中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (27): 3395-3403.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0201
所属专题: 中医最新文章合集; 泌尿系统疾病最新文章合集; 高血压最新文章合集
柯江华1,2, 段姝伟2, 刘林昌2, 李爽2, 柯雨景1,2, 曲逸伦1,2, 姚进1,2, 陈香美1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-22
修回日期:2022-04-28
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-05-26
通讯作者:
陈香美
基金资助:
Jianghua KE1,2, Shuwei DUAN2, Linchang LIU2, Shuang LI2, Yujing KE1,2, Yilun QU1,2, Jin YAO1,2, Xiangmei CHEN1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-22
Revised:2022-04-28
Published:2022-09-20
Online:2022-05-26
Contact:
Xiangmei CHEN
About author:摘要: 背景 IgA肾病(IgAN)是全世界最常见的原发性肾小球疾病,同时也是引起肾实质恶性高血压(MHT)的主要原因之一。既往研究认为伴MHT的IgAN临床病情和肾脏病变程度均比无MHT的IgAN严重,但尚不清楚IgAN患者发生MHT的中医证候特点。 目的 分析原发性IgAN患者发生MHT的中西医相关因素,探索其中医证候特点。 方法 纳入2013年12月至2021年9月在中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心经肾穿刺活检确诊的518例原发性IgAN患者为研究对象,应用PASS 15.0软件中的变量相关性检验进行样本量估算,最终纳入伴MHT的IgAN患者17例作为IgAN-MHT组,按照1∶5比例随机抽取同时期85例无MHT的IgAN患者作为IgAN组,比较两组临床、病理及中医证候的差异。采用Lasso回归对93个中医证候信息进行筛选降维,进一步采用多因素Logistic回归分析探讨伴MHT的IgAN的中医证候相关因素。 结果 IgAN-MHT组首发临床表现为头痛头晕或恶心呕吐比例,临床诊断为肾病综合征比例,入院时平均动脉压、最高收缩压、最高舒张压、血尿素氮、血肌酐、血无机磷、血镁、24 h尿蛋白定量水平、慢性肾脏病(CKD) 3~5期的比例、血瘀证比例,气虚证中神疲乏力、四肢倦怠、胫酸腿软、头目眩晕、头痛、恶心、呕吐症状的比例,阴虚证中视物模糊、飞蚊症症状的比例,血瘀证中爪甲青紫、舌色紫暗症状的比例,肾内动脉硬化比例高于IgAN组;而首发临床表现为尿检异常比例、高血压病史比例、临床诊断为慢性肾炎综合征的比例、血IgM、血IgG水平、估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR)水平低于IgAN组(P<0.05)。两组伴肾小管萎缩/间质纤维化病变(T病变)比例比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。IgAN-MHT组的常见中医证型为气阴两虚兼血瘀证。IgAN-MHT和血瘀证呈正相关(P<0.05),IgAN-MHT患者男性比例、24 h尿蛋白定量水平和气虚证呈正相关(P<0.05),无机磷、血钾和阴虚证呈负相关(P<0.05),IgAN-MHT患者肾小管萎缩/间质纤维化和血瘀证呈正相关(P=0.040)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,头痛〔OR=7.895,95%CI(1.643,37.935),P=0.010〕、视物模糊〔OR=5.499,95%CI(1.207,25.053),P=0.028〕、口干喜饮〔OR=10.079,95%CI(2.289,44.373),P=0.002〕、爪甲青紫〔OR=18.312,95%CI(2.179,153.884),P=0.007〕是伴MHT的原发性IgAN的影响因素。 结论 (1)伴MHT的原发性IgAN患者肾功能更差,肾脏病理损伤更重。(2)伴MHT的原发性IgAN的常见中医证型为气阴两虚兼血瘀证。(3)伴MHT的原发性IgAN患者临床、病理指标与中医气虚证、阴虚证和血瘀证具有一定相关性。(4)中医证候中头痛、视物模糊、口干喜饮、爪甲青紫是伴MHT的原发性IgAN相关因素。早发现、早诊断、早治疗,关注并改善患者的气虚、阴虚、血瘀相关症状,有可能减少IgAN患者伴MHT的发生。
| 组别 | 例数 | 男性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄( | BMI( | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 首发临床症状〔n(%)〕 | 高血压史〔n(%)〕 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿检异常 | 肉眼血尿 | 水肿 | 头痛头晕或恶心呕吐 | ||||||||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 47(55.3) | 38.0±10.9 | 24.7±3.8 | 27(31.8) | 32(37.6) | 63(74.1) | 12(14.1) | 9(10.6) | 5(5.9) | 35(41.2) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 33.4±11.0 | 24.2±4.0 | 3(17.6) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 0 | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 2(11.8) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.512a | 1.560b | 0.553b | 1.360a | 0.416a | 7.140a | 1.530a | 1.128a | 13.770a | 5.301a | |
| P值 | 0.474 | 0.122 | 0.581 | 0.244 | 0.519 | 0.008 | 0.216 | 0.288 | <0.001 | 0.021 | |
| 组别 | 临床诊断〔n(%)〕 | 入院时平均动脉压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕 | 最高收缩压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕d | 最高舒张压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕d | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||
| 慢性肾炎综合征 | 肾病综合征 | 急性肾损伤 | |||||||||
| IgAN组 | 84(98.8) | 1(1.2) | 0 | 97(89,105) | 160(147,175) | 100(100,110) | 14.2(10.3,20.8) | ||||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 10(58.8) | 4(23.5) | 1(5.9) | 101(93,113) | 200(185,215) | 140(130,145) | 11.5(9.9,19.5) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 26.070a | —c | —c | -2.017 | -5.041 | -5.599 | -0.799 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.167 | 0.044 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.424 | ||||
| 组别 | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 血清总蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 白蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 血葡萄糖( | 血尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 血尿酸〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 总胆固醇〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | |||
