中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (23): 2885-2893.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0425
丁梓峻1, 周南男1, 罗星2, 罗洁羽1, 郝文娟1, 张春江1, 金鑫3, 赵丹1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-10
修回日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-08-15
发布日期:2025-06-17
通讯作者:
赵丹
作者贡献:
丁梓峻提出主要研究目标、查阅文献、统计分析、完成论文的撰写及修改,参与现场调查和数据收集;周南男、罗星进行数据的收集与整理,参与统计分析,负责图、表的绘制与展示;罗洁羽、郝文娟参与现场调查、数据收集、问卷录入与整理;张春江、金鑫参与研究设计,技术支持;赵丹负责研究整体设计、质量控制、调查培训、论文的指导和审校,对本文整体负责。
基金资助:
DING Zijun1, ZHOU Nannan1, LUO Xing2, LUO Jieyu1, HAO Wenjuan1, ZHANG Chunjiang1, JIN Xin3, ZHAO Dan1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-10
Revised:2024-12-16
Published:2025-08-15
Online:2025-06-17
Contact:
ZHAO Dan
摘要: 背景 了解维持性血液透析(MHD)患者认知障碍的情况及影响因素,可能对提高MHD患者生活质量、减轻家属与社会负担有较大帮助。 目的 调查MHD患者的认知障碍情况,并探究其可能的影响因素。 方法 采用方便抽样法,选取2023年4月—2024年4月在石河子市3家血透中心(包括石河子大学第一附属医院肾病内科、石河子市人民医院肾病内科、朗肾血液透析中心)行MHD的患者。采集患者的人口学特征、认知障碍程度、睡眠情况、独立生活能力、血清α-Klotho、β-Klotho、成纤维细胞生长因子23(FGF-23)水平及其他常见实验室检查指标。以蒙特利尔认知量表(MoCA)评估认知功能,阿森斯失眠量表(AIS-8)评估睡眠情况,功能活动问卷(FAQ)评估独立生活能力,通过ELISA法测定血清α-Klotho、β-Klotho、FGF-23水平,以单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析筛选影响因素,通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)验证影响因素对认知障碍的预测价值,并绘制列线图。 结果 共调查MHD患者276例,认知障碍发生率为76.4%(211/276),其中轻度认知障碍患者145例,中度认知障碍患者66例。存在可疑失眠(21.4%)或失眠(25.4%)患者较多。无独立生活能力的患者占14.9%(41/276)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄(OR=1.038,95%CI=1.004~1.072)、睡眠障碍(OR=1.179,95%CI=1.051~1.322)是MHD患者发生认知障碍的危险因素(P<0.05)。高水平血清α-Klotho(OR=0.996,95%CI=0.994~0.998)、高水平血清β-Klotho(OR=0.750,95%CI=0.661~0.852)、受教育年限长(OR=0.800,95%CI=0.699~0.915)是MHD患者发生认知障碍的保护因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线下面积(AUC)显示,年龄(AUC=0.732,95%CI=0.667~0.797)、睡眠障碍(AUC=0.710,95%CI=0.638~0.783)、α-Klotho(AUC=0.774,95%CI=0.709~0.839)、β-Klotho(AUC=0.741,95%CI=0.663~0.819)、受教育年限(AUC=0.718,95%CI=0.647~0.789)对于MHD患者认知障碍的发生均具有预测价值。年龄、睡眠障碍、血清α-Klotho、血清β-Klotho、受教育年限联合(P=-0.004×α-Klotho-0.287×β-Klotho+0.370×年龄-0.223×受教育年限+0.165×AIS-8评分+6.658)预测MHD患者发生认知障碍的AUC为0.894(95%CI=0.851~0.937,P<0.001),灵敏度为82.9%,特异度为78.5%。 结论 MHD患者认知障碍发生率较高,占76%左右,且年龄、睡眠障碍、受教育年限、α-Klotho、β-Klotho水平是重要的影响因素。医护人员及患者家属应提高对认知障碍的认识,对重点患者积极开展筛查和干预工作,以改善患者的生活质量,减轻患者的家庭和社会负担。
中图分类号:
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄( | 受教育年限[M(P25,P75),年] | 透析龄[M(P25,P75),月] | 高血压[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 冠心病[例(%)] | 心力衰竭[例(%)] | 乙肝[例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 认知正常组 | 65 | 45(69.2) | 20(30.8) | 46.3±11.6 | 12(9,15) | 20(12,58) | 49(75.4) | 20(30.8) | 14(21.5) | 3(4.6) | 9(13.8) |
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 145 | 88(60.7) | 57(39.3) | 53.4±12.7 | 9(9,12) | 31(15,60) | 105(72.4) | 37(25.5) | 36(24.8) | 16(11.0) | 16(11.0) |
