

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (04): 461-466.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.346
Special Issue: 高血压最新文章合辑
• Original Research·Population Health • Previous Articles Next Articles
Longitudinal Cohort Study of the Association of Triglyceride-glucose Index with Hypertension among Teachers from a University
1.School of Nursing,Anhui Medical University,Hefei 230032,China
2.Department of Internal Medicine,Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
*Corresponding author:LIU Annuo,Professor,Master supervisor;E-mail:w971002y@sohu.com
Received:2021-05-11
Revised:2021-12-20
Published:2022-02-05
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
刘安诺
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Yuanjing, LIU Annuo.
Longitudinal Cohort Study of the Association of Triglyceride-glucose Index with Hypertension among Teachers from a University [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(04): 461-466.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.346
| TyG指数水平 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(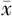 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | BMI〔n(%)〕 | SBP (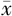 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP (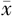 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <18.5 kg/m2 | 18.5~<24 .0 kg/m2 | 24.0~<28.0 kg/m2 | ≥28.0 kg/m2 | |||||
| Q1 | 149 | 36(24.2) | 113(75.8) | 45.9±11.6 | 9(6.0) | 116(77.9) | 22(14.8) | 2(1.3) | 109±12 | 72±8 |
| Q2 | 150 | 57(38.0) | 93(62.0) | 48.7±13.4 | 7(4.7) | 103(68.7) | 40(26.7) | 0 | 111±12 | 73±8 |
| Q3 | 152 | 80(52.6) | 72(47.4) | 50.4±13.8 | 5(3.3) | 91(59.9) | 46(30.3) | 10(6.6) | 112±10 | 75±7 |
| Q4 | 151 | 97(64.2) | 54(35.8) | 51.4±12.6 | 2(1.3) | 73(48.3) | 65(43.0) | 11(7.3) | 115±10 | 77±7 |
| 检验统计量值 | 55.30a | 5.74b | 53.12a | 7.68b | 13.02b | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
Table 1 Comparison of characteristics of university teachers in quartile groups of triglyceride-glucose index
| TyG指数水平 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(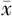 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | BMI〔n(%)〕 | SBP (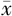 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP (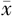 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <18.5 kg/m2 | 18.5~<24 .0 kg/m2 | 24.0~<28.0 kg/m2 | ≥28.0 kg/m2 | |||||
| Q1 | 149 | 36(24.2) | 113(75.8) | 45.9±11.6 | 9(6.0) | 116(77.9) | 22(14.8) | 2(1.3) | 109±12 | 72±8 |
| Q2 | 150 | 57(38.0) | 93(62.0) | 48.7±13.4 | 7(4.7) | 103(68.7) | 40(26.7) | 0 | 111±12 | 73±8 |
| Q3 | 152 | 80(52.6) | 72(47.4) | 50.4±13.8 | 5(3.3) | 91(59.9) | 46(30.3) | 10(6.6) | 112±10 | 75±7 |
| Q4 | 151 | 97(64.2) | 54(35.8) | 51.4±12.6 | 2(1.3) | 73(48.3) | 65(43.0) | 11(7.3) | 115±10 | 77±7 |
| 检验统计量值 | 55.30a | 5.74b | 53.12a | 7.68b | 13.02b | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.453 | 0.224 | 1.572(1.014,2.439) | 4.084 | 0.043 | |
| Q3 | 0.819 | 0.216 | 2.268(1.484,3.466) | 14.313 | <0.001 | |
| Q4 | 1.175 | 0.230 | 3.237(2.063,5.080) | 26.123 | <0.001 | |
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | -0.847 | 0.176 | 0.429(0.304,0.605) | 23.188 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(以实际值纳入) | 0.050 | 0.006 | 1.051(1.038,1.064) | 60.670 | <0.001 | |
