中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (08): 1015-1021.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0361
收稿日期:2022-02-25
修回日期:2022-06-28
出版日期:2023-03-15
发布日期:2022-10-20
通讯作者:
于洪军
基金资助:
CHEN Panpan1, YU Hongjun1,*( ), QIU Jun2
), QIU Jun2
Received:2022-02-25
Revised:2022-06-28
Published:2023-03-15
Online:2022-10-20
Contact:
YU Hongjun
摘要: 背景 在身体活动与健康的研究领域中,采用科学的研究方法对不同群体的身体活动水平进行测量与评价是这一领域中的一个关键问题。哈佛校友健康研究量表(HAHS-PAQ)作为身体活动测量的经典量表之一,在许多国家和不同群体中得到了验证,但目前该量表针对中国大学生的信效度研究还尚未有报道。 目的 对HAHS-PAQ进行汉化,并在中国大学生中进行信效度检验。 方法 采用Brislin法对HAHS-PAQ进行汉化,本研究于2017年12月至2018年4月招募清华大学一年级大学生作为调查对象,分别有116例、166例受试者完成了信度、效度研究,采用Spearman秩相关分析检验中文版HAHS-PAQ的重测信度和以ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速度计为效标的效标效度。采用Bland-Altman作图法对中文版HAHS-PAQ与ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速度计两种身体活动水平测量方法的一致性进行检验。 结果 中文版HAHS-PAQ的总能耗、步行、爬楼梯和运动或休闲娱乐能耗的重测信度分别为0.504、0.570、0.711、0.429(P<0.05);中文版HAHS-PAQ与ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速度计测量的每周总能耗、中高强度能耗和步行能耗的相关系数分别为0.441、0.258、0.312(P<0.05);Bland-Altman图结果显示,中文版HAHS-PAQ与ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速度计测量的总能耗值的平均值为1 778.78,其中有94.6%(157/166)的点在95%CI以内。 结论 中文版HAHS-PAQ经过中国大学生样本的交叉验证,具有较好的信度和效度,且易于推广,可以作为中国大学生身体活动水平的调查工具,为今后中国大学生的运动指导和干预提供依据。
| 性别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 身高(cm) | 体质量(kg) | BMI(kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 58 | 18.7±1.4 | 175.31±5.74 | 66.3±11.1 | 21.5±3.2 |
| 女性 | 58 | 18.9±0.9 | 163.21±4.87 | 55.3±6.9 | 20.8±2.4 |
| t值 | -0.73 | 12.51 | 6.39 | 1.45 | |
| P值 | 0.428 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.137 |
表1 信度研究受试者基本特征比较(±s)
Table 1 Comparison of basic characteristics of participants in the reliability study
| 性别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 身高(cm) | 体质量(kg) | BMI(kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 58 | 18.7±1.4 | 175.31±5.74 | 66.3±11.1 | 21.5±3.2 |
| 女性 | 58 | 18.9±0.9 | 163.21±4.87 | 55.3±6.9 | 20.8±2.4 |
| t值 | -0.73 | 12.51 | 6.39 | 1.45 | |
| P值 | 0.428 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.137 |
| 性别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 身高(cm) | 体质量(kg) | BMI(kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 99 | 18.5±1.1 | 175.29±6.08 | 66.6±11.6 | 21.7±3.4 |
| 女性 | 67 | 18.8±0.9 | 163.07±4.83 | 55.7±7.0 | 21.0±2.5 |
| t值 | -1.66 | 14.39 | 7.52 | 1.53 | |
| P值 | 0.141 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.152 |
表2 效度研究受试者基本特征比较(±s)
Table 2 Comparision ofbasicial characteristics of validity study
| 性别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 身高(cm) | 体质量(kg) | BMI(kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 99 | 18.5±1.1 | 175.29±6.08 | 66.6±11.6 | 21.7±3.4 |
| 女性 | 67 | 18.8±0.9 | 163.07±4.83 | 55.7±7.0 | 21.0±2.5 |
| t值 | -1.66 | 14.39 | 7.52 | 1.53 | |
| P值 | 0.141 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.152 |
| 各种活动 | 第1次量表评分 | 第2次量表评分 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总能耗 | 2 838.82±1 494.17 | 2 579.56±1 691.08 | 0.504 | <0.001 |
| 步行 | 1 309.42±870.42 | 1 028.28±714.37 | 0.570 | <0.001 |
| 爬楼梯 | 302.33±185.26 | 294.00±219.31 | 0.711 | <0.001 |
| 运动或休闲娱乐 | 1 227.07±1 114.96 | 1 257.28±1 383.71 | 0.429 | <0.001 |
表3 中文版HAHS-PAQ 2次测量的信度检验(±s,卡路里/周)
