中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 3495-3506.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0831
所属专题: 社区卫生服务最新研究合辑; 基层医疗资源配置最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2024-08-15
修回日期:2025-03-23
出版日期:2025-10-05
发布日期:2025-08-28
通讯作者:
袁岗
作者贡献:
卢祖洵提出主要研究目标;彭崟负责研究的构思与设计,研究的实施,撰写论文,进行数据的收集与整理,统计学处理,图、表的绘制与展示;李丽清、袁岗进行论文的修订;李丽清负责文章的质量控制与审查,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:
LI Liqing1, PENG Yin2, LU Zuxun3, YUAN Gang2,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-15
Revised:2025-03-23
Published:2025-10-05
Online:2025-08-28
Contact:
YUAN Gang
摘要: 背景 随着人口老龄化和慢性病患者比例的增加,人民群众对基层医疗资源的需求呈多样化、复杂化的态势。不同地区、不同人群对基层医疗资源的需求存在差异,部分地区面临基层医疗资源匮乏的问题,严重制约基层医疗卫生服务的覆盖率和质量,极大影响居民的就医体验和健康状况。 目的 为推动基层医疗卫生服务体系高质量发展,引入健康距离模型,分析2011—2021年我国基层医疗资源配置失配度的时空演变过程,为合理制订区域卫生规划、优化医疗资源配置方案、提高基层医疗卫生服务能力、推动医疗卫生服务高质量发展提供参考。 方法 从卫生物力、人力、保障资源三个层面建立基层医疗资源失配度评价指标体系,从《中国卫生健康统计年鉴》《中国统计年鉴》获取数据,采用双层规划模型和健康距离模型测算2011—2021年基层医疗资源配置失配度。 结果 2011—2021年我国基层医疗资源配置整体失配度有明显的下降趋势,但是区际、省际间失配度差异不断扩大。2011年东、中、西部地区失配度平均值分别为0.633、0.624、0.754,分别为中度失配、轻度匹配和重度失配。2021年东、中、西部地区失配度平均值分别为0.479、0.522、0.639,分别为中度匹配、轻度匹配和中度失配。 结论 尽管我国基层医疗资源配置的整体失配度呈下降趋势,但仍然存在明显的差异,医疗资源配置的不均衡性仍在加剧。为持续优化基层医疗配置,推动基层医疗卫生服务体系高质量发展,提升我国医疗卫生体系的效能,需注重区域间资源配置的均衡性,因地制宜地制定差异化政策,以进一步优化医疗资源配置,提升基层医疗卫生服务的覆盖率和质量。
中图分类号:
| 目标层 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 单位 | 性质 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基层医疗资源失配度评价指标体系 | 卫生物力资源 | 基层医疗卫生机构数(m1) | 个 | 正向 | 《中国卫生健康统计年鉴》 |
| 基层医疗卫生机构床位数(m2) | 万张 | 正向 | 《中国统计年鉴》 | ||
| 卫生人力资源 | 基层医疗卫生机构人员数(m3) | 万人 | 正向 | 《中国卫生健康统计年鉴》 | |
| 卫生保障资源 | 人均国内生产总值(m4) | 元/人 | 正向 | 《中国统计年鉴》 |
表1 基层医疗资源失配度评价指标体系
Table 1 Evaluation index system of primary medical resources mismatch degree
| 目标层 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 单位 | 性质 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基层医疗资源失配度评价指标体系 | 卫生物力资源 | 基层医疗卫生机构数(m1) | 个 | 正向 | 《中国卫生健康统计年鉴》 |
| 基层医疗卫生机构床位数(m2) | 万张 | 正向 | 《中国统计年鉴》 | ||
| 卫生人力资源 | 基层医疗卫生机构人员数(m3) | 万人 | 正向 | 《中国卫生健康统计年鉴》 | |
