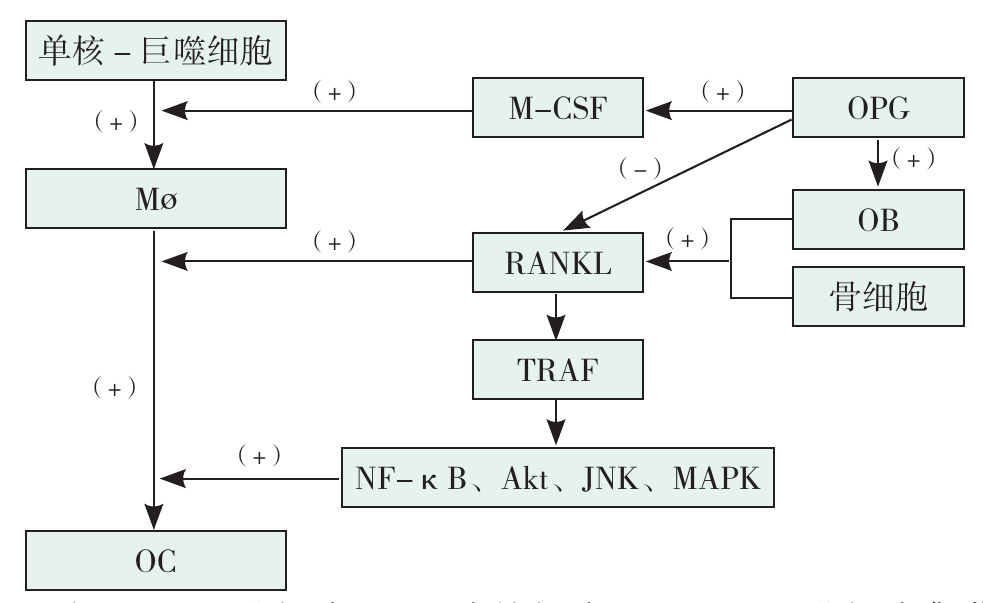
图2 OC分化相关机制注:Mø=巨噬细胞,OC=破骨细胞,M-CSF=巨噬细胞集落刺激因子,OPG=骨保护素,RANKL=核因子受体活化因子配体,TRAF=肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子,NF-κB=核因子κB,JNK=c-Jun氨基末端激酶。
Figure 2 OC differentiation-related mechanisms
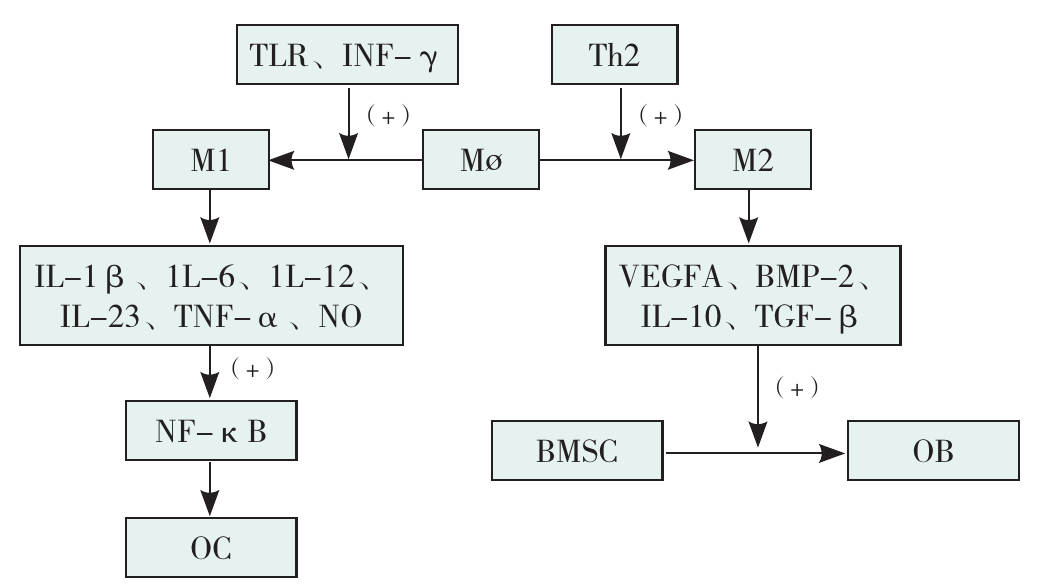
图3 巨噬细胞极化与OB、OC分化的相关机制注:TLR=Toll样受体,IFN-γ=干扰素γ,M1=经典活化的巨噬细胞,M2=选择性活化的巨噬细胞,IL-1α=白介素1α,IL-1β=白介素1β,IL-6=白介素6,IL-12=白介素12,IL-23=白介素23,TNF-α=肿瘤坏死因子α,NO=一氧化氮,VEGFA=血管内皮生长因子A,IL-10=白介素10。
Figure 3 Mechanisms associated with macrophage polarization involvement in OB and OC differentiation
| [1] |
中华医学会物理医学与康复学分会. 骨质疏松症康复治疗指南(2024版)[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2024, 24(6): 626-636.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2022, 15(6): 573-611.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
梁松林, 成文翔, 张鹏, 等. 成骨细胞程序性死亡的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2024, 30(3): 385-390.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
童安莉, 陈璐璐, 丁桂芝. 成骨细胞骨形成机制研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 1999, 5(3): 60-64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.1999.03.020.
