中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 2404-2413.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0173
收稿日期:2022-02-14
修回日期:2022-05-03
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-03-04
通讯作者:
赵亚利
基金资助:
Wenhan MA1, Yi CHANG2, Chao XU2, Yali ZHAO1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-14
Revised:2022-05-03
Published:2022-07-05
Online:2022-03-04
Contact:
Yali ZHAO
About author:摘要: 背景 以团队为单位开展工作正在成为我国家庭医生签约服务的主要提供形式,但是目前尚缺乏专门针对团队的、能够反映团队整体有效性的评估工具。 目的 在投入-中介-产出-再投入(IMOI)模型基础上建立一套北京市家庭医生签约服务团队有效性评估指标,以指导家庭医生签约服务团队的自我改进与持续发展。 方法 通过文献分析法和个人访谈法,初步构建家庭医生签约服务团队有效性评估指标体系。2021年5—7月,采用德尔菲法分别对24、21名专家进行两轮专家咨询,结合课题组分析与专家建议确定评估指标。运用网络层次分析法确定指标权重。 结果 两轮专家咨询的问卷回收率分别为87.5%(21/24)、100.0%(21/21),专家权威系数为0.88~0.91。两轮专家咨询的指标重要性协调系数分别为0.138(P<0.001)、0.255(P<0.001),可行性协调系数分别为0.263(P<0.001)、0.257(P<0.001)。最终构建了71个家庭医生签约服务团队评估指标,其中一级指标7个(团队建设、成员素质、团队关系、团队过程、团队服务结果、认知及满意度、团队再发展,权重分别为0.155、0.155、0.097、0.141、0.155、0.155、0.141)、二级指标16个、三级指标48个。 结论 本研究构建了基于IMOI模型的北京市家庭医生签约服务团队有效性评估指标,从团队视角反映了家庭医生签约服务团队的有效性,可为北京市家庭医生签约服务团队的考评与发展提供参考。
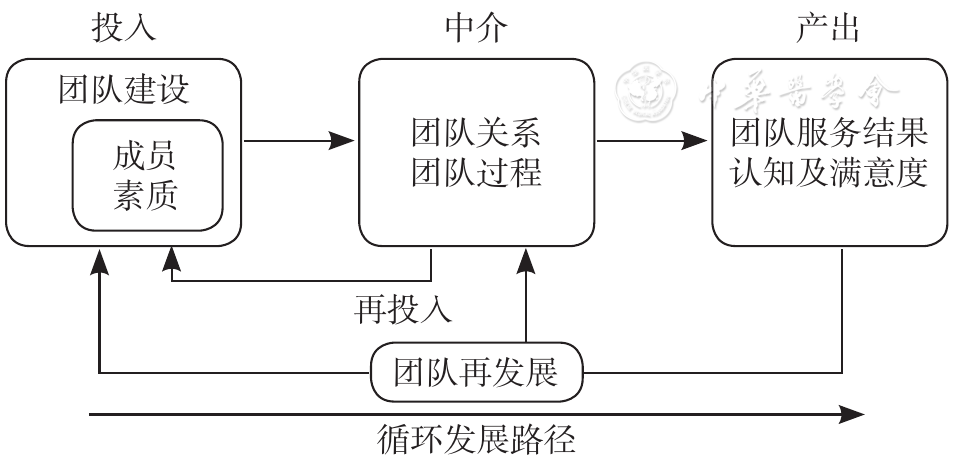
图1 北京市家医团队有效性评估指标的IMOI模型注:IMOI模型=投入-中介-产出-再投入模型;家医团队=家庭医生签约服务团队
Figure 1 The IMOI model used in the development of an effectiveness evaluation system for family doctor teams in Beijing
| 标度 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 1 | i元素与j元素同等重要 |
| 3 | i元素比j元素略重要 |
| 5 | i元素比j元素较重要 |
| 7 | i元素比j元素非常重要 |
| 9 | i元素比j元素绝对重要 |
| 2,4,6,8 | 分别代表上述相邻判断的中间值 |
| 倒数 | j元素对i元素的重要性标度 |
表1 SAATY九分标度法的重要性标度值定义
Table 1 Definition of the numerical value of the SAATY's 1-9 scale
| 标度 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 1 | i元素与j元素同等重要 |
| 3 | i元素比j元素略重要 |
| 5 | i元素比j元素较重要 |
| 7 | i元素比j元素非常重要 |
| 9 | i元素比j元素绝对重要 |
| 2,4,6,8 | 分别代表上述相邻判断的中间值 |
| 倒数 | j元素对i元素的重要性标度 |
| 基本情况 | 例数 | 基本情况 | 例数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 学历 | ||||
| 男 | 6(28.6) | 本科 | 7(33.3) | ||
| 女 | 15(71.4) | 硕士研究生 | 8(38.1) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 博士研究生 | 5(23.8) | |||
| 30~39 | 1(4.8) | 其他 | 1(4.8) | ||
| 40~49 | 15(71.4) | 专业 | |||
| ≥50 | 5(23.8) | 临床医学 | 13(61.9) | ||
| 工作年限(年) | 护理 | 2(9.5) | |||
| 10~19 | 7(33.3) | 公共卫生 | 4(19.0) | ||
| 20~29 | 9(42.9) | 管理学 | 2(9.5) | ||
| ≥30 | 5(23.8) | 工作领域 | |||
| 职称 | 卫生行政管理单位 | 4(19.0) | |||
| 副高级 | 8(38.1) | 社区卫生服务机构 | 11(52.4) | ||
| 正高级 | 13(61.9) | 高校 | 4(19.0) | ||
| 其他 | 2(9.5) | ||||
表2 德尔菲咨询专家基本信息〔n(%)〕
Table 2 Basic information of experts attending consultations using Delphi technique
| 基本情况 | 例数 | 基本情况 | 例数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 学历 | ||||
| 男 | 6(28.6) | 本科 | 7(33.3) | ||
| 女 | 15(71.4) | 硕士研究生 | 8(38.1) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 博士研究生 | 5(23.8) | |||
| 30~39 | 1(4.8) | 其他 | 1(4.8) | ||
| 40~49 | 15(71.4) | 专业 | |||
| ≥50 | 5(23.8) | 临床医学 | 13(61.9) | ||
| 工作年限(年) | 护理 | 2(9.5) | |||
| 10~19 | 7(33.3) | 公共卫生 | 4(19.0) | ||
| 20~29 | 9(42.9) | 管理学 | 2(9.5) | ||
| ≥30 | 5(23.8) | 工作领域 | |||
| 职称 | 卫生行政管理单位 | 4(19.0) | |||
| 副高级 | 8(38.1) | 社区卫生服务机构 | 11(52.4) | ||
| 正高级 | 13(61.9) | 高校 | 4(19.0) | ||
| 其他 | 2(9.5) | ||||
| 一级指标 | 熟悉程度 | 判断系数 | 权威系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 团队建设 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.90 |
| 成员素质 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.89 |
| 团队关系 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.88 |
| 团队过程 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| 团队服务结果 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| 认知及满意度 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| 团队再发展 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.90 |
表3 家医团队有效性评估指标一级指标专家权威程度
Table 3 Expert authority coefficients for first-level indicators of the Family Doctor Team Effectiveness Evaluation System
| 一级指标 | 熟悉程度 | 判断系数 | 权威系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 团队建设 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.90 |
| 成员素质 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.89 |
| 团队关系 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.88 |
| 团队过程 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| 团队服务结果 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| 认知及满意度 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| 团队再发展 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.90 |
| 指标 | 重要性 | 可行性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 协调系数 | χ2值 | P值 | 协调系数 | χ2值 | P值 | ||
| 第一轮 | |||||||
| 一级指标 | 0.133 | 16.711 | 0.010 | 0.350 | 44.041 | <0.001 | |
| 二级指标 | 0.124 | 54.007 | <0.001 | 0.279 | 121.843 | <0.001 | |
| 三级指标 | 0.126 | 274.127 | <0.001 | 0.253 | 549.916 | <0.001 | |
| 第二轮 | |||||||