| BMI(kg/m2,以18.5~<24.0为参照) | ||||||
| <18.5 | 0.463 | 0.427 | 1.589(0.688,3.671) | 1.177 | 0.278 | |
| 24.0~<28.0 | 0.761 | 0.172 | 2.140(1.529,2.996) | 19.640 | <0.001 | |
| ≥28.0 | 1.573 | 0.266 | 4.820(2.864,8.111) | 35.073 | <0.001 | |
| γ-GGT(U/L,以男≤50,女≤32为参照) | ||||||
| 男>50,女>32 | 0.469 | 0.190 | 1.599(1.103,2.319) | 6.124 | 0.013 | |
| ALT(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.414 | 0.175 | 1.512(1.072,2.133) | 5.563 | 0.018 | |
| AST(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 1.219(0.601,2.471) | 0.302 | 0.583 | |
| TC(mmol/L,以<5.2为参照) | ||||||
| ≥5.2 | 0.326 | 0.153 | 1.386(1.027,1.870) | 4.542 | 0.033 | |
| LDL-C(mmol/L,以<3.4为参照) | ||||||
| ≥3.4 | 0.401 | 0.163 | 1.493(1.086,2.053) | 6.089 | 0.014 | |
| HDL-C(mmol/L,以≥1.0为参照) | ||||||
| <1.0 | 0.428 | 0.197 | 1.534(1.044,2.254) | 4.738 | 0.029 | |
| UA(μmol/L,以男≤420,女≤360为参照) | ||||||
| 男>420,女>360 | 0.731 | 0.196 | 2.076(1.415,3.048) | 13.920 | <0.001 | |
| BUN(mmol/L,以≤7.1为参照) | ||||||
| >7.1 | 0.902 | 0.376 | 2.464(1.179,5.151) | 5.743 | 0.017 | |
Table 2 Univariate analysis of association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension using generalized estimating equation
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.453 | 0.224 | 1.572(1.014,2.439) | 4.084 | 0.043 | |
| Q3 | 0.819 | 0.216 | 2.268(1.484,3.466) | 14.313 | <0.001 | |
| Q4 | 1.175 | 0.230 | 3.237(2.063,5.080) | 26.123 | <0.001 | |
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | -0.847 | 0.176 | 0.429(0.304,0.605) | 23.188 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(以实际值纳入) | 0.050 | 0.006 | 1.051(1.038,1.064) | 60.670 | <0.001 | |
| BMI(kg/m2,以18.5~<24.0为参照) | ||||||
| <18.5 | 0.463 | 0.427 | 1.589(0.688,3.671) | 1.177 | 0.278 | |
| 24.0~<28.0 | 0.761 | 0.172 | 2.140(1.529,2.996) | 19.640 | <0.001 | |
| ≥28.0 | 1.573 | 0.266 | 4.820(2.864,8.111) | 35.073 | <0.001 | |
| γ-GGT(U/L,以男≤50,女≤32为参照) | ||||||
| 男>50,女>32 | 0.469 | 0.190 | 1.599(1.103,2.319) | 6.124 | 0.013 | |
| ALT(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.414 | 0.175 | 1.512(1.072,2.133) | 5.563 | 0.018 | |
| AST(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 1.219(0.601,2.471) | 0.302 | 0.583 | |
| TC(mmol/L,以<5.2为参照) | ||||||
| ≥5.2 | 0.326 | 0.153 | 1.386(1.027,1.870) | 4.542 | 0.033 | |
| LDL-C(mmol/L,以<3.4为参照) | ||||||
| ≥3.4 | 0.401 | 0.163 | 1.493(1.086,2.053) | 6.089 | 0.014 | |
| HDL-C(mmol/L,以≥1.0为参照) | ||||||
| <1.0 | 0.428 | 0.197 | 1.534(1.044,2.254) | 4.738 | 0.029 | |
| UA(μmol/L,以男≤420,女≤360为参照) | ||||||
| 男>420,女>360 | 0.731 | 0.196 | 2.076(1.415,3.048) | 13.920 | <0.001 | |
| BUN(mmol/L,以≤7.1为参照) | ||||||
| >7.1 | 0.902 | 0.376 | 2.464(1.179,5.151) | 5.743 | 0.017 | |
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.345 | 0.197 | 1.411(0.960,2.075) | 3.07 | 0.080 | |
| Q3 | 0.436 | 0.209 | 1.546(1.026,2.330) | 4.34 | 0.037 | |
| Q4 | 0.627 | 0.223 | 1.872(1.209,2.901) | 7.89 | 0.005 | |
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of the association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension using generalized estimating equation
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.345 | 0.197 | 1.411(0.960,2.075) | 3.07 | 0.080 | |
| Q3 | 0.436 | 0.209 | 1.546(1.026,2.330) | 4.34 | 0.037 | |
| Q4 | 0.627 | 0.223 | 1.872(1.209,2.901) | 7.89 | 0.005 | |
| 变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | P交互值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.034 | |||||||