| 中度认知障碍组 | 66 | 41(62.1) | 25(37.9) | 63.6±12.0 | 9(6,9) | 24(12,48) | 39(59.1) | 16(24.2) | 9(13.6) | 5(7.6) | 5(7.6) |
| 检验统计量值 | 1.437b | 33.078a | 46.652 | 4.607 | 5.032b | 0.854b | 3.381b | 2.466b | 1.338b | ||
| P值 | 0.487 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.100 | 0.081 | 0.653 | 0.184 | 0.291 | 0.512 | ||
| 组别 | 睡眠障碍[例(%)] | 独立生活能力异常[例(%)] | 收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | α-Klotho [M(P25,P75),μg/L] | β-Klotho[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | |||||
| 无失眠 | 可疑失眠 | 失眠 | |||||||||
| 认知正常组 | 52(80.0) | 6(9.2) | 7(10.8) | 2(3.1) | 134(127,144) | 80(77,89) | 832.09(665.71,995.51) | 11.16(7.37,14.27) | |||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 74(51.0) | 38(26.2) | 33(22.8) | 11(7.6) | 140(132,148) | 81(74,88) | 635.21(560.01,763.12) | 8.03(6.21,9.62) | |||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 21(31.8) | 15(22.7) | 30(45.5) | 28(42.4) | 137(131,151) | 80(69,90) | 496.40(389.82,601.61) | 6.63(5.31,7.91) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | 37.034b | 52.847b | 9.215 | 1.721 | 74.145 | 47.490 | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.010 | 0.423 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 组别 | FGF-23 [M(P25,P75),μg/L] | C反应蛋白[M(P25,P75),mg/L] | 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 红细胞计数( | 血小板计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 血红蛋白( | 白蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 99.62(57.35,167.55) | 3.88(2.27,8.79) | 7.04(5.50,8.20) | 3.71±0.69 | 204(169,257) | 110.25±19.93 | 42.90(39.55,46.00) | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 97.37(43.84,147.72) | 5.29(2.24,10.09) | 6.57(5.24,8.01) | 3.69±0.71 | 185(159,246) | 109.81±21.42 | 42.70(39.60,45.15) | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 79.32(35.88,131.25) | 7.03(3.58,12.21) | 6.81(4.87,8.52) | 3.69±0.77 | 196(162,258) | 109.65±23.93 | 42.35(39.40,44.32) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.702 | 5.301 | 0.455 | 0.009a | 3.874 | 0.014a | 2.208 | ||||
| P值 | 0.259 | 0.071 | 0.797 | 0.991 | 0.144 | 0.987 | 0.332 | ||||
| 组别 | 肌酐( | 尿素氮[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 尿酸( | 三酰甘油[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 总胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 低密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 高密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 893.49±322.12 | 21.59(17.34,26.32) | 382.03±120.52 | 1.85(1.03,2.12) | 4.00(3.34,4.56) | 2.48(1.89,2.75) | 1.03(0.81,1.24) | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 872.07±288.09 | 23.16(18.20,27.84) | 383.62±101.54 | 1.93(1.64,2.35) | 4.14(3.27,4.79) | 2.33(1.91,2.74) | 0.94(0.81,1.18) | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 784.67±258.18 | 22.04(18.80,27.53) | 369.47±108.66 | 1.93(1.26,2.91) | 4.32(3.47,4.99) | 2.36(1.88,2.76) | 0.90(0.80,1.06) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.767a | 1.005 | 0.407a | 6.156 | 1.409 | 0.400 | 6.624 | ||||
