中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 1802-1810.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0808
所属专题: 心肌梗死最新文章合辑; 心血管最新文章合辑
张国莉1, 赵荣荣2, 彭国恬1, 孙瑞仪1, 乔鹏宇1, 燕芳红1,3, 韩琳1,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-12
修回日期:2024-01-04
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-28
通讯作者:
韩琳
基金资助:
ZHANG Guoli1, ZHAO Rongrong2, PENG Guotian1, SUN Ruiyi1, QIAO Pengyu1, YAN Fanghong1,3, HAN Lin1,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-12
Revised:2024-01-04
Published:2024-05-20
Online:2024-02-28
Contact:
HAN Lin
摘要: 背景 ST段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)术后远期发生主要不良心血管事件(MACEs)的风险大,指南指出准确的早期危险分层对STEMI患者PCI术后MACEs的管理具有重要意义。目前,常用的风险评分系统包括年龄、血肌酐和射血分数(ACEF)评分、心肌梗死溶栓(TIMI)评分、Zwolle评分、首次心肌梗死血管成形术(PAMI)评分、使用控制阿昔单抗和装置的研究以降低晚期血管成形术并发症(CADILLAC),然而哪种风险评分系统更适用于预测STEMI患者PCI治疗远期预后尚无定论。目的 分析我国STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs发生的危险因素并比较我国目前常用的ACEF、TIMI、Zwolle、PAMI、CADILLAC五种风险评分系统对其远期MACEs发生风险的预测价值。方法 回顾性选取2016年6月—2020年6月在甘肃省人民医院心内科成功完成首次PCI术的687例STEMI患者为研究对象。收集患者一般资料与实验室及影像学检查结果,患者入组后均采用ACEF、TIMI、Zwolle、PAMI、CADILLAC风险评分系统进行评分。出院后通过电话及门诊复查方式随访患者,每年随访1次,随访时间截至2023年8月,主要记录随访期间患者MACEs的发生情况。采用多因素Logistic回归分析探究STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs发生的影响因素。绘制不同风险评分系统诊断MACEs的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线),采用DeLong检验比较各风险评分系统的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)。结果 687例STEMI患者接受了PCI术,随访过程中44例患者因基本资料数据缺失过多被剔除,最终纳入643例患者,中位随访时间为37(25,49)个月。至随访结束共有134例发生MACEs,发生率为20.8%。MACEs组和非MACEs组年龄、住院时间、Killip分级、脑利钠肽前体、纤维蛋白原、贫血、左心室射血分数、估算肾小球滤过率、血肌酐、瓣膜返流比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示:住院时间延长(OR=1.071,95%CI=1.012~1.134,P=0.018)、血肌酐升高(OR=1.018,95%CI=1.006~1.030,P=0.003)、纤维蛋白原升高(OR=1.226,95%CI=1.066~1.409,P=0.004)为患者发生MACEs的危险因素,左心室射血分数增加(OR=0.980,95%CI=0.960~1.000,P=0.045)、瓣膜轻度返流(OR=0.377,95%CI=0.151~0.938,P=0.036)和中度返流(OR=0.164,95%CI=0.051~0.522,P=0.002)为患者发生MACEs的保护因素。MACEs组的ACEF、TIMI、Zwolle、PAMI、CADILLAC风险评分系统得分均高于非MACEs组(P<0.05)。绘制5种风险评分系统预测STEMI患者PCI术后远期发生MACEs的ROC曲线,5种风险评分系统对STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs的预测价值比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 住院时间、血肌酐水平、纤维蛋白原、左心室射血分数、瓣膜返流状态是影响STEMI患者PCI术后远期发生MACEs的影响因素。ACEF、TIMI、Zwolle、PAMI、CADILLAC五种风险评分系统均能预测STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs的发生,但从区分度和灵敏度方面考虑推荐使用CADILLAC评分。
| 项目 | ACEF | TIMI | Zwolle | PAMI | CADILLAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 病史 | |||||
| 糖尿病 | + | + | |||
| 高血压 | + | ||||
| 心绞痛 | + | ||||
| 心肌缺血时间 | + | + | |||
| 体格检查 | |||||
| 收缩压 | + | ||||
| 心率 | + | + | |||
| 体质量 | + | ||||
| 影像学检查 | |||||
| 梗死部位 | + | + | + | ||
| 左心室射血分数 | + | + | |||