| IgAN组 | 15.0(12.4,18.8) | 65.1(62.1,71.0) | 39.3(36.0,42.3) | 5.1±1.0 | 5.6(4.4,6.8) | 98.2(74.3,123.3) | 374.5(295.7,447.0) | 4.4(3.6,5.0) | |||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 12.3(11.5,16.6) | 60.3(56.7,69.9) | 38.0(34.3,41.2) | 4.6±0.7 | 8.0(6.4,15.6) | 171.4(105.7,391.2) | 428.4(357.7,451.2) | 4.2(3.6,4.7) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | -1.747 | -1.670 | -1.280 | 1.956b | -4.117 | -3.637 | -1.863 | -0.144 | |||
| P值 | 0.081 | 0.095 | 0.201 | 0.053 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.062 | 0.886 | |||
| 组别 | 三酰甘油〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 高密度脂蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 低密度脂蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 钙( | 无机磷〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 镁〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 钾( | 钠( | 补体C3〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | ||
| IgAN组 | 1.7(1.3,2.5) | 1.0(0.8,1.3) | 2.8(2.3,3.2) | 2.2±0.1 | 1.2(1.0,1.3) | 0.8(0.8,0.9) | 4.0±0.3 | 141.1±2.1 | 106.0(94.6,120.0) | ||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 1.6(1.2,2.0) | 0.8(0.7,1.2) | 2.7(2.2,3.3) | 2.2±0.1 | 1.3(1.1,1.7) | 0.9(0.9,0.9) | 4.2±0.6 | 140.7±2.7 | 109.0(82.9,122.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | -0.804 | -1.280 | -0.260 | 0.511b | -2.048 | -2.366 | -1.847b | 0.564b | -0.445 | ||
| P值 | 0.422 | 0.201 | 0.795 | 0.610 | 0.041 | 0.018 | 0.068 | 0.574 | 0.657 | ||
| 组别 | 补体C4( | 血IgA〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 血IgE〔M(P25,P75),IU/ml〕 | 血IgG〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 血IgM〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 24 h尿蛋白定量〔M(P25,P75),g/24 h〕 | 24 h尿蛋白定量分级〔n(%)〕 | ||||
| <1 g/24 h | 1~3.5 g/24 h | ≥3.5 g/24 h | |||||||||
| IgAN组 | 25.6±7.0 | 291.0(221.0,361.0) | 45.8(19.8,93.2) | 1 130.0(951.0,1 275.0) | 103.0(67.1,146.0) | 1.0(0.6,1.9) | 40(47.1) | 43(50.6) | 2(2.4) | ||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 27.2±8.4 | 314.0(246.0,374.5) | 75.3(30.8,230.0) | 959.0(716.5,1 135.0) | 65.4(40.2,107.3) | 2.0(1.4,3.9) | 2(11.8) | 9(52.9) | 6(35.3) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | -0.808b | -0.673 | -1.598 | -2.155 | -2.492 | -3.444 | 18.920a | ||||
| P值 | 0.421 | 0.501 | 0.110 | 0.031 | 0.013 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| 组别 | 血红蛋白( | 血小板计数( | 尿红细胞检查(镜检)〔M(P25,P75),/HPF〕 | eGFR〔M(P25,P75),ml·min-1·(1.73 m2)-1〕 | CKD分期〔n(%)〕 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3a | 3b | 4 | 5 | ||||||
| IgAN组 | 131.0±17.7 | 243.7±54.8 | 6.5(3.0,18.3) | 80.5(57.3,105.4) | 33(38.8) | 28(32.9) | 13(15.3) | 9(10.6) | 2(2.4) | 0 | |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 129.4±23.3 | 225.1±55.6 | 4.0(0.5,11.8) | 46.7(19.1,76.9) | 1(5.9) | 5(29.4) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 2(11.8) | 3(17.6) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.310b | 1.277b | -1.130 | -3.722 | 19.122c | ||||||
| P值 | 0.757 | 0.205 | 0.259 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||||
表1 两组患者的临床资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of clinical data of IgA nephropathy patients with and without malignant hypertension
| 组别 | 例数 | 男性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄( | BMI( | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 首发临床症状〔n(%)〕 | 高血压史〔n(%)〕 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿检异常 | 肉眼血尿 | 水肿 | 头痛头晕或恶心呕吐 | ||||||||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 47(55.3) | 38.0±10.9 | 24.7±3.8 | 27(31.8) | 32(37.6) | 63(74.1) | 12(14.1) | 9(10.6) | 5(5.9) | 35(41.2) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 33.4±11.0 | 24.2±4.0 | 3(17.6) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 0 | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 2(11.8) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.512a | 1.560b | 0.553b | 1.360a | 0.416a | 7.140a | 1.530a | 1.128a | 13.770a | 5.301a | |
