中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 2589-2596.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0027
周诗宇1,2, 谌绍林1, 邓仁丽1, 代米1, 刘涛3, 田坤明1,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-21
修回日期:2023-03-24
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-03-30
通讯作者:
田坤明
基金资助:
ZHOU Shiyu1,2, CHEN Shaolin1, DENG Renli1, DAI Mi1, LIU Tao3, TIAN Kunming1,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-21
Revised:2023-03-24
Published:2023-07-20
Online:2023-03-30
Contact:
TIAN Kunming
摘要: 背景 随着代谢性疾病发病率的上升,代谢综合征(MS)的预防与控制引起广泛的关注。而脂质比值是重要的筛查指标之一,与MS之间的关系成为热点研究话题。 目的 基于贵州省多阶段横断面研究人群分析三酰甘油/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(TG/HDL-C)、总胆固醇/HDL-C(TC/HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/HDL-C(LDL-C/HDL-C)及非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(non-HDL-C)与MS发病风险的关联及预测价值评价。 方法 回顾性选取贵州省参与2010年全国疾病监测地区慢性病及危险因素调查、2013年中国慢性病及其危险因素监测、2015年中国成人慢性病与营养监测和2018年中国成人慢性病与营养监测的21 727例自然人群为研究对象,收集研究对象的基线资料,根据是否患有MS将研究对象分为MS组(n=4 981)和非MS组(n=16 746)。绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分别评价男性和女性TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C和non-HDL-C对MS的预测价值。通过Delong检验比较脂质比值预测MS发生的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)的差异。采用多因素Logistic回归分析模型分析脂质比值与MS之间的优势比(OR)和95%置信区间(CI),评价按调查时间、年龄、性别、BMI、吸烟、饮酒分层的研究对象发生MS的影响因素。 结果 MS组与非MS组研究对象年龄、性别、民族、受教育程度、婚姻状况、吸烟、饮酒情况、BMI、TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。TG/HDL-C的AUC大于TC/HDL-C(Z=17.822,P<0.001)、LDL-C/HDL-C(Z=23.813,P<0.001)、non-HDL-C(Z=27.608,P<0.001)。男性TG/HDL-C的AUC大于女性(Z=4.299,P<0.001),LDL-C/HDL-C的AUC小于女性(Z=2.061,P=0.039)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,在<60岁、≥60岁、男性、女性、BMI<24.0 kg/m2、BMI≥24.0 kg/m2、吸烟、未吸烟、饮酒、未饮酒人群中,TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C是发生MS的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 TG/HDL-C对MS具有良好的预测效果,TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C是发生MS的影响因素,在实际临床工作中应该更重视女性、BMI<24.0 kg/m2、未吸烟及未饮酒人群的脂质比值情况。
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 民族〔n(%)〕 | 受教育程度〔n(%)〕 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 汉族 | 其他 | 小学以下 | 小学 | 初中 | 高中/中专 | 大专及以上 | |||
| 非MS组 | 16 746 | 47.7±15.9 | 8 282(49.5) | 8 464(50.5) | 9 808(58.6) | 6 938(41.4) | 6 994(41.7) | 3 301(19.7) | 4 567(27.3) | 1 235(7.4) | 649(3.9) |
| MS组 | 4 981 | 53.9±14.0 | 1 857(37.3) | 3 124(62.7) | 3 281(65.9) | 1 700(34.1) | 2 434(48.9) | 911(18.3) | 1 161(23.3) | 330(6.6) | 145(2.9) |
| 检验统计量值 | 26.47a | 228.64 | 85.44 | 84.26 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 组别 | 婚姻状况〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒〔n(%)〕 | ||||||||
| 已婚 | 其他 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | ||||||
| 非MS组 | 13 946(83.3) | 2 800(16.7) | 5 258(31.4) | 11 488(68.6) | 5 593(33.4) | 11 153(66.6) | |||||
| MS组 | 4 285(86.0) | 696(14.0) | 1 203(24.2) | 3 778(75.8) | 1 413(28.4) | 3 568(71.6) | |||||
| 检验统计量值 | 21.46 | 96.49 | 44.48 | ||||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| 组别 | BMI (kg/m2) | TG/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | TC/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | LDL-C/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | non-HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | ||||||
