中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (31): 3961-3967.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0921
收稿日期:2024-04-10
修回日期:2024-11-08
出版日期:2025-11-05
发布日期:2025-09-23
通讯作者:
王海蓉
作者贡献:
张佳、王海蓉提出研究思路,设计研究方案;张佳、赵婧、苏怡帆负责数据收集、采集和统计学分析;张佳负责论文起草、绘制图表等;王海蓉负责最终版本修订,对论文整体负责。
基金资助:
ZHANG Jia1, WANG Hairong2,*( ), ZHAO Jing1, SU Yifan1
), ZHAO Jing1, SU Yifan1
Received:2024-04-10
Revised:2024-11-08
Published:2025-11-05
Online:2025-09-23
Contact:
WANG Hairong
摘要: 背景 肺癌是导致中国癌症死亡的首要原因。高危人群早期筛查是发现肺癌,改善预后最有效且关键的方法。目前对于肺癌患者一级亲属这一集中高危群体的筛查行为影响因素研究少有报道。 目的 采用多因素Logistic回归分析和决策树模型分析肺癌患者一级亲属的肺癌早期筛查行为影响因素。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2023年3—6月山西省肿瘤医院呼吸内科与胸外科住医院治疗的310名肺癌患者一级亲属为调查对象。采用一般资料调查表、肺癌知识问卷、中文版肺癌筛查健康信念和癌症担忧量表进行调查。分析影响肺癌筛查行为的因素,分别建立Logistic回归模型与决策树模型,并比较2种模型的预测效果。 结果 肺癌患者一级亲属接受过肺癌筛查率为23.9%(74/310),总体肺癌知识知晓率为75.2%(4 662/6 200),56.5%(175/310)愿意接受肺癌筛查。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示年龄、医疗保险类型、是否获得过肺癌筛查建议、筛查的意愿、感知障碍、感知效益、感知风险是肺癌患者一级亲属肺癌筛查行为的影响因素(P<0.05),决策树模型结果显示感知障碍和年龄是一级亲属肺癌筛查行为的影响因素,Logistic回归模型与决策树模型的预测效果比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 肺癌患者一级亲属的整体肺癌认知水平较高但对筛查手段的认知较低,健康信念及筛查意愿处于中等水平,肺癌筛查率偏低。医务人员可联合应用两种模型,采取措施使一级亲属建立正确的筛查认知与健康信念,以期促进一级亲属的筛查行为。
中图分类号:
| 项目 | 总数(n=310) | 有肺癌筛查行为组(n=74) | 无肺癌筛查行为组(n=236) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[名(%)] | 2.805a | 0.094 | |||
| 男 | 158(51.0) | 44(59.5) | 114(48.3) | ||
| 女 | 152(49.0) | 30(40.5) | 122(51.7) | ||
| 年龄[名(%)] | 29.717a | <0.001 | |||
| 40~49岁 | 177(57.1) | 22(29.7) | 155(65.7) | ||
| 50~74岁 | 133(42.9) | 52(70.3) | 81(34.3) | ||
| BMI[名(%)] | -1.951b | 0.051 | |||
| <24.0 kg/m2 | 155(50.0) | 43(58.1) | 112(47.5) | ||
| 24.0~ kg/m2 | 113(36.5) | 26(35.1) | 87(36.9) | ||
| ≥28.0 kg/m2 | 42(13.5) | 5(6.8) | 37(15.7) | ||
| 长期居住地[名(%)] | 25.815a | <0.001 | |||
| 地级市及以上 | 131(42.3) | 50(67.6) | 81(34.3) | ||
| 县城 | 108(34.8) | 16(21.6) | 92(39.0) | ||
| 农村/乡镇 | 71(22.9) | 8(10.8) | 63(26.7) | ||
| 婚姻状况[名(%)] | 0.022a | 0.882 | |||
| 已婚 | 290(93.5) | 70(94.6) | 220(93.2) | ||
| 未婚/离异/丧偶 | 20(6.5) | 4(5.4) | 16(6.8) | ||
| 文化程度[名(%)] | -3.383b | <0.001 | |||
