中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (16): 2005-2014.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0317
杨宛君1,2, 李丝雨1,2, 李易轩1,2, 刘春宇2,3, 高明超2,4, 郦春锦5, 翟华强1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-14
修回日期:2023-10-23
出版日期:2024-06-05
发布日期:2024-04-08
通讯作者:
翟华强
作者贡献:
杨宛君进行前期文献调研,设计研究方案,开展文献的检索与筛选、图谱的绘制与分析,撰写原稿;李丝雨、李易轩参与图谱的绘制与分析、论文的撰写;刘春宇、高明超、郦春锦负责文献检索与筛选,参与论文修订;郦春锦、翟华强对研究进行构思与设计,负责论文的审校和修订;翟华强对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:
YANG Wanjun1,2, LI Siyu1,2, LI Yixuan1,2, LIU Chunyu2,3, GAO Mingchao2,4, LI Chunjin5, ZHAI Huaqiang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-14
Revised:2023-10-23
Published:2024-06-05
Online:2024-04-08
Contact:
ZHAI Huaqiang
摘要: 背景 社区卫生服务机构在保障人民健康工作中发挥着重要作用,开展社区中医药服务可明显改善患者生命质量,缓解"看病难、看病贵"问题。对社区卫生服务机构的中医药服务开展情况进行文献计量学分析,可以为进一步提高社区中医药服务能力提供依据和方向。 目的 基于文献计量学和科学知识图谱分析,探讨我国社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务的发展进程、研究热点。 方法 于2023-01-01,在中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普中文期刊服务平台检索建库至2022-12-31发表的相关文献。采用Excel软件对年度发文量和来源期刊、来源院校进行统计分析,采用CiteSpace 6.1.R6软件对研究机构进行科研合作网络分析,对关键词进行聚类分析和突现分析,采用VOSviewer 1.6.18软件对作者、关键词进行频次统计和共现分析。 结果 共纳入文献920篇。其中,期刊论文813篇,来源于270种期刊,载文量最高的期刊为《中医药管理杂志》(80篇);学位论文107篇,来源于38所院校,发文量最高的院校为北京中医药大学和广州中医药大学(均为14篇)。共涉及研究机构449个,发文量最高的机构为北京中医药大学(23篇)。发文量排在前2位的作者为施永兴(27篇)、鲍勇(18篇),作者共现分析可形成12个聚类,同一聚类内的多个作者间合作密切,但尚未形成广泛的合作网络。共涉及关键词1 252个,形成了以"中医药""社区"等为标签的13个聚类,"中医体质"和"糖尿病"相关研究有望成为本领域相关研究的前沿热点。 结论 我国社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关研究正处于稳定发展期,但在研究方法的丰富性、较大影响力和较大规模合作网络形成等方面仍存在不足,需结合多学科研究方法,加强社区卫生服务机构之间及高校与社区卫生服务机构之间的合作。
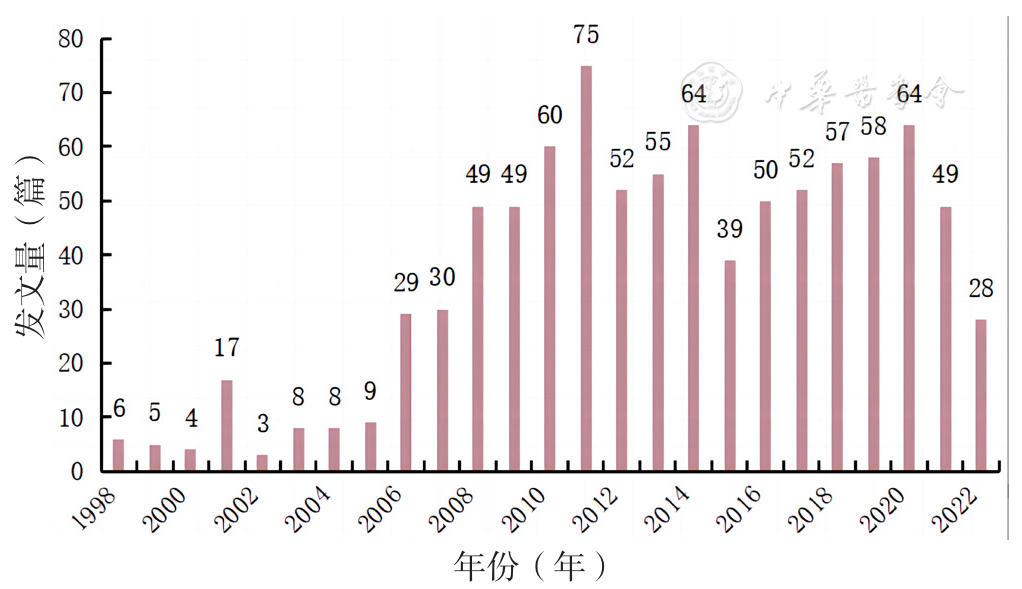
图2 1998—2022年社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的年度发文量
