中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 3493-3501.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0393
收稿日期:2022-05-31
修回日期:2022-08-02
出版日期:2022-10-05
发布日期:2022-08-18
通讯作者:
王爽
基金资助:
Kai YU, Jiachun WANG, Zhaoyuan ZHOU, Xinyue CHEN, Shuang WANG*( )
)
Received:2022-05-31
Revised:2022-08-02
Published:2022-10-05
Online:2022-08-18
Contact:
Shuang WANG
About author:摘要: 背景 慢性病已成为危害我国居民健康的重大公共卫生问题,国家政策强调要发挥基层在慢性病管理中的"主战场"作用。 目的 了解我国基层慢性病管理领域研究主题、热点和发展趋势,旨在为后续研究提供参考。 方法 于2021年9月,通过检索万方数据知识服务平台、中国知网、中国生物医学文献数据库、维普中文科技期刊全文数据库,获取关于基层慢性病管理的文献,检索时限均为建库至2021-09-13。应用Endnote X9软件,从年度发文数量、期刊分布、发文机构分布等方面进行统计分析;运用VOSviewer 1.6.14软件进行高频关键词分析、关键词共现聚类分析、关键词共现时间线分析,并对知识图谱进行可视化。 结果 共纳入自1977年以来发表的研究型文献4 060篇,发文量整体上呈现上升趋势。发文量最多的期刊是《中国全科医学》,共发文329篇(8.10%)。复旦大学是发表基层慢性病管理相关文献数量最多的机构〔1.75%(71/4 060)〕。高频关键词分析结果显示,出现频次排在前10位的关键词依次为慢性病〔8.75%(895/10 224)〕、社区〔7.49%(766/10 224)〕、老年人〔4.90%(501/10 224)〕、糖尿病〔4.62%(472/10 224)〕、高血压〔4.28%(438/10 224)〕、慢性阻塞性肺疾病〔4.22%(431/10 224)〕、患病率〔4.04%(413/10 224)〕、影响因素〔3.29%(336/10 224)〕、危险因素〔2.60%(266/10 224)〕和生活质量〔1.95%(199/10 224)〕。关键词共现聚类分析结果显示,热点研究主题主要集中在社区老年人慢性病管理、慢性病危险因素的流行病学、高血压和糖尿病等慢性病的管理与社区综合防治,以及以慢性阻塞性肺疾病为主的慢性病社区护理与康复4个方面。关键词共现时间线分析结果显示,分级诊疗与家庭医生签约服务、信息化与"互联网+"、心理/睡眠健康、共病、全科医生与药学服务是近年来新兴的研究主题。 结论 我国基层慢性病管理领域研究总体呈现上升趋势,高血压、糖尿病、慢性阻塞性肺疾病的基层管理是研究者关注的热点话题,分级诊疗与家庭医生签约服务、信息化与"互联网+"、心理/睡眠健康、共病、全科医生与药学服务相关研究方兴未艾。
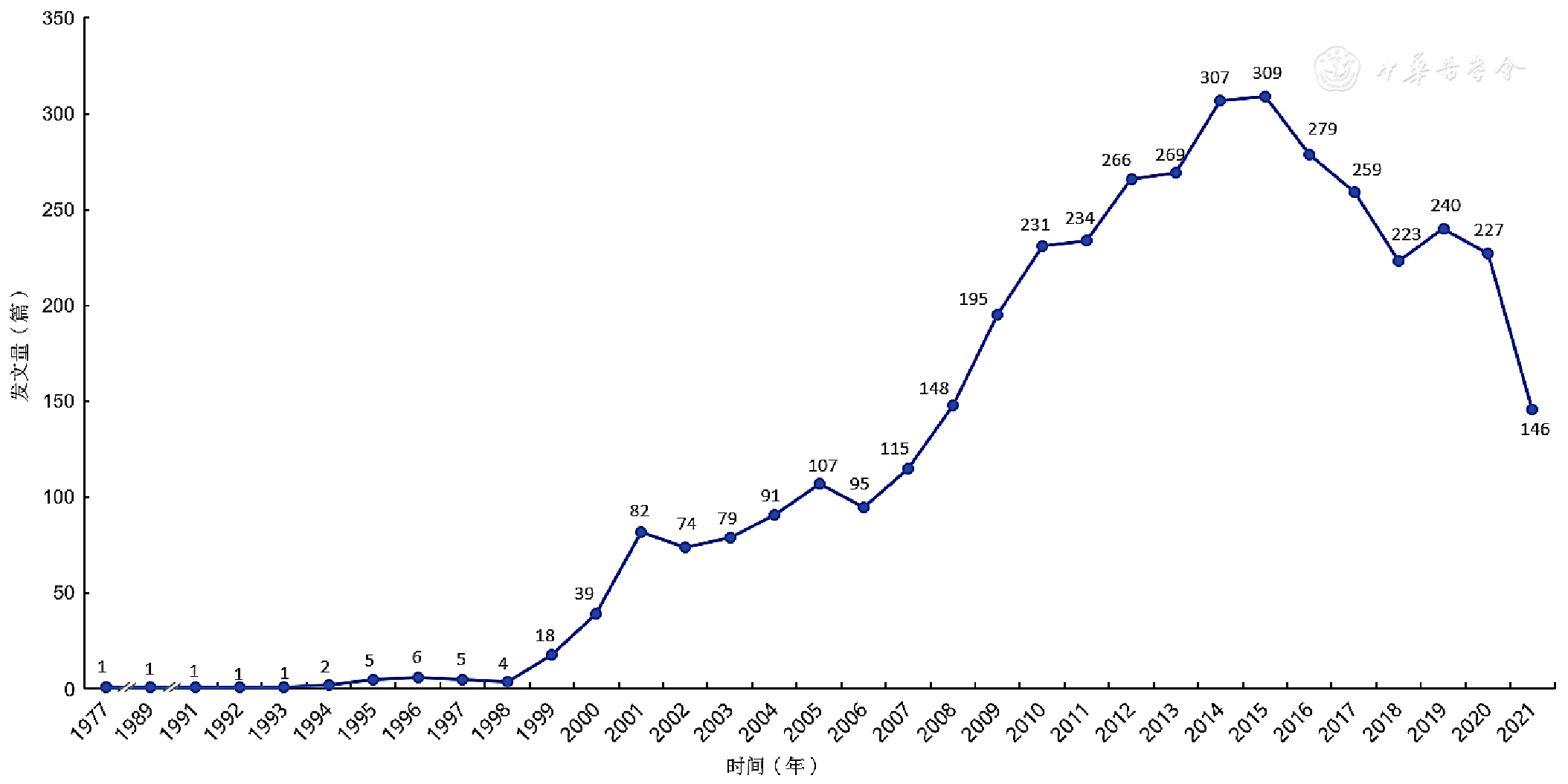
图2 国内基层慢性病管理研究发文量的年度变化趋势(截至2021-09-13)
Figure 2 The trend of annual number of studies on chronic disease management in primary care in China published since 1977(up to 2021-09-13)
| 排序 | 期刊名称 | 发文量 | 排序 | 期刊名称 | 发文量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 《中国全科医学》 | 329(8.10) | 31 | 《预防医学情报杂志》 | 29(0.71) |
| 2 | 《中国慢性病预防与控制》 | 195(4.80) | 32 | 《公共卫生与预防医学》 | 27(0.67) |
| 3 | 《中国老年学杂志》 | 154(3.79) | 33 | 《护士进修杂志》 | 26(0.64) |
| 4 | 《现代预防医学》 | 113(2.78) | 34 | 《中国卫生事业管理》 | 24(0.59) |
| 5 | 《护理研究》 | 108(2.66) | 35 | 《海南医学》 | 23(0.57) |
| 6 | 《中国公共卫生》 | 103(2.54) | 36 | 《国际护理学杂志》 | 23(0.57) |
| 7 | 《中华全科医师杂志》 | 73(1.80) | 37 | 《河北医药》 | 22(0.54) |
| 8 | 《中华全科医学》 | 70(1.72) | 38 | 《中国药物与临床》 | 21(0.52) |
| 9 | 《中国健康教育》 | 64(1.58) | 39 | 《实用临床医药杂志》 | 21(0.52) |
| 10 | 《职业与健康》 | 61(1.50) | 40 | 《解放军护理杂志》 | 20(0.49) |