| 一级指标 | 0.173 | 21.736 | 0.001 | 0.339 | 42.764 | <0.001 | |
| 二级指标 | 0.116 | 39.015 | 0.001 | 0.294 | 98.721 | <0.001 | |
| 三级指标 | 0.261 | 318.858 | <0.001 | 0.247 | 286.015 | <0.001 | |
表4 家医团队有效性评估指标专家咨询协调系数
Table 4 Kendall's W for expert consensuses on indicators of the Family Doctor Team Effectiveness Evaluation System in two rounds of consultations
| 指标 | 重要性 | 可行性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 协调系数 | χ2值 | P值 | 协调系数 | χ2值 | P值 | ||
| 第一轮 | |||||||
| 一级指标 | 0.133 | 16.711 | 0.010 | 0.350 | 44.041 | <0.001 | |
| 二级指标 | 0.124 | 54.007 | <0.001 | 0.279 | 121.843 | <0.001 | |
| 三级指标 | 0.126 | 274.127 | <0.001 | 0.253 | 549.916 | <0.001 | |
| 第二轮 | |||||||
| 一级指标 | 0.173 | 21.736 | 0.001 | 0.339 | 42.764 | <0.001 | |
| 二级指标 | 0.116 | 39.015 | 0.001 | 0.294 | 98.721 | <0.001 | |
| 三级指标 | 0.261 | 318.858 | <0.001 | 0.247 | 286.015 | <0.001 | |
| 指标 | 重要性 | 可行性 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中位数(分) | 7~9分百分比(%) | 均值(分) | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 满分比(%) | 权重 | 中位数(分) | 7~9分百分比(%) | 均值(分) | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 满分比(%) | |||
| B1团队建设 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.90 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.48 | 1.86 | 0.25 | 42.90 | ||
| C1团队结构 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 52.40 | ||
| C11团队构成 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 95.00 | 0.035 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.86 | 0.23 | 66.70 | ||
| C12团队人员与服务目标人数比 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.19 | 1.33 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.33 | 1.28 | 0.15 | 71.40 | ||
| C2流程制度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.57 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 95.20 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.29 | 1.19 | 0.14 | 66.70 | ||
| C21团队计划 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.76 | 1.58 | 0.20 | 52.40 | 0.017 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.71 | 1.45 | 0.19 | 47.60 | ||
| C22团队责任制度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 90.50 | 0.035 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.38 | 2.42 | 0.33 | 52.40 | ||
| C3团队能力 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.90 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 90.50 | 0.052 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.71 | 2.19 | 0.33 | 19.00 | ||
| C31团队综合知识 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.67 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 38.10 | 0.026 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.33 | 1.59 | 0.22 | 38.10 | ||
| C32团队综合技能 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.95 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 57.10 | 0.026 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.24 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 19.00 | ||
| B2成员素质 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.81 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 23.80 | ||
| C4个人能力 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.86 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 76.20 | 0.078 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.57 | 1.78 | 0.27 | 14.30 | ||
| C41基本医疗服务能力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.48 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 76.20 | 0.039 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.76 | 1.45 | 0.19 | 47.60 | ||
| C42基本公共卫生服务能力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.57 | 1.03 | 0.12 | 81.00 | 0.039 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.62 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | ||
| C5个人资质 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 66.70 | 0.078 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.33 | 1.56 | 0.21 | 28.60 | ||
| C51学历 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 33.30 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| C52职称 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.19 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 23.80 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 2.40 | 0.30 | 71.40 | ||
| C53工作年限 | 7 | 81.0 | 7.19 | 1.63 | 0.23 | 28.60 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| B3团队关系 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.097 | 5 | 47.6 | 5.76 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 4.80 | ||
| C6团队认知 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.24 | 1.18 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.049 | 7 | 57.1 | 5.95 | 1.83 | 0.31 | 4.80 | ||