| P值 | 0.065 | 0.605 | 0.666 | 0.046 | 0.494 | 0.819 | 0.036 | ||||
| 组别 | 血钾[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 血钠( | 血氯( | 血钙( | 血镁( | 血磷[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | BMI ( | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 4.65(4.23,5.21) | 139.89±3.58 | 98.71±3.69 | 2.15±0.18 | 1.08±0.13 | 1.66(1.28,2.19) | 23.6±3.4 | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 4.60(4.10,5.26) | 140.04±4.24 | 99.42±3.95 | 2.13±0.20 | 1.05±0.16 | 1.66(1.40,2.01) | 22.8±3.5 | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 4.49(3.99,4.91) | 140.39±3.77 | 98.87±3.78 | 2.12±0.17 | 1.02±0.14 | 1.61(1.39,1.91) | 22.6±3.7 | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 3.689 | 2.683a | 0.935a | 0.244a | 3.246a | 0.782 | 1.554a | ||||
| P值 | 0.158 | 0.070 | 0.394 | 0.784 | 0.040 | 0.676 | 0.213 | ||||
| 组别 | 甲状旁腺激素[M(P25,P75),ng/L] | 铁蛋白[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | 叶酸[M(P25,P75),nmol/L] | 维生素B12 [M(P25,P75),ng/L] | 血清铁[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | ||||||
| 认知正常组 | 337.20(170.60,439.05) | 195.70(73.79,459.90) | 17.09(12.22,29.90) | 555.20(421.05,789.75) | 11.60(9.18,15.14) | ||||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 268.86(166.90,423.00) | 197.30(73.03,365.50) | 14.18(10.06,20.98) | 514.70(365.55,689.65) | 10.38(7.09,14.37) | ||||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 247.20(146.70,390.40) | 212.60(133.95,426.62) | 14.91(11.39,24.01) | 478.60(381.00,636.80) | 11.56(8.63,17.47) | ||||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.581 | 3.393 | 5.179 | 2.046 | 4.815 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.275 | 0.183 | 0.075 | 0.360 | 0.090 | ||||||
表1 不同认知功能组间临床资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of clinical data between different cognitive function groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄( | 受教育年限[M(P25,P75),年] | 透析龄[M(P25,P75),月] | 高血压[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 冠心病[例(%)] | 心力衰竭[例(%)] | 乙肝[例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 认知正常组 | 65 | 45(69.2) | 20(30.8) | 46.3±11.6 | 12(9,15) | 20(12,58) | 49(75.4) | 20(30.8) | 14(21.5) | 3(4.6) | 9(13.8) |
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 145 | 88(60.7) | 57(39.3) | 53.4±12.7 | 9(9,12) | 31(15,60) | 105(72.4) | 37(25.5) | 36(24.8) | 16(11.0) | 16(11.0) |
| 中度认知障碍组 | 66 | 41(62.1) | 25(37.9) | 63.6±12.0 | 9(6,9) | 24(12,48) | 39(59.1) | 16(24.2) | 9(13.6) | 5(7.6) | 5(7.6) |