| 11 | 《实用预防医学》 | 58(1.43) | 41 | 《浙江临床医学》 | 20(0.49) |
| 12 | 《浙江预防医学》 | 57(1.40) | 42 | 《中国误诊学杂志》 | 19(0.47) |
| 13 | 《中华现代护理杂志》 | 48(1.18) | 43 | 《华南预防医学》 | 18(0.44) |
| 14 | 《中国实用护理杂志》 | 48(1.18) | 44 | 《现代中西医结合杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 15 | 《临床肺科杂志》 | 42(1.03) | 45 | 《实用医学杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 16 | 《护理学杂志》 | 42(1.03) | 46 | 《中华护理杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 17 | 《医学与社会》 | 42(1.03) | 47 | 《中国健康心理学杂志》 | 17(0.42) |
| 18 | 《中国医药导报》 | 40(0.99) | 48 | 《中国康复医学杂志》 | 17(0.42) |
| 19 | 《中国预防医学杂志》 | 38(0.94) | 49 | 《中国卫生统计》 | 17(0.42) |
| 20 | 《山西医药杂志》 | 38(0.94) | 50 | 《广东医学》 | 17(0.42) |
| 21 | 《中国基层医药》 | 38(0.94) | 51 | 《老年医学与保健》 | 16(0.39) |
| 22 | 《重庆医学》 | 37(0.91) | 52 | 《检验医学与临床》 | 16(0.39) |
| 23 | 《中华流行病学杂志》 | 36(0.89) | 53 | 《中华预防医学杂志》 | 16(0.39) |
| 24 | 《中华健康管理学杂志》 | 36(0.89) | 54 | 《中国卫生经济》 | 16(0.39) |
| 25 | 《护理实践与研究》 | 34(0.84) | 55 | 《心脑血管病防治》 | 16(0.39) |
| 26 | 《护理学报》 | 34(0.84) | 56 | 《护理管理杂志》 | 16(0.39) |
| 27 | 《齐鲁护理杂志》 | 34(0.84) | 57 | 《浙江医学》 | 15(0.37) |
| 28 | 《实用心脑肺血管病杂志》 | 33(0.81) | 58 | 《临床荟萃》 | 15(0.37) |
| 29 | 《中华疾病控制杂志》 | 31(0.76) | 59 | 《山东医药》 | 15(0.37) |
| 30 | 《中华老年医学杂志》 | 29(0.71) | 60 | 《上海精神医学》 | 15(0.37) |
表1 国内基层慢性病管理研究发文量≥15篇的期刊〔n(%),篇〕
Table 1 Journals in which at least 15 articles about chronic disease management in primary care in China have been published since 1977
| 排序 | 期刊名称 | 发文量 | 排序 | 期刊名称 | 发文量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 《中国全科医学》 | 329(8.10) | 31 | 《预防医学情报杂志》 | 29(0.71) |
| 2 | 《中国慢性病预防与控制》 | 195(4.80) | 32 | 《公共卫生与预防医学》 | 27(0.67) |
| 3 | 《中国老年学杂志》 | 154(3.79) | 33 | 《护士进修杂志》 | 26(0.64) |
| 4 | 《现代预防医学》 | 113(2.78) | 34 | 《中国卫生事业管理》 | 24(0.59) |
| 5 | 《护理研究》 | 108(2.66) | 35 | 《海南医学》 | 23(0.57) |
| 6 | 《中国公共卫生》 | 103(2.54) | 36 | 《国际护理学杂志》 | 23(0.57) |
| 7 | 《中华全科医师杂志》 | 73(1.80) | 37 | 《河北医药》 | 22(0.54) |
| 8 | 《中华全科医学》 | 70(1.72) | 38 | 《中国药物与临床》 | 21(0.52) |
| 9 | 《中国健康教育》 | 64(1.58) | 39 | 《实用临床医药杂志》 | 21(0.52) |
| 10 | 《职业与健康》 | 61(1.50) | 40 | 《解放军护理杂志》 | 20(0.49) |
| 11 | 《实用预防医学》 | 58(1.43) | 41 | 《浙江临床医学》 | 20(0.49) |
| 12 | 《浙江预防医学》 | 57(1.40) | 42 | 《中国误诊学杂志》 | 19(0.47) |
| 13 | 《中华现代护理杂志》 | 48(1.18) | 43 | 《华南预防医学》 | 18(0.44) |
