中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 4215-4224.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0358
• 文献计量学分析 • 上一篇
李苗苗1,2, 吴雪1, 景城阳1, 张乐1, 赵晖3,*( ), 廖星1,*(
), 廖星1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-20
修回日期:2023-08-01
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-08-08
通讯作者:
赵晖, 廖星
作者贡献:
李苗苗进行文章的构思与设计,数据分析,以及论文的撰写;吴雪、景城阳、张乐负责资料整理和数据提取;廖星、赵晖负责文章整体质量控制,最终版本修订和审校。
基金资助:
LI Miaomiao1,2, WU Xue1, JING Chengyang1, ZHANG Le1, ZHAO Hui3,*( ), LIAO Xing1,*(
), LIAO Xing1,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-20
Revised:2023-08-01
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2024-08-08
Contact:
ZHAO Hui, LIAO Xing
摘要: 背景 面对一定时间内原始研究数量的激增,耗时较长的传统系统综述较难及时为临床实践提供循证依据。快速综述(RR)作为系统综述方法的拓展,通过简化步骤和流程,可在有限时间内整合现有研究,从而满足快速决策的需求。目前RR已经被广泛应用到医学研究领域,但其应用现状尚不清楚。 目的 采用文献计量学方法探究RR的研究现状与热点。 方法 基于中国知网和Web of Science核心合集数据库检索2001—2023年有关RR的应用研究,采用文献计量学软件CiteSpace和VOSviewer对中英文文献的年发文量、国家、机构、作者、期刊、关键词等内容进行可视化分析。 结果 共纳入中文文献151篇,英文文献1 197篇。2001—2023年RR应用研究发文量逐步上升,但国外较国内发文量多且增加趋势明显;英国是发文量最多的国家(252篇),加拿大多伦多大学是发文量最多的机构(52篇),北京大学第三医院发文量居国内首位(23篇);国内发文量最多的期刊是《中国医院用药评价与分析》(22篇),国外发文量最多的期刊是BMJ Open(42篇);国内以门鹏、翟所迪、赵紫楠等为主的作者团队发表研究较多;国外以NUSSBAUMER-STREIT、GARTLEHNER、TRICCO等为主的作者团队发表研究较多;国内引用频次较多的文献以RR应用和方法学介绍、药物或技术的快速评估、新型冠状病毒感染(COVID-19)的影响等内容为主,国外引用频次较多的文献以COVID-19影响、治疗和流行病学因素的快速评估,或快速综述方法学研究等内容为主;国内研究热点主要集中在慢性或重大疾病干预安全性、有效性、经济性的快速卫生技术评估领域,国外研究热点主要集中在COVID-19病因、干预、诊断、预防及影响,儿童药物干预安全性及有效性、中老年人群医疗卫生保健、癌症治疗或死亡风险等与决策制定相关的快速证据综合领域。 结论 目前国内外医学领域RR应用研究发展差异较大,国外RR应用研究趋向成熟,国内尚处于初步发展阶段。未来可借鉴国外应用经验,不断拓宽国内RR发展领域。
中图分类号:
| 序号 | 国家 | 发文量(篇) | 序号 | 机构 | 发文量(篇) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | England(英国) | 252 | 1 | Univ Toronto(多伦多大学) | 52 |
| 2 | USA(美国) | 217 | 2 | Kings Coll London(伦敦国王学院) | 34 |
| 3 | Canada(加拿大) | 214 | 3 | Monash Univ(莫纳什大学) | 33 |
| 4 | Australia(澳大利亚) | 205 | 4 | Univ Sydney(悉尼大学) | 30 |
| 5 | 中国 | 187 | 5 | Univ ottawa(渥太华大学) | 25 |
| 6 | Germany(德国) | 57 | 6 | Univ Oxford(牛津大学) | 23 |
| 7 | Scotland(苏格兰) | 52 | 7 | 北京大学第三医院 | 23 |
| 8 | Ireland(爱尔兰) | 43 | 8 | McMaster Univ(麦克马斯特大学) | 23 |
| 9 | South Africa(南非) | 42 | 9 | UCL(伦敦大学) | 23 |
| 10 | Swizerland(瑞士) | 30 | 10 | Univ Queensland(昆士兰大学) | 21 |
表1 RR在医学研究领域的应用研究发文量排名前十的国家和机构
Table 1 Top 10 countries and institutions by the publication volume of RR application in the medical field
| 序号 | 国家 | 发文量(篇) | 序号 | 机构 | 发文量(篇) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | England(英国) | 252 | 1 | Univ Toronto(多伦多大学) | 52 |
| 2 | USA(美国) | 217 | 2 | Kings Coll London(伦敦国王学院) | 34 |
| 3 | Canada(加拿大) | 214 | 3 | Monash Univ(莫纳什大学) | 33 |
