

Chinese General Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2027-2035.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0690
Special Issue: 新型冠状病毒肺炎最新文章合辑; COVID-19疫情防控研究
• Original Research·Focus on Hot Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-10-12
Revised:2023-03-21
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2023-03-30
Contact:
HUANG Jiaoling
通讯作者:
黄蛟灵
作者简介:基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0690
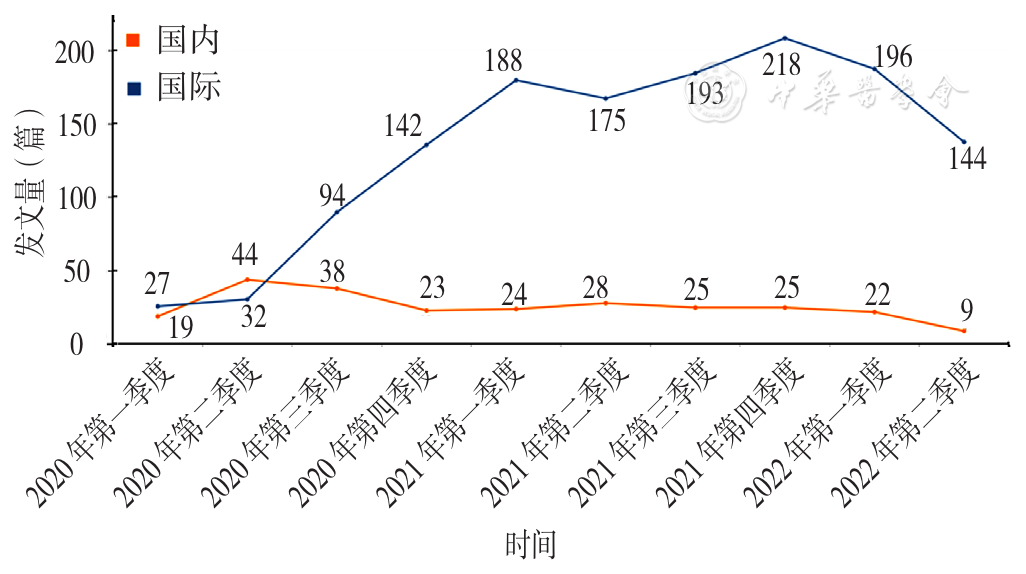
Figure 3 Seasonal trends in the number of domestic and international studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic published during 2020 to 2022
| 序号 | 国内文献 | 国际文献 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 62 | 0.55 | impact | 124 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 医务人员 | 55 | 0.31 | covid 19 | 80 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 新冠疫情 | 54 | 0.39 | care | 77 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 基层医院 | 18 | 0.29 | health | 66 | 0.13 |
| 5 | 全科医生 | 17 | 0.09 | risk | 58 | 0.17 |
| 6 | 防治原则 | 11 | 0.00 | mental health | 52 | 0.15 |
| 7 | 皮肤问题 | 11 | 0.00 | depression | 47 | 0.35 |
| 8 | 防护装备 | 11 | 0.00 | mortality | 46 | 0.09 |
| 9 | 皮肤病 | 11 | 0.00 | management | 43 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 焦虑 | 11 | 0.05 | outcome | 40 | 0.07 |
| 11 | 医护人员 | 9 | 0.06 | prevalence | 39 | 0.12 |
| 12 | 抑郁 | 8 | 0.11 | outbreak | 36 | 0.11 |
| 13 | 影响因素 | 8 | 0.15 | health care | 35 | 0.14 |
| 14 | 心理健康 | 8 | 0.11 | primary care | 34 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 防控工作 | 7 | 0.10 | anxiety | 33 | 0.05 |
| 16 | 医疗队 | 7 | 0.04 | sar | 33 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 发热门诊 | 6 | 0.10 | disease | 33 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 疫情 | 6 | 0.02 | burnout | 31 | 0.10 |
| 19 | 心理状态 | 6 | 0.08 | disorder | 29 | 0.11 |
| 20 | 社区 | 6 | 0.08 | telemedicine | 28 | 0.07 |
Table 1 Top 20 keywords with the highest frequency of use in China's and international studies
| 序号 | 国内文献 | 国际文献 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 62 | 0.55 | impact | 124 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 医务人员 | 55 | 0.31 | covid 19 | 80 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 新冠疫情 | 54 | 0.39 | care | 77 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 基层医院 | 18 | 0.29 | health | 66 | 0.13 |
| 5 | 全科医生 | 17 | 0.09 | risk | 58 | 0.17 |
| 6 | 防治原则 | 11 | 0.00 | mental health | 52 | 0.15 |
| 7 | 皮肤问题 | 11 | 0.00 | depression | 47 | 0.35 |
| 8 | 防护装备 | 11 | 0.00 | mortality | 46 | 0.09 |
| 9 | 皮肤病 | 11 | 0.00 | management | 43 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 焦虑 | 11 | 0.05 | outcome | 40 | 0.07 |
