中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (23): 2904-2912.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0594
收稿日期:2023-05-26
修回日期:2023-12-06
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-05-08
通讯作者:
王广梅
作者贡献:
吴明华提出研究思路,设计研究方案,研究命题的提出、设计;张林负责进行试验或调查、调查对象的选取、样本的采集、指标化验与检测等;张林、高锦负责数据收集、采集、清洗和统计学分析、绘制图表等;高锦负责论文起草;王广梅负责最终版本修订,对论文负责。
基金资助:
ZHANG Lin1, GAO Jin2, WU Minghua3, WANG Guangmei4,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-26
Revised:2023-12-06
Published:2024-08-15
Online:2024-05-08
Contact:
WANG Guangmei
摘要: 背景 脑梗死是由各种原因引起的局部脑组织区域供血障碍,通脑饮为江苏省中医院治疗脑梗死的协定方,但具体作用机制尚不清楚。 目的 本研究旨在通过网络药理学和临床试验,解释通脑饮治疗脑梗死的机制。 方法 选取2019年1月—2020年6月江苏省中医院收治的199例脑梗死患者。根据随机数字表法,将患者分为对照组(97例)和试验组(102例)。两组均接受稳定型脑梗死的标准化治疗,试验组加用通脑饮治疗。治疗前和治疗2周时,两组均采用美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(NIHSS)评估卒中引起的功能损害程度,采用改良Rankin量表(mRS)评估神经功能的恢复情况。从TCMSP和文献中筛选通脑饮的化学成分,选择生物利用度(OB)≥30%和药物相似性(DL)≥0.18要求的成分寻找该处方的有效成分。利用OMIM和GeneCards数据库分析通脑饮治疗脑梗死的分子靶点。在筛选出共同靶点后,用Cytoscape软件、String数据库分别绘制化合物和靶蛋白的网络图、构建蛋白相互作用(PPI)网络和基因本体论(GO)功能及京都基因和基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析。最后,进行分子对接实验,确定通脑饮治疗脑梗死的主要活性成分。 结果 治疗后,试验组NIHSS、mRS评分均低于对照组(P<0.05)。最终得到通脑饮活性成分60个,潜在靶点147个,疾病相关靶点5 167个,药物与疾病的交集靶点121个。KEGG信号通路富集分析获得前列腺癌症、神经活性配体-受体相互作用、白介素(IL)-17信号通路、催乳素信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、钙信号通路等。分子对接显示,通脑饮治疗脑卒中的主要活性成分β谷甾醇、山柰酚和胡萝卜素与核心蛋白雄激素受体(AR)有较好的结合性。 结论 通脑饮可能通过激活AR来治疗脑梗死。IL-17信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路和催乳素信号通路也是潜在的机制。
| 组别 | 例数 | NIHSS评分 | mRS评分 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | Z配对值 | P值 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | Z配对值 | P值 | ||
| 对照组 | 96 | 3.0(2.0,6.0) | 1.5(1.0,3.0) | -5.577 | <0.001 | 2.5(1.0,4.0) | 2.0(1.0,2.0) | -5.759 | <0.001 |
| 试验组 | 102 | 2.0(1.0,6.0) | 1.0(0,2.0) | -5.592 | <0.001 | 1.0(1.0,4.0) | 1.0(1.0,4.0) | -2.586 | 0.010 |
| Z值 | -1.714 | -3.192 | -0.427 | -2.053 | |||||
| P值 | 0.087 | 0.001 | 0.669 | 0.040 | |||||
表1 两组患者治疗前后NIHSS、mRS评分比较[M(P25,P75),分]
Table 1 Comparison of NIHSS and mRS scores before and after treatment between the two groups of patients
| 组别 | 例数 | NIHSS评分 | mRS评分 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | Z配对值 | P值 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | Z配对值 | P值 | ||
| 对照组 | 96 | 3.0(2.0,6.0) | 1.5(1.0,3.0) | -5.577 | <0.001 | 2.5(1.0,4.0) | 2.0(1.0,2.0) | -5.759 | <0.001 |
| 试验组 | 102 | 2.0(1.0,6.0) | 1.0(0,2.0) | -5.592 | <0.001 | 1.0(1.0,4.0) | 1.0(1.0,4.0) | -2.586 | 0.010 |
| Z值 | -1.714 | -3.192 | -0.427 | -2.053 | |||||
| P值 | 0.087 | 0.001 | 0.669 | 0.040 | |||||
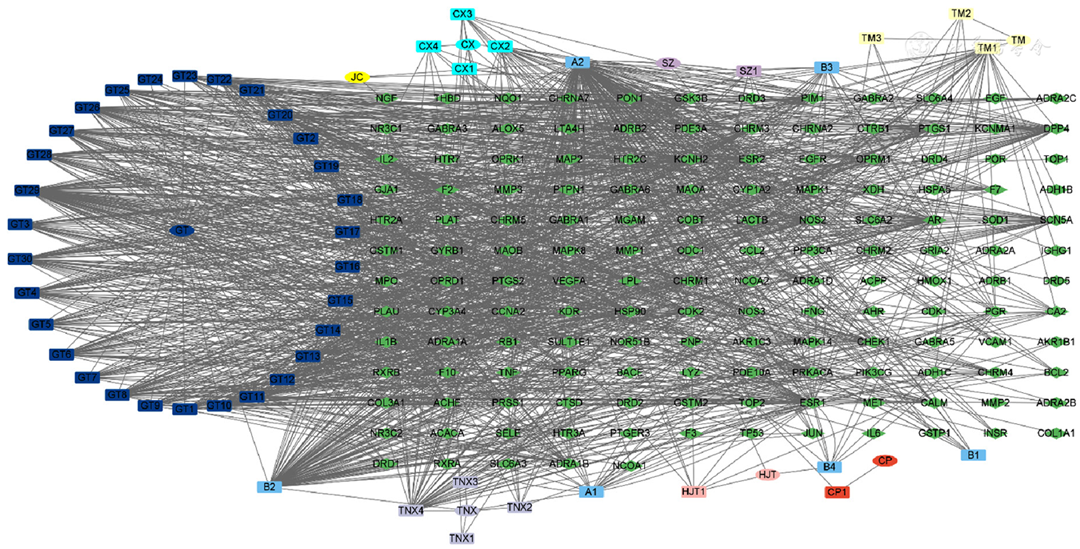
图2 通脑饮中化学成分网络图注:蓝色节点表示这些成分共享的化合物;深蓝色节点代表钩藤的化合物;青色节点代表川芎的化合物;灰色节点代表天南星的化合物;紫色节点代表水蛭的化合物;粉红色的节点代表红景天的化合物;黄色节点代表天麻的化合物;橙色节点代表僵蚕的化合物;红色节点代表九节菖蒲的化合物;绿色节点表示通脑饮相关的靶点。
Figure 2 Network map of chemical components in Tongnao Decoction
| 药物 | ID | 成分 | OB(%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX | MOL001494 | Mandenol | 42 | 0.2 |
| MOL002135 | Myricanone | 40.6 | 0.5 | |
| MOL002140 | Perlolyrine | 65.95 | 0.3 | |
| MOL002151 | senkyunone | 47.66 | 0.2 | |
| MOL002157 | wallichilide | 42.31 | 0.7 | |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000433 | FA | 68.96 | 0.7 | |
| GT | MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 | |
| MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 0.2 | |