| 小学及以下 | 36(11.6) | 4(5.4) | 32(13.6) | ||
| 初中 | 120(38.7) | 18(24.3) | 102(43.2) | ||
| 高中/中专 | 90(29.0) | 34(45.9) | 56(23.7) | ||
| 大学及以上 | 64(20.6) | 18(24.3) | 46(19.5) | ||
| 职业[名(%)] | 24.082a | <0.001 | |||
| 农民 | 52(16.8) | 6(8.1) | 46(19.5) | ||
| 工人 | 44(14.2) | 9(12.2) | 35(14.8) | ||
| 自由职业 | 76(24.5) | 14(18.9) | 62(26.3) | ||
| 企业厂矿 | 46(14.8) | 16(21.6) | 30(12.7) | ||
| 机关及事业单位 | 65(21.0) | 27(36.5) | 38(16.1) | ||
| 无业 | 27(8.7) | 2(2.7) | 25(10.6) | ||
| 家庭人均月收入[名(%)] | -5.074b | <0.001 | |||
| <2 000元 | 53(17.1) | 2(2.7) | 51(21.6) | ||
| 2 000~5 000元 | 190(61.3) | 43(58.1) | 147(62.3) | ||
| >5 000元 | 67(21.6) | 29(39.2) | 38(16.1) | ||
| 医疗保险类型[名(%)] | 20.079a | <0.001 | |||
| 城乡居民基本医疗保险 | 226(72.9) | 39(52.7) | 187(79.2) | ||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 84(27.1) | 35(47.3) | 49(21.8) | ||
| 有无商业医疗保险[名(%)] | 6.255a | 0.012 | |||
| 有 | 68(21.9) | 24(33.3) | 44(18.6) | ||
| 无 | 242(78.1) | 50(66.7) | 192(81.4) | ||
| 吸烟史[名(%)] | 0.948a | 0.330 | |||
| 有 | 111(35.8) | 30(40.5) | 81(34.3) | ||
| 无 | 199(64.2) | 44(59.5) | 155(65.7) | ||
| 强度适中的体育锻炼[名(%)] | -3.969b | <0.001 | |||
| 0次/周 | 183(59.0) | 30(40.5) | 153(64.8) | ||
| 1~3次/周 | 74(23.9) | 22(29.7) | 52(22.0) | ||
| 4~7次/周 | 53(17.1) | 22(29.7) | 31(13.1) | ||
| 与患者的关系[名(%)] | — | 0.241 | |||
| 子女 | 234(75.5) | 51(68.9) | 183(77.5) | ||
| 兄弟姐妹 | 71(22.9) | 22(29.7) | 49(20.8) | ||
| 父母 | 5(1.6) | 1(1.4) | 4(1.7) | ||
| 患者确诊肺癌病程[名(%)] | -3.168b | 0.002 | |||
| <3个月 | 121(39.0) | 21(28.4) | 100(42.4) | ||
| 3~6个月 | 84(27.1) | 16(21.6) | 68(28.8) | ||
| >6~12个月 | 62(20.0) | 20(27.0) | 42(17.8) | ||
| >12个月 | 43(13.9) | 17(23.0) | 26(11.0) | ||
| 有无其余血亲亲属恶性肿瘤史[名(%)] | 24.875a | <0.001 | |||
| 有 | 48(15.5) | 25(33.8) | 23(9.7) | ||
| 无 | 262(84.5) | 49(66.2) | 213(90.3) | ||
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议[名(%)] | 21.259a | <0.001 | |||
| 是 | 29(9.4) | 17(23.0) | 12(5.1) | ||
| 否 | 281(90.6) | 57(77.0) | 224(94.9) | ||
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查[名(%)] | 42.377a | <0.001 | |||
| 是 | 175(56.5) | 66(89.2) | 109(46.2) | ||
| 否 | 135(43.5) | 8(10.8) | 127(53.8) | ||