Table 3 Reliability of HAHS-PAQ-C in the first and second tests
| 各种活动 | 第1次量表评分 | 第2次量表评分 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总能耗 | 2 838.82±1 494.17 | 2 579.56±1 691.08 | 0.504 | <0.001 |
| 步行 | 1 309.42±870.42 | 1 028.28±714.37 | 0.570 | <0.001 |
| 爬楼梯 | 302.33±185.26 | 294.00±219.31 | 0.711 | <0.001 |
| 运动或休闲娱乐 | 1 227.07±1 114.96 | 1 257.28±1 383.71 | 0.429 | <0.001 |
| 各种活动 | 中文版HAHS-PAQ | ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速计 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总能耗 | 1 779.15 ±1 134.97(卡路里/周) | 1 778.42±1 003.77(卡路里/周) | 0.441 | <0.001 |
| 中高强度活动 | 1 155.65±954.56(卡路里/周) | 347.21 ± 144.40(min) | 0.258 | <0.001 |
| 步行 | 622.44 ± 460.86(MET-min/wk) | 38 730.02 ± 15 506.72(步数) | 0.312 | 0.003 |
表4 中文版HAHS-PAQ和ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速度计测量值的相关性(±s)
Table 4 Correlation between the result measured by ActiGraph wGT3X-BT accelerometer and that reported by HAHS-PAQ-C
| 各种活动 | 中文版HAHS-PAQ | ActiGraph wGT3X-BT加速计 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总能耗 | 1 779.15 ±1 134.97(卡路里/周) | 1 778.42±1 003.77(卡路里/周) | 0.441 | <0.001 |
| 中高强度活动 | 1 155.65±954.56(卡路里/周) | 347.21 ± 144.40(min) | 0.258 | <0.001 |
| 步行 | 622.44 ± 460.86(MET-min/wk) | 38 730.02 ± 15 506.72(步数) | 0.312 | 0.003 |
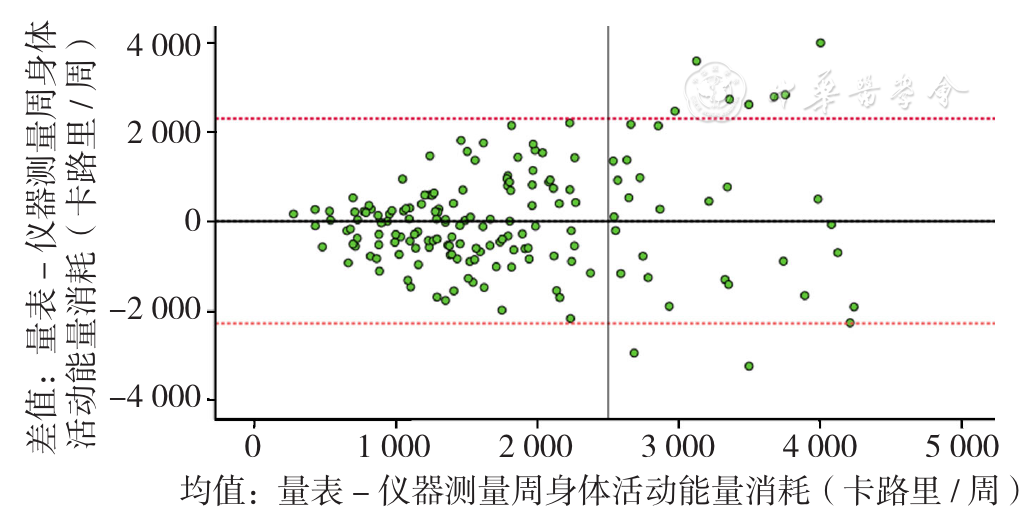
图1 HAHS-PAQ和加速度计测量总能耗结果的Bland-Altman图
Figure 1 Bland-Altman plot of total energy consumption measured by ActiGraph wGT3X-BT accelerometer and that reported by HAHS-PAQ
| [1] |
GBD Causes of Death Collaborators. Global,regional,and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories,1980-2017:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet,2018,392(10159):1736-1788. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7.
|
| [2] |
US Department of Health Human Services. 2018 Physical activity guidelines advisory committee scientific report[EB/OL].(2019-12-12)[2020-11-04].
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
张力为. 体育科学研究方法[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2002.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
齐茨,方富熹. 跨文化发展心理学的研究方法和新趋势[J]. 心理学报,1991,23(2):188-197.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
钱炜炜. 居民食品素养问卷的汉化与信效度检验[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2020.
|
| [35] |
穆欣,李娟,刘瑞荣,等. 首发脑卒中患者自我管理行为及影响因素的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志,2016,51(3):289-293. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.0254-1796.2016.03.006.
|
| [36] |
梁蝴蝶,李静,李晓静,等. 首发脑卒中病人生活质量现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 护理研究,2012,26(16):1458-1461. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2012.16.008.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
陈卉. Bland-Altman分析在临床测量方法一致性评价中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计,2007,24(3):308-309,315. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2007.03.029.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
王军利,张冰,贾丽雅,等. Actigraph(GT3X)加速度计测量我国19~29岁人群身体活动能耗的效度研究[J]. 体育科学,2012,32(12):71-77,92. DOI:10.16469/j.css.2012.12.011.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
王晓波. 国际体力活动长问卷在中国老年人群中应用的信度和效度[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2015,35(20):5912-5914. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.20.115.