| 心功能分级 | + | + | + | + | |
| TIMI血流分级 | + | + | |||
| 病变血管支数 | + | + | |||
| 实验室检查 | |||||
| 血肌酐 | + | ||||
| eGFR | + | ||||
| 血红蛋白计数 | + |
表1 不同风险评分系统指标
Table 1 Different risk scoring system indicators
| 项目 | ACEF | TIMI | Zwolle | PAMI | CADILLAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 病史 | |||||
| 糖尿病 | + | + | |||
| 高血压 | + | ||||
| 心绞痛 | + | ||||
| 心肌缺血时间 | + | + | |||
| 体格检查 | |||||
| 收缩压 | + | ||||
| 心率 | + | + | |||
| 体质量 | + | ||||
| 影像学检查 | |||||
| 梗死部位 | + | + | + | ||
| 左心室射血分数 | + | + | |||
| 心功能分级 | + | + | + | + | |
| TIMI血流分级 | + | + | |||
| 病变血管支数 | + | + | |||
| 实验室检查 | |||||
| 血肌酐 | + | ||||
| eGFR | + | ||||
| 血红蛋白计数 | + |
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 性别(男/女) | 高血压[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 血脂异常[例(%)] | 脑卒中[例(%)] | 吸烟[例(%)] | 饮酒[例(%)] | 发生急性心肌缺血时间>4 h[例(%)] | 身高[M(P25,P75),cm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非MACEs组 | 509 | 60.0(52.0,66.0) | 436/73 | 231(45.4) | 96(18.9) | 17(3.3) | 46(9.0) | 323(63.5) | 162(31.8) | 442(86.8) | 170.0(165.0,172.0) | |
| MACEs组 | 134 | 64.0(54.0,69.0) | 112/22 | 71(53.0) | 30(22.3) | 5(3.7) | 18(13.4) | 78(58.2) | 31(23.1) | 121(90.3) | 170.0(165.0,173.9) | |
| Z(χ2)值 | -2.428 | 0.363a | 2.461a | 0.838a | 0.049a | 2.287a | 1.548a | 3.816a | 1.167a | -1.287 | ||
| P值 | 0.015 | 0.547 | 0.117 | 0.360 | 0.824 | 0.130 | 0.213 | 0.051 | 0.280 | 0.198 | ||
| 组别 | 体质量[M(P25,P75),kg] | 收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 心率[M(P25,P75),次/min] | 住院时间[M(P25,P75),d] | Killip分级[例(%)] | 糖化血红蛋白[M(P25,P75),%] | |||||
| Ⅰ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅲ级+Ⅳ级 | ||||||||||
| 非MACEs组 | 70.0(65.0,78.3) | 125(115,140) | 80(70,88) | 76(66,85) | 7(5,10) | 429(84.3) | 68(13.4) | 12(2.3) | 5.7(5.3,6.2) | |||
| MACEs组 | 76.0(64.7,79.8) | 125(113,139) | 78(69,86) | 77(67,86) | 8.0(5,11) | 100(74.6) | 25(18.7) | 9(6.7) | 5.7(5.4,6.3) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.296 | -0.668 | -1.370 | -0.293 | -3.024 | 9.431a | -0.359 | |||||
| P值 | 0.767 | 0.504 | 0.171 | 0.769 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.719 | |||||
| 组别 | 空腹血糖[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 中性粒细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 淋巴细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 高密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 低密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | ||||
| 非MACEs组 | 6.6(5.4,8.7) | 9.3(7.1,11.8) | 7.0(5.0,9.7) | 1.4(1.0,1.8) | 1.0(0.8,1.1) | 2.3(1.9,2.9) | 41.0(26.0,65.6) | 105.0(40.0,235.0) | ||||