Figure 2 Annual publication volumn in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions from 1998 to 2022
| 期刊名称 | 载文量(篇) | 百分比(%) | 期刊入库情况 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中医药管理杂志 | 80 | 9.8 | — |
| 中国全科医学 | 48 | 5.9 | 北大核心、CA、JST、WJCI |
| 中国社区医师 | 28 | 3.4 | JST |
| 社区医学杂志 | 25 | 3.1 | CA |
| 中国中医药现代远程教育 | 23 | 2.8 | JST |
| 中国初级卫生保健 | 22 | 2.7 | JST |
| 社区卫生保健 | 16 | 2.0 | — |
| 中华全科医学 | 16 | 2.0 | — |
| 光明中医 | 15 | 1.8 | JST |
| 上海医药 | 14 | 1.7 | CA、JST |
| 中国中医药信息杂志 | 14 | 1.7 | CA、JST、CSCD扩展版 |
| 卫生软科学 | 13 | 1.6 | JST |
| 医药前沿 | 12 | 1.5 | — |
| 中国农村卫生事业管理 | 11 | 1.4 | — |
| 中国医药导报 | 10 | 1.2 | CA、JST |
表1 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关813篇期刊论文的来源期刊分布(前15位)
Table 1 Distribution of source journals of 813 articles related to traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions(top 15)
| 期刊名称 | 载文量(篇) | 百分比(%) | 期刊入库情况 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中医药管理杂志 | 80 | 9.8 | — |
| 中国全科医学 | 48 | 5.9 | 北大核心、CA、JST、WJCI |
| 中国社区医师 | 28 | 3.4 | JST |
| 社区医学杂志 | 25 | 3.1 | CA |
| 中国中医药现代远程教育 | 23 | 2.8 | JST |
| 中国初级卫生保健 | 22 | 2.7 | JST |
| 社区卫生保健 | 16 | 2.0 | — |
| 中华全科医学 | 16 | 2.0 | — |
| 光明中医 | 15 | 1.8 | JST |
| 上海医药 | 14 | 1.7 | CA、JST |
| 中国中医药信息杂志 | 14 | 1.7 | CA、JST、CSCD扩展版 |
| 卫生软科学 | 13 | 1.6 | JST |
| 医药前沿 | 12 | 1.5 | — |
| 中国农村卫生事业管理 | 11 | 1.4 | — |
| 中国医药导报 | 10 | 1.2 | CA、JST |
| 高校名称 | 发文量(篇) | 百分比(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 北京中医药大学 | 14 | 13.1 |
| 广州中医药大学 | 14 | 13.1 |
| 上海中医药大学 | 8 | 7.5 |