| 知识水平( | 16.77±2.21 | 14.50±3.36 | 6.725c | <0.001 | |
| 健康信念总分( | 103.89±7.55 | 88.12±8.02 | 14.972c | <0.001 | |
| 感知障碍维度( | 51.78±3.75 | 44.81±3.89 | 13.572c | <0.001 | |
| 感知效益维度( | 18.84±1.87 | 16.01±1.90 | 11.237c | <0.001 | |
| 感知风险维度( | 5.99±1.07 | 4.69±1.21 | 8.822c | <0.001 | |
| 自我效能维度( | 27.28±2.98 | 22.61±3.31 | 10.838c | <0.001 | |
| 癌症担忧( | 12.28±2.74 | 11.30±2.72 | 2.709c | 0.007 | |
表1 肺癌患者一级亲属肺癌筛查行为比较
Table 1 Comparison of lung cancer screening behavior of first-degree relatives of lung cancer patients
| 项目 | 总数(n=310) | 有肺癌筛查行为组(n=74) | 无肺癌筛查行为组(n=236) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[名(%)] | 2.805a | 0.094 | |||
| 男 | 158(51.0) | 44(59.5) | 114(48.3) | ||
| 女 | 152(49.0) | 30(40.5) | 122(51.7) | ||
| 年龄[名(%)] | 29.717a | <0.001 | |||
| 40~49岁 | 177(57.1) | 22(29.7) | 155(65.7) | ||
| 50~74岁 | 133(42.9) | 52(70.3) | 81(34.3) | ||
| BMI[名(%)] | -1.951b | 0.051 | |||
| <24.0 kg/m2 | 155(50.0) | 43(58.1) | 112(47.5) | ||
| 24.0~ kg/m2 | 113(36.5) | 26(35.1) | 87(36.9) | ||
| ≥28.0 kg/m2 | 42(13.5) | 5(6.8) | 37(15.7) | ||
| 长期居住地[名(%)] | 25.815a | <0.001 | |||
| 地级市及以上 | 131(42.3) | 50(67.6) | 81(34.3) | ||
| 县城 | 108(34.8) | 16(21.6) | 92(39.0) | ||
| 农村/乡镇 | 71(22.9) | 8(10.8) | 63(26.7) | ||
| 婚姻状况[名(%)] | 0.022a | 0.882 | |||
| 已婚 | 290(93.5) | 70(94.6) | 220(93.2) | ||
| 未婚/离异/丧偶 | 20(6.5) | 4(5.4) | 16(6.8) | ||
| 文化程度[名(%)] | -3.383b | <0.001 | |||
| 小学及以下 | 36(11.6) | 4(5.4) | 32(13.6) | ||
| 初中 | 120(38.7) | 18(24.3) | 102(43.2) | ||
| 高中/中专 | 90(29.0) | 34(45.9) | 56(23.7) | ||
| 大学及以上 | 64(20.6) | 18(24.3) | 46(19.5) | ||
| 职业[名(%)] | 24.082a | <0.001 | |||
| 农民 | 52(16.8) | 6(8.1) | 46(19.5) | ||
| 工人 | 44(14.2) | 9(12.2) | 35(14.8) | ||
| 自由职业 | 76(24.5) | 14(18.9) | 62(26.3) | ||
| 企业厂矿 | 46(14.8) | 16(21.6) | 30(12.7) | ||
| 机关及事业单位 | 65(21.0) | 27(36.5) | 38(16.1) | ||
| 无业 | 27(8.7) | 2(2.7) | 25(10.6) | ||
| 家庭人均月收入[名(%)] | -5.074b | <0.001 | |||
| <2 000元 | 53(17.1) | 2(2.7) | 51(21.6) | ||
| 2 000~5 000元 | 190(61.3) | 43(58.1) | 147(62.3) | ||
| >5 000元 | 67(21.6) | 29(39.2) | 38(16.1) | ||
| 医疗保险类型[名(%)] | 20.079a | <0.001 | |||
