中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (05): 612-621.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0281
所属专题: 老年人群健康最新文章合辑; 用药最新文章合辑; 老年人合理用药专题研究; 患者报告结局最新文章合辑; 老年问题最新文章合辑
许惠靖1, 吴善玉1,*( ), 蒋佳玮2, 吴元虹1, 王晓辉1, 高歌1, 王哲1, 王宇宇1
), 蒋佳玮2, 吴元虹1, 王晓辉1, 高歌1, 王哲1, 王宇宇1
收稿日期:2023-04-05
修回日期:2023-07-02
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2023-11-21
通讯作者:
吴善玉
基金资助:
XU Huijing1, WU Shanyu1,*( ), JIANG Jiawei2, WU Yuanhong1, WANG Xiaohui1, GAO Ge1, WANG Zhe1, WANG Yuyu1
), JIANG Jiawei2, WU Yuanhong1, WANG Xiaohui1, GAO Ge1, WANG Zhe1, WANG Yuyu1
Received:2023-04-05
Revised:2023-07-02
Published:2024-02-15
Online:2023-11-21
Contact:
WU Shanyu
摘要: 背景 老年多重用药人群数量庞大,用药形势严峻,为保证用药患者生命长度与质量最大化,亟需使用特异性测评工具更加全面、客观地评估患者用药后的益处及风险。 目的 汉化基于患者报告结局用药相关生活质量量表(PROMPT-QoL),并评价该量表在老年多重用药患者中的信度和效度。 方法 征得原作者的授权,采用Brislin的双人直译-回译法、文化调适、认知性访谈,形成中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿。于2022年6—8月便利选取延吉市公园街道、北山街道及河南街道社区卫生服务中心、延吉市医院及延边大学附属医院门诊就诊、健康体检、取药的老年多重用药患者作为调查对象。采用条目-维度相关分析法和决断值法进行项目分析;采用条目水平的内容效度指数(I-CVI)、全体一致量表水平的内容效度指数(S-CVI/UA)和平均S-CVI(S-CVI/Ave)评价量表的内容效度;采用探索性因子分析(EFA)和验证性因子分析(CFA)检验结构效度;采用内部一致性(Cronbach's α系数)和折半信度检验量表的信度。 结果 共调查590例患者,回收有效资料564份,有效回收率为95.8%。其中234份资料应用于第一阶段的项目分析和EFA,330份资料应用于第二阶段的CFA。各条目得分与各维度得分的相关系数为0.504~0.915(P<0.01),各条目决断值(CR值)均>3.0(P<0.05);I-CVI为0.89~1.00,S-CVI/UA为0.91>0.80,S-CVI/Ave为0.99>0.90;EFA共提取8个公因子,与源问卷结构基本相符,其中条目G34在所属公因子上的载荷量<0.40,故删除条目G34;对剩余41个条目进行CFA,χ2/df=2.160,拟合优度指数(GFI)=0.791,规范拟合指数(NFI)=0.848,增值拟合指数(IFI)=0.912,比较拟合指数(CFI)=0.911,非标准拟合指数(TLI)=0.902,近似误差均方根(RMSEA)=0.059;总量表Cronbach's α系数为0.839,各维度Cronbach's α系数为0.823~0.955(P<0.01);各维度的折半信度为0.815~0.957(P<0.01)。 结论 经汉化和文化调适后的中文版PROMPT-QoL信效度良好,可应用于我国老年多重用药患者的用药相关生活质量水平的评估。
| 项目 | 例数 | 构成比(%) | 项目 | 例数 | 构成比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 确诊疾病患病年限(年) | ||||
| 男 | 245 | 43.4 | <5 | 131 | 23.3 |
| 女 | 319 | 56.6 | 5~10 | 285 | 50.5 |
| 年龄(岁) | >10 | 148 | 26.2 | ||
| 60~69 | 230 | 40.8 | 自感疾病控制情况 | ||
| 70~79 | 279 | 49.4 | 差 | 38 | 6.7 |
| 80~89 | 55 | 9.8 | 一般 | 290 | 51.5 |
| 民族 | 好 | 236 | 41.8 | ||
| 汉族 | 391 | 69.3 | 每月药费支出(元) | ||
| 朝鲜族及其他 | 173 | 30.7 | <100 | 14 | 2.5 |
| 文化程度 | 100~200 | 8 | 15.1 | ||
| 小学及以下 | 222 | 39.4 | >200~500 | 243 | 43.0 |
| 初中 | 200 | 35.4 | >500 | 222 | 39.4 |
| 高中及中专 | 102 | 18.1 | 每日用药种类(种) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 40 | 7.1 | 5~10 | 358 | 63.5 |
| 婚姻状况 | 11~15 | 106 | 18.8 | ||
| 已婚 | 431 | 76.4 | >15 | 100 | 17.7 |
| 未婚/离异/丧偶 | 133 | 23.6 | 用药年限(年) | ||
| 居住情况 | <1 | 20 | 3.5 | ||
| 独居 | 83 | 14.7 | 1~4 | 135 | 23.9 |
| 与配偶同住 | 309 | 54.8 | 5~9 | 245 | 43.4 |
| 其他 | 172 | 30.5 | 10~20 | 118 | 20.9 |
| 家庭人均月收入(元) | >20 | 46 | 8.3 | ||
| <3 000 | 303 | 53.7 | 是否经历过用药不良反应 | ||
| 3 000~5 000 | 208 | 36.9 | 否 | 125 | 22.2 |