| 复旦大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 黑龙江中医药大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 南京中医药大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 山东大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 成都中医药大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 杭州师范大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 河南中医药大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 上海交通大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 中国中医科学院 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 福建医科大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
| 甘肃中医药大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
| 广西中医药大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
表2 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关107篇学位论文的来源高校分布(前15位)
Table 2 Distribution of source universities of 107 articles related to traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions(top 15)
| 高校名称 | 发文量(篇) | 百分比(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 北京中医药大学 | 14 | 13.1 |
| 广州中医药大学 | 14 | 13.1 |
| 上海中医药大学 | 8 | 7.5 |
| 复旦大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 黑龙江中医药大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 南京中医药大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 山东大学 | 5 | 4.7 |
| 成都中医药大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 杭州师范大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 河南中医药大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 上海交通大学 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 中国中医科学院 | 3 | 2.8 |
| 福建医科大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
| 甘肃中医药大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
| 广西中医药大学 | 2 | 1.9 |
| 研究机构 | 发文量(篇) | Degree值 |
|---|---|---|
| 北京中医药大学 | 23 | 10 |
| 上海交通大学 | 16 | 9 |
| 广州中医药大学 | 14 | 1 |
| 中国中医科学院 | 13 | 8 |
| 上海中医药大学 | 13 | 6 |
| 南京中医药大学 | 13 | 3 |
| 杭州师范大学 | 11 | 1 |
| 上海市中医药社区卫生服务研究中心 | 10 | 16 |