| C61团队有共同的目标和愿景 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.19 | 1.12 | 0.14 | 57.10 | 0.025 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.33 | 1.93 | 0.31 | 19.00 | ||
| C62以患者为中心的工作原则 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.33 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 61.90 | 0.025 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.10 | 2.28 | 0.37 | 14.30 | ||
| C7团队成员凝聚力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.33 | 1.16 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.049 | 5 | 42.9 | 5.71 | 2.08 | 0.36 | 9.50 | ||
| C71团队成员相互信任和支持 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.14 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 61.90 | 0.025 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.38 | 1.96 | 0.31 | 14.30 | ||
| C72团队成员及时有效共享家庭医生服务信息 | 8 | 95.2 | 7.95 | 1.16 | 0.15 | 47.60 | 0.025 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.86 | 1.98 | 0.29 | 23.80 | ||
| B4团队过程 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.141 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.95 | 2.40 | 0.34 | 38.10 | ||
| C8团队运营管理 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.48 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 85.70 | 0.071 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.76 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 14.30 | ||
| C81团队长主持并推动团队工作 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.38 | 1.43 | 0.17 | 81.00 | 0.016 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.29 | 1.27 | 0.17 | 23.80 | ||
| C82团队与患者分享健康计划信息 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.57 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 38.10 | 0.008 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.71 | 1.15 | 0.17 | 9.50 | ||
| C83团队根据居民需求改进服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.016 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.76 | 1.18 | 0.17 | 9.50 | ||
| C84团队会根据绩效及服务调整目标 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.10 | 1.00 | 0.12 | 52.40 | 0.016 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.86 | 1.65 | 0.24 | 14.30 | ||
| C85团队成员的工作量相对合理 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.016 | 7 | 66.7 | 6.81 | 1.50 | 0.22 | 9.50 | ||
| C9团队服务内容 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 66.70 | 0.071 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.29 | 2.37 | 0.32 | 42.90 | ||
| C91基本医疗服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.64 | 0.07 | 81.00 | 0.011 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.14 | 1.46 | 0.18 | 66.70 | ||
| C92公共卫生服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 76.20 | 0.010 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.95 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 57.10 | ||
| C93优先预约服务 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.10 | 1.34 | 0.17 | 61.90 | 0.007 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.86 | 1.46 | 0.19 | 52.40 | ||
| C94双向转诊服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.48 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 71.40 | 0.009 | 9 | 76.2 | 7.57 | 2.44 | 0.32 | 57.10 | ||
| C95出诊服务 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.20 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 65.00 | 0.008 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.90 | 2.36 | 0.34 | 30.00 | ||
| C96药品配送与用药指导服务 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.14 | 2.50 | 0.35 | 42.90 | 0.004 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.67 | 2.35 | 0.35 | 23.80 | ||
| C97长期处方服务 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.62 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | 0.005 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.29 | 2.47 | 0.34 | 52.40 | ||
| C98中医药"治未病"服务 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.24 | 2.28 | 0.31 | 38.10 | 0.004 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.10 | 2.39 | 0.34 | 38.10 | ||
| C99签约"四个一"服务 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.29 | 1.10 | 0.13 | 61.90 | 0.009 | 8 | 81.0 | 7.62 | 1.40 | 0.18 | 38.10 | ||
| C100信息平台服务 | 8 | 76.2 | 7.48 | 1.63 | 0.22 | 42.90 | 0.004 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.43 | 1.47 | 0.20 | 33.30 | ||
| B5团队服务结果 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 81.00 | ||
| C10服务数量 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.19 | 1.33 | 0.16 | 66.70 | ||
| C101总签约率 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.33 | 1.16 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.017 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.05 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 61.90 | ||
