

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (08): 995-1006.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.046
Special Issue: 高血压最新文章合辑
• Evidence-based Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension:a Meta-analysis
Department of Basic Medicine,Guizhou Health Vocational College,Tongren 554300,China
*Corresponding author:ZHANG Ping,Lecturer;E-mail:545077638@qq.com
Received:2021-07-12
Revised:2021-11-25
Published:2022-03-15
Online:2022-03-02
通讯作者:
张平
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Ping, ZOU Jing, GAO Cunzhou, WU Aiping, LI Rongshan.
Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(08): 995-1006.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.046
| 第一作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 病例数(T/C) | 研究类型 | 平均年龄(T/C,岁) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | 随访时间(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||||
| ABOLGHASMI [ | 2011 | 伊朗 | 19/22 | RCT | (49±13.2)/(50±10.1) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2011 | 捷克 | 55/56 | RCT | (61.4±9.6)/(60.1±9.4) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 郭鑫[ | 2012 | 中国 | 57/58 | RCT | (61.8±11.5)/(59.0±11.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ②⑥ | 8 |
| 马彬[ | 2012 | 中国 | 56/56 | RCT | - | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+卡维地洛12.5~50.0 mg/d | ①⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 张俊松[ | 2012 | 中国 | 58/66 | RCT | (63.4±14.3)/(63.8±13.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 24 |
| OXLUND [ | 2013 | 丹麦 | 61/58 | RCT | (62.9±7.1)/(63.9±6.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 16 |
| NI [ | 2014 | 中国 | 40/36 | RCT | (55.7±12.3)/(54.9±14.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②⑦ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2014 | 捷克 | 74/76 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 8 |
| WILLIAMS [ | 2015 | 英国 | 285/274 /282/285 | RCT | 61.4±9.6 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂基础降压治疗+多沙唑嗪4~8 mg/d基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5~10 mg/d | ①⑤ | 12 |
| 盖延红[ | 2015 | 中国 | 73/71 | RCT | 61.5±9.7 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③④⑥ | 12 |
| DJOUMESSI [ | 2016 | 喀麦隆 | 9/8 | RCT | (64.6±9.6)/(61.0±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+坎地沙坦8 mg/d,阿替洛尔100 mg/d或甲基多巴750 mg/d | ①⑤ | 4 |
| OLIVERAS [ | 2016 | 西班牙 | 13/11 | RCT | (64.9±8.2)/(61.9±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 24 |
| ROSA [ | 2016 | 捷克 | 50/51 | RCT | (59±9) /(56±12) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②⑦⑧ | 48 |
| YANG [ | 2016 | 中国 | 15/15 | RCT | (44.7±10.8) /(43.4±15.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 曾潇[ | 2016 | 中国 | 78/82 | RCT | (60.7±7.7)/(61.0±8.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑥⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 卢旭[ | 2017 | 中国 | 41/38 | RCT | (73.45±5.88) /(71.11±7.15) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 48 |
