中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (03): 293-303.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0558
所属专题: 呼吸疾病文章合辑
郭栋伟1, 张鹏飞1,*( ), 任明君2, 廖丽君1, 黄茹妍2, 罗湘蓉2
), 任明君2, 廖丽君1, 黄茹妍2, 罗湘蓉2
收稿日期:2022-07-26
修回日期:2022-08-22
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2022-09-30
通讯作者:
张鹏飞
基金资助:
GUO Dongwei1, ZHANG Pengfei1,*( ), REN Mingjun2, LIAO Lijun1, HUANG Ruyan2, LUO Xiangrong2
), REN Mingjun2, LIAO Lijun1, HUANG Ruyan2, LUO Xiangrong2
Received:2022-07-26
Revised:2022-08-22
Published:2023-01-20
Online:2022-09-30
Contact:
ZHANG Pengfei
About author:摘要: 背景 银杏叶提取物(GBE)能抑制慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)大鼠气道及全身炎性反应,改善气道重塑,但其具体作用机制尚不清楚。 目的 探讨GBE通过磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)信号通路调控肺泡巨噬细胞自噬防治COPD的作用机制。 方法 于2020年11月至2022年3月,选取90只SPF级雄性Wistar大鼠随机分为正常对照组、COPD模型组、GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组,每组15只。正常对照组第1 、14天向气管内注入0.9%氯化钠溶液,其余时间进行正常饲养。COPD模型组、GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组和Taselisib组采用香烟熏吸联合气管内注入脂多糖(LPS)的方法构建COPD大鼠模型。GBE组于实验的第15~28天腹腔注射舒血宁注射液,比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组于实验的第29~42天分别给予Akt抑制剂比卡鲁胺、mTOR抑制剂雷帕霉素、PI3K抑制剂Taselisib进行干预。HE染色观察各组大鼠肺泡病理改变及气道重塑情况;酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测大鼠肺泡灌洗液(BALF)与血清白介素6(IL-6)和白介素-8(IL-8)水平;显微镜下计数各组大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞数量;透射电镜观察各组大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞的超微结构;蛋白免疫印迹法(WB)检测各组大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞自噬相关蛋白表达水平并计算微管相关蛋白轻链3(LC3)-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值。 结果 造模结束后各组大鼠数量为:正常对照组12只、COPD模型组11只、GBE组12只、比卡鲁胺组12只、雷帕霉素组12只、Taselisib组11只。HE染色结果显示,GBE组与各抑制剂组大鼠肺泡损伤程度较COPD模型组减轻;GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组肺平均内衬间隔(MLI)与平均肺泡面积(MAA)小于COPD模型组,平均肺泡数(MAN)大于COPD模型组(P<0.05);GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组支气管壁结构较COPD模型组完整。COPD模型组BALF与血清IL-6、IL-8水平高于其他各组(P<0.05)。正常对照组巨噬细胞数量低于其他各组(P<0.05),COPD模型组巨噬细胞数量高于其他各组(P<0.05)。透射电镜观察显示GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组肺泡巨噬细胞的自噬溶酶体较COPD模型组多。正常对照组的PI3Kp110α、Akt、p-Ak、mTOR、p-mTOR表达水平高于其他各组,LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值低于其他各组(P<0.05);COPD模型组与GBE组、比卡鲁胺组、雷帕霉素组、Taselisib组比较,PI3Kp110α、Akt、p-Akt、mTOR、p-mTOR表达水平升高,LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值降低(P<0.05)。 结论 GBE能通过调控PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路,维持COPD大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞的自噬功能,减轻巨噬细胞浸润,抑制炎性反应及肺泡破坏,改善气道重塑。
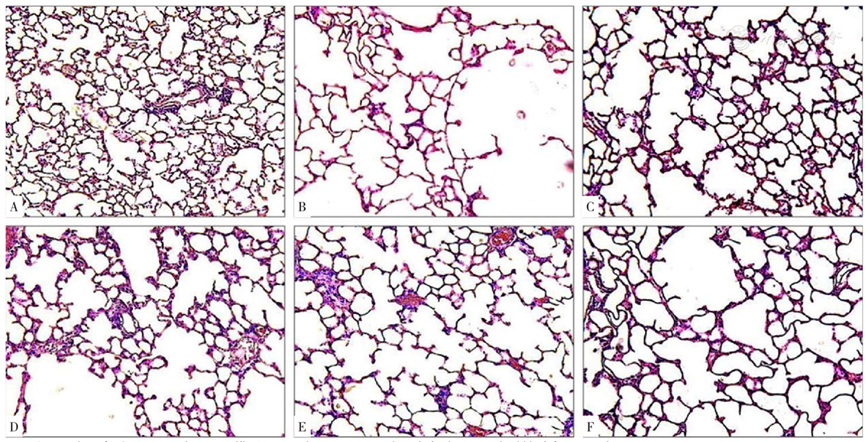
图1 各组大鼠肺泡病理改变(200×)注:A为正常对照组,B为COPD模型组,C为GBE组,D为比卡鲁胺组,E为雷帕霉素组,F为Taselisib组
Figure 1 Pathological changes of alveoli in rats of normal control,COPD model,GBE,bicalutamide,rapamycin and taselisib groups