| 非MS组 | 22.5±3.0 | 0.84(0.54,1.19) | 3.15(2.68,3.93) | 1.88(1.38,2.33) | 3.14(2.62,3.87) | ||||||
| MS组 | 25.9±3.6 | 2.00(1.30,3.02) | 4.32(3.60,5.25) | 2.58(2.00,3.20) | 4.00(3.24,4.67) | ||||||
| 检验统计量值 | 60.60a | 70.08b | 57.35b | 48.66b | 42.80b | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
表1 两组研究对象基线特征对比
Table 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between subjects without and with metabolic syndrome
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 民族〔n(%)〕 | 受教育程度〔n(%)〕 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 汉族 | 其他 | 小学以下 | 小学 | 初中 | 高中/中专 | 大专及以上 | |||
| 非MS组 | 16 746 | 47.7±15.9 | 8 282(49.5) | 8 464(50.5) | 9 808(58.6) | 6 938(41.4) | 6 994(41.7) | 3 301(19.7) | 4 567(27.3) | 1 235(7.4) | 649(3.9) |
| MS组 | 4 981 | 53.9±14.0 | 1 857(37.3) | 3 124(62.7) | 3 281(65.9) | 1 700(34.1) | 2 434(48.9) | 911(18.3) | 1 161(23.3) | 330(6.6) | 145(2.9) |
| 检验统计量值 | 26.47a | 228.64 | 85.44 | 84.26 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 组别 | 婚姻状况〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒〔n(%)〕 | ||||||||
| 已婚 | 其他 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | ||||||
| 非MS组 | 13 946(83.3) | 2 800(16.7) | 5 258(31.4) | 11 488(68.6) | 5 593(33.4) | 11 153(66.6) | |||||
| MS组 | 4 285(86.0) | 696(14.0) | 1 203(24.2) | 3 778(75.8) | 1 413(28.4) | 3 568(71.6) | |||||
| 检验统计量值 | 21.46 | 96.49 | 44.48 | ||||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| 组别 | BMI (kg/m2) | TG/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | TC/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | LDL-C/HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75)〕 | non-HDL-C 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | ||||||
| 非MS组 | 22.5±3.0 | 0.84(0.54,1.19) | 3.15(2.68,3.93) | 1.88(1.38,2.33) | 3.14(2.62,3.87) | ||||||
| MS组 | 25.9±3.6 | 2.00(1.30,3.02) | 4.32(3.60,5.25) | 2.58(2.00,3.20) | 4.00(3.24,4.67) | ||||||
| 检验统计量值 | 60.60a | 70.08b | 57.35b | 48.66b | 42.80b | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.18 | 0.826 | (0.820,0.833) | 79.6 | 74.8 |
| TC/HDL-C | 3.68 | 0.767 | (0.759,0.775) | 72.8 | 68.7 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.27 | 0.727 | (0.718,0.735) | 63.2 | 72.8 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.46 mmol/L | 0.699 | (0.691,0.708) | 69.0 | 62.0 |
表2 TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C对所有研究对象发生MS的预测价值
Table 2 Predictive values of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C for metabolic syndrome in all subjects
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.18 | 0.826 | (0.820,0.833) | 79.6 | 74.8 |
| TC/HDL-C | 3.68 | 0.767 | (0.759,0.775) | 72.8 | 68.7 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.27 | 0.727 | (0.718,0.735) | 63.2 | 72.8 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.46 mmol/L | 0.699 | (0.691,0.708) | 69.0 | 62.0 |
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.25 | 0.850 | (0.841,0.859) | 84.7 | 73.5 |
| TC/HDL-C | 4.01 | 0.779 | (0.767,0.792) | 64.4 | 79.1 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.31 | 0.719 | (0.706,0.733) | 63.0 | 72.0 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.74 mmol/L | 0.704 | (0.690,0.717) | 61.7 | 70.8 |
表3 男性TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C对发生MS的预测价值