| P值 | 0.474 | 0.122 | 0.581 | 0.244 | 0.519 | 0.008 | 0.216 | 0.288 | <0.001 | 0.021 | |
| 组别 | 临床诊断〔n(%)〕 | 入院时平均动脉压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕 | 最高收缩压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕d | 最高舒张压〔M(P25,P75),mm Hg〕d | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | ||||||
| 慢性肾炎综合征 | 肾病综合征 | 急性肾损伤 | |||||||||
| IgAN组 | 84(98.8) | 1(1.2) | 0 | 97(89,105) | 160(147,175) | 100(100,110) | 14.2(10.3,20.8) | ||||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 10(58.8) | 4(23.5) | 1(5.9) | 101(93,113) | 200(185,215) | 140(130,145) | 11.5(9.9,19.5) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 26.070a | —c | —c | -2.017 | -5.041 | -5.599 | -0.799 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.167 | 0.044 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.424 | ||||
| 组别 | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 血清总蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 白蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 血葡萄糖( | 血尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 血尿酸〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 总胆固醇〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | |||
| IgAN组 | 15.0(12.4,18.8) | 65.1(62.1,71.0) | 39.3(36.0,42.3) | 5.1±1.0 | 5.6(4.4,6.8) | 98.2(74.3,123.3) | 374.5(295.7,447.0) | 4.4(3.6,5.0) | |||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 12.3(11.5,16.6) | 60.3(56.7,69.9) | 38.0(34.3,41.2) | 4.6±0.7 | 8.0(6.4,15.6) | 171.4(105.7,391.2) | 428.4(357.7,451.2) | 4.2(3.6,4.7) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | -1.747 | -1.670 | -1.280 | 1.956b | -4.117 | -3.637 | -1.863 | -0.144 | |||
| P值 | 0.081 | 0.095 | 0.201 | 0.053 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.062 | 0.886 | |||
| 组别 | 三酰甘油〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 高密度脂蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 低密度脂蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 钙( | 无机磷〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 镁〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 钾( | 钠( | 补体C3〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | ||
| IgAN组 | 1.7(1.3,2.5) | 1.0(0.8,1.3) | 2.8(2.3,3.2) | 2.2±0.1 | 1.2(1.0,1.3) | 0.8(0.8,0.9) | 4.0±0.3 | 141.1±2.1 | 106.0(94.6,120.0) | ||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 1.6(1.2,2.0) | 0.8(0.7,1.2) | 2.7(2.2,3.3) | 2.2±0.1 | 1.3(1.1,1.7) | 0.9(0.9,0.9) | 4.2±0.6 | 140.7±2.7 | 109.0(82.9,122.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | -0.804 | -1.280 | -0.260 | 0.511b | -2.048 | -2.366 | -1.847b | 0.564b | -0.445 | ||
| P值 | 0.422 | 0.201 | 0.795 | 0.610 | 0.041 | 0.018 | 0.068 | 0.574 | 0.657 | ||
| 组别 | 补体C4( | 血IgA〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 血IgE〔M(P25,P75),IU/ml〕 | 血IgG〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 血IgM〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 24 h尿蛋白定量〔M(P25,P75),g/24 h〕 | 24 h尿蛋白定量分级〔n(%)〕 | ||||
| <1 g/24 h | 1~3.5 g/24 h | ≥3.5 g/24 h | |||||||||
| IgAN组 | 25.6±7.0 | 291.0(221.0,361.0) | 45.8(19.8,93.2) | 1 130.0(951.0,1 275.0) | 103.0(67.1,146.0) | 1.0(0.6,1.9) | 40(47.1) | 43(50.6) | 2(2.4) | ||
| IgAN-MHT组 | 27.2±8.4 | 314.0(246.0,374.5) | 75.3(30.8,230.0) | 959.0(716.5,1 135.0) | 65.4(40.2,107.3) | 2.0(1.4,3.9) | 2(11.8) | 9(52.9) | 6(35.3) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | -0.808b | -0.673 | -1.598 | -2.155 | -2.492 | -3.444 | 18.920a | ||||
| P值 | 0.421 | 0.501 | 0.110 | 0.031 | 0.013 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| 组别 | 血红蛋白( | 血小板计数( | 尿红细胞检查(镜检)〔M(P25,P75),/HPF〕 | eGFR〔M(P25,P75),ml·min-1·(1.73 m2)-1〕 | CKD分期〔n(%)〕 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3a | 3b | 4 | 5 | ||||||