| 11 | 医护人员 | 9 | 0.06 | prevalence | 39 | 0.12 |
| 12 | 抑郁 | 8 | 0.11 | outbreak | 36 | 0.11 |
| 13 | 影响因素 | 8 | 0.15 | health care | 35 | 0.14 |
| 14 | 心理健康 | 8 | 0.11 | primary care | 34 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 防控工作 | 7 | 0.10 | anxiety | 33 | 0.05 |
| 16 | 医疗队 | 7 | 0.04 | sar | 33 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 发热门诊 | 6 | 0.10 | disease | 33 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 疫情 | 6 | 0.02 | burnout | 31 | 0.10 |
| 19 | 心理状态 | 6 | 0.08 | disorder | 29 | 0.11 |
| 20 | 社区 | 6 | 0.08 | telemedicine | 28 | 0.07 |
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 核酸检测 | 26 | 0.861 | 2020 | 核酸检测;防控措施;新冠感染;防控工作;新型冠状病毒 |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 25 | 0.999 | 2021 | 疫情防控;紧密型医联体;卫生院;消费券;健康扶贫 |
| 2 | 新冠疫情 | 23 | 0.986 | 2021 | 新冠感染疫情;心理健康;医联体;人文关怀;新型冠状病毒 |
| 3 | 医务人员 | 21 | 0.984 | 2021 | 医务人员;心理状态;医疗队;疫情防控;新型冠状病毒 |
| 4 | 发热门诊 | 21 | 0.934 | 2020 | 发热门诊;基层医院;疫情;调查;发热患者 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 18 | 0.938 | 2020 | 影响因素;家庭医生;认知;护理人员;防范路径 |
| 6 | 联防联控 | 16 | 0.966 | 2020 | 联防联控;卫生健康;封闭管理;社区;习近平 |
| 7 | 全科医生 | 15 | 0.933 | 2020 | 全科医生;健康教育;糖尿病;健康管理;全科医生培训 |
| 8 | 抑郁 | 13 | 0.918 | 2020 | 抑郁;焦虑;心理韧性;中老年人;心理应对 |
| 9 | 家庭医生签约 | 12 | 0.975 | 2021 | 家庭医生签约服务;医疗机构;方舱医院;公立医院改革;中医院 |
Table 2 Cluster details of keywords in China's studies on primary ealthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 核酸检测 | 26 | 0.861 | 2020 | 核酸检测;防控措施;新冠感染;防控工作;新型冠状病毒 |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 25 | 0.999 | 2021 | 疫情防控;紧密型医联体;卫生院;消费券;健康扶贫 |
| 2 | 新冠疫情 | 23 | 0.986 | 2021 | 新冠感染疫情;心理健康;医联体;人文关怀;新型冠状病毒 |
| 3 | 医务人员 | 21 | 0.984 | 2021 | 医务人员;心理状态;医疗队;疫情防控;新型冠状病毒 |
| 4 | 发热门诊 | 21 | 0.934 | 2020 | 发热门诊;基层医院;疫情;调查;发热患者 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 18 | 0.938 | 2020 | 影响因素;家庭医生;认知;护理人员;防范路径 |
| 6 | 联防联控 | 16 | 0.966 | 2020 | 联防联控;卫生健康;封闭管理;社区;习近平 |
| 7 | 全科医生 | 15 | 0.933 | 2020 | 全科医生;健康教育;糖尿病;健康管理;全科医生培训 |
| 8 | 抑郁 | 13 | 0.918 | 2020 | 抑郁;焦虑;心理韧性;中老年人;心理应对 |
| 9 | 家庭医生签约 | 12 | 0.975 | 2021 | 家庭医生签约服务;医疗机构;方舱医院;公立医院改革;中医院 |
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | telemedicine | 20 | 0.796 | 2020 | public health perspective;autonomy power dynamics;antibiotic use;comparing medication;clinical pharmacist visit transition |
| 1 | care | 20 | 0.809 | 2020 | covid-19 pandemic;covid-19 infection;cov-2 infection;nursing home;ethnic disparities in covid-19 infection |
| 2 | infection | 16 | 0.681 | 2020 | other high-risk group;severe asthma;cov-2 transmission fear;knowledge attitude developing country |