| 组别 | 只数 | MLI(μm) | MAN(个/mm2) | MAA(μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 47.59±4.74 | 206.91±31.14 | 4 573.30±789.90 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 123.01±21.94a | 85.36±14.73a | 11 512.17±3 579.00a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 73.58±8.23ab | 131.37±19.26ab | 7 124.91±1 748.43ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 78.16±8.54ab | 135.78±20.68ab | 7 272.16±1 450.47ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 80.75±14.69ab | 134.38±28.50ab | 7 879.51±2 038.87ab |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 75.01±8.37ab | 149.44±19.83ab | 6 720.84±1 028.26ab |
| F值 | 44.564 | 33.002 | 14.992 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表1 各组大鼠MLI、MAN、MAA的比较(±s)
Table 1 Comparison of mean linear intercept,mean alveolar area and mean alveolar number in rats of six groups
| 组别 | 只数 | MLI(μm) | MAN(个/mm2) | MAA(μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 47.59±4.74 | 206.91±31.14 | 4 573.30±789.90 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 123.01±21.94a | 85.36±14.73a | 11 512.17±3 579.00a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 73.58±8.23ab | 131.37±19.26ab | 7 124.91±1 748.43ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 78.16±8.54ab | 135.78±20.68ab | 7 272.16±1 450.47ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 80.75±14.69ab | 134.38±28.50ab | 7 879.51±2 038.87ab |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 75.01±8.37ab | 149.44±19.83ab | 6 720.84±1 028.26ab |
| F值 | 44.564 | 33.002 | 14.992 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
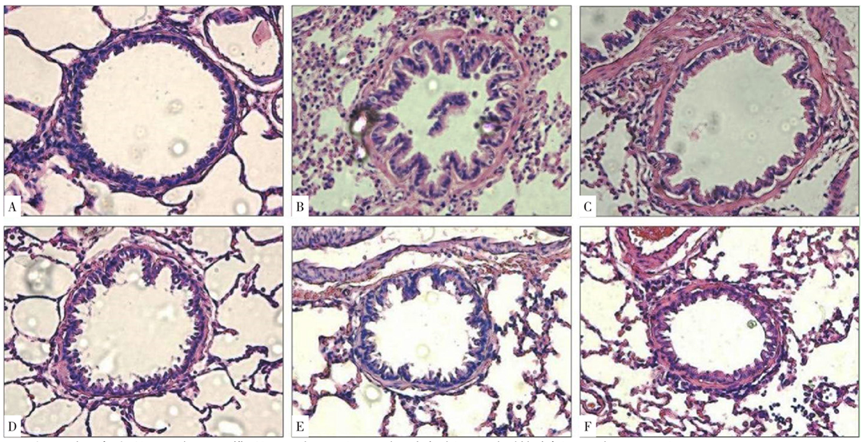
图2 各组大鼠气道重塑的比较(400×)注:A为正常对照组,B为COPD模型组,C为GBE组,D为比卡鲁胺组,E为雷帕霉素组,F为Taselisib组
Figure 2 Comparison of airway remodeling status in rats of normal control,COPD model,GBE,bicalutamide,rapamycin and taselisib groups
| 组别 | 只数 | IL-6 | IL-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 28.52±4.10 | 36.29±4.41 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 243.26±13.93a | 222.49±8.12a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 34.39±2.01ab | 114.98±7.37ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 20.58±2.83abc | 73.75±3.82abc |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 28.97±4.23bd | 101.42±7.27abcd |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 28.15±6.40bcd | 75.50±3.01abce |
| F值 | 1 923.260 | 1 282.215 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表2 各组大鼠BALF中IL-6、IL-8水平的比较(±s,pg/ml)
Table 2 Comparison of levels of IL-6 and IL-8 in alveolar lavage fluid in rats of six groups
| 组别 | 只数 | IL-6 | IL-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 28.52±4.10 | 36.29±4.41 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 243.26±13.93a | 222.49±8.12a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 34.39±2.01ab | 114.98±7.37ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 20.58±2.83abc | 73.75±3.82abc |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 28.97±4.23bd | 101.42±7.27abcd |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 28.15±6.40bcd | 75.50±3.01abce |