| KRIEGER[ | 2018 | 巴西 | 84/78 | RCT | (54±11.1)/(56.3±9.7) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯12.5~50.0 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+可乐定0.1~0.3 mg/d | ①②③④⑧ | 12 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 2018 | 多国 | 191/212 | RCT | 74(65,80) /71(63,78) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯23 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ① | 32 |
| 杨晶敏[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40/40/40 | RCT | (54.7±10.7)/(54.7±8.5) / (57.9±11.3) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5 mg基础降压治疗+特拉唑嗪2 mg/d | ②⑦ | 12 |
| 黄娟[ | 2020 | 中国 | 45/49 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+倍他乐克50 mg/d | ① ③④ | 8 |
Table 1 Basic characteristics of included studies
| 第一作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 病例数(T/C) | 研究类型 | 平均年龄(T/C,岁) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | 随访时间(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||||
| ABOLGHASMI [ | 2011 | 伊朗 | 19/22 | RCT | (49±13.2)/(50±10.1) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2011 | 捷克 | 55/56 | RCT | (61.4±9.6)/(60.1±9.4) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 郭鑫[ | 2012 | 中国 | 57/58 | RCT | (61.8±11.5)/(59.0±11.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ②⑥ | 8 |
| 马彬[ | 2012 | 中国 | 56/56 | RCT | - | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+卡维地洛12.5~50.0 mg/d | ①⑦⑧ | 8 |
| 张俊松[ | 2012 | 中国 | 58/66 | RCT | (63.4±14.3)/(63.8±13.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑦⑧ | 24 |
| OXLUND [ | 2013 | 丹麦 | 61/58 | RCT | (62.9±7.1)/(63.9±6.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 16 |
| NI [ | 2014 | 中国 | 40/36 | RCT | (55.7±12.3)/(54.9±14.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②⑦ | 12 |
| VA'CLAVÍK [ | 2014 | 捷克 | 74/76 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 8 |
| WILLIAMS [ | 2015 | 英国 | 285/274 /282/285 | RCT | 61.4±9.6 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂基础降压治疗+多沙唑嗪4~8 mg/d基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5~10 mg/d | ①⑤ | 12 |
| 盖延红[ | 2015 | 中国 | 73/71 | RCT | 61.5±9.7 | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③④⑥ | 12 |
| DJOUMESSI [ | 2016 | 喀麦隆 | 9/8 | RCT | (64.6±9.6)/(61.0±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+坎地沙坦8 mg/d,阿替洛尔100 mg/d或甲基多巴750 mg/d | ①⑤ | 4 |
| OLIVERAS [ | 2016 | 西班牙 | 13/11 | RCT | (64.9±8.2)/(61.9±6.6) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25~50 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②③ ④⑥⑦⑧ | 24 |
| ROSA [ | 2016 | 捷克 | 50/51 | RCT | (59±9) /(56±12) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯25 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+肾脏去交感神经术 | ①②⑦⑧ | 48 |
| YANG [ | 2016 | 中国 | 15/15 | RCT | (44.7±10.8) /(43.4±15.2) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20~40 mg/d | 基础降压治疗 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 曾潇[ | 2016 | 中国 | 78/82 | RCT | (60.7±7.7)/(61.0±8.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①⑥⑦⑧ | 12 |