| 国家中医药管理局 | 7 | 6 |
| 上海中医药大学附属曙光医院 | 7 | 5 |
| 国家卫生健康委员会 | 7 | 4 |
| 中医药大学第三附属医院 | 7 | 2 |
| 安徽中医药大学 | 6 | 1 |
| 复旦大学公共卫生学院 | 6 | 1 |
| 浙江中医药大学 | 6 | 0 |
表3 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的前15位发文机构及中心性
Table 3 Top 15 institutions and degree values of papers related to traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 研究机构 | 发文量(篇) | Degree值 |
|---|---|---|
| 北京中医药大学 | 23 | 10 |
| 上海交通大学 | 16 | 9 |
| 广州中医药大学 | 14 | 1 |
| 中国中医科学院 | 13 | 8 |
| 上海中医药大学 | 13 | 6 |
| 南京中医药大学 | 13 | 3 |
| 杭州师范大学 | 11 | 1 |
| 上海市中医药社区卫生服务研究中心 | 10 | 16 |
| 国家中医药管理局 | 7 | 6 |
| 上海中医药大学附属曙光医院 | 7 | 5 |
| 国家卫生健康委员会 | 7 | 4 |
| 中医药大学第三附属医院 | 7 | 2 |
| 安徽中医药大学 | 6 | 1 |
| 复旦大学公共卫生学院 | 6 | 1 |
| 浙江中医药大学 | 6 | 0 |
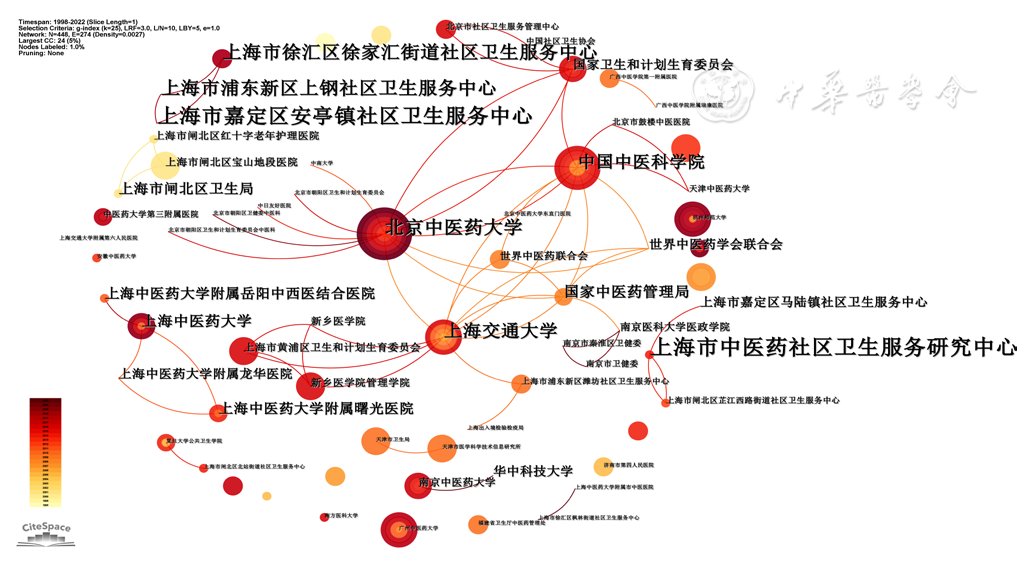
图3 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的研究机构合作网络图
Figure 3 Institution collaborative network for papers related to traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 作者 | 发文量(篇) |
|---|---|
| 施永兴 | 27 |
| 鲍勇 | 18 |
| 彭慧珍 | 11 |
| 刘登 | 9 |
| 陈楚杰 | 9 |
| 任建萍 | 8 |
| 张雪亮 | 8 |
| 朱宏敏 | 8 |
| 潘华峰 | 8 |
| 闪增郁 | 8 |
| 张敏 | 7 |
| 潘毅慧 | 7 |
| 王霞娣 | 7 |
| 章亚萍 | 7 |
表4 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献发文量排在前15位的作者
Table 4 Top 15 authors in number of published papers related to traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 作者 | 发文量(篇) |
|---|---|
| 施永兴 | 27 |
| 鲍勇 | 18 |
| 彭慧珍 | 11 |
| 刘登 | 9 |
| 陈楚杰 | 9 |
| 任建萍 | 8 |
| 张雪亮 | 8 |
| 朱宏敏 | 8 |
| 潘华峰 | 8 |
| 闪增郁 | 8 |
| 张敏 | 7 |
| 潘毅慧 | 7 |
| 王霞娣 | 7 |
| 章亚萍 | 7 |
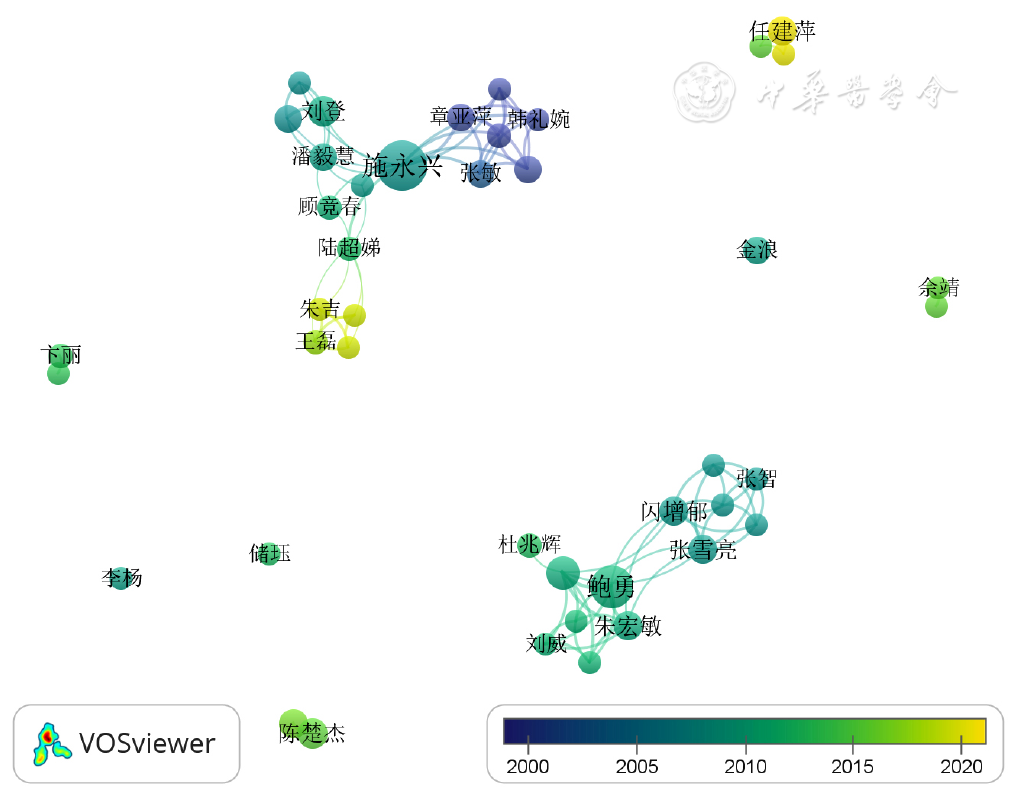
图4 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的作者共现网络叠加视图
Figure 4 Collaborative map in overlay visualization of authors in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 关键词 | 出现频次(次) |