| 4 | Australia(澳大利亚) | 205 | 4 | Univ Sydney(悉尼大学) | 30 |
| 5 | 中国 | 187 | 5 | Univ ottawa(渥太华大学) | 25 |
| 6 | Germany(德国) | 57 | 6 | Univ Oxford(牛津大学) | 23 |
| 7 | Scotland(苏格兰) | 52 | 7 | 北京大学第三医院 | 23 |
| 8 | Ireland(爱尔兰) | 43 | 8 | McMaster Univ(麦克马斯特大学) | 23 |
| 9 | South Africa(南非) | 42 | 9 | UCL(伦敦大学) | 23 |
| 10 | Swizerland(瑞士) | 30 | 10 | Univ Queensland(昆士兰大学) | 21 |
| 序号 | CNKI期刊 | 发文量(篇) | 序号 | WOS期刊 | 发文量(篇) | IF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 《中国医院用药评价与分析》 | 22 | 1 | BMJ Open | 42 | 3.006 |
| 2 | 《中国新药杂志》 | 17 | 2 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 31 | 4.614 |
| 3 | 《中国药房》 | 17 | 3 | Systematic Reviews | 23 | 3.136 |
| 4 | 《中国医院药学杂志》 | 10 | 4 | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 15 | 12.008 |
| 5 | 《临床药物治疗杂志》 | 9 | 5 | Journal of Clinical Epidemiology | 14 | 7.407 |
| 6 | 《中国药业》 | 7 | 6 | Plos One | 13 | 3.752 |
| 7 | 《医药导报》 | 6 | 7 | Advances in Integrative Medicine | 12 | — |
| 8 | 《中国循证医学杂志》 | 5 | 8 | British Dental Journal | 11 | 2.727 |
| 9 | 《中国合理用药探索》 | 5 | 9 | BMC Health Services Research | 10 | 2.908 |
| 10 | 《中国药学杂志》 | 5 | 10 | Research Synthesis Methods | 10 | 9.308 |
表2 RR在医学研究领域的应用研究发文量排名前十的期刊
Table 2 Top 10 journals by the publication volume of RR application in the medical field
| 序号 | CNKI期刊 | 发文量(篇) | 序号 | WOS期刊 | 发文量(篇) | IF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 《中国医院用药评价与分析》 | 22 | 1 | BMJ Open | 42 | 3.006 |
| 2 | 《中国新药杂志》 | 17 | 2 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 31 | 4.614 |
| 3 | 《中国药房》 | 17 | 3 | Systematic Reviews | 23 | 3.136 |
| 4 | 《中国医院药学杂志》 | 10 | 4 | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 15 | 12.008 |
| 5 | 《临床药物治疗杂志》 | 9 | 5 | Journal of Clinical Epidemiology | 14 | 7.407 |
| 6 | 《中国药业》 | 7 | 6 | Plos One | 13 | 3.752 |
| 7 | 《医药导报》 | 6 | 7 | Advances in Integrative Medicine | 12 | — |
| 8 | 《中国循证医学杂志》 | 5 | 8 | British Dental Journal | 11 | 2.727 |
| 9 | 《中国合理用药探索》 | 5 | 9 | BMC Health Services Research | 10 | 2.908 |
| 10 | 《中国药学杂志》 | 5 | 10 | Research Synthesis Methods | 10 | 9.308 |
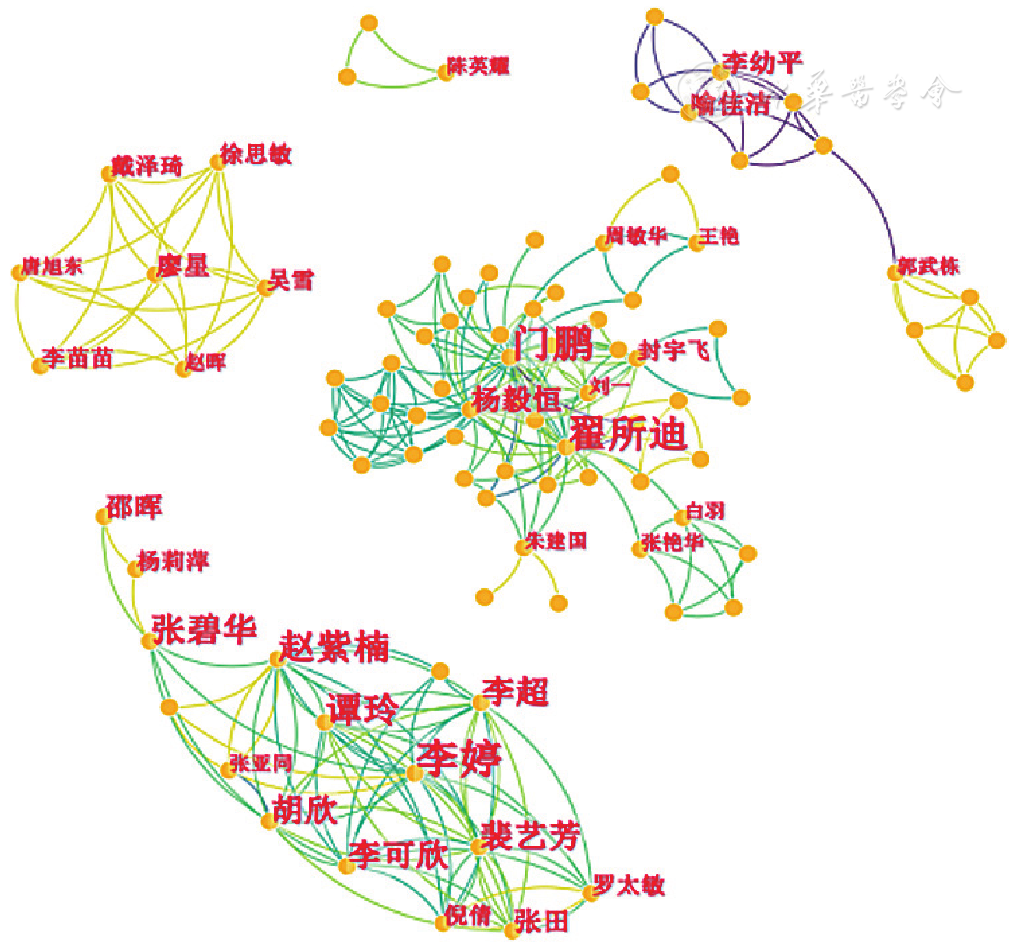
图2 RR在医学研究领域的中文应用研究作者合作网络图谱
Figure 2 A collaborative network mapping of research authors of articles in Chinese of RR application in the medical field
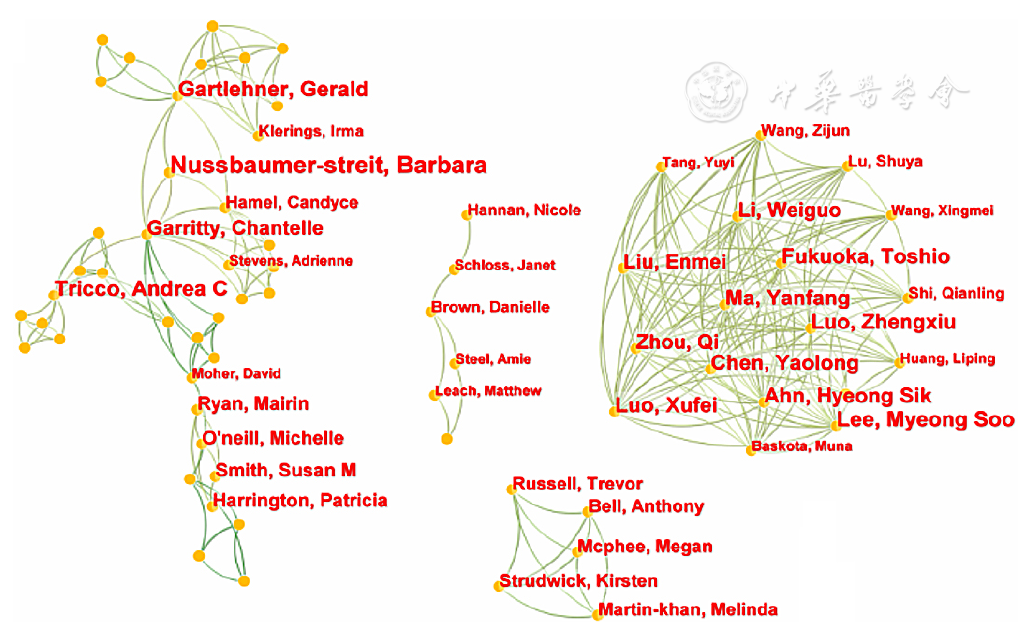
图3 RR在医学研究领域的英文应用研究作者合作网络图谱
Figure 3 A collaborative network mapping of research authors of articles in English of RR application in the medical field
| 数据库 | 序号 | 第一作者 | 题目 | 期刊 | 发表年份(年) | 被引频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNKI | 1 | 唐惠林[ | 药物快速卫生技术评估方法及应用 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2016 | 72 |