| 卫生保障资源 | 人均国内生产总值(m4) | 元/人 | 正向 | 《中国统计年鉴》 |
| 地区 | 2011年 | 2012年 | 2013年 | 2014年 | 2015年 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京市 | 0.721 | 0.702 | 0.681 | 0.665 | 0.645 | 0.618 | 0.583 | 0.541 | 0.511 | 0.503 | 0.438 |
| 天津市 | 0.797 | 0.783 | 0.769 | 0.758 | 0.755 | 0.744 | 0.722 | 0.699 | 0.684 | 0.688 | 0.652 |
| 河北省 | 0.414 | 0.411 | 0.412 | 0.404 | 0.399 | 0.387 | 0.370 | 0.357 | 0.363 | 0.373 | 0.362 |
| 山西省 | 0.653 | 0.651 | 0.651 | 0.653 | 0.657 | 0.654 | 0.631 | 0.624 | 0.619 | 0.622 | 0.585 |
| 内蒙古自治区 | 0.752 | 0.741 | 0.730 | 0.721 | 0.713 | 0.702 | 0.685 | 0.668 | 0.659 | 0.659 | 0.616 |
| 辽宁省 | 0.690 | 0.675 | 0.674 | 0.670 | 0.669 | 0.662 | 0.654 | 0.641 | 0.642 | 0.646 | 0.634 |
| 吉林省 | 0.795 | 0.784 | 0.776 | 0.769 | 0.770 | 0.764 | 0.757 | 0.749 | 0.747 | 0.730 | 0.719 |
| 黑龙江省 | 0.774 | 0.766 | 0.760 | 0.758 | 0.760 | 0.758 | 0.752 | 0.749 | 0.738 | 0.744 | 0.734 |
| 上海市 | 0.717 | 0.708 | 0.691 | 0.672 | 0.654 | 0.621 | 0.588 | 0.554 | 0.533 | 0.523 | 0.470 |
| 江苏省 | 0.525 | 0.530 | 0.515 | 0.501 | 0.485 | 0.467 | 0.424 | 0.398 | 0.373 | 0.355 | 0.305 |
| 浙江省 | 0.694 | 0.688 | 0.680 | 0.672 | 0.657 | 0.640 | 0.617 | 0.592 | 0.570 | 0.563 | 0.526 |
| 安徽省 | 0.663 | 0.654 | 0.647 | 0.642 | 0.641 | 0.634 | 0.612 | 0.594 | 0.580 | 0.556 | 0.539 |
| 福建省 | 0.690 | 0.673 | 0.656 | 0.642 | 0.630 | 0.614 | 0.588 | 0.559 | 0.538 | 0.531 | 0.496 |
| 江西省 | 0.662 | 0.634 | 0.633 | 0.624 | 0.617 | 0.607 | 0.589 | 0.582 | 0.572 | 0.567 | 0.549 |
| 山东省 | 0.249 | 0.223 | 0.195 | 0.198 | 0.193 | 0.207 | 0.204 | 0.199 | 0.202 | 0.209 | 0.196 |
| 河南省 | 0.298 | 0.315 | 0.308 | 0.301 | 0.294 | 0.287 | 0.267 | 0.254 | 0.250 | 0.239 | 0.231 |
| 湖北省 | 0.616 | 0.597 | 0.573 | 0.551 | 0.538 | 0.518 | 0.500 | 0.472 | 0.460 | 0.472 | 0.433 |
| 湖南省 | 0.528 | 0.510 | 0.496 | 0.476 | 0.446 | 0.432 | 0.420 | 0.421 | 0.402 | 0.399 | 0.388 |
| 广东省 | 0.568 | 0.560 | 0.552 | 0.549 | 0.534 | 0.516 | 0.492 | 0.470 | 0.450 | 0.437 | 0.403 |
| 广西壮族自治区 | 0.693 | 0.681 | 0.669 | 0.657 | 0.650 | 0.644 | 0.633 | 0.622 | 0.608 | 0.599 | 0.578 |