Table 3 Predictive values of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C for metabolic syndrome in males
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.25 | 0.850 | (0.841,0.859) | 84.7 | 73.5 |
| TC/HDL-C | 4.01 | 0.779 | (0.767,0.792) | 64.4 | 79.1 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.31 | 0.719 | (0.706,0.733) | 63.0 | 72.0 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.74 mmol/L | 0.704 | (0.690,0.717) | 61.7 | 70.8 |
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.08 | 0.823 | (0.814,0.831) | 79.8 | 74.4 |
| TC/HDL-C | 3.57 | 0.767 | (0.757,0.777) | 74.0 | 68.1 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.23 | 0.737 | (0.727,0.748) | 63.9 | 73.9 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.46 mmol/L | 0.697 | (0.687,0.708) | 68.1 | 62.3 |
表4 女性TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C对发生MS的预测价值
Table 4 Predictive values of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C for metabolic syndrome in females
| 指标 | 最佳截断值 | AUC | 95%CI | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDL-C | 1.08 | 0.823 | (0.814,0.831) | 79.8 | 74.4 |
| TC/HDL-C | 3.57 | 0.767 | (0.757,0.777) | 74.0 | 68.1 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.23 | 0.737 | (0.727,0.748) | 63.9 | 73.9 |
| non-HDL-C | 3.46 mmol/L | 0.697 | (0.687,0.708) | 68.1 | 62.3 |
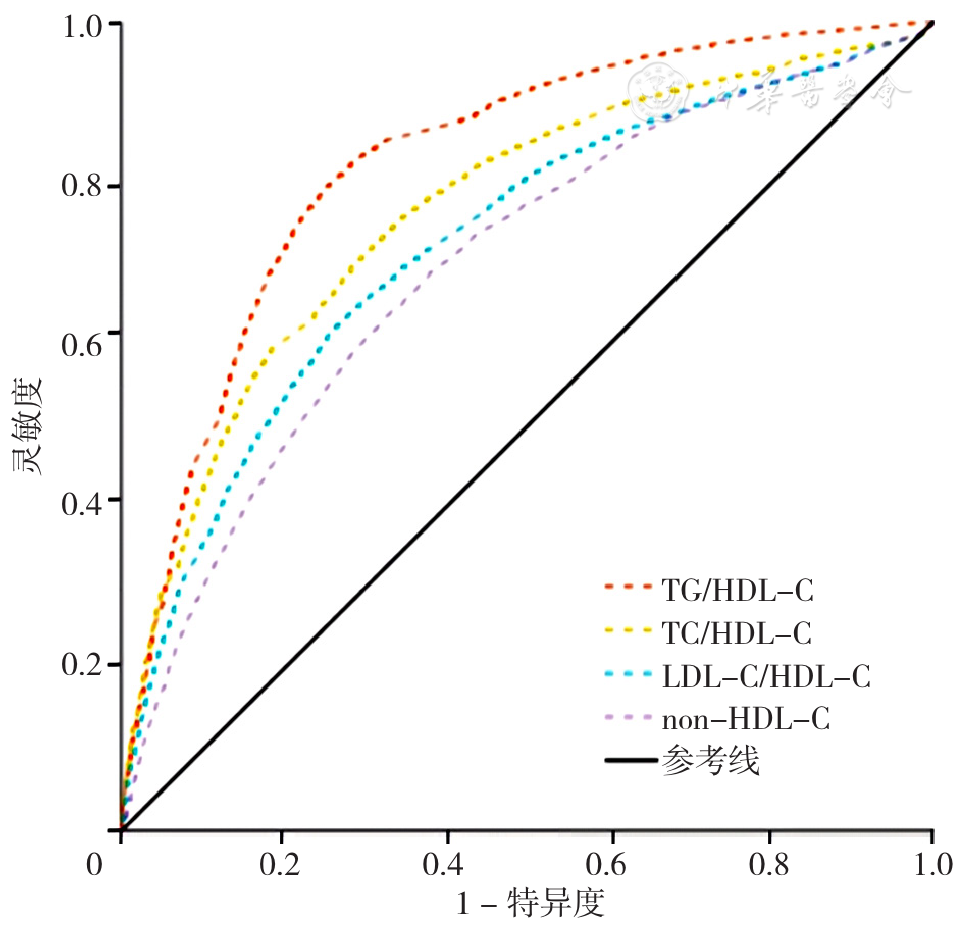
图1 TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C预测MS发生的ROC曲线注:TG/HDL-C=三酰甘油/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇,TC/HDL-C=总胆固醇/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇,LDL-C/HDL-C=低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇,non-HDL-C=非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。
Figure 1 ROC curves of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C in predicting metabolic syndrome
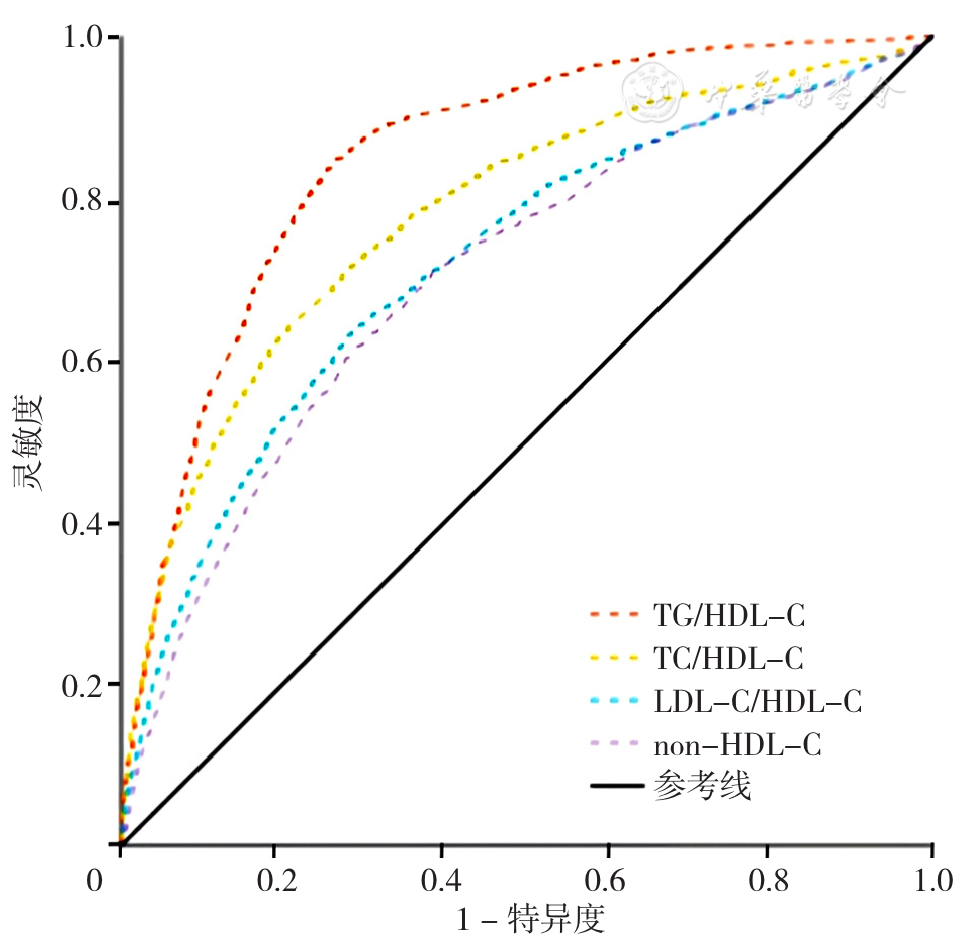
图2 男性TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C预测MS发生的ROC曲线
Figure 2 ROC curves of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C in predicting metabolic syndrome in males
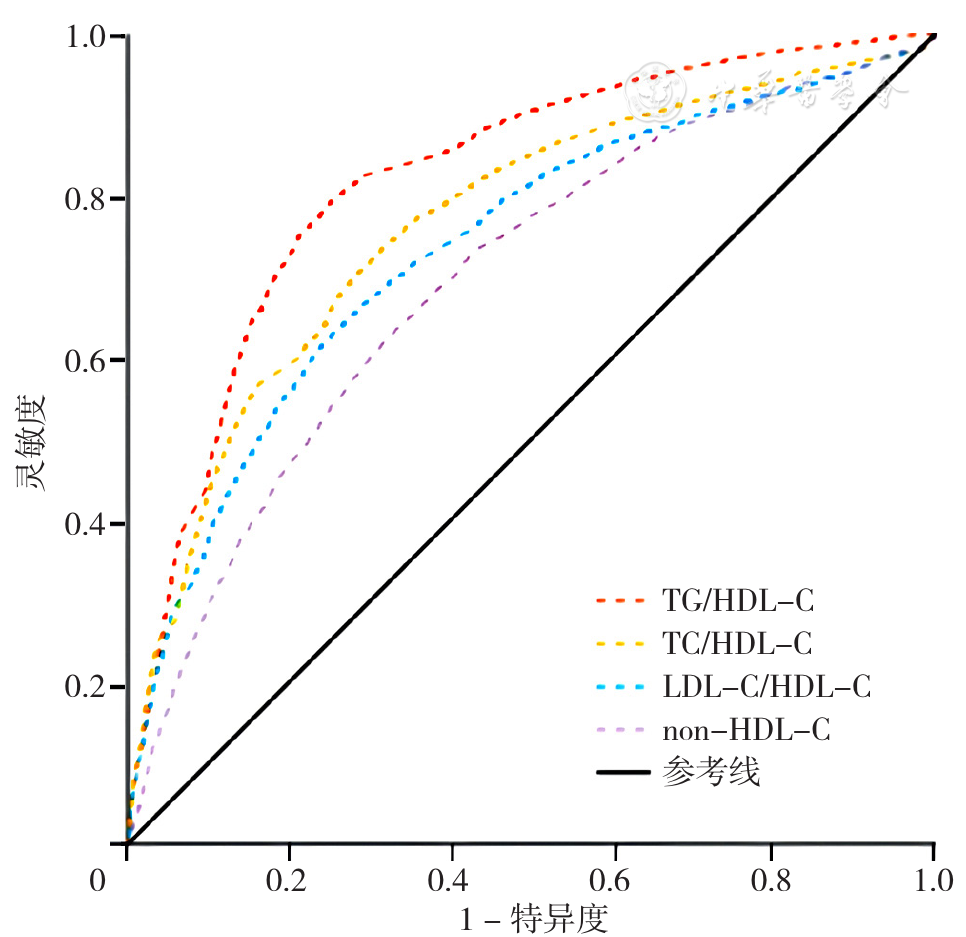
图3 女性TG/HDL-C、TC/HDL-C、LDL-C/HDL-C、non-HDL-C预测MS发生的ROC曲线
Figure 3 ROC curves of TG/HDL-C ratio,TC/HDL-C ratio,LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and non-HDL-C in predicting metabolic syndrome in females
| 指标 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| TG/HDL-C | 0.702 | 0.015 | 2 082.535 | 2.017(1.957,2.079) | <0.001 | 0.754 | 0.016 | 2 181.414 | 2.125(2.059,2.194) | <0.001 | 0.612 | 0.016 | 1 412.027 | 1.844(1.786,1.904) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.773 | 0.016 | 2 408.562 | 2.166(2.100,2.234) | <0.001 | 0.784 | 0.016 | 2 340.215 | 2.191(2.123,2.262) | <0.001 | 0.639 | 0.017 | 1 434.831 | 1.895(1.833,1.959) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.950 | 0.021 | 2 103.997 | 2.586(2.483,2.693) | <0.001 | 0.953 | 0.021 | 2 004.395 | 2.594(2.488,2.705) | <0.001 | 0.735 | 0.023 | 1 048.645 | 2.085(1.994,2.180) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.615 | 0.016 | 1 454.581 | 1.849(1.791,1.908) | <0.001 | 0.585 | 0.016 | 1 263.490 | 1.794(1.737,1.853) | <0.001 | 0.455 | 0.017 | 674.806 | 1.575(1.522,1.630) | <0.001 |
表5 发生MS影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Table 5 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of associated factors of metabolic syndrome