| 14 | 《中国实用护理杂志》 | 48(1.18) | 44 | 《现代中西医结合杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 15 | 《临床肺科杂志》 | 42(1.03) | 45 | 《实用医学杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 16 | 《护理学杂志》 | 42(1.03) | 46 | 《中华护理杂志》 | 18(0.44) |
| 17 | 《医学与社会》 | 42(1.03) | 47 | 《中国健康心理学杂志》 | 17(0.42) |
| 18 | 《中国医药导报》 | 40(0.99) | 48 | 《中国康复医学杂志》 | 17(0.42) |
| 19 | 《中国预防医学杂志》 | 38(0.94) | 49 | 《中国卫生统计》 | 17(0.42) |
| 20 | 《山西医药杂志》 | 38(0.94) | 50 | 《广东医学》 | 17(0.42) |
| 21 | 《中国基层医药》 | 38(0.94) | 51 | 《老年医学与保健》 | 16(0.39) |
| 22 | 《重庆医学》 | 37(0.91) | 52 | 《检验医学与临床》 | 16(0.39) |
| 23 | 《中华流行病学杂志》 | 36(0.89) | 53 | 《中华预防医学杂志》 | 16(0.39) |
| 24 | 《中华健康管理学杂志》 | 36(0.89) | 54 | 《中国卫生经济》 | 16(0.39) |
| 25 | 《护理实践与研究》 | 34(0.84) | 55 | 《心脑血管病防治》 | 16(0.39) |
| 26 | 《护理学报》 | 34(0.84) | 56 | 《护理管理杂志》 | 16(0.39) |
| 27 | 《齐鲁护理杂志》 | 34(0.84) | 57 | 《浙江医学》 | 15(0.37) |
| 28 | 《实用心脑肺血管病杂志》 | 33(0.81) | 58 | 《临床荟萃》 | 15(0.37) |
| 29 | 《中华疾病控制杂志》 | 31(0.76) | 59 | 《山东医药》 | 15(0.37) |
| 30 | 《中华老年医学杂志》 | 29(0.71) | 60 | 《上海精神医学》 | 15(0.37) |
| 排序 | 机构名称 | 发文量 | 排序 | 机构名称 | 发文量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 复旦大学 | 71(1.75) | 37 | 贵阳医学院 | 13(0.32) |
| 2 | 首都医科大学 | 68(1.67) | 38 | 首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院 | 13(0.32) |
| 3 | 华中科技大学 | 55(1.35) | 39 | 广州医学院 | 13(0.32) |
| 4 | 中国疾病预防控制中心 | 49(1.21) | 40 | 吉林大学 | 13(0.32) |
| 5 | 北京大学 | 47(1.16) | 41 | 华北理工大学 | 13(0.32) |
| 6 | 复旦大学附属中山医院 | 40(0.99) | 42 | 北京大学人民医院 | 13(0.32) |
| 7 | 南京医科大学 | 39(0.96) | 43 | 上海市疾病预防控制中心 | 13(0.32) |
| 8 | 四川大学华西医院 | 38(0.94) | 44 | 辽宁医学院 | 12(0.30) |
| 9 | 东南大学 | 30(0.74) | 45 | 广州医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 10 | 郑州大学 | 28(0.69) | 46 | 新疆医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 11 | 上海交通大学 | 27(0.67) | 47 | 昆明医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 12 | 首都医科大学附属复兴医院 | 25(0.62) | 48 | 复旦大学附属华东医院 | 12(0.30) |
| 13 | 天津医科大学 | 25(0.62) | 49 | 中国医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 14 | 哈尔滨医科大学 | 24(0.59) | 50 | 上海市浦东新区沪东社区卫生服务中心 | 12(0.30) |
| 15 | 四川大学 | 24(0.59) | 51 | 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 16 | 山西医科大学 | 23(0.57) | 52 | 西安交通大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 17 | 深圳市慢性病防治中心 | 22(0.54) | 53 | 深圳市福田区人民医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 18 | 中南大学 | 22(0.54) | 54 | 湖北医药学院 | 11(0.27) |