| IgAN组 | 131.0±17.7 | 243.7±54.8 | 6.5(3.0,18.3) | 80.5(57.3,105.4) | 33(38.8) | 28(32.9) | 13(15.3) | 9(10.6) | 2(2.4) | 0 | |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 129.4±23.3 | 225.1±55.6 | 4.0(0.5,11.8) | 46.7(19.1,76.9) | 1(5.9) | 5(29.4) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 2(11.8) | 3(17.6) | |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.310b | 1.277b | -1.130 | -3.722 | 19.122c | ||||||
| P值 | 0.757 | 0.205 | 0.259 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 主证 | 兼证 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺脾气虚证 | 气阴两虚证 | 肝肾阴虚证 | 脾肾阳虚证 | 水湿 | 痰湿 | 湿热 | 寒湿 | 血瘀 | 肝郁 | 浊毒 | ||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 15(17.6) | 39(45.9) | 18(21.2) | 13(15.3) | 9(10.6) | 10(11.8) | 22(25.9) | 1(1.2) | 20(23.5) | 16(18.8) | 7(8.2) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 1(5.9) | 5(29.4) | 0 | 9(52.9) | 3(17.6) | 0 |
| χ2值 | 0.052 | 0.127 | 0 | 0 | 0.170 | 0.082 | 0 | — | 4.664 | 0 | 0.491 | |
| P值 | 0.820 | 0.722 | 1 | 1 | 0.680 | 0.775 | 1 | 1 | 0.031 | 1 | 0.484 | |
表2 两组患者中医主证及兼证的比较〔n(%)〕
Table 2 Comparison of main syndromes and concurrent syndromes of TCM in IgA nephropathy patients with and without malignant hypertension
| 组别 | 例数 | 主证 | 兼证 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺脾气虚证 | 气阴两虚证 | 肝肾阴虚证 | 脾肾阳虚证 | 水湿 | 痰湿 | 湿热 | 寒湿 | 血瘀 | 肝郁 | 浊毒 | ||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 15(17.6) | 39(45.9) | 18(21.2) | 13(15.3) | 9(10.6) | 10(11.8) | 22(25.9) | 1(1.2) | 20(23.5) | 16(18.8) | 7(8.2) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 3(17.6) | 1(5.9) | 5(29.4) | 0 | 9(52.9) | 3(17.6) | 0 |
| χ2值 | 0.052 | 0.127 | 0 | 0 | 0.170 | 0.082 | 0 | — | 4.664 | 0 | 0.491 | |
| P值 | 0.820 | 0.722 | 1 | 1 | 0.680 | 0.775 | 1 | 1 | 0.031 | 1 | 0.484 | |
| 组别 | 例数 | 气虚证 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易感冒 | 神疲乏力 | 少气懒言 | 自汗 | 四肢倦怠 | 胫酸腿软 | 头目眩晕 | 头痛 | 恶心 | 呕吐 | 便溏 | ||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 30(35.3) | 40(47.1) | 17(20.0) | 33(38.8) | 14(16.5) | 4(4.7) | 22(25.9) | 18(21.2) | 7(8.2) | 3(3.5) | 10(11.8) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 4(23.5) | 13(76.5) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 10(58.8) | 12(70.6) | 5(29.4) | 4(23.5) | 4(23.5) |
| χ2值 | 0.882 | 4.910 | 2.452 | 0.537 | 3.886 | 7.897 | 7.140 | 16.66 | 4.250 | 6.013 | 0.811 | |
| P值 | 0.348 | 0.027 | 0.117 | 0.464 | 0.049 | 0.005 | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.014 | 0.368 | |
| 组别 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | ||||||||||
| 视物模糊 | 飞蚊症 | 耳聋 | 手足心热 | 盗汗 | 口干/咽燥 | 舌苔干燥 | 面色黧黑 | 爪甲青紫 | 定位刺痛、夜间加重 | 舌色紫暗 | ||
| IgAN组 | 21(24.7) | 3(3.5) | 6(7.1) | 34(40.0) | 18(21.2) | 28(32.9) | 7(8.2) | 16(18.8) | 2(2.4) | 7(8.2) | 17(20.0) | |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 12(70.6) | 6(35.3) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 5(29.4) | 4(23.5) | 2(11.8) | 8(47.1) | |
| χ2值 | 13.627 | 14.039 | 5.217 | 0.008 | 0 | 0.426 | 4.25 | 0.432 | 7.969 | 0 | 4.239 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.928 | 1 | 0.514 | 0.039 | 0.511 | 0.005 | 1 | 0.040 | |
表3 两组患者中医症候比较〔n(%)〕
Table 3 Comparison of TCM symptoms in IgA nephropathy patients with and without malignant hypertension
| 组别 | 例数 | 气虚证 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易感冒 | 神疲乏力 | 少气懒言 | 自汗 | 四肢倦怠 | 胫酸腿软 | 头目眩晕 | 头痛 | 恶心 | 呕吐 | 便溏 | ||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 30(35.3) | 40(47.1) | 17(20.0) | 33(38.8) | 14(16.5) | 4(4.7) | 22(25.9) | 18(21.2) | 7(8.2) | 3(3.5) | 10(11.8) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 4(23.5) | 13(76.5) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 10(58.8) | 12(70.6) | 5(29.4) | 4(23.5) | 4(23.5) |
| χ2值 | 0.882 | 4.910 | 2.452 | 0.537 | 3.886 | 7.897 | 7.140 | 16.66 | 4.250 | 6.013 | 0.811 | |
| P值 | 0.348 | 0.027 | 0.117 | 0.464 | 0.049 | 0.005 | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.014 | 0.368 | |
| 组别 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | ||||||||||
| 视物模糊 | 飞蚊症 | 耳聋 | 手足心热 | 盗汗 | 口干/咽燥 | 舌苔干燥 | 面色黧黑 | 爪甲青紫 | 定位刺痛、夜间加重 | 舌色紫暗 | ||
