中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 1761-1774.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0645
所属专题: 神经系统疾病最新文章合集; 脑健康最新研究合集
收稿日期:2023-05-24
修回日期:2023-12-08
出版日期:2024-05-15
发布日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
陈会生
作者贡献:
牛靖元、于嘉祥负责文章的构思与设计,文献筛选与提取,撰写论文;陈会生负责文章的质量控制及审校,对文章整体负责;于嘉祥、崔钰负责数据处理、论文的修订。
基金资助:
NIU Jingyuan1, CHEN Huisheng2,*( ), YU Jiaxiang1, CUI Yu2
), YU Jiaxiang1, CUI Yu2
Received:2023-05-24
Revised:2023-12-08
Published:2024-05-15
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
CHEN Huisheng
摘要: 背景 急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)是一种严重的脑血管疾病,给社会和患者造成了沉重的负担。川芎嗪类注射液已被广泛用于AIS的治疗,且疗效明显,但目前还缺乏川芎嗪类注射液之间直接或间接比较。 目的 系统评价川芎嗪类注射液辅助治疗72 h内AIS的疗效性和安全性。 方法 计算机检索中国知网(CNKI)、万方数据知识服务平台、维普网(VIP)、PubMed、Cochrane Library、Embase和Web of Science数据库中有关川芎嗪类注射液治疗AIS的随机对照试验,检索时限从建库至2023年4月。由2位研究员独立筛选文献、提取资料并用Cochrane评价工具对文献进行质量评价,采用RevMan 5.3、Stata 17、Addis及RStudio软件进行统计分析,比较不同川芎嗪类注射液的疗效及安全性差异并进行排序。 结果 共纳入71篇文献,总样本量7 304例,干预措施包括:丹参川芎嗪注射液(DSCXQ)、参芎葡萄糖注射液(SXPTT)、杏芎氯化钠注射液(XXLHN)、磷酸川芎嗪注射液(LSCXQ)和盐酸川芎嗪注射液(YSCXQ)分别联合常规西医治疗(CT)及单独CT。直接Meta分析结果显示:川芎嗪类注射液联合CT的总有效率、美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(NIHSS)评分、纤维蛋白原水平、不良反应发生率均优于单独CT(P<0.05)。网状Meta分析结果显示:在总有效率方面,累积概率排序为:SXPTT+CT(0.60)>YSCXQ+CT(0.20)>LSCXQ+CT(0.15)>DSCXQ+CT(0.03)>XXLHN+CT(0.02)>CT(0);在降低NIHSS评分方面,累积概率排序为:SXPTT+CT(0.55)>XXLHN+CT(0.26)>YSCXQ+CT(0.12)>DSCXQ+CT(0.07)>CT(0);在降低纤维蛋白原水平方面,累积概率排序为:XXLHN+CT(0.32)>LSCXQ+CT(0.22)>DSCXQ+CT(0.17)>SXPTT+CT(0.15)>YSCXQ+CT(0.14)>CT(0);在安全性方面,累积概率排序为:SXPTT+CT(0.79)>XXLHN+CT(0.13)>CT(0.04)>DSCXQ+CT(0.03)>YSCXQ+CT(0.01)。 结论 川芎嗪类注射液辅助治疗AIS疗效显著、安全性好,其中参芎葡萄糖注射液在总有效率方面和改善NIHSS评分方面最佳、不良反应最少;杏芎氯化钠注射液在降低纤维蛋白原水平方面最有优势。
| 步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| 1 | cerebral ischemic stroke [MeSH Terms] |
| 2 | acute ischemic stroke [Title/Abstract] |
| 3 | stroke *[Title/Abstract] |
| 4 | apoplexy *[Title/Abstract] |
| 5 | 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 |
| 6 | traditional Chinese medicine [MeSH Terms] |
| 7 | traditional Chinese medicine injection [Title/Abstract] |
| 8 | TCM [Title/Abstract] |
| 9 | TCMI [Title/Abstract] |
| 10 | 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 |
| 11 | randomized,controlled trial [MeSH Terms] |
| 12 | randomized controlled trial [Title/Abstract] |
| 13 | clinical trial [Title/Abstract] |
| 14 | clinical study [Title/Abstract] |
| 15 | placebo [Title/Abstract] |
| 16 | groups [Title/Abstract] |
| 17 | 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 |
| 18 | 5 and 10 and 17 |
表1 PubMed检索策略
Table 1 PubMed search strategy
| 步骤 | 检索式 |
|---|---|
| 1 | cerebral ischemic stroke [MeSH Terms] |
| 2 | acute ischemic stroke [Title/Abstract] |
| 3 | stroke *[Title/Abstract] |
| 4 | apoplexy *[Title/Abstract] |
| 5 | 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 |
| 6 | traditional Chinese medicine [MeSH Terms] |
| 7 | traditional Chinese medicine injection [Title/Abstract] |
| 8 | TCM [Title/Abstract] |
| 9 | TCMI [Title/Abstract] |
| 10 | 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 |
| 11 | randomized,controlled trial [MeSH Terms] |
| 12 | randomized controlled trial [Title/Abstract] |
| 13 | clinical trial [Title/Abstract] |
| 14 | clinical study [Title/Abstract] |
| 15 | placebo [Title/Abstract] |
| 16 | groups [Title/Abstract] |
| 17 | 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 |
| 18 | 5 and 10 and 17 |
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 样本量(例) | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 病程(h) | 干预措施 | 疗程(周) | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | T | C | T | C | |||||
| 杨敏[ | 2022 | 42 | 42 | 22/19 | 22/20 | 47~76 | 48~77 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 王飞[ | 2022 | 50 | 50 | 28/22 | 28/22 | 41~75 | ≤69 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | |
| 董琦[ | 2020 | 43 | 43 | 19/24 | 21/22 | 42~69 | ≤49 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② | |
| 鹿滨麒[ | 2021 | 40 | 40 | 24/16 | 23/17 | 41~75 | 40~76 | ≤70 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 赵冬太[ | 2021 | 50 | 47 | 27/23 | 25/22 | 60~79 | 60~78 | ≤6 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 张叶飞[ | 2020 | 43 | 43 | 25/18 | 24/19 | 55~76 | 54~75 | ≤45 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 眭晨燕[ | 2019 | 40 | 40 | 19/21 | 18/22 | 41~79 | 42~80 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 李丹琪[ | 2018 | 40 | 40 | 24/16 | 23/17 | 59~74 | 57~73 | ≤12 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 张跃栓[ | 2018 | 60 | 60 | 31/29 | 33/27 | 42~75 | 43~76 | ≤68 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 宋会英[ | 2018 | 48 | 48 | 26/22 | 27/21 | 42~78 | 43~80 | ≤6 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ |
| 张大为[ | 2017 | 43 | 43 | 52/34 | 48~76 | 48~76 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ | |
| 段高锋[ | 2017 | 50 | 50 | 27/23 | 30/20 | 42~72 | 43~68 | ≤22 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 李婷[ | 2017 | 105 | 98 | 61/44 | 59/39 | 47~79 | 46~77 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 江乾[ | 2017 | 59 | 59 | 34/25 | 33/26 | 43~72 | 45~73 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ③ |
| 杨红芳[ | 2017 | 43 | 43 | 24/19 | 22/21 | 45~75 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ | |
| 宋秋英[ | 2017 | 50 | 50 | 28/22 | 27/23 | 47~72 | 48~71 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 任志学[ | 2016 | 48 | 48 | 31/17 | 28/20 | 45~78 | 47~79 | ≤12 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 屈杰[ | 2016 | 75 | 75 | 41/34 | 42/33 | 42~78 | 41~79 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 张宝慧[ | 2016 | 55 | 55 | 31/24 | 59~76 | 59~74 | ≤36 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① | |
| 李春丽[ | 2016 | 84 | 84 | 54/30 | 52/32 | 62~79 | 61~77 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 王雪梅[ | 2016 | 56 | 56 | 29/27 | 31/25 | 49~72 | 51~73 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 蓝宇[ | 2015 | 40 | 40 | 21/19 | 20/20 | 54~72 | 56~70 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 王明朋[ | 2015 | 64 | 64 | 36/28 | 35/29 | 46~75 | 47~74 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 常良[ | 2015 | 35 | 35 | 41/29 | 46~74 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | ||