| 指标 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| TG/HDL-C | 0.702 | 0.015 | 2 082.535 | 2.017(1.957,2.079) | <0.001 | 0.754 | 0.016 | 2 181.414 | 2.125(2.059,2.194) | <0.001 | 0.612 | 0.016 | 1 412.027 | 1.844(1.786,1.904) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.773 | 0.016 | 2 408.562 | 2.166(2.100,2.234) | <0.001 | 0.784 | 0.016 | 2 340.215 | 2.191(2.123,2.262) | <0.001 | 0.639 | 0.017 | 1 434.831 | 1.895(1.833,1.959) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.950 | 0.021 | 2 103.997 | 2.586(2.483,2.693) | <0.001 | 0.953 | 0.021 | 2 004.395 | 2.594(2.488,2.705) | <0.001 | 0.735 | 0.023 | 1 048.645 | 2.085(1.994,2.180) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.615 | 0.016 | 1 454.581 | 1.849(1.791,1.908) | <0.001 | 0.585 | 0.016 | 1 263.490 | 1.794(1.737,1.853) | <0.001 | 0.455 | 0.017 | 674.806 | 1.575(1.522,1.630) | <0.001 |
| 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010年12月—2012年12月 | 2015年11月—2016年3月 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.506 | 0.029 | 314.505 | 1.659(1.569,1.755) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 1.386 | 0.058 | 572.017 | 4.000(3.571,4.481) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.417 | 0.031 | 186.555 | 1.517(1.429,1.611) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 1.219 | 0.052 | 547.307 | 3.383(3.055,3.747) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.273 | 0.038 | 50.566 | 1.314(1.219,1.416) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 1.305 | 0.058 | 498.896 | 3.689(3.289,4.136) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.328 | 0.030 | 119.270 | 1.388(1.308,1.471) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.676 | 0.048 | 201.016 | 1.966(1.791,2.159) | <0.001 |
| 2013年1月—2014年5月 | 2018年10月—2019年5月 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 1.416 | 0.061 | 538.187 | 4.119(3.655,4.643) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.316 | 0.022 | 205.398 | 1.372(1.314,1.432) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 1.170 | 0.046 | 633.923 | 3.222(2.941,3.529) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.348 | 0.026 | 185.495 | 1.416(1.347,1.489) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 1.198 | 0.054 | 484.570 | 3.315(2.980,3.688) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.498 | 0.045 | 119.949 | 1.645(1.505,1.799) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.796 | 0.043 | 347.135 | 2.216(2.038,2.410) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.318 | 0.031 | 104.051 | 1.375(1.293,1.462) | <0.001 |
表6 按调查时间分层后发生MS影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Table 6 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of associated factors of metabolic syndrome in subjects stratified by survey time
| 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010年12月—2012年12月 | 2015年11月—2016年3月 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.506 | 0.029 | 314.505 | 1.659(1.569,1.755) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 1.386 | 0.058 | 572.017 | 4.000(3.571,4.481) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.417 | 0.031 | 186.555 | 1.517(1.429,1.611) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 1.219 | 0.052 | 547.307 | 3.383(3.055,3.747) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.273 | 0.038 | 50.566 | 1.314(1.219,1.416) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 1.305 | 0.058 | 498.896 | 3.689(3.289,4.136) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.328 | 0.030 | 119.270 | 1.388(1.308,1.471) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.676 | 0.048 | 201.016 | 1.966(1.791,2.159) | <0.001 |