| 城乡居民基本医疗保险 | 226(72.9) | 39(52.7) | 187(79.2) | ||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 84(27.1) | 35(47.3) | 49(21.8) | ||
| 有无商业医疗保险[名(%)] | 6.255a | 0.012 | |||
| 有 | 68(21.9) | 24(33.3) | 44(18.6) | ||
| 无 | 242(78.1) | 50(66.7) | 192(81.4) | ||
| 吸烟史[名(%)] | 0.948a | 0.330 | |||
| 有 | 111(35.8) | 30(40.5) | 81(34.3) | ||
| 无 | 199(64.2) | 44(59.5) | 155(65.7) | ||
| 强度适中的体育锻炼[名(%)] | -3.969b | <0.001 | |||
| 0次/周 | 183(59.0) | 30(40.5) | 153(64.8) | ||
| 1~3次/周 | 74(23.9) | 22(29.7) | 52(22.0) | ||
| 4~7次/周 | 53(17.1) | 22(29.7) | 31(13.1) | ||
| 与患者的关系[名(%)] | — | 0.241 | |||
| 子女 | 234(75.5) | 51(68.9) | 183(77.5) | ||
| 兄弟姐妹 | 71(22.9) | 22(29.7) | 49(20.8) | ||
| 父母 | 5(1.6) | 1(1.4) | 4(1.7) | ||
| 患者确诊肺癌病程[名(%)] | -3.168b | 0.002 | |||
| <3个月 | 121(39.0) | 21(28.4) | 100(42.4) | ||
| 3~6个月 | 84(27.1) | 16(21.6) | 68(28.8) | ||
| >6~12个月 | 62(20.0) | 20(27.0) | 42(17.8) | ||
| >12个月 | 43(13.9) | 17(23.0) | 26(11.0) | ||
| 有无其余血亲亲属恶性肿瘤史[名(%)] | 24.875a | <0.001 | |||
| 有 | 48(15.5) | 25(33.8) | 23(9.7) | ||
| 无 | 262(84.5) | 49(66.2) | 213(90.3) | ||
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议[名(%)] | 21.259a | <0.001 | |||
| 是 | 29(9.4) | 17(23.0) | 12(5.1) | ||
| 否 | 281(90.6) | 57(77.0) | 224(94.9) | ||
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查[名(%)] | 42.377a | <0.001 | |||
| 是 | 175(56.5) | 66(89.2) | 109(46.2) | ||
| 否 | 135(43.5) | 8(10.8) | 127(53.8) | ||
| 知识水平( | 16.77±2.21 | 14.50±3.36 | 6.725c | <0.001 | |
| 健康信念总分( | 103.89±7.55 | 88.12±8.02 | 14.972c | <0.001 | |
| 感知障碍维度( | 51.78±3.75 | 44.81±3.89 | 13.572c | <0.001 | |
| 感知效益维度( | 18.84±1.87 | 16.01±1.90 | 11.237c | <0.001 | |
| 感知风险维度( | 5.99±1.07 | 4.69±1.21 | 8.822c | <0.001 | |
| 自我效能维度( | 27.28±2.98 | 22.61±3.31 | 10.838c | <0.001 | |
| 癌症担忧( | 12.28±2.74 | 11.30±2.72 | 2.709c | 0.007 | |
| 变量 | 赋值方式 |
|---|---|
| 年龄 | 40~49岁=1,50~74岁=2 |
| 长期居住地 | 地级市及以上(Z1=1,Z2=0),县城(Z1=0,Z2=1),农村/乡镇(Z1=0,Z2=0) |
| 文化程度 | 小学及以下=1,初中=2,高中/中专=3,大学及以上=4 |