| 海南省 | 0.894 | 0.885 | 0.876 | 0.866 | 0.859 | 0.850 | 0.839 | 0.828 | 0.818 | 0.807 | 0.783 |
| 重庆市 | 0.746 | 0.728 | 0.708 | 0.692 | 0.676 | 0.658 | 0.644 | 0.631 | 0.612 | 0.604 | 0.577 |
| 四川省 | 0.380 | 0.356 | 0.340 | 0.327 | 0.324 | 0.321 | 0.292 | 0.269 | 0.249 | 0.250 | 0.247 |
| 贵州省 | 0.760 | 0.738 | 0.723 | 0.715 | 0.706 | 0.697 | 0.680 | 0.667 | 0.656 | 0.643 | 0.643 |
| 云南省 | 0.744 | 0.729 | 0.713 | 0.705 | 0.698 | 0.684 | 0.660 | 0.638 | 0.623 | 0.612 | 0.603 |
| 西藏自治区 | 0.904 | 0.895 | 0.883 | 0.873 | 0.865 | 0.858 | 0.842 | 0.828 | 0.819 | 0.805 | 0.796 |
| 陕西省 | 0.682 | 0.668 | 0.662 | 0.652 | 0.649 | 0.642 | 0.623 | 0.611 | 0.602 | 0.606 | 0.589 |
| 甘肃省 | 0.791 | 0.773 | 0.773 | 0.768 | 0.765 | 0.761 | 0.751 | 0.747 | 0.743 | 0.740 | 0.729 |
| 青海省 | 0.897 | 0.888 | 0.878 | 0.871 | 0.863 | 0.854 | 0.842 | 0.830 | 0.820 | 0.820 | 0.803 |
| 宁夏回族自治区 | 0.893 | 0.887 | 0.879 | 0.874 | 0.871 | 0.864 | 0.849 | 0.838 | 0.830 | 0.822 | 0.800 |
| 新疆维吾尔自治区 | 0.808 | 0.792 | 0.776 | 0.763 | 0.765 | 0.759 | 0.739 | 0.723 | 0.711 | 0.720 | 0.685 |
| 东部 | 0.633 | 0.622 | 0.609 | 0.599 | 0.589 | 0.575 | 0.553 | 0.531 | 0.517 | 0.512 | 0.479 |
| 中部 | 0.624 | 0.614 | 0.606 | 0.597 | 0.590 | 0.582 | 0.566 | 0.556 | 0.546 | 0.541 | 0.522 |
| 西部 | 0.754 | 0.740 | 0.728 | 0.718 | 0.712 | 0.704 | 0.687 | 0.673 | 0.661 | 0.657 | 0.639 |
| 全国 | 0.677 | 0.665 | 0.654 | 0.645 | 0.637 | 0.627 | 0.608 | 0.592 | 0.580 | 0.576 | 0.552 |
表2 我国基层医疗资源配置失配度(2011—2021年)
Table 2 The allocation mismatch of primary medical resources in China from 2011 to 2021
| 地区 | 2011年 | 2012年 | 2013年 | 2014年 | 2015年 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京市 | 0.721 | 0.702 | 0.681 | 0.665 | 0.645 | 0.618 | 0.583 | 0.541 | 0.511 | 0.503 | 0.438 |
| 天津市 | 0.797 | 0.783 | 0.769 | 0.758 | 0.755 | 0.744 | 0.722 | 0.699 | 0.684 | 0.688 | 0.652 |
| 河北省 | 0.414 | 0.411 | 0.412 | 0.404 | 0.399 | 0.387 | 0.370 | 0.357 | 0.363 | 0.373 | 0.362 |