| 2013年1月—2014年5月 | 2018年10月—2019年5月 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 1.416 | 0.061 | 538.187 | 4.119(3.655,4.643) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.316 | 0.022 | 205.398 | 1.372(1.314,1.432) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 1.170 | 0.046 | 633.923 | 3.222(2.941,3.529) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.348 | 0.026 | 185.495 | 1.416(1.347,1.489) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 1.198 | 0.054 | 484.570 | 3.315(2.980,3.688) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.498 | 0.045 | 119.949 | 1.645(1.505,1.799) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.796 | 0.043 | 347.135 | 2.216(2.038,2.410) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.318 | 0.031 | 104.051 | 1.375(1.293,1.462) | <0.001 |
| 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <60岁 | BMI≥24.0 kg/m2 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.587 | 0.018 | 1 058.071 | 1.798(1.736,1.863) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.587 | 0.021 | 758.886 | 1.799(1.725,1.875) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.665 | 0.020 | 1 123.435 | 1.945(1.871,2.022) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.614 | 0.022 | 791.114 | 1.849(1.771,1.930) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.809 | 0.027 | 895.766 | 2.245(2.129,2.367) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.719 | 0.029 | 620.317 | 2.051(1.938,2.170) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.499 | 0.021 | 585.697 | 1.646(1.581,1.714) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.435 | 0.022 | 386.594 | 1.545(1.479,1.614) | <0.001 |
| ≥60岁 | 吸烟 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.818 | 0.036 | 518.742 | 2.266(2.112,2.431) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.519 | 0.026 | 411.062 | 1.681(1.599,1.768) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.686 | 0.031 | 482.558 | 1.986(1.868,2.112) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.559 | 0.028 | 395.385 | 1.750(1.656,1.849) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.725 | 0.040 | 333.402 | 2.065(1.911,2.233) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.628 | 0.040 | 249.303 | 1.872(1.731,2.023) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.458 | 0.031 | 212.690 | 1.581(1.487,1.681) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.445 | 0.032 | 191.440 | 1.560(1.465,1.662) | <0.001 |
| 男 | 未吸烟 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.517 | 0.020 | 675.827 | 1.677(1.613,1.744) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.712 | 0.021 | 1 182.143 | 2.039(1.958,2.124) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.596 | 0.023 | 670.215 | 1.815(1.735,1.899) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.735 | 0.021 | 1 260.735 | 2.086(2.004,2.173) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.669 | 0.032 | 438.479 | 1.950(1.832,2.076) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.864 | 0.027 | 1 012.208 | 2.373(2.250,2.502) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.467 | 0.026 | 324.746 | 1.595(1.516,1.678) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.512 | 0.020 | 630.121 | 1.668(1.603,1.736) | <0.001 |