| 卢旭[ | 2017 | 中国 | 41/38 | RCT | (73.45±5.88) /(71.11±7.15) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 48 |
| KRIEGER[ | 2018 | 巴西 | 84/78 | RCT | (54±11.1)/(56.3±9.7) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯12.5~50.0 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+可乐定0.1~0.3 mg/d | ①②③④⑧ | 12 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 2018 | 多国 | 191/212 | RCT | 74(65,80) /71(63,78) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯23 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+安慰剂 | ① | 32 |
| 杨晶敏[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40/40/40 | RCT | (54.7±10.7)/(54.7±8.5) / (57.9±11.3) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+比索洛尔5 mg基础降压治疗+特拉唑嗪2 mg/d | ②⑦ | 12 |
| 黄娟[ | 2020 | 中国 | 45/49 | RCT | (60.4±9.5)/(59.7±9.9) | 基础降压治疗+螺内酯20 mg/d | 基础降压治疗+倍他乐克50 mg/d | ① ③④ | 8 |
| 第一作者 | 随机方法 | 盲法 | 分配隐藏 | 结果数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABOLGHASMI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 郭鑫[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 马彬[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 张俊松[ | 纳入顺序编号奇偶分配 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OXLUND[ | 网站生成的随机化方案 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| NI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| WILLIAMS[ | 计算机随机数字发生器 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 盖延红[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| DJOUMESSI[ | 未报告 | 单盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OLIVERAS[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSA[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| YANG[ | SPSS 19.0软件 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 曾潇[ | SPSS软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 卢旭[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| KRIEGER[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 杨晶敏[ | RandA1.0随机化软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 黄娟[ | 未报告 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 不完整 | 是,未报告对照组治疗后安全性指标 | 不清楚 |
Table 2 Results of bias risk assessment of included studies
| 第一作者 | 随机方法 | 盲法 | 分配隐藏 | 结果数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABOLGHASMI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 郭鑫[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 马彬[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 张俊松[ | 纳入顺序编号奇偶分配 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OXLUND[ | 网站生成的随机化方案 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| NI[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| VA'CLAVÍK[ | 简单无分层随机化 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| WILLIAMS[ | 计算机随机数字发生器 | 双盲 | 中心药房分配 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 盖延红[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| DJOUMESSI[ | 未报告 | 单盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| OLIVERAS[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSA[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| YANG[ | SPSS 19.0软件 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 曾潇[ | SPSS软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 卢旭[ | 随机数字表 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| KRIEGER[ | 未报告 | 开放标签 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| ROSSIGNOL[ | 未报告 | 双盲 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 杨晶敏[ | RandA1.0随机化软件 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 完整 | 否 | 不清楚 |
