中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (23): 2924-2933.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0864
收稿日期:2023-11-19
修回日期:2024-05-28
出版日期:2025-08-15
发布日期:2025-06-17
通讯作者:
李江涛
作者贡献:
李浩负责文章的选题、研究设计、文献筛选、数据提取、统计分析、图表绘制、撰写文章;李江涛负责选题指导、文章的质量控制,对文章整体负责,监督管理;刘丹负责文献筛选、数据提取;王建军负责文献筛选时有歧异进行讨论及统计分析。
LI Hao1, LI Jiangtao2,*( ), LIU Dan3, WANG Jianjun1
), LIU Dan3, WANG Jianjun1
Received:2023-11-19
Revised:2024-05-28
Published:2025-08-15
Online:2025-06-17
Contact:
LI Jiangtao
摘要: 背景 系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)是一种慢性多系统自身免疫性疾病,目前已有3种生物制剂被批准用于治疗SLE,分别为贝利尤单抗、阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普,但目前尚缺乏直接比较3种药物疗效及安全性的研究。 目的 通过网状Meta分析探索贝利尤单抗、阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普治疗SLE的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 检索PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、Embase中有关贝利尤单抗、阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普治疗SLE的随机对照试验,检索时间为建库至2023年8月。通过纳入、排除标准筛选文献,获取数据,采用RevMan 5.4.1软件、R语言4.3.1和ADDIS 1.16.8软件对数据进行直接或网状Meta分析。 结果 经过筛选后纳入12项随机对照试验,共计4 789例患者,其中试验组2 721例,安慰剂组2 068例。直接Meta分析结果显示,贝利尤单抗、阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普SLE应答指数4(SRI4)缓解率均高于安慰剂组(OR=1.62,95%CI=1.40~1.88,P<0.001;OR=2.39,95%CI=1.70~3.37,P<0.001;OR=6.28,95%CI=3.20~12.33,P<0.001)。贝利尤单抗、阿尼鲁单抗口服皮质类固醇剂量减少所占比例高于安慰剂组(OR=1.48,95%CI=1.09~2.02,P<0.001;OR=2.45,95%CI=1.69~3.54,P<0.001),严重复发率(SF)低于安慰剂组(OR=0.59,95%CI=0.49~0.71,P<0.001;OR=0.52,95%CI=0.39~0.69,P<0.001)。阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普总不良事件(TAEs)发生率高于安慰剂组(OR=1.80,95%CI=1.25~2.59,P=0.001;OR=2.13,95%CI=1.18~3.83,P=0.01);阿尼鲁单抗严重不良事件(SAEs)发生率低于安慰剂组(OR=0.67,95%CI=0.46~0.97,P=0.04)。与安慰剂组比较,贝利尤单抗和安慰剂组TAEs发生率(OR=0.89,95%CI=0.72~1.08,P=0.24)和SAEs发生率(OR=0.82,95%CI=0.59~1.12,P=0.25)比较,差异无统计学意义。网状Meta分析结果显示,3种生物制剂治疗后的SRI4缓解率的概率排序为泰它西普>阿尼鲁单抗>贝利尤单抗(皮下注射)>贝利尤单抗(静脉注射);TAEs发生率的概率排序为泰它西普>阿尼鲁单抗>贝利尤单抗(静脉注射)>贝利尤单抗(皮下注射)。 结论 3种药物治疗SLE皆具有良好的临床疗效,其中泰它西普疗效更为显著,阿尼鲁单抗和泰它西普虽然增加了用药后的TAEs发生率,但降低了SAEs发生率,贝利尤单抗在安全性方面更为稳定。
中图分类号:
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| #1 | "Lupus Erythematosus,Systemic"[Mesh] |
| #2 | ((((Systemic Lupus Erythematosus[Title/Abstract])OR(Lupus Erythematosus Disseminatus[Title/Abstract]))OR(Libman-Sacks Disease[Title/Abstract]))OR(Disease,Libman-Sacks[Title/Abstract]))OR(Libman Sacks Disease[Title/Abstract]) |
| #3 | #1 OR #2 |
| #4 | "belimumab" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #5 | (LymphoStat-B[Title/Abstract])OR(Benlysta[Title/Abstract]) |
| #6 | #4 OR #5 |
