中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (36): 4578-4585.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0434
所属专题: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2024-06-25
修回日期:2025-04-28
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-04
通讯作者:
王祺
作者贡献:
范学明进行文章的构思和设计;杨宁宁进行结果的分析和解释;郑症进行研究数据的收集整理和统计学处理;吴玉梅、王祺进行论文的修订,对文章整体监督管理。
FAN Xueming, YANG Ningning, ZHENG Zheng, WU Yumei, WANG Qi*( )
)
Received:2024-06-25
Revised:2025-04-28
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-12-04
Contact:
WANG Qi
摘要: 背景 2型糖尿病(T2DM)与代谢相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)常合并存在,二者通过胰岛素抵抗、脂代谢异常及慢性炎症等机制相互作用,显著增加了微血管病变风险,但现有研究对相关危险因素的定量分析及预测模型构建不足,亟需明确关键生物标志物以指导早期干预。 目的 研究T2DM合并MAFLD患者微血管病变发生的相关因素及预测价值。 方法 回顾性分析2021年1月—2023年8月安徽医科大学附属六安医院接收的T2DM合并MAFLD患者的临床资料,通过病历系统记录按照1∶1的比例,选取110例发生微血管病变的患者及110例未发生微血管病变的患者为建模组,选取同期106例T2DM合并MAFLD患者为验证组,另外将出现微血管病变者划分到发生组(n=110),未出现微血管病变者划分到未发生组(n=110)。通过病历系统记录内容收集患者一般资料及实验室检查结果,计算非酒精性脂肪肝纤维化评分(NFS)、肝纤维化4因子指数(FIB-4)、甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG)。采用共线性分析筛选方差膨胀系数(VIF)<10的指标进行多因素Logistic回归分析,构建受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,判断各指标对T2DM合并MAFLD患者发生微血管病变的预测效果。 结果 建模队列和验证队列基线资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。发生微血管病变的T2DM合并MAFLD患者中,44例(40.0%)发生糖尿病肾病,29例(26.4%)发生糖尿病视网膜病变,37例(33.6%)发生糖尿病肾病合并糖尿病视网膜病变。未发生组与发生组患者吸烟史、糖尿病病程、C反应蛋白(CRP)、TyG、三酰甘油(TG)、FIB-4、NFS比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,有吸烟史(OR=8.298,95%CI=1.957~35.175)、糖尿病病程长(OR=2.638,95%CI=1.515~4.596)、CRP升高(OR=7.918,95%CI=4.013~15.624)、TyG升高(OR=1.533,95%CI=1.171~2.006)、TG升高(OR=2.055,95%CI=1.475~2.862)、FIB-4升高(OR=29.598,95%CI=9.179~95.437)、NFS升高(OR=3.433,95%CI=2.113~5.576)为T2DM合并MAFLD患者发生微血管病变的危险因素(P<0.05)。CRP、TyG、糖尿病病程、吸烟史、TG、NFS、FIB-4预测T2DM合并MAFLD患者发生微血管病变的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.964(95%CI=0.944~0.984,P<0.001)、0.620(95%CI=0.546~0.693,P=0.002)、0.795(95%CI=0.737~0.853,P=0.001)、0.605(95%CI=0.530~0.679,P=0.004)、0.663(95%CI=0.592~0.735,P<0.001)、0.730(95%CI=0.664~0.796,P<0.001)、0.743(95%CI=0.678~0.808,P<0.001)。基于上述指标构建预测模型,建模队列AUC(95%CI)为0.990(0.990~1.000),预测价值较好。 结论 临床可通过对T2DM合并MAFLD患者的CRP、TyG、糖尿病病程、吸烟史、TG、NFS、FIB-4的观察和检测对微血管病变发生进行有效预测,有利于T2DM合并MAFLD患者中筛选发生微血管病变的高危患者。
| 指标 | 建模队列(n=220) | 验证队列(n=106) | t(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 138/82 | 76/30 | 2.553a | 0.110 |
| 年龄(岁) | 68.7±9.1 | 68.9±9.1 | 0.028 | 0.978 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 67(30.5) | 35(33.0) | 0.219a | 0.640 |
| 受教育程度[例(%)] | 0.046a | 0.830 | ||