| 黄娟[ | 未报告 | 未报告 | 未报告 | 不完整 | 是,未报告对照组治疗后安全性指标 | 不清楚 |
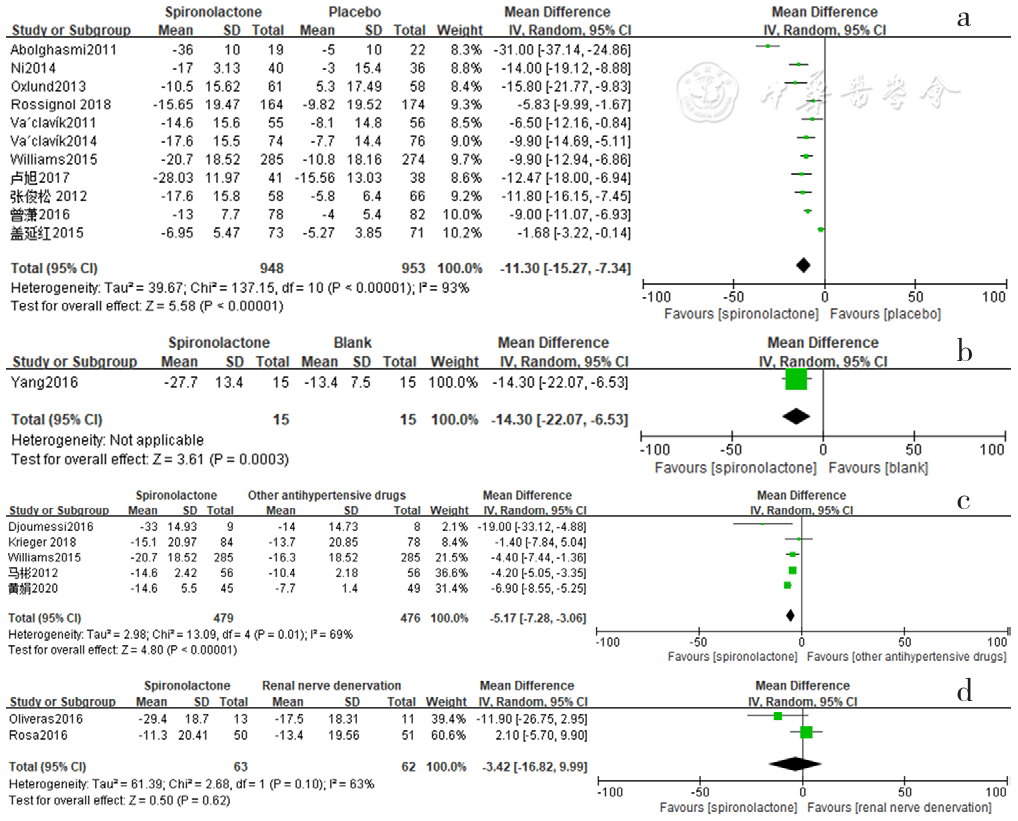
Figure 2 Forest plot of the effect of reducing clinic systolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
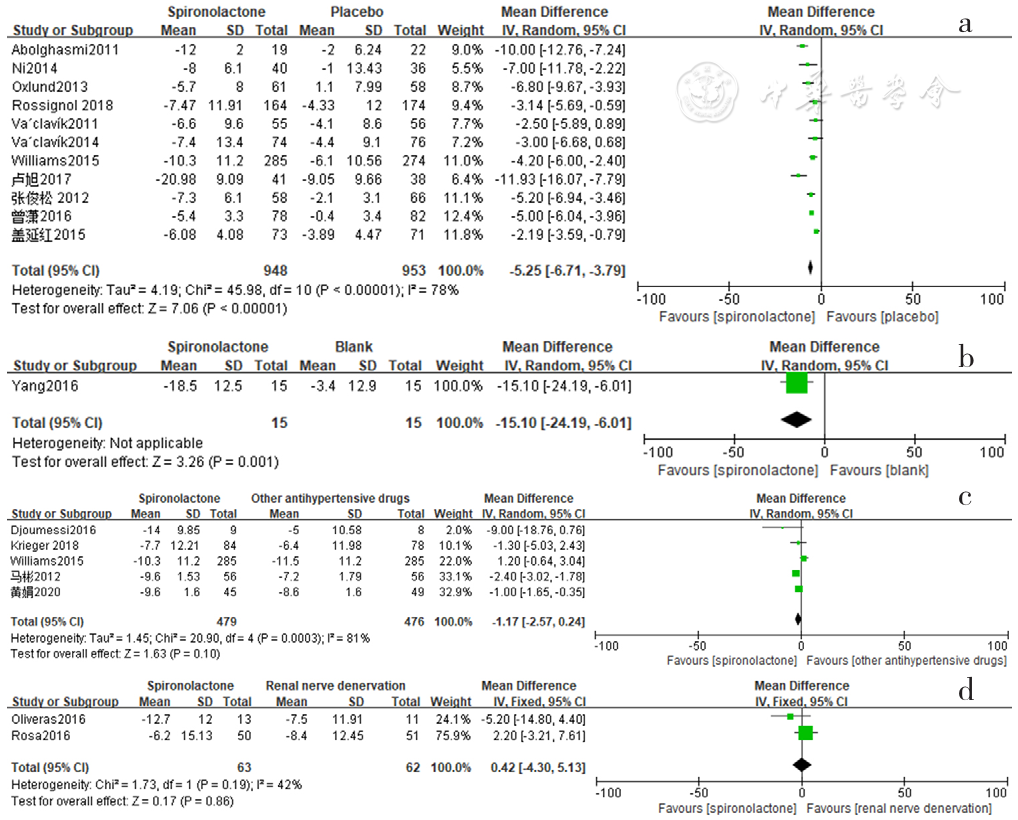
Figure 3 Forest plot of the effect of reducing clinic diastolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
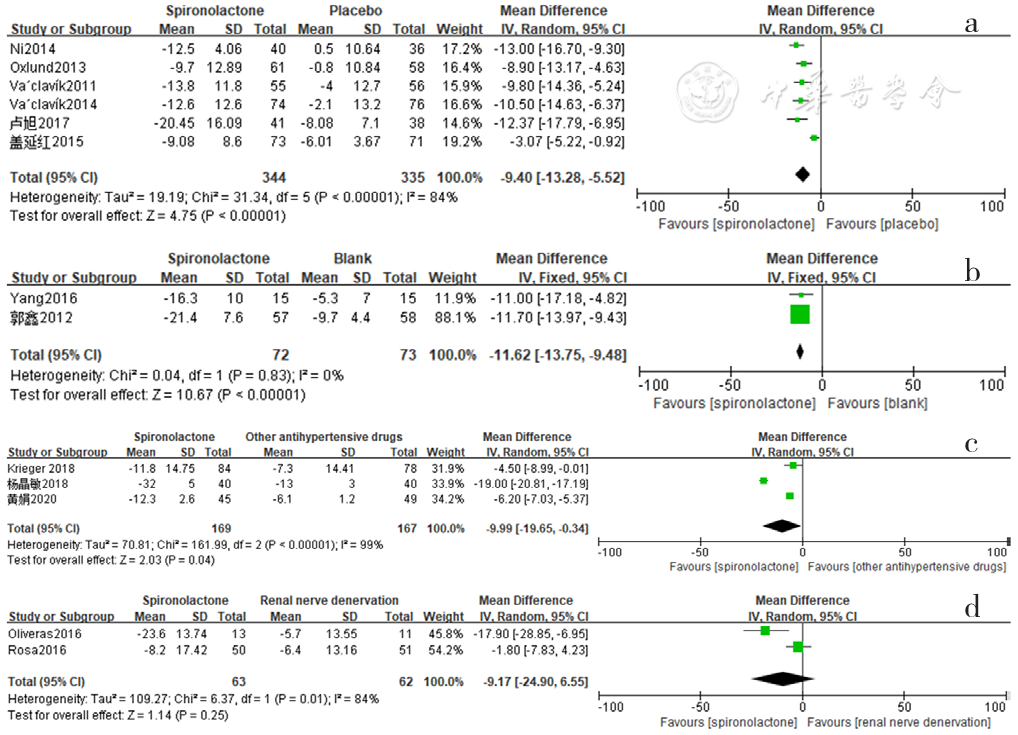
Figure 6 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
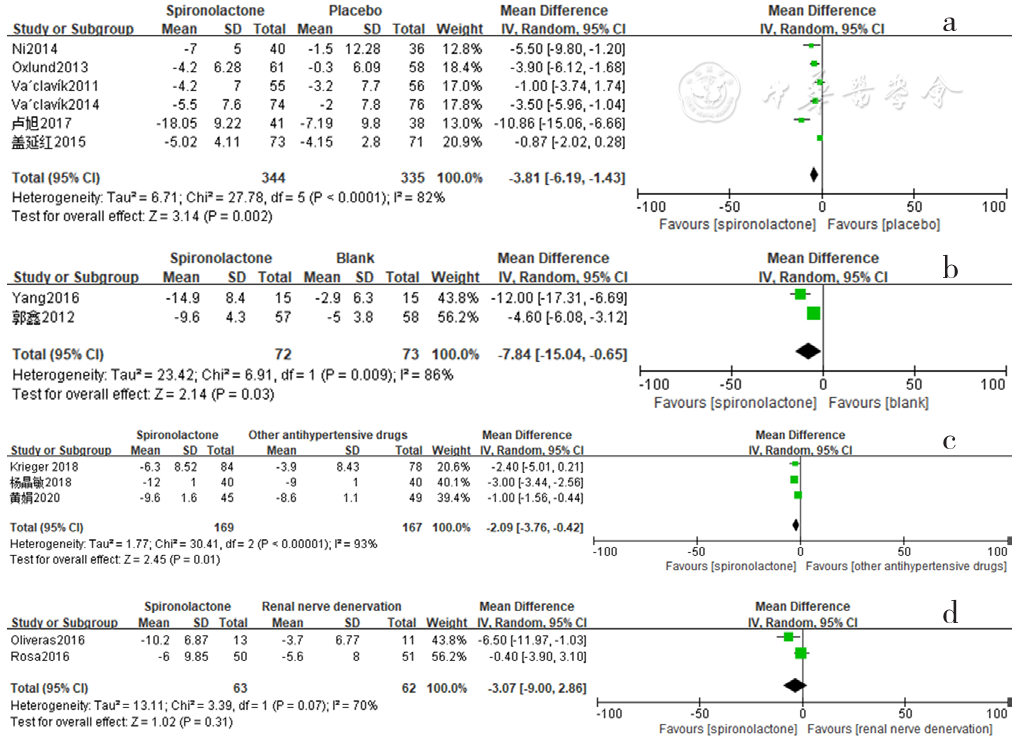
Figure 7 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
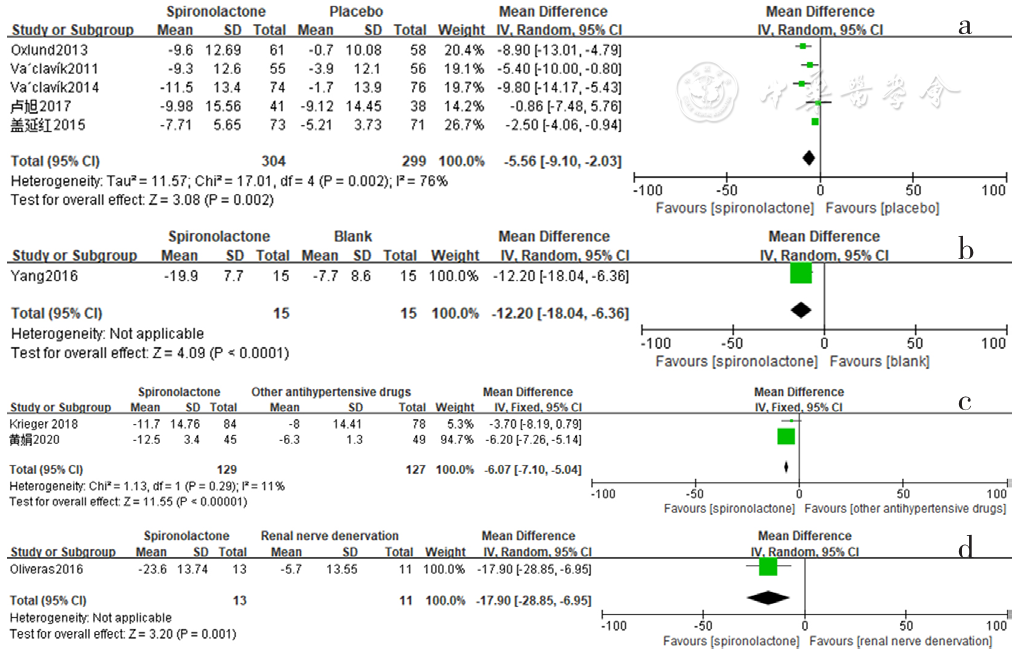
Figure 8 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing daytime systolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
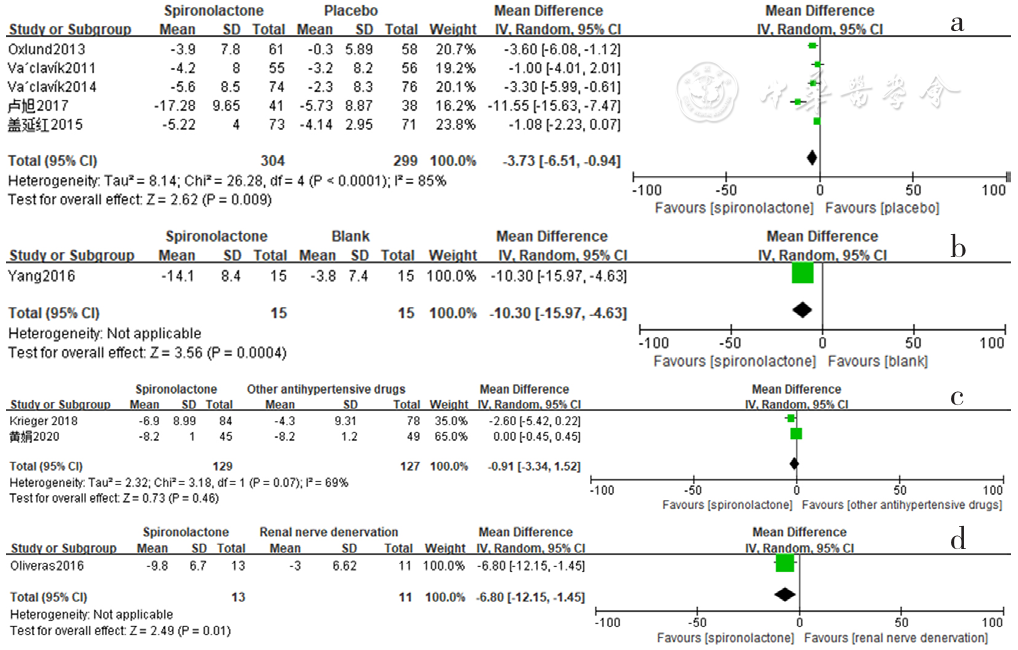
Figure 9 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing daytime diastolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
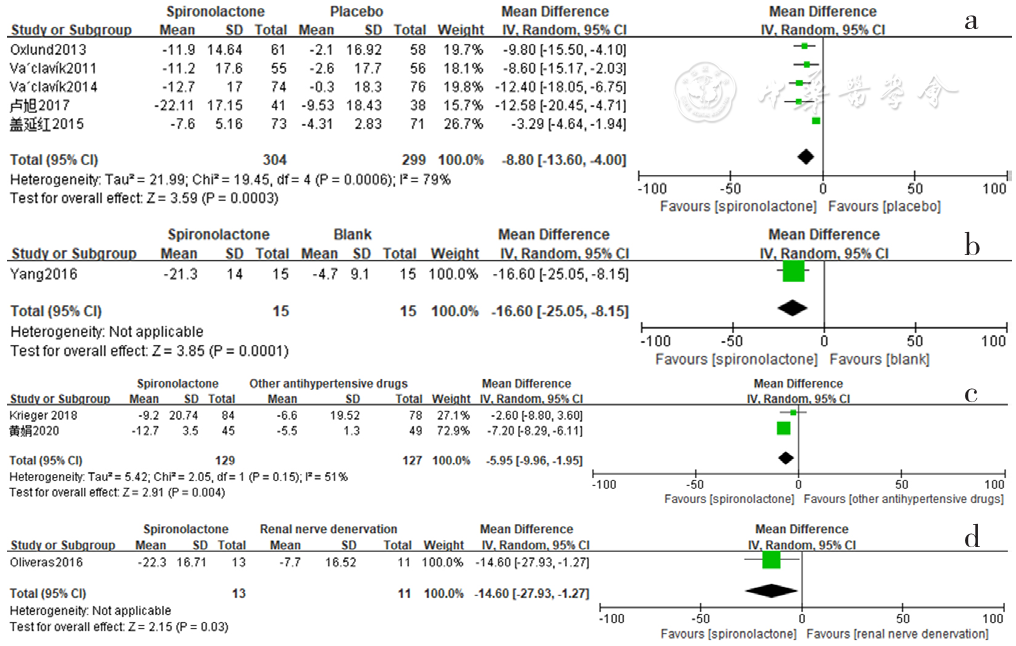
Figure 10 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing nighttime systolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
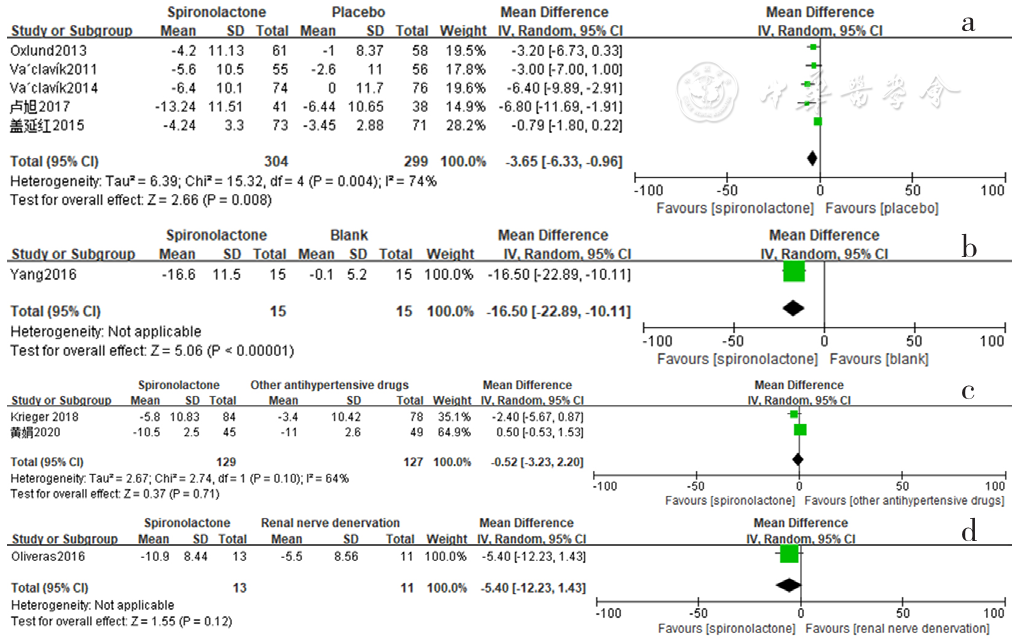
Figure 11 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing nighttime diastolic blood pressure compared with that of placebo,no-treatment(blank),other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation
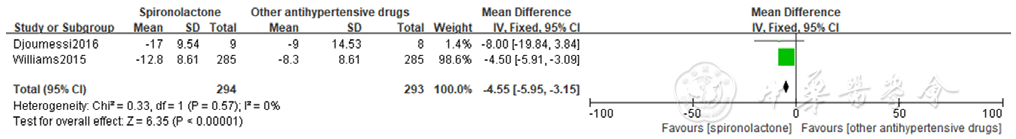
Figure 12 Forest plot of the effect of spironolactone on reducing self-measured home systolic blood pressure compared with that of other antihypertensive drugs
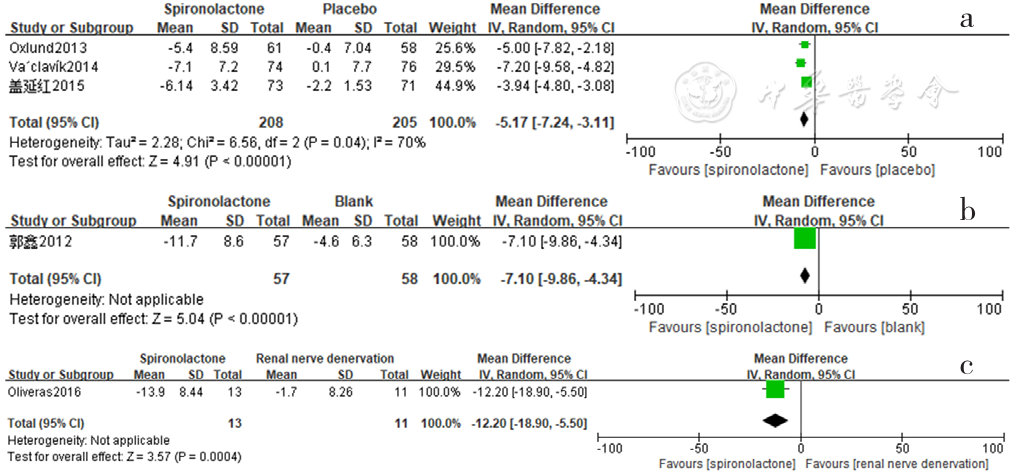
Figure 15 Forest plot of the effect of reducing 24-hour pulse pressure of spironolactone versus placebo,no-treatment(blank) and renal sympathetic denervation
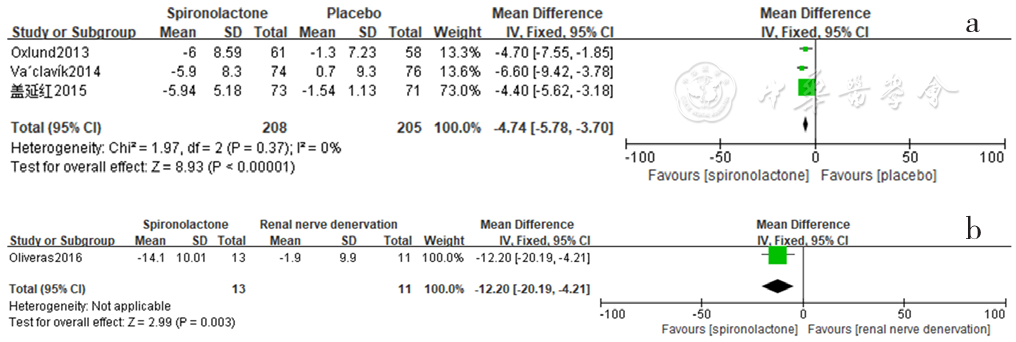
Figure 16 Forest plot of the effect of reducing daytime pulse pressure of spironolactone compared with that of placebo and renal sympathetic denervation
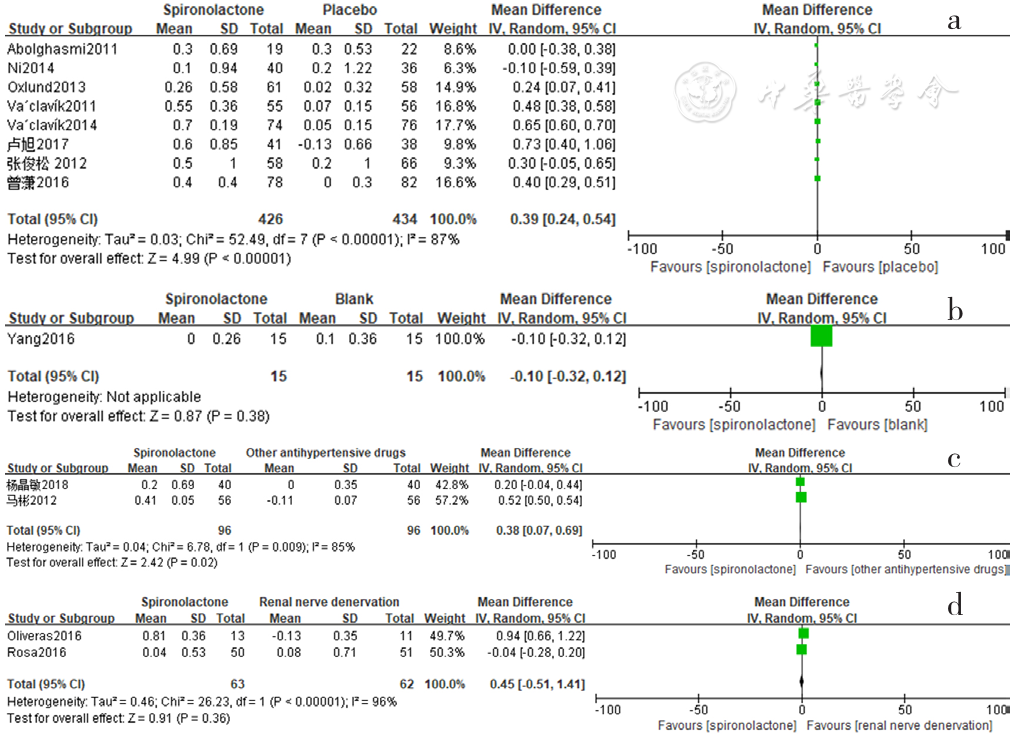
Figure 18 Forest plot of the changes in serum potassium levels of spironolactone-treated group compared with those of placebo,blank,other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation groups
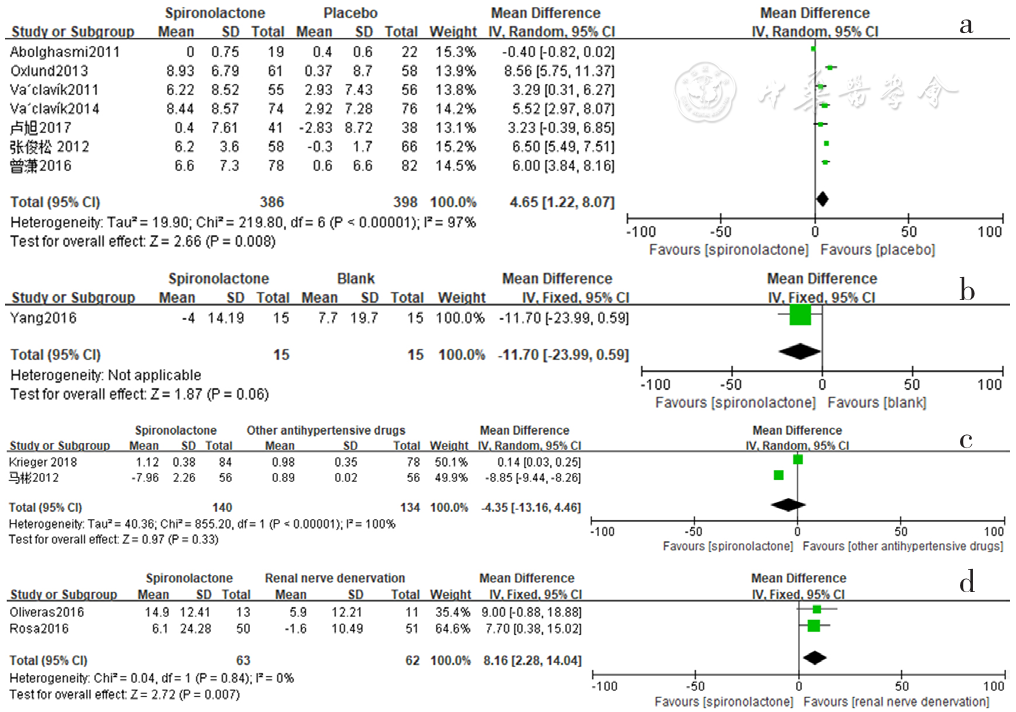
Figure 19 Forest plot of the changes in serum creatinine levels of spironolactone-treated group compared with those of placebo,blank,other antihypertensive drugs and renal sympathetic denervation groups
| [1] | CAREY R M, CALHOUN D A, BAKRIS G L,et al. Resistant hypertension:detection,evaluation,and management:a scientific statement from the American heart association[J]. Hypertension,2018,72(5):e53-90. DOI:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084. |