| >5 000 | 53 | 9.4 | 是 | 439 | 77.8 |
| 医疗付费方式 | 用药一般态度 | ||||
| 城镇职工医保 | 110 | 19.5 | 药物治疗 | 253 | 44.8 |
| 城乡居民医保 | 328 | 58.2 | 补充和替代疗法 | 24 | 4.3 |
| 其他 | 126 | 22.3 | 药物治疗联合替代疗法 | 287 | 50.9 |
| CCI分级 | |||||
| 中度 | 206 | 36.5 | |||
| 重度 | 358 | 63.5 | |||
表1 老年多重用药患者一般人口学资料(n=564)
Table 1 General demographic data of elderly patients with polypharmacy
| 项目 | 例数 | 构成比(%) | 项目 | 例数 | 构成比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 确诊疾病患病年限(年) | ||||
| 男 | 245 | 43.4 | <5 | 131 | 23.3 |
| 女 | 319 | 56.6 | 5~10 | 285 | 50.5 |
| 年龄(岁) | >10 | 148 | 26.2 | ||
| 60~69 | 230 | 40.8 | 自感疾病控制情况 | ||
| 70~79 | 279 | 49.4 | 差 | 38 | 6.7 |
| 80~89 | 55 | 9.8 | 一般 | 290 | 51.5 |
| 民族 | 好 | 236 | 41.8 | ||
| 汉族 | 391 | 69.3 | 每月药费支出(元) | ||
| 朝鲜族及其他 | 173 | 30.7 | <100 | 14 | 2.5 |
| 文化程度 | 100~200 | 8 | 15.1 | ||
| 小学及以下 | 222 | 39.4 | >200~500 | 243 | 43.0 |
| 初中 | 200 | 35.4 | >500 | 222 | 39.4 |
| 高中及中专 | 102 | 18.1 | 每日用药种类(种) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 40 | 7.1 | 5~10 | 358 | 63.5 |
| 婚姻状况 | 11~15 | 106 | 18.8 | ||
| 已婚 | 431 | 76.4 | >15 | 100 | 17.7 |
| 未婚/离异/丧偶 | 133 | 23.6 | 用药年限(年) | ||
| 居住情况 | <1 | 20 | 3.5 | ||
| 独居 | 83 | 14.7 | 1~4 | 135 | 23.9 |
| 与配偶同住 | 309 | 54.8 | 5~9 | 245 | 43.4 |
| 其他 | 172 | 30.5 | 10~20 | 118 | 20.9 |
| 家庭人均月收入(元) | >20 | 46 | 8.3 | ||
| <3 000 | 303 | 53.7 | 是否经历过用药不良反应 | ||
| 3 000~5 000 | 208 | 36.9 | 否 | 125 | 22.2 |
| >5 000 | 53 | 9.4 | 是 | 439 | 77.8 |
| 医疗付费方式 | 用药一般态度 | ||||
| 城镇职工医保 | 110 | 19.5 | 药物治疗 | 253 | 44.8 |
| 城乡居民医保 | 328 | 58.2 | 补充和替代疗法 | 24 | 4.3 |
| 其他 | 126 | 22.3 | 药物治疗联合替代疗法 | 287 | 50.9 |
| CCI分级 | |||||
| 中度 | 206 | 36.5 | |||
| 重度 | 358 | 63.5 | |||
| 条目 | r值 | 条目 | r值 | 条目 | r值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | 0.721a | D16 | 0.710a | E30 | 0.665a |
| B3 | 0.751a | D17 | 0.777a | F31 | 0.807a |
| B4 | 0.692a | D18 | 0.697a | F32 | 0.789a |
| B5 | 0.528a | D19 | 0.738a | F33 | 0.826a |
| B6 | 0.792a | D20 | 0.612a | G34 | 0.504a |
| B7 | 0.722a | D21 | 0.789a | G35 | 0.843a |
| B8 | 0.772a | E22 | 0.661a | G36 | 0.915a |
| B9 | 0.799a | E23 | 0.571a | G37 | 0.890a |
| B10 | 0.752a | E24 | 0.621a | H38 | 0.766a |
| C11 | 0.822a | E25 | 0.693a | H39 | 0.851a |
| C12 | 0.805a | E26 | 0.712a | H40 | 0.870a |
| C13 | 0.869a | E27 | 0.737a | I41 | 0.905a |
| D14 | 0.751a | E28 | 0.683a | I42 | 0.897a |
| D15 | 0.740a | E29 | 0.751a | I43 | 0.802a |
表2 中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿条目-维度相关性分析(n=234)
Table 2 The item-dimension correlation analysis of test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 条目 | r值 | 条目 | r值 | 条目 | r值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | 0.721a | D16 | 0.710a | E30 | 0.665a |
| B3 | 0.751a | D17 | 0.777a | F31 | 0.807a |
| B4 | 0.692a | D18 | 0.697a | F32 | 0.789a |