| 2 | 李幼平[ | 快速评估方法与流程的探索 | 中国循证医学杂志 | 2014 | 28 | |
| 3 | 郭巍[ | 新型冠状病毒肺炎流行对HIV感染者卫生需求影响的快速评估 | 中华流行病学杂志 | 2020 | 22 | |
| 4 | 栾曾惠[ | 沙库巴曲缬沙坦快速技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2017 | 18 | |
| 5 | 韩晶[ | 重组人血小板生成素治疗原发性免疫性和肿瘤化疗后血小板减少症的快速卫生技术评估 | 中国新药杂志 | 2020 | 16 | |
| 6 | 门鹏[ | 利格列汀治疗2型糖尿病有效性和安全性的快速评估及其在中国的经济性分析 | 药物流行病学杂志 | 2017 | 15 | |
| 7 | 喻佳洁[ | 达芬奇手术系统安全性和有效性的快速评估 | 中国循证医学杂志 | 2014 | 14 | |
| 8 | 赵紫楠[ | 索利那新治疗膀胱过度活动症的快速卫生技术评估 | 中国药业 | 2019 | 11 | |
| 9 | 赵紫楠[ | 乙酰左卡尼汀预防和治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的快速卫生技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2019 | 10 | |
| 10 | 王颖[ | 卡贝缩宫素预防剖宫产产后出血的快速卫生技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2019 | 10 | |
| WOS | 1 | BROOKS[ | The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it:rapid review of the evidence | Lancet | 2020 | 5 417 |
| 2 | RAWSON[ | Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus:a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing | Clinical Infectious Diseases | 2020 | 702 | |
| 3 | LANGFORD[ | Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19:a living rapid review and meta-analysis | Clinical Microbiology and Infection | 2020 | 581 | |
| 4 | KISELY[ | Occurrence,prevention,and management of the psychological effects of emerging virus outbreaks on healthcare workers:rapid review and meta-analysis | BMJ-British Medical Journal | 2020 | 548 | |
| 5 | LEISMAN[ | Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19:a rapid systematic review,meta-analysis,and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes | Lancet Respiratory Medicine | 2020 | 435 | |
| 6 | TRICCO[ | A scoping review of rapid review methods | BMC Medicine | 2015 | 433 | |
| 7 | GANANN[ | Expediting systematic reviews:methods and implications of rapid reviews | Implementation Science | 2010 | 409 | |
| 8 | CHOU[ | Epidemiology of and risk factors for coronavirus infection in health care workers:a living rapid review | Annals of Internal Medicine | 2020 | 355 | |
| 9 | PRETI[ | The psychological impact of epidemic and pandemic outbreaks on healthcare workers:rapid review of the evidence | Current Psychiatry Reports | 2020 | 336 | |
| 10 | NUSSBAUMER-STREIT[ | Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19:a rapid review | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 2020 | 297 |
表3 RR在医学研究领域的应用研究被引频次排名前十的文献
Table 3 The 10 most cited studies of RR application in the medical field
| 数据库 | 序号 | 第一作者 | 题目 | 期刊 | 发表年份(年) | 被引频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNKI | 1 | 唐惠林[ | 药物快速卫生技术评估方法及应用 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2016 | 72 |