| 19 | 南京中医药大学 | 21(0.52) | 55 | 江苏省疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 20 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院 | 21(0.52) | 56 | 宁夏医科大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 21 | 潍坊医学院 | 20(0.49) | 57 | 南通大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 22 | 安徽医科大学 | 20(0.49) | 58 | 北京市西城区疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 23 | 同济大学 | 20(0.49) | 59 | 北京市疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 24 | 深圳市福田区慢性病防治院 | 19(0.47) | 60 | 北京积水潭医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 25 | 山东大学 | 19(0.47) | 61 | 南方医科大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 26 | 湖州师范学院 | 18(0.44) | 62 | 中国医学科学院 | 11(0.27) |
| 27 | 福建医科大学 | 17(0.42) | 63 | 上海交通大学附属第一人民医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 28 | 南京市疾病预防控制中心 | 17(0.42) | 64 | 上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 29 | 石河子大学 | 16(0.39) | 65 | 西安医学院 | 10(0.25) |
| 30 | 蚌埠医学院 | 15(0.37) | 66 | 郑州大学第一附属医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 31 | 复旦大学附属华山医院 | 15(0.37) | 67 | 海南医学院 | 10(0.25) |
| 32 | 成都市第三人民医院 | 14(0.34) | 68 | 河北联合大学 | 10(0.25) |
| 33 | 北京大学第一医院 | 14(0.34) | 69 | 华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 34 | 中国人民解放军总医院 | 14(0.34) | 70 | 东南大学附属中大医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 35 | 首都医科大学宣武医院 | 13(0.32) | 71 | 北京市丰台区方庄社区卫生服务中心 | 10(0.25) |
| 36 | 首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院 | 13(0.32) | 72 | 上海市松江区疾病预防控制中心 | 10(0.25) |
表2 国内基层慢性病管理研究发文量≥10篇的机构〔n(%),篇〕
Table 2 Instituion authors with at least 10 articles about chronic disease management in primary care in China published since 1977
| 排序 | 机构名称 | 发文量 | 排序 | 机构名称 | 发文量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 复旦大学 | 71(1.75) | 37 | 贵阳医学院 | 13(0.32) |
| 2 | 首都医科大学 | 68(1.67) | 38 | 首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院 | 13(0.32) |
| 3 | 华中科技大学 | 55(1.35) | 39 | 广州医学院 | 13(0.32) |
| 4 | 中国疾病预防控制中心 | 49(1.21) | 40 | 吉林大学 | 13(0.32) |
| 5 | 北京大学 | 47(1.16) | 41 | 华北理工大学 | 13(0.32) |