| [2] | TSUJIMOTO T, KAJIO H. Spironolactone use and improved outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with resistant hypertension[J]. J Am Heart Assoc,2020,9(23):e018827. DOI:10.1161/jaha.120.018827. |
| [3] | HIGGINS J, GREEN S.Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (version 5.1.0),2011[EB/OL].[2021-04-11].. |
| [4] | ABOLGHASMI R, TAZIKI O. Efficacy of low dose spironolactone in chronic kidney disease with resistant hypertension[J]. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl,2011,22(1):75-78. |
| [5] | VÁCLAVÍK J, SEDLÁK R, PLACHÝ M,et al. Addition of spironolactone in patients with resistant arterial hypertension (ASPIRANT)[J]. Hypertension,2011,57(6):1069-1075. DOI:10.1161/hypertensionaha.111.169961. |
| [6] | 郭鑫. 醛固酮受体拮抗剂—螺内酯治疗难治性高血压的疗效观察[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2012. |
| [7] | 马彬. 小剂量安体舒通治疗顽固性高血压疗效分析[J]. 中国实用医药,2012,7(23):35-37. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2012.23.098. |
| [8] | 张俊松,邓节喜,郭寿贵,等. 螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的随机、单盲、对照试验[J]. 海南医学院学报,2012,18(6):788-790,793. DOI:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.2012.06.013. |
| [9] | OXLUND C S, HENRIKSEN J E, TARNOW L,et al. Low dose spironolactone reduces blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus:a double blind randomized clinical trial[J]. J Hypertens,2013,31(10):2094-2102. DOI:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283638b1a. |
| [10] | NI X Y, ZHANG J S, ZHANG P,et al. Effects of spironolactone on dialysis patients with refractory hypertension:a randomized controlled study[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich),2014,16(9):658-663. DOI:10.1111/jch.12374. |
| [11] | VÁCLAVÍK J, SEDLÁK R, JARKOVSKÝ J,et al. Effect of spironolactone in resistant arterial hypertension:a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled trial (ASPIRANT-EXT)[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2014,93(27):e162. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000000162. |
| [12] | WILLIAMS B, MACDONALD T M, MORANT S,et al. Spironolactone versus placebo,bisoprolol,and doxazosin to determine the optimal treatment for drug-resistant hypertension (PATHWAY-2):a randomised,double-blind,crossover trial[J]. Lancet,2015,386(10008):2059-2068. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00257-3. |
| [13] | 盖延红,栾晓东,朱为勇,等. 螺内酯治疗不同年龄难治性高血压的疗效差别[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2015,7(4):537-538,541. DOI:10.3969/j.1674-4055.2015.04.33. |
| [14] | DJOUMESSI R N, NOUBIAP J J, KAZE F F,et al. Effect of low-dose spironolactone on resistant hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus:a randomized controlled trial in a sub-Saharan African population[J]. BMC Res Notes,2016,9:187. DOI:10.1186/s13104-016-1987-5. |
| [15] | OLIVERAS A, ARMARIO P, CLARÀ A,et al. Spironolactone versus sympathetic renal denervation to treat true resistant hypertension:results from the DENERVHTA study-a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hypertens,2016,34(9):1863-1871. DOI:10.1097/hjh.0000000000001025. |