| C102签约居民重点人群占比 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.10 | 1.86 | 0.23 | 70.00 | ||
| C103签约65岁以上老年人占比 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 95.20 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| C11服务质量 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.52 | 1.25 | 0.15 | 85.70 | 0.052 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.43 | 1.33 | 0.18 | 28.60 | ||
| C111签约服务履约情况 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 81.00 | 0.021 | 9 | 81.0 | 8.00 | 1.82 | 0.23 | 61.90 | ||
| C112全科预约诊疗流程运行情况 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.010 | 9 | 76.2 | 7.81 | 1.60 | 0.20 | 57.10 | ||
| C113慢性病(高血压、糖尿病)规范管理率 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.00 | 1.48 | 0.19 | 61.90 | 0.010 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 52.40 | ||
| C12服务效果 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.57 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 85.70 | 0.052 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.05 | 1.40 | 0.20 | 19.00 | ||
| C121签约居民续签率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.00 | 0.017 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.86 | 1.82 | 0.23 | 57.10 | ||
| C122签约患者基层就诊率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.015 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 2.42 | 0.32 | 52.40 | ||
| C123门诊就诊居民签约率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.015 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.76 | 2.39 | 0.31 | 61.90 | ||
| C124签约居民健康知识知晓率 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.10 | 1.09 | 0.13 | 57.10 | 0.007 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.90 | 2.30 | 0.33 | 28.60 | ||
| B6认知及满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.155 | 8 | 90.5 | 7.33 | 2.29 | 0.31 | 38.10 | ||
| C13签约居民认知及满意度 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.078 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.67 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 38.10 | ||
| C131签约居民对家医团队成员的知晓率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.43 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 66.70 | 0.017 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.48 | 1.97 | 0.26 | 47.60 | ||
| C132签约居民对家医团队服务态度满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 85.70 | 0.026 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.67 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | ||
| C133签约居民对家医团队技术水平满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.026 | 8 | 76.2 | 7.57 | 1.89 | 0.25 | 47.60 | ||
| C14团队成员满意度 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.34 | 0.16 | 71.40 | 0.078 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.48 | 1.75 | 0.23 | 38.10 | ||
| C141团队成员对团队合作的满意度 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.10 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 57.10 | 0.039 | 7 | 81.0 | 7.10 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 33.30 | ||
| C142团队人员对待遇的满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.43 | 0.93 | 0.11 | 71.40 | 0.039 | 8 | 66.7 | 7.43 | 1.96 | 0.26 | 47.60 | ||
| B7团队再发展 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.141 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.67 | 1.43 | 0.21 | 14.30 | ||
| C15团队稳定性 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.00 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 52.40 | 0.055 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.57 | 1.40 | 0.21 | 4.80 | ||
| C151团队长稳定性 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.10 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 28.60 | 0.055 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.14 | 1.32 | 0.18 | 19.00 | ||
| C16团队激励 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.00 | 0.086 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.10 | 1.58 | 0.22 | 19.00 | ||
| C161团队绩效 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 76.20 | 0.057 | 7 | 66.7 | 6.76 | 2.47 | 0.37 | 28.60 | ||
| C162团队成员职称晋升情况 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 33.30 | 0.029 | 7 | 71.4 | 7.10 | 2.30 | 0.32 | 33.30 | ||
表5 北京市家医团队有效性评估指标及其权重
Table 5 Indicators and their weights of the Family Doctor Team Effectiveness Evaluation System for family doctor teams in Beijing
| 指标 | 重要性 | 可行性 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中位数(分) | 7~9分百分比(%) | 均值(分) | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 满分比(%) | 权重 | 中位数(分) | 7~9分百分比(%) | 均值(分) | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 满分比(%) | |||
| B1团队建设 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.90 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.48 | 1.86 | 0.25 | 42.90 | ||