| IgAN组 | 21(24.7) | 3(3.5) | 6(7.1) | 34(40.0) | 18(21.2) | 28(32.9) | 7(8.2) | 16(18.8) | 2(2.4) | 7(8.2) | 17(20.0) | |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 12(70.6) | 6(35.3) | 5(29.4) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) | 7(41.2) | 5(29.4) | 5(29.4) | 4(23.5) | 2(11.8) | 8(47.1) | |
| χ2值 | 13.627 | 14.039 | 5.217 | 0.008 | 0 | 0.426 | 4.25 | 0.432 | 7.969 | 0 | 4.239 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.928 | 1 | 0.514 | 0.039 | 0.511 | 0.005 | 1 | 0.040 | |
| 组别 | 例数 | M病变 | E病变 | S病变 | T病变 | C病变 | 肾内动脉硬化 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M1 | E0 | E1 | S0 | S1 | T0 | T1 | T2 | C0 | C1 | C2 | |||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 48(56.5) | 37(43.5) | 66(77.6) | 19(22.4) | 27(31.8) | 58(68.2) | 40(47.1) | 34(40.0) | 11(12.9) | 60(70.6) | 24(28.2) | 1(1.2) | 55(64.7) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.3) | 16(94.1) | 1(5.9) | 1(5.9) | 16(94.1) | 3(17.6) | 4(23.5) | 10(58.8) | 11(64.7) | 6(35.3) | 0 | 16(94.1) |
| χ2值 | 0.394 | 1.505 | 3.554 | 15.515 | — | 5.793 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.530 | 0.220 | 0.059 | <0.001 | 0.644 | 0.016 | ||||||||
表4 两组IgAN患者肾脏病理牛津分型的比较〔n(%)〕
Table 4 Comparison of Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy in IgA nephropathy patients with and without malignant hypertension
| 组别 | 例数 | M病变 | E病变 | S病变 | T病变 | C病变 | 肾内动脉硬化 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M1 | E0 | E1 | S0 | S1 | T0 | T1 | T2 | C0 | C1 | C2 | |||
| IgAN组 | 85 | 48(56.5) | 37(43.5) | 66(77.6) | 19(22.4) | 27(31.8) | 58(68.2) | 40(47.1) | 34(40.0) | 11(12.9) | 60(70.6) | 24(28.2) | 1(1.2) | 55(64.7) |
| IgAN-MHT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.3) | 16(94.1) | 1(5.9) | 1(5.9) | 16(94.1) | 3(17.6) | 4(23.5) | 10(58.8) | 11(64.7) | 6(35.3) | 0 | 16(94.1) |
| χ2值 | 0.394 | 1.505 | 3.554 | 15.515 | — | 5.793 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.530 | 0.220 | 0.059 | <0.001 | 0.644 | 0.016 | ||||||||
| 指标 | IgAN-MHT | |
|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | |
| 气虚证 | 0.009 | 0.928 |
| 阴虚证 | -0.065 | 0.519 |
| 水湿证 | 0.082 | 0.415 |
| 痰湿证 | -0.071 | 0.480 |
| 湿热证 | 0.030 | 0.766 |
| 寒湿证 | -0.044 | 0.657 |
| 血瘀证 | 0.664 | <0.001 |
| 肝郁证 | 0.044 | 0.659 |
| 浊毒证 | -0.121 | 0.224 |
表5 IgAN-MHT与中医证型的相关性
Table 5 Correlation of malignant hypertension in IgA nephropathy with TCM syndromes
| 指标 | IgAN-MHT | |
|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | |
| 气虚证 | 0.009 | 0.928 |
| 阴虚证 | -0.065 | 0.519 |
| 水湿证 | 0.082 | 0.415 |
| 痰湿证 | -0.071 | 0.480 |
| 湿热证 | 0.030 | 0.766 |
| 寒湿证 | -0.044 | 0.657 |
| 血瘀证 | 0.664 | <0.001 |
| 肝郁证 | 0.044 | 0.659 |
| 浊毒证 | -0.121 | 0.224 |
| 临床指标 | 气虚证 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | |
| 性别(以女性为参照) | 0.485 | 0.049 | 0.118 | 0.653 | -0.044 | 0.868 |
| 年龄 | -0.151 | 0.563 | 0.012 | 0.963 | -0.096 | 0.713 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.019 | 0.942 | -0.240 | 0.354 | -0.182 | 0.485 |
| 饮酒史 | 0.207 | 0.426 | -0.247 | 0.339 | -0.167 | 0.521 |
| 入院时收缩压 | -0.013 | 0.962 | 0.539 | 0.025 | 0.133 | 0.611 |
| 入院时舒张压 | 0.025 | 0.924 | 0.343 | 0.178 | 0.060 | 0.818 |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.050 | 0.848 | 0.024 | 0.926 | 0.192 | 0.459 |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.138 | 0.597 | 0.232 | 0.370 | 0.132 | 0.612 |
| 血清总蛋白 | -0.176 | 0.499 | 0.293 | 0.254 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 白蛋白 | -0.151 | 0.564 | 0.293 | 0.254 | 0 | 1.000 |
| 血葡萄糖 | 0.025 | 0.924 | 0.110 | 0.675 | -0.193 | 0.459 |
| 血尿素氮 | 0.302 | 0.240 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.048 | 0.855 |
| 血肌酐 | 0.427 | 0.087 | -0.317 | 0.215 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 血尿酸 | 0.377 | 0.136 | -0.415 | 0.098 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 总胆固醇 | 0.151 | 0.564 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.313 | 0.222 |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.251 | 0.331 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.361 | 0.155 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.031 | 0.911 | 0.346 | 0.206 | 0.278 | 0.315 |