| [16] | ROSA J, WIDIMSKÝ P, WALDAUF P,et al. Role of adding spironolactone and renal denervation in true resistant hypertension:one-year outcomes of randomized PRAGUE-15 study[J]. Hypertension,2016,67(2):397-403. DOI:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06526. |
| [17] | YANG L R, ZHANG H M, CAI M,et al. Effect of spironolactone on patients with resistant hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens,2016,38(5):464-468. DOI:10.3109/10641963.2015.1131290. |
| [18] | 曾潇,周宁,曹少雄,等. 小剂量螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的临床研究[J]. 江西医药,2016,51(8):742-745. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2016.08.006. |
| [19] | 卢旭.小剂量螺内酯在老年难治性高血压患者中疗效及安全性分析[D].北京:解放军总医院(北京301医院)&军医进修学院,2017. |
| [20] | KRIEGER E M, DRAGER L F, GIORGI D M A,et al. Spironolactone versus clonidine as a fourth-drug therapy for resistant hypertension:the ReHOT randomized study (resistant hypertension optimal treatment)[J]. Hypertension,2018,71(4):681-690. DOI:10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10662. |
| [21] | ROSSIGNOL P, CLAGGETT B L, LIU J,et al. Spironolactone and resistant hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Am J Hypertens,2018,31(4):407-414. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpx210. |
| [22] | 杨晶敏,杨文,刘洁云. 螺内酯、特拉唑嗪、比索洛尔对难治性高血压患者的治疗效果及安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2018,21(31):3845-3849. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.31.014. |
| [23] | 黄娟.螺内酯治疗顽固性高血压的疗效及安全性[J].当代医药论丛,2020,18(15):126-128. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2020.15.090. |
| [24] | LOTUFO P A, PEREIRA A C, VASCONCELLOS P S,et al. Resistant hypertension:risk factors,subclinical atherosclerosis,and comorbidities among adults-the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil)[J]. J Clin Hypertens:Greenwich,2015,17(1):74-80. DOI:10.1111/jch.12433. |
| [25] | CAO G Z, CHEN C, LIN Q S,et al. Prevalence,clinical characteristics and echocardiography parameters of non-resistant,resistant and refractory hypertension in Chinese[J]. Postgrad Med,2017,129(2):187-192. DOI:10.1080/00325481.2017.1272398. |
| [26] | HWANG A Y, DIETRICH E, PEPINE C J,et al. Resistant hypertension:mechanisms and treatment[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep,2017,19(7):1-11. DOI:10.1007/s11906-017-0754-x. |
| [27] | SIDDIQUI M, CALHOUN D A. Refractory versus resistant hypertension[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens,2017,26(1):14-19. DOI:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000286. |
| [28] | SALLES G F, RIBEIRO F M, GUIMARÃES G M,et al. A reduced heart rate variability is independently associated with a blunted nocturnal blood pressure fall in patients with resistant hypertension[J]. J Hypertens,2014,32(3):644-651. DOI:10.1097/HJH.0000000000000068. |
