

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (04): 461-466.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.346
Special Issue: 高血压最新文章合集
• Original Research·Population Health • Previous Articles Next Articles
Longitudinal Cohort Study of the Association of Triglyceride-glucose Index with Hypertension among Teachers from a University
1.School of Nursing,Anhui Medical University,Hefei 230032,China
2.Department of Internal Medicine,Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
*Corresponding author:LIU Annuo,Professor,Master supervisor;E-mail:w971002y@sohu.com
Received:2021-05-11
Revised:2021-12-20
Published:2022-02-05
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
刘安诺
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Yuanjing, LIU Annuo.
Longitudinal Cohort Study of the Association of Triglyceride-glucose Index with Hypertension among Teachers from a University [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(04): 461-466.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.346
| TyG指数水平 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(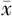 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | BMI〔n(%)〕 | SBP (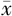 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP (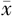 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <18.5 kg/m2 | 18.5~<24 .0 kg/m2 | 24.0~<28.0 kg/m2 | ≥28.0 kg/m2 | |||||
| Q1 | 149 | 36(24.2) | 113(75.8) | 45.9±11.6 | 9(6.0) | 116(77.9) | 22(14.8) | 2(1.3) | 109±12 | 72±8 |
| Q2 | 150 | 57(38.0) | 93(62.0) | 48.7±13.4 | 7(4.7) | 103(68.7) | 40(26.7) | 0 | 111±12 | 73±8 |
| Q3 | 152 | 80(52.6) | 72(47.4) | 50.4±13.8 | 5(3.3) | 91(59.9) | 46(30.3) | 10(6.6) | 112±10 | 75±7 |
| Q4 | 151 | 97(64.2) | 54(35.8) | 51.4±12.6 | 2(1.3) | 73(48.3) | 65(43.0) | 11(7.3) | 115±10 | 77±7 |
| 检验统计量值 | 55.30a | 5.74b | 53.12a | 7.68b | 13.02b | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
Table 1 Comparison of characteristics of university teachers in quartile groups of triglyceride-glucose index
| TyG指数水平 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(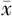 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | BMI〔n(%)〕 | SBP (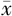 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP (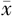 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <18.5 kg/m2 | 18.5~<24 .0 kg/m2 | 24.0~<28.0 kg/m2 | ≥28.0 kg/m2 | |||||
| Q1 | 149 | 36(24.2) | 113(75.8) | 45.9±11.6 | 9(6.0) | 116(77.9) | 22(14.8) | 2(1.3) | 109±12 | 72±8 |
| Q2 | 150 | 57(38.0) | 93(62.0) | 48.7±13.4 | 7(4.7) | 103(68.7) | 40(26.7) | 0 | 111±12 | 73±8 |
| Q3 | 152 | 80(52.6) | 72(47.4) | 50.4±13.8 | 5(3.3) | 91(59.9) | 46(30.3) | 10(6.6) | 112±10 | 75±7 |
| Q4 | 151 | 97(64.2) | 54(35.8) | 51.4±12.6 | 2(1.3) | 73(48.3) | 65(43.0) | 11(7.3) | 115±10 | 77±7 |
| 检验统计量值 | 55.30a | 5.74b | 53.12a | 7.68b | 13.02b | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.453 | 0.224 | 1.572(1.014,2.439) | 4.084 | 0.043 | |
| Q3 | 0.819 | 0.216 | 2.268(1.484,3.466) | 14.313 | <0.001 | |
| Q4 | 1.175 | 0.230 | 3.237(2.063,5.080) | 26.123 | <0.001 | |
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | -0.847 | 0.176 | 0.429(0.304,0.605) | 23.188 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(以实际值纳入) | 0.050 | 0.006 | 1.051(1.038,1.064) | 60.670 | <0.001 | |
| BMI(kg/m2,以18.5~<24.0为参照) | ||||||
| <18.5 | 0.463 | 0.427 | 1.589(0.688,3.671) | 1.177 | 0.278 | |
| 24.0~<28.0 | 0.761 | 0.172 | 2.140(1.529,2.996) | 19.640 | <0.001 | |
| ≥28.0 | 1.573 | 0.266 | 4.820(2.864,8.111) | 35.073 | <0.001 | |
| γ-GGT(U/L,以男≤50,女≤32为参照) | ||||||
| 男>50,女>32 | 0.469 | 0.190 | 1.599(1.103,2.319) | 6.124 | 0.013 | |
| ALT(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.414 | 0.175 | 1.512(1.072,2.133) | 5.563 | 0.018 | |