| MOL008455 | 3-oxo-22α-hydroxyurs-12-en-27,28-dioc acid | 32.33 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008456 | (3E,4R)-4-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-3-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methylidene]oxolan-2-one | 51.78 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008457 | Tetrahydroalstonine | 32.42 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008458 | Angustidine | 51.85 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008460 | geissoschizinc acid | 49.92 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008463 | SMR000232338 | 56.74 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008465 | (E)-16,17-Didehydro-17-methoxy-17,18-seco-3-beta-yohimban-16-carboxylic acid methyl ester | 32.75 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008467 | Rhynchophylline A | 68.68 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008468 | methyl(E)-2-[(2S,3Z,12bS)-3-ethylidene-2,4,6,7,12,12b-hexahydro-1H-indolo[3,2-h]quinolizin-2-yl]-3-methoxyprop-2-enoate | 56.83 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008469 | Rhynchophylline | 41.82 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008470 | SMR000232333 | 78.38 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008471 | Isorhyncophylline | 47.31 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008472 | hirsutasideA | 70.34 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008473 | (E)-2-[(3S,6'S,7'S,8'aS)-6'-ethyl-2-keto-spiro[indoline-3,1'-indolizidine]-7'-yl]-3-methoxy-acrylic acid methyl ester | 57.85 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008474 | (E)-2-[(3R,6'S,7'S,8'aS)-6'-ethyl-2-keto-spiro[indoline-3,1'-indolizidine]-7'-yl]-3-methoxy-acrylic acid methyl ester | 54.47 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008475 | Mitraphyllic acid | 31.7 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008476 | hirsutasideB | 40.21 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008477 | corynoxeine | 57.13 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008478 | methyl(E)-2-[(2S,3R,12bS)-3-vinyl-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12b-octahydroindolo[3,2-h]quinolizin-2-yl]-3-methoxy-prop-2-enoate | 31.94 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008481 | (1'R,3S,4a'S,5a'S,10a'R)-1'-methyl-2-oxo-1',4a',5',5a',7',8',10',10a'-octahydrospiro[indoline-3,6'-pyrano[3,4-f]indolizine]-4'-carboxylic acid | 105.22 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008482 | (2S,12bR)-methyl 2-((E)-1-oxobut-2-en-2-yl)-1,2,6,7,12,12b-hexahydroindolo[2,3-a]quinolizine-3-carboxylate | 42.07 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008484 | vincoside lactam_qt | 50.81 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008485 | hirsutasideC | 34.27 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008487 | hirsutine | 34.44 | 0.4 | |
| MOL008488 | yohimbine | 46.42 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008489 | delta(sup 18)-Hirsutine | 41.64 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008490 | isocorynantheic acid | 72.36 | 0.6 | |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.3 | |
| MOL008635 | coryincine | 38.27 | 0.8 | |
| TNX | MOL013146 | 8,11,14-Docosatrienoic acid,methyl ester | 43.23 | 0.3 |
| MOL013156 | [(2R)-2-[[[(2R)-2-(benzoylamino)-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]methyl]-3-phenylpropyl] acetate | 38.88 | 0.6 | |
| MOL001510 | 24-epicampesterol | 37.58 | 0.7 | |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000953 | CLR | 37.87 | 0.7 | |
| HGT | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 |
| MOL001525 | daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000569 | gallic acid | 61.85 | 0.3 | |
| JJCP | MOL001987 | β-sitosterol | 33.94 | 0.7 |
| TM | MOL000296 | β-sitosterol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL008173 | daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL005399 | alexandrin | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| JC | MOPL001532 | phytosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL000953 | Cholesterol | 37.87 | 0.7 | |
| MOL001525 | Daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 | |
| SZ | MOL000433 | glutamic acid | 68.96 | 0.7 |
| MOL006967 | Xanthine | 44.72 | 0.2 |
表2 通脑饮中的有效成分
Table 2 Active ingredients in Tongnao Decoction