| F值 | 1 923.260 | 1 282.215 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 组别 | 只数 | IL-6 | IL-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 80.56±12.72 | 17.63±1.95 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 242.43±74.86a | 85.79±17.19a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 181.92±44.39ab | 67.57±11.83ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 137.37±18.40abc | 45.16±2.69abc |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 59.49±13.63bcd | 65.20±4.39abd |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 162.26±54.13abe | 33.67±1.67abcde |
| F值 | 29.251 | 94.826 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表3 各组大鼠血清IL-6、IL-8水平比较(±s,pg/ml)
Table 3 Comparison of serum levels of IL-6 and IL-8 in the rats of six groups
| 组别 | 只数 | IL-6 | IL-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 12 | 80.56±12.72 | 17.63±1.95 |
| COPD模型组 | 11 | 242.43±74.86a | 85.79±17.19a |
| GBE组 | 12 | 181.92±44.39ab | 67.57±11.83ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 12 | 137.37±18.40abc | 45.16±2.69abc |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 12 | 59.49±13.63bcd | 65.20±4.39abd |
| Taselisib组 | 11 | 162.26±54.13abe | 33.67±1.67abcde |
| F值 | 29.251 | 94.826 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 组别 | 巨噬细胞数量(×106个/g) |
|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 1.35±0.09 |
| COPD模型组 | 3.68±0.20a |
| GBE组 | 2.51±0.14ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 2.49±0.11ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 2.29±0.18ab |
| Taselisib组 | 2.30±0.01ab |
| F值 | 87.380 |
| P值 | <0.001 |
表4 各组大鼠单位重量肺组织肺泡巨噬细胞数量的比较(±s,n=3)
Table 4 Comparison of the number of alveolar macrophages per unit weight in lung tissues of rats in six groups
| 组别 | 巨噬细胞数量(×106个/g) |
|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 1.35±0.09 |
| COPD模型组 | 3.68±0.20a |
| GBE组 | 2.51±0.14ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 2.49±0.11ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 2.29±0.18ab |
| Taselisib组 | 2.30±0.01ab |
| F值 | 87.380 |
| P值 | <0.001 |
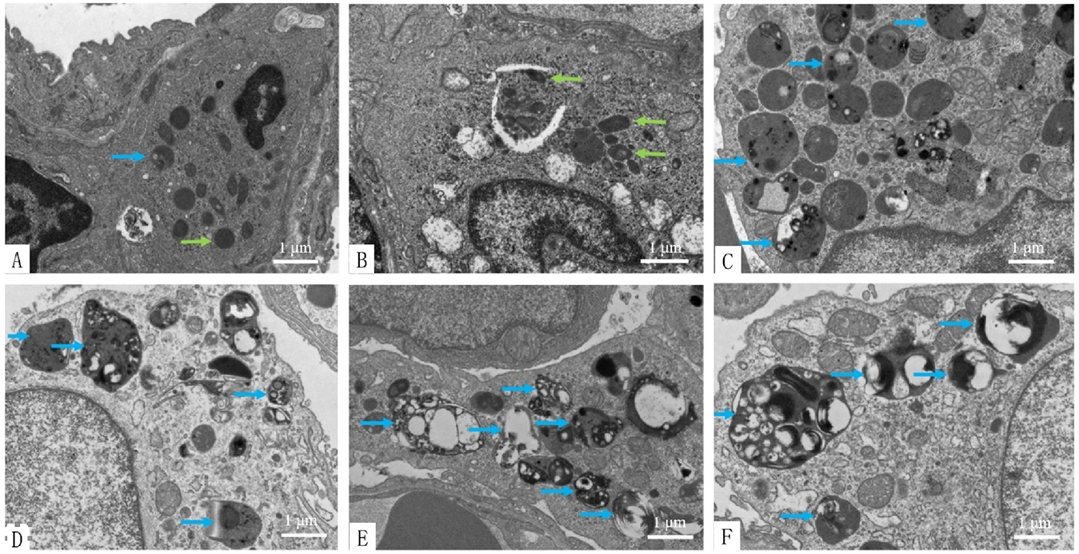
图4 各组肺泡巨噬细胞透射电镜图(7 000×)注:A为正常对照组,B为COPD模型组,C为GBE组,D为比卡鲁胺组,E为雷帕霉素组,F为Taselisib组
Figure 4 Transmission electron micrographs of alveolar macrophages in normal control,COPD model,GBE,bicalutamide,rapamycin and taselisib groups
| 组别 | PI3Kp110α | Akt | p-Akt | mTOR | p-mTOR | LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 1.11±0.23 | 0.98±0.11 | 0.55±0.02 | 0.77±0.12 | 0.47±0.02 | 1.02±0.01 |
| COPD模型组 | 0.81±0.18a | 0.73±0.13a | 0.42±0.01a | 0.59±0.10a | 0.42±0.02a | 1.20±0.03a |
| GBE组 | 0.51 ±0.15ab | 0.51±0.12ab | 0.23±0.10ab | 0.43±0.07ab | 0.37±0.02ab | 1.38±0.07ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 0.48±0.17ab | 0.46±0.11ab | 0.11±0.06ab | 0.37±0.09ab | 0.36±0.02ab | 1.40±0.08ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 0.36±0.08ab | 0.34±0.09ab | 0.20±0.09ab | 0.31±0.07ab | 0.14±0.03abcd | 1.43±0.15ab |
| Taselisib组 | 0.24±0.09ab | 0.19±0.06abcd | 0.22±0.11ab | 0.23±0.07abc | 0.33±0.02abce | 1.39±0.08ab |
| F值 | 11.783 | 21.185 | 15.120 | 15.078 | 76.594 | 11.798 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表5 各组大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞中自噬相关蛋白表达水平比较(±s,n=3)