| 男(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.253 | 0.249 | 1.288(0.790,2.098) | 1.031 | 0.310 | |||
| Q3 | 0.127 | 0.263 | 1.136(0.679,1.901) | 0.235 | 0.628 | |||
| Q4 | 0.854 | 0.299 | 2.349(1.308,4.217) | 8.183 | 0.004 | |||
| 女(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.343 | 0.344 | 1.410(0.719,2.764) | 0.999 | 0.317 | |||
| Q3 | 0.485 | 0.352 | 1.625(0.815,3.238) | 1.904 | 0.168 | |||
| Q4 | 0.759 | 0.342 | 2.135(1.093,4.172) | 4.929 | 0.026 | |||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.047 | |||||||
| 18~44(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.247 | 0.362 | 1.280(0.630,2.600) | 0.467 | 0.494 | |||
| Q3 | -0.031 | 0.528 | 0.970(0.344,2.732) | 0.003 | 0.954 | |||
| Q4 | 0.678 | 0.464 | 1.969(0.794,4.884) | 2.137 | 0.144 | |||
| 45~54(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.412 | 0.481 | 1.510(0.588,3.879) | 0.734 | 0.392 | |||
| Q3 | 1.102 | 0.462 | 3.011(1.217,7.451) | 5.685 | 0.017 | |||
| Q4 | 1.244 | 0.574 | 3.468(1.126,10.678) | 4.697 | 0.030 | |||
| ≥55(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.408 | 0.269 | 1.505(0.889,2.547) | 2.312 | 0.128 | |||
| Q3 | 0.460 | 0.273 | 1.584(0.927,2.706) | 2.837 | 0.092 | |||
| Q4 | 0.383 | 0.309 | 1.466(0.799,2.689) | 1.529 | 0.216 | |||
| BMI | 0.034 | |||||||
| 体质量正常(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.243 | 0.271 | 1.276(0.750,2.168) | 0.809 | 0.368 | |||
| Q3 | 0.636 | 0.280 | 1.888(1.091,3.267) | 5.161 | 0.023 | |||
| Q4 | 0.882 | 0.304 | 2.416(1.331,4.385) | 8.417 | 0.004 | |||
| 超重肥胖(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.560 | 0.313 | 1.751(0.949,3.230) | 3.209 | 0.073 | |||
| Q3 | 0.335 | 0.328 | 1.398(0.736,2.658) | 1.047 | 0.306 | |||
| Q4 | 0.546 | 0.331 | 1.726(0.902,3.302) | 2.719 | 0.099 | |||
Table 4 Multivariate analysis of the association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension by sex,age,and BMI using generalized estimating equation
| 变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | P交互值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.034 | |||||||
| 男(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.253 | 0.249 | 1.288(0.790,2.098) | 1.031 | 0.310 | |||
| Q3 | 0.127 | 0.263 | 1.136(0.679,1.901) | 0.235 | 0.628 | |||
| Q4 | 0.854 | 0.299 | 2.349(1.308,4.217) | 8.183 | 0.004 | |||
| 女(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.343 | 0.344 | 1.410(0.719,2.764) | 0.999 | 0.317 | |||
| Q3 | 0.485 | 0.352 | 1.625(0.815,3.238) | 1.904 | 0.168 | |||
| Q4 | 0.759 | 0.342 | 2.135(1.093,4.172) | 4.929 | 0.026 | |||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.047 | |||||||
| 18~44(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.247 | 0.362 | 1.280(0.630,2.600) | 0.467 | 0.494 | |||
| Q3 | -0.031 | 0.528 | 0.970(0.344,2.732) | 0.003 | 0.954 | |||
| Q4 | 0.678 | 0.464 | 1.969(0.794,4.884) | 2.137 | 0.144 | |||
| 45~54(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.412 | 0.481 | 1.510(0.588,3.879) | 0.734 | 0.392 | |||
| Q3 | 1.102 | 0.462 | 3.011(1.217,7.451) | 5.685 | 0.017 | |||
| Q4 | 1.244 | 0.574 | 3.468(1.126,10.678) | 4.697 | 0.030 | |||
| ≥55(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.408 | 0.269 | 1.505(0.889,2.547) | 2.312 | 0.128 | |||
| Q3 | 0.460 | 0.273 | 1.584(0.927,2.706) | 2.837 | 0.092 | |||
| Q4 | 0.383 | 0.309 | 1.466(0.799,2.689) | 1.529 | 0.216 | |||
| BMI | 0.034 | |||||||
| 体质量正常(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.243 | 0.271 | 1.276(0.750,2.168) | 0.809 | 0.368 | |||