| 检验统计量值 | 1.437b | 33.078a | 46.652 | 4.607 | 5.032b | 0.854b | 3.381b | 2.466b | 1.338b | ||
| P值 | 0.487 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.100 | 0.081 | 0.653 | 0.184 | 0.291 | 0.512 | ||
| 组别 | 睡眠障碍[例(%)] | 独立生活能力异常[例(%)] | 收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | α-Klotho [M(P25,P75),μg/L] | β-Klotho[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | |||||
| 无失眠 | 可疑失眠 | 失眠 | |||||||||
| 认知正常组 | 52(80.0) | 6(9.2) | 7(10.8) | 2(3.1) | 134(127,144) | 80(77,89) | 832.09(665.71,995.51) | 11.16(7.37,14.27) | |||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 74(51.0) | 38(26.2) | 33(22.8) | 11(7.6) | 140(132,148) | 81(74,88) | 635.21(560.01,763.12) | 8.03(6.21,9.62) | |||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 21(31.8) | 15(22.7) | 30(45.5) | 28(42.4) | 137(131,151) | 80(69,90) | 496.40(389.82,601.61) | 6.63(5.31,7.91) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | 37.034b | 52.847b | 9.215 | 1.721 | 74.145 | 47.490 | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.010 | 0.423 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 组别 | FGF-23 [M(P25,P75),μg/L] | C反应蛋白[M(P25,P75),mg/L] | 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 红细胞计数( | 血小板计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 血红蛋白( | 白蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 99.62(57.35,167.55) | 3.88(2.27,8.79) | 7.04(5.50,8.20) | 3.71±0.69 | 204(169,257) | 110.25±19.93 | 42.90(39.55,46.00) | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 97.37(43.84,147.72) | 5.29(2.24,10.09) | 6.57(5.24,8.01) | 3.69±0.71 | 185(159,246) | 109.81±21.42 | 42.70(39.60,45.15) | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 79.32(35.88,131.25) | 7.03(3.58,12.21) | 6.81(4.87,8.52) | 3.69±0.77 | 196(162,258) | 109.65±23.93 | 42.35(39.40,44.32) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.702 | 5.301 | 0.455 | 0.009a | 3.874 | 0.014a | 2.208 | ||||
| P值 | 0.259 | 0.071 | 0.797 | 0.991 | 0.144 | 0.987 | 0.332 | ||||
| 组别 | 肌酐( | 尿素氮[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 尿酸( | 三酰甘油[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 总胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 低密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 高密度脂蛋白[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 893.49±322.12 | 21.59(17.34,26.32) | 382.03±120.52 | 1.85(1.03,2.12) | 4.00(3.34,4.56) | 2.48(1.89,2.75) | 1.03(0.81,1.24) | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 872.07±288.09 | 23.16(18.20,27.84) | 383.62±101.54 | 1.93(1.64,2.35) | 4.14(3.27,4.79) | 2.33(1.91,2.74) | 0.94(0.81,1.18) | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 784.67±258.18 | 22.04(18.80,27.53) | 369.47±108.66 | 1.93(1.26,2.91) | 4.32(3.47,4.99) | 2.36(1.88,2.76) | 0.90(0.80,1.06) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.767a | 1.005 | 0.407a | 6.156 | 1.409 | 0.400 | 6.624 | ||||