| AST(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 1.219(0.601,2.471) | 0.302 | 0.583 | |
| TC(mmol/L,以<5.2为参照) | ||||||
| ≥5.2 | 0.326 | 0.153 | 1.386(1.027,1.870) | 4.542 | 0.033 | |
| LDL-C(mmol/L,以<3.4为参照) | ||||||
| ≥3.4 | 0.401 | 0.163 | 1.493(1.086,2.053) | 6.089 | 0.014 | |
| HDL-C(mmol/L,以≥1.0为参照) | ||||||
| <1.0 | 0.428 | 0.197 | 1.534(1.044,2.254) | 4.738 | 0.029 | |
| UA(μmol/L,以男≤420,女≤360为参照) | ||||||
| 男>420,女>360 | 0.731 | 0.196 | 2.076(1.415,3.048) | 13.920 | <0.001 | |
| BUN(mmol/L,以≤7.1为参照) | ||||||
| >7.1 | 0.902 | 0.376 | 2.464(1.179,5.151) | 5.743 | 0.017 | |
Table 2 Univariate analysis of association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension using generalized estimating equation
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.453 | 0.224 | 1.572(1.014,2.439) | 4.084 | 0.043 | |
| Q3 | 0.819 | 0.216 | 2.268(1.484,3.466) | 14.313 | <0.001 | |
| Q4 | 1.175 | 0.230 | 3.237(2.063,5.080) | 26.123 | <0.001 | |
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | -0.847 | 0.176 | 0.429(0.304,0.605) | 23.188 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(以实际值纳入) | 0.050 | 0.006 | 1.051(1.038,1.064) | 60.670 | <0.001 | |
| BMI(kg/m2,以18.5~<24.0为参照) | ||||||
| <18.5 | 0.463 | 0.427 | 1.589(0.688,3.671) | 1.177 | 0.278 | |
| 24.0~<28.0 | 0.761 | 0.172 | 2.140(1.529,2.996) | 19.640 | <0.001 | |
| ≥28.0 | 1.573 | 0.266 | 4.820(2.864,8.111) | 35.073 | <0.001 | |
| γ-GGT(U/L,以男≤50,女≤32为参照) | ||||||
| 男>50,女>32 | 0.469 | 0.190 | 1.599(1.103,2.319) | 6.124 | 0.013 | |
| ALT(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.414 | 0.175 | 1.512(1.072,2.133) | 5.563 | 0.018 | |
| AST(U/L,以≤40为参照) | ||||||
| >40 | 0.198 | 0.361 | 1.219(0.601,2.471) | 0.302 | 0.583 | |
| TC(mmol/L,以<5.2为参照) | ||||||
| ≥5.2 | 0.326 | 0.153 | 1.386(1.027,1.870) | 4.542 | 0.033 | |
| LDL-C(mmol/L,以<3.4为参照) | ||||||
| ≥3.4 | 0.401 | 0.163 | 1.493(1.086,2.053) | 6.089 | 0.014 | |
| HDL-C(mmol/L,以≥1.0为参照) | ||||||
| <1.0 | 0.428 | 0.197 | 1.534(1.044,2.254) | 4.738 | 0.029 | |
| UA(μmol/L,以男≤420,女≤360为参照) | ||||||
| 男>420,女>360 | 0.731 | 0.196 | 2.076(1.415,3.048) | 13.920 | <0.001 | |
| BUN(mmol/L,以≤7.1为参照) | ||||||
| >7.1 | 0.902 | 0.376 | 2.464(1.179,5.151) | 5.743 | 0.017 | |
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.345 | 0.197 | 1.411(0.960,2.075) | 3.07 | 0.080 | |
| Q3 | 0.436 | 0.209 | 1.546(1.026,2.330) | 4.34 | 0.037 | |
| Q4 | 0.627 | 0.223 | 1.872(1.209,2.901) | 7.89 | 0.005 | |
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of the association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension using generalized estimating equation
| 自变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG指数(以Q1为参照) | ||||||
| Q2 | 0.345 | 0.197 | 1.411(0.960,2.075) | 3.07 | 0.080 | |
| Q3 | 0.436 | 0.209 | 1.546(1.026,2.330) | 4.34 | 0.037 | |
| Q4 | 0.627 | 0.223 | 1.872(1.209,2.901) | 7.89 | 0.005 | |
| 变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | P交互值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.034 | |||||||
| 男(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.253 | 0.249 | 1.288(0.790,2.098) | 1.031 | 0.310 | |||
| Q3 | 0.127 | 0.263 | 1.136(0.679,1.901) | 0.235 | 0.628 | |||
| Q4 | 0.854 | 0.299 | 2.349(1.308,4.217) | 8.183 | 0.004 | |||
| 女(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.343 | 0.344 | 1.410(0.719,2.764) | 0.999 | 0.317 | |||
| Q3 | 0.485 | 0.352 | 1.625(0.815,3.238) | 1.904 | 0.168 | |||
| Q4 | 0.759 | 0.342 | 2.135(1.093,4.172) | 4.929 | 0.026 | |||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.047 | |||||||
| 18~44(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.247 | 0.362 | 1.280(0.630,2.600) | 0.467 | 0.494 | |||
| Q3 | -0.031 | 0.528 | 0.970(0.344,2.732) | 0.003 | 0.954 | |||
| Q4 | 0.678 | 0.464 | 1.969(0.794,4.884) | 2.137 | 0.144 | |||
| 45~54(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.412 | 0.481 | 1.510(0.588,3.879) | 0.734 | 0.392 | |||