| 药物 | ID | 成分 | OB(%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX | MOL001494 | Mandenol | 42 | 0.2 |
| MOL002135 | Myricanone | 40.6 | 0.5 | |
| MOL002140 | Perlolyrine | 65.95 | 0.3 | |
| MOL002151 | senkyunone | 47.66 | 0.2 | |
| MOL002157 | wallichilide | 42.31 | 0.7 | |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000433 | FA | 68.96 | 0.7 | |
| GT | MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 | |
| MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 0.2 | |
| MOL008455 | 3-oxo-22α-hydroxyurs-12-en-27,28-dioc acid | 32.33 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008456 | (3E,4R)-4-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-3-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methylidene]oxolan-2-one | 51.78 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008457 | Tetrahydroalstonine | 32.42 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008458 | Angustidine | 51.85 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008460 | geissoschizinc acid | 49.92 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008463 | SMR000232338 | 56.74 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008465 | (E)-16,17-Didehydro-17-methoxy-17,18-seco-3-beta-yohimban-16-carboxylic acid methyl ester | 32.75 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008467 | Rhynchophylline A | 68.68 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008468 | methyl(E)-2-[(2S,3Z,12bS)-3-ethylidene-2,4,6,7,12,12b-hexahydro-1H-indolo[3,2-h]quinolizin-2-yl]-3-methoxyprop-2-enoate | 56.83 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008469 | Rhynchophylline | 41.82 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008470 | SMR000232333 | 78.38 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008471 | Isorhyncophylline | 47.31 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008472 | hirsutasideA | 70.34 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008473 | (E)-2-[(3S,6'S,7'S,8'aS)-6'-ethyl-2-keto-spiro[indoline-3,1'-indolizidine]-7'-yl]-3-methoxy-acrylic acid methyl ester | 57.85 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008474 | (E)-2-[(3R,6'S,7'S,8'aS)-6'-ethyl-2-keto-spiro[indoline-3,1'-indolizidine]-7'-yl]-3-methoxy-acrylic acid methyl ester | 54.47 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008475 | Mitraphyllic acid | 31.7 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008476 | hirsutasideB | 40.21 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008477 | corynoxeine | 57.13 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008478 | methyl(E)-2-[(2S,3R,12bS)-3-vinyl-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12b-octahydroindolo[3,2-h]quinolizin-2-yl]-3-methoxy-prop-2-enoate | 31.94 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008481 | (1'R,3S,4a'S,5a'S,10a'R)-1'-methyl-2-oxo-1',4a',5',5a',7',8',10',10a'-octahydrospiro[indoline-3,6'-pyrano[3,4-f]indolizine]-4'-carboxylic acid | 105.22 | 0.7 | |
| MOL008482 | (2S,12bR)-methyl 2-((E)-1-oxobut-2-en-2-yl)-1,2,6,7,12,12b-hexahydroindolo[2,3-a]quinolizine-3-carboxylate | 42.07 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008484 | vincoside lactam_qt | 50.81 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008485 | hirsutasideC | 34.27 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008487 | hirsutine | 34.44 | 0.4 | |
| MOL008488 | yohimbine | 46.42 | 0.8 | |
| MOL008489 | delta(sup 18)-Hirsutine | 41.64 | 0.6 | |
| MOL008490 | isocorynantheic acid | 72.36 | 0.6 | |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.3 | |
| MOL008635 | coryincine | 38.27 | 0.8 | |
| TNX | MOL013146 | 8,11,14-Docosatrienoic acid,methyl ester | 43.23 | 0.3 |
| MOL013156 | [(2R)-2-[[[(2R)-2-(benzoylamino)-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]methyl]-3-phenylpropyl] acetate | 38.88 | 0.6 | |