| 3 | stress | 15 | 0.756 | 2020 | surgical breast cancer care;multicenter retrospective cohort study;nursing student;young individual;cascading pathologies |
| 4 | topic areas | 13 | 0.822 | 2020 | rapid evidence synthesis;users perception;urgent need;living kidney donation;kidney transplantation |
| 5 | depression | 11 | 0.902 | 2020 | psychological distress;healthcare professional;depression anxiety;high level;australian frontline healthcare worker |
| 6 | vas | 9 | 0.873 | 2020 | containment sheet-a;frugal innovation;total knee arthroplasty;correct personal protective equipment use;mastery learning |
| 7 | diagnosis | 9 | 0.972 | 2020 | covid-19 policy intervention;equity harm;racial disparity;stroke patient;scoping review |
| 8 | acute myocardial infection | 5 | 0.954 | 2020 | acute coronary syndrome;era;breast cancer management pathway;map-c study;study protocol |
| 9 | health economics | 5 | 0.932 | 2021 | metropolitan health care worker;home-dwelling people;covid-19 restriction;psychological symptom;self-directed e-learning intervention |
Table 3 Cluster details of keywords in international studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | telemedicine | 20 | 0.796 | 2020 | public health perspective;autonomy power dynamics;antibiotic use;comparing medication;clinical pharmacist visit transition |
| 1 | care | 20 | 0.809 | 2020 | covid-19 pandemic;covid-19 infection;cov-2 infection;nursing home;ethnic disparities in covid-19 infection |
| 2 | infection | 16 | 0.681 | 2020 | other high-risk group;severe asthma;cov-2 transmission fear;knowledge attitude developing country |
| 3 | stress | 15 | 0.756 | 2020 | surgical breast cancer care;multicenter retrospective cohort study;nursing student;young individual;cascading pathologies |
| 4 | topic areas | 13 | 0.822 | 2020 | rapid evidence synthesis;users perception;urgent need;living kidney donation;kidney transplantation |
| 5 | depression | 11 | 0.902 | 2020 | psychological distress;healthcare professional;depression anxiety;high level;australian frontline healthcare worker |
| 6 | vas | 9 | 0.873 | 2020 | containment sheet-a;frugal innovation;total knee arthroplasty;correct personal protective equipment use;mastery learning |
| 7 | diagnosis | 9 | 0.972 | 2020 | covid-19 policy intervention;equity harm;racial disparity;stroke patient;scoping review |
| 8 | acute myocardial infection | 5 | 0.954 | 2020 | acute coronary syndrome;era;breast cancer management pathway;map-c study;study protocol |
| 9 | health economics | 5 | 0.932 | 2021 | metropolitan health care worker;home-dwelling people;covid-19 restriction;psychological symptom;self-directed e-learning intervention |
| [1] |
人民日报. 习近平:健全国家公共卫生应急管理体系[EB/OL].(2020-02-29)[2022-08-14].