| Q3 | 0.636 | 0.280 | 1.888(1.091,3.267) | 5.161 | 0.023 | |||
| Q4 | 0.882 | 0.304 | 2.416(1.331,4.385) | 8.417 | 0.004 | |||
| 超重肥胖(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.560 | 0.313 | 1.751(0.949,3.230) | 3.209 | 0.073 | |||
| Q3 | 0.335 | 0.328 | 1.398(0.736,2.658) | 1.047 | 0.306 | |||
| Q4 | 0.546 | 0.331 | 1.726(0.902,3.302) | 2.719 | 0.099 | |||
| [1] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5301.2019.03.001. |
| [2] | MILLS K T, BUNDY J D, KELLY T N,et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control:a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries[J]. Circulation,2016,134(6):441-450. |
| [3] | 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2019概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2020,35(9):833-854. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2020.09.001. |
| [4] | 辛青,张成秋,谭小燕,等. 高校教职工高血压患病情况及影响因素[J]. 中国卫生统计,2013,30(6):874-876,878. |
| [5] | WANG F, HAN L, HU D. Fasting insulin,insulin resistance and risk of hypertension in the general population:a meta-analysis[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2017,464:57-63. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2016.11.009. |
| [6] | GUERRERO-ROMERO F, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA L E, GONZÁLEZ-ORTIZ M,et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose,a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2010,95(7):3347-3351. DOI:10.1210/jc.2010-0288. |
| [7] | SÁNCHEZ-ÍÑIGO L, NAVARRO-GONZÁLEZ D, PASTRANA-DELGADO J,et al. Association of triglycerides and new lipid markers with the incidence of hypertension in a Spanish cohort[J]. J Hypertens,2016,34(7):1257-1265. |
| [8] | ZHENG R, MAO Y. Triglyceride and glucose(TyG) index as a predictor of incident hypertension:a 9-year longitudinal population-based study[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2017,16(1):175. |
| [9] | WANG K, HE G, ZHANG Y,et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index and its interaction with obesity on hypertension risk in Chinese:a population-based study[J]. J Hum Hypertens,2020,35(3):232-239. DOI:10.1038/s41371-020-0326-4. |
| [10] | ZHU B, WANG J, CHEN K,et al. A high triglyceride glucose index is more closely associated with hypertension than lipid or glycemic parameters in elderly individuals:a cross-sectional survey from the Reaction Study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2020,19(1):112. DOI:10.1186/s12933-020-01077-6. |
| [11] | ZENG Z Y, LIU S X, XU H,et al. Association of triglyceride glucose index and its combination of obesity indices with prehypertension in lean individuals:a cross-sectional study of Chinese adults[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2020,22(6):1025-1032. DOI:10.1111/jch.13878. |
| [12] | LIU X Z, FAN J, PAN S J. METS-IR,a novel simple insulin resistance indexes,is associated with hypertension in normal-weight Chinese adults[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2019,21(8):1075-1081. DOI:10.1111/jch.13591. |
| [13] | MORALES-GURROLA G, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA L E, CASTELLANOS-JUÁREZ F X,et al. The triglycerides and glucose index is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in metabolically obese normal-weight subjects[J]. J Endocrinol Invest,2020,43(7):995-1000. DOI:10.1007/s40618-020-01184-x. |