| 山西省 | 0.653 | 0.651 | 0.651 | 0.653 | 0.657 | 0.654 | 0.631 | 0.624 | 0.619 | 0.622 | 0.585 |
| 内蒙古自治区 | 0.752 | 0.741 | 0.730 | 0.721 | 0.713 | 0.702 | 0.685 | 0.668 | 0.659 | 0.659 | 0.616 |
| 辽宁省 | 0.690 | 0.675 | 0.674 | 0.670 | 0.669 | 0.662 | 0.654 | 0.641 | 0.642 | 0.646 | 0.634 |
| 吉林省 | 0.795 | 0.784 | 0.776 | 0.769 | 0.770 | 0.764 | 0.757 | 0.749 | 0.747 | 0.730 | 0.719 |
| 黑龙江省 | 0.774 | 0.766 | 0.760 | 0.758 | 0.760 | 0.758 | 0.752 | 0.749 | 0.738 | 0.744 | 0.734 |
| 上海市 | 0.717 | 0.708 | 0.691 | 0.672 | 0.654 | 0.621 | 0.588 | 0.554 | 0.533 | 0.523 | 0.470 |
| 江苏省 | 0.525 | 0.530 | 0.515 | 0.501 | 0.485 | 0.467 | 0.424 | 0.398 | 0.373 | 0.355 | 0.305 |
| 浙江省 | 0.694 | 0.688 | 0.680 | 0.672 | 0.657 | 0.640 | 0.617 | 0.592 | 0.570 | 0.563 | 0.526 |
| 安徽省 | 0.663 | 0.654 | 0.647 | 0.642 | 0.641 | 0.634 | 0.612 | 0.594 | 0.580 | 0.556 | 0.539 |
| 福建省 | 0.690 | 0.673 | 0.656 | 0.642 | 0.630 | 0.614 | 0.588 | 0.559 | 0.538 | 0.531 | 0.496 |
| 江西省 | 0.662 | 0.634 | 0.633 | 0.624 | 0.617 | 0.607 | 0.589 | 0.582 | 0.572 | 0.567 | 0.549 |
| 山东省 | 0.249 | 0.223 | 0.195 | 0.198 | 0.193 | 0.207 | 0.204 | 0.199 | 0.202 | 0.209 | 0.196 |
| 河南省 | 0.298 | 0.315 | 0.308 | 0.301 | 0.294 | 0.287 | 0.267 | 0.254 | 0.250 | 0.239 | 0.231 |
| 湖北省 | 0.616 | 0.597 | 0.573 | 0.551 | 0.538 | 0.518 | 0.500 | 0.472 | 0.460 | 0.472 | 0.433 |
| 湖南省 | 0.528 | 0.510 | 0.496 | 0.476 | 0.446 | 0.432 | 0.420 | 0.421 | 0.402 | 0.399 | 0.388 |
| 广东省 | 0.568 | 0.560 | 0.552 | 0.549 | 0.534 | 0.516 | 0.492 | 0.470 | 0.450 | 0.437 | 0.403 |
| 广西壮族自治区 | 0.693 | 0.681 | 0.669 | 0.657 | 0.650 | 0.644 | 0.633 | 0.622 | 0.608 | 0.599 | 0.578 |
| 海南省 | 0.894 | 0.885 | 0.876 | 0.866 | 0.859 | 0.850 | 0.839 | 0.828 | 0.818 | 0.807 | 0.783 |
| 重庆市 | 0.746 | 0.728 | 0.708 | 0.692 | 0.676 | 0.658 | 0.644 | 0.631 | 0.612 | 0.604 | 0.577 |
| 四川省 | 0.380 | 0.356 | 0.340 | 0.327 | 0.324 | 0.321 | 0.292 | 0.269 | 0.249 | 0.250 | 0.247 |
| 贵州省 | 0.760 | 0.738 | 0.723 | 0.715 | 0.706 | 0.697 | 0.680 | 0.667 | 0.656 | 0.643 | 0.643 |