| P值 | 0.065 | 0.605 | 0.666 | 0.046 | 0.494 | 0.819 | 0.036 | ||||
| 组别 | 血钾[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 血钠( | 血氯( | 血钙( | 血镁( | 血磷[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | BMI ( | ||||
| 认知正常组 | 4.65(4.23,5.21) | 139.89±3.58 | 98.71±3.69 | 2.15±0.18 | 1.08±0.13 | 1.66(1.28,2.19) | 23.6±3.4 | ||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 4.60(4.10,5.26) | 140.04±4.24 | 99.42±3.95 | 2.13±0.20 | 1.05±0.16 | 1.66(1.40,2.01) | 22.8±3.5 | ||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 4.49(3.99,4.91) | 140.39±3.77 | 98.87±3.78 | 2.12±0.17 | 1.02±0.14 | 1.61(1.39,1.91) | 22.6±3.7 | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 3.689 | 2.683a | 0.935a | 0.244a | 3.246a | 0.782 | 1.554a | ||||
| P值 | 0.158 | 0.070 | 0.394 | 0.784 | 0.040 | 0.676 | 0.213 | ||||
| 组别 | 甲状旁腺激素[M(P25,P75),ng/L] | 铁蛋白[M(P25,P75),μg/L] | 叶酸[M(P25,P75),nmol/L] | 维生素B12 [M(P25,P75),ng/L] | 血清铁[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | ||||||
| 认知正常组 | 337.20(170.60,439.05) | 195.70(73.79,459.90) | 17.09(12.22,29.90) | 555.20(421.05,789.75) | 11.60(9.18,15.14) | ||||||
| 轻度认知障碍组 | 268.86(166.90,423.00) | 197.30(73.03,365.50) | 14.18(10.06,20.98) | 514.70(365.55,689.65) | 10.38(7.09,14.37) | ||||||
| 中度认知障碍组 | 247.20(146.70,390.40) | 212.60(133.95,426.62) | 14.91(11.39,24.01) | 478.60(381.00,636.80) | 11.56(8.63,17.47) | ||||||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.581 | 3.393 | 5.179 | 2.046 | 4.815 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.275 | 0.183 | 0.075 | 0.360 | 0.090 | ||||||
| 项目 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -0.485 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.429 | <0.001 |
| 收缩压 | -0.111 | 0.066 |
| AIS-8得分 | -0.412 | <0.001 |
| FAQ得分 | -0.424 | <0.001 |
| α-Klotho | 0.557 | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.423 | <0.001 |
| FGF-23 | 0.124 | 0.039 |
| 三酰甘油 | -0.001 | 0.990 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.162 | 0.007 |
| 血镁 | 0.178 | 0.003 |
表2 MHD患者MoCA得分与临床指标的Spearman秩相关分析
Table 2 Spearman correlation analysis of MoCA score and clinical indicators in patients on maintenance hemodialysis
| 项目 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -0.485 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.429 | <0.001 |
| 收缩压 | -0.111 | 0.066 |
| AIS-8得分 | -0.412 | <0.001 |
| FAQ得分 | -0.424 | <0.001 |
| α-Klotho | 0.557 | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.423 | <0.001 |
| FGF-23 | 0.124 | 0.039 |
| 三酰甘油 | -0.001 | 0.990 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.162 | 0.007 |
| 血镁 | 0.178 | 0.003 |