| 低密度脂蛋白 | 0.047 | 0.867 | -0.142 | 0.614 | -0.139 | 0.620 |
| 钙 | 0.038 | 0.886 | 0.244 | 0.345 | -0.096 | 0.713 |
| 无机磷 | 0.176 | 0.499 | -0.525 | 0.030 | 0.072 | 0.783 |
| 镁 | 0.417 | 0.096 | 0.012 | 0.963 | -0.012 | 0.963 |
| 钾 | 0.201 | 0.439 | -0.634 | 0.006 | -0.409 | 0.103 |
| 钠 | -0.226 | 0.383 | -0.305 | 0.234 | -0.144 | 0.580 |
| 24 h尿蛋白定量 | 0.503 | 0.040 | -0.366 | 0.149 | -0.361 | 0.155 |
| 血红蛋白 | 0.251 | 0.330 | -0.085 | 0.744 | -0.156 | 0.549 |
| 血小板计数 | -0.063 | 0.811 | -0.232 | 0.370 | -0.289 | 0.261 |
| 尿红细胞检查(镜检)/HPF | -0.202 | 0.436 | -0.147 | 0.572 | 0.085 | 0.746 |
| eGFR | -0.352 | 0.166 | 0.268 | 0.298 | 0.072 | 0.783 |
表6 IgAN-MHT患者西医临床指标与中医证型的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis of Western medicine clinical indicators and TCM syndromes in IgA nephropathy patients with malignant hypertension
| 临床指标 | 气虚证 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | |
| 性别(以女性为参照) | 0.485 | 0.049 | 0.118 | 0.653 | -0.044 | 0.868 |
| 年龄 | -0.151 | 0.563 | 0.012 | 0.963 | -0.096 | 0.713 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.019 | 0.942 | -0.240 | 0.354 | -0.182 | 0.485 |
| 饮酒史 | 0.207 | 0.426 | -0.247 | 0.339 | -0.167 | 0.521 |
| 入院时收缩压 | -0.013 | 0.962 | 0.539 | 0.025 | 0.133 | 0.611 |
| 入院时舒张压 | 0.025 | 0.924 | 0.343 | 0.178 | 0.060 | 0.818 |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.050 | 0.848 | 0.024 | 0.926 | 0.192 | 0.459 |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.138 | 0.597 | 0.232 | 0.370 | 0.132 | 0.612 |
| 血清总蛋白 | -0.176 | 0.499 | 0.293 | 0.254 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 白蛋白 | -0.151 | 0.564 | 0.293 | 0.254 | 0 | 1.000 |
| 血葡萄糖 | 0.025 | 0.924 | 0.110 | 0.675 | -0.193 | 0.459 |
| 血尿素氮 | 0.302 | 0.240 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.048 | 0.855 |
| 血肌酐 | 0.427 | 0.087 | -0.317 | 0.215 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 血尿酸 | 0.377 | 0.136 | -0.415 | 0.098 | -0.072 | 0.783 |
| 总胆固醇 | 0.151 | 0.564 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.313 | 0.222 |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.251 | 0.331 | -0.244 | 0.345 | -0.361 | 0.155 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.031 | 0.911 | 0.346 | 0.206 | 0.278 | 0.315 |
| 低密度脂蛋白 | 0.047 | 0.867 | -0.142 | 0.614 | -0.139 | 0.620 |
| 钙 | 0.038 | 0.886 | 0.244 | 0.345 | -0.096 | 0.713 |
| 无机磷 | 0.176 | 0.499 | -0.525 | 0.030 | 0.072 | 0.783 |
| 镁 | 0.417 | 0.096 | 0.012 | 0.963 | -0.012 | 0.963 |
| 钾 | 0.201 | 0.439 | -0.634 | 0.006 | -0.409 | 0.103 |
| 钠 | -0.226 | 0.383 | -0.305 | 0.234 | -0.144 | 0.580 |
| 24 h尿蛋白定量 | 0.503 | 0.040 | -0.366 | 0.149 | -0.361 | 0.155 |
| 血红蛋白 | 0.251 | 0.330 | -0.085 | 0.744 | -0.156 | 0.549 |
| 血小板计数 | -0.063 | 0.811 | -0.232 | 0.370 | -0.289 | 0.261 |
| 尿红细胞检查(镜检)/HPF | -0.202 | 0.436 | -0.147 | 0.572 | 0.085 | 0.746 |
| eGFR | -0.352 | 0.166 | 0.268 | 0.298 | 0.072 | 0.783 |
| 临床指标 | 气虚证 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | |
| M病变 | 0.288 | 0.263 | -0.132 | 0.612 | 0.203 | 0.434 |
| E病变 | 0.185 | 0.478 | -0.299 | 0.244 | 0.236 | 0.362 |
| S病变 | -0.185 | 0.478 | -0.209 | 0.420 | -0.236 | 0.362 |
| T病变 | 0.207 | 0.207 | 0.161 | 0.537 | 0.502 | 0.040 |
| C病变 | 0.030 | 0.908 | -0.132 | 0.612 | -0.044 | 0.868 |
表7 IgAN-MHT患者病理指标与中医证型的相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis of pathological indices and TCM syndromes in IgA nephropathy patients with malignant hypertension
| 临床指标 | 气虚证 | 阴虚证 | 血瘀证 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | |
| M病变 | 0.288 | 0.263 | -0.132 | 0.612 | 0.203 | 0.434 |
| E病变 | 0.185 | 0.478 | -0.299 | 0.244 | 0.236 | 0.362 |
| S病变 | -0.185 | 0.478 | -0.209 | 0.420 | -0.236 | 0.362 |
| T病变 | 0.207 | 0.207 | 0.161 | 0.537 | 0.502 | 0.040 |
| C病变 | 0.030 | 0.908 | -0.132 | 0.612 | -0.044 | 0.868 |
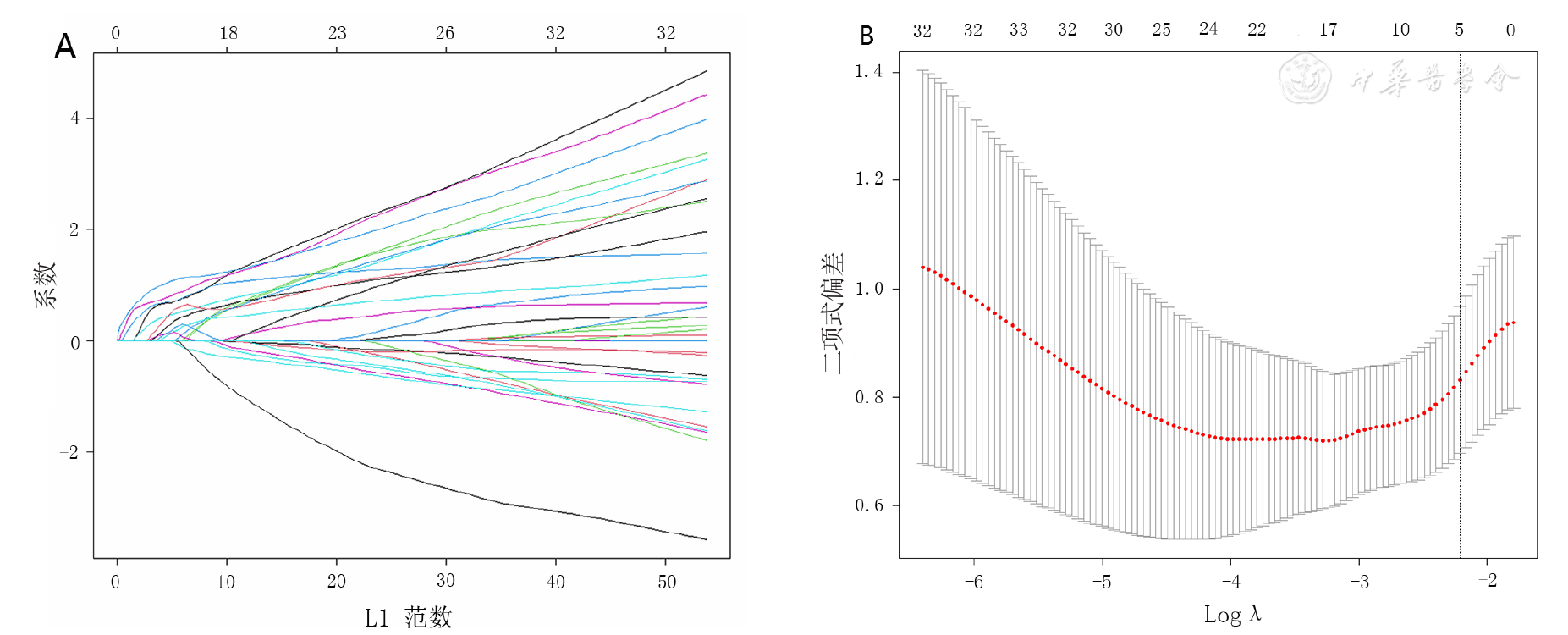