| [29] | DAUGHERTY S L, POWERS J D, MAGID D J,et al. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients[J]. Circulation,2012,125(13):1635-1642. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.068064. |
| [30] | 那开宪.应重视醛固酮受体拮抗剂在心血管疾病中的应用[J].中国临床医生杂志,2016,44(11):1-3. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2016.11.001. |
| [31] | ROSSIGNOL P, CLAGGETT B L, LIU J,et al. Spironolactone and resistant hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Am J Hypertens,2018,31(4):407-414. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpx210. |
| [32] | TSUJIMOTO T, KAJIO H. Spironolactone use and improved outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with resistant hypertension[J]. J Am Heart Assoc,2020,9(23):e018827. DOI:10.1161/jaha.120.018827. |
| [33] | CHEN C, ZHU X Y, LI D,et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of spironolactone in patients with resistant hypertension:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2020,99(34):e21694. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000021694. |
| [34] | MUXFELDT E S, CHEDIER B, RODRIGUES C I S. Resistant and refractory hypertension:two sides of the same disease?[J]. J Bras Nefrol,2019,41(2):266-274. DOI:10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2018-0108. |
| [35] | CAREY R M, CALHOUN D A, BAKRIS G L,et al. Resistant hypertension:detection,evaluation,and management:a scientific statement from the American heart association[J]. Hypertension,2018,72(5):e53-90. DOI:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084. |
| [36] | ACELAJADO M C, HUGHES Z H, OPARIL S,et al. Treatment of resistant and refractory hypertension[J]. Circ Res,2019,124(7):1061-1070. DOI:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312156. |
| [37] | 赵林蔚,朱利杰,张优,等. 肾动脉射频消融去交感神经术研究进展[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2017,31(2):194-196. DOI:10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2017.02.029. |
| [38] | TOUYZ R M. Reactive oxygen species,vascular oxidative stress,and redox signaling in hypertension:what is the clinical significance?[J]. Hypertension,2004,44(3):248-252. DOI:10.1161/01.HYP.0000138070.47616.9d. |
| [39] | KHOSLA N, KALAITZIDIS R, BAKRIS G L. Predictors of hyperkalemia risk following hypertension control with aldosterone blockade[J]. Am J Nephrol,2009,30(5):418-424. DOI:10.1159/000237742. |
| [1] | XU Jialan, YAN Hong, WEN Jun, ZHOU Zitong, WANG Siyu. Prevalence of Potentially Inappropriate Medication in Older Adults with Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | WU Wenjun, WEI Jingjing, LI Xue, REN Hongjie, YU Rui, PENG Guangcao, ZHU Mingjun. Regularity of Prescriptions for Coronary Heart Disease with Hypertension Based on Latent Structure and Association Rules [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3787-3795. |
| [3] | BAI Jiaxin, CHEN Yu, ZHOU Yiheng, LIU Lidi, YANG Rong, YAO Yi, YUAN Bo, ZHANG Yonggang, LEI Yi, ZENG Rui, JIA Yu, LIAO Xiaoyang. Assessment and Treatment of Early-onset Hypertension: Position Statement of the British and Irish Hypertension Association and Its Implications for Clinical Management of Early-onset Hypertension in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3741-3746. |