| 2 | 李幼平[ | 快速评估方法与流程的探索 | 中国循证医学杂志 | 2014 | 28 | |
| 3 | 郭巍[ | 新型冠状病毒肺炎流行对HIV感染者卫生需求影响的快速评估 | 中华流行病学杂志 | 2020 | 22 | |
| 4 | 栾曾惠[ | 沙库巴曲缬沙坦快速技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2017 | 18 | |
| 5 | 韩晶[ | 重组人血小板生成素治疗原发性免疫性和肿瘤化疗后血小板减少症的快速卫生技术评估 | 中国新药杂志 | 2020 | 16 | |
| 6 | 门鹏[ | 利格列汀治疗2型糖尿病有效性和安全性的快速评估及其在中国的经济性分析 | 药物流行病学杂志 | 2017 | 15 | |
| 7 | 喻佳洁[ | 达芬奇手术系统安全性和有效性的快速评估 | 中国循证医学杂志 | 2014 | 14 | |
| 8 | 赵紫楠[ | 索利那新治疗膀胱过度活动症的快速卫生技术评估 | 中国药业 | 2019 | 11 | |
| 9 | 赵紫楠[ | 乙酰左卡尼汀预防和治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的快速卫生技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2019 | 10 | |
| 10 | 王颖[ | 卡贝缩宫素预防剖宫产产后出血的快速卫生技术评估 | 临床药物治疗杂志 | 2019 | 10 | |
| WOS | 1 | BROOKS[ | The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it:rapid review of the evidence | Lancet | 2020 | 5 417 |
| 2 | RAWSON[ | Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus:a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing | Clinical Infectious Diseases | 2020 | 702 | |
| 3 | LANGFORD[ | Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19:a living rapid review and meta-analysis | Clinical Microbiology and Infection | 2020 | 581 | |
| 4 | KISELY[ | Occurrence,prevention,and management of the psychological effects of emerging virus outbreaks on healthcare workers:rapid review and meta-analysis | BMJ-British Medical Journal | 2020 | 548 | |
| 5 | LEISMAN[ | Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19:a rapid systematic review,meta-analysis,and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes | Lancet Respiratory Medicine | 2020 | 435 | |
| 6 | TRICCO[ | A scoping review of rapid review methods | BMC Medicine | 2015 | 433 | |
| 7 | GANANN[ | Expediting systematic reviews:methods and implications of rapid reviews | Implementation Science | 2010 | 409 | |
| 8 | CHOU[ | Epidemiology of and risk factors for coronavirus infection in health care workers:a living rapid review | Annals of Internal Medicine | 2020 | 355 | |
| 9 | PRETI[ | The psychological impact of epidemic and pandemic outbreaks on healthcare workers:rapid review of the evidence | Current Psychiatry Reports | 2020 | 336 | |
| 10 | NUSSBAUMER-STREIT[ | Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19:a rapid review | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 2020 | 297 |
| 序号 | CNKI关键词 | 频次(次) | 序号 | WOS关键词 | 频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 快速卫生技术评估 | 130 | 1 | rapid review | 192 |
| 2 | 安全性 | 68 | 2 | systematic review | 96 |
| 3 | 有效性 | 67 | 3 | health | 87 |