| B5 | 0.528a | D19 | 0.738a | F33 | 0.826a |
| B6 | 0.792a | D20 | 0.612a | G34 | 0.504a |
| B7 | 0.722a | D21 | 0.789a | G35 | 0.843a |
| B8 | 0.772a | E22 | 0.661a | G36 | 0.915a |
| B9 | 0.799a | E23 | 0.571a | G37 | 0.890a |
| B10 | 0.752a | E24 | 0.621a | H38 | 0.766a |
| C11 | 0.822a | E25 | 0.693a | H39 | 0.851a |
| C12 | 0.805a | E26 | 0.712a | H40 | 0.870a |
| C13 | 0.869a | E27 | 0.737a | I41 | 0.905a |
| D14 | 0.751a | E28 | 0.683a | I42 | 0.897a |
| D15 | 0.740a | E29 | 0.751a | I43 | 0.802a |
| 条目 | 高分组(n=63) | 低分组(n=63) | CR值 | df | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | 3.39±1.18 | 2.76±0.95 | 3.231 | 107.178 | 0.002 |
| B3 | 3.11±1.15 | 2.29±1.08 | 4.075 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B4 | 3.74±1.01 | 3.12±0.69 | 3.885 | 96.833 | <0.001 |
| B5 | 4.25±0.89 | 3.55±1.06 | 3.939 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B6 | 3.42±1.07 | 2.62±1.03 | 4.212 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B7 | 2.95±1.29 | 1.95±0.97 | 4.773 | 102.868 | <0.001 |
| B8 | 3.00±1.38 | 2.35±0.87 | 3.084 | 91.783 | 0.003 |
| B9 | 3.19±1.30 | 2.41±0.96 | 3.750 | 101.675 | <0.001 |
| B10 | 3.47±1.10 | 2.74±0.85 | 4.073 | 104.219 | <0.001 |
| C11 | 4.35±0.55 | 3.88±0.71 | 4.061 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| C12 | 4.32±0.54 | 3.73±0.78 | 4.935 | 116.007 | <0.001 |
| C13 | 4.46±0.66 | 3.53±0.85 | 6.828 | 119.722 | <0.001 |
| D14 | 4.46±0.68 | 3.29±0.94 | 7.949 | 117.686 | <0.001 |
| D15 | 4.32±0.66 | 3.17±0.89 | 8.046 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| D16 | 4.39±0.65 | 3.41±1.01 | 6.478 | 112.284 | <0.001 |
| D17 | 4.84±0.46 | 4.09±0.97 | 5.606 | 95.016 | <0.001 |
| D18 | 4.58±0.50 | 3.56±0.95 | 7.604 | 101.272 | <0.001 |
| D19 | 4.86±0.40 | 4.09±0.99 | 5.799 | 88.125 | <0.001 |
| D20 | 4.82±0.50 | 4.30±0.74 | 4.602 | 114.864 | <0.001 |
| D21 | 4.67±0.58 | 3.41±0.99 | 8.729 | 106.904 | <0.001 |
| E22 | 3.23±1.10 | 2.24±0.95 | 5.338 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E23 | 3.58±1.12 | 2.92±1.24 | 3.050 | 121.000 | 0.003 |
| E24 | 3.25±1.09 | 2.35±1.20 | 4.321 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E25 | 3.26±1.20 | 2.35±1.21 | 4.194 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E26 | 3.86±0.95 | 2.94±0.74 | 5.907 | 105.117 | <0.001 |
| E27 | 3.79±1.05 | 2.68±0.96 | 6.106 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E28 | 3.86±1.14 | 3.26±0.97 | 3.170 | 121.000 | 0.002 |