| #7 | "anifrolumab" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #8 | (Saphnelo[Title/Abstract])OR(MEDI-546[Title/Abstract]) |
| #9 | #7 OR #8 |
| #10 | "telitacicept" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #11 | "randomized controlled trial"[pt] OR "controlled clinical trial"[pt] OR randomized[tiab] OR placebo[tiab] OR "drug therapy"[sh] OR randomly[tiab] OR trial[tiab] OR groups[tiab] |
| #12 | #6 AND #9 AND #10 |
| #13 | #3 AND #11 AND #12 |
表1 PubMed检索策略
Table 1 Searching strategies in the PubMed
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| #1 | "Lupus Erythematosus,Systemic"[Mesh] |
| #2 | ((((Systemic Lupus Erythematosus[Title/Abstract])OR(Lupus Erythematosus Disseminatus[Title/Abstract]))OR(Libman-Sacks Disease[Title/Abstract]))OR(Disease,Libman-Sacks[Title/Abstract]))OR(Libman Sacks Disease[Title/Abstract]) |
| #3 | #1 OR #2 |
| #4 | "belimumab" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #5 | (LymphoStat-B[Title/Abstract])OR(Benlysta[Title/Abstract]) |
| #6 | #4 OR #5 |
| #7 | "anifrolumab" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #8 | (Saphnelo[Title/Abstract])OR(MEDI-546[Title/Abstract]) |
| #9 | #7 OR #8 |
| #10 | "telitacicept" [Supplementary Concept] |
| #11 | "randomized controlled trial"[pt] OR "controlled clinical trial"[pt] OR randomized[tiab] OR placebo[tiab] OR "drug therapy"[sh] OR randomly[tiab] OR trial[tiab] OR groups[tiab] |
| #12 | #6 AND #9 AND #10 |
| #13 | #3 AND #11 AND #12 |
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 国家(个) | 临床试验(期) | 试验组 | 对照组 | 疗程(周) | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | ||||||
| WALLACE[ | 2009 | 2 | Ⅱ | 111 | 41.8±11.7 | B | 113 | 42.2±10.9 | A | 52 | ④ |
| NAVARRA[ | 2011 | 13 | Ⅲ | 290 | 35.4±10.8 | B | 287 | 36.2±11.8 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| FURIE[ | 2011 | 19 | Ⅲ | 273 | 40.5±11.1 | B | 275 | 40.0±11.9 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| ZHANG[ | 2017 | 3 | Ⅲ | 451 | 32.3±9.65 | B | 226 | 31.7±9.18 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| STOHL[ | 2017 | 30 | Ⅲ | 556 | 38.1±12.1 | C | 280 | 39.6±12.6 | A | 52 | ①②④ |
| FURIE[ | 2017 | 14 | ⅡB | 99 | 39.1±11.9 | D | 102 | 39.3±12.9 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| FURIE[ | 2019 | 18 | Ⅲ | 180 | 42.0±12.0 | D | 184 | 41.0±12.3 | A | 52 | ②③④ |
| WU[ | 2019 | 1 | ⅡB | 63 | NA | E | 62 | NA | A | 48 | ①④ |
| BRUNNER[ | 2020 | 10 | Ⅱ | 53 | 14.0(12.0,15.0) | B | 40 | 15.0(14.0,16.0) | A | 52 | ①④ |