| MACEs组 | 6.8(5.3,9.4) | 9.3(7.4,12.0) | 7.2(5.4,10.0) | 1.3(1.0,1.7) | 1.0(0.8,1.1) | 2.2(1.7,2.8) | 43.0(26.3,74.0) | 113.0(43.0,278.4) | ||||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.191 | -0.417 | -0.711 | -1.306 | -0.059 | -1.341 | -0.608 | -0.099 | ||||
| P值 | 0.849 | 0.676 | 0.477 | 0.191 | 0.953 | 0.180 | 0.543 | 0.549 | ||||
| 组别 | 同型半胱氨酸[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 超敏肌钙蛋白[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | 乳酸脱氢酶峰值[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 肌酸激酶峰值[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 肌酸激酶同工酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 脑利钠肽前体[M(P25,P75),ng/L] | ||||||
| 非MACEs组 | 17.5(11.8,34.9) | 0.7(0.1,3.0) | 511.4(320.3,819.0) | 1 170.3(242.0,3 347.0) | 107.8(28.0,273.3) | 675.2(247.2,1 860.5) | ||||||
| MACEs组 | 17.8(11.6,29.7) | 0.8(0.0,5.1) | 523.2(321.0,875.6) | 1 097.4(251.3,2 799.0) | 89.8(25.6,259.9) | 996.5(342.9,2 773.0) | ||||||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.138 | -0.451 | -0.560 | -0.576 | -0.728 | -2.399 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.890 | 0.652 | 0.575 | 0.564 | 0.467 | 0.016 | ||||||
| 组别 | 入院凝血酶原时间[M(P25,P75),s] | 入院活化部分凝血酶原时间[M(P25,P75),s] | 血肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 纤维蛋白原[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 贫血[例(%)] | 左心室射血分数[M(P25,P75),%] | 支架数目[M(P25,P75),个] | 心腔大小正常[例(%)] | 室壁瘤[例(%)] | |||
| 非MACEs组 | 13.4(12.8,14.0) | 35.6(32.5,39.5) | 66.0(58.0,75.6) | 3.3(2.8,4.2) | 89(17.5) | 52.0(46.0,59.0) | 2(1,2) | 308(60.5) | 13(2.6) | |||
| MACEs组 | 13.5(12.8,14.2) | 35.7(32.7,39.9) | 72.0(60.1,85.3) | 3.6(2.9,4.7) | 38(28.4) | 50.0(43.0,56.5) | 2(1,2) | 92(68.7) | 6(4.5) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.786 | -0.210 | -3.786 | -2.635 | 7.912a | -2.397 | -1.155 | 2.994a | 1.369a | |||
| P值 | 0.432 | 0.833 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.248 | 0.084 | 0.242 | |||
| 组别 | eGFR[例(%)] | TIMI血流分级[例(%)] | 瓣膜返流[例(%)] | 心肌梗死部位[例(%)] | 病变血管数[例(%)] | |||||||
| 异常 | 正常 | 无复流/慢血流 | 正常血流 | 轻度返流 | 中度返流 | 重度返流 | 前壁 | 非前壁 | 单支 | 双支 | 左主干或三支病变 | |
| 非MACEs组 | 35(6.9) | 474(93.1) | 279(54.8) | 230(45.2) | 450(88.4) | 47(9.2) | 12(2.4) | 241(47.3) | 268(52.7) | 117(23.0) | 163(32.0) | 229(45.0) |
| MACEs组 | 1(0.8) | 133(99.2) | 78(58.2) | 56(41.8) | 114(85.1) | 9(6.7) | 11(8.2) | 64(47.8) | 70(52.2) | 26(19.4) | 36(26.9) | 72(53.7) |
| Z(χ2)值 | 7.541a | 0.495a | 11.060a | 0.007a | 3.256a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.006 | 0.482 | 0.004 | 0.932 | 0.196 | |||||||
表2 非MACEs组和MACEs组患者一般资料比较结果
Table 2 Comparison of general data between non-MACES group and MACEs group