| MOL001510 | 24-epicampesterol | 37.58 | 0.7 | |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000953 | CLR | 37.87 | 0.7 | |
| HGT | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 |
| MOL001525 | daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000569 | gallic acid | 61.85 | 0.3 | |
| JJCP | MOL001987 | β-sitosterol | 33.94 | 0.7 |
| TM | MOL000296 | β-sitosterol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL008173 | daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL005399 | alexandrin | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| JC | MOPL001532 | phytosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 |
| MOL000953 | Cholesterol | 37.87 | 0.7 | |
| MOL001525 | Daucosterol | 36.91 | 0.8 | |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.2 | |
| SZ | MOL000433 | glutamic acid | 68.96 | 0.7 |
| MOL006967 | Xanthine | 44.72 | 0.2 |
| UniP-ID | Protein names | Degree |
|---|---|---|
| P03372 | Estrogen receptor(ESR1) | 51 |
| P10275 | Androgen receptor(AR) | 47 |
| P00734 | Prothrombin(F2) | 44 |
| P35354 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2(PTGS2) | 43 |
| P27487 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4(DPP4) | 39 |
| P24941 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2(CDK2) | 37 |
| P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha(HSP90) | 35 |
| P49841 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta(GSK3B) | 34 |
| P35228 | Nitric oxide synthase,inducible(NOS2) | 34 |
| P23219 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1(PTGS1) | 33 |
| Q14524 | Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha(SCN5A) | 30 |
| P11229 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1(CHRM1) | 29 |
| P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase(ACHE) | 29 |
| P07477 | Trypsin-1(PRSS1) | 28 |
| Q92731 | Estrogen receptor beta(ESR2) | 28 |
| P37231 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma(PPARG) | 27 |
| P35368 | Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor(ADRA1B) | 26 |
| Q12809 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 2(KCNH2) | 26 |
| P00742 | Coagulation factor X(F10) | 25 |
| P20309 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3(CHRM3) | 25 |
表3 通脑饮治疗脑梗死的关键靶点
Table 3 Key targets of Tongnao Decoction in the treatment of cerebral infarction
| UniP-ID | Protein names | Degree |
|---|---|---|
| P03372 | Estrogen receptor(ESR1) | 51 |
| P10275 | Androgen receptor(AR) | 47 |
| P00734 | Prothrombin(F2) | 44 |
| P35354 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2(PTGS2) | 43 |
| P27487 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4(DPP4) | 39 |
| P24941 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2(CDK2) | 37 |
| P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha(HSP90) | 35 |
| P49841 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta(GSK3B) | 34 |
| P35228 | Nitric oxide synthase,inducible(NOS2) | 34 |
| P23219 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1(PTGS1) | 33 |
| Q14524 | Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha(SCN5A) | 30 |
| P11229 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1(CHRM1) | 29 |
| P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase(ACHE) | 29 |
| P07477 | Trypsin-1(PRSS1) | 28 |
| Q92731 | Estrogen receptor beta(ESR2) | 28 |
| P37231 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma(PPARG) | 27 |
| P35368 | Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor(ADRA1B) | 26 |
| Q12809 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 2(KCNH2) | 26 |
| P00742 | Coagulation factor X(F10) | 25 |
| P20309 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3(CHRM3) | 25 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
沈璐莹,徐红,李宏辉,等. 协定方通脑饮治疗痰瘀阻络型急性脑梗死疗效观察[J]. 北京中医药,2021,40(10):1058-1060. DOI:10.16025/j.1674-1307.2021.10.002.