| 高中及以下 | 92(41.8) | 43(40.6) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 128(58.2) | 63(49.4) | ||
| 家族慢性疾病史[例(%)] | 0.377a | 0.539 | ||
| 有 | 48(21.8) | 20(18.9) | ||
| 无 | 172(78.2) | 86(81.1) | ||
| 家庭月收入情况[例(%)] | 0.336a | 0.562 | ||
| ≤5 000元 | 86(39.1) | 45(42.5) | ||
| >5 000元 | 134(60.9) | 61(57.5) | ||
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.44±2.56 | 22.58±2.53 | 0.464 | 0.643 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 6.80±1.33 | 6.95±1.35 | 0.949 | 0.343 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 7.34±1.37 | 7.29±1.28 | 0.315 | 0.753 |
| TyG | 9.34±1.26 | 9.30±1.32 | 0.264 | 0.792 |
| SBP(mmHg) | 129±14 | 126±10 | 1.683 | 0.093 |
| DBP(mmHg) | 84±8 | 83±8 | 1.037 | 0.300 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.06±0.15 | 1.04±0.14 | 1.152 | 0.250 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.73±0.31 | 2.78±0.29 | 1.393 | 0.165 |
| HbAlc(%) | 9.82±0.99 | 9.98±0.98 | 0.514 | 0.607 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.49±1.31 | 8.53±1.33 | 0.257 | 0.797 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 6.26±0.88 | 6.23±0.85 | 0.292 | 0.771 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 4.24±0.57 | 4.30±0.59 | 0.880 | 0.379 |
| FIB-4 | 1.37±0.26 | 1.36±0.28 | 0.634 | 0.526 |
| NFS(分) | -0.45±0.57 | -0.40±0.53 | 0.455 | 0.649 |
| PT(s) | 11.21±2.15 | 11.26±2.18 | 0.196 | 0.845 |
| APTT(s) | 28.43±3.17 | 28.64±3.05 | 0.567 | 0.571 |
| TT(s) | 12.23±1.75 | 12.30±1.81 | 0.335 | 0.738 |
| AST(U/L) | 24.25±9.81 | 22.82±7.65 | 1.320 | 0.188 |
| ALT(U/L) | 27.93±6.54 | 27.16±6.10 | 1.017 | 0.310 |
| PLT(×109/L) | 144.55±10.49 | 147.16±20.69 | 1.512 | 0.131 |
| ALB(mg/L) | 12.57±1.18 | 12.79±1.11 | 1.607 | 0.109 |
表1 建模队列与验证队列基线资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of baseline data between modeling queue and validation queue
| 指标 | 建模队列(n=220) | 验证队列(n=106) | t(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 138/82 | 76/30 | 2.553a | 0.110 |
| 年龄(岁) | 68.7±9.1 | 68.9±9.1 | 0.028 | 0.978 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 67(30.5) | 35(33.0) | 0.219a | 0.640 |
| 受教育程度[例(%)] | 0.046a | 0.830 | ||
| 高中及以下 | 92(41.8) | 43(40.6) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 128(58.2) | 63(49.4) | ||
| 家族慢性疾病史[例(%)] | 0.377a | 0.539 | ||
| 有 | 48(21.8) | 20(18.9) | ||
| 无 | 172(78.2) | 86(81.1) | ||
| 家庭月收入情况[例(%)] | 0.336a | 0.562 | ||
| ≤5 000元 | 86(39.1) | 45(42.5) | ||
| >5 000元 | 134(60.9) | 61(57.5) | ||