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 性别(男/女) | 高血压[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 血脂异常[例(%)] | 脑卒中[例(%)] | 吸烟[例(%)] | 饮酒[例(%)] | 发生急性心肌缺血时间>4 h[例(%)] | 身高[M(P25,P75),cm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非MACEs组 | 509 | 60.0(52.0,66.0) | 436/73 | 231(45.4) | 96(18.9) | 17(3.3) | 46(9.0) | 323(63.5) | 162(31.8) | 442(86.8) | 170.0(165.0,172.0) | |
| MACEs组 | 134 | 64.0(54.0,69.0) | 112/22 | 71(53.0) | 30(22.3) | 5(3.7) | 18(13.4) | 78(58.2) | 31(23.1) | 121(90.3) | 170.0(165.0,173.9) | |
| Z(χ2)值 | -2.428 | 0.363a | 2.461a | 0.838a | 0.049a | 2.287a | 1.548a | 3.816a | 1.167a | -1.287 | ||
| P值 | 0.015 | 0.547 | 0.117 | 0.360 | 0.824 | 0.130 | 0.213 | 0.051 | 0.280 | 0.198 | ||
| 组别 | 体质量[M(P25,P75),kg] | 收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 心率[M(P25,P75),次/min] | 住院时间[M(P25,P75),d] | Killip分级[例(%)] | 糖化血红蛋白[M(P25,P75),%] | |||||
| Ⅰ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅲ级+Ⅳ级 | ||||||||||
| 非MACEs组 | 70.0(65.0,78.3) | 125(115,140) | 80(70,88) | 76(66,85) | 7(5,10) | 429(84.3) | 68(13.4) | 12(2.3) | 5.7(5.3,6.2) | |||
| MACEs组 | 76.0(64.7,79.8) | 125(113,139) | 78(69,86) | 77(67,86) | 8.0(5,11) | 100(74.6) | 25(18.7) | 9(6.7) | 5.7(5.4,6.3) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.296 | -0.668 | -1.370 | -0.293 | -3.024 | 9.431a | -0.359 | |||||
| P值 | 0.767 | 0.504 | 0.171 | 0.769 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.719 | |||||
| 组别 | 空腹血糖[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 中性粒细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 淋巴细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 高密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 低密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | ||||
| 非MACEs组 | 6.6(5.4,8.7) | 9.3(7.1,11.8) | 7.0(5.0,9.7) | 1.4(1.0,1.8) | 1.0(0.8,1.1) | 2.3(1.9,2.9) | 41.0(26.0,65.6) | 105.0(40.0,235.0) | ||||
| MACEs组 | 6.8(5.3,9.4) | 9.3(7.4,12.0) | 7.2(5.4,10.0) | 1.3(1.0,1.7) | 1.0(0.8,1.1) | 2.2(1.7,2.8) | 43.0(26.3,74.0) | 113.0(43.0,278.4) | ||||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.191 | -0.417 | -0.711 | -1.306 | -0.059 | -1.341 | -0.608 | -0.099 | ||||
| P值 | 0.849 | 0.676 | 0.477 | 0.191 | 0.953 | 0.180 | 0.543 | 0.549 | ||||
| 组别 | 同型半胱氨酸[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 超敏肌钙蛋白[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | 乳酸脱氢酶峰值[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 肌酸激酶峰值[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 肌酸激酶同工酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 脑利钠肽前体[M(P25,P75),ng/L] | ||||||
| 非MACEs组 | 17.5(11.8,34.9) | 0.7(0.1,3.0) | 511.4(320.3,819.0) | 1 170.3(242.0,3 347.0) | 107.8(28.0,273.3) | 675.2(247.2,1 860.5) | ||||||