| 云南省 | 0.744 | 0.729 | 0.713 | 0.705 | 0.698 | 0.684 | 0.660 | 0.638 | 0.623 | 0.612 | 0.603 |
| 西藏自治区 | 0.904 | 0.895 | 0.883 | 0.873 | 0.865 | 0.858 | 0.842 | 0.828 | 0.819 | 0.805 | 0.796 |
| 陕西省 | 0.682 | 0.668 | 0.662 | 0.652 | 0.649 | 0.642 | 0.623 | 0.611 | 0.602 | 0.606 | 0.589 |
| 甘肃省 | 0.791 | 0.773 | 0.773 | 0.768 | 0.765 | 0.761 | 0.751 | 0.747 | 0.743 | 0.740 | 0.729 |
| 青海省 | 0.897 | 0.888 | 0.878 | 0.871 | 0.863 | 0.854 | 0.842 | 0.830 | 0.820 | 0.820 | 0.803 |
| 宁夏回族自治区 | 0.893 | 0.887 | 0.879 | 0.874 | 0.871 | 0.864 | 0.849 | 0.838 | 0.830 | 0.822 | 0.800 |
| 新疆维吾尔自治区 | 0.808 | 0.792 | 0.776 | 0.763 | 0.765 | 0.759 | 0.739 | 0.723 | 0.711 | 0.720 | 0.685 |
| 东部 | 0.633 | 0.622 | 0.609 | 0.599 | 0.589 | 0.575 | 0.553 | 0.531 | 0.517 | 0.512 | 0.479 |
| 中部 | 0.624 | 0.614 | 0.606 | 0.597 | 0.590 | 0.582 | 0.566 | 0.556 | 0.546 | 0.541 | 0.522 |
| 西部 | 0.754 | 0.740 | 0.728 | 0.718 | 0.712 | 0.704 | 0.687 | 0.673 | 0.661 | 0.657 | 0.639 |
| 全国 | 0.677 | 0.665 | 0.654 | 0.645 | 0.637 | 0.627 | 0.608 | 0.592 | 0.580 | 0.576 | 0.552 |
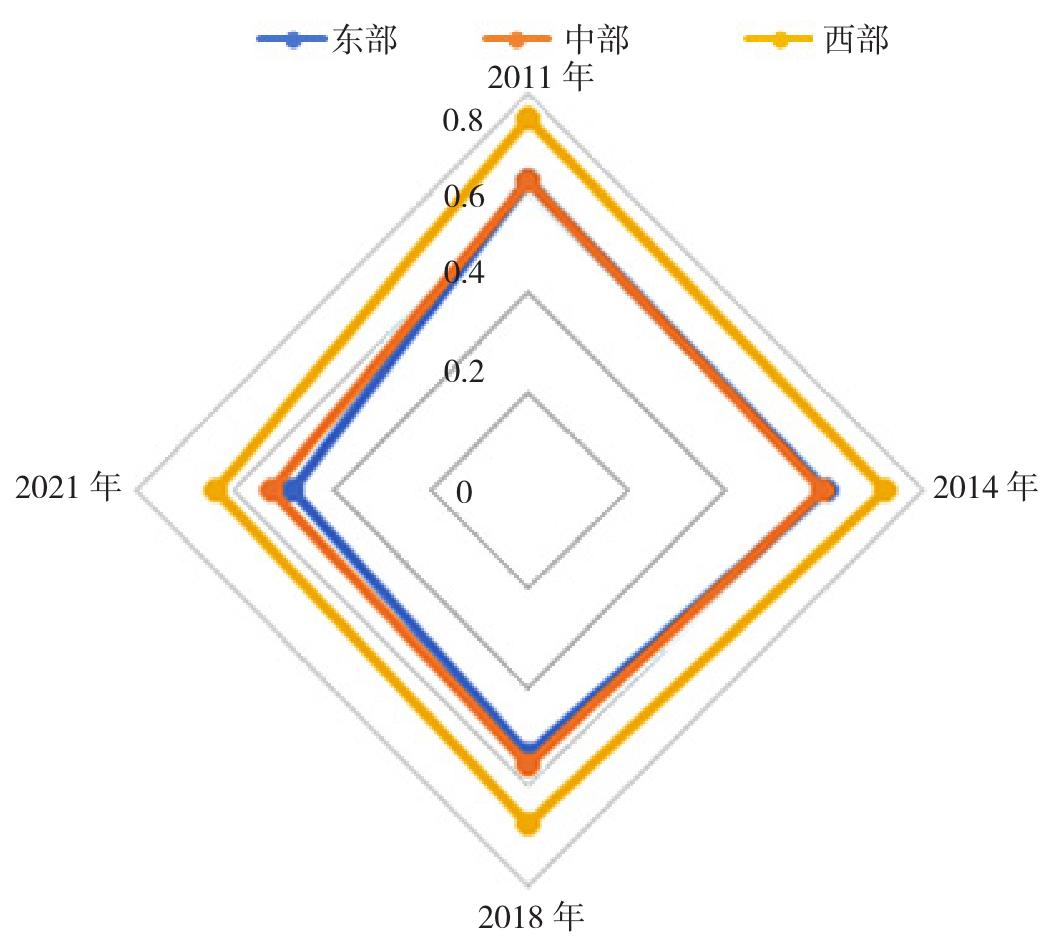
图3 我国基层医疗资源配置失配度等级空间分布图(2011、2014、2018、2021年)
Figure 3 Spatial distribution map of mismatch degree of primary medical resource allocation in China(2011、2014、2018、2021)
| 年份 | 基尼系数 | 贡献率(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 | 组内基尼系数 | 组间基尼系数 | 超变密度基尼系数 | 组内贡献率 | 组间贡献率 | 超变密度贡献率 | |
| 2011年 | 0.130 | 0.040 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 30.42 | 34.74 | 34.85 |
| 2012年 | 0.132 | 0.035 | 0.072 | 0.025 | 26.54 | 54.36 | 19.10 |
| 2013年 | 0.135 | 0.036 | 0.073 | 0.026 | 26.48 | 54.37 | 19.15 |
| 2014年 | 0.137 | 0.036 | 0.074 | 0.026 | 26.47 | 54.17 | 19.36 |
| 2015年 | 0.141 | 0.037 | 0.077 | 0.027 | 26.48 | 54.53 | 18.99 |
| 2016年 | 0.144 | 0.038 | 0.079 | 0.027 | 26.58 | 54.78 | 18.65 |
| 2017年 | 0.151 | 0.040 | 0.082 | 0.029 | 26.72 | 54.16 | 19.12 |
| 2018年 | 0.158 | 0.042 | 0.085 | 0.031 | 26.77 | 53.83 | 19.40 |
| 2019年 | 0.163 | 0.044 | 0.087 | 0.032 | 26.82 | 53.35 | 19.83 |