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.44±2.56 | 22.58±2.53 | 0.464 | 0.643 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 6.80±1.33 | 6.95±1.35 | 0.949 | 0.343 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 7.34±1.37 | 7.29±1.28 | 0.315 | 0.753 |
| TyG | 9.34±1.26 | 9.30±1.32 | 0.264 | 0.792 |
| SBP(mmHg) | 129±14 | 126±10 | 1.683 | 0.093 |
| DBP(mmHg) | 84±8 | 83±8 | 1.037 | 0.300 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.06±0.15 | 1.04±0.14 | 1.152 | 0.250 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.73±0.31 | 2.78±0.29 | 1.393 | 0.165 |
| HbAlc(%) | 9.82±0.99 | 9.98±0.98 | 0.514 | 0.607 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.49±1.31 | 8.53±1.33 | 0.257 | 0.797 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 6.26±0.88 | 6.23±0.85 | 0.292 | 0.771 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 4.24±0.57 | 4.30±0.59 | 0.880 | 0.379 |
| FIB-4 | 1.37±0.26 | 1.36±0.28 | 0.634 | 0.526 |
| NFS(分) | -0.45±0.57 | -0.40±0.53 | 0.455 | 0.649 |
| PT(s) | 11.21±2.15 | 11.26±2.18 | 0.196 | 0.845 |
| APTT(s) | 28.43±3.17 | 28.64±3.05 | 0.567 | 0.571 |
| TT(s) | 12.23±1.75 | 12.30±1.81 | 0.335 | 0.738 |
| AST(U/L) | 24.25±9.81 | 22.82±7.65 | 1.320 | 0.188 |
| ALT(U/L) | 27.93±6.54 | 27.16±6.10 | 1.017 | 0.310 |
| PLT(×109/L) | 144.55±10.49 | 147.16±20.69 | 1.512 | 0.131 |
| ALB(mg/L) | 12.57±1.18 | 12.79±1.11 | 1.607 | 0.109 |
| 微血管病变类型 | 发生例数 | 占比(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 糖尿病肾病 | 44 | 40.0 |
| 糖尿病视网膜病变 | 29 | 26.4 |
| 糖尿病肾病合并糖尿病视网膜病变 | 37 | 33.6 |
表2 T2DM合并MAFLD患者微血管病变情况
Table 2 Microvascular lesions in patients with T2DM combined with MAFLD
| 微血管病变类型 | 发生例数 | 占比(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 糖尿病肾病 | 44 | 40.0 |
| 糖尿病视网膜病变 | 29 | 26.4 |
| 糖尿病肾病合并糖尿病视网膜病变 | 37 | 33.6 |
| 项目 | 未发生组(n=110) | 发生组(n=110) | t(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 68/42 | 70/40 | 0.078a | 0.780 |
| 年龄(岁) | 68.8±8.9 | 68.6±9.1 | 0.150 | 0.881 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 22(20.0) | 45(40.9) | 11.353a | 0.001 |
| 受教育程度[例(%)] | 0.083a | 0.774 | ||
| 高中及以下 | 35(31.8) | 37(33.6) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 75(68.2) | 73(66.4) | ||
| 家族慢性疾病史[例(%)] | 0.107a | 0.744 | ||
| 有 | 25(22.7) | 23(20.9) | ||
| 无 | 85(77.3) | 87(79.1) | ||
| 家庭月收入情况[例(%)] | 0.076a | 0.782 | ||
| ≤5 000元 | 42(38.2) | 44(40.0) | ||
| >5 000元 | 68(61.8) | 66(60.0) | ||
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.43±2.25 | 22.45±2.27 | 0.100 | 0.921 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 6.14±1.09 | 7.47±1.15 | 8.804 | <0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 5.64±1.47 | 9.05±1.23 | 18.659 | <0.001 |