| MACEs组 | 17.8(11.6,29.7) | 0.8(0.0,5.1) | 523.2(321.0,875.6) | 1 097.4(251.3,2 799.0) | 89.8(25.6,259.9) | 996.5(342.9,2 773.0) | ||||||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.138 | -0.451 | -0.560 | -0.576 | -0.728 | -2.399 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.890 | 0.652 | 0.575 | 0.564 | 0.467 | 0.016 | ||||||
| 组别 | 入院凝血酶原时间[M(P25,P75),s] | 入院活化部分凝血酶原时间[M(P25,P75),s] | 血肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 纤维蛋白原[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 贫血[例(%)] | 左心室射血分数[M(P25,P75),%] | 支架数目[M(P25,P75),个] | 心腔大小正常[例(%)] | 室壁瘤[例(%)] | |||
| 非MACEs组 | 13.4(12.8,14.0) | 35.6(32.5,39.5) | 66.0(58.0,75.6) | 3.3(2.8,4.2) | 89(17.5) | 52.0(46.0,59.0) | 2(1,2) | 308(60.5) | 13(2.6) | |||
| MACEs组 | 13.5(12.8,14.2) | 35.7(32.7,39.9) | 72.0(60.1,85.3) | 3.6(2.9,4.7) | 38(28.4) | 50.0(43.0,56.5) | 2(1,2) | 92(68.7) | 6(4.5) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.786 | -0.210 | -3.786 | -2.635 | 7.912a | -2.397 | -1.155 | 2.994a | 1.369a | |||
| P值 | 0.432 | 0.833 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.248 | 0.084 | 0.242 | |||
| 组别 | eGFR[例(%)] | TIMI血流分级[例(%)] | 瓣膜返流[例(%)] | 心肌梗死部位[例(%)] | 病变血管数[例(%)] | |||||||
| 异常 | 正常 | 无复流/慢血流 | 正常血流 | 轻度返流 | 中度返流 | 重度返流 | 前壁 | 非前壁 | 单支 | 双支 | 左主干或三支病变 | |
| 非MACEs组 | 35(6.9) | 474(93.1) | 279(54.8) | 230(45.2) | 450(88.4) | 47(9.2) | 12(2.4) | 241(47.3) | 268(52.7) | 117(23.0) | 163(32.0) | 229(45.0) |
| MACEs组 | 1(0.8) | 133(99.2) | 78(58.2) | 56(41.8) | 114(85.1) | 9(6.7) | 11(8.2) | 64(47.8) | 70(52.2) | 26(19.4) | 36(26.9) | 72(53.7) |
| Z(χ2)值 | 7.541a | 0.495a | 11.060a | 0.007a | 3.256a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.006 | 0.482 | 0.004 | 0.932 | 0.196 | |||||||
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.964 | 0.326 | 1.010(0.990~1.030) |
| 住院时间 | 0.069 | 0.029 | 5.585 | 0.018 | 1.071(1.012~1.134) |
| eGFR分级正常 | 1.614 | 1.040 | 2.406 | 0.121 | 5.021(0.654~38.577) |
| 血肌酐 | 0.018 | 0.006 | 8.819 | 0.003 | 1.018(1.006~1.030) |
| 脑利纳肽前体 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.480 | 0.224 | 1.000(1.000~1.000) |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 0.203 | 0.071 | 8.142 | 0.004 | 1.226(1.066~1.409) |
| 左心室射血分数 | -0.021 | 0.010 | 4.008 | 0.045 | 0.980(0.960~1.000) |
| 贫血 | 0.411 | 0.246 | 2.787 | 0.095 | 1.508(0.931~2.443) |
| 瓣膜返流(以重度返流为参照) | |||||
| 轻度返流 | -0.976 | 0.465 | 4.400 | 0.036 | 0.377(0.151~0.938) |
| 中度返流 | -1.809 | 0.591 | 9.358 | 0.002 | 0.164(0.051~0.522) |
| Killip分级(以Ⅲ级+Ⅳ级为参照) | |||||
| Ⅰ级 | -0.620 | 0.539 | 1.326 | 0.250 | 0.538(0.187~1.546) |
| Ⅱ级 | -0.450 | 0.567 | 0.631 | 0.427 | 0.637(0.210~1.937) |