| E29 | 3.63±1.08 | 2.70±1.11 | 4.718 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E30 | 3.84±1.15 | 2.95±1.28 | 4.020 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F31 | 4.14±0.72 | 3.58±0.77 | 4.196 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F32 | 4.04±0.73 | 3.55±0.75 | 3.658 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F33 | 3.96±0.73 | 3.45±0.83 | 3.602 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G34 | 4.23±1.07 | 3.50±1.04 | 3.819 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G35 | 3.88±0.95 | 2.41±0.91 | 8.754 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G36 | 4.04±1.02 | 2.39±1.05 | 8.767 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G37 | 4.12±1.00 | 2.30±1.16 | 9.223 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H38 | 4.58±0.57 | 4.11±0.77 | 3.839 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H39 | 4.35±0.58 | 3.85±0.79 | 3.963 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H40 | 4.33±0.69 | 3.65±0.85 | 4.833 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I41 | 4.12±0.91 | 3.36±0.82 | 4.884 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I42 | 4.19±0.90 | 3.36±0.76 | 5.566 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I43 | 4.28±0.88 | 3.62±0.74 | 4.513 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
表3 中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿各条目区分度分析结果(n=234,±s,分)
Table 3 Results of the differentiation analysis of each item in the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 条目 | 高分组(n=63) | 低分组(n=63) | CR值 | df | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | 3.39±1.18 | 2.76±0.95 | 3.231 | 107.178 | 0.002 |
| B3 | 3.11±1.15 | 2.29±1.08 | 4.075 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B4 | 3.74±1.01 | 3.12±0.69 | 3.885 | 96.833 | <0.001 |
| B5 | 4.25±0.89 | 3.55±1.06 | 3.939 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B6 | 3.42±1.07 | 2.62±1.03 | 4.212 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| B7 | 2.95±1.29 | 1.95±0.97 | 4.773 | 102.868 | <0.001 |
| B8 | 3.00±1.38 | 2.35±0.87 | 3.084 | 91.783 | 0.003 |
| B9 | 3.19±1.30 | 2.41±0.96 | 3.750 | 101.675 | <0.001 |
| B10 | 3.47±1.10 | 2.74±0.85 | 4.073 | 104.219 | <0.001 |
| C11 | 4.35±0.55 | 3.88±0.71 | 4.061 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| C12 | 4.32±0.54 | 3.73±0.78 | 4.935 | 116.007 | <0.001 |
| C13 | 4.46±0.66 | 3.53±0.85 | 6.828 | 119.722 | <0.001 |
| D14 | 4.46±0.68 | 3.29±0.94 | 7.949 | 117.686 | <0.001 |
| D15 | 4.32±0.66 | 3.17±0.89 | 8.046 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| D16 | 4.39±0.65 | 3.41±1.01 | 6.478 | 112.284 | <0.001 |
| D17 | 4.84±0.46 | 4.09±0.97 | 5.606 | 95.016 | <0.001 |
| D18 | 4.58±0.50 | 3.56±0.95 | 7.604 | 101.272 | <0.001 |
| D19 | 4.86±0.40 | 4.09±0.99 | 5.799 | 88.125 | <0.001 |
| D20 | 4.82±0.50 | 4.30±0.74 | 4.602 | 114.864 | <0.001 |
| D21 | 4.67±0.58 | 3.41±0.99 | 8.729 | 106.904 | <0.001 |
| E22 | 3.23±1.10 | 2.24±0.95 | 5.338 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E23 | 3.58±1.12 | 2.92±1.24 | 3.050 | 121.000 | 0.003 |