| 女 | 饮酒 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.810 | 0.026 | 936.864 | 2.252(2.138,2.372) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.437 | 0.022 | 399.819 | 1.548(1.483,1.615) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.749 | 0.024 | 960.991 | 2.117(2.019,2.220) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.539 | 0.026 | 415.314 | 1.715(1.628,1.806) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.895 | 0.031 | 810.141 | 2.447(2.301,2.603) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.677 | 0.039 | 303.992 | 1.966(1.822,2.122) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.501 | 0.023 | 471.829 | 1.651(1.578,1.728) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.453 | 0.030 | 232.299 | 1.573(1.484,1.667) | <0.001 |
| BMI<24.0 kg/m2 | 未饮酒 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.722 | 0.025 | 861.994 | 2.060(1.963,2.162) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.813 | 0.023 | 1 242.186 | 2.257(2.157,2.361) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.767 | 0.026 | 888.475 | 2.156(2.049,2.267) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.756 | 0.021 | 1 255.901 | 2.131(2.044,2.222) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.894 | 0.035 | 667.657 | 2.445(2.284,2.616) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.849 | 0.027 | 956.474 | 2.336(2.214,2.465) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.585 | 0.027 | 479.911 | 1.795(1.704,1.892) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.513 | 0.021 | 592.127 | 1.670(1.602,1.740) | <0.001 |
表7 按年龄、性别、BMI、饮酒、吸烟情况分层发生MS影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Table 7 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with metabolic syndrome in subjects stratified by age,sex,BMI,drinking and smoking
| 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | 分组 | β | SE | Waldχ2值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <60岁 | BMI≥24.0 kg/m2 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.587 | 0.018 | 1 058.071 | 1.798(1.736,1.863) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.587 | 0.021 | 758.886 | 1.799(1.725,1.875) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.665 | 0.020 | 1 123.435 | 1.945(1.871,2.022) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.614 | 0.022 | 791.114 | 1.849(1.771,1.930) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.809 | 0.027 | 895.766 | 2.245(2.129,2.367) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.719 | 0.029 | 620.317 | 2.051(1.938,2.170) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.499 | 0.021 | 585.697 | 1.646(1.581,1.714) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.435 | 0.022 | 386.594 | 1.545(1.479,1.614) | <0.001 |