表3 STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of long-term MACEs after PCI in STEMI patients
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.964 | 0.326 | 1.010(0.990~1.030) |
| 住院时间 | 0.069 | 0.029 | 5.585 | 0.018 | 1.071(1.012~1.134) |
| eGFR分级正常 | 1.614 | 1.040 | 2.406 | 0.121 | 5.021(0.654~38.577) |
| 血肌酐 | 0.018 | 0.006 | 8.819 | 0.003 | 1.018(1.006~1.030) |
| 脑利纳肽前体 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.480 | 0.224 | 1.000(1.000~1.000) |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 0.203 | 0.071 | 8.142 | 0.004 | 1.226(1.066~1.409) |
| 左心室射血分数 | -0.021 | 0.010 | 4.008 | 0.045 | 0.980(0.960~1.000) |
| 贫血 | 0.411 | 0.246 | 2.787 | 0.095 | 1.508(0.931~2.443) |
| 瓣膜返流(以重度返流为参照) | |||||
| 轻度返流 | -0.976 | 0.465 | 4.400 | 0.036 | 0.377(0.151~0.938) |
| 中度返流 | -1.809 | 0.591 | 9.358 | 0.002 | 0.164(0.051~0.522) |
| Killip分级(以Ⅲ级+Ⅳ级为参照) | |||||
| Ⅰ级 | -0.620 | 0.539 | 1.326 | 0.250 | 0.538(0.187~1.546) |
| Ⅱ级 | -0.450 | 0.567 | 0.631 | 0.427 | 0.637(0.210~1.937) |
| 组别 | 例数 | ACEF评分 | TIMI评分 | Zwolle评分 | PAMI评分 | CADILLAC评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非MACEs组 | 509 | 1.1(1.0,1.3) | 6.0(4.0,7.0) | 4.0(3.0,6.0) | 2.0(0,4.0) | 4.0(2.0,6.0) |
| MACEs组 | 134 | 1.2(1.0,1.5) | 6.0(5.0,8.0) | 5.0(3.0,7.0) | 2.0(2.0,6.0) | 4.0(2.0,7.0) |
| Z值 | -2.925 | -2.333 | -2.524 | -3.288 | -3.434 | |
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.012 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
表4 非MACEs组和MACEs组患者5种风险评分系统得分比较[M(P25,P75),分]
Table 4 Comparison of 5 risk score systems between non-MACES group and MACEs group
| 组别 | 例数 | ACEF评分 | TIMI评分 | Zwolle评分 | PAMI评分 | CADILLAC评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非MACEs组 | 509 | 1.1(1.0,1.3) | 6.0(4.0,7.0) | 4.0(3.0,6.0) | 2.0(0,4.0) | 4.0(2.0,6.0) |
| MACEs组 | 134 | 1.2(1.0,1.5) | 6.0(5.0,8.0) | 5.0(3.0,7.0) | 2.0(2.0,6.0) | 4.0(2.0,7.0) |
| Z值 | -2.925 | -2.333 | -2.524 | -3.288 | -3.434 | |
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.012 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
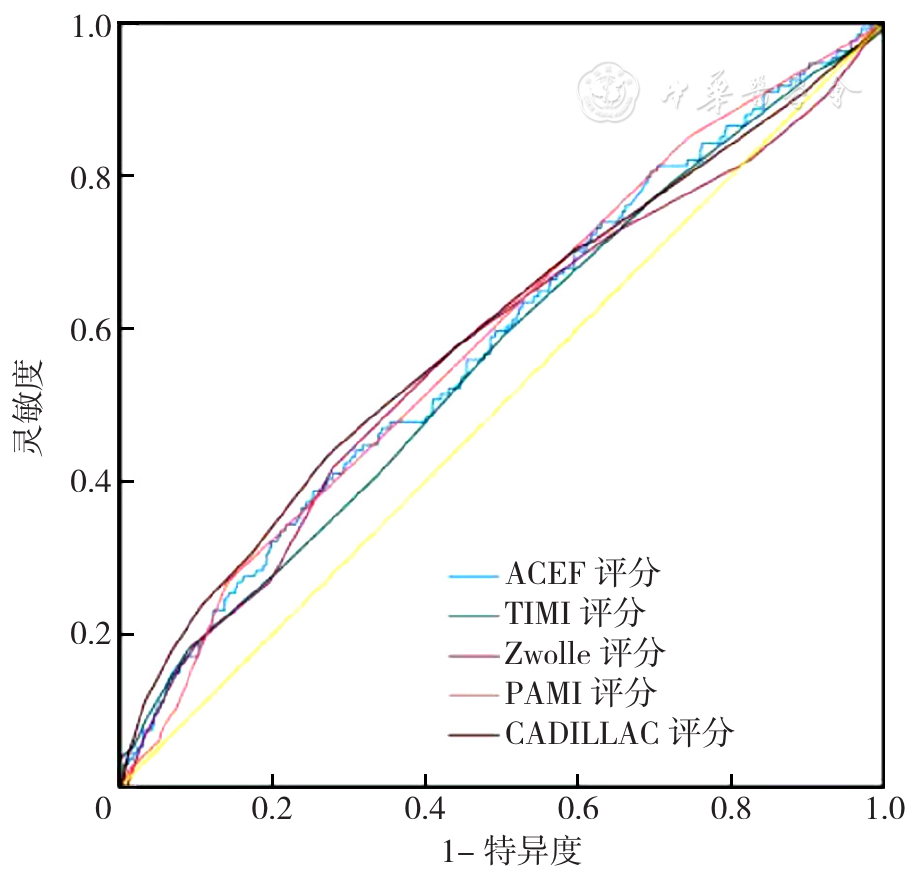
图1 5种风险评分系统预测STEMI患者PCI术后远期发生MACEs的ROC曲线注:ACEF=年龄、血肌酐和射血分数,TIMI=心肌梗死溶栓,PAMI=首次心肌梗死血管成形术,CADILLAC=使用控制阿昔单抗和装置的研究以降低晚期血管成形术并发症。
Figure 1 ROC curves of five risk scoring systems predicting MACEs after PCI in STEMI patients
| 指标 | AUC | 95%CI | 最佳截断值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACEF评分 | 0.582 | (0.527~0.637) | 1.34分 | 0.388 | 0.747 | 0.135 | 0.003 |
| TIMI评分 | 0.565 | (0.509~0.620) | 8.50分 | 0.179 | 0.912 | 0.091 | 0.021 |
| Zwolle评分 | 0.570 | (0.513~0.627) | 5.50分 | 0.418 | 0.721 | 0.139 | 0.012 |
| PAMI评分 | 0.589 | (0.535~0.643) | 5.00分 | 0.269 | 0.859 | 0.127 | 0.002 |