| C1团队结构 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 52.40 | ||
| C11团队构成 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 95.00 | 0.035 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.86 | 0.23 | 66.70 | ||
| C12团队人员与服务目标人数比 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.19 | 1.33 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.33 | 1.28 | 0.15 | 71.40 | ||
| C2流程制度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.57 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 95.20 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.29 | 1.19 | 0.14 | 66.70 | ||
| C21团队计划 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.76 | 1.58 | 0.20 | 52.40 | 0.017 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.71 | 1.45 | 0.19 | 47.60 | ||
| C22团队责任制度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 90.50 | 0.035 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.38 | 2.42 | 0.33 | 52.40 | ||
| C3团队能力 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.90 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 90.50 | 0.052 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.71 | 2.19 | 0.33 | 19.00 | ||
| C31团队综合知识 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.67 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 38.10 | 0.026 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.33 | 1.59 | 0.22 | 38.10 | ||
| C32团队综合技能 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.95 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 57.10 | 0.026 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.24 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 19.00 | ||
| B2成员素质 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.81 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 23.80 | ||
| C4个人能力 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.86 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 76.20 | 0.078 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.57 | 1.78 | 0.27 | 14.30 | ||
| C41基本医疗服务能力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.48 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 76.20 | 0.039 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.76 | 1.45 | 0.19 | 47.60 | ||
| C42基本公共卫生服务能力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.57 | 1.03 | 0.12 | 81.00 | 0.039 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.62 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | ||
| C5个人资质 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 66.70 | 0.078 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.33 | 1.56 | 0.21 | 28.60 | ||
| C51学历 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 33.30 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| C52职称 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.19 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 23.80 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 2.40 | 0.30 | 71.40 | ||
| C53工作年限 | 7 | 81.0 | 7.19 | 1.63 | 0.23 | 28.60 | 0.026 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| B3团队关系 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.097 | 5 | 47.6 | 5.76 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 4.80 | ||
| C6团队认知 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.24 | 1.18 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.049 | 7 | 57.1 | 5.95 | 1.83 | 0.31 | 4.80 | ||
| C61团队有共同的目标和愿景 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.19 | 1.12 | 0.14 | 57.10 | 0.025 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.33 | 1.93 | 0.31 | 19.00 | ||
| C62以患者为中心的工作原则 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.33 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 61.90 | 0.025 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.10 | 2.28 | 0.37 | 14.30 | ||
| C7团队成员凝聚力 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.33 | 1.16 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.049 | 5 | 42.9 | 5.71 | 2.08 | 0.36 | 9.50 | ||
| C71团队成员相互信任和支持 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.14 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 61.90 | 0.025 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.38 | 1.96 | 0.31 | 14.30 | ||
| C72团队成员及时有效共享家庭医生服务信息 | 8 | 95.2 | 7.95 | 1.16 | 0.15 | 47.60 | 0.025 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.86 | 1.98 | 0.29 | 23.80 | ||
| B4团队过程 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.141 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.95 | 2.40 | 0.34 | 38.10 | ||
| C8团队运营管理 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.48 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 85.70 | 0.071 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.76 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 14.30 | ||