| TyG | 9.12±1.01 | 9.56±1.05 | 3.167 | 0.002 |
| SBP(mmHg) | 129±13 | 129±13 | 0.073 | 0.942 |
| DBP(mmHg) | 84±11 | 84±10 | 0.065 | 0.949 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.05±0.21 | 1.07±0.24 | 0.658 | 0.511 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.78±0.35 | 2.69±0.37 | 1.853 | 0.065 |
| HbAlc(%) | 9.85±0.51 | 9.78±0.62 | 0.914 | 0.361 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.32±1.45 | 8.65±1.62 | 1.592 | 0.113 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 6.31±1.28 | 6.20±1.15 | 0.670 | 0.503 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 3.96±0.81 | 4.52±0.95 | 4.705 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 1.24±0.25 | 1.51±0.34 | 6.710 | <0.001 |
| NFS | -0.68±0.54 | -0.21±0.68 | 5.677 | <0.001 |
| PT(s) | 11.26±2.81 | 11.16±2.66 | 0.271 | 0.787 |
| APTT(s) | 28.55±3.58 | 28.32±3.45 | 0.485 | 0.628 |
| TT(s) | 12.25±3.21 | 12.20±2.78 | 0.123 | 0.902 |
| AST(U/L) | 23.26±8.72 | 25.24±10.89 | 1.489 | 0.138 |
| ALT(U/L) | 27.11±6.32 | 28.75±6.76 | 1.859 | 0.064 |
| PLT(×109/L) | 143.32±10.86 | 145.77±10.12 | 1.731 | 0.085 |
| ALB(mg/L) | 12.45±1.09 | 12.68±1.26 | 1.448 | 0.149 |
表3 未发生组与发生组患者基线资料比较
Table 3 Comparison of baseline data between the non-occurrence group and the occurrence group of patients
| 项目 | 未发生组(n=110) | 发生组(n=110) | t(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 68/42 | 70/40 | 0.078a | 0.780 |
| 年龄(岁) | 68.8±8.9 | 68.6±9.1 | 0.150 | 0.881 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 22(20.0) | 45(40.9) | 11.353a | 0.001 |
| 受教育程度[例(%)] | 0.083a | 0.774 | ||
| 高中及以下 | 35(31.8) | 37(33.6) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 75(68.2) | 73(66.4) | ||
| 家族慢性疾病史[例(%)] | 0.107a | 0.744 | ||
| 有 | 25(22.7) | 23(20.9) | ||
| 无 | 85(77.3) | 87(79.1) | ||
| 家庭月收入情况[例(%)] | 0.076a | 0.782 | ||
| ≤5 000元 | 42(38.2) | 44(40.0) | ||
| >5 000元 | 68(61.8) | 66(60.0) | ||
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.43±2.25 | 22.45±2.27 | 0.100 | 0.921 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 6.14±1.09 | 7.47±1.15 | 8.804 | <0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 5.64±1.47 | 9.05±1.23 | 18.659 | <0.001 |
| TyG | 9.12±1.01 | 9.56±1.05 | 3.167 | 0.002 |
| SBP(mmHg) | 129±13 | 129±13 | 0.073 | 0.942 |
| DBP(mmHg) | 84±11 | 84±10 | 0.065 | 0.949 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.05±0.21 | 1.07±0.24 | 0.658 | 0.511 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.78±0.35 | 2.69±0.37 | 1.853 | 0.065 |