| E24 | 3.25±1.09 | 2.35±1.20 | 4.321 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E25 | 3.26±1.20 | 2.35±1.21 | 4.194 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E26 | 3.86±0.95 | 2.94±0.74 | 5.907 | 105.117 | <0.001 |
| E27 | 3.79±1.05 | 2.68±0.96 | 6.106 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E28 | 3.86±1.14 | 3.26±0.97 | 3.170 | 121.000 | 0.002 |
| E29 | 3.63±1.08 | 2.70±1.11 | 4.718 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| E30 | 3.84±1.15 | 2.95±1.28 | 4.020 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F31 | 4.14±0.72 | 3.58±0.77 | 4.196 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F32 | 4.04±0.73 | 3.55±0.75 | 3.658 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| F33 | 3.96±0.73 | 3.45±0.83 | 3.602 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G34 | 4.23±1.07 | 3.50±1.04 | 3.819 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G35 | 3.88±0.95 | 2.41±0.91 | 8.754 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G36 | 4.04±1.02 | 2.39±1.05 | 8.767 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| G37 | 4.12±1.00 | 2.30±1.16 | 9.223 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H38 | 4.58±0.57 | 4.11±0.77 | 3.839 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H39 | 4.35±0.58 | 3.85±0.79 | 3.963 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| H40 | 4.33±0.69 | 3.65±0.85 | 4.833 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I41 | 4.12±0.91 | 3.36±0.82 | 4.884 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I42 | 4.19±0.90 | 3.36±0.76 | 5.566 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| I43 | 4.28±0.88 | 3.62±0.74 | 4.513 | 121.000 | <0.001 |
| 条目 | 因子1 | 因子2 | 因子3 | 因子4 | 因子5 | 因子6 | 因子7 | 因子8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B9.病因及预防方法 | 0.828 | |||||||
| B3.药品规格 | 0.757 | |||||||
| B6.规律用药的理由 | 0.752 | |||||||
| B8.药物可能引起的副作用及解决办法 | 0.736 | |||||||
| B10.疾病症状、程度和治疗方法 | 0.726 | |||||||
| B2.药品规格 | 0.721 | |||||||
| B7.忘服/漏服药物的应对措施 | 0.703 | |||||||
| B4.药物的适应证 | 0.618 | |||||||
| B5.用法用量 | 0.438 | |||||||
| D17.外观或体表皮肤 | 0.826 | |||||||
| D19.视觉、听觉或语言功能 | 0.787 | |||||||
| D21.日常活动或社交活动 | 0.749 | |||||||
| D18.吞咽、消化、排尿或排便功能 | 0.691 | |||||||
| D14.行动能力 | 0.676 | |||||||
| D20.性生活或性欲 | 0.665 | |||||||
| D15.睡眠情况 | 0.634 | |||||||
| D16.记忆力或思维过程 | 0.604 | |||||||
| E29.药物之间的相互作用 | 0.771 | |||||||
| E27.每餐(或每日)使用多种药物 | 0.711 | |||||||
| E26.调整药物类型、用药剂量或使用方法 | 0.687 | |||||||
| E24.产生耐药性,导致药效降低 | 0.676 | |||||||
| E28.在其他人面前使用药物 | 0.646 | |||||||
| E22.药物不良反应 | 0.632 | |||||||
| E25.长期或终身使用药物 | 0.601 | |||||||
| E30.使用药物让您觉得您不像其他同龄人一样健康 | 0.582 | |||||||
| E23.每天规律且严格遵医嘱用药 | 0.477 | |||||||
| G36.医院诊疗流程问题 | 0.882 | |||||||
| G37.医院就诊取药问题 | 0.865 | |||||||
| G35.费用问题 | 0.784 | |||||||