| 季巍伟[ | 2015 | 70 | 70 | 39/31 | 38/32 | 41~76 | 40~77 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 刘梅[ | 2014 | 68 | 68 | 39/29 | 40/28 | 40~74 | 41~76 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 林翔东[ | 2014 | 43 | 43 | 30/13 | 27/16 | 45~80 | 41~78 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 赵淑萍[ | 2013 | 55 | 55 | 63/47 | 55~72 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ | ||
| 王天秋[ | 2013 | 40 | 40 | 24/18 | 22/18 | 52~71 | 54~73 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ |
| 雷进[ | 2012 | 30 | 30 | 18/12 | 20/10 | 45~79 | 46~80 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 张勇[ | 2012 | 40 | 40 | 25/15 | 27/13 | 35~80 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ | |
| 刘昌灵[ | 2011 | 34 | 34 | 19/15 | 20/13 | 41~79 | 40~80 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 李海云[ | 2011 | 74 | 74 | NA | NA | 51~78 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | |
| 杨正宇[ | 2010 | 31 | 31 | 21/10 | 20/11 | 50~66 | 55~65 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 林培贤[ | 2009 | 30 | 30 | 19/11 | 20/10 | 38~78 | 35~80 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 李研[ | 2021 | 54 | 48 | 33/21 | 28/20 | 54~76 | ≤60 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ | |
| 闫纪琳[ | 2021 | 83 | 82 | 51/32 | 53/29 | 54~75 | ≤20 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ | |
| 杨贤科[ | 2021 | 60 | 60 | 39/21 | 41/19 | 51~69 | 51~71 | ≤22 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 杨淑娟[ | 2020 | 134 | 134 | 69/65 | 72/62 | 45~77 | 48~76 | ≤72 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 刘琴兰[ | 2022 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 15/15 | 60~80 | 60~79 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 宋元良[ | 2021 | 49 | 49 | 30/19 | 31/18 | 51~75 | 50~77 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 尤晓涵[ | 2020 | 38 | 38 | 21/17 | 20/18 | 60~80 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③④ | |
| 笪正[ | 2020 | 20 | 20 | 11/9 | 12/8 | 54~75 | 54~74 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 张玉彬[ | 2019 | 41 | 41 | 24/17 | 23/18 | 42~79 | 42~78 | ≤6 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 刘其镇[ | 2019 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 18/12 | 43~70 | 44~71 | ≤13 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 田华宜[ | 2019 | 52 | 51 | 28/24 | 28/23 | 48~69 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ | |
| 吴文斌[ | 2017 | 38 | 38 | 24/14 | 25/13 | 53~80 | 52~80 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王朝阳[ | 2015 | 38 | 38 | 26/12 | 28/10 | 42~76 | 41~75 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 孙红国[ | 2015 | 120 | 120 | 71/49 | 61/53 | 18~75 | ≤12 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ | |
| 章玉华[ | 2013 | 34 | 34 | 19/15 | 20/14 | 47~78 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① | |
| 王小平[ | 2013 | 32 | 32 | 20/12 | 21/11 | 41~70 | 42~70 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 孙寒静[ | 2013 | 39 | 39 | 22/17 | 19/20 | 40~70 | 40~79 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 严春开[ | 2012 | 40 | 40 | 29/11 | 27/13 | 45~70 | 53~70 | ≤49 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 卢万向[ | 2010 | 50 | 50 | 34/16 | 36/14 | 50~80 | 51~80 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 汤美霞[ | 2005 | 68 | 68 | 46/22 | 44/24 | 48~78 | 53~77 | ≤46 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 谷元奎[ | 2002 | 65 | 62 | 36/29 | 34/28 | 41~80 | 39~79 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ |
| 杨政治[ | 2010 | 52 | 50 | 27/25 | 27/23 | 55~73 | 54~74 | ≤72 | LSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王英莲[ | 2009 | 21 | 21 | 12/9 | 9/12 | 45~73 | 46~72 | ≤72 | LSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ③ |
| 樊海梅[ | 2022 | 53 | 53 | 31/22 | 33/20 | 45~76 | 47~75 | ≤19 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 李娜[ | 2019 | 53 | 53 | 27/26 | 28/25 | 43~77 | 43~76 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 杜志先[ | 2018 | 60 | 60 | 34/26 | 30/30 | 40~65 | ≤36 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①② | |
| 闫伟丽[ | 2017 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 14/16 | 55~79 | 53~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 宋卫红[ | 2017 | 38 | 38 | 21/17 | 23/15 | 43~72 | 41~76 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 秦连发[ | 2017 | 45 | 45 | 26/19 | 25/20 | 58~79 | 57~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③ |
| 管友红[ | 2017 | 40 | 36 | 22/18 | 18/18 | 40~79 | 45~76 | ≤24 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 孙培丽[ | 2017 | 45 | 45 | 26/19 | 24/21 | 47~73 | 45~74 | ≤11 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 牟鸣[ | 2015 | 65 | 65 | 39/26 | 36/29 | 58~79 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①③ | |
| 张宁[ | 2015 | 50 | 50 | 38/12 | 42/8 | 46~78 | 56~80 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王琪[ | 2013 | 81 | 81 | 52/29 | 51/30 | 43~74 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ | |
| 李啬夫[ | 2008 | 70 | 60 | 42/28 | 34/26 | 45~75 | 41~71 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | 2 | ① |
| 李海军[ | 2014 | 50 | 50 | 26/24 | 29/21 | 35~77 | 32~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | YSCXQ+CT | 2 | ① |
表2 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of the included literature
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 样本量(例) | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 病程(h) | 干预措施 | 疗程(周) | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | T | C | T | C | |||||
| 杨敏[ | 2022 | 42 | 42 | 22/19 | 22/20 | 47~76 | 48~77 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 王飞[ | 2022 | 50 | 50 | 28/22 | 28/22 | 41~75 | ≤69 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | |
| 董琦[ | 2020 | 43 | 43 | 19/24 | 21/22 | 42~69 | ≤49 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② | |
| 鹿滨麒[ | 2021 | 40 | 40 | 24/16 | 23/17 | 41~75 | 40~76 | ≤70 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 赵冬太[ | 2021 | 50 | 47 | 27/23 | 25/22 | 60~79 | 60~78 | ≤6 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 张叶飞[ | 2020 | 43 | 43 | 25/18 | 24/19 | 55~76 | 54~75 | ≤45 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 眭晨燕[ | 2019 | 40 | 40 | 19/21 | 18/22 | 41~79 | 42~80 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 李丹琪[ | 2018 | 40 | 40 | 24/16 | 23/17 | 59~74 | 57~73 | ≤12 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 张跃栓[ | 2018 | 60 | 60 | 31/29 | 33/27 | 42~75 | 43~76 | ≤68 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 宋会英[ | 2018 | 48 | 48 | 26/22 | 27/21 | 42~78 | 43~80 | ≤6 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ |
| 张大为[ | 2017 | 43 | 43 | 52/34 | 48~76 | 48~76 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ | |
| 段高锋[ | 2017 | 50 | 50 | 27/23 | 30/20 | 42~72 | 43~68 | ≤22 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 李婷[ | 2017 | 105 | 98 | 61/44 | 59/39 | 47~79 | 46~77 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 江乾[ | 2017 | 59 | 59 | 34/25 | 33/26 | 43~72 | 45~73 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ③ |
| 杨红芳[ | 2017 | 43 | 43 | 24/19 | 22/21 | 45~75 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ | |
| 宋秋英[ | 2017 | 50 | 50 | 28/22 | 27/23 | 47~72 | 48~71 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 任志学[ | 2016 | 48 | 48 | 31/17 | 28/20 | 45~78 | 47~79 | ≤12 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 屈杰[ | 2016 | 75 | 75 | 41/34 | 42/33 | 42~78 | 41~79 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 张宝慧[ | 2016 | 55 | 55 | 31/24 | 59~76 | 59~74 | ≤36 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① | |
| 李春丽[ | 2016 | 84 | 84 | 54/30 | 52/32 | 62~79 | 61~77 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 王雪梅[ | 2016 | 56 | 56 | 29/27 | 31/25 | 49~72 | 51~73 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 蓝宇[ | 2015 | 40 | 40 | 21/19 | 20/20 | 54~72 | 56~70 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 王明朋[ | 2015 | 64 | 64 | 36/28 | 35/29 | 46~75 | 47~74 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ |
| 常良[ | 2015 | 35 | 35 | 41/29 | 46~74 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | ||
| 季巍伟[ | 2015 | 70 | 70 | 39/31 | 38/32 | 41~76 | 40~77 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 刘梅[ | 2014 | 68 | 68 | 39/29 | 40/28 | 40~74 | 41~76 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 林翔东[ | 2014 | 43 | 43 | 30/13 | 27/16 | 45~80 | 41~78 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 赵淑萍[ | 2013 | 55 | 55 | 63/47 | 55~72 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ | ||
| 王天秋[ | 2013 | 40 | 40 | 24/18 | 22/18 | 52~71 | 54~73 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ |
| 雷进[ | 2012 | 30 | 30 | 18/12 | 20/10 | 45~79 | 46~80 | ≤24 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 张勇[ | 2012 | 40 | 40 | 25/15 | 27/13 | 35~80 | ≤48 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②④ | |
| 刘昌灵[ | 2011 | 34 | 34 | 19/15 | 20/13 | 41~79 | 40~80 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 李海云[ | 2011 | 74 | 74 | NA | NA | 51~78 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ | |
| 杨正宇[ | 2010 | 31 | 31 | 21/10 | 20/11 | 50~66 | 55~65 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 林培贤[ | 2009 | 30 | 30 | 19/11 | 20/10 | 38~78 | 35~80 | ≤72 | DSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 李研[ | 2021 | 54 | 48 | 33/21 | 28/20 | 54~76 | ≤60 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③④ | |
| 闫纪琳[ | 2021 | 83 | 82 | 51/32 | 53/29 | 54~75 | ≤20 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ | |
| 杨贤科[ | 2021 | 60 | 60 | 39/21 | 41/19 | 51~69 | 51~71 | ≤22 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 杨淑娟[ | 2020 | 134 | 134 | 69/65 | 72/62 | 45~77 | 48~76 | ≤72 | XXLHN+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 刘琴兰[ | 2022 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 15/15 | 60~80 | 60~79 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①② |
| 宋元良[ | 2021 | 49 | 49 | 30/19 | 31/18 | 51~75 | 50~77 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 尤晓涵[ | 2020 | 38 | 38 | 21/17 | 20/18 | 60~80 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③④ | |
| 笪正[ | 2020 | 20 | 20 | 11/9 | 12/8 | 54~75 | 54~74 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 张玉彬[ | 2019 | 41 | 41 | 24/17 | 23/18 | 42~79 | 42~78 | ≤6 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 刘其镇[ | 2019 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 18/12 | 43~70 | 44~71 | ≤13 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 田华宜[ | 2019 | 52 | 51 | 28/24 | 28/23 | 48~69 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ | |
| 吴文斌[ | 2017 | 38 | 38 | 24/14 | 25/13 | 53~80 | 52~80 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王朝阳[ | 2015 | 38 | 38 | 26/12 | 28/10 | 42~76 | 41~75 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 孙红国[ | 2015 | 120 | 120 | 71/49 | 61/53 | 18~75 | ≤12 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ | |
| 章玉华[ | 2013 | 34 | 34 | 19/15 | 20/14 | 47~78 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① | |
| 王小平[ | 2013 | 32 | 32 | 20/12 | 21/11 | 41~70 | 42~70 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ② |
| 孙寒静[ | 2013 | 39 | 39 | 22/17 | 19/20 | 40~70 | 40~79 | ≤72 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 严春开[ | 2012 | 40 | 40 | 29/11 | 27/13 | 45~70 | 53~70 | ≤49 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 卢万向[ | 2010 | 50 | 50 | 34/16 | 36/14 | 50~80 | 51~80 | ≤48 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 汤美霞[ | 2005 | 68 | 68 | 46/22 | 44/24 | 48~78 | 53~77 | ≤46 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 谷元奎[ | 2002 | 65 | 62 | 36/29 | 34/28 | 41~80 | 39~79 | ≤24 | YSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ①③④ |
| 杨政治[ | 2010 | 52 | 50 | 27/25 | 27/23 | 55~73 | 54~74 | ≤72 | LSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王英莲[ | 2009 | 21 | 21 | 12/9 | 9/12 | 45~73 | 46~72 | ≤72 | LSCXQ+CT | CT | 2 | ③ |
| 樊海梅[ | 2022 | 53 | 53 | 31/22 | 33/20 | 45~76 | 47~75 | ≤19 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①②④ |
| 李娜[ | 2019 | 53 | 53 | 27/26 | 28/25 | 43~77 | 43~76 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 杜志先[ | 2018 | 60 | 60 | 34/26 | 30/30 | 40~65 | ≤36 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①② | |
| 闫伟丽[ | 2017 | 30 | 30 | 16/14 | 14/16 | 55~79 | 53~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ |
| 宋卫红[ | 2017 | 38 | 38 | 21/17 | 23/15 | 43~72 | 41~76 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ②③ |
| 秦连发[ | 2017 | 45 | 45 | 26/19 | 25/20 | 58~79 | 57~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①②③ |
| 管友红[ | 2017 | 40 | 36 | 22/18 | 18/18 | 40~79 | 45~76 | ≤24 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 孙培丽[ | 2017 | 45 | 45 | 26/19 | 24/21 | 47~73 | 45~74 | ≤11 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①④ |