| 4 | 经济性 | 61 | 4 | impact | 77 |
| 5 | 卫生技术评估 | 16 | 5 | mental health | 69 |
| 6 | 非小细胞肺癌 | 8 | 6 | care | 63 |
| 7 | 卫生经济学 | 7 | 7 | quality | 58 |
| 8 | 心力衰竭 | 6 | 8 | outcomes | 51 |
| 9 | 骨质疏松症 | 3 | 9 | management | 49 |
| 10 | 中成药 | 3 | 10 | intervention | 49 |
表4 RR在医学研究领域的应用研究中出现频次排名前十的关键词
Table 4 Top 10 keywords of RR application in the medical field
| 序号 | CNKI关键词 | 频次(次) | 序号 | WOS关键词 | 频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 快速卫生技术评估 | 130 | 1 | rapid review | 192 |
| 2 | 安全性 | 68 | 2 | systematic review | 96 |
| 3 | 有效性 | 67 | 3 | health | 87 |
| 4 | 经济性 | 61 | 4 | impact | 77 |
| 5 | 卫生技术评估 | 16 | 5 | mental health | 69 |
| 6 | 非小细胞肺癌 | 8 | 6 | care | 63 |
| 7 | 卫生经济学 | 7 | 7 | quality | 58 |
| 8 | 心力衰竭 | 6 | 8 | outcomes | 51 |
| 9 | 骨质疏松症 | 3 | 9 | management | 49 |
| 10 | 中成药 | 3 | 10 | intervention | 49 |
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 中心性 | 起始(年) | 终点(年) | 2014—2023年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 快速评估 | 2014 | 2.41 | 2014 | 2017 | |
| 达托霉素 | 2017 | 1.31 | 2017 | 2017 | |
| 专家共识 | 2022 | 1.95 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 罗沙司他 | 2022 | 1.16 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 中成药 | 2022 | 1.16 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 心力衰竭 | 2020 | 0.93 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 肾性贫血 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 埃克替尼 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 便秘 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 抑制剂 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 |
表5 RR在国内医学研究领域的应用研究关键词突现性分析
Table 5 Top 10 keywords with strongest citation bursts of RR application in the domestic medical field
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 中心性 | 起始(年) | 终点(年) | 2014—2023年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 快速评估 | 2014 | 2.41 | 2014 | 2017 | |
| 达托霉素 | 2017 | 1.31 | 2017 | 2017 | |
| 专家共识 | 2022 | 1.95 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 罗沙司他 | 2022 | 1.16 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 中成药 | 2022 | 1.16 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 心力衰竭 | 2020 | 0.93 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 肾性贫血 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 埃克替尼 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 便秘 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| 抑制剂 | 2022 | 0.77 | 2022 | 2023 |
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 中心性 | 起始(年) | 终点(年) | 2003—2023年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质量控制 | 2004 | 3.28 | 2004 | 2018 | |