| I42.药物给您带来多大程度的幸福感? | 0.846 | |||||||
| I41.您在多大程度上对药物感到满意? | 0.835 | |||||||
| I43.总体而言,您的药物多大程度上改善了您的生活 | 0.786 | |||||||
| C13.药物起效速度 | 0.793 | |||||||
| C11.症状缓解情况 | 0.763 | |||||||
| C12.疾病治愈效果 | 0.700 | |||||||
| F33.在旅途中或外出工作时便于携带 | 0.791 | |||||||
| F32.简便的用药方法 | 0.774 | |||||||
| F31.合适的药物形态 | 0.757 | |||||||
| H38.信任医生为您开的处方药 | 0.572 | |||||||
| H39.医务人员态度友好、热情,并为您解答用药相关问题 | 0.525 | |||||||
| H40.遇到用药问题时,医务人员为您提供解决办法 | 0.514 | |||||||
| 特征根 | 5.116 | 4.326 | 4.198 | 3.101 | 2.976 | 2.311 | 2.199 | 1.874 |
| 累积方差贡献率 | 12.477 | 23.028 | 33.268 | 40.830 | 48.090 | 53.727 | 59.089 | 63.659 |
表4 中文版PROMPT-QoL量表施测稿因子载荷矩阵(n=234)
Table 4 The factor loading matrix in the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 条目 | 因子1 | 因子2 | 因子3 | 因子4 | 因子5 | 因子6 | 因子7 | 因子8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B9.病因及预防方法 | 0.828 | |||||||
| B3.药品规格 | 0.757 | |||||||
| B6.规律用药的理由 | 0.752 | |||||||
| B8.药物可能引起的副作用及解决办法 | 0.736 | |||||||
| B10.疾病症状、程度和治疗方法 | 0.726 | |||||||
| B2.药品规格 | 0.721 | |||||||
| B7.忘服/漏服药物的应对措施 | 0.703 | |||||||
| B4.药物的适应证 | 0.618 | |||||||
| B5.用法用量 | 0.438 | |||||||
| D17.外观或体表皮肤 | 0.826 | |||||||
| D19.视觉、听觉或语言功能 | 0.787 | |||||||
| D21.日常活动或社交活动 | 0.749 | |||||||
| D18.吞咽、消化、排尿或排便功能 | 0.691 | |||||||
| D14.行动能力 | 0.676 | |||||||
| D20.性生活或性欲 | 0.665 | |||||||
| D15.睡眠情况 | 0.634 | |||||||
| D16.记忆力或思维过程 | 0.604 | |||||||
| E29.药物之间的相互作用 | 0.771 | |||||||
| E27.每餐(或每日)使用多种药物 | 0.711 | |||||||
| E26.调整药物类型、用药剂量或使用方法 | 0.687 | |||||||
| E24.产生耐药性,导致药效降低 | 0.676 | |||||||
| E28.在其他人面前使用药物 | 0.646 | |||||||
| E22.药物不良反应 | 0.632 | |||||||
| E25.长期或终身使用药物 | 0.601 | |||||||
| E30.使用药物让您觉得您不像其他同龄人一样健康 | 0.582 | |||||||
| E23.每天规律且严格遵医嘱用药 | 0.477 | |||||||
| G36.医院诊疗流程问题 | 0.882 | |||||||
| G37.医院就诊取药问题 | 0.865 | |||||||
| G35.费用问题 | 0.784 | |||||||
| I42.药物给您带来多大程度的幸福感? | 0.846 | |||||||
| I41.您在多大程度上对药物感到满意? | 0.835 | |||||||
| I43.总体而言,您的药物多大程度上改善了您的生活 | 0.786 | |||||||
| C13.药物起效速度 | 0.793 | |||||||
| C11.症状缓解情况 | 0.763 | |||||||
| C12.疾病治愈效果 | 0.700 | |||||||
| F33.在旅途中或外出工作时便于携带 | 0.791 | |||||||
| F32.简便的用药方法 | 0.774 | |||||||
| F31.合适的药物形态 | 0.757 | |||||||
| H38.信任医生为您开的处方药 | 0.572 | |||||||
| H39.医务人员态度友好、热情,并为您解答用药相关问题 | 0.525 | |||||||
| H40.遇到用药问题时,医务人员为您提供解决办法 | 0.514 | |||||||
| 特征根 | 5.116 | 4.326 | 4.198 | 3.101 | 2.976 | 2.311 | 2.199 | 1.874 |
| 累积方差贡献率 | 12.477 | 23.028 | 33.268 | 40.830 | 48.090 | 53.727 | 59.089 | 63.659 |
| 维度 | 条目数(个) | 量表编号 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 源问卷 | 调整后 | 源问卷 | 调整后 | |
| B.医药信息 | 9 | 9 | 2~10 | 2~10 |
| C.药物疗效满意度 | 3 | 3 | 11~13 | 11~13 |
| D.药物副作用的影响 | 8 | 8 | 14~21 | 14~21 |
| E.用药心理影响 | 9 | 9 | 22~30 | 22~30 |
| F.用药便利性 | 3 | 3 | 31~33 | 31~33 |
| G.药品可及性 | 4 | 3 | 34~37 | 34~36 |
| H.医患关系 | 3 | 3 | 38~40 | 37~39 |