| 2020年 | 0.164 | 0.044 | 0.088 | 0.033 | 26.71 | 53.40 | 19.89 |
| 2021年 | 0.174 | 0.047 | 0.095 | 0.033 | 26.72 | 54.43 | 18.86 |
表3 基层医疗资源配置失配度Dagum基尼系数及贡献率
Table 3 The Dagum Gini coefficient and contribution rate of primary medical resource allocation mismatch
| 年份 | 基尼系数 | 贡献率(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 | 组内基尼系数 | 组间基尼系数 | 超变密度基尼系数 | 组内贡献率 | 组间贡献率 | 超变密度贡献率 | |
| 2011年 | 0.130 | 0.040 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 30.42 | 34.74 | 34.85 |
| 2012年 | 0.132 | 0.035 | 0.072 | 0.025 | 26.54 | 54.36 | 19.10 |
| 2013年 | 0.135 | 0.036 | 0.073 | 0.026 | 26.48 | 54.37 | 19.15 |
| 2014年 | 0.137 | 0.036 | 0.074 | 0.026 | 26.47 | 54.17 | 19.36 |
| 2015年 | 0.141 | 0.037 | 0.077 | 0.027 | 26.48 | 54.53 | 18.99 |
| 2016年 | 0.144 | 0.038 | 0.079 | 0.027 | 26.58 | 54.78 | 18.65 |
| 2017年 | 0.151 | 0.040 | 0.082 | 0.029 | 26.72 | 54.16 | 19.12 |
| 2018年 | 0.158 | 0.042 | 0.085 | 0.031 | 26.77 | 53.83 | 19.40 |
| 2019年 | 0.163 | 0.044 | 0.087 | 0.032 | 26.82 | 53.35 | 19.83 |
| 2020年 | 0.164 | 0.044 | 0.088 | 0.033 | 26.71 | 53.40 | 19.89 |
| 2021年 | 0.174 | 0.047 | 0.095 | 0.033 | 26.72 | 54.43 | 18.86 |
| 年份 | Moran指数 | 期望E | 标准差 | Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.065 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2012年 | 0.105 | -0.033 | 0.078 | 1.758 | 0.039 |
| 2013年 | 0.106 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.772 | 0.038 |
| 2014年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.078 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2015年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.071 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2016年 | 0.111 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.827 | 0.034 |
| 2017年 | 0.117 | -0.033 | 0.077 | 1.912 | 0.028 |
| 2018年 | 0.122 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.968 | 0.025 |
| 2019年 | 0.126 | -0.033 | 0.081 | 2.020 | 0.022 |
| 2020年 | 0.128 | -0.033 | 0.085 | 2.051 | 0.020 |
| 2021年 | 0.148 | -0.033 | 0.076 | 2.296 | 0.011 |