| 牟鸣[ | 2015 | 65 | 65 | 39/26 | 36/29 | 58~79 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ①③ | |
| 张宁[ | 2015 | 50 | 50 | 38/12 | 42/8 | 46~78 | 56~80 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ① |
| 王琪[ | 2013 | 81 | 81 | 52/29 | 51/30 | 43~74 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | CT | 2 | ④ | |
| 李啬夫[ | 2008 | 70 | 60 | 42/28 | 34/26 | 45~75 | 41~71 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | 2 | ① |
| 李海军[ | 2014 | 50 | 50 | 26/24 | 29/21 | 35~77 | 32~78 | ≤72 | SXPTT+CT | YSCXQ+CT | 2 | ① |
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 26[ | P=1.00,I2=0 | 3.63(2.90~4.56) | <0.000 01 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 4[ | P=0.58,I2=0 | 2.71(1.66~4.42) | <0.000 1 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 10[ | P=0.94,I2=0 | 5.17(3.26~8.22) | <0.000 01 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 7[ | P=0.98,I2=0 | 3.81(2.40~6.04) | <0.000 01 |
| LSCXQ+CT与CT | 1[ | 6.18(1.91~20.04) | 0.002 | |
| SXPTT+CT与LSCXQ+CT | 1[ | 1.91(0.83~4.42) | 0.13 | |
| SXPTT+CT与YSCXQ+CT | 1[ | 4.04(1.22~13.43) | 0.002 |
表3 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS总有效率的直接Meta分析及异质性检验
Table 3 Direct Meta-analysis and heterogeneity test of total effective rates of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 26[ | P=1.00,I2=0 | 3.63(2.90~4.56) | <0.000 01 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 4[ | P=0.58,I2=0 | 2.71(1.66~4.42) | <0.000 1 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 10[ | P=0.94,I2=0 | 5.17(3.26~8.22) | <0.000 01 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 7[ | P=0.98,I2=0 | 3.81(2.40~6.04) | <0.000 01 |
| LSCXQ+CT与CT | 1[ | 6.18(1.91~20.04) | 0.002 | |
| SXPTT+CT与LSCXQ+CT | 1[ | 1.91(0.83~4.42) | 0.13 | |
| SXPTT+CT与YSCXQ+CT | 1[ | 4.04(1.22~13.43) | 0.002 |
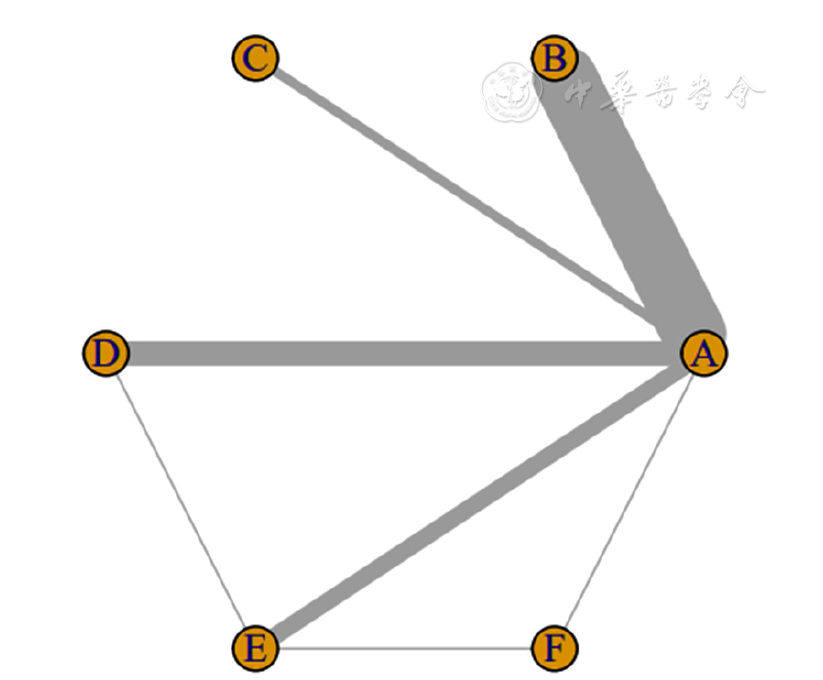
图3 总有效率的证据网络图注:A为常规西医治疗,B为丹参川芎嗪注射液剂联合常规西医治疗,C为杏芎氯化钠注射液联合常规西医治疗,D为盐酸川芎嗪注射液联合常规西医治疗,E为参芎葡萄糖注射液联合常规西医治疗,F为磷酸川芎嗪注射液联合常规西医治疗。
Figure 3 Evidence network diagram for efficiency
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 1.51(0.78~3.02) | 1.00 | |||
| SXPTT+CT | 0.82(0.46~1.44) | 0.54(0.27~1.05) | 1.00 | ||
| LSCXQ+CT | 1.14(0.50~2.56) | 0.75(0.29~1.77) | 1.40(0.70~2.81) | 1.00 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 1.17(0.72~1.92) | 0.77(0.44~1.37) | 1.43(0.88~2.41) | 1.03(0.49~2.21) | 1.00 |
| CT | 4.36(2.84~6.71) | 2.87(1.72~4.71) | 5.32(3.42~8.45) | 3.81(1.87~7.92) | 3.72(2.91~4.70) |
表4 不同川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗AIS总有效率的网状Meta分析[OR(95%CI)]
Table 4 Network Meta-analysis of the total effective rates of different types of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 1.51(0.78~3.02) | 1.00 | |||
| SXPTT+CT | 0.82(0.46~1.44) | 0.54(0.27~1.05) | 1.00 | ||
| LSCXQ+CT | 1.14(0.50~2.56) | 0.75(0.29~1.77) | 1.40(0.70~2.81) | 1.00 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 1.17(0.72~1.92) | 0.77(0.44~1.37) | 1.43(0.88~2.41) | 1.03(0.49~2.21) | 1.00 |
| CT | 4.36(2.84~6.71) | 2.87(1.72~4.71) | 5.32(3.42~8.45) | 3.81(1.87~7.92) | 3.72(2.91~4.70) |
| 干预措施 | 直接 | 间接 | 网状 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SXPTT+CT与YSCXQ+CT | 4.50(1.40~19.00) | 0.82(0.43~1.50) | 1.20(0.69~2.20) | 0.013 7 |
| LSCXQ+CT与SXPTT+CT | 0.51(0.20~1.20) | 1.30(0.38~5.60) | 0.69(0.32~1.50) | 0.235 8 |
| CT与YSCXQ+CT | 1.70(1.20~2.20) | 0.03(-1.30~1.20) | 1.50(1.10~1.90) | 0.011 0 |
| CT与SXPTT+CT | 1.40(0.93~1.80) | 2.90(1.90~4.00) | 1.70(1.22~2.20) | 0.005 0 |
| CT与LSCXQ+CT | 1.90(0.76~3.40) | 0.93(-0.07~2.00) | 1.30(0.58~2.10) | 0.236 9 |
表5 不同川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗AIS总有效率的节点劈裂法结果[OR(95%CI)]
Table 5 Node splitting method results of total effective rate of different types of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy
| 干预措施 | 直接 | 间接 | 网状 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SXPTT+CT与YSCXQ+CT | 4.50(1.40~19.00) | 0.82(0.43~1.50) | 1.20(0.69~2.20) | 0.013 7 |
| LSCXQ+CT与SXPTT+CT | 0.51(0.20~1.20) | 1.30(0.38~5.60) | 0.69(0.32~1.50) | 0.235 8 |
| CT与YSCXQ+CT | 1.70(1.20~2.20) | 0.03(-1.30~1.20) | 1.50(1.10~1.90) | 0.011 0 |
| CT与SXPTT+CT | 1.40(0.93~1.80) | 2.90(1.90~4.00) | 1.70(1.22~2.20) | 0.005 0 |
| CT与LSCXQ+CT | 1.90(0.76~3.40) | 0.93(-0.07~2.00) | 1.30(0.58~2.10) | 0.236 9 |
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 19[ | P<0.0001,I2=98% | -3.65(-4.33~-2.98) | <0.000 01 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 4[ | P<0.0001,I2=96% | -3.87(-5.66~-2.07) | <0.000 1 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 9[ | P<0.0001,I2=94% | -3.49(-4.64~-2.34) | <0.000 01 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 4[ | P<0.0001,I2=99% | -4.48(-8.45~-0.51) | <0.03 |
表6 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS患者NIHSS评分的直接Meta分析及异质性检验
Table 6 Direct Meta-analysis and heterogeneity test of NIHSS score of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 19[ | P<0.0001,I2=98% | -3.65(-4.33~-2.98) | <0.000 01 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 4[ | P<0.0001,I2=96% | -3.87(-5.66~-2.07) | <0.000 1 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 9[ | P<0.0001,I2=94% | -3.49(-4.64~-2.34) | <0.000 01 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 4[ | P<0.0001,I2=99% | -4.48(-8.45~-0.51) | <0.03 |
| 干预措施 | 剔除文献(篇) | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | 异质性可能来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 7[ | 12[ | P<0.12,I2=46% | -1.82(-2.21~-1.42) | 年龄、病程 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 2[ | 2[ | P<0.27,I2=18% | -3.51(-4.01~-3.01) | 性别、病程 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 3[ | 6[ | P<0.10,I2=45% | -2.73(-3.29~-2.17) | 病程 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 1[ | 3[ | P<0.98,I2=0 | -2.68(-3.18~-2.18) | 病程 |
表7 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS患者NIHSS评分的敏感性分析
Table 7 Sensitivity analysis of NIHSS score of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 剔除文献(篇) | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | 异质性可能来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 7[ | 12[ | P<0.12,I2=46% | -1.82(-2.21~-1.42) | 年龄、病程 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 2[ | 2[ | P<0.27,I2=18% | -3.51(-4.01~-3.01) | 性别、病程 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 3[ | 6[ | P<0.10,I2=45% | -2.73(-3.29~-2.17) | 病程 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 1[ | 3[ | P<0.98,I2=0 | -2.68(-3.18~-2.18) | 病程 |