| ≥60岁 | 吸烟 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.818 | 0.036 | 518.742 | 2.266(2.112,2.431) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.519 | 0.026 | 411.062 | 1.681(1.599,1.768) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.686 | 0.031 | 482.558 | 1.986(1.868,2.112) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.559 | 0.028 | 395.385 | 1.750(1.656,1.849) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.725 | 0.040 | 333.402 | 2.065(1.911,2.233) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.628 | 0.040 | 249.303 | 1.872(1.731,2.023) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.458 | 0.031 | 212.690 | 1.581(1.487,1.681) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.445 | 0.032 | 191.440 | 1.560(1.465,1.662) | <0.001 |
| 男 | 未吸烟 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.517 | 0.020 | 675.827 | 1.677(1.613,1.744) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.712 | 0.021 | 1 182.143 | 2.039(1.958,2.124) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.596 | 0.023 | 670.215 | 1.815(1.735,1.899) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.735 | 0.021 | 1 260.735 | 2.086(2.004,2.173) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.669 | 0.032 | 438.479 | 1.950(1.832,2.076) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.864 | 0.027 | 1 012.208 | 2.373(2.250,2.502) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.467 | 0.026 | 324.746 | 1.595(1.516,1.678) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.512 | 0.020 | 630.121 | 1.668(1.603,1.736) | <0.001 |
| 女 | 饮酒 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.810 | 0.026 | 936.864 | 2.252(2.138,2.372) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.437 | 0.022 | 399.819 | 1.548(1.483,1.615) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.749 | 0.024 | 960.991 | 2.117(2.019,2.220) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.539 | 0.026 | 415.314 | 1.715(1.628,1.806) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.895 | 0.031 | 810.141 | 2.447(2.301,2.603) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.677 | 0.039 | 303.992 | 1.966(1.822,2.122) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.501 | 0.023 | 471.829 | 1.651(1.578,1.728) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.453 | 0.030 | 232.299 | 1.573(1.484,1.667) | <0.001 |
| BMI<24.0 kg/m2 | 未饮酒 | ||||||||||
| TG/HDL-C | 0.722 | 0.025 | 861.994 | 2.060(1.963,2.162) | <0.001 | TG/HDL-C | 0.813 | 0.023 | 1 242.186 | 2.257(2.157,2.361) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 0.767 | 0.026 | 888.475 | 2.156(2.049,2.267) | <0.001 | TC/HDL-C | 0.756 | 0.021 | 1 255.901 | 2.131(2.044,2.222) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.894 | 0.035 | 667.657 | 2.445(2.284,2.616) | <0.001 | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.849 | 0.027 | 956.474 | 2.336(2.214,2.465) | <0.001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.585 | 0.027 | 479.911 | 1.795(1.704,1.892) | <0.001 | non-HDL-C | 0.513 | 0.021 | 592.127 | 1.670(1.602,1.740) | <0.001 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2021,41(5):482-548. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210825-08063.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
赵文华,宁光. 2010年中国慢性病监测项目的内容与方法[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2012,46(5):477-479. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.05.023.