图2 采用Lasso回归模型筛选伴MHTIgAN的中医相关因素注:图A为中医变量各自对应的Lasso回归系数,图B为Lasso回归模型和10折交叉验证法筛选中医变量
Figure 2 Screening TCM-related factors of malignant hypertension in IgA nephropathyby LASSO regression model
| 指标 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形寒肢冷 | -0.724 | 0.614 | 1.392 | 0.238 | 0.485 | (0.146,1.614) |
| 肌肤干燥 | -0.836 | 0.795 | 1.106 | 0.293 | 0.433 | (0.091,2.058) |
| 爪甲青紫 | 2.547 | 0.916 | 7.733 | 0.005 | 12.769 | (2.121,76.882) |
| 口唇青紫 | -0.414 | 0.617 | 0.450 | 0.502 | 0.661 | (0.197,2.217 ) |
| 面色晦暗 | -0.773 | 0.613 | 1.590 | 0.207 | 0.462 | (0.139,1.535) |
| 颧红 | 1.037 | 0.764 | 1.842 | 0.175 | 2.821 | (0.631,12.618) |
| 头痛 | 2.190 | 0.595 | 13.553 | <0.001 | 8.933 | (2.784,28.663) |
| 视物模糊 | 1.990 | 0.589 | 11.424 | 0.001 | 7.314 | (2.307,23.189) |
| 飞蚊症 | 2.702 | 0.777 | 12.105 | 0.001 | 14.909 | (3.254,68.311) |
| 耳聋 | 1.702 | 0.680 | 6.263 | 0.012 | 5.486 | (1.446,20.809) |
| 口干喜饮 | 2.416 | 0.604 | 16.022 | <0.001 | 11.200 | (3.431,36.557) |
| 喜热饮 | -0.934 | 0.675 | 1.913 | 0.167 | 0.393 | (0.105,1.476) |
| 恶心 | 1.535 | 0.663 | 5.369 | 0.020 | 4.643 | (1.267,17.013) |
| 胁肋胀满 | -0.967 | 1.077 | 0.806 | 0.369 | 0.380 | (0.046,3.138) |
| 四肢倦怠 | 1.267 | 0.573 | 4.888 | 0.027 | 3.550 | (1.155,10.914) |
| 肢体关节疼痛 | -0.629 | 0.800 | 0.617 | 0.432 | 0.533 | (0.111,2.559) |
| 泄泻 | 0.758 | 0.883 | 0.737 | 0.391 | 2.133 | (0.378,12.034) |
表8 患者中医指标对伴MHTIgAN影响的单因素Logistic回归分析
Table 8 Univariate Logistic regression analysis of TCM indicators associated with malignant hypertension in IgA nephropathy
| 指标 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形寒肢冷 | -0.724 | 0.614 | 1.392 | 0.238 | 0.485 | (0.146,1.614) |
| 肌肤干燥 | -0.836 | 0.795 | 1.106 | 0.293 | 0.433 | (0.091,2.058) |
| 爪甲青紫 | 2.547 | 0.916 | 7.733 | 0.005 | 12.769 | (2.121,76.882) |
| 口唇青紫 | -0.414 | 0.617 | 0.450 | 0.502 | 0.661 | (0.197,2.217 ) |
| 面色晦暗 | -0.773 | 0.613 | 1.590 | 0.207 | 0.462 | (0.139,1.535) |
| 颧红 | 1.037 | 0.764 | 1.842 | 0.175 | 2.821 | (0.631,12.618) |
| 头痛 | 2.190 | 0.595 | 13.553 | <0.001 | 8.933 | (2.784,28.663) |
| 视物模糊 | 1.990 | 0.589 | 11.424 | 0.001 | 7.314 | (2.307,23.189) |
| 飞蚊症 | 2.702 | 0.777 | 12.105 | 0.001 | 14.909 | (3.254,68.311) |
| 耳聋 | 1.702 | 0.680 | 6.263 | 0.012 | 5.486 | (1.446,20.809) |
| 口干喜饮 | 2.416 | 0.604 | 16.022 | <0.001 | 11.200 | (3.431,36.557) |
| 喜热饮 | -0.934 | 0.675 | 1.913 | 0.167 | 0.393 | (0.105,1.476) |
| 恶心 | 1.535 | 0.663 | 5.369 | 0.020 | 4.643 | (1.267,17.013) |
| 胁肋胀满 | -0.967 | 1.077 | 0.806 | 0.369 | 0.380 | (0.046,3.138) |
| 四肢倦怠 | 1.267 | 0.573 | 4.888 | 0.027 | 3.550 | (1.155,10.914) |
| 肢体关节疼痛 | -0.629 | 0.800 | 0.617 | 0.432 | 0.533 | (0.111,2.559) |
| 泄泻 | 0.758 | 0.883 | 0.737 | 0.391 | 2.133 | (0.378,12.034) |
| 指标 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 头痛 | 2.066 | 0.801 | 6.658 | 0.010 | 7.895 | (1.643,37.935) |
| 视物模糊 | 1.705 | 0.774 | 4.853 | 0.028 | 5.499 | (1.207,25.053) |
| 口干喜饮 | 2.310 | 0.756 | 9.334 | 0.002 | 10.079 | (2.289,44.373) |
| 爪甲青紫 | 2.908 | 1.086 | 7.167 | 0.007 | 18.312 | (2.179,153.884) |
表9 患者中医指标对伴MHT的原发性IgAN影响的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 9 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of TCM indicators associated with malignant hypertension in IgA nephropathy
| 指标 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 头痛 | 2.066 | 0.801 | 6.658 | 0.010 | 7.895 | (1.643,37.935) |
| 视物模糊 | 1.705 | 0.774 | 4.853 | 0.028 | 5.499 | (1.207,25.053) |
| 口干喜饮 | 2.310 | 0.756 | 9.334 | 0.002 | 10.079 | (2.289,44.373) |
| 爪甲青紫 | 2.908 | 1.086 | 7.167 | 0.007 | 18.312 | (2.179,153.884) |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
陈仆,陈香美,谢院生,等. 伴MHTIgA肾病的临床病理特征及其与肾血管病变的相关性[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2008,24(6):392-397. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7097.2008.06.005.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
陈天新,陈波,陈薪薪,等. 伴与不伴原发性肾脏病的MHT肾损害临床病理特点及预后对比分析[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2020,28(9):900. DOI:10.16439/j.cnki.1673-7245.2020.09.030.