|---|---|
| 社区卫生服务 | 317 |
| 中医药 | 252 |
| 社区卫生服务机构 | 137 |
| 中医适宜技术 | 86 |
| 中医药服务 | 81 |
| 社区 | 79 |
| 中医 | 56 |
| 治未病思想 | 49 |
| 现状研究 | 42 |
| 社区卫生 | 31 |
| 需求 | 28 |
| 高血压 | 28 |
| 调查研究 | 26 |
| 对策 | 25 |
| 社区中医药服务 | 23 |
| 社区居民 | 22 |
| 影响因素 | 21 |
| 基层医疗卫生机构 | 20 |
| 上海市 | 19 |
| 中医药疗法 | 19 |
表5 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的关键词分布(前20位)
Table 5 Distribution top 20 high-frequency keywords in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 关键词 | 出现频次(次) |
|---|---|
| 社区卫生服务 | 317 |
| 中医药 | 252 |
| 社区卫生服务机构 | 137 |
| 中医适宜技术 | 86 |
| 中医药服务 | 81 |
| 社区 | 79 |
| 中医 | 56 |
| 治未病思想 | 49 |
| 现状研究 | 42 |
| 社区卫生 | 31 |
| 需求 | 28 |
| 高血压 | 28 |
| 调查研究 | 26 |
| 对策 | 25 |
| 社区中医药服务 | 23 |
| 社区居民 | 22 |
| 影响因素 | 21 |
| 基层医疗卫生机构 | 20 |
| 上海市 | 19 |
| 中医药疗法 | 19 |
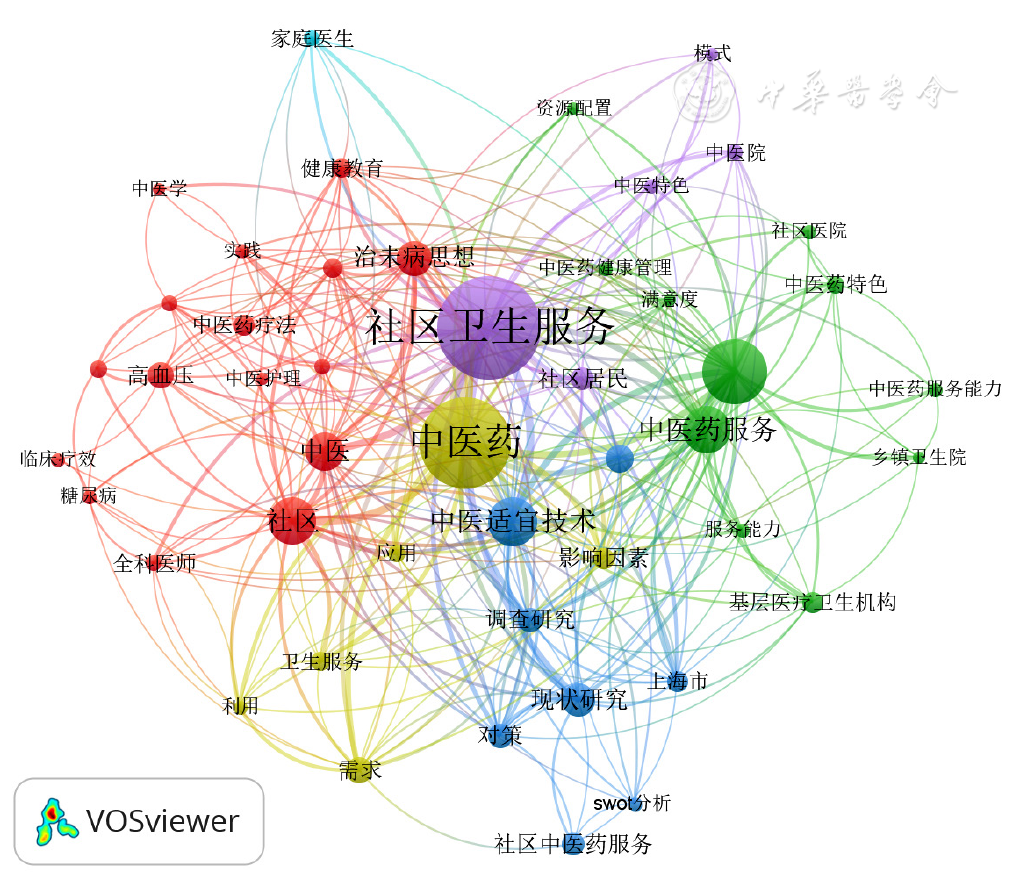
图5 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的关键词共现网络视图
Figure 5 Keywords co-occurrence network visualization in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions

图6 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的关键词共现网络密度视图
Figure 6 Keywords co-occurrence network density visualization in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 聚类编号 | 聚类标签 | 聚类轮廓值 | 聚类文献发表年份的平均值(年) | 依据LLR算法提取出的标签词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 中医药 | 0.893 | 2009 | 中医药;适宜技术;需求;中医;人力资源 |
| 1 | 中医 | 0.809 | 2010 | 中医;治未病;中医药;对策;健康管理 |
| 2 | 社区 | 0.795 | 2012 | 社区;服务能力;中医护理;全科医生;培训 |
| 3 | 社区卫生 | 0.879 | 2008 | 社区卫生;中医特色;中医治疗;健康保障;农村 |
| 4 | 中医院 | 0.96 | 2005 | 中医院;社区居民;医联体;闸北区;卫生改革 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 0.929 | 2009 | 影响因素;上海市;卫生服务;中医科;发展策略 |
| 6 | 公共卫生 | 0.948 | 2010 | 公共卫生;社区医疗;中药;社区医疗卫生服务;劳务工 |