| HbAlc(%) | 9.85±0.51 | 9.78±0.62 | 0.914 | 0.361 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.32±1.45 | 8.65±1.62 | 1.592 | 0.113 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 6.31±1.28 | 6.20±1.15 | 0.670 | 0.503 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 3.96±0.81 | 4.52±0.95 | 4.705 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 1.24±0.25 | 1.51±0.34 | 6.710 | <0.001 |
| NFS | -0.68±0.54 | -0.21±0.68 | 5.677 | <0.001 |
| PT(s) | 11.26±2.81 | 11.16±2.66 | 0.271 | 0.787 |
| APTT(s) | 28.55±3.58 | 28.32±3.45 | 0.485 | 0.628 |
| TT(s) | 12.25±3.21 | 12.20±2.78 | 0.123 | 0.902 |
| AST(U/L) | 23.26±8.72 | 25.24±10.89 | 1.489 | 0.138 |
| ALT(U/L) | 27.11±6.32 | 28.75±6.76 | 1.859 | 0.064 |
| PLT(×109/L) | 143.32±10.86 | 145.77±10.12 | 1.731 | 0.085 |
| ALB(mg/L) | 12.45±1.09 | 12.68±1.26 | 1.448 | 0.149 |
| 变量 | VIF值 | 容忍度 |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | 2.684 | 0.373 |
| TyG | 1.100 | 0.909 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 1.393 | 0.718 |
| 吸烟史 | 1.085 | 0.922 |
| TG | 1.120 | 0.892 |
| FIB-4 | 1.314 | 0.761 |
| NFS | 1.141 | 0.876 |
表4 共线性分析结果
Table 4 Results of the collinearity analysis
| 变量 | VIF值 | 容忍度 |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | 2.684 | 0.373 |
| TyG | 1.100 | 0.909 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 1.393 | 0.718 |
| 吸烟史 | 1.085 | 0.922 |
| TG | 1.120 | 0.892 |
| FIB-4 | 1.314 | 0.761 |
| NFS | 1.141 | 0.876 |
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 2.069 | 0.347 | 35.602 | <0.001 | 7.918 | 4.013~15.624 |
| TyG | 0.427 | 0.137 | 9.664 | 0.002 | 1.533 | 1.171~2.006 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 0.970 | 0.283 | 11.739 | 0.001 | 2.638 | 1.515~4.596 |
| 吸烟史 | 2.116 | 0.737 | 8.244 | 0.004 | 8.298 | 1.957~35.175 |
| TG | 0.720 | 0.169 | 18.116 | <0.001 | 2.055 | 1.475~2.862 |
| NFS | 1.233 | 0.248 | 24.817 | <0.001 | 3.433 | 2.113~5.576 |
| FIB-4 | 3.388 | 0.597 | 32.164 | <0.001 | 29.598 | 9.179~95.437 |
表5 T2DM合并MAFLD患者微血管病变发生风险多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Table 5 Results of multivariate Logistic regression analysis of microvascular lesions in patients with T2DM combined with MAFLD
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 2.069 | 0.347 | 35.602 | <0.001 | 7.918 | 4.013~15.624 |
| TyG | 0.427 | 0.137 | 9.664 | 0.002 | 1.533 | 1.171~2.006 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 0.970 | 0.283 | 11.739 | 0.001 | 2.638 | 1.515~4.596 |