| C81团队长主持并推动团队工作 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.38 | 1.43 | 0.17 | 81.00 | 0.016 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.29 | 1.27 | 0.17 | 23.80 | ||
| C82团队与患者分享健康计划信息 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.57 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 38.10 | 0.008 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.71 | 1.15 | 0.17 | 9.50 | ||
| C83团队根据居民需求改进服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.016 | 7 | 76.2 | 6.76 | 1.18 | 0.17 | 9.50 | ||
| C84团队会根据绩效及服务调整目标 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.10 | 1.00 | 0.12 | 52.40 | 0.016 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.86 | 1.65 | 0.24 | 14.30 | ||
| C85团队成员的工作量相对合理 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.19 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 57.10 | 0.016 | 7 | 66.7 | 6.81 | 1.50 | 0.22 | 9.50 | ||
| C9团队服务内容 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.81 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 66.70 | 0.071 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.29 | 2.37 | 0.32 | 42.90 | ||
| C91基本医疗服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.64 | 0.07 | 81.00 | 0.011 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.14 | 1.46 | 0.18 | 66.70 | ||
| C92公共卫生服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 76.20 | 0.010 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.95 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 57.10 | ||
| C93优先预约服务 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.10 | 1.34 | 0.17 | 61.90 | 0.007 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.86 | 1.46 | 0.19 | 52.40 | ||
| C94双向转诊服务 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.48 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 71.40 | 0.009 | 9 | 76.2 | 7.57 | 2.44 | 0.32 | 57.10 | ||
| C95出诊服务 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.20 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 65.00 | 0.008 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.90 | 2.36 | 0.34 | 30.00 | ||
| C96药品配送与用药指导服务 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.14 | 2.50 | 0.35 | 42.90 | 0.004 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.67 | 2.35 | 0.35 | 23.80 | ||
| C97长期处方服务 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.62 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | 0.005 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.29 | 2.47 | 0.34 | 52.40 | ||
| C98中医药"治未病"服务 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.24 | 2.28 | 0.31 | 38.10 | 0.004 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.10 | 2.39 | 0.34 | 38.10 | ||
| C99签约"四个一"服务 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.29 | 1.10 | 0.13 | 61.90 | 0.009 | 8 | 81.0 | 7.62 | 1.40 | 0.18 | 38.10 | ||
| C100信息平台服务 | 8 | 76.2 | 7.48 | 1.63 | 0.22 | 42.90 | 0.004 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.43 | 1.47 | 0.20 | 33.30 | ||
| B5团队服务结果 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 95.20 | 0.155 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 81.00 | ||
| C10服务数量 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.052 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.19 | 1.33 | 0.16 | 66.70 | ||
| C101总签约率 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.33 | 1.16 | 0.14 | 71.40 | 0.017 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.05 | 1.47 | 0.18 | 61.90 | ||
| C102签约居民重点人群占比 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.10 | 1.86 | 0.23 | 70.00 | ||
| C103签约65岁以上老年人占比 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 95.20 | 0.017 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.14 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 71.40 | ||
| C11服务质量 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.52 | 1.25 | 0.15 | 85.70 | 0.052 | 7 | 85.7 | 7.43 | 1.33 | 0.18 | 28.60 | ||
| C111签约服务履约情况 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.95 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 81.00 | 0.021 | 9 | 81.0 | 8.00 | 1.82 | 0.23 | 61.90 | ||
| C112全科预约诊疗流程运行情况 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.010 | 9 | 76.2 | 7.81 | 1.60 | 0.20 | 57.10 | ||
| C113慢性病(高血压、糖尿病)规范管理率 | 9 | 85.7 | 8.00 | 1.48 | 0.19 | 61.90 | 0.010 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.95 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 52.40 | ||
| C12服务效果 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.57 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 85.70 | 0.052 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.05 | 1.40 | 0.20 | 19.00 | ||