| 7 | 临床疗效 | 0.995 | 2015 | 临床疗效;消渴症;益气健脾化瘀;太阴人;体质证型 |
| 8 | 中医专科 | 0.981 | 2006 | 中医专科;中医师;需求与利用;卫生院;中医医疗服务 |
| 9 | 高血压 | 0.98 | 2009 | 高血压;慢性非传染性疾病;分布特点;中医证素;发病率 |
| 10 | 中医学 | 0.946 | 2011 | 中医学;人才培养;实践;培养模式;培养 |
| 11 | 中医药学 | 0.965 | 2006 | 中医药学;贡献率;地位和作用;医学模式;小康社会 |
| 12 | 门诊部 | 0.997 | 2011 | 门诊部;中医针灸;针灸;作用机制;膝骨性关节炎 |
表6 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的关键词聚类情况
Table 6 Clustering of keywords in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| 聚类编号 | 聚类标签 | 聚类轮廓值 | 聚类文献发表年份的平均值(年) | 依据LLR算法提取出的标签词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 中医药 | 0.893 | 2009 | 中医药;适宜技术;需求;中医;人力资源 |
| 1 | 中医 | 0.809 | 2010 | 中医;治未病;中医药;对策;健康管理 |
| 2 | 社区 | 0.795 | 2012 | 社区;服务能力;中医护理;全科医生;培训 |
| 3 | 社区卫生 | 0.879 | 2008 | 社区卫生;中医特色;中医治疗;健康保障;农村 |
| 4 | 中医院 | 0.96 | 2005 | 中医院;社区居民;医联体;闸北区;卫生改革 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 0.929 | 2009 | 影响因素;上海市;卫生服务;中医科;发展策略 |
| 6 | 公共卫生 | 0.948 | 2010 | 公共卫生;社区医疗;中药;社区医疗卫生服务;劳务工 |
| 7 | 临床疗效 | 0.995 | 2015 | 临床疗效;消渴症;益气健脾化瘀;太阴人;体质证型 |
| 8 | 中医专科 | 0.981 | 2006 | 中医专科;中医师;需求与利用;卫生院;中医医疗服务 |
| 9 | 高血压 | 0.98 | 2009 | 高血压;慢性非传染性疾病;分布特点;中医证素;发病率 |
| 10 | 中医学 | 0.946 | 2011 | 中医学;人才培养;实践;培养模式;培养 |
| 11 | 中医药学 | 0.965 | 2006 | 中医药学;贡献率;地位和作用;医学模式;小康社会 |
| 12 | 门诊部 | 0.997 | 2011 | 门诊部;中医针灸;针灸;作用机制;膝骨性关节炎 |
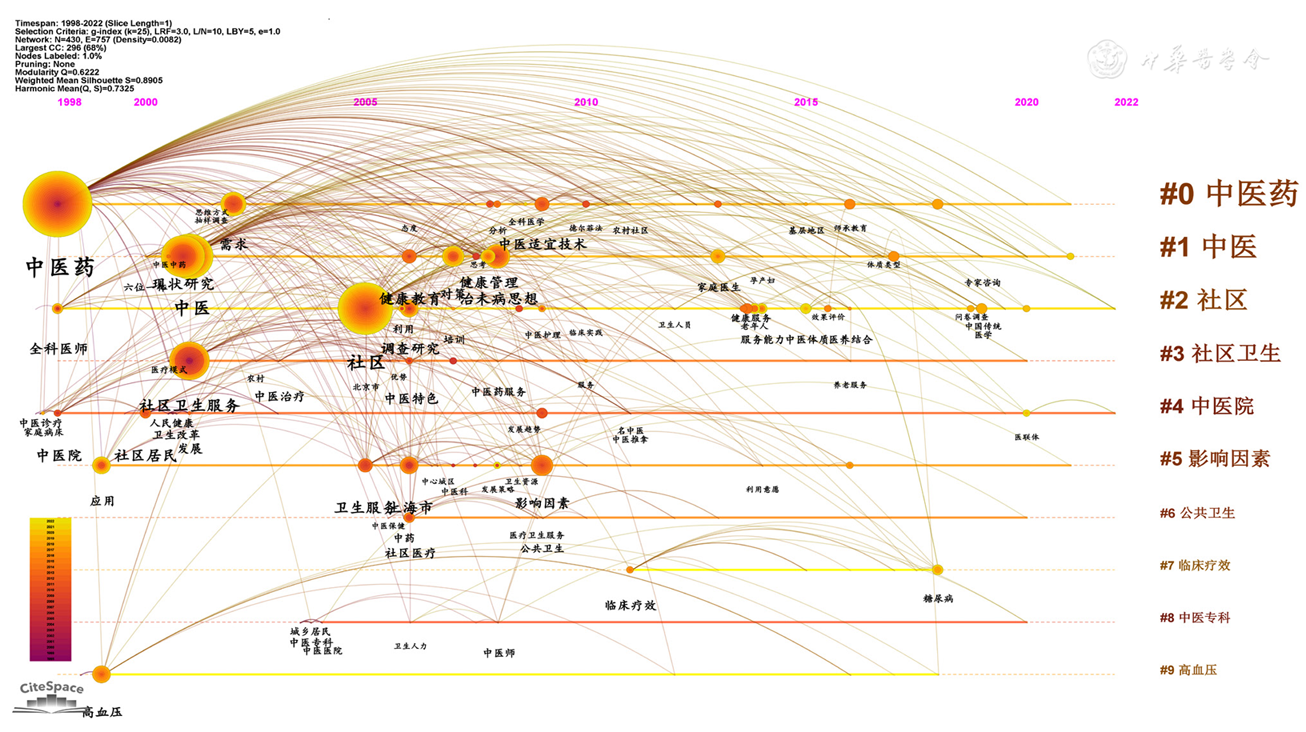
图7 社区卫生服务机构开展中医药服务相关文献的关键词时间线图
Figure 7 Timeline of keywords in the field of traditional Chinese medicine services in community health service institutions
| [1] |
原卫生部,国家中医药管理局. 城市社区卫生服务机构管理办法(试行)[A/OL].(2006-06-29) [2023-01-01].
|
| [2] |
汤大朋,马新飞,倪菲菲,等. "健康中国"背景下中医药服务能力的内涵构成及提升路径对策[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2019,36(3):198-200.