| 项目 | 控制年龄 | 控制α-Klotho | 控制β-Klotho | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | — | — | -0.459 | <0.001 | -0.466 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.273 | <0.001 | 0.446 | <0.001 | 0.396 | <0.001 |
| AIS-8得分 | -0.359 | <0.001 | -0.396 | <0.001 | -0.408 | <0.001 |
| FAQ得分 | -0.313 | <0.001 | -0.385 | <0.001 | -0.428 | <0.001 |
| α-Klotho | 0.509 | <0.001 | — | — | 0.450 | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.435 | <0.001 | 0.344 | <0.001 | — | — |
| FGF-23 | 0.045 | 0.457 | 0.038 | 0.526 | 0.039 | 0.524 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.210 | <0.001 | 0.103 | 0.089 | 0.178 | 0.003 |
| 血镁 | 0.145 | 0.016 | 0.066 | 0.274 | 0.096 | 0.111 |
表3 MHD患者MoCA得分与临床指标的偏相关性分析
Table 3 Partial correlation analysis of MoCA score and clinical indicators in patients on maintenance hemodialysis
| 项目 | 控制年龄 | 控制α-Klotho | 控制β-Klotho | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | — | — | -0.459 | <0.001 | -0.466 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.273 | <0.001 | 0.446 | <0.001 | 0.396 | <0.001 |
| AIS-8得分 | -0.359 | <0.001 | -0.396 | <0.001 | -0.408 | <0.001 |
| FAQ得分 | -0.313 | <0.001 | -0.385 | <0.001 | -0.428 | <0.001 |
| α-Klotho | 0.509 | <0.001 | — | — | 0.450 | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.435 | <0.001 | 0.344 | <0.001 | — | — |
| FGF-23 | 0.045 | 0.457 | 0.038 | 0.526 | 0.039 | 0.524 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 | 0.210 | <0.001 | 0.103 | 0.089 | 0.178 | 0.003 |
| 血镁 | 0.145 | 0.016 | 0.066 | 0.274 | 0.096 | 0.111 |
| 相关因素 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.062 | 0.012 | 25.215 | <0.001 | 1.063(1.038~1.089) |
| 受教育年限 | -0.272 | 0.051 | 28.724 | <0.001 | 0.762(0.689~0.841) |
| AIS-8得分 | 0.214 | 0.051 | 17.908 | <0.001 | 1.239(1.122~1.368) |
| FAQ得分 | 0.266 | 0.093 | 8.171 | 0.004 | 1.304(1.087~1.565) |
| α-Klotho | -0.005 | 0.001 | 35.592 | <0.001 | 0.995(0.994~0.997) |
| β-Klotho | -0.336 | 0.052 | 41.785 | <0.001 | 0.714(0.645~0.791) |
表4 MHD患者发生认知障碍影响因素的单因素Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Univariate unconditional Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of cognitive impairment in maintenance hemodialysis patients
| 相关因素 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.062 | 0.012 | 25.215 | <0.001 | 1.063(1.038~1.089) |
| 受教育年限 | -0.272 | 0.051 | 28.724 | <0.001 | 0.762(0.689~0.841) |
| AIS-8得分 | 0.214 | 0.051 | 17.908 | <0.001 | 1.239(1.122~1.368) |
| FAQ得分 | 0.266 | 0.093 | 8.171 | 0.004 | 1.304(1.087~1.565) |
| α-Klotho | -0.005 | 0.001 | 35.592 | <0.001 | 0.995(0.994~0.997) |
| β-Klotho | -0.336 | 0.052 | 41.785 | <0.001 | 0.714(0.645~0.791) |
| 相关因素 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.037 | 0.017 | 4.954 | 0.026 | 1.038(1.004~1.072) |