| 6 | 复旦大学附属中山医院 | 40(0.99) | 42 | 北京大学人民医院 | 13(0.32) |
| 7 | 南京医科大学 | 39(0.96) | 43 | 上海市疾病预防控制中心 | 13(0.32) |
| 8 | 四川大学华西医院 | 38(0.94) | 44 | 辽宁医学院 | 12(0.30) |
| 9 | 东南大学 | 30(0.74) | 45 | 广州医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 10 | 郑州大学 | 28(0.69) | 46 | 新疆医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 11 | 上海交通大学 | 27(0.67) | 47 | 昆明医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 12 | 首都医科大学附属复兴医院 | 25(0.62) | 48 | 复旦大学附属华东医院 | 12(0.30) |
| 13 | 天津医科大学 | 25(0.62) | 49 | 中国医科大学 | 12(0.30) |
| 14 | 哈尔滨医科大学 | 24(0.59) | 50 | 上海市浦东新区沪东社区卫生服务中心 | 12(0.30) |
| 15 | 四川大学 | 24(0.59) | 51 | 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 16 | 山西医科大学 | 23(0.57) | 52 | 西安交通大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 17 | 深圳市慢性病防治中心 | 22(0.54) | 53 | 深圳市福田区人民医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 18 | 中南大学 | 22(0.54) | 54 | 湖北医药学院 | 11(0.27) |
| 19 | 南京中医药大学 | 21(0.52) | 55 | 江苏省疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 20 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院 | 21(0.52) | 56 | 宁夏医科大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 21 | 潍坊医学院 | 20(0.49) | 57 | 南通大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 22 | 安徽医科大学 | 20(0.49) | 58 | 北京市西城区疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 23 | 同济大学 | 20(0.49) | 59 | 北京市疾病预防控制中心 | 11(0.27) |
| 24 | 深圳市福田区慢性病防治院 | 19(0.47) | 60 | 北京积水潭医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 25 | 山东大学 | 19(0.47) | 61 | 南方医科大学 | 11(0.27) |
| 26 | 湖州师范学院 | 18(0.44) | 62 | 中国医学科学院 | 11(0.27) |
| 27 | 福建医科大学 | 17(0.42) | 63 | 上海交通大学附属第一人民医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 28 | 南京市疾病预防控制中心 | 17(0.42) | 64 | 上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院 | 11(0.27) |
| 29 | 石河子大学 | 16(0.39) | 65 | 西安医学院 | 10(0.25) |
| 30 | 蚌埠医学院 | 15(0.37) | 66 | 郑州大学第一附属医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 31 | 复旦大学附属华山医院 | 15(0.37) | 67 | 海南医学院 | 10(0.25) |
| 32 | 成都市第三人民医院 | 14(0.34) | 68 | 河北联合大学 | 10(0.25) |
| 33 | 北京大学第一医院 | 14(0.34) | 69 | 华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 34 | 中国人民解放军总医院 | 14(0.34) | 70 | 东南大学附属中大医院 | 10(0.25) |
| 35 | 首都医科大学宣武医院 | 13(0.32) | 71 | 北京市丰台区方庄社区卫生服务中心 | 10(0.25) |