|
| [2] |
刘梦林. 公共危机事件中基层社区治理的局限性及对策探析:以我国此次新冠肺炎疫情应对为例[J]. 行政科学论坛,2020,7(8):18-22.
|
| [3] |
吴莹,葛道顺. 特大城市公共卫生安全风险与基层治理应对:基于新冠肺炎疫情下北京、上海、武汉的社区防疫经验[J]. 学习与实践,2020,37(9):75-84. DOI:10.19624/j.cnki.cn42-1005/c.2020.09.009.
|
| [4] |
卢祖洵,徐鸿彬,李丽清,等. 关于加强基层医疗卫生服务建设的建议:兼论推进疫情防控关口前移[J]. 行政管理改革,2020,12(3):23-29. DOI:10.14150/j.cnki.1674-7453.2020.03.003.
|
| [5] |
刘则渊,陈悦,侯海燕. 科学知识图谱:方法与应用[M]. 北京:人民出版社,2008:3-5.
|
| [6] |
陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. DOI:10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009.
|
| [7] |
吴晓秋,吕娜. 基于关键词共现频率的热点分析方法研究[J]. 情报理论与实践,2012,35(8):115-119. DOI:10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2012.08.026.
|
| [8] |
刘军. 整体网分析:UCINET软件实用指南[M]. 2版.上海:格致出版社,2014.
|
| [9] |
蔡建东,马婧,袁媛. 国外CSCL理论的演进与前沿热点问题:基于Citespace的可视化分析[J]. 现代教育技术,2012,22(5):10-16. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-8097.2012.05.002.
|
| [10] |
陈超美. CiteSpace中的Burst Detection[EB/OL].(2012-05-03)[2022-08-14].
|
| [11] |
秦晓楠,卢小丽,武春友. 国内生态安全研究知识图谱:基于Citespace的计量分析[J]. 生态学报,2014,34(13):3693-3703. DOI:10.5846/stxb201211081566.
|
| [12] |
WHO. Timeline:WHO's COVID-19 response[EB/OL].(2022-03-28)[2022-08-14].
|
| [13] |
人民日报. 关于疫情防控工作,总书记的最新指示来了![EB/OL].(2020-02-14)[2022-08-14].
|
| [14] |
唐燕. 新冠肺炎疫情防控中的社区治理挑战应对:基于城乡规划与公共卫生视角[J]. 南京社会科学,2020,31(3):8-14,27. DOI:10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2020.03.002.
|
| [15] |
陈迎春,常静肼,张全红,等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情下湖北省基层卫生机构联防联控协作机制分析[J]. 医学与社会,2020,33(9):10-14. DOI:10.13723/j.yxysh.2020.09.003.
|
| [16] |
牟岚,金新政. 远程医疗发展现状综述[J]. 卫生软科学,2012,26(6):506-509.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
苏斌原,叶苑秀,张卫,等. 新冠肺炎疫情不同时间进程下民众的心理应激反应特征[J]. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版),2020,65(3):79-94.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] | |
| [29] |
张宴萍,褚连芳,庄开岑,等. 新冠肺炎疫情下医务人员压力、焦虑、抑郁状况及影响因素研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2021,48(1):38-43.