| 受教育年限 | -0.223 | 0.069 | 10.568 | 0.001 | 0.800(0.699~0.915) |
| AIS-8得分 | 0.164 | 0.059 | 7.865 | 0.005 | 1.179(1.051~1.322) |
| FAQ得分 | 0.004 | 0.104 | 0.001 | 0.973 | 1.004(0.819~1.229) |
| α-Klotho | -0.004 | 0.001 | 18.596 | <0.001 | 0.996(0.994~0.998) |
| β-Klotho | -0.287 | 0.065 | 19.785 | <0.001 | 0.750(0.661~0.852) |
表5 MHD患者发生认知障碍影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 5 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors of cognitive impairment in maintenance hemodialysis patients
| 相关因素 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.037 | 0.017 | 4.954 | 0.026 | 1.038(1.004~1.072) |
| 受教育年限 | -0.223 | 0.069 | 10.568 | 0.001 | 0.800(0.699~0.915) |
| AIS-8得分 | 0.164 | 0.059 | 7.865 | 0.005 | 1.179(1.051~1.322) |
| FAQ得分 | 0.004 | 0.104 | 0.001 | 0.973 | 1.004(0.819~1.229) |
| α-Klotho | -0.004 | 0.001 | 18.596 | <0.001 | 0.996(0.994~0.998) |
| β-Klotho | -0.287 | 0.065 | 19.785 | <0.001 | 0.750(0.661~0.852) |
| 指标 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 最佳截断值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Klotho | 0.774 | 0.709~0.839 | 63.0 | 80.0 | 659.48 μg/L | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.741 | 0.663~0.819 | 89.6 | 53.8 | 10.94 μg/L | <0.001 |
| 年龄 | 0.732 | 0.667~0.797 | 58.8 | 78.5 | 54.5 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.718 | 0.647~0.789 | 70.1 | 66.2 | 10.5 | <0.001 |
| AIS-8评分 | 0.710 | 0.638~0.783 | 65.4 | 72.3 | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| 模型1 | 0.827 | 0.766~0.887 | 77.3 | 75.4 | <0.001 | |
| 模型2 | 0.894 | 0.851~0.937 | 82.9 | 78.5 | <0.001 |
表6 不同指标对MHD患者发生认知障碍的预测价值
Table 6 The predictive value of different indexes for cognitive impairment in maintenance hemodialysis patients
| 指标 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 最佳截断值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Klotho | 0.774 | 0.709~0.839 | 63.0 | 80.0 | 659.48 μg/L | <0.001 |
| β-Klotho | 0.741 | 0.663~0.819 | 89.6 | 53.8 | 10.94 μg/L | <0.001 |
| 年龄 | 0.732 | 0.667~0.797 | 58.8 | 78.5 | 54.5 | <0.001 |
| 受教育年限 | 0.718 | 0.647~0.789 | 70.1 | 66.2 | 10.5 | <0.001 |
| AIS-8评分 | 0.710 | 0.638~0.783 | 65.4 | 72.3 | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| 模型1 | 0.827 | 0.766~0.887 | 77.3 | 75.4 | <0.001 | |
| 模型2 | 0.894 | 0.851~0.937 | 82.9 | 78.5 | <0.001 |
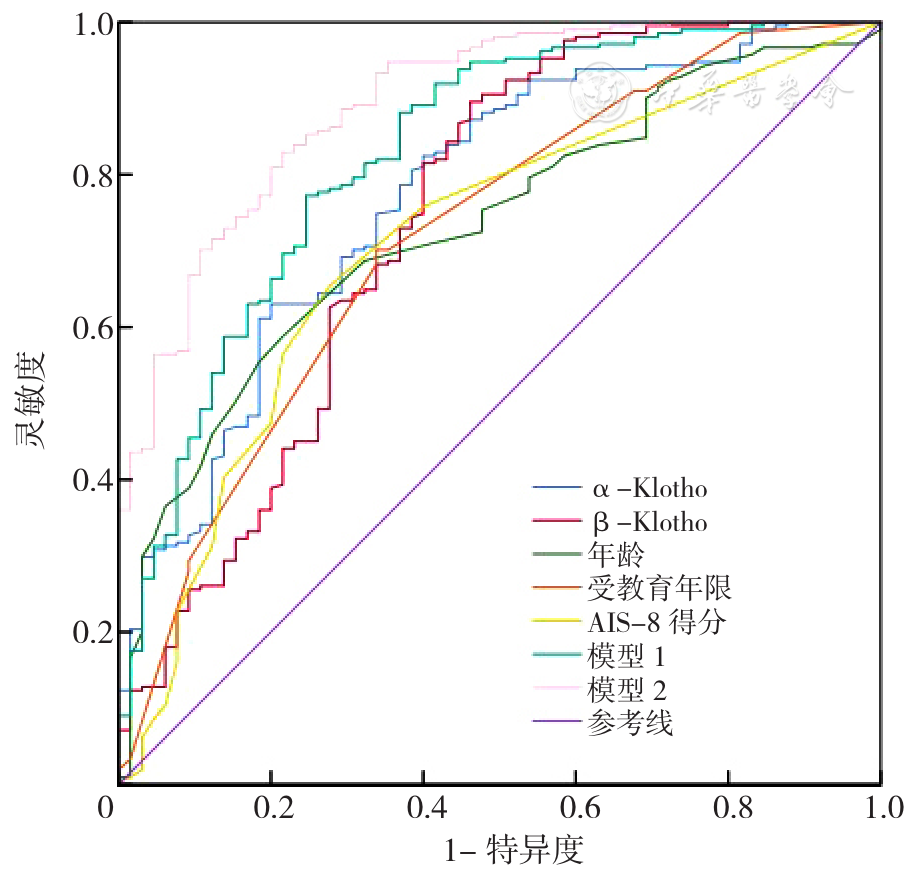
图1 不同指标预测MHD患者发生认知障碍的ROC曲线注:AIS-8=阿森斯失眠量表;模型1为α-Klotho和β-Klotho联合分析(P=-0.005×α-Klotho-0.040×β-Klotho+6.490);模型2为α-Klotho、β-Klotho、年龄、受教育年限、AIS-8评分联合分析(P=-0.004×α-Klotho-0.287×β-Klotho+0.370×年龄-0.223×受教育年限+0.165×AIS-8评分+6.658)。
Figure 1 ROC curves for various indicators predicting cognitive impairment in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders(DSM-5®)[EB/OL].(2013-05-22)[2024-08-01].