| 36 | 首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院 | 13(0.32) | 72 | 上海市松江区疾病预防控制中心 | 10(0.25) |
| 出现频次排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次〔n(%),次〕 | 关联强度 | 出现频次排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次〔n(%),次〕 | 关联强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 慢性病 | 895(8.75) | 1 846 | 26 | 调查 | 76(0.74) | 160 |
| 2 | 社区 | 766(7.49) | 1 635 | 27 | 康复 | 71(0.69) | 143 |
| 3 | 老年人 | 501(4.90) | 1 138 | 28 | 脑卒中 | 59(0.58) | 125 |
| 4 | 糖尿病 | 472(4.62) | 1 119 | 29 | 依从性 | 58(0.57) | 153 |
| 5 | 高血压 | 438(4.28) | 980 | 30 | 肺功能 | 57(0.56) | 132 |
| 6 | 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 431(4.22) | 840 | 31 | 疾病管理 | 56(0.55) | 135 |
| 7 | 患病率 | 413(4.04) | 939 | 32 | 需求 | 54(0.53) | 123 |
| 8 | 影响因素 | 336(3.29) | 749 | 33 | 农村 | 53(0.52) | 113 |
| 9 | 危险因素 | 266(2.60) | 615 | 34 | 血脂异常 | 51(0.50) | 133 |
| 10 | 生活质量 | 199(1.95) | 421 | 35 | 护理干预 | 45(0.44) | 94 |
| 11 | 超重/肥胖 | 180(1.76) | 560 | 36 | 自我效能 | 42(0.41) | 123 |
| 12 | 慢性病管理 | 171(1.67) | 352 | 37 | 问卷调查 | 42(0.41) | 91 |
| 13 | 社区护理 | 156(1.53) | 340 | 38 | 生产质量 | 41(0.40) | 88 |
| 14 | 行为生活方式 | 143(1.40) | 386 | 39 | 分级诊疗 | 35(0.34) | 68 |
| 15 | 健康教育 | 142(1.39) | 303 | 40 | 冠心病 | 34(0.33) | 71 |
| 16 | 社区干预 | 135(1.32) | 286 | 41 | 吸烟 | 33(0.32) | 76 |
| 17 | 肺疾病 | 124(1.21) | 290 | 42 | 焦虑 | 31(0.30) | 84 |
| 18 | 流行病学 | 121(1.18) | 286 | 43 | 社区管理 | 30(0.29) | 58 |
| 19 | 效果评价 | 109(1.07) | 241 | 44 | 上海 | 27(0.26) | 72 |
| 20 | 慢性肾脏病 | 94(0.92) | 241 | 45 | 预后 | 27(0.26) | 55 |
| 21 | 精神分裂症 | 87(0.85) | 127 | 46 | 效果 | 26(0.25) | 63 |
| 22 | 健康管理 | 86(0.84) | 189 | 47 | 社会支持 | 24(0.23) | 61 |
| 23 | 抑郁 | 86(0.84) | 201 | 48 | 知识 | 24(0.23) | 81 |
| 24 | 慢性心力衰竭 | 81(0.79) | 148 | 49 | 知晓率 | 23(0.22) | 66 |
| 25 | 自我管理 | 80(0.78) | 194 | 50 | 控制率 | 17(0.17) | 57 |
表3 出现频次排在前50位的高频关键词及其关联强度
Table 3 Top 50 high-frequency keywords and their correlation intensity
| 出现频次排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次〔n(%),次〕 | 关联强度 | 出现频次排序 | 关键词 | 出现频次〔n(%),次〕 | 关联强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 慢性病 | 895(8.75) | 1 846 | 26 | 调查 | 76(0.74) | 160 |
| 2 | 社区 | 766(7.49) | 1 635 | 27 | 康复 | 71(0.69) | 143 |
| 3 | 老年人 | 501(4.90) | 1 138 | 28 | 脑卒中 | 59(0.58) | 125 |