|
| [3] |
乔东鸽,张琰,车旭. 新医改背景下中医药社区卫生服务发展策略研究[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2022,20(15):172-174. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2022.15.064.
|
| [4] | |
| [5] | |
| [6] |
李杰. 科学知识图谱原理及应用:VOSviewer和CitNetExplorer初学者指南[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2018.
|
| [7] |
李杰,魏瑞斌. VOSviewer应用现状及其知识基础研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报,2022,34(6):61-71. DOI:10.13998/j.cnki.issn1002-1248.21-0843.
|
| [8] |
陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. DOI:10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] | |
| [12] | |
| [13] |
蔡传,张明明,吕红城. 中医药服务对高血压患者健康管理效果分析[J]. 社区医学杂志,2019,17(18):1156-1159. DOI:10.19790/j.cnki.JCM.2019.18.17.
|
| [14] |
陈悦,陈超美,胡志刚. 引文空间分析原理与应用:CiteSpace实用指南[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2014.
|
| [15] |
陆超娣,施永兴,严非. 上海市中心城区社区卫生服务中心中医药服务现状调查:附中心城区社区卫生服务中心一日门诊分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2006,9(21):1786-1788. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2006.21.019.
|
| [16] |
施永兴,贺金仙,章亚萍,等. 关于上海市民对中医药社区卫生服务的调查[J]. 中医药管理杂志,2000,8(4):42-44. DOI:10.16690/j.cnki.1007-9203.2000.04.019.
|
| [17] |
霍清萍,鲍勇. 发挥中医学优势发展具有中国特色的社区卫生服务[J]. 中国卫生经济,2001,20(9):39-40. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-0743.2001.09.019.
|
| [18] |
郭丽君,鲍勇,孙炜,等. 社区医务人员对中医"治未病"政策的认知情况及发展建议[J]. 中国全科医学,2016,19(1):34-41. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.01.007.
|
| [19] | |
| [20] | |
| [21] | |
| [22] |
国家卫生部,国家发展计划委员会,教育部,等. 关于发展城市社区卫生服务的若干意见[A/OL].(1999-07-16) [2023-01-01].
|
| [23] |
霍清萍,鲍勇,熊平. 发挥中医药学优势建立具有中国特色的社区卫生服务模式[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2001,17(7):391-393. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4663.2001.07.003.
|
| [24] |
卫生部,国家中医药管理局. 社区卫生服务中心中医药服务管理基本规范[A/OL].(2003-11-25) [2023-10-23].
|
| [25] |
国家中医药管理局,原卫生部,人力资源和社会保障部,等. 基层中医药服务能力提升工程实施方案[A/OL].(2012-09-28) [2023-01-01].
|
| [26] |
国家中医药管理局. 全国社区中医药工作先进单位建设标准(2013年版)[A/OL].(2013-09-29) [2023-03-03].
|
| [27] |
国家卫生健康委办公厅. 社区卫生服务中心服务能力评价指南(2019年版)[A/OL].(2019-03-19) [2023-10-23].
|
| [28] |
陈楚杰,潘华峰,冯毅翀,等. 广州市社区卫生服务利用者对中医药服务的利用现状与需求分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2010,13(16):1742-1744. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2010.16.009.
|
| [29] |
刘步平,方春平,陈楚杰,等. 发展智慧中医药社区卫生服务亟待破解的关键要素[J]. 现代医院,2018,18(10):1474-1477. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-332X.2018.10.022.
|
| [30] |
高倩. 上海市基层社区中医医疗资源信息研究[D]. 上海:上海中医药大学,2020.
|
| [31] |
蔡民坤,林伟良,洪涛,等. 社区卫生服务中心中医药参与家庭医生服务现状和对策[J]. 中国农村卫生事业管理,2013,33(8):868-870.
|
| [32] |
陈雁,庄向慧,潘宇峰. 家庭医生团队在社区中医"治未病"工作中的实践[J]. 健康教育与健康促进,2020,15(3):337-339. DOI:10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.202003038.
|
| [33] |
王宏长,浦斌红,潘明. 试论中医家庭医生在社区卫生服务中的作用[J]. 上海中医药大学学报,2011,25(6):89-91. DOI:10.16306/j.1008-861x.2011.06.002.
|
| [34] |
潘公益,于庆璐,杨烨. 家庭医生(中医-康复)团队的探索与实践[J]. 中医药导报,2019,25(3):21-23,34. DOI:10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2019.03.005.
|
| [35] |
叶静雪,曾庆秋,钱宁,等. 基层医疗机构2型糖尿病患者家庭医生团队中医药健康管理服务现状调查分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(11):1265-1269. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.00.433.
|
| [36] |
侯进,蔡利强,康建忠,等. 基于SERVQUAL量表的以家庭医生为主体的社区中医药健康管理服务评价[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(28):3441-3445. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.384.