| 宫颈癌 | 2006 | 2.38 | 2006 | 2018 | |
| 卫生技术评估 | 2008 | 2.89 | 2008 | 2019 | |
| 随机对照试验 | 2010 | 3.83 | 2010 | 2018 | |
| 系统综述 | 2011 | 7.62 | 2014 | 2017 | |
| 循证实践 | 2014 | 6.24 | 2014 | 2018 | |
| 全系统综述 | 2015 | 6.70 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| 因果关系 | 2016 | 2.38 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 质量 | 2004 | 3.76 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| 护理 | 2014 | 3.59 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| 试验 | 2017 | 2.37 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| 死亡 | 2018 | 2.78 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| 满意度 | 2018 | 2.78 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| 体系 | 2019 | 2.87 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| COVID-19 | 2020 | 2.52 | 2021 | 2023 |
表6 RR在医学研究领域的应用研究关键词突现性分析
Table 6 Top 15 keywords with strongest citation bursts of RR application in foreign medical field
| 关键词 | 年份(年) | 中心性 | 起始(年) | 终点(年) | 2003—2023年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质量控制 | 2004 | 3.28 | 2004 | 2018 | |
| 宫颈癌 | 2006 | 2.38 | 2006 | 2018 | |
| 卫生技术评估 | 2008 | 2.89 | 2008 | 2019 | |
| 随机对照试验 | 2010 | 3.83 | 2010 | 2018 | |
| 系统综述 | 2011 | 7.62 | 2014 | 2017 | |
| 循证实践 | 2014 | 6.24 | 2014 | 2018 | |
| 全系统综述 | 2015 | 6.70 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| 因果关系 | 2016 | 2.38 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 质量 | 2004 | 3.76 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| 护理 | 2014 | 3.59 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| 试验 | 2017 | 2.37 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| 死亡 | 2018 | 2.78 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| 满意度 | 2018 | 2.78 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| 体系 | 2019 | 2.87 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| COVID-19 | 2020 | 2.52 | 2021 | 2023 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
李幼平,喻佳洁,孙鑫. 快速评估方法与流程的探索[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2014,14(5):497-500.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] | |
| [10] |
郭巍,翁惠玲,白桦,等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎流行对HIV感染者卫生需求影响的快速评估[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2020,41(5):662-666. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200314-00345.
|
| [11] |
栾曾惠,张亚同,赵紫楠,等. 沙库巴曲缬沙坦快速技术评估[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志,2017,15(11):50-53. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2017.11.011.
|
| [12] |
韩晶,门鹏,刘维,等. 重组人血小板生成素治疗原发性免疫性和肿瘤化疗后血小板减少症的快速卫生技术评估[J]. 中国新药杂志,2020,29(5):589-594.