| C121签约居民续签率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.00 | 0.017 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.86 | 1.82 | 0.23 | 57.10 | ||
| C122签约患者基层就诊率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.015 | 9 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 2.42 | 0.32 | 52.40 | ||
| C123门诊就诊居民签约率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.015 | 9 | 81.0 | 7.76 | 2.39 | 0.31 | 61.90 | ||
| C124签约居民健康知识知晓率 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.10 | 1.09 | 0.13 | 57.10 | 0.007 | 7 | 81.0 | 6.90 | 2.30 | 0.33 | 28.60 | ||
| B6认知及满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.71 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 85.70 | 0.155 | 8 | 90.5 | 7.33 | 2.29 | 0.31 | 38.10 | ||
| C13签约居民认知及满意度 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 66.70 | 0.078 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.67 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 38.10 | ||
| C131签约居民对家医团队成员的知晓率 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.43 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 66.70 | 0.017 | 8 | 85.7 | 7.48 | 1.97 | 0.26 | 47.60 | ||
| C132签约居民对家医团队服务态度满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.76 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 85.70 | 0.026 | 9 | 85.7 | 7.67 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 52.40 | ||
| C133签约居民对家医团队技术水平满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 76.20 | 0.026 | 8 | 76.2 | 7.57 | 1.89 | 0.25 | 47.60 | ||
| C14团队成员满意度 | 9 | 90.5 | 8.24 | 1.34 | 0.16 | 71.40 | 0.078 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.48 | 1.75 | 0.23 | 38.10 | ||
| C141团队成员对团队合作的满意度 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.10 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 57.10 | 0.039 | 7 | 81.0 | 7.10 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 33.30 | ||
| C142团队人员对待遇的满意度 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.43 | 0.93 | 0.11 | 71.40 | 0.039 | 8 | 66.7 | 7.43 | 1.96 | 0.26 | 47.60 | ||
| B7团队再发展 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 81.00 | 0.141 | 7 | 61.9 | 6.67 | 1.43 | 0.21 | 14.30 | ||
| C15团队稳定性 | 9 | 95.2 | 8.00 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 52.40 | 0.055 | 7 | 71.4 | 6.57 | 1.40 | 0.21 | 4.80 | ||
| C151团队长稳定性 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.10 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 28.60 | 0.055 | 7 | 76.2 | 7.14 | 1.32 | 0.18 | 19.00 | ||
| C16团队激励 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.67 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.00 | 0.086 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.10 | 1.58 | 0.22 | 19.00 | ||
| C161团队绩效 | 9 | 100.0 | 8.62 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 76.20 | 0.057 | 7 | 66.7 | 6.76 | 2.47 | 0.37 | 28.60 | ||
| C162团队成员职称晋升情况 | 7 | 90.5 | 7.52 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 33.30 | 0.029 | 7 | 71.4 | 7.10 | 2.30 | 0.32 | 33.30 | ||
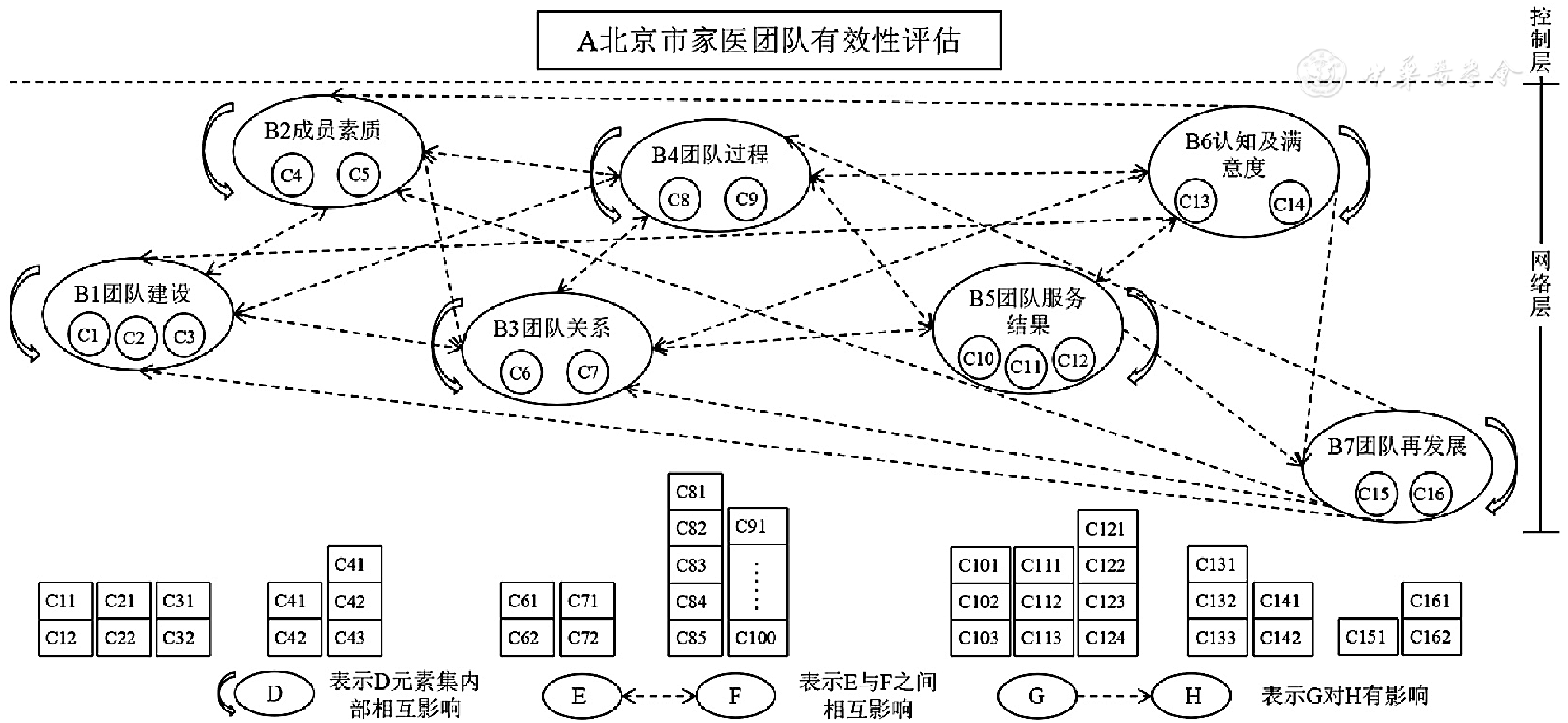
图2 北京市家医团队有效性评估网络层次结构注:A表示目标,网络层中的B1~B7表示一级指标,网络层中的C1~C16表示二级指标,方框中的C11~C162表示三级指标
Figure 2 Network hierarchy of the Family Doctor Team Effectiveness Evaluation System for family doctor teams in Beijing
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
国家卫生健康委老龄健康司.全国老龄办关于做好老年人冬春季新冠肺炎疫情防控工作的通知[A/OL].(2021-02-08)[2021-12-05].
|
| [5] |
国家卫生健康委基层卫生健康司. 关于做好2020年基本公共卫生服务项目工作的通知[A/OL].(2020-06-16)[2021-12-05].
|
| [6] |
国家卫生健康委医政医管局.关于印发长期处方管理规范(试行)的通知[A/OL].(2021-08-12)[2021-12-05].
|
| [7] |
国家卫生健康委办公厅关于进一步加强贫困地区卫生健康人才队伍建设的通知[A/OL].(2019-04-18)[2021-12-05].
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
杨肖锋.团队有效性研究进展综述[J].管理观察,2018,38(4):35-39.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
马文翰,史大桢,赵亚利.基于IMOI模型构建家庭医生签约服务团队评估指标的系统综述[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(7):797-802. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.235.
|
| [21] |
王华芬,王惠琴,宋剑平,等.护理绩效独立考核指标体系的建立[J].中华护理杂志,2015,50(3):262-266. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2015.03.001.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
张宇斐,柴建军,胡冰水,等. 基于德尔菲法和层次分析法的现代医院门诊医疗质控指标体系构建与应用[J]. 中国医院,2021,25(3):36-39. DOI:10.19660/j.issn.1671-0592.2021.3.11.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
贺纯纯,王应明.网络层次分析法研究述评[J].科技管理研究,2014,34(3):204-208,213.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
杨练,张雪莉,景琳,等.基于网络层次分析法的乡村医生政府补助性收入策略指标体系研究[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(16):1943-1945,1950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.16.020.