| [4] | QIN Bangguo, SUN Jin, LI Man, QIU Jiaojiao, CHENG Bokai, ZHU Ping, WANG Shuxia. Relationship between Non-high-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in a Community-based Hypertensive Population [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3753-3760. |
| [5] | ZHANG Tianyu, YU Haibo, CHEN Fei, LI Xin, ZHANG Jiajia, ZHAN Xiaokai, SHEN Man, TANG Ran, FAN Sibin, ZHAO Fengyi, HUANG Zhongxia. Meta-analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Systemic Treatment for POEMS Syndrome [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [6] | QUAN Jialin, ZHU Lin, SU Yu, CHEN Zekai, CHEN Ziqi, ZHANG Zhuofan. Research on the Improvement Effect of Exercise Modes on the Executive Function of Overweight or Obese Children or Adolescents: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [7] | HAN Xiao, LI Qiyu, GE Pu, FAN Siyuan, LIU Diyue, WU Yibo, ZHANG Qingshuang. The Impact of Behavioral Lifestyle on Quality of Life in Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [8] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [9] | TANG Shangfeng, HUANG Yangzhen, PAN Yangyang, ZHENG Yanxi, XIONG Zhongbao, ZHANG Kangkang, SONG Jia, WEI Yilin, WANG Chunying, DONG Heng, CHEN Manwei, QING Hua. Specification for the Integration of Healthcare and Prevention Services in Hypertension at the Primary Level [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3089-3095. |
| [10] | WEI Yunhong, YANG Li, WANG Yulu, YE Qiufang, DAI Anni, HE Yan. Study on Cardiopulmonary Function During Different Exercise Stages in Patients with Obesity-related Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2972-2978. |
| [11] | JIANG Shihua, ZHU Zheng, REN Yingying, ZHU Yaolei, WANG Yue, GAO Xibin. Meta Analysis of the Prevalence and Risk Factors of Myopia in Chinese Children and Adolescents [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [12] | HE Jinyu, ZHULIDUZI Jiesisibieke, ZHANG Ning, LIU Min, LIANG Wannian. Research on Blood Pressure Control and Its Determinants Among Hypertensive Patients Under Standardized Management in China: Status, Challenges, and Future Directions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2968-2971. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaolin, LI Qiuyue, ZHOU Yanjun, ZHANG Jinhui, LIANG Tao. Incidence and Risk of Cardiovascular Toxicity with Fruquintinib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [14] | LI Hao, LI Jiangtao, LIU Dan, WANG Jianjun. Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab, Anifrolumab, and Telitacicept on the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [15] | CHEN Youlan, LAN Yanqi, WU Ahua, ZHANG Haixia, HUANG Jiankang, GUO Zhinan. The Health Management Effect of Contracted Family Doctor Services under the Joint Management of Three Teachers in Xiamen City on Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2769-2775. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||