| 职业 | 农民(Z1=1,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0),工人(Z1=0,Z2=1,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0),自由职业(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=1,Z4=0,Z5=0),企业厂矿(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=1,Z5=0),机关及事业单位(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=1),无业(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0) |
| 家庭人均月收入 | <2 000元=1,2 000~5 000元=2,>5 000元=3 |
| 医疗保险类型 | 城乡居民基本医疗保险=1,城镇职工基本医疗保险=2 |
| 有无商业医疗保险 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 强度适中的体育锻炼 | 0次/周=1,1~3次/周=2,4~7次/周=3 |
| 患者确诊肺癌病程 | <3个月=1,3~6个月=2,>6~12个月=3,>12个月=4 |
| 有无其余血亲亲属恶性肿瘤史 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 知识水平 | 实测值 |
| 感知障碍 | 实测值 |
| 感知效益 | 实测值 |
| 感知风险 | 实测值 |
| 自我效能 | 实测值 |
| 患癌担忧 | 实测值 |
表2 自变量赋值情况
Table 2 Independent variable assignment
| 变量 | 赋值方式 |
|---|---|
| 年龄 | 40~49岁=1,50~74岁=2 |
| 长期居住地 | 地级市及以上(Z1=1,Z2=0),县城(Z1=0,Z2=1),农村/乡镇(Z1=0,Z2=0) |
| 文化程度 | 小学及以下=1,初中=2,高中/中专=3,大学及以上=4 |
| 职业 | 农民(Z1=1,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0),工人(Z1=0,Z2=1,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0),自由职业(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=1,Z4=0,Z5=0),企业厂矿(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=1,Z5=0),机关及事业单位(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=1),无业(Z1=0,Z2=0,Z3=0,Z4=0,Z5=0) |
| 家庭人均月收入 | <2 000元=1,2 000~5 000元=2,>5 000元=3 |
| 医疗保险类型 | 城乡居民基本医疗保险=1,城镇职工基本医疗保险=2 |
| 有无商业医疗保险 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 强度适中的体育锻炼 | 0次/周=1,1~3次/周=2,4~7次/周=3 |
| 患者确诊肺癌病程 | <3个月=1,3~6个月=2,>6~12个月=3,>12个月=4 |
| 有无其余血亲亲属恶性肿瘤史 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 知识水平 | 实测值 |
| 感知障碍 | 实测值 |
| 感知效益 | 实测值 |
| 感知风险 | 实测值 |
| 自我效能 | 实测值 |
| 患癌担忧 | 实测值 |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(以40~49岁为参照) | |||||
| 50~74岁 | 1.306 | 0.548 | 5.689 | 0.017 | 3.692(1.262~10.801) |
| 医疗保险类型(以城乡居民基本医疗保险为参照) | |||||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 2.183 | 1.034 | 4.461 | 0.035 | 8.874(1.170~67.279) |
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议(以否为参照) | |||||
| 是 | 1.732 | 0.779 | 4.940 | 0.026 | 5.653(1.227~26.040) |
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查(以否为参照) | |||||
| 是 | 1.781 | 0.739 | 5.808 | 0.016 | 5.934(1.395~25.248) |