| GINZLER[ | 2022 | 6 | Ⅲ/Ⅳ | 298 | 38.6±11.1 | B | 149 | 39.3±12.2 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| MORAND[ | 2022 | 16 | Ⅲ | 180 | 43.1±12.0 | D | 182 | 41.1±11.5 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| WU[ | 2022 | 1 | Ⅲ | 167 | NA | E | 168 | NA | A | 52 | ①④ |
表2 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 国家(个) | 临床试验(期) | 试验组 | 对照组 | 疗程(周) | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | ||||||
| WALLACE[ | 2009 | 2 | Ⅱ | 111 | 41.8±11.7 | B | 113 | 42.2±10.9 | A | 52 | ④ |
| NAVARRA[ | 2011 | 13 | Ⅲ | 290 | 35.4±10.8 | B | 287 | 36.2±11.8 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| FURIE[ | 2011 | 19 | Ⅲ | 273 | 40.5±11.1 | B | 275 | 40.0±11.9 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| ZHANG[ | 2017 | 3 | Ⅲ | 451 | 32.3±9.65 | B | 226 | 31.7±9.18 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| STOHL[ | 2017 | 30 | Ⅲ | 556 | 38.1±12.1 | C | 280 | 39.6±12.6 | A | 52 | ①②④ |
| FURIE[ | 2017 | 14 | ⅡB | 99 | 39.1±11.9 | D | 102 | 39.3±12.9 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| FURIE[ | 2019 | 18 | Ⅲ | 180 | 42.0±12.0 | D | 184 | 41.0±12.3 | A | 52 | ②③④ |
| WU[ | 2019 | 1 | ⅡB | 63 | NA | E | 62 | NA | A | 48 | ①④ |
| BRUNNER[ | 2020 | 10 | Ⅱ | 53 | 14.0(12.0,15.0) | B | 40 | 15.0(14.0,16.0) | A | 52 | ①④ |
| GINZLER[ | 2022 | 6 | Ⅲ/Ⅳ | 298 | 38.6±11.1 | B | 149 | 39.3±12.2 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| MORAND[ | 2022 | 16 | Ⅲ | 180 | 43.1±12.0 | D | 182 | 41.1±11.5 | A | 52 | ①②③④ |
| WU[ | 2022 | 1 | Ⅲ | 167 | NA | E | 168 | NA | A | 52 | ①④ |
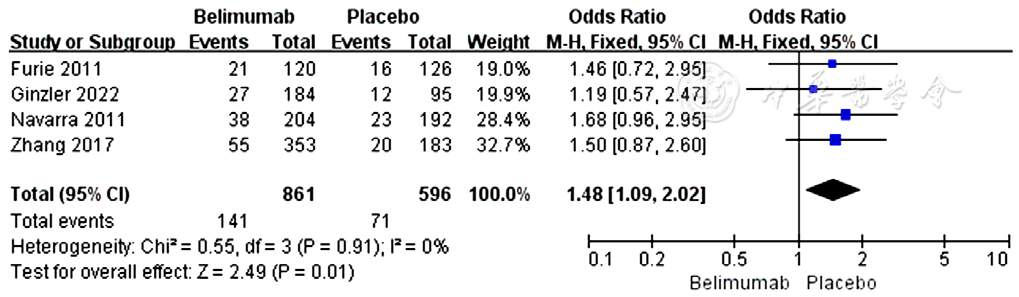
图5 贝利尤单抗组和安慰剂组皮质类固醇剂量减少所占比例比较的森林图
Figure 5 Forest plots of the proportion of SLE patients with reduced corticosteroid dosage in the belimumab group vs placebo group
| 不良事件 | 研究数量(篇) | 贝利尤单抗组 | 安慰剂组 | I2值(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 事件例数 | 总例数 | 事件例数 | 总例数 | ||||||
| 总不良事件 | 6[ | 1 298 | 1 528 | 981 | 1 115 | 0 | 0.96 | 0.93(0.73~1.18) | 0.55 |
| 严重不良事件 | 5[ | 214 | 1 475 | 186 | 1 075 | 56 | 0.06 | 0.82(0.59~1.12) | 0.25 |
| 上呼吸道感染 | 6[ | 239 | 1 528 | 199 | 1 115 | 32 | 0.20 | 0.90(0.73~1.12) | 0.35 |
| 尿路感染 | 5[ | 154 | 1 475 | 118 | 1 075 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.04(0.80~1.35) | 0.78 |
| 腹泻 | 6[ | 147 | 1 528 | 93 | 1 115 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.28(0.97~1.69) | 0.08 |
| 头痛 | 6[ | 214 | 1 528 | 187 | 1 115 | 38 | 0.15 | 0.95(0.76~1.19) | 0.67 |
| 关节痛 | 4[ | 154 | 1 005 | 137 | 840 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99(0.76~1.28) | 0.93 |