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 0.28(-2.58~3.11) | 0 | ||
| SXPTT+CT | 0.96(-1.95~3.80) | 0.69(-2.67~3.99) | 0 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | -0.07(-1.99~1.87) | -0.34(-2.92~2.23) | -1.02(-3.65~1.65) | 0 |
| CT | -3.57(-5.17~-1.97) | -3.84(-6.18~-1.51) | -4.52(-6.89~-2.13) | -3.50(-4.59~-2.41) |
表8 不同川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗AIS患者NIHSS评分的网状Meta分析[MD(95%CI)]
Table 8 Network Meta-analysis of NIHSS score of different types of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional Western medical therapy
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 0.28(-2.58~3.11) | 0 | ||
| SXPTT+CT | 0.96(-1.95~3.80) | 0.69(-2.67~3.99) | 0 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | -0.07(-1.99~1.87) | -0.34(-2.92~2.23) | -1.02(-3.65~1.65) | 0 |
| CT | -3.57(-5.17~-1.97) | -3.84(-6.18~-1.51) | -4.52(-6.89~-2.13) | -3.50(-4.59~-2.41) |
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 8[ | P<0.000 1,I2=96% | -0.86(-1.26~-0.46) | <0.000 1 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 1[ | -0.84(-1.01~-0.67) | <0.000 01 | |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 5[ | P<0.000 1,I2=99% | -0.81(-1.49~-0.14) | <0.02 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.09,I2=59% | -0.77(-1.13~-0.41) | <0.000 01 |
| LSCXQ+CT与CT | 1[ | -0.69(-0.91~-0.47) | 0.09 |
表9 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS患者纤维蛋白原水平的直接Meta分析及异质性检验
Table 9 Direct Meta-analysis and heterogeneity test of fibrinogen level of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 8[ | P<0.000 1,I2=96% | -0.86(-1.26~-0.46) | <0.000 1 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 1[ | -0.84(-1.01~-0.67) | <0.000 01 | |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 5[ | P<0.000 1,I2=99% | -0.81(-1.49~-0.14) | <0.02 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.09,I2=59% | -0.77(-1.13~-0.41) | <0.000 01 |
| LSCXQ+CT与CT | 1[ | -0.69(-0.91~-0.47) | 0.09 |
| 干预措施 | 剔除文献(篇) | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | 异质性可能来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 4[ | 4[ | P=0.40,I2=41% | -0.79(-0.94~-0.65) | 年龄、卒中程度 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 2[ | 3[ | P=0.28,I2=22% | -1.03(-1.13~-0.92) | 年龄、性别 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 1[ | 2[ | P=0.39,I2=0 | -0.97(-1.21~-0.72) | 性别 |
表10 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS患者纤维蛋白原水平的敏感性分析
Table 10 Sensitivity analysis of fibrinogen level of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 剔除文献(篇) | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | MD(95%CI) | 异质性可能来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 4[ | 4[ | P=0.40,I2=41% | -0.79(-0.94~-0.65) | 年龄、卒中程度 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 2[ | 3[ | P=0.28,I2=22% | -1.03(-1.13~-0.92) | 年龄、性别 |
| SXPTT+CT与CT | 1[ | 2[ | P=0.39,I2=0 | -0.97(-1.21~-0.72) | 性别 |
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 0.05(-1.34~1.40) | 0 | |||
| SXPTT+CT | -0.06(-1.03~0.86) | -0.10(-1.59~1.38) | 0 | ||
| LSCXQ+CT | -0.11(-1.48~1.25) | -0.18(-1.90~1.63) | -0.05(-1.46~1.42) | 0 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 0.05(-0.67~0.76) | -0.00(-1.32~1.36) | 0.13(-0.75~1.01) | 0.18(-1.16~1.46) | 0 |
| CT | -0.81(-1.38~0.25) | -0.86(-2.08~0.40) | -0.74(-1.52~0.03) | -0.68(-1.94~0.52) | -0.86(-1.30~-0.42) |
表11 不同川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗AIS患者纤维蛋白原水平的网状Meta分析[MD(95%CI)]
Table 11 Network Meta-analysis of fibrinogen level of different types of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | LSCXQ+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 0.05(-1.34~1.40) | 0 | |||
| SXPTT+CT | -0.06(-1.03~0.86) | -0.10(-1.59~1.38) | 0 | ||
| LSCXQ+CT | -0.11(-1.48~1.25) | -0.18(-1.90~1.63) | -0.05(-1.46~1.42) | 0 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 0.05(-0.67~0.76) | -0.00(-1.32~1.36) | 0.13(-0.75~1.01) | 0.18(-1.16~1.46) | 0 |
| CT | -0.81(-1.38~0.25) | -0.86(-2.08~0.40) | -0.74(-1.52~0.03) | -0.68(-1.94~0.52) | -0.86(-1.30~-0.42) |
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 16[ | P=0.70,I2=35% | 1.21(0.76~1.92) | 0.42 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 2[ | P=0.37,I2=0 | 1.20(0.36~4.02) | 0.77 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.42,I2=24% | 2.04(0.81~5.17) | 0.13 |
| SXPTT +CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.89,I2=0 | 0.48(0.16~1.44) | 0.19 |
表12 川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗和常规西医治疗AIS患者不良反应的直接Meta分析及异质性检验
Table 12 Direct Meta-analysis and heterogeneity test of adverse reactions of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy and conventional western medical therapy alone
| 干预措施 | 文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSCXQ+CT与CT | 16[ | P=0.70,I2=35% | 1.21(0.76~1.92) | 0.42 |
| XXLHN+CT与CT | 2[ | P=0.37,I2=0 | 1.20(0.36~4.02) | 0.77 |
| YSCXQ+CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.42,I2=24% | 2.04(0.81~5.17) | 0.13 |
| SXPTT +CT与CT | 3[ | P=0.89,I2=0 | 0.48(0.16~1.44) | 0.19 |
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 2.09(0.29~20.38) | 1 | ||
| SXPTT+CT | 5.85(0.95~52.13) | 2.71(0.35~24.51) | 1 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 1.98(0.50~10.45) | 0.94(0.16~5.20) | 0.34(0.07~1.54) | 1 |
| CT | 2.59(0.76~12.15) | 1.21(0.25~5.98) | 0.45(0.10~1.71) | 1.30(0.67~2.57) |
表13 不同川芎嗪类注射液联合常规西医治疗AIS患者不良反应的网状Meta分析[OR(95%CI)]
Table 13 Network Meta-analysis of adverse reactions of different types of ligustrazine injection combined with conventional western medical therapy
| 干预措施 | YSCXQ+CT | XXLHN+CT | SXPTT+CT | DSCXQ+CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXLHN+CT | 2.09(0.29~20.38) | 1 | ||
| SXPTT+CT | 5.85(0.95~52.13) | 2.71(0.35~24.51) | 1 | |
| DSCXQ+CT | 1.98(0.50~10.45) | 0.94(0.16~5.20) | 0.34(0.07~1.54) | 1 |
| CT | 2.59(0.76~12.15) | 1.21(0.25~5.98) | 0.45(0.10~1.71) | 1.30(0.67~2.57) |
| [1] | |
| [2] |
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global,regional,and national burden of stroke and its risk factors,1990-2019:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Neurol,2021,20(10):795-820. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0.