| 感知障碍 | 0.399 | 0.118 | 11.434 | 0.001 | 1.491(1.183~1.880) |
| 感知效益 | 0.390 | 0.180 | 4.688 | 0.030 | 1.476(1.038~2.101) |
| 感知风险 | 0.487 | 0.243 | 4.022 | 0.045 | 1.628(1.011~2.620) |
表3 肺癌患者一级亲属肺癌筛查行为的Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Logistic regression analysis of lung cancer screening behavior of first-degree relatives of lung cancer patients
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(以40~49岁为参照) | |||||
| 50~74岁 | 1.306 | 0.548 | 5.689 | 0.017 | 3.692(1.262~10.801) |
| 医疗保险类型(以城乡居民基本医疗保险为参照) | |||||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 2.183 | 1.034 | 4.461 | 0.035 | 8.874(1.170~67.279) |
| 是否获得过肺癌筛查建议(以否为参照) | |||||
| 是 | 1.732 | 0.779 | 4.940 | 0.026 | 5.653(1.227~26.040) |
| 是否愿意定期参加肺癌筛查(以否为参照) | |||||
| 是 | 1.781 | 0.739 | 5.808 | 0.016 | 5.934(1.395~25.248) |
| 感知障碍 | 0.399 | 0.118 | 11.434 | 0.001 | 1.491(1.183~1.880) |
| 感知效益 | 0.390 | 0.180 | 4.688 | 0.030 | 1.476(1.038~2.101) |
| 感知风险 | 0.487 | 0.243 | 4.022 | 0.045 | 1.628(1.011~2.620) |
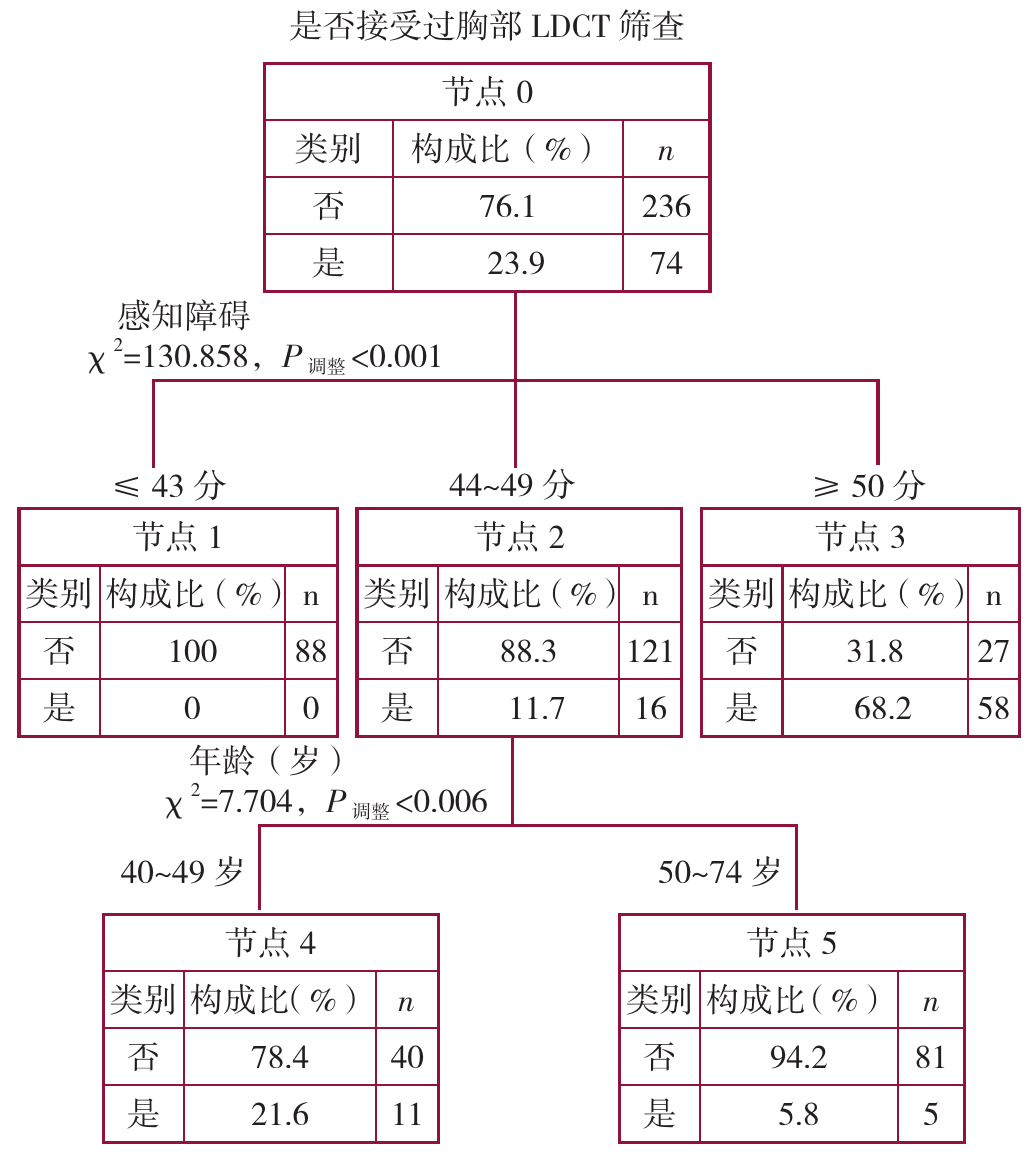
图1 肺癌患者一级亲属筛查行为影响因素的决策树分析注:LDCT=低剂量螺旋CT。
Figure 1 Decision tree analysis of influencing factors of screening behavior of first-degree relatives of lung cancer patients
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
焦玮,曹湘博,聂刚,等. 癌症焦虑量表在乳腺癌患者术后复发恐惧检测中的应用[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2014(36):4571-4573. DOI:10.3760/j.issn.1674-2907.2014.36.012.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
陈万青,李霓,曹毛毛,等. 2013—2017年中国城市癌症早诊早治项目基线结果分析[J]. 中国肿瘤,2020,29(1):1-6.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
温艳,于连政,杜灵彬,等. 中国3省城市癌症早诊早治项目地区肺癌高危人群的低剂量螺旋CT筛查依从性及相关因素分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2021,55(5):633-639.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
谷俊东,滑峰,钟殿胜,等. 肺癌家族聚集性的系统评价[J]. 中国肺癌杂志,2010,13(3):224-229.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
National Lung Screening Trial Research Team,
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
赫捷,李霓,陈万青,等. 中国肺癌筛查与早诊早治指南(2021,北京)[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2021,43(3):243-268.