|
| [50] |
屈宁宁,李可基. 国际体力活动问卷中文版的信度和效度研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2004,25(3):265-268. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2004.03.021.
|
| [51] |
于洪军,仇军. 运用PASE量表测量中国老年人体力活动的信效度验证[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2014,38(5):45-49,60. DOI:10.16099/j.cnki.jsus.2014.05.027.
|
| [52] |
李米环,李国强. 中老年女性营养及体力活动问卷的信效度评价[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2008,31(3):359-361. DOI:10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2008.03.024.
|
| [53] |
李米环,李国强. 基于能量代谢与体质量指数关系的体力活动问卷的信效度评价[J]. 现代预防医学,2009,36(11):2082-2085.
|
| [54] |
杨春军,张清. 中文版绝经后女性妇女健康倡议体力活动问卷的信效度研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2016,19(1):88-91. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.01.018.
|
| [55] |
段艳平,韦晓娜,
|
| [56] |
马冠生,栾德春,刘爱玲,等. 中国成年职业人群身体活动问卷的设计和评价[J]. 营养学报,2007,29(3):217-221. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2007.03.007.
|
| [57] |
张燕,赵岳,董胜雯,等. 中文版孕期身体活动问卷信效度评定[J]. 中华护理杂志,2013,48(9):825-827. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2013.09.019.
|
| [58] |
李新,王艳,李晓彤,等. 青少年体力活动问卷(PAQ-A)中文版的修订及信效度研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2015,38(5):63-67. DOI:10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2015.05.012.
|
| [59] |
刘爱玲,马冠生,张倩,等. 小学生7天体力活动问卷信度和效度的评价[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2003,24(10):901-904. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2003.10.013.
|
| [60] |
杨曦,陈婧祎,翟屹,等. 全球儿童青少年身体活动问卷评价的系统综述[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2019,53(12):1290-1295. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.12.016.
|
| [61] |
| [1] | 王健男, 孙金明. 临终关怀志愿服务动机量表汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4595-4601. |
| [2] | 张迪, 李鸿鹏, 马江, 聂谦, 孙剑峰, 吴志鹏, 张宏才, 赵珏. 眼针带针运动对经皮冠状动脉介入术治疗患者术后心率变异性及预后的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4535-4544. |
| [3] | 罗娜, 阮艳琴, 雷平光, 万崇华, 万克艳, 宋莹, 陈莹. 炎症性肠病患者报告结局测定量表的测量学特性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4602-4607. |
| [4] | 蹇秋枫, 徐荣华, 姚倩, 周媛媛. 中国老年脑卒中患者认知障碍患病率和影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [5] | 孟江涛, 杨思宇, 孙蕾, 雷瑞宁, 赵晓霞. 弥散张量成像联合运动诱发电位评估脑梗死偏瘫患者运动功能预后价值的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4098-4102. |
| [6] | 陈希, 章娟, 李霖, 张佳琪, 吴耀丽, 郭慧, 王超群. 中国中老年人体力活动与全因死亡风险的关系:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3890-3895. |
| [7] | 程经纬, 乔军军, 尹振, 胡俊鹏, 王庆贺, 柳杨青, 汪艳芳. 《2022 ISPAD临床实践共识指南:儿童和青少年糖尿病患儿运动》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3719-3724. |
| [8] | 温雯, 张凯楠, 陈玉岚, 李瑜, 张向阳. 代谢指数作为预测因子与阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的相关性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3740-3747. |
| [9] | 何莉, 张逸凡, 沈雪纯, 孙燕, 赵洋. 中国大陆地区居民慢性病共病的流行趋势:一项Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3599-3607. |
| [10] | 王倩倩, 王晓航, 周潇滢, 邱山虎, 孙子林. 运动是减重之本[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3471-3476. |
| [11] | 蒋秋惠, 李学军. 运动不是减重之本[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3477-3481. |
| [12] | 徐哲, 张金霞, 张秀红, 谢开红. 中老年人睡眠时间与全因死亡风险关系的队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3507-3512. |
| [13] | 孙晓蕾, 雷晓龙, 林佳声, 李克良, 郭澳, 张晓辉. 高能量激光联合特定运动疗法对特发性脊柱侧凸伴腰痛患者多裂肌超声形态学的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(27): 3456-3462. |
| [14] | 郑思婷, 何春渝, 周均, 孔叶, 杨薪瑶, 周海英, 魏晓霏. 脑卒中运动功能障碍患者自我管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3230-3237. |
| [15] | 何荣, 张丽, 李鹏, 张晓玲, 张国, 臧懿然, 吴寿岭, 孙丽霞. 有氧运动对不同血糖水平男性人群动脉僵硬度的即时影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 2997-3004. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