| 吸烟史 | 2.116 | 0.737 | 8.244 | 0.004 | 8.298 | 1.957~35.175 |
| TG | 0.720 | 0.169 | 18.116 | <0.001 | 2.055 | 1.475~2.862 |
| NFS | 1.233 | 0.248 | 24.817 | <0.001 | 3.433 | 2.113~5.576 |
| FIB-4 | 3.388 | 0.597 | 32.164 | <0.001 | 29.598 | 9.179~95.437 |
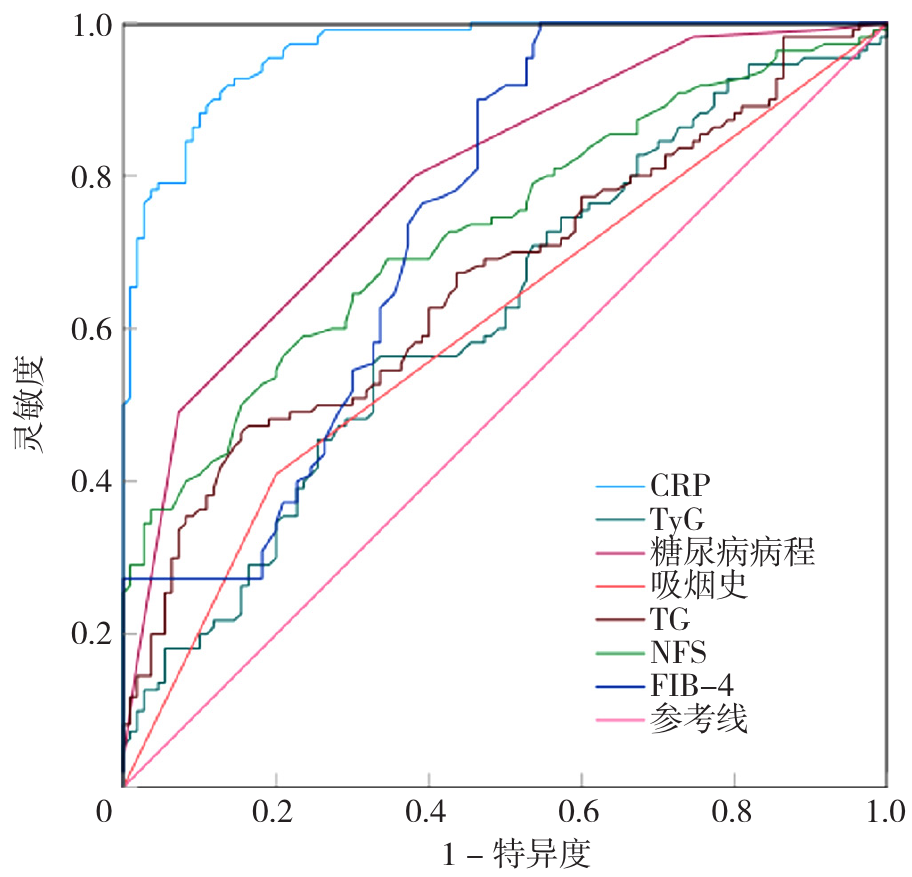
图1 CRP、TyG、糖尿病病程、吸烟史、TG、NFS、FIB-4预测T2DM合并MAFLD患者发生微血管病变风险的ROC曲线注:CRP=C反应蛋白,TyG=甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数,TG=三酰甘油,FIB-4=肝纤维化4因子指数,NFS=非酒精性脂肪肝纤维化评分。
Figure 1 ROC curves of CRP,TyG,duration of diabetes,smoking history,TG,NFS,and FIB-4 in predicting microvascular lesions in patients with T2DM combined with MAFLD
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | AUC | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 7.50 mg/L | 0.882 | 0.900 | 0.782 | 0.964 | 0.944~0.984 |
| TyG | 9.63 | 0.555 | 0.673 | 0.227 | 0.620 | 0.546~0.693 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 7.00年 | 0.491 | 0.927 | 0.418 | 0.795 | 0.737~0.853 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.409 | 0.800 | 0.209 | 0.605 | 0.530~0.679 | |
| TG | 4.73 mmg/L | 0.464 | 0.845 | 0.309 | 0.663 | 0.592~0.735 |
| NFS | 1.45 | 0.591 | 0.764 | 0.355 | 0.730 | 0.664~0.796 |
| FIB-4 | -0.80 | 1.000 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.743 | 0.678~0.808 |
表6 CRP、TyG、糖尿病病程、吸烟史、TG、NFS、FIB-4对T2DM合并MAFLD患者发生微血管病变风险的预测价值
Table 6 Performance evaluation of CRP,TyG,duration of diabetes,smoking history,TG,NFS,and FIB-4 in predicting microvascular lesions in patients with T2DM complicated with MAFLD
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | AUC | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 7.50 mg/L | 0.882 | 0.900 | 0.782 | 0.964 | 0.944~0.984 |
| TyG | 9.63 | 0.555 | 0.673 | 0.227 | 0.620 | 0.546~0.693 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 7.00年 | 0.491 | 0.927 | 0.418 | 0.795 | 0.737~0.853 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.409 | 0.800 | 0.209 | 0.605 | 0.530~0.679 | |
| TG | 4.73 mmg/L | 0.464 | 0.845 | 0.309 | 0.663 | 0.592~0.735 |
| NFS | 1.45 | 0.591 | 0.764 | 0.355 | 0.730 | 0.664~0.796 |
| FIB-4 | -0.80 | 1.000 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.743 | 0.678~0.808 |
| 指标 | 建模队列(n=220) | 验证队列(n=106) |
|---|---|---|
| 区分度 | ||
| AUC(95%CI) | 0.990(0.990~1.000) | 1.000(0.990~1.000) |
| 灵敏度(%) | 97.00 | 100.00 |
| 特异度(%) | 95.00 | 96.00 |
| 正确指数 | 0.960 | 0.980 |
| 校准度 | ||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow检验P值 | 0.923 | 0.999 |
表7 预测模型在建模队列和验证队列中的性能
Table 7 Performance of the prediction model in the modeling queue and the validation queue