|
| [13] |
门鹏,顾歆纯,翟所迪. 利格列汀治疗2型糖尿病有效性和安全性的快速评估及其在中国的经济性分析[J]. 药物流行病学杂志,2017,26(6):375-381. DOI:10.19960/j.cnki.issn1005-0698.2017.06.002.
|
| [14] |
喻佳洁,王应强,李幼平,等. 达芬奇手术系统安全性和有效性的快速评估[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2014,14(5):530-540.
|
| [15] |
赵紫楠,李婷,李超,等. 索利那新治疗膀胱过度活动症的快速卫生技术评估[J]. 中国药业,2019,28(19):1-5. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2019.19.001.
|
| [16] |
赵紫楠,吕俊玲,李超,等. 乙酰左卡尼汀预防和治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的快速卫生技术评估[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志,2019,17(6):11-13,45. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2019.06.003.
|
| [17] |
王颖,谭湘萍,门鹏,等. 卡贝缩宫素预防剖宫产产后出血的快速卫生技术评估[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志,2019,17(6):14-18. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2019.06.004.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
张凯,张晓勃,施锦涛,等. 间充质干细胞治疗椎间盘退行性疾病:基于Web of Science数据库的文献计量及可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3031-3038.
|
| [29] |
陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. DOI:10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
刘世贤,王凯旋,窦蕾,等. 国内外药物经济学评价研究的文献计量及可视化分析[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2021,41(22):2368-2374,2384. DOI:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2021.22.18.
|
| [38] |
|
| [1] | 王健健, 卢珊, 张研, 潘杰. 门急诊服务敏感疾病的研究进展:基于CiteSpace的文献计量分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(34): 4248-4255. |
| [2] | 余如霞, 姜婧, 王湫澄, 王越, 赵小月. 人工智能在阿尔茨海默病临床诊疗中的研究热点及前沿趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(26): 3218-3226. |
| [3] | 杨宛君, 李丝雨, 李易轩, 刘春宇, 高明超, 郦春锦, 翟华强. 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(16): 2005-2014. |
| [4] | 丁礼雪, 李玉红, 张玉东. 基于CiteSpace的非稳态负荷相关研究热点及前沿的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 1008-1014. |
| [5] | 杨辉. 医学中的全科医学[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 0-C2. |
| [6] | 董娜, 崔婷, 王露露, 师荣慧, 冯洁, 黄晓俊. 人工智能在胃癌诊治中的研究趋势:20年的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 493-501. |
| [7] | 施博文, 马慧敏, 潘言志, 马赫, 杨晨, 熊巨洋. 移动健康技术在慢性病管理中应用进展的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(04): 485-492. |
| [8] | 钟萍萍, 南亚昀, 彭琳琳, 周宇婷, 陈琼. 2003—2022年老年人多重用药文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4404-4411. |
| [9] | 冯晓玉, 李婉玲, 吕思漫, 倪翠萍, 王浩成, 刘宇. 基于文献计量学的interRAI家庭护理评估工具国际研究现状及热点分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4351-4358. |
| [10] | 徐健, 戴芳芳, 潘文雷, 黄倩, 陆萍, 王剑峰, 贾环, 杨宇琪, 黄蛟灵. "健康中国"背景下我国社区中医药服务研究热点和前沿趋势的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4343-4350. |
| [11] | 王佳欣, 赵亚利. 国内外医疗团队合作评估工具系统综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3951-3962. |
| [12] | 王敏, 郭文军, 陈永真, 凤心雨, 汤忠泉, 赵晓敏, 欧婷, 戴昕妤, 李云涛. 基于Web of Science数据库的未分化疾病文献计量学和可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3930-3938. |
| [13] | 任延峰, 刘世蒙, 陶颖, 陈英耀. 抑郁症患者药物治疗偏好的系统综述:基于离散选择实验和优劣尺度法[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3559-3564. |
| [14] | 张莉, 郑薇, 王佳, 袁仙仙, 韩卫玲, 黄俊花, 田志红, 李光辉. 中国卫生行业标准与美国医学研究所指南评价我国单胎孕妇妊娠期体质量增长与妊娠结局的比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 2959-2967. |
| [15] | 郑晓, 田峰, 陈一鸣, 薛本立, 石磊, 张持晨. 2002—2022年我国多重慢病领域研究热点及演进趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2567-2573. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