表4 基层医疗资源配置失配度全局Moran指数
Table 4 Global Moran index of primary medical resource allocation mismatch
| 年份 | Moran指数 | 期望E | 标准差 | Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.065 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2012年 | 0.105 | -0.033 | 0.078 | 1.758 | 0.039 |
| 2013年 | 0.106 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.772 | 0.038 |
| 2014年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.078 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2015年 | 0.108 | -0.033 | 0.071 | 1.796 | 0.036 |
| 2016年 | 0.111 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.827 | 0.034 |
| 2017年 | 0.117 | -0.033 | 0.077 | 1.912 | 0.028 |
| 2018年 | 0.122 | -0.033 | 0.079 | 1.968 | 0.025 |
| 2019年 | 0.126 | -0.033 | 0.081 | 2.020 | 0.022 |
| 2020年 | 0.128 | -0.033 | 0.085 | 2.051 | 0.020 |
| 2021年 | 0.148 | -0.033 | 0.076 | 2.296 | 0.011 |
| [1] |
冯文洁. 健康中国战略背景下我国基层医疗资源配置问题研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2019.
|
| [2] |
薛宇,王长青. 区域医疗卫生资源配置复合系统双层目标优化模型构建[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2018,35(12):881-884.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
谢金亮,方鹏骞. 我国医疗卫生资源省际间的配置公平性和利用效率研究[J]. 中国卫生经济,2013,32(1):60-62.
|
| [11] |
卫柯臻. 我国医疗卫生资源配置效率的测度及影响因素研究[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学,2017.
|
| [12] |
常湘,曹阳. 我国医疗机构资源配置效率及公平性分析[J]. 现代商贸工业,2018,39(24):143-146. DOI:10.19311/j.cnki.1672-3198.2018.24.064.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
周江评. "空间不匹配"假设与城市弱势群体就业问题:美国相关研究及其对中国的启示[J]. 现代城市研究,2004,19(9):8-14. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6000.2004.09.003.
|
| [16] |
李雪铭,田深圳,杨俊,等. 城市人居环境的失配度——以辽宁省14个市为例[J]. 地理研究,2014,33(4):687-697.
|
| [17] |
张新成,梁学成,宋晓,等. 黄河流域旅游产业高质量发展的失配度时空格局及成因分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2020,34(12):201-208. DOI:10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2020.350.
|
| [18] |
王俊豪,贾婉文. 中国医疗卫生资源配置与利用效率分析[J]. 财贸经济,2021,42(2):20-35.
|
| [19] |
朱丽,任勇. 县域医疗卫生服务纵向整合制度逻辑:基于"结构—过程"的分析视角[J]. 社会政策研究,2023(3):20-35.