| 指标 | 建模队列(n=220) | 验证队列(n=106) |
|---|---|---|
| 区分度 | ||
| AUC(95%CI) | 0.990(0.990~1.000) | 1.000(0.990~1.000) |
| 灵敏度(%) | 97.00 | 100.00 |
| 特异度(%) | 95.00 | 96.00 |
| 正确指数 | 0.960 | 0.980 |
| 校准度 | ||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow检验P值 | 0.923 | 0.999 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
中国老年型糖尿病防治临床指南编写组,中国老年医学学会老年内分泌代谢分会,中国老年保健医学研究会老年内分泌与代谢分会,等. 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2022,61(1):12-50. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211027-00751.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [1] | 刘瑞越, 杨雪梅, 赵乃慧, 温薪冉, 蔡汐, 梁雅靖, 马佳佳, 吴寿岭, 崔刘福. 不同年龄段超敏C反应蛋白与白蛋白比值对新发心血管疾病的影响:一项队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(36): 4566-4577. |
| [2] | 曾明慧, 蒯文涛, 陈林, 韩家鑫, 徐连欣, 葛立颖, 代容容, 宓余强, 徐亮. 2型糖尿病对核苷(酸)类似物治疗慢性乙型肝炎效果的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(35): 4414-4420. |
| [3] | 徐君, 张劼. 2型糖尿病患者心率变异性与脑梗死的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(35): 4409-4413. |
| [4] | 杨冰清, 扬天元, 侯辰雪, 王琦. 无创模型在评估慢性乙型肝炎合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者肝纤维化中的比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4067-4074. |
| [5] | 阳坚, 吴传安, 周海蓉, 田峰, 迟春花. 三酰甘油葡萄糖-体质指数对2型糖尿病合并代谢相关脂肪性肝病的诊断价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4075-4081. |
| [6] | 赵玉晴, 王伟, 陈立沅, 油惠娟, 魏莹, 王清路, 杨风英. 肝脏巨噬细胞极化:运动防治非酒精性脂肪性肝病的新靶向[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3456-3465. |
| [7] | 张宇诺, 李瑞斌, 王玮. 血清Nesfatin-1和Ghrelin水平与糖脂代谢及2型糖尿病的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3264-3270. |
| [8] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [9] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [10] | 吴莎, 张代义, 李晋, 宣勤考, 钱晓东, 朱传武, 浦剑虹, 朱莉. 基于体检队列的代谢相关脂肪性肝病与高血糖关联及联合预测模型构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2861-2869. |
| [11] | 刘月影, 王雪丽, 刘雨秋, 魏立民. 空腹C肽与糖尿病病程比值与2型糖尿病发生代谢相关脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2852-2860. |
| [12] | 王鹏, 仇丽霞, 许姗姗, 张洋, 张晶, 杜晓菲. 代谢相关脂肪性肝病与2型糖尿病共同管理研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2846-2851. |
| [13] | 白雪, 陈倩倩, 李婕. 慢病管理创新实践:糖肝全-专管理新模式[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2841-2845. |
| [14] | 吕露露, 祝万洁, 肖明洋, 李祎珂, 张娟. 原发性高血压患者血压昼夜节律与血浆氧化的低密度脂蛋白/β2-糖蛋白I复合物及颈动脉粥样硬化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2228-2233. |
| [15] | 赵晓晓, 柯立鑫, 荀杨芹, 王海博, 高武霖, 乔天慈, 卢笑晖, 武继彪, 卢存存. 1990—2021年全球与中国老年2型糖尿病的疾病负担调查与未来趋势预测[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2050-2058. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