|
| [37] |
王琦,盛增秀. 中医体质学说[M]. 南京:江苏科学技术出版社,1982.
|
| [38] |
周翼. 中医体质辨识在高血压分级管理中的应用与探讨[J]. 保健医学研究与实践,2016,13(1):41-46. DOI:10.11986/j.issn.1673-873X.2016.01.010.
|
| [39] | |
| [40] |
郁东海,叶盛,胡晓萍,等. 上海市浦东新区中西医结合公共卫生服务体系糖尿病管理项目成效评价[J]. 中国初级卫生保健,2021,35(11):42-44. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2021.11.0013.
|
| [41] |
蒋良华,翁哲芳,胡小英,等. 中西医结合防治干预对社区糖尿病患者中医体质的影响[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(2):6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.2018.02.005.
|
| [42] |
陈海艳,许光远,张晓明. 健脾疏肝法对糖尿病胃轻瘫患者的临床作用及焦虑状态的影响[J]. 医学食疗与健康,2020,18(24):28-29.
|
| [43] |
王海焱,秦灵灵,刘铜华,等. 中药复方糖耐康结合西医常规疗法治疗2型糖尿病足临床研究[J]. 国际中医中药杂志,2022,44(12):1358-1364. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115398-20220108-00078.
|
| [44] |
施莹,赖龙胜,黄腾蛟,等. 黄连温胆汤联合贝那普利治疗湿热中阻型糖尿病肾病临床观察[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2021,19(11):144-147. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2021.11.054.
|
| [1] | 高翔, 陈红, 周蓉, 石建伟, 俞文雅, 吕奕鹏, 周良, 王朝昕, 黄雷. 基于签约服务费的家庭医生团队绩效"二次分配"指标体系构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(16): 1930-1934. |
| [2] | 甘静雯, 巩亚楠. 北京市某区社区卫生服务中心内部绩效管理实践研究与效果评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(16): 1942-1949. |
| [3] | 马佳, 张敏珏, 张韶伟, 于海燕, 陈慎, 古丽拜尔·马木提, 洪娟, 陆媛. 社区管理的老年2型糖尿病患者并发轻度认知功能障碍相关影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(16): 1984-1989. |
| [4] | 刘舒嫣, 姚弥, 张家玮, 祁祯楠, 齐建光, 冼俊芳, 迟春花. 北京市与深圳市儿童分级诊疗相关政策对比分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(13): 1550-1555. |
| [5] | 陈红, 周蓉, 石建伟, 俞文雅, 吕奕鹏, 周良, 高翔, 黄雷, 王朝昕. 基于签约服务费的家庭医生团队绩效"一次分配"指标体系构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(13): 1556-1560. |
| [6] | 刘畅, 王宇菲. 基于文献计量分析的我国异地就医研究现状与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1525-1532. |
| [7] | 吴月苹, 牛亚冬, 张亮, 张翔, 吴建, 苗豫东. 中国社区卫生服务发展的挑战与优化路径[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(10): 1162-1165. |
| [8] | 李娅玲, 顾燕峰, 郑艳玲, 蔡学民, 王伟, 余海燕, 杜兆辉. 城市社区卫生服务中心发展情况调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(10): 1166-1172. |
| [9] | 姜晓利, 彭海波, 许凌烽, 徐娜, 尹呈良, 孟文奇, 柳松艺, 尹文强, 陈钟鸣, 马东平, 于倩倩. 家庭医生签约服务背景下签约居民基层首诊效果评价研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(10): 1231-1237. |
| [10] | 熊刘芳, 邹晓昭, 马涵英, 赵铁夫. 社区卫生服务中心长程家庭医生签约需求的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(10): 1238-1244. |
| [11] | 范晶, 魏珊, 李丽秋, 郑秀丽, 李言, 牛建英, 王玲, 许成燕. 社区老年人群蛋白尿及肾功能异常发生率及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(09): 1048-1053. |
| [12] | 丁礼雪, 李玉红, 张玉东. 基于CiteSpace的非稳态负荷相关研究热点及前沿的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(08): 1008-1014. |
| [13] | 孙可, 孙超, 郝金娟, 许华钊, 马燕, 胡慧秀. 我国不同场所老年人失能状况的差异化分析:基于23 922例老年人的调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(07): 886-892. |
| [14] | 贾丽燕, 赵能江, 闫冰, 张智海, 占娜, 林远冰, 刘建平, 杨叔禹. 基层医师对糖尿病中医类指南知悉程度与使用现状的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(05): 589-596. |
| [15] | 牛路瑶, 营心语, 张树琴, 安志新, 季婧雅, 刘跃华, 高月霞. 价值共创视角下糖尿病社区管理模式实践与思考[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(05): 563-569. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