|
| [12] |
陈永强, 戴尅戎, 裘世静. 骨改建的细胞学基础[J]. 国外医学创伤与外科基本问题分册, 1989, 10(2): 85-89.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
汪小敏, 王祥, 曹林忠, 等. RANK/RANKL/OPG信号轴在骨质疏松与炎性肠病相关性中的作用机制[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2017, 10(5): 499-504. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2017.05.012.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] | |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
耿锐, 陆军. 巨噬细胞的胞葬作用与炎症性疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2023, 42(3): 466-474.
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
李敏, 林俊. 细胞凋亡途径及其机制[J]. 国际妇产科学杂志, 2014, 41(2): 103-107.
|
| [61] |
|
| [1] | 张媛, 陈冠华, 吕珊珊, 荆亚莉. 甲状腺功能正常的2型糖尿病患者甲状腺激素敏感性指标与骨质疏松症的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3653-3659. |
| [2] | 赵玉晴, 王伟, 陈立沅, 油惠娟, 魏莹, 王清路, 杨风英. 肝脏巨噬细胞极化:运动防治非酒精性脂肪性肝病的新靶向[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3456-3465. |
| [3] | 熊鑫, 李洋, 石峰, 杨连, 段维, 陈蓓, 李勇, 赵林伟, 付泉水, 范小萍, 杨国庆. 基于人工智能的胸腰椎骨密度测定系统及其校准研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2398-2406. |
| [4] | 谭文彬, 李佳, 刘明玉, 路永欣, 程雅欣. 神经系统疾病及相关治疗药物对骨质疏松症影响的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2092-2100. |
| [5] | 贺婷, 李佳, 谭文彬. 循环系统疾病与继发性骨质疏松症的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2101-2112. |
| [6] | 陈钡钡, 李佳, 谭文彬. 内分泌代谢系统疾病与继发性骨质疏松症的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2082-2091. |
| [7] | 李佳, 谭文彬. 继发性骨质疏松症防治困境与对策探究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2075-2081. |
| [8] | 孙清, 吴玉霄, 崔立敏. 中国2型糖尿病患者肌少-骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1520-1526. |
| [9] | 刘洋晓讴, 孙艳格, 于溯, 杜雪平, 黄凯, 闫岩, 李超. FRAX对北京地区居民骨折风险的预测价值及干预阈值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(07): 838-843. |
| [10] | 任凌萱, 卢子琪, 齐威, 冯志杰. 基于单细胞转录组学测序的巨噬细胞在肝硬化-肝癌疾病进展中的功能研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(29): 3654-3663. |
| [11] | 杨超富, 谭国庆, 徐展望. 骨质疏松中衰老相关分泌表型调控机制的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(29): 3685-3695. |
| [12] | 苏瑾, 寿涓, 顾文钦, 易春涛, 徐莉苹, 程莉莉, 丁宏娟, 周鹏, 吴颖华, 秦杰, 薛斌, 魏百川, 王谦, 彭燕, 程毅敏, 杨蓝, 卫洋洋, 王磊, 祁瑨麟, 邵迎, 蔡立明. 基于Markov链的上海市枫林社区骨质疏松全人群防治工作的成本效果分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(22): 2789-2796. |
| [13] | 何海洋, 杨嘉玲, 雷迅. 绝经后女性骨质疏松症患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(11): 1370-1379. |
| [14] | 彭逸伦, 李杨, 王晓桃. 多发性骨髓瘤细胞通过PI3K/AKT信号通路促进M2巨噬细胞极化的机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 978-984. |
| [15] | 曾令烽, 杨伟毅, 梁桂洪, 肖萧, 罗明辉, 潘建科, 韩燕鸿, 黄和涛, 赵金龙, 徐南俊, 周光辉, 张献泉, 梁伟雄, 欧爱华, 刘军, 广东省中医药学会骨关节退变与损伤专业委员会. 骨质疏松高危人群中医症状评估专家问卷调查和结果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 2986-2991. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||