|
| [30] |
吴卫. 大型公立医院后勤管理绩效评价研究[D]. 北京:北京建筑大学,2020.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
邓雪,李家铭,曾浩健,等.层次分析法权重计算方法分析及其应用研究[J].数学的实践与认识,2012,42(7):93-100.
|
| [35] |
肖跃.网络安全服务项目质量评价体系研究[D]. 北京:北京邮电大学,2020.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
朱光兴,郭东强. 高校科技创新团队绩效评价体系构建:基于AHP-IMOI模型[J].教育评论,2019,37(6):71-77.
|
| [38] |
张颖,季聪华,李秋爽,等. 中医临床实践指南制修订中德尔菲法的统计分析方法[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(1):249-251.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
毛强,茅宁. 影响团队有效性的团队组合因素和中介因素:基于"IMOI"模型的评述[C]. 大连:第五届中国管理学年会(MAM2010)论文集,2010:2544-2553.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
北京市卫生健康委员会. 北京市卫生健康委员会关于印发2020年北京市家庭医生签约服务绩效评价工作方案的通知[A/OL]. (2020-10-13)[2021-12-06].
|
| [45] |
北京市卫生健康委员会北京市中医管理局关于开展2019年度社区卫生与基本公共卫生服务绩效考核的通知[A/OL]. (2021-02-01)[2021-12-06].
|
| [46] |
江燕燕. 跨期视角下的高校科研创新团队绩效综合评价研究[J]. 产业科技创新,2020,2(11):26-28.
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
AAFP. Vision and principles of a quality measurement strategy for primary care(position paper)[EB/OL].[2021-12-06].
|
| [50] | |
| [51] |
汪洋,韩建军,许岩丽. 大洋彼岸的涛声:美国新版初级卫生保健质量评估策略对中国全科医疗服务质量评估体系的启示[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(16):1889-1899. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.293.
|
| [1] | 郝爱华, 曾韦霖, 李观海, 夏英华, 陈亮. 基于全科医生视角的家庭医生团队签约现状调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4261-4268. |
| [2] | 郭亚红, 郭浩乾, 宁艳花, 姜婷, 李美曼, 吕兄兄, 孔维娟, 刘海燕. 基于家庭医生签约服务构建老年人"互联网+"家庭护理管理模式[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(23): 2876-2881. |
| [3] | 赵琳琳, 邵爽, 罗琪, 陈小垒, 杜娟. 国内家庭医生团队医防融合实践策略研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(22): 2715-2719. |
| [4] | 徐佳玙, 颜骅, 方军波, 王海琴, 郭佩, 沈福来, 王形松. 基于标化工作量的社区卫生服务机构家庭医生团队工作开展现状研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(13): 1641-1647. |
| [5] | 孟文奇, 柳松艺, 姜晓利, 彭海波, 李子鑫, 于倩倩, 尹文强, 孙葵, 陈钟鸣, 郭洪伟. 基于扎根理论的家庭医生签约服务效果影响机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(10): 1192-1197. |
| [6] | 周其如, 李举双, 郝春, 汪永刚, 沈睿, 朱敏贤, 程新. 预约诊疗服务对家庭医生签约服务结果质量的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(10): 1198-1204. |
| [7] | 马志强, 吴香兰. 基于信任源模型的全科医疗服务医患信任问题及对策建议[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(10): 1172-1178. |
| [8] | 徐萍萍, 赵静, 李春晓, 李林峰, 刘森元. 我国中央层面家庭医生签约服务政策量化评价:基于PMC指数模型[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 440-446. |
| [9] | 李心言, 韩优莉. 家庭医生签约服务中引入竞争机制的影响及其启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 447-452,459. |
| [10] | 马志强, 张宝丽, 郭乐. 签约服务情境下全科医生岗位胜任力自评量表的开发与信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 477-485. |
| [11] | 马志强, 郭乐, 李钊, 葛柏麟. 签约服务情境下基于扎根理论的全科医生胜任力模型构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 460-466,485. |
| [12] | 刘智敏, 冯磊. 家庭医生签约服务协议的内容分析及优化路径探索[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 453-459. |
| [13] | 柳松艺, 孟文奇, 彭海波, 姜晓利, 李子鑫, 于倩倩, 尹文强, 陈钟鸣, 孙葵, 郭洪伟. 签约居民对家庭医生签约服务连续性的评价及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(34): 4312-4317. |
| [14] | 姚岗, 张诚, 徐健, 潘文雷, 陈晨, 朱敏, 王朝昕, 黄蛟灵. 中青年楼宇人群对家庭医生签约服务的需求及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(22): 2773-2781. |
| [15] | 徐健, 姚岗, 潘文雷, 戴芳芳, 黄倩, 刘蕊, 李欣, 周良, 黄蛟灵. 中青年楼宇人群的家庭医生签约服务需求满足状况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(22): 2782-2789. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