|
| [7] | |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中华急诊医学教育学院,北京市心肺脑复苏重点实验室,首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院急诊医学临床研究中心,等. 中国高血压急症诊治规范[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2020,29(9):1154-1161. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2020.09.003.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
陈香美,邓跃毅,谢院生. IgA肾病西医诊断和中医辨证分型的实践指南[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2013,33(5):583-585.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
张惠雅,窦艳娜,刘栋,等. 血清IgM水平与IgA肾病疾病严重程度及预后的相关性[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2020,36(1):41-44. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-7097.2020.01.007.
|
| [19] |
温碧玉. 血清IgG与IgA肾病不良预后的相关性研究[D]. 太原:山西医科大学,2020.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
徐迎华. 狼疮性肾炎肾小管间质损害相关分析[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2018.
|
| [22] |
程小红,于小勇,毛加荣. IgA肾病的病理改变与中医微观辨证[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2014,15(2):185-186.
|
| [23] | |
| [24] |
占永立,李秀英,李深,等. 17例肾性MHT临床与病理分析[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2006,7(2):101-103. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2006.02.014.
|
| [25] |
陈一峰,方寒蕊,王浩,等. 高血压200例脉象及病机分析[J]. 中国社区医师,2021,37(27):91-92. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2021.27.045.
|
| [26] | |
| [27] |
廖辉,李丹萍,陈强,等. "泻南补北"法治疗阴虚阳亢型高血压病疗效观察[J]. 中国针灸,2006,26(2):91-93.
|
| [28] |
蔺晓源,杨晓丹,姚福胜,等. 原发性高血压病"本虚标实"的中医病机与治疗[J]. 中医药学报,2018,46(6):10-12. DOI:10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.180169.
|
| [29] |
杨晓萍,唐岚,张琪琳,等. 高血压性肾损害的中医症状证型分析[J]. 山东中医药大学学报,2014,38(1):28-30. DOI:10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2014.01.008.
|
| [30] |
焦欣,蔺晓源,雍苏南. 基于名老中医经验的高血压病病名、病因、病机、证型研究[J]. 中医药信息,2020,37(4):31-35. DOI:10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.200095.
|
| [1] | 秦凤银, 张绮珊, 赖锦佳, 黄奕敏, 韩郭茵, 孙兴兰, 王芬, 谭益冰. 广东省社区居民脑卒中高危筛查意向的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4283-4289. |
| [2] | 郝爱华, 曾韦霖, 李观海, 夏英华, 陈亮. 基于全科医生视角的家庭医生团队签约现状调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4261-4268. |
| [3] | 李殿江, 潘恩春, 孙中明, 文进博, 王苗苗, 武鸣, 沈冲. 社区2型糖尿病患者临床惰性现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4296-4301. |
| [4] | 王越, 陈晴, 刘鲁蓉. 中国老年人抑郁检出率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [5] | 王丽娜, 高鹏飞, 曹帆, 葛莹, 颜维, 何岱昆. 不同性别人群非酒精性脂肪性肝病患病现况及影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4143-4151. |
| [6] | 彰金, 丁治国, 祁烁, 李颖, 李伟强, 张媛媛, 周通. 血清甲状腺激素水平与心力衰竭患者住院期间预后的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4125-4129. |
| [7] | 周俞余, 高川, 崔埔安, 王亚平, 何仲. 更年期综合征患者绝经激素治疗中医患共同决策质量的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4181-4186. |
| [8] | 梁譞, 那飞扬, 秦梦瑶, 杨辉, 郭丽, 郭琪, 任蕾, 陈德, 刘东海, 张蓉芳. 儿童支气管哮喘合并阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的临床特征及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4225-4230. |
| [9] | 李芊芊, 陈循睿, 张文颖, 袁海花, 张燕捷, 姜斌, 刘峰. 晚期肿瘤患者化疗期间对社区卫生服务需求的调查及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4173-4180. |
| [10] | 高德康, 危少华, 马孝明, 杜鹏, 邢春根, 曹春. 肝癌大范围肝切除术后骨骼肌减少的危险因素及其与术后并发症的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4031-4037. |
| [11] | 王明欢, 李玉红, 俞敏, 王友刚, 俞巧稚, 杨方方, 袁德慧, 张柳. 妊娠晚期女性非稳态负荷对不良妊娠结局的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4064-4069. |
| [12] | 袁德慧, 李玉红, 熊敏, 俞敏, 马瑞亮, 杨方方, 俞巧稚, 王明欢. 妊娠女性不同时期非稳态负荷状况及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4057-4063. |
| [13] | 张帅, 李琴, 李东锋, 肖金平, 李云鹏. 使用固体燃料与中国老年人高血压发病风险的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4001-4006. |
| [14] | 张娟, 李海芬, 李小曼, 姚苗, 马惠珍, 马强. 糖尿病足溃疡复发风险预测模型的构建:基于Logistic回归和支持向量机及BP神经网络模型[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4013-4019. |
| [15] | 高婧, 周尚成, 高三德, 邹冠炀, 陈颖尧. 基于欧洲五维健康量表的中医治未病门诊就诊患者健康相关生命质量及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4043-4050. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