| I.用药总体生活质量 | 3 | 3 | 41~43 | 40~42 |
表5 EFA前后中文版PROMPT-QoL量表施测稿各维度及条目结构调整对照表
Table 5 Comparison table of dimension and items structure adjustment before and after exploratory factor analysis in the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 维度 | 条目数(个) | 量表编号 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 源问卷 | 调整后 | 源问卷 | 调整后 | |
| B.医药信息 | 9 | 9 | 2~10 | 2~10 |
| C.药物疗效满意度 | 3 | 3 | 11~13 | 11~13 |
| D.药物副作用的影响 | 8 | 8 | 14~21 | 14~21 |
| E.用药心理影响 | 9 | 9 | 22~30 | 22~30 |
| F.用药便利性 | 3 | 3 | 31~33 | 31~33 |
| G.药品可及性 | 4 | 3 | 34~37 | 34~36 |
| H.医患关系 | 3 | 3 | 38~40 | 37~39 |
| I.用药总体生活质量 | 3 | 3 | 41~43 | 40~42 |
| 指标 | χ2/df | GFI | NFI | IFI | CFI | TLI | RMSEA(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 修正前 | 2.786 | 0.752 | 0.802 | 0.863 | 0.862 | 0.850 | 0.074(0.070,0.077) |
| 修正后 | 2.160 | 0.791 | 0.848 | 0.912 | 0.911 | 0.902 | 0.059(0.055,0.063) |
| 参考标准 | <3.00 | >0.90 | >0.80 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | <0.08 |
表6 中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿模型修正前后各适配值结果及参考值(n=330)
Table 6 Value of each fitting index and its reference range of the model before and after modification for the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 指标 | χ2/df | GFI | NFI | IFI | CFI | TLI | RMSEA(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 修正前 | 2.786 | 0.752 | 0.802 | 0.863 | 0.862 | 0.850 | 0.074(0.070,0.077) |
| 修正后 | 2.160 | 0.791 | 0.848 | 0.912 | 0.911 | 0.902 | 0.059(0.055,0.063) |
| 参考标准 | <3.00 | >0.90 | >0.80 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | <0.08 |
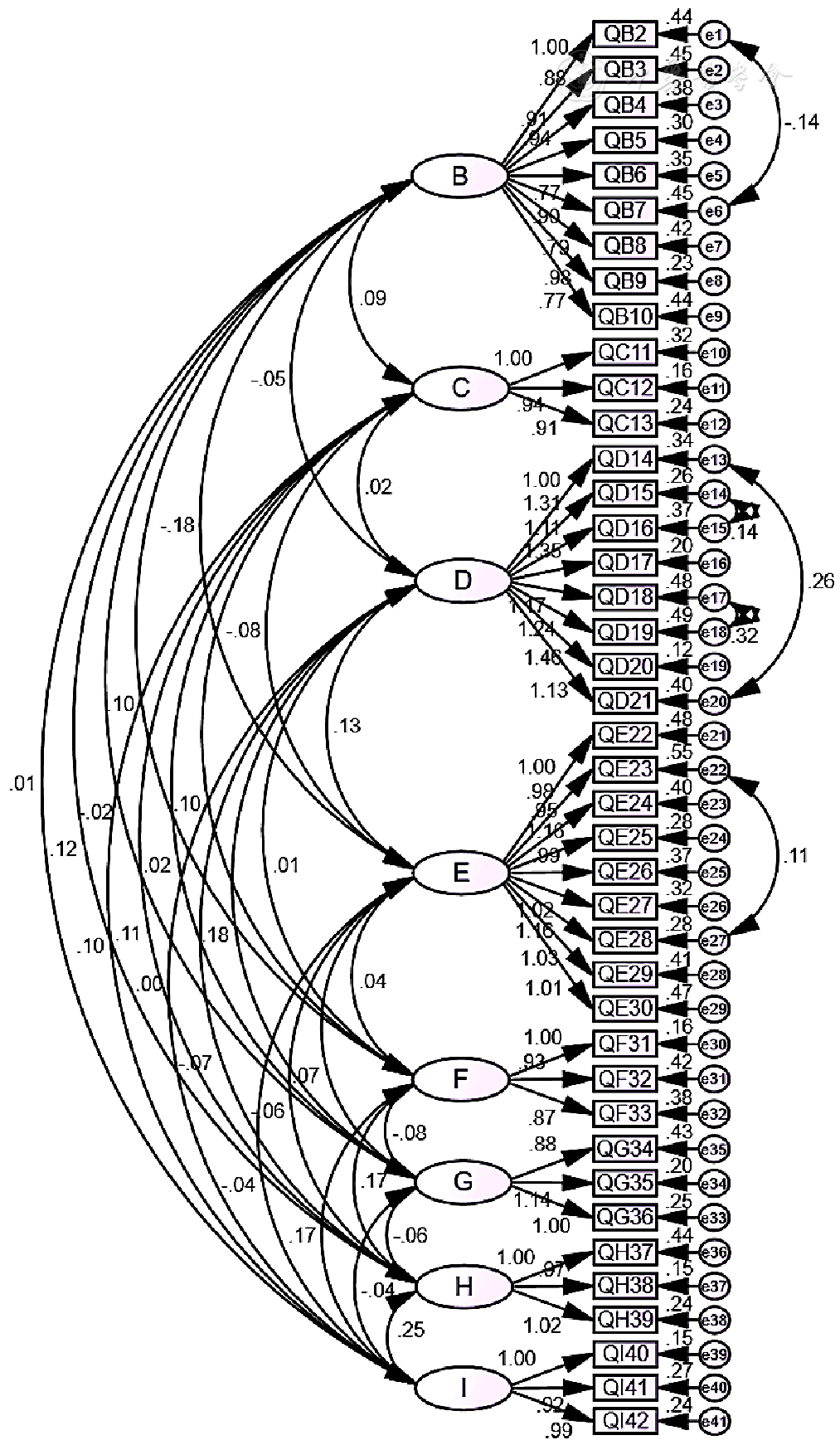
图2 中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿最终CFA条目因子载荷情况注:B=医药信息,C=药物疗效满意度,D=药物副作用的影响,E=用药心理影响,F=用药便利性,G=药品可及性,H=医患关系,I=用药总体生活质量。
Figure 2 Factor loadings of the final CFA items in the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 维度 | 条目数(个) | Cronbach's α系数 | 折半信度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B.医药信息 | 9 | 0.930 | 0.891 |
| C.药物疗效满意度 | 3 | 0.823 | 0.819 |
| D.药物副作用的影响 | 8 | 0.955 | 0.957 |
| E.用药心理影响 | 9 | 0.927 | 0.937 |
| F.用药便利性 | 3 | 0.831 | 0.815 |
| G.药品可及性 | 3 | 0.855 | 0.867 |
| H.医患关系 | 3 | 0.836 | 0.830 |
| I.用药总体生活质量 | 3 | 0.833 | 0.823 |
表7 中文版PROMPT-QoL施测稿各维度信度(n=564)
Table 7 The reliability of the dimensions in the test draft of the Chinese version of the PROMPT-QoL scale
| 维度 | 条目数(个) | Cronbach's α系数 | 折半信度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B.医药信息 | 9 | 0.930 | 0.891 |
| C.药物疗效满意度 | 3 | 0.823 | 0.819 |
| D.药物副作用的影响 | 8 | 0.955 | 0.957 |
| E.用药心理影响 | 9 | 0.927 | 0.937 |
| F.用药便利性 | 3 | 0.831 | 0.815 |
| G.药品可及性 | 3 | 0.855 | 0.867 |
| H.医患关系 | 3 | 0.836 | 0.830 |
| I.用药总体生活质量 | 3 | 0.833 | 0.823 |
| [1] |
中国发展研究基金会. 创新铸就健康基业:公共卫生领域的创新研究[M]. 北京:中国发展出版社,2019.