|
| [10] |
刘兵,李苹,朱玫烨,等. 决策树模型与logistic回归模型在胃癌高危人群干预效果影响因素分析中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计,2018,35(1):70-73.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [11] |
闫蕊,赵守梅,张馨心,等. 决策树与Logistic回归模型在老年人社区养老意愿影响因素分析中的应用研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(1):87-93.
|
| [12] |
张永贞,高秋生,崔王飞,等. 2014—2018年山西省城市癌症早诊早治项目筛查结果分析[J]. 中国肿瘤,2021,30(2):131-136. DOI:10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2021.02.A005.
|
| [13] |
中国肺癌防治联盟,中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺癌学组,中国医师协会呼吸医师分会肺癌工作委员会. 肺癌筛查与管理中国专家共识[J]. 国际呼吸杂志,2019,39(21):1604-1615.
|
| [14] |
陈莉莉,丁高恒,刘玉琴,等. 甘肃省居民肺癌防治知识知晓情况调查及影响因素分析[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗,2022,35(7):642-647. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-0904.2022.07.010.
|
| [15] |
乔楠,曹凌,苏芳,等. 山西省居民癌症防治核心知识知晓情况分析[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床,2022,34(2):132-136.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [1] | 那飞扬, 张蓉芳, 赵启君, 梁譞, 王雍, 王雁南. 学龄期儿童支气管哮喘控制率及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(33): 4187-4191. |
| [2] | 严明, 董佳惠, 陆益婷, 赵洋, 方力争, 徐志杰. 社区残疾人慢性病共病治疗负担现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4015-4023. |
| [3] | 陈莹莹, 温勇, 舒星宇. 慢性病共病中老年人失能状况的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4024-4030. |
| [4] | 刘春燕, 邓朝晖, 宋颖博, 杨芳, 史茜, 李永鑫, 张新. 新疆地区居民高血压、糖尿病、血脂异常患病及共病情况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4031-4037. |
| [5] | 王慧, 胡银环, 冯显东, 刘莎, 汪洋帆. 农村慢性病与非慢性病居民心理健康状况及心理健康服务需求比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(31): 3968-3973. |
| [6] | 徐百川, 王艳, 张彭, 李艺婷, 刘飞来, 谢洋. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病共病肺癌筛查工具分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3847-3852. |
| [7] | 唐玲, 张国良, 李振坤, 司圣波, 刘强, 陈任, 任佰玲. 中老年慢性病患者卫生服务利用及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3688-3693. |
| [8] | 俞海荣, 陈申, 黄静宜, 张园园, 李孟超, 崔焱, 季明辉, 沈洁淼. 吞咽障碍患者隐性误吸现况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3619-3624. |
| [9] | 刘小雪, 吕良, 冯琬婷, 杨会芳, 滕屹霖, 马天佩, 张韬, 姜侠, 龙璐, 廖加强, 樊萌语, 汪川, 杨代兰, 李佳圆, 张本. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖指数纵向轨迹与老年人肝脏硬度状况的关联研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3668-3673. |
| [10] | 李仪丙, 贾鸿博, 樊小农, 赵文君, 刘巍, 葛文逸, 李宋姣, 雷康辰, 张梦龙, 张薇薇, 陈阳, 李礼. 卒中后吞咽障碍预后影响因素的综合评估:一项伞形综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3631-3637. |
| [11] | 朱晨, 余嘉文, 江昊, 甘盼盼, 夏天, 徐海涛, 杜瀛瀛. 消化系统肿瘤血脂特征对正常相位角的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3385-3390. |
| [12] | 胡洁蔓, 谭斐翔, 袁安新, 陈世宇, 唐楚蕾, 殷月姮, 巴磊, 许勤. 结直肠癌患者术后衰弱变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [13] | 丑欣彤, 彭瀚瑜, 马慧, 张珍, 苏先, 邱红燕. 产妇对避孕决策的偏好及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [14] | 魏姣花, 彭慧如, 彭建业, 谭文婷, 黄金娥, 方立. MOTS-c在心房颤动患者血清中的表达及其与心房重构的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [15] | 褚艺婧, 严雨格, 顾杰, 席彪, 祝墡珠, 黄蛟灵. 中国基层医务人员留用意愿影响因素分析:基于城乡差异比较[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3161-3168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