| 4 | 糖尿病 | 472(4.62) | 1 119 | 29 | 依从性 | 58(0.57) | 153 |
| 5 | 高血压 | 438(4.28) | 980 | 30 | 肺功能 | 57(0.56) | 132 |
| 6 | 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 431(4.22) | 840 | 31 | 疾病管理 | 56(0.55) | 135 |
| 7 | 患病率 | 413(4.04) | 939 | 32 | 需求 | 54(0.53) | 123 |
| 8 | 影响因素 | 336(3.29) | 749 | 33 | 农村 | 53(0.52) | 113 |
| 9 | 危险因素 | 266(2.60) | 615 | 34 | 血脂异常 | 51(0.50) | 133 |
| 10 | 生活质量 | 199(1.95) | 421 | 35 | 护理干预 | 45(0.44) | 94 |
| 11 | 超重/肥胖 | 180(1.76) | 560 | 36 | 自我效能 | 42(0.41) | 123 |
| 12 | 慢性病管理 | 171(1.67) | 352 | 37 | 问卷调查 | 42(0.41) | 91 |
| 13 | 社区护理 | 156(1.53) | 340 | 38 | 生产质量 | 41(0.40) | 88 |
| 14 | 行为生活方式 | 143(1.40) | 386 | 39 | 分级诊疗 | 35(0.34) | 68 |
| 15 | 健康教育 | 142(1.39) | 303 | 40 | 冠心病 | 34(0.33) | 71 |
| 16 | 社区干预 | 135(1.32) | 286 | 41 | 吸烟 | 33(0.32) | 76 |
| 17 | 肺疾病 | 124(1.21) | 290 | 42 | 焦虑 | 31(0.30) | 84 |
| 18 | 流行病学 | 121(1.18) | 286 | 43 | 社区管理 | 30(0.29) | 58 |
| 19 | 效果评价 | 109(1.07) | 241 | 44 | 上海 | 27(0.26) | 72 |
| 20 | 慢性肾脏病 | 94(0.92) | 241 | 45 | 预后 | 27(0.26) | 55 |
| 21 | 精神分裂症 | 87(0.85) | 127 | 46 | 效果 | 26(0.25) | 63 |
| 22 | 健康管理 | 86(0.84) | 189 | 47 | 社会支持 | 24(0.23) | 61 |
| 23 | 抑郁 | 86(0.84) | 201 | 48 | 知识 | 24(0.23) | 81 |
| 24 | 慢性心力衰竭 | 81(0.79) | 148 | 49 | 知晓率 | 23(0.22) | 66 |
| 25 | 自我管理 | 80(0.78) | 194 | 50 | 控制率 | 17(0.17) | 57 |
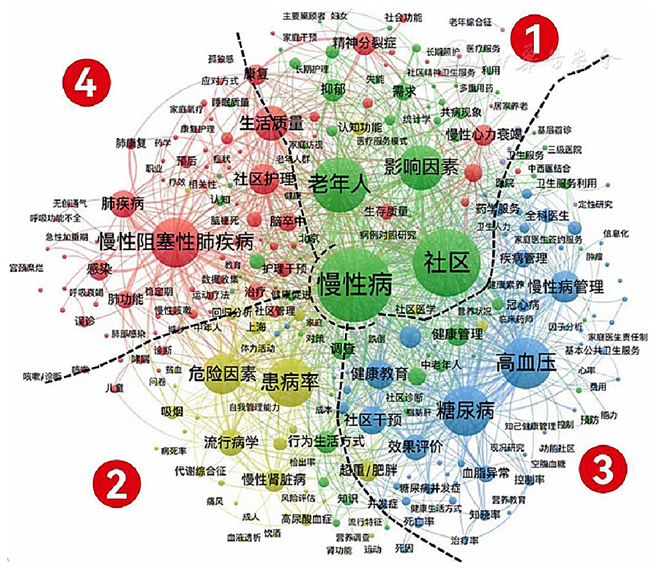
图3 关键词共现聚类可视化图谱注:每个圆形节点代表1个关键词,节点的大小与关键词出现的频次成正比,连线代表2个关键词间存在共现关系,连线的粗细、长短分别与2个关键词间的关联强度成正、反比,节点的颜色(所在片区)代表其所属的聚类
Figure 3 Co-occurrence clustering map of keywords
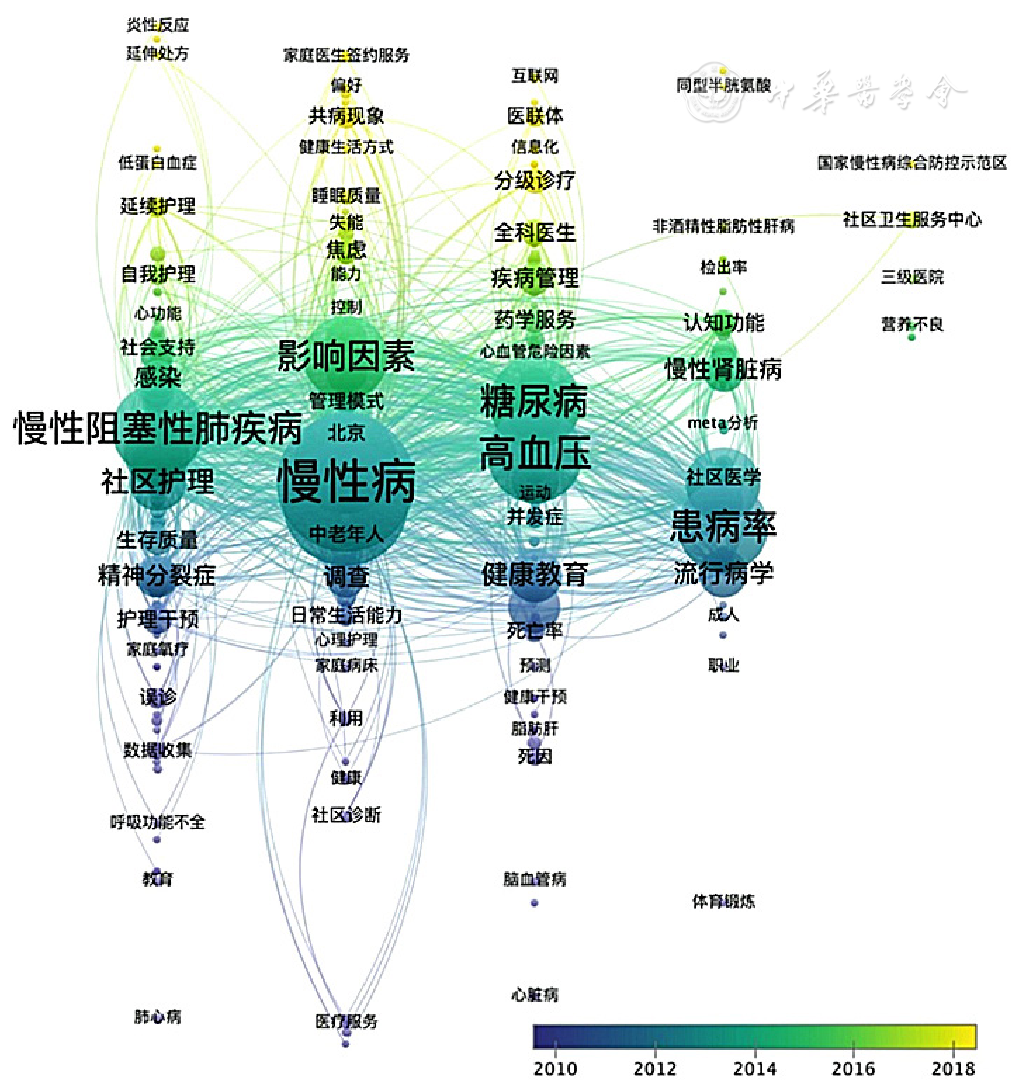
图4 关键词共现时间线可视化图谱注:每个圆形节点代表1个关键词,节点的大小与关键词出现的频次成正比,连线代表2个关键词间存在共现关系,不同颜色(位置)代表着不同的关键词出现年份,节点颜色越蓝(位置越偏下方)代表关键词出现得越早,节点颜色越黄(位置越偏上方)表示关键词新兴度越高;受限于篇幅,部分出现频次较低、重要性较弱的关键词标签被隐藏
Figure 4 Timeline visualization of co-occurring keywords
| [1] |
World Health Organization. World health statistics 2021:monitoring health for the SDGs,sustainable development goals[EB/OL]. (2021-05-20)[2022-03-01].
|
| [2] |
中共中央. "十四五"规划和2035远景目标的发展环境、指导方针和主要目标[EB/OL]. (2021-03-11)[2022-03-02].
|
| [3] |
国务院办公厅. 关于印发中国防治慢性病中长期规划(2017—2025年)的通知[A/OL]. (2017-2-14)[2022-03-02].
|
| [4] |
中共中央,国务院. "健康中国2030"规划纲要[EB/OL]. (2016-10-25)[2022-03-02].