| CADILLAC评分 | 0.595 | (0.538~0.652) | 5.50分 | 0.433 | 0.729 | 0.162 | 0.001 |
表5 5种风险评分系统对STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs的预测价值
Table 5 Predictive value of five risk score systems for long-term MACEs after PCI in STEMI patients
| 指标 | AUC | 95%CI | 最佳截断值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACEF评分 | 0.582 | (0.527~0.637) | 1.34分 | 0.388 | 0.747 | 0.135 | 0.003 |
| TIMI评分 | 0.565 | (0.509~0.620) | 8.50分 | 0.179 | 0.912 | 0.091 | 0.021 |
| Zwolle评分 | 0.570 | (0.513~0.627) | 5.50分 | 0.418 | 0.721 | 0.139 | 0.012 |
| PAMI评分 | 0.589 | (0.535~0.643) | 5.00分 | 0.269 | 0.859 | 0.127 | 0.002 |
| CADILLAC评分 | 0.595 | (0.538~0.652) | 5.50分 | 0.433 | 0.729 | 0.162 | 0.001 |
| 指标 | ΔAUC | Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACEF评分比CADILLAC评分 | 0.013 | 0.493 | 0.622 |
| ACEF评分比PAMI评分 | 0.007 | 0.234 | 0.815 |
| ACEF评分比TIMI评分 | 0.017 | 0.540 | 0.589 |
| ACEF评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.012 | 0.390 | 0.697 |
| CADILLAC评分比PAMI评分 | 0.006 | 0.259 | 0.796 |
| CADILLAC评分比TIMI评分 | 0.030 | 1.097 | 0.273 |
| CADILLAC评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.025 | 1.244 | 0.214 |
| PAMI评分比TIMI评分 | 0.024 | 1.156 | 0.248 |
| PAMI评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.018 | 0.773 | 0.440 |
| TIMI评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.005 | 0.216 | 0.829 |
表6 5种风险评分系统预测STEMI患者PCI术后远期MACEs的AUC比较
Table 6 AUC comparison of five risk scoring systems predicting long-term MACEs after PCI in STEMI patients
| 指标 | ΔAUC | Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACEF评分比CADILLAC评分 | 0.013 | 0.493 | 0.622 |
| ACEF评分比PAMI评分 | 0.007 | 0.234 | 0.815 |
| ACEF评分比TIMI评分 | 0.017 | 0.540 | 0.589 |
| ACEF评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.012 | 0.390 | 0.697 |
| CADILLAC评分比PAMI评分 | 0.006 | 0.259 | 0.796 |
| CADILLAC评分比TIMI评分 | 0.030 | 1.097 | 0.273 |
| CADILLAC评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.025 | 1.244 | 0.214 |
| PAMI评分比TIMI评分 | 0.024 | 1.156 | 0.248 |
| PAMI评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.018 | 0.773 | 0.440 |
| TIMI评分比Zwolle评分 | 0.005 | 0.216 | 0.829 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
中华医学会心血管病学分会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死诊断和治疗指南(2019)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2019,47(10):766-783. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253?3758.2019.10.003.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
李子孝,王春娟,王伊龙,等. 卒中临床诊疗和疾病管理核心数据元及定义专家共识[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2020,15(4):416-434. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5765.2020.04.01.