| [14] | BARZEGAR N, TOHIDI M, HASHEMINIA M,et al. The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on incident cardiovascular events during 16 years of follow-up:tehran lipid and glucose study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2020,19(1):155. |
| [15] | LEE S H, HAN K, YANG H K,et al. A novel criterion for identifying metabolically obese but normal weight individuals using the product of triglycerides and glucose[J]. Nutr Diabetes,2015,5(4):e149. DOI:10.1038/nutd.2014.46. |
| [16] | 汤宁,宋秋月,易东,等. 医学纵向数据建模方法及其统计分析策略[J]. 中国卫生统计,2019,36(3):441-444,447. |
| [17] | RAHMAN S, ISLAM S, HAQUE T,et al. Association between serum liver enzymes and hypertension:a cross-sectional study in Bangladeshi adults[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord,2020,20(1):128. DOI:10.1186/s12872-020-01411-6. |
| [18] | YU Z, CORESH J, QI G,et al. A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study supports causal effects of kidney function on blood pressure[J]. Kidney Int,2020,98(3):708-716. |
| [19] | 中国肥胖问题工作组. 中国成人超重和肥胖症预防与控制指南(节录)[J]. 营养学报,2004,26(1):1-4. |
| [20] | 诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001. |
| [21] | 高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科共识专家组. 中国高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(3):235-248. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.03.021. |
| [22] | 万学红,卢雪峰. 诊断学[M]. 9版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2018:343-364. |
| [23] | RIECHMANN-WOLF M, JANKOWIAK S, SCHULZ A,et al. Self-reported cardiovascular health of teachers:results from the 5-year follow-up of the Gutenberg health study cohort[J]. Int Arch Occup Environ Health,2021,94(2):251-259. |
| [24] | MINH H V, TIEN H A, SINH C T,et al. Assessment of preferred methods to measure insulin resistance in Asian patients with hypertension[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2021,23(3):529-537. DOI:10.1111/jch.14155. |
| [25] | WANG Y, YANG W, JIANG X. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and hypertension:a meta-analysis[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med,2021,8:644035. |
| [26] | SIMONENKO V B, GORIUTSKII V N, DULIN P A. The role of insulin resistance in pathogenesis of arterial hypertension[J]. Klin Med(Mosk),2014,92(9):27-33. |
| [27] | NAKAGOMI A, SUNAMI Y, KAWASAKI Y,et al. Sex difference in the association between surrogate markers of insulin resistance and arterial stiffness[J]. J Diabetes Complications,2020,34(6):107442. DOI:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.107442. |
| [28] | COLANGELO L A, VU T H, SZKLO M,et al. Is the association of hypertension with cardiovascular events stronger among the lean and normal weight than among the overweight and obese? The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis[J]. Hypertension,2015,66(2):286-293. DOI:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04863. |
| [1] | WU Wenjun, WEI Jingjing, LI Xue, REN Hongjie, YU Rui, PENG Guangcao, ZHU Mingjun. Regularity of Prescriptions for Coronary Heart Disease with Hypertension Based on Latent Structure and Association Rules [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3787-3795. |
| [2] | BAI Jiaxin, CHEN Yu, ZHOU Yiheng, LIU Lidi, YANG Rong, YAO Yi, YUAN Bo, ZHANG Yonggang, LEI Yi, ZENG Rui, JIA Yu, LIAO Xiaoyang. Assessment and Treatment of Early-onset Hypertension: Position Statement of the British and Irish Hypertension Association and Its Implications for Clinical Management of Early-onset Hypertension in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3741-3746. |