|
| [22] |
王丽敏,张梅,李镒冲,等. 2013年中国慢性病及其危险因素监测总体方案[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2018,52(2):191-194. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2018.02.015.
|
| [23] |
中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
中国肥胖问题工作组数据汇总分析协作组. 我国成人体重指数和腰围对相关疾病危险因素异常的预测价值:适宜体重指数和腰围切点的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2002,23(1):5-10.
|
| [26] |
人类年龄段划分新标准[J]. 现代养生,2005,21(9):16.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies[J]. Lancet,2004,363(9403):157-163. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(03)15268-3.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [1] | 秦邦国, 孙瑾, 李曼, 邱娇娇, 程柏凯, 朱平, 王曙霞. 农村高血压人群非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与左心室肥厚的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3753-3760. |
| [2] | 张睿敏, 董哲毅, 李爽, 王倩, 陈香美. 基于肾活检病理诊断的糖尿病肾病中医相关因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3307-3313. |
| [3] | 殷佳慧, 杨昕晖, 王京京, 张雅静, 王丽娟, 付佐娣, 孔祥双, 郭光霞, 李玉凤. 腰高比和腰臀比及BMI对代谢综合征的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3258-3263. |
| [4] | 潘琦, 任菁菁, 马方晖, 胡梦杰. 全科医师对AI辅助诊疗系统的认知与需求调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [5] | 韩冰, 杜淑珍, 孟晓雪, 张璐, 陈梓娴, 滕凤玲. 心力衰竭患者血浆骨膜蛋白水平与心肌纤维化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2979-2984. |
| [6] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [7] | 刘月影, 王雪丽, 刘雨秋, 魏立民. 空腹C肽与糖尿病病程比值与2型糖尿病发生代谢相关脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2852-2860. |
| [8] | 杨菲, 韩正, 付晓雅, 顾瀚东, 顾可羿, 王为强. 体重正常人群中身体圆度指数与心血管代谢性共病的相关性研究:三酰甘油葡萄糖乘积指数的中介作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2798-2805. |
| [9] | 刘美霞, 尹金念, 吴玫, 杨星, 周全湘, 杨敬源. 体重指数对三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与认知功能关联的影响:一项贵州农村老年人群的现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| [10] | 梁恒妙, 黄锶哲, 陈玉婷, 刘策, 王慧君, 杜庆锋. 健康体检人群血尿酸水平与胰岛素抵抗程度关系的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2635-2642. |
| [11] | 李春贤, 刘安诺. 成年人肥胖和脂质相关指标对代谢综合征的影响及预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2595-2603. |
| [12] | 张露艺, 于瑞洪, 王琪, 张小宇, 李响, 王仲璇, 朱东山. 昼夜节律综合征和代谢综合征对主、客观认知功能的影响:基于平阴队列的横断面研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2481-2490. |
| [13] | 李思清, 王萱萱, 谢坤, 高淑红, 陈家应, 张朝阳. 我国村医医疗服务能力现状与提升策略研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2376-2383. |
| [14] | 韩正, 孙梦, 傅方琳, 潘姚佳, 王为强. 50岁及以上人群三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与心血管代谢性共病关系的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2278-2284. |
| [15] | 王志军, 张士博, 刘杰, 李东琦, 郑美佳, 周建芝. 高血压患者三酰甘油葡萄糖体质量指数与夜间高血压的相关性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2212-2221. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