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
程振达. 基层条件下慢性肺心病的早期诊断和预防措施探讨:附105例临床分析[J]. 铁道医学,1977,2(1):37-38,64.
|
| [7] |
唐智柳,傅华,信亚东,等. 城市基层医院发展的动力和方向刍议[J]. 中国卫生资源,1998,1(2):78-79.
|
| [8] |
徐望红,张勇,王继伟,等. 中日两国慢性病防控策略比较及政策启示[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2016,24(8):593-596. DOI:10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2016.08.009.
|
| [9] |
贺丹,刘厚莲. 中国人口老龄化发展态势、影响及应对策略[J].中共中央党校(国家行政学院)学报,2019,23(4):84-90. DOI:10.14119/j.cnki.zgxb.2019.04.011.
|
| [10] |
国务院办公厅. 关于印发中国防治慢性病中长期规划(2017—2025年)的通知[A/OL]. (2017-01-22)[2022-03-02].
|
| [11] |
习近平. 在中国共产党第十九次全国代表大会上的报告[EB/OL]. (2017-10-28)[2022-03-02].
|
| [12] |
中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2021,36(6):521-545. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.06.001.
|
| [13] |
王世豪,王至婉. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病呼吸肌疲劳的康复锻炼研究进展[J]. 护理研究,2021,35(20):3641-3646. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2021.20.013.
|
| [14] |
邓诗姣,刘心怡,陈文,等. 家庭医生签约服务工作现状与满意度分析[J]. 卫生经济研究,2022,39(2):78-84. DOI:10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2022.02.006.
|
| [15] |
张艳. "互联网+医疗健康"背景下的慢性病管理模式与平台构建研究[J]. 网络安全技术与应用,2021,21(4):132-134.
|
| [16] |
张淑娥,王燕萍,王鸿妮,等. 近10年国内分级诊疗学术叙事的焦点结构及趋势特征研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(10):1246-1253. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.00.014.
|
| [17] |
李果,姜荣环,郭成军,等. 综合医院心内科门诊患者抑郁和焦虑障碍患病率调查[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2014,42(12):1035-1038. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2014.12.012.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
黎艳娜,王艺桥. 我国老年人慢性病共病现状及模式研究[J].中国全科医学,2021,24(31):3955-3962. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.295.
|
| [25] |
贾春伶,张娟涛,张丽霞,等. 社区老年慢性病患者多重用药现状和处方干预认知度调查[J]. 人民军医,2019,62(6):534-538,541.
|
| [26] |
王思蒙,张晨,孙雪,等. 社区老年人潜在不适当用药及其应对模式的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(13):1551-1556. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0077.
|
| [27] |
沈晨,侯惠如,杨庭树,等. 居家老年共病患者多重用药现况调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华保健医学杂志,2021,23(6):586-588. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3245.2021.06.008.
|
| [28] |
潘婉玉,张春慧,张振香,等. 老年慢性病共病患者多重用药管理分析与评论[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(13):1545-1550. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.00.009.
|
| [1] | 姚裕忠, 马晓骏, 宋懽, 钟瑜. 基于"全专精准管理"的糖尿病"1358模式"对社区糖尿病患者的管理效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4308-4314. |
| [2] | 秦凤银, 张绮珊, 赖锦佳, 黄奕敏, 韩郭茵, 孙兴兰, 王芬, 谭益冰. 广东省社区居民脑卒中高危筛查意向的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4283-4289. |
| [3] | 冯晓玉, 李婉玲, 吕思漫, 倪翠萍, 王浩成, 刘宇. 基于文献计量学的interRAI家庭护理评估工具国际研究现状及热点分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4351-4358. |
| [4] | 李殿江, 潘恩春, 孙中明, 文进博, 王苗苗, 武鸣, 沈冲. 社区2型糖尿病患者临床惰性现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4296-4301. |
| [5] | 林恺, 姚弥, 陈章, 纪欣鑫, 林润琪, 陈永松, Sim MOIRA. 2型糖尿病治疗负担的概念框架及应对方式:基于视频记录分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4302-4307. |
| [6] | 黄锦玲, 曾志嵘. 我国城市社区卫生服务政策演进逻辑及走向研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4239-4245. |
| [7] | 杨慧, 胡汝为, 刘汝青, 卢俊峰, 吴兢兰. 糖尿病患者社区卫生服务体验与血糖控制效果的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4290-4295. |
| [8] | 徐健, 戴芳芳, 潘文雷, 黄倩, 陆萍, 王剑峰, 贾环, 杨宇琪, 黄蛟灵. "健康中国"背景下我国社区中医药服务研究热点和前沿趋势的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4343-4350. |
| [9] | 王婕, 李仕明, 魏士飞, 王宁利. 重视基层卫生服务在儿童近视防控行为干预中的作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4213-4217. |
| [10] | 余新艳, 赵珺, 赵晓晔, 姜清茹, 陈雅田, 王艳, 张海澄. 移动智慧医疗在基层老年慢性病患者心血管病防控中的应用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4167-4172. |
| [11] | 李芊芊, 陈循睿, 张文颖, 袁海花, 张燕捷, 姜斌, 刘峰. 晚期肿瘤患者化疗期间对社区卫生服务需求的调查及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4173-4180. |
| [12] | 尹朝霞, 茅立东, 张宝双, 黄茵, 冯阳, 王云飞. 深圳市家庭医生签约儿童社区门诊疾病谱研究及其对全科住院医师规范化培训的启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4218-4224. |
| [13] | 于德华. 全科医学思维引导下的科学研究构思[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3872-3876. |
| [14] | 刘锐, 曹宇, 褚爱群, 吴欢云. 上海市社区药学服务开展现状及药师融入家庭医生团队情况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3922-3929. |
| [15] | 周英达, 卓书雄, 杨郗, 金花, 于德华. 社区全科未分化疾病临床路径的实施现状及构建策略研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3939-3944. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