| 恶心 | 5[ | 137 | 1 475 | 104 | 1 075 | 65 | 0.02 | 1.16(0.88~1.54) | 0.28 |
| 鼻咽炎 | 4[ | 128 | 1 086 | 81 | 837 | 41 | 0.17 | 1.22(0.90~1.64) | 0.20 |
| 鼻窦炎 | 4[ | 105 | 1 005 | 86 | 840 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.10(0.81~1.49) | 0.56 |
表3 贝利尤单抗组与安慰剂组静脉注射不良事件发生率的Meta分析结果
Table 3 Forest plots of incidence rate of adverse events in the intravenous belimumab group vs placebo group
| 不良事件 | 研究数量(篇) | 贝利尤单抗组 | 安慰剂组 | I2值(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 事件例数 | 总例数 | 事件例数 | 总例数 | ||||||
| 总不良事件 | 6[ | 1 298 | 1 528 | 981 | 1 115 | 0 | 0.96 | 0.93(0.73~1.18) | 0.55 |
| 严重不良事件 | 5[ | 214 | 1 475 | 186 | 1 075 | 56 | 0.06 | 0.82(0.59~1.12) | 0.25 |
| 上呼吸道感染 | 6[ | 239 | 1 528 | 199 | 1 115 | 32 | 0.20 | 0.90(0.73~1.12) | 0.35 |
| 尿路感染 | 5[ | 154 | 1 475 | 118 | 1 075 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.04(0.80~1.35) | 0.78 |
| 腹泻 | 6[ | 147 | 1 528 | 93 | 1 115 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.28(0.97~1.69) | 0.08 |
| 头痛 | 6[ | 214 | 1 528 | 187 | 1 115 | 38 | 0.15 | 0.95(0.76~1.19) | 0.67 |
| 关节痛 | 4[ | 154 | 1 005 | 137 | 840 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99(0.76~1.28) | 0.93 |
| 恶心 | 5[ | 137 | 1 475 | 104 | 1 075 | 65 | 0.02 | 1.16(0.88~1.54) | 0.28 |
| 鼻咽炎 | 4[ | 128 | 1 086 | 81 | 837 | 41 | 0.17 | 1.22(0.90~1.64) | 0.20 |
| 鼻窦炎 | 4[ | 105 | 1 005 | 86 | 840 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.10(0.81~1.49) | 0.56 |
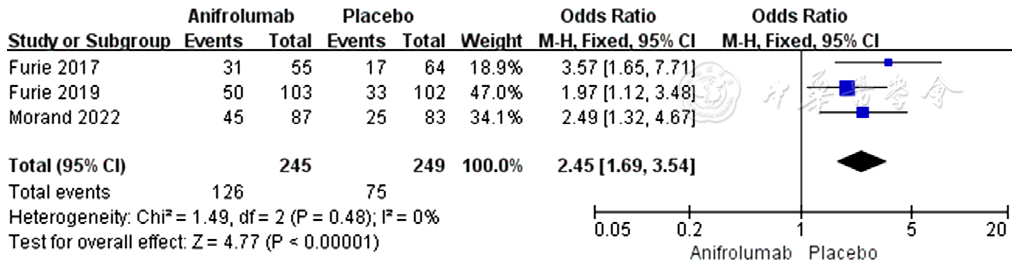
图9 阿尼鲁单抗组与安慰剂组皮质类固醇剂量减少所占比例比较的森林图
Figure 9 Forest plots of the proportion of SLE patients with reduced corticosteroid dosage in the anifrolumab vs placebo group
| 不良事件 | 研究数量(篇) | 阿尼鲁单抗组 | 安慰剂组 | I2值(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 事件例数 | 总例数 | 事件例数 | 总例数 | ||||||
| 总不良事件 | 3[ | 404 | 459 | 375 | 467 | 0 | 0.50 | 1.80(1.25~2.59) | 0.001 |
| 严重不良事件 | 3[ | 56 | 459 | 80 | 467 | 16 | 0.30 | 0.67(0.46~0.97) | 0.04 |
| 上呼吸道感染 | 3[ | 74 | 459 | 46 | 467 | 21 | 0.28 | 1.76(1.19~2.60) | 0.005 |
| 鼻咽炎 | 3[ | 76 | 459 | 46 | 467 | 0 | 0.49 | 1.82(1.23~2.70) | 0.003 |
| 尿路感染 | 3[ | 57 | 459 | 63 | 467 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.91(0.62~1.33) | 0.63 |
| 支气管炎 | 3[ | 45 | 459 | 21 | 467 | 0 | 0.47 | 2.31(1.35~3.94) | 0.002 |
| 带状疱疹 | 3[ | 28 | 459 | 7 | 467 | 0 | 0.66 | 4.26(1.84~9.85) | <0.001 |
| 头痛 | 3[ | 40 | 459 | 47 | 467 | 0 | 0.51 | 0.85(0.55~1.33) | 0.48 |
表4 阿尼鲁单抗组较安慰剂组不良事件发生率森林图结果
Table 4 Forest plots of the incidence rate of adverse events in the anifrolumab group vs placebo group