|
| [20] |
侯杰,李卫东,张杰斐,等. 城市数字经济发展水平的分布动态、地区差异与收敛性研究[J]. 统计与决策,2023,39(13):10-15. DOI:10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2023.13.002.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
周晓艳,郝慧迪,叶信岳,等. 黄河流域区域经济差异的时空动态分析[J]. 人文地理,2016,31(5):119-125.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] | |
| [25] |
郭雨晖. 智慧城市建设对基本公共服务供给与均等化的影响研究[D]. 成都:电子科技大学,2022.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
徐琴. 省域发展的空间逻辑——兼论"强省会"战略的地方实践[J]. 现代经济探讨,2020(6):107-110.
|
| [28] |
李丽清,周绪,赵玉兰,等. 我国东中西部地区基层医疗资源配置与经济发展耦合协调关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(22):2777-2784.
|
| [29] |
葛鹏飞,韩永楠,武宵旭. 中国创新与经济发展的耦合协调性测度与评价[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究,2020,37(10):101-117. DOI:10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2020.10.006.
|
| [30] |
许锋. 基于Moran指数和谱图论的空间自相关测度方法优化[J]. 城市发展研究,2021,28(12):92-101,41.
|
| [31] |
李庆. 空间相关性对各省市生态文明建设的影响分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,2019,29(9):91-98.
|
| [32] |
张劲松,王飙,金亚男. 民族地区反贫困问题研究现状、热点与趋势——基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 统计与管理,2022,37(1):100-108.
|
| [1] | 梁振宁, 周清平, 刘涵月, 詹胜帆, 于瑶, 钱怡. 人口老龄化背景下我国老年全科医生人力资源配置公平性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(28): 3507-3511. |
| [2] | 陈东冉, 徐培兰, 丁蕾, 李玉华. 新疆维吾尔自治区全科医生配置公平性及需求预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(28): 3512-3517. |
| [3] | 史穆然, 武宁, 宋丽娟. 我国中医全科医生队伍发展现状及统计优化建议[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1560-1566. |
| [4] | 邱林萍, 宋国强, 刘梦, 姜城蕾, 孙先红. 我国省间基层医疗卫生机构医护资源分布特征研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(31): 3911-3918. |
| [5] | 李筱纯, 郝模, 李程跃, 蒲川. 重庆市慢性病防控资源配置适宜程度研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(25): 3178-3183. |
| [6] | 李丽清, 刘文慧, 杨苏乐, 林慧英. 基层医疗资源配置与经济高质量发展的耦合协调及其预测分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(25): 3164-3170. |
| [7] | 张兰, 张瑞华, 吴雪莲, 杨燕, 段桂敏, 赵大仁. 中国西部地区全科医生资源配置公平性分析及需求预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(25): 3171-3177. |
| [8] | 刘影, 姜俊丞, 景汇泉. 我国中老年人群慢性病患病率及患病种类区域差异与医疗卫生资源的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1452-1459. |
| [9] | 李娅玲, 顾燕峰, 郑艳玲, 蔡学民, 王伟, 余海燕, 杜兆辉. 城市社区卫生服务中心发展情况调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(10): 1166-1172. |
| [10] | 刘影, 姜俊丞, 景汇泉. 我国东、中、西部地区中老年人失能及其影响因素的区域差异研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(07): 877-885. |
| [11] | 高点, 史卢少博, 林锦慧, 王兴民, 王冬. 基于DEA-GIS方法的我国农村医疗卫生资源配置效率及公平性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(07): 849-856. |
| [12] | 李丽清, 杨苏乐, 万里晗, 卢祖洵. 基于fsQCA组态视角的我国医疗资源配置效率提升路径分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 413-419. |
| [13] | 张峥岩, 王振中, 张伋, 宫恩莹, 邵瑞太. 医疗保健生态学模型在卫生服务研究中的应用现状及启示:一项概况性评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 391-399. |
| [14] | 周录玲, 刘素珍, 李航. 四川省基层医疗卫生机构状况及居家医疗服务开展现状调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 433-439. |
| [15] | 闫温馨, 张石默, 刘珏. 2005—2021年我国卫生人力资源发展趋势及公平性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 408-426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