|
| [3] |
中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组,彭斌,等. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2018,51(9):666-682.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
胡灵芝. 静脉溶栓联合高压氧治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效评估[J]. 浙江医学,2019,41(11):1204-1206,1217. DOI:10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2019.41.11.2017-1522.
|
| [7] |
李萌青,王宇,张云云. 中药注射剂治疗急性缺血性脑卒中的临床研究进展[J]. 中国中医急症,2019,28(6):1112-1116. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2019.06.052.
|
| [8] |
柴学,黄清玲,黄雨,等. 急性脑梗死患者凝血功能与脑血流量的关系[J]. 临床神经病学杂志,2021,34(4):297-299. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1648.2021.04.016.
|
| [9] |
熊百炼,李慧. 曲克芦丁脑蛋白水解物联合疏血通治疗急性脑梗死临床疗效观察[J]. 中国药物经济学,2014,9(3):230-231.
|
| [10] |
顾任钧,李子赟,李鹏飞,等. 川芎嗪注射液对急性缺血性脑卒中疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 世界中医药,2020,15(19):2900-2909. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2020.19.012.
|
| [11] |
中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南撰写组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2010[J]. 中国全科医学,2011,14(35):4013-4017.
|
| [12] |
脑卒中患者临床神经功能缺损程度评分标准(1995)[J]. 中华神经科杂志,1996,29(6):381-383.
|
| [13] |
杨敏,张晶,杨柏新. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者的影响[J]. 中外医学研究,2022,20(10):40-43. DOI:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2022.10.011.
|
| [14] |
王飞. 丹参川芎嗪联合丁苯酞治疗急性缺血性卒中患者的效果[J]. 中国民康医学,2022,34(18):106-108. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2022.18.032.
|
| [15] |
董琦,富奇志. 丹参川芎嗪注射液对急性脑梗死患者血清TNF-α、hs-CRP、IL-6水平的影响[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2020,24(8):1238-1240. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2020.08.002.
|
| [16] |
鹿滨麒. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合丁苯酞氯化钠注射液治疗急性缺血性脑卒中的效果及对miRNA-145、miRNA-146a水平的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2021,6(9):139-141. DOI:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202109048.
|
| [17] |
赵冬太. 丹参川芎嗪注射液辅助阿替普酶对老年脑梗死急性期神经功能及血液流变学的影响[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2021,42(13):126-128.
|
| [18] |
张叶飞,周黎琴. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合阿托伐他汀钙片治疗糖尿病合并急性脑梗死临床研究[J]. 新中医,2020,52(6):74-77. DOI:10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2020.06.024.
|
| [19] |
眭晨燕,胡玲玲,王引明. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合阿加曲班对急性脑梗死患者D-二聚体及血清炎性细胞因子水平的影响[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2019,23(11):14-16,19. DOI:10.7619/jcmp.201911004.
|
| [20] |
李丹琪. 丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死疗效及对SOD、Hcy及神经功能恢复的影响[J]. 亚太传统医药,2018,14(6):175-176. DOI:10.11954/ytctyy.201806067.
|
| [21] |
张跃栓. 丹参川芎嗪配合依达拉奉和常规西药治疗急性脑梗死疗效及对血清IL-6、MMP9水平的影响[J]. 哈尔滨医药,2018,38(1):6-7.
|
| [22] |
宋会英. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合重组组织型纤溶酶原激活剂静脉溶栓对急性脑梗死患者NIHSS评分及血清神经元特异性烯醇化酶髓鞘碱性蛋白水平变化的影响[J]. 中国药物与临床,2018,18(11):2023-2025. DOI:10.11655/zgywylc2018.11.073.
|
| [23] |
张大为. 丹参川穹联合小剂量阿司匹林治疗急性脑梗死的预后观察[J]. 中国卫生工程学,2017,16(2):223-224,227. DOI:10.19937/j.issn.1671-4199.2017.02.038.
|
| [24] |
段高锋,曾韬. 丹参川芎嗪注射液辅治缺血性脑卒中的临床效果[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2017,2(34):121-122. DOI:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.201734059.
|
| [25] |
李婷,王煜,张立,等. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合阿托伐他汀治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J]. 现代药物与临床,2017,32(10):1872-1875. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.10.013.
|
| [26] |
江乾,范夏女,陈左平. 丹参川穹嗪辅助治疗急性脑梗死对血液流变学及炎性细胞因子的影响[J]. 当代医学,2017,23(12):62-64. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2017.12.027.
|
| [27] | |
| [28] |
宋秋英,方红丽,吴滨. 丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(S1):246-247.
|
| [29] |
任志学. 依达拉奉注射液联合丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2016,24(9):91-93. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2016.09.024.
|
| [30] |
屈杰,刘锋昌. 依达拉奉联合丹参川芎嗪治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效研究[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2016,1(24):112-113. DOI:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.2016.24.055.
|
| [31] |
张宝慧. 丹参川芎嗪辅助治疗急性脑梗死的疗效分析[J]. 大家健康(中旬版),2016,10(10):78.
|
| [32] |
李春丽,扎西草,孙燕辉. 丹参川芎嗪注射液对急性脑梗死老年患者血清血管细胞间黏附分子-1、细胞间黏附分子-1、内皮素-1和一氧化氮水平的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2016,25(19):2088-2090.
|
| [33] |
王雪梅,张孟列. 丹参川芎嗪注射液对急性脑梗死患者溶血磷脂酸、血浆内皮素及P选择素的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2016,25(19):2118-2120. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.19.023.
|
| [34] |
蓝宇,肖建新,郑天勇,等. 丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死的疗效及对溶血磷脂酸、P选择素的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2015,24(8):840-842. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2015.08.016.
|
| [35] |
王明朋,罗文成,杨金球. 依达拉奉联合丹参川芎嗪治疗急性脑梗死疗效观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2015,24(14):1533-1535. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2015.14.019.
|
| [36] | |
| [37] |
季巍伟,尤克,黄菊明. 脑梗死急性期丹参川芎嗪联合依达拉奉治疗的疗效观察[C]//2015年老年医学学术年会论文汇编. 杭州,2015:149.