| Q3 | 1.102 | 0.462 | 3.011(1.217,7.451) | 5.685 | 0.017 | |||
| Q4 | 1.244 | 0.574 | 3.468(1.126,10.678) | 4.697 | 0.030 | |||
| ≥55(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.408 | 0.269 | 1.505(0.889,2.547) | 2.312 | 0.128 | |||
| Q3 | 0.460 | 0.273 | 1.584(0.927,2.706) | 2.837 | 0.092 | |||
| Q4 | 0.383 | 0.309 | 1.466(0.799,2.689) | 1.529 | 0.216 | |||
| BMI | 0.034 | |||||||
| 体质量正常(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.243 | 0.271 | 1.276(0.750,2.168) | 0.809 | 0.368 | |||
| Q3 | 0.636 | 0.280 | 1.888(1.091,3.267) | 5.161 | 0.023 | |||
| Q4 | 0.882 | 0.304 | 2.416(1.331,4.385) | 8.417 | 0.004 | |||
| 超重肥胖(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.560 | 0.313 | 1.751(0.949,3.230) | 3.209 | 0.073 | |||
| Q3 | 0.335 | 0.328 | 1.398(0.736,2.658) | 1.047 | 0.306 | |||
| Q4 | 0.546 | 0.331 | 1.726(0.902,3.302) | 2.719 | 0.099 | |||
Table 4 Multivariate analysis of the association of triglyceride-glucose index with hypertension by sex,age,and BMI using generalized estimating equation
| 变量 | b | SE | OR(95%CI) | Wald χ2值 | P值 | P交互值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.034 | |||||||
| 男(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.253 | 0.249 | 1.288(0.790,2.098) | 1.031 | 0.310 | |||
| Q3 | 0.127 | 0.263 | 1.136(0.679,1.901) | 0.235 | 0.628 | |||
| Q4 | 0.854 | 0.299 | 2.349(1.308,4.217) | 8.183 | 0.004 | |||
| 女(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.343 | 0.344 | 1.410(0.719,2.764) | 0.999 | 0.317 | |||
| Q3 | 0.485 | 0.352 | 1.625(0.815,3.238) | 1.904 | 0.168 | |||
| Q4 | 0.759 | 0.342 | 2.135(1.093,4.172) | 4.929 | 0.026 | |||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.047 | |||||||
| 18~44(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.247 | 0.362 | 1.280(0.630,2.600) | 0.467 | 0.494 | |||
| Q3 | -0.031 | 0.528 | 0.970(0.344,2.732) | 0.003 | 0.954 | |||
| Q4 | 0.678 | 0.464 | 1.969(0.794,4.884) | 2.137 | 0.144 | |||
| 45~54(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.412 | 0.481 | 1.510(0.588,3.879) | 0.734 | 0.392 | |||
| Q3 | 1.102 | 0.462 | 3.011(1.217,7.451) | 5.685 | 0.017 | |||
| Q4 | 1.244 | 0.574 | 3.468(1.126,10.678) | 4.697 | 0.030 | |||
| ≥55(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.408 | 0.269 | 1.505(0.889,2.547) | 2.312 | 0.128 | |||
| Q3 | 0.460 | 0.273 | 1.584(0.927,2.706) | 2.837 | 0.092 | |||
| Q4 | 0.383 | 0.309 | 1.466(0.799,2.689) | 1.529 | 0.216 | |||
| BMI | 0.034 | |||||||
| 体质量正常(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.243 | 0.271 | 1.276(0.750,2.168) | 0.809 | 0.368 | |||
| Q3 | 0.636 | 0.280 | 1.888(1.091,3.267) | 5.161 | 0.023 | |||
| Q4 | 0.882 | 0.304 | 2.416(1.331,4.385) | 8.417 | 0.004 | |||
| 超重肥胖(以TyG指数Q1为参照) | ||||||||
| Q2 | 0.560 | 0.313 | 1.751(0.949,3.230) | 3.209 | 0.073 | |||
| Q3 | 0.335 | 0.328 | 1.398(0.736,2.658) | 1.047 | 0.306 | |||
| Q4 | 0.546 | 0.331 | 1.726(0.902,3.302) | 2.719 | 0.099 | |||
| [1] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5301.2019.03.001. |
| [2] | MILLS K T, BUNDY J D, KELLY T N,et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control:a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries[J]. Circulation,2016,134(6):441-450. |
| [3] | 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2019概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2020,35(9):833-854. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2020.09.001. |
| [4] | 辛青,张成秋,谭小燕,等. 高校教职工高血压患病情况及影响因素[J]. 中国卫生统计,2013,30(6):874-876,878. |
| [5] | WANG F, HAN L, HU D. Fasting insulin,insulin resistance and risk of hypertension in the general population:a meta-analysis[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2017,464:57-63. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2016.11.009. |
| [6] | GUERRERO-ROMERO F, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA L E, GONZÁLEZ-ORTIZ M,