|
| [6] |
吴明华,张秀胜. 自拟通脑饮治疗急性脑梗死痰瘀阻络证220例[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2012,39(10):2003-2005. DOI:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2012.10.122.wumh.037.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
钟迪,张舒婷,吴波. 《中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018》解读[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2019,19(11):897-901. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2019.11.015.
|
| [17] |
周曾,凤兆海,徐竞,等. 丁苯酞联合低剂量重组组织型纤溶酶原激活物静脉溶栓治疗超早期脑梗死老年患者的疗效观察[J]. 天津医药,2023,51(10):1141-1146. DOI:10.11958/20230414.
|
| [18] |
赛俊杰,张环,韩红星,等. 发病4.5至9.0小时前循环大血管闭塞急性缺血性卒中患者行桥接治疗与直接取栓的疗效及安全性对比分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(10):649-658. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2023.10.001.
|
| [19] |
王巧宇,刘莹,申金田,等. 基于分子对接和网络药理学的僵蚕息风止痉作用机制分析[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版),2021,31(5):426-430,437. DOI:10.13312/j.issn.1671-7783.y210059.
|
| [20] |
UniProt Consortium. UniProt:a worldwide hub of protein knowledge[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2019,47(D1):D506-515. DOI:10.1093/nar/gky1049.
|
| [21] |
The UniProt Consortium. UniProt:the universal protein knowledgebase[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2017,45(D1):D158-169. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkw1099.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
王从过. 长期服用阿司匹林预防缺血性脑卒中的临床与实验研究[D]. 蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2023.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [1] | 胡宇驰, 代松源, 赵玲, 赵璐露. 迷走神经刺激在慢性心力衰竭炎症及凋亡机制中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(24): 3044-3050. |
| [2] | 胡桂萍, 林平, 赵振娟, 王旖旎, 鄢明强, 孙晓. 膳食炎症潜能与急性冠脉综合征患者冠状动脉病变严重程度的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(24): 3000-3006. |
| [3] | 和军辉, 万大国, 董静, 张娟. 泛免疫炎症值、全身免疫炎症指数与急性冠脉综合征患者易损斑块的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(24): 2976-2981. |
| [4] | 陈思琪, 肖瑾, 田思雨, 张佳, 汪淑婷, 张馨丹, 朱焰, 陈敏. 基于肠道干细胞探讨肠神经系统调节肠道炎症的机制研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2858-2863. |
| [5] | 李川, 吴云冲, 杨颜颜, 卢桃, 刘玉娟, 林世德. 内质网应激在肝脏疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(21): 2679-2684. |
| [6] | 肖雨倩, 白艳杰, 王岩, 孙可心, 万俊, 陈淑颖, 陈丽敏. 星形胶质细胞外囊泡在卒中后认知障碍中的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(20): 2551-2556. |
| [7] | 黄亚, 倪文吉, 张锐, 李丹丹, 周颖, 金涛, 钟勇. 中老年体检人群系统免疫炎症指数和系统炎症反应指数与微量白蛋白尿的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(18): 2186-2191. |
| [8] | 李思思, 何强, 徐有青. 全身炎症反应指数对急性胰腺炎患者严重程度的评估价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(17): 2104-2108. |
| [9] | 赵柠煊, 姜琳, 胡美婧, 姚强, 毛一能, 朱彩蓉. 中国中老年人C反应蛋白累积升高次数与躯体和非躯体抑郁症状的关系:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(17): 2070-2076. |
| [10] | 张春悦, 方力群. 急性前庭综合征患者脑梗死的临床特征及相关因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(14): 1678-1684. |
| [11] | 刁翯, 白文佩, 赵立东. 左慈丸的化学成分及治疗围绝经期听力损失的作用机制研究:基于网络药理学与分子对接技术[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1493-1503. |
| [12] | 尹婷婷, 徒文静, 张苏闽, 李伊婷, 徐桂华. 炎症性肠病患者食物素养与避免/限制性食物摄入障碍的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1445-1451. |
| [13] | 张瑾怡, 张世忠. 心血管疾病与心理疾病流行病学及相关机制研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 893-899. |
| [14] | 秦晓宇, 张斌森, 张笑佳, 逯晓婷, 刘鸿鑫, 王春爱. 电针对术后认知功能障碍模型大鼠炎症反应和铁死亡影响的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(06): 723-732. |
| [15] | 秦芳, 马甜甜, 于子夫, 刘西花. 有氧运动抑制炎症反应改善ApoE-/-动脉粥样硬化小鼠心肌纤维化机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(05): 557-562. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