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] | NIU Ben, ZHU Xiaoqian, YANG Chen, LIANG Wannian, LIU Jue. Evolution and Trends of Domestic and International Research Hotspots in the Field of Large Language Models in Medicine Based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3200-3208. |
| [2] | ZHAO Can, SHEN Ying, CHEN Peimeng, PENG Houxuan, XI Qian, GU Jinmei, QIN Li, LIANG Ruiying, ZUO Yanli. An Assessment Research on Consultation Competence of RTME Graduates Trained Via the "5+3" Pathway in Township Health Centers in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2731-2739. |
| [3] | WEI Xu, YIN Yuhui, WANG Xu, YU Ruowen, ZHANG Yili, SUN Kai, WANG Hui, XIE Shiming, LI Yan, QIN Xiaokuan, YIN Xunlu, LI Linghui, ZHU Liguo. Study on the Assessment System of Bone Health Service Capacity of Primary Healthcare Institutions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2354-2362. |
| [4] | WANG Songzhu, YAO Yi, ZHOU Yiheng, ZHAO Jiaxi, YANG Rong, ZHAO Qian, ZHANG Rui, DAI Hua, LI Dongze, LIAO Xiaoyang, YANG Hui. Analysis of Research Hotspots and Development Trends of General Practice in the Last Five Years: a Visualization Analysis Based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [5] | ZHOU Fang, DONG Yuan, WU Xiankui, JI Ying. An Evaluation of Basic Public Health Services Quality for Floating Population in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2363-2369. |
| [6] | GUO Xiangyun, ZHANG Yili, LI Ting, FENG Tianxiao, LI Linghui, SUN Kai, WANG Xu, QIN Xiaokuan, TIAN Jinzhou, ZHU Liguo, WEI Xu. Analysis of Prevalence Trends and Factors Influencing Key Bone Health Conditions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2346-2353. |
| [7] | LIN Chunmei, LI Sisi, ZHANG Yanchun, ZHANG Lifang, QIN Jiangmei. Evaluation and Measurement of Primary Health Services Based on Patients' Experience in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(13): 1553-1559. |
| [8] | DENG Jie, TAO Liyuan, LIU Nan, LI Jun, YAN Wenxin, QIN Chenyuan, LIU Qiao, DU Min, WANG Yaping, LIU Jue. Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Version of the Modified COVID-19 Yorkshire Rehabilitation Scale [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(13): 1642-1648. |
| [9] | LI Bingsong, LYU Yitong, LEI Tianchu, LIU Yuchen, ZHEN Xuemei, WANG Jian. Research on the Integrated Development of TCM and Primary Health Care under ROCCIPI Framework [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1549-1552. |
| [10] | GE Qiong, HU Jiakang, YU Yuqi, LAI Wenwen, LUO Shiwen, LU Quqin. Bibliometric Analysis of RNA-seq Technology in Liver Cancer Research [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1473-1478. |
| [11] | GU Mingyu, QIN Tingting, QIAO Kun, BAI Xinyuan, WANG Yao, YANG Yutong, LI Xingming. A Network Meta-analysis of Primary Hypertension Management Patterns in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(10): 1265-1272. |
| [12] | LIU Xinxin, SUI Jinhui, WU Bangdong, LIU Yan, LIANG Xiaohui, ZHAO Yang. Research on the Influencing Factors and Countermeasures of Fertility Willingness among Different Age Groups in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 973-979. |
| [13] | LIN Yifang, JIA Jie. Consideration on Strategies for Harmonious Growth of Community Rehabilitation and Primary Health Care [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 905-910. |
| [14] | CHENG Qi, YU Wenbing, LI Keke, ZUO You, JIAO Qianxin, LIU Xinhao, GAO Lili. A CiteSpace-based Analysis of Hotspots and Cutting-edge Trends in Mental Health among Middle School Students Research [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(07): 853-862. |
| [15] | ZHANG Peng, LIU Lidi, LIAO Xiaoyang, WU Jia, YANG Ziyu, ZHANG Yalin. The Job Satisfaction and Influencing Factors among General Practitioners in Primary Healthcare Institutions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(07): 869-874. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||