| 不良事件 | 研究数量(篇) | 阿尼鲁单抗组 | 安慰剂组 | I2值(%) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 事件例数 | 总例数 | 事件例数 | 总例数 | ||||||
| 总不良事件 | 3[ | 404 | 459 | 375 | 467 | 0 | 0.50 | 1.80(1.25~2.59) | 0.001 |
| 严重不良事件 | 3[ | 56 | 459 | 80 | 467 | 16 | 0.30 | 0.67(0.46~0.97) | 0.04 |
| 上呼吸道感染 | 3[ | 74 | 459 | 46 | 467 | 21 | 0.28 | 1.76(1.19~2.60) | 0.005 |
| 鼻咽炎 | 3[ | 76 | 459 | 46 | 467 | 0 | 0.49 | 1.82(1.23~2.70) | 0.003 |
| 尿路感染 | 3[ | 57 | 459 | 63 | 467 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.91(0.62~1.33) | 0.63 |
| 支气管炎 | 3[ | 45 | 459 | 21 | 467 | 0 | 0.47 | 2.31(1.35~3.94) | 0.002 |
| 带状疱疹 | 3[ | 28 | 459 | 7 | 467 | 0 | 0.66 | 4.26(1.84~9.85) | <0.001 |
| 头痛 | 3[ | 40 | 459 | 47 | 467 | 0 | 0.51 | 0.85(0.55~1.33) | 0.48 |
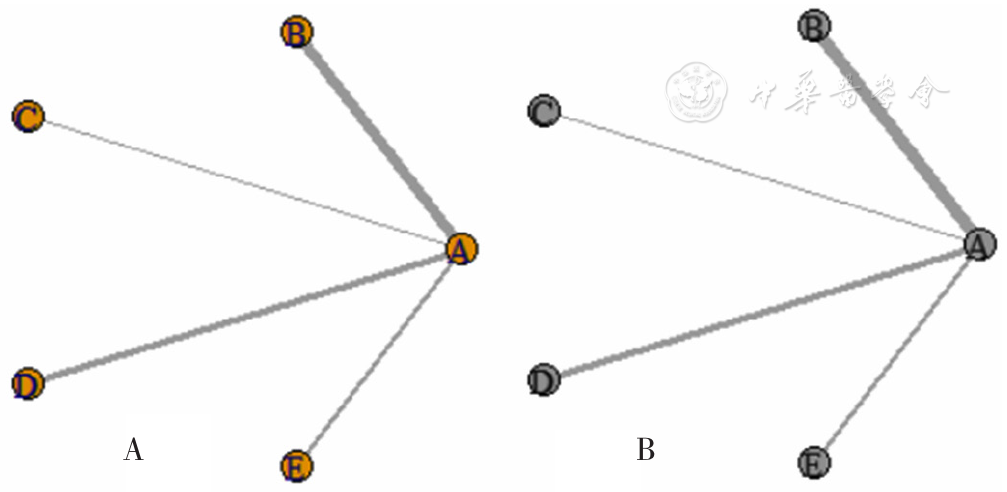
图13 3种生物制剂治疗SLE患者的SRI4缓解率和TAEs发生率的网络证据图注:A为SRI4缓解率,B为TAEs发生率。
Figure 13 Network graphs of SRI4 relief rate and the incidence of TAEs of three biological agents in the treatment of SLE
| 干预措施 | 阿尼鲁单抗 | 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 泰它西普 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 1.38(0.86~2.38) | |||
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 1.29(0.67~2.51) | 0.95(0.53~1.56) | ||
| 泰它西普 | 0.33(0.17~0.66)a | 0.24(0.13~0.43)a | 0.25(0.12~0.52)a | |
| 安慰剂组 | 2.20(1.43~3.46)a | 1.59(1.22~2.03)a | 1.69(1.06~2.81)a | 6.67 (3.97~11.52)a |
表5 3种生物制剂与安慰剂治疗SLE患者SRI4缓解率比较的贝叶斯网状Meta分析[OR(95%CI)]
Table 5 Bayesian network meta-analysis results of SRI4 relief rate of three biological agents and placebo in the treatment of SLE
| 干预措施 | 阿尼鲁单抗 | 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 泰它西普 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 1.38(0.86~2.38) | |||
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 1.29(0.67~2.51) | 0.95(0.53~1.56) | ||
| 泰它西普 | 0.33(0.17~0.66)a | 0.24(0.13~0.43)a | 0.25(0.12~0.52)a | |
| 安慰剂组 | 2.20(1.43~3.46)a | 1.59(1.22~2.03)a | 1.69(1.06~2.81)a | 6.67 (3.97~11.52)a |
| 药物 | Rank1 | Rank2 | Rank3 | Rank4 | Rank5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿尼鲁单抗 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 0 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 0 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.02 |
| 安慰剂 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.98 |
| 泰它西普 | 1.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表6 3种生物制剂与安慰剂治疗SLE患者SRI4缓解率的概率排序结果
Table 6 Probability ranking results of SRI4 relief rate of three biological agents and placebo in the treatment of SLE