Table 5 Comparison of expression levels of autophagy-related proteins in alveolar macrophages of rats in six groups
| 组别 | PI3Kp110α | Akt | p-Akt | mTOR | p-mTOR | LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 1.11±0.23 | 0.98±0.11 | 0.55±0.02 | 0.77±0.12 | 0.47±0.02 | 1.02±0.01 |
| COPD模型组 | 0.81±0.18a | 0.73±0.13a | 0.42±0.01a | 0.59±0.10a | 0.42±0.02a | 1.20±0.03a |
| GBE组 | 0.51 ±0.15ab | 0.51±0.12ab | 0.23±0.10ab | 0.43±0.07ab | 0.37±0.02ab | 1.38±0.07ab |
| 比卡鲁胺组 | 0.48±0.17ab | 0.46±0.11ab | 0.11±0.06ab | 0.37±0.09ab | 0.36±0.02ab | 1.40±0.08ab |
| 雷帕霉素组 | 0.36±0.08ab | 0.34±0.09ab | 0.20±0.09ab | 0.31±0.07ab | 0.14±0.03abcd | 1.43±0.15ab |
| Taselisib组 | 0.24±0.09ab | 0.19±0.06abcd | 0.22±0.11ab | 0.23±0.07abc | 0.33±0.02abce | 1.39±0.08ab |
| F值 | 11.783 | 21.185 | 15.120 | 15.078 | 76.594 | 11.798 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
张鹏飞,廖丽君,谭玉萍. 银杏叶提取物治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2017,20(15):1906-1910. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.15.024.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
张鹏飞,廖丽君,邓祯,等. 银杏叶提取物的药理作用及其临床应用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2017,44(2):426-429. DOI:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2017.02.069.
|
| [11] |
梁炜,杨红梅,梁爱武,等. 银杏叶提取物对慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠CRP、TNF-α的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志,2017,33(12):1936-1938. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.12.010.
|
| [12] |
谭玉萍,王朝晖,姚萍,等. 银杏叶提取物对慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠气道及肺血管重塑的影响[J]. 中华肺部疾病杂志(电子版),2017,10(6):662-667. DOI:10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-6902.2017.06.005.
|
| [13] |
黄文锋,陈斯宁,吴嘉冬,等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠模型的构建[J]. 现代医药卫生,2019,35(6):801-803. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2019.06.001.
|
| [14] |
禹茜,胡军涛,赖洁,等. 三种方法提取大鼠原代巨噬细胞的生物学特点比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(24):3863-3868. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0315.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
施诚龙,陈冲,高永军,等. PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路在细胞自噬中作用及机制的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2021,61(27):102-105. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2021.27.027.
|
| [28] |
韩长鸣,戴晓玥,段前梅,等. 鲍曼不动杆菌荚膜通过抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路促进鼠巨噬细胞自噬和凋亡[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版),2020,30(1):1-6. DOI:10.13312/j.issn.1671-7783.y190124.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
周秀,张慧,钟小宁. 哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白在慢性炎症性肺部疾病中的研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志,2018,34(24):4180-4182,4186. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2018.24.040.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
谭玉萍,张鹏飞,冯玉清,等. GBE对COPD大鼠血清和肺泡灌洗液中IL-1、IL-8含量的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2018,28(5):7-10. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2018.05.002.