|
| [38] |
刘梅. 依达拉奉单用、联用丹参川芎嗪治疗急性脑梗死疗效及安全性评估[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2014,23(19):2105-2107. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2014.19.022.
|
| [39] |
林翔东,吴红星,邵爱民. 丹参川芎嗪注射液对急性脑梗死患者的治疗作用及血清vasostatin-2、sICAM-1水平的影响[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2014,24(21):3079-3081.
|
| [40] | |
| [41] | |
| [42] |
雷进,罗丽华. 丹参川芎嗪联合尤瑞克林对急性脑梗死患者血浆内皮素的影响及疗效观察[J]. 中国医药指南,2012,10(35):287-288. DOI:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2012.35.482.
|
| [43] |
张勇,侯静,胡勇,等. 丹参川芎嗪注射液联合依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死临床观察[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2012,10(2):168-169. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2012.02.025.
|
| [44] |
刘昌灵. 丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死的疗效和对血流动力学的影响[J]. 中国医学创新,2011,8(5):88-89. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2011.05.053.
|
| [45] |
李海云. 早期使用丹参川芎嗪治疗急性脑梗死的临床观察[J]. 健康必读月刊,2011(4):45.
|
| [46] |
杨正宇,张红莲,罗晓惠. 丹参川芎嗪联合脑蛋白水解物治疗急性脑梗死31例疗效观察[J]. 云南中医中药杂志,2010,31(3):21-22. DOI:10.16254/j.cnki.53-1120/r.2010.03.060.
|
| [47] |
林培贤. 血瘀证型脑梗死患者急性期血浆LPA、CD62p表达及丹参川芎嗪注射液干预作用的临床研究[D]. 福州:福建中医学院,2009.
|
| [48] |
李研,于彩敏. 杏芎氯化钠注射液辅助治疗缺血性脑卒中的效果及安全性观察[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2021,33(6):105-109. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2021.06.023.
|
| [49] |
闫纪琳,郑连红,李海涛,等. 杏芎氯化钠注射液联合阿替普酶治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J]. 药物评价研究,2021,44(8):1717-1721. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2021.08.022.
|
| [50] |
杨贤科,钱浓,彭先波,等. 杏芎氯化钠注射液联合依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者神经功能、脑血流灌注及氧化应激水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2021,21(7):1374-1378. DOI:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2021.07.038.
|
| [51] | |
| [52] | |
| [53] |
宋元良. 盐酸川芎嗪注射液联合丁苯酞软胶囊治疗急性脑梗死效果及对血液流变学的影响研究[J]. 贵州医药,2021,45(7):1114-1115. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2021.07.053.
|
| [54] |
尤晓涵,杨淼,明霞光,等. 盐酸川芎嗪注射液联合丁苯酞软胶囊治疗急性脑梗死疗效及对患者血液流变学影响[J]. 陕西中医,2020,41(6):743-745,757. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2020.06.012.
|
| [55] |
笪正,嵇虎,翟正平,等. 长春西汀联合川芎嗪综合治疗急性脑梗死的安全性及对防止不良事件的作用[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2020,28(S1):249-251.
|
| [56] |
张玉彬. 盐酸川芎嗪联合阿替普酶静脉溶栓对缺血性脑卒中急性期患者的治疗效果[J]. 河南医学研究,2019,28(21):3944-3945. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2019.21.057.
|
| [57] |
刘其镇,李素诊. 盐酸川芎嗪注射液辅助治疗脑梗死的疗效观察[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2019,12(32):45-46. DOI:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2019.32.024.
|
| [58] |
田华宜. 川芎嗪注射液合奥扎格雷钠对急性缺血性脑卒中效果观察[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2019,19(2):100-102. DOI:10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2019.02.050.
|
| [59] |
吴文斌,陈小红. 依达拉奉联合川芎嗪治疗脑梗死患者的临床效果观察[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2017,2(26):16-17. DOI:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.201726008.
|
| [60] |
王朝阳,张茂林,鲁启洪. 川芎嗪注射液对急性缺血性脑卒中患者血清MMP-9及神经功能缺损的影响[J]. 吉林中医药,2015,35(2):133-135. DOI:10.13463/j.cnki.jlzyy.2015.02.009.
|
| [61] |
孙红国,于福恩,万明花,等. 川芎嗪对脑梗死患者血流变及血小板指标的影响[J]. 海南医学院学报,2015,21(5):709-711,714. DOI:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20150407.008.
|
| [62] |
章玉华,蔡祥增,郭名和. 川芎嗪对急性脑梗死患者血清超敏C反应蛋白、白细胞介素-6、基质金属蛋白酶-9水平的影响[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2013,17(17):78-80. DOI:10.7619/jcmp.201317026.
|
| [63] |
王小平,马金梁. 川芎嗪对急性脑梗死患者血清hs-CRP的影响[J]. 中华全科医学,2013,11(8):1241,1278. DOI:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2013.08.078.
|
| [64] |
孙寒静,郑缅华,梁天山. 川芎嗪注射液对急性脑梗死患者血清sCD40L及hs-CRP水平的影响[J]. 上海中医药大学学报,2013,27(4):39-41. DOI:10.16306/j.1008-861x.2013.04.029.
|
| [65] |
严春开. 盐酸川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗塞临床疗效的分析[J]. 求医问药(下半月),2012,10(5):162-163.
|
| [66] |
卢万向. 川芎嗪联合尼莫地平治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J]. 中国实用医药,2010,5(34):139-140. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2010.34.225.
|
| [67] | |
| [68] |
谷元奎,艾庆岩,张忠山. 降纤酶联合川芎嗪注射液治疗脑梗塞急性期65例疗效观察[J]. 中国中医急症,2002,11(4):249-250. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2002.04.007.
|
| [69] |
杨政治. 川芎嗪注射液辅助治疗急性脑梗死52例临床疗效观察[J]. 中国社区医师(医学专业),2010,12(21):159. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2010.21.164.
|
| [70] |
王英莲,杨学瑞,姜宇宙. 低分子肝素钙联合川芎嗪注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床观察[J]. 中国医药导报,2009,6(8):67-68. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7210.2009.08.042.
|
| [71] |
樊海梅,王蓉,吴雪梅. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合依达拉奉治疗缺血性脑卒中的临床观察[J]. 中国民间疗法,2022,30(2):86-88. DOI:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2022.0231.
|
| [72] |
李娜. 急性脑血栓应用参芎葡萄糖注射液+奥扎格雷治疗的效果分析[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(69):139-140. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.69.093.
|
| [73] | |
| [74] |
闫伟丽. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合奥扎格雷治疗急性脑血栓的效果观察[J]. 河南医学研究,2017,26(3):514-515.
|
| [75] |
宋卫红. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合脑蛋白水解物治疗对急性脑梗死患者神经功能及血液流变学的影响[J]. 内科,2017,12(3):370-371,386. DOI:10.16121/j.cnki.cn45-1347/r.2017.03.23.
|
| [76] |
秦连发. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合脑蛋白水解物对急性脑梗塞患者血液流变学的影响[J]. 国际医药卫生导报,2017,23(7):1027-1029. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-1245.2017.07.032.
|
| [77] |
管友红,杨艳,徐爱群. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死疗效观察[J]. 淮海医药,2017,35(4):482-484. DOI:10.14126/j.cnki.1008-7044.2017.04.046.
|
| [78] |
孙培丽. 参芎注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效及对患者血清神经元特异性烯醇化酶、血清神经肽Y、S-100β水平的影响[J]. 中国临床医生杂志,2017,45(11):47-49. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2017.11.017.