| 药物 | Rank1 | Rank2 | Rank3 | Rank4 | Rank5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿尼鲁单抗 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 0 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 0 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.02 |
| 安慰剂 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.98 |
| 泰它西普 | 1.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 干预措施 | 阿尼鲁单抗 | 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 泰它西普 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 1.90(1.16~3.19) | |||
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 2.32(1.15~4.66) | 1.22(0.65~2.24) | ||
| 泰它西普 | 0.82(0.37~1.86) | 0.44(0.20~0.89) | 0.35(0.15~0.84) | |
| 安慰剂 | 1.81(1.20~2.76) | 0.96(0.71~1.28) | 0.79(0.45~1.34) | 2.21(1.13~4.37) |
表7 3种生物制剂与安慰剂治疗SLE患者TAEs发生率的贝叶斯网状Meta分析结果[OR(95%CI)]
Table 7 Bayesian network meta-analysis results of the incidence of TAEs of three biological agents and placebo in the treatment of SLE
| 干预措施 | 阿尼鲁单抗 | 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 泰它西普 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 1.90(1.16~3.19) | |||
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 2.32(1.15~4.66) | 1.22(0.65~2.24) | ||
| 泰它西普 | 0.82(0.37~1.86) | 0.44(0.20~0.89) | 0.35(0.15~0.84) | |
| 安慰剂 | 1.81(1.20~2.76) | 0.96(0.71~1.28) | 0.79(0.45~1.34) | 2.21(1.13~4.37) |
| 药物 | Rank1 | Rank2 | Rank3 | Rank4 | Rank5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿尼鲁单抗 | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 0 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.45 | 0.20 |
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 0 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.74 |
| 安慰剂 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.06 |
| 泰它西普 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 |
表8 3种生物制剂与安慰剂TAEs发生率的概率排序
Table 8 Probability ranking results of the incidence of TAEs of three biological agents and placebo in the treatment of SLE
| 药物 | Rank1 | Rank2 | Rank3 | Rank4 | Rank5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿尼鲁单抗 | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| 贝利尤单抗(静脉注射) | 0 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.45 | 0.20 |
| 贝利尤单抗(皮下注射) | 0 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.74 |
| 安慰剂 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.06 |
| 泰它西普 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
FDA approves GSK's BENLYSTA as the first medicine for adult patients with active lupus nephritis in the US[EB/OL]. (2020-12-17)[2023-10-10].