|
| [36] |
张鹏飞,梁炜,谭玉萍,等. 银杏叶提取物对慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠肺组织MMP-1及MMP-9表达的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2017,44(4):849-851,898. DOI:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2017.04.060.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
赵晶,秦合伟,李彦杰,等. 血管软化丸调控PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路影响细胞自噬及抗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2020,38(1):65-69,268. DOI:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2020.01.015.
|
| [39] |
崔晓丽,魏振,沈辉,等. 雷帕霉素通过激活LC3介导的细胞自噬改善ApoE4/5×FAD小鼠的认知功能[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(8):1400-1408. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2021.08.008.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
呙阳,周洁,赖小宝,等. 不同毒力的分枝杆菌感染促进小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞自噬及mTOR和AKT磷酸化[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2020,36(12):1057-1062. DOI:10.13423/j.cnki.cjcmi.009108.
|
| [42] |
庞琪,刘晓菊,施凯,等. 香烟烟雾对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者单核细胞源性巨噬细胞吞噬功能的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2014,94(12):895-898. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2014.12.005.
|
| [43] |
赵红星,丁佩山,刘荣玉. 吞噬及饥饿诱导巨噬细胞自噬对其吞噬功能的影响[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2011,46(5):401-404. DOI:10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2011.05.001.
|
| [1] | 徐百川, 王艳, 张彭, 李艺婷, 刘飞来, 谢洋. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病共病肺癌筛查工具分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3847-3852. |
| [2] | 高桂英, 胡阳, 张世益, 孟怡, 邓洁. 运动康复改善冠状动脉微循环障碍的相关机制研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2570-2576. |
| [3] | 朱子一, 何贵新, 秦伟彬, 宋惠, 张利文, 唐伟智, 杨斐斐, 刘凌云, 欧阳彬. 线粒体自噬改善心肌梗死后心肌纤维化及其中医药干预的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2294-2300. |
| [4] | 金锋, 黎旺玲, 谢飞. 基于"慢阻肺防治平台"的闭环管理案例研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2059-2064. |
| [5] | 陈典, 隆寰宇, 张丛溪, 褚岚和, 李姝润, 陈亚红. 2025年GOLD慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊断、治疗、管理及预防全球策略更新要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 1937-1949. |
| [6] | 郦奇锋, 隆寰宇, 王泽茂, 封敏, 陈亚红, 胡征. 物联网技术在基层医疗卫生机构肺功能检查与管理中的应用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1674-1675. |
| [7] | 宋荣维, 吴春香, 于杰, 路宇晴, 张锋英. 基于社区居民的保留比率的肺量计异常人群特征研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1185-1192. |
| [8] | 吴俊, 张玲, 顾东伟, 郑磊, 赵祝香, 赵子文. 单纯性支气管扩张症与支气管扩张症-慢性阻塞性肺疾病重叠综合征患者的病原菌对比研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 729-736. |
| [9] | 潘子涵, 李姝润, 陈亚红. 物联网技术在慢性阻塞性肺疾病管理中的研究进展与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4446-4454. |
| [10] | 杨天祎, 司徒炫明, 曲木诗玮, 王思远, 江山, 杨汀. 30秒坐立试验联合慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者自我评估测试评分对运动性低氧的预测价值及临床应用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(33): 4119-4124. |
| [11] | 秦燕勤, 董浩然, 杨静帆, 李海博, 赵鹏, 李建生. 补肺益肾组分方Ⅲ组分配伍对慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠气道重塑的干预作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(33): 4196-4203. |
| [12] | 李春阳, 王佳佳, 卫梦雨, 李建生. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者报告结局测评工具研究现状[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(31): 3896-3904. |
| [13] | 祁海燕, 王捷, 罗玉玺, 武云. 高尿酸血症与慢性肺源性心脏病的相关性研究:基于LASSO回归与倾向性评分匹配法[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(24): 2954-2960. |
| [14] | 杨梓钰, 张瑞, 廖晓阳, 雷弋, 贾禹, 杨荣, 李东泽. 美国预防临床服务指南工作组《慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查推荐意见》更新与解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(14): 1661-1665. |
| [15] | 陈典, 隆寰宇, 李姝润, 陈亚红. 2024年GOLD慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊断、治疗、管理及预防全球策略更新要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(13): 1533-1543. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