| [3] | QIN Bangguo, SUN Jin, LI Man, QIU Jiaojiao, CHENG Bokai, ZHU Ping, WANG Shuxia. Relationship between Non-high-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in a Community-based Hypertensive Population [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3753-3760. |
| [4] | HAN Xiao, LI Qiyu, GE Pu, FAN Siyuan, LIU Diyue, WU Yibo, ZHANG Qingshuang. The Impact of Behavioral Lifestyle on Quality of Life in Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [5] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [6] | TANG Shangfeng, HUANG Yangzhen, PAN Yangyang, ZHENG Yanxi, XIONG Zhongbao, ZHANG Kangkang, SONG Jia, WEI Yilin, WANG Chunying, DONG Heng, CHEN Manwei, QING Hua. Specification for the Integration of Healthcare and Prevention Services in Hypertension at the Primary Level [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3089-3095. |
| [7] | WEI Yunhong, YANG Li, WANG Yulu, YE Qiufang, DAI Anni, HE Yan. Study on Cardiopulmonary Function During Different Exercise Stages in Patients with Obesity-related Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2972-2978. |
| [8] | HE Jinyu, ZHULIDUZI Jiesisibieke, ZHANG Ning, LIU Min, LIANG Wannian. Research on Blood Pressure Control and Its Determinants Among Hypertensive Patients Under Standardized Management in China: Status, Challenges, and Future Directions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2968-2971. |
| [9] | LIU Yueying, WANG Xueli, LIU Yuqiu, WEI Limin. Correlation of Fasting C-peptide to Diabetes Duration Ration and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Metabolism-related Fatty Liver Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2852-2860. |
| [10] | CHEN Youlan, LAN Yanqi, WU Ahua, ZHANG Haixia, HUANG Jiankang, GUO Zhinan. The Health Management Effect of Contracted Family Doctor Services under the Joint Management of Three Teachers in Xiamen City on Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2769-2775. |
| [11] | LIU Meixia, YIN Jinnian, WU Mei, YANG Xing, ZHOU Quanxiang, YANG Jingyuan. Impact of Body Mass Index on the Association of Triglyceride Glucose Index with Cognitive Function: a Cross-sectional Study in Rural Older Adults in Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| [12] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Ziying, JIN Aiqiong, TANG Lingling, ZHENG Zique, MA Jingtai, ZHAO Jianguo, ZENG Weilin, XIAO Jianpeng, NIE Hui, YANG Ying. Analysis of Factors Influencing Avoidable Hospitalization for Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [13] | WANG Zhijun, ZHANG Shibo, LIU Jie, LI Dongqi, ZHENG Meijia, ZHOU Jianzhi. Correlation Analysis between TyG-BMI Index and Nocturnal Hypertension in Patients with Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2212-2221. |
| [14] | ZHANG Zhidong, JIN Hua, HU Jihong, JIANG Lu, WANG Li, LONG Kaichong, ZHANG Ronghua. Analysis and Prediction of the Incidence and Mortality Trends of Hypertensive Nephropathy in China from 1990 to 2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2262-2269. |
| [15] | HE Yan, CUI Saixian, HU Yang, NI Qing, GAN Lulu, LIU Qian, DAI Anni, LIU Shijie, YANG Li. Influencing Factors on Urinary Sodium Excretion in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Associated Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2222-2227. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||