|
| [2] |
GBD Viewpoint Collaborators. Five insights from the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. Lancet,2020,396(10258): 1135-1159. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31404-5.
|
| [3] |
王可,唐静,杨昆,等. 中国14省27家医院住院老年慢病患者多重用药现状横断面研究[J]. 药物流行病学杂志,2022,31(1): 38-44. DOI:10.19960/j.cnki.issn1005-0698.2022.01.006.
|
| [4] |
徐倩. 老年住院患者共病与多重用药的分析[D]. 昆明:昆明医科大学,2017.
|
| [5] |
王永利,栾文艳,郭亚雯,等. 居家老年多病共存患者多重用药体验的质性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(17): 2197-2202. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2014.22.001.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
许清安,常履华,万崇华,等. 基于健康调查量表的脑卒中患者报告结局与临床客观指标的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2018,21(6): 643-647. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.00.193.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
蒋红莲,闫伟,路云. 老年共病指数的应用与推广问题研究[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2020,28(7): 548-551. DOI:10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2020.07.017.
|
| [19] |
郑日昌. 心理测量学[M]. 北京:人民教育出版社,1999.
|
| [20] |
吴明隆. 问卷统计分析实务:SPSS操作与应用[M]. 重庆:重庆大学出版社,2010.
|
| [21] |
王永利,张振香,林蓓蕾,等. 用药生活问卷的汉化及其在社区老年多重用药患者中的信效度分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(15): 1864-1872. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.234.
|
| [22] |
李嘉音. 预立医疗照护计划参与问卷汉化及在社区老年慢病患者中的应用研究[D]. 郑州:郑州大学,2021.
|
| [23] |
李跃平,黄子杰. 验证性因子分析在量表结构效度考核中作用[J]. 中国公共卫生,2007,23(10): 1198-1199. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-0580.2007.10.024.
|
| [24] |
吴明隆. 结构方程模型:AMOS的操作与应用[M]. 重庆:重庆大学出版社,2009.
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 崔宇阳, 程桂荣, 曾燕, 黄招兰, 谭伟. 社区老年人婚姻状况和社会支持及生活习惯与认知障碍的关联:基于湖北老年记忆队列基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3240-3247. |
| [4] | 燕芳红, 彭国恬, 张国莉, 孙瑞仪, 马玉霞, 韩琳. 医联体内老年慢性病管理内容的匹配分析:基于"指南-实践-需求"视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3119-3126. |
| [5] | 于文华, 李建国, 段文燕, 高旭妍, 李夏夏, 张子龙, 张丽, 马丽娜. 老年人功能受损评估量表在社区老年人中的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [6] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [7] | 李嘉欣, 刘钟桧, 谢硕, 付志方, 孙丹, 焦红梅. 分解代谢及炎症状态的生物标志物变化趋势对老年患者慢性危重症的早期预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2993-2999. |
| [8] | 赵晓晴, 郭桐桐, 张欣怡, 李林虹, 张亚, 嵇丽红, 董志伟, 高倩倩, 蔡伟芹, 郑文贵, 井淇. 社区老年人认知障碍风险预测模型的构建与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [9] | 石小天, 王珊, 杨华昱, 杨一帆, 李旭, 马清. 中国老年人体重指数和死亡的相关性:一项队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2791-2797. |
| [10] | 刘美霞, 尹金念, 吴玫, 杨星, 周全湘, 杨敬源. 体重指数对三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与认知功能关联的影响:一项贵州农村老年人群的现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| [11] | 唐笑睿, 徐晶晶, 顾子君, 王清玉, 林征, 朱秋瑞, 雷阳. 糖尿病自我护理指数量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2643-2651. |
| [12] | 郝爱华, 曾子莹, 金爱琼, 唐玲玲, 郑梓悫, 马景泰, 赵建国, 曾韦霖, 肖建鹏, 聂辉, 杨颖. 老年高血压患者可避免住院的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [13] | 陈巧巧, 苏萍, 赵颖颖, 逄锦宏, 施婕, 王雅倩, 李秋春, 何蕊言, 王玥, 陈学禹, 乔俊鹏, 迟蔚蔚. 三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与老年人群新发心脏代谢性共病的相关性:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2270-2277. |
| [14] | 蒋小曼, 徐欣怡, 丁玲玉, 郭银宁, 缪雪怡, 陈丽, 许勤. 老年胃癌患者术前衰弱与代谢综合征的临床特征及相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2134-2141. |
| [15] | 王碧晴, 张萍, 杨红霞, 王倩, 鞠春晓, 赵俊男, 梅俊, 张颖, 徐凤芹. 中国老年高血压患者轻度认知障碍患病率及发展趋势的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2186-2192. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