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [1] | 郑博月, 付积艺, 吴佳霏, 王珺, 李慧. 卡非佐米治疗多发性骨髓瘤的疗效及安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3806-3814. |
| [2] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [3] | 肖彩红, 崔瑾, 全菲, 晏明熙, 卢春霞, 陈迎龙. 苗药竹技药灸疗法治疗勃起功能障碍的临床疗效:一项随机对照研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3300-3306. |
| [4] | 马盼盼, 王思静, 游娜, 丁大法, 鲁一兵. Danuglipron与Orforglipron治疗2型糖尿病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [5] | 何芸, 范焕芳, 马盼, 许绍青, 杨柳, 金明哲, 张明蕊, 陈佳琪. 不同针灸治疗方式干预乳腺癌术后上肢淋巴水肿效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1788-1794. |
| [6] | 朱胜杰, 刁华琼, 杭晓屹, 孙文军. 不同中成药注射液治疗后循环缺血性眩晕效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1795-1808. |
| [7] | 迟洵, 刘思思, 陈巧, 胡玥, 王伟仙. 不同营养筛查工具对肝硬化患者营养筛查适用性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1395-1402. |
| [8] | 谷明宇, 秦廷廷, 乔昆, 白欣苑, 王尧, 杨宇彤, 李星明. 中国基层高血压管理模式的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1265-1272. |
| [9] | 刘浏, 徐文航, 吕宾, 范一宏. 维得利珠单抗与乌司奴单抗作为初治生物制剂在中重度活动期克罗恩病患者中的疗效比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(08): 948-953. |
| [10] | 牛国辉, 谢加阳, 朱登纳, 崔博, 赵会玲, 王明梅, 冯欢欢, 张萌萌, 李停停. 维生素D治疗全面性发育迟缓患儿的临床疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 346-351. |
| [11] | 罗思富, 金梦龙, 苏比努尔·居热提, 刘紫阳, 付真彦. 不同民族动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病患者中等剂量他汀类药物治疗的疗效差异研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4522-4526. |
| [12] | 郭佳, 曹春梅, 刘国纯, 郑满, 朱芮含, 龙伟. 不同运动方式对失眠患者睡眠影响效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4376-4387. |
| [13] | 檀紫瑞, 申青, 刘俊英, 陈砚凝, 姚继方. 表皮生长因子受体非热点突变型非小细胞肺癌一线应用表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂及化疗的疗效对比研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4426-4434. |
| [14] | 肖华, 王云芸, 王益, 董林, 常聪, 卢家春, 呼永河, 王文春. 青鹏软膏超声波导入对膝关节军事训练伤的疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4014-4020. |
| [15] | 黄腾佳, 曹曦, 陈蕾, 李子滢, 秦莉花. 非药物治疗脑卒中后肩手综合征有效性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2921-2930. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