|
| [79] |
牟鸣,张杰,沈志敏,等. 参芎葡萄糖注射液联合脑蛋白水解物治疗急性脑梗塞的疗效及对神经功能缺损和血液流变学的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2015,15(2):321-324. DOI:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2015.02.031.
|
| [80] |
张宁. 参芎葡萄糖结合奥扎格雷对急性脑血栓神经功能及预后的影响[J]. 中国实用医药,2015,10(1):106-107. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2015.01.077.
|
| [81] |
王琪. 参芎葡萄糖联合奥扎格雷治疗急性脑血栓形成的疗效观察[J]. 河北医药,2013,35(17):2587-2588. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2013.17.010.
|
| [82] |
李啬夫,丁玲. 参芎注射液治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J]. 中南药学,2008,6(3):364-366.
|
| [83] |
李海军,甄志刚,王磊,等. 参芎葡萄糖注射液治疗急性脑梗死50例[J]. 陕西中医,2014,35(3):306-307. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2014.03.031.
|
| [84] |
倪小佳,陈耀龙,蔡业峰. 中西医结合脑卒中循证实践指南(2019)[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2020,20(8):901-912.
|
| [85] |
金玉青,洪远林,李建蕊,等. 川芎的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中药与临床,2013,4(3):44-48.
|
| [86] | |
| [87] |
刘剑敏,董俊丽,唐静宜,等. 磷酸川芎嗪通过激活AMPK对HT22细胞在氧糖剥夺损伤中的保护作用[J]. 中成药,2020,42(8):2173-2176. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.08.042.
|
| [88] |
杨凯,蔡庆丰,范建荣. 川芎嗪注射液联合常规疗法对大面积脑栓塞患者支架植入术后血小板血流变学及疗效的影响[J]. 中国药师,2016,19(11):2078-2080. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2016.11.021.
|
| [89] |
李晓娜,汪晓筠,朱艳媚,等. 盐酸川芎嗪通过干预GABAR和FOXP2的表达保护低压低氧大鼠学习记忆[J]. 中国药理学通报,2017,33(9):1285-1290. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2017.09.019.
|
| [90] |
曹艳花,刘珊珊. 磷酸川芎嗪与盐酸川芎嗪对大鼠局灶性脑缺血模型的作用比较[J]. 食品与药品,2008,10(9):37-39. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2008.05.012.
|
| [91] |
朱卫,张晓彪. 银杏叶制剂对脑血管病治疗的概况[J]. 国外医学(脑血管疾病分册),1998,6(4):235-238.
|
| [92] |
胡波,孙圣刚,梅元武,等. 银杏叶提取物在大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤中的保护作用[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2003,23(6):436-440.
|
| [93] | |
| [94] |
方彬宇,朱婷,张淑霞,等. 杏芎氯化钠注射液改善凝血纤溶系统抗脑缺血-再灌注损伤作用及分子机制研究[J]. 中药材,2022,45(1):199-203. DOI:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2022.01.035.
|
| [95] |
刘佳,闫建齐. 急性脑梗死患者血浆内皮素及血液流变学指标检测分析[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志,2015,33(2):187-188. DOI:10.13704/j.cnki.jyyx.2015.02.028.
|
| [96] |
颜昌云,朱志刚,唐云宏. 同型半胱氨酸超敏C反应蛋白纤维蛋白原与脑梗死严重程度及复发的相关性分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志,2016,19(21):84-85. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2016.21.048.
|
| [97] |
高素颖,冀瑞俊,颜应琳,等. 血清同型半胱氨酸、纤维蛋白原、胱抑素C水平与急性脑梗死患者NIHSS评分的相关性分析[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2020,15(4):389-393. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5765.2020.04.011.
|
| [98] |
高阳,王桂倩,王健,等. 丹参川芎嗪注射液临床应用专家共识[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44(14):2937-2942. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190509.503.
|
| [99] |
朱德才,张昌林,廖映迪. 丹参治疗缺血性脑卒中潜在效应机制的网络药理学研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021,19(5):737-744. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2021.05.007.
|
| [100] |
田燕,方煜,胡明. 丹参川芎嗪注射液与参芎葡萄糖注射液治疗脑梗死的成本-效果分析[J]. 中国药房,2018,29(4):487-492. DOI:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2018.04.14.
|
| [101] |
| [1] | 吴凯瑞, 叶宇, 李娇月, 裴蓓, 李学军, 程红亮. 脾胃培源方加减联合针刺治疗慢性萎缩性胃炎伴肠化生效果的多中心临床随机对照试验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(20): 2466-2475. |
| [2] | 谭书法, 张磊昌, 高强强, 欧艳, 黄水兰. 生物制剂和小分子药物治疗溃疡性结肠炎有效性与安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(17): 2155-2166. |
| [3] | 白鑫, 武新宇, 赵尊, 柳舒心, 刘斯淼, 薛宇航, 徐俊玲, 高永举. 131I治疗血清甲状腺球蛋白抗体阳性分化型甲状腺癌远处转移的疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(15): 1833-1837. |
| [4] | 谢翼, 徐俊马, 胥方琴, 俪超, 陈辰, 邵婵. 肌少症指数对老年急性缺血性脑卒中患者预后的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(11): 1326-1330. |
| [5] | 王明航, 韩伟红, 毕丽婵, 杨江, 李建生. 中医辨证治疗方案对老年社区获得性肺炎出院后患者生存质量和疗效满意度的评价研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 1001-1007. |
| [6] | 邓煜璇, 黄学君, 江妍霞. 二甲双胍治疗糖尿病肾病的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(03): 262-267. |
| [7] | 张翼升, 唐福波, 孙亚如, 钟远鸣, 李智斐. 经皮内镜后路经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术联合高度可调钛质融合器治疗腰椎滑脱合并腰椎管狭窄症的临床疗效分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4464-4471. |
| [8] | 张懂理, 沈冲, 张卫川, 陈海滨, 赵建军. 程序性死亡因子1/程序性死亡因子1配体抑制剂治疗肾细胞癌有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3815-3822. |
| [9] | 刘睿方, 徐方兴, 刘同库, 周玉杰, 吴小凡. "Crowbar Effect"技术促进球囊跨过高阻力冠状动脉慢性完全性闭塞病变的有效性和安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3683-3688. |
| [10] | 黄丹, 张琪涵, 宋歌, 王晴, 李瑀, 吉训明, 王媛. 间歇性低氧训练预防急性低氧损伤有效性和安全性的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3640-3644. |
| [11] | 张勇, 蔡翔, 宁菲菲, 梁潇, 郭宁. 沙库巴曲缬沙坦与达格列净治疗血压偏低的扩张型心肌病疗效及安全性比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(23): 2912-2917. |
| [12] | 何梅, 李荟, 母立峰, 杨明. 阿兹夫定对新型冠状病毒感染患者肝肾功能影响的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2476-2481. |
| [13] | 陈璐璐, 张利苹, 李静文, 董文杰, 吴欣爱. 程序性死亡受体1抑制剂联合呋喹替尼后线治疗转移性结直肠癌的临床疗效和安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(18): 2262-2267. |
| [14] | 王秋琴, 章雨桐, 徐语晨, 柏亚妹, 陈华, 姜荣荣, 严姝霞, 王庆, 徐桂华, 谢颖, 乔春, 杨娟. 刮痧联合药物治疗原发性帕金森病的短期临床疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(17): 2155-2161. |
| [15] | 张丽娜, 王岩, 张抗怀, 李友佳. 新型降糖药物替西帕肽的临床研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(15): 1902-1908. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