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
姚燕,杨芳,王丽娟,等. 蒙特利尔认知评估量表在轻度认知功能障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2012,38(4):730-735.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
梁耀先,赵新菊,韦洮.中国血液透析行业发展调研报告[J].中国血液净化,2024,23(5):321-329.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
达静静,孙月,陈金春,等. 血液灌流对维持性血液透析患者蛋白质能量消耗及长期预后的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2023,103(8):559-565. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20220925-02022.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [1] | 吴越, 王雪彤, 柯碧莲. 近视性黄斑病变低视力患者视觉相关生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [2] | 郝爱华, 曾子莹, 金爱琼, 唐玲玲, 郑梓悫, 马景泰, 赵建国, 曾韦霖, 肖建鹏, 聂辉, 杨颖. 老年高血压患者可避免住院的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [3] | 王碧晴, 张萍, 杨红霞, 王倩, 鞠春晓, 赵俊男, 梅俊, 张颖, 徐凤芹. 中国老年高血压患者轻度认知障碍患病率及发展趋势的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2186-2192. |
| [4] | 刘宇婷, 仇丽霞, 李育玲. 衰弱对中国老年人认知功能的影响:有调节的链式中介效应研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2119-2126. |
| [5] | 景涛, 戴永梅, 罗健英, 罗维, 季烨林凡, 彭驰, 张翠军, 曹彦俊, 郑清, 黄玉, 沈鹤军. 中国高中生的体质指数、膳食知识掌握水平、静坐时长及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2025-2032. |
| [6] | 黄志杰, 麦志华, 王皓翔, 何煜明, 邓巧妍, 戴燃然, 周志衡. 老年"三高"共患情况和家庭功能的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2001-2010. |
| [7] | 赵璨, 申颖, 奚谦, 彭厚瑄, 覃金琼, 王璇, 郑艳萍, 覃丽, 左延莉. 广西壮族自治区乡镇卫生院多重慢病患者的住院费用及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2039-2049. |
| [8] | 朱荣芳, 靳晶晶, 梁向楠, 钱玥彤, 耿同会, 白亚玲, 徐金升. 平均血小板体积与维持性血液透析患者血管通路事件的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(15): 1855-1861. |
| [9] | 绳菁煜, 刘凡凡, 马梅, 田霖, 刘雨桐, 刘凤敏, 高杉, 于春泉. 冠心病患者血尿素氮与血清白蛋白比值与颈动脉斑块的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(15): 1831-1839. |
| [10] | 张树静, 孙立新, 曹雨晴. 人乳头瘤病毒相关宫颈腺癌与非人乳头瘤相关宫颈腺癌的临床病理特征比较及预后研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1758-1764. |
| [11] | 夏玉雯, 石慧峰, 李梦诗, 张敬旭, 王晓莉. 中国农村地区留守儿童女性看护人抑郁的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1717-1722. |
| [12] | 徐军, 高亚南, 徐涯鑫, 姚亭, 陈亚梅. 炎症性肠病患者疾病负担的潜在剖面分析及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1744-1750. |
| [13] | 柴依依, 叶青芳, 林平, 李玲. 寒地城市冠心病患者运动认知风险综合征发生现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1730-1736. |
| [14] | 何梅亮, 刘修良, 赵梅桂, 郭艳芳, 徐英. 社区电子健康档案使用情况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1628-1634. |
| [15] | 刘斐然, 陈明皇, 赵率红, 白文佩. 随机森林模型在输卵管再通术后妊娠预测中的应用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1361-1366. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