|
| [14] |
郭颖,张瑞生. 中国成人心脏瓣膜病超声心动图规范化检查专家共识[J]. 中国循环杂志,2021,36(2):109-125. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.02.00.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
梁峰,胡大一,方全,等. 基于指南的ST段抬高型心肌梗死后长期二级预防治疗与风险因素控制最新进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(8):888-900,908. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.029.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
高斯德,刘青波,丁晓松,等. ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后近期和远期预后的性别差异[J]. 中国循环杂志,2019,34(7):646-652. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.07.005.
|
| [21] |
梁峰,胡大一,方全,等. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死的再灌注治疗[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2019,11(3):263-274. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2019.03.02.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
吕俊兴,许海燕,杨跃进,等. 中国急性心肌梗死患者住院时间及其延长的影响因素分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志,2020,36(10):890-894. DOI:10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2020.10.004.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
郭超,罗晓亮,高晓津,等. 不同评分系统对急性心肌梗死合并心源性休克患者近期死亡预测价值的比较[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(7):529-535. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.07.005.
|
| [32] |
高国峰,周林丽,张冬,等. ACEF评分在中国经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者中的预测价值研究[J]. 中国循环杂志,2019,34(11):1047-1054. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.11.002.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
黄思壮,高斯德,林徐泽,等. TIMI危险评分对ST段抬高型冠状动脉非阻塞性心肌梗死患者远期预后的预测价值[J]. 中国循环杂志,2022,37(11):1091-1096. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2022.11.003.
|
| [35] |
李相儒,左惠娟,杨红霞,等. 35岁及以下成年STEMI患者的临床特点及其预后研究[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2021,49(11):1124-1129. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20210805-00672.
|
| [36] |
赵振燕,杨进刚,赵延延,等. 中国省、市和县级医院ST段抬高型心肌梗死住院患者就诊时间差异和延迟就诊的相关因素分析[J]. 中国循环杂志,2020,35(6):554-559. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2020.06.006.
|
| [37] |
|
| [1] | 贾高鹏, 陈秋雨. 老年急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后心绞痛复发风险预测模型构建和验证:基于CYP2C19相关基因检测[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3779-3786. |
| [2] | 胡洁蔓, 谭斐翔, 袁安新, 陈世宇, 唐楚蕾, 殷月姮, 巴磊, 许勤. 结直肠癌患者术后衰弱变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [3] | 丑欣彤, 彭瀚瑜, 马慧, 张珍, 苏先, 邱红燕. 产妇对避孕决策的偏好及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [4] | 魏姣花, 彭慧如, 彭建业, 谭文婷, 黄金娥, 方立. MOTS-c在心房颤动患者血清中的表达及其与心房重构的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [5] | 褚艺婧, 严雨格, 顾杰, 席彪, 祝墡珠, 黄蛟灵. 中国基层医务人员留用意愿影响因素分析:基于城乡差异比较[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3161-3168. |
| [6] | 余孜孜, 刘杜丽, 李熙敏, 阮春怡, 尹向阳, 蔡乐. 农村高血压患病和自我管理现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [7] | 范博阳, 张玉, 孙雯宁, 张慧芳, 王英杰, 张奥, 赵洋, 王海鹏. 基层医生慢性病医防融合服务行为意向及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [8] | 李春生, 王宥匀, 宋明莎, 乔慧. 宁夏回族自治区农村居民卫生服务利用现状及其影响因素研究——基于健康贫困脆弱性视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3169-3179. |
| [9] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [10] | 何金玉, 朱丽都孜·解思思别克, 张宁, 刘民, 梁万年. 我国规范化管理高血压患者血压控制及影响因素研究的现状、挑战与未来展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2968-2971. |
| [11] | 吴越, 王雪彤, 柯碧莲. 近视性黄斑病变低视力患者视觉相关生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [12] | 丁梓峻, 周南男, 罗星, 罗洁羽, 郝文娟, 张春江, 金鑫, 赵丹. 维持性血液透析患者认知障碍情况及其影响因素:一项多中心横断面研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2885-2893. |
| [13] | 顼禹同, 苏未, 唐颂, 马爽. 中国居民对中医态度与行为的比较研究:基于中国综合社会调查2011年和2021年数据的实证分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2915-2923. |
| [14] | 王久格, 湛武逸, 何安霞. 急性心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后早期微循环灌注对左心室功能的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2878-2884. |
| [15] | 尉晓霞, 陈诺, 王娟娟, 朱静芬. 职校生抑郁和焦虑情绪对吸烟行为的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2826-2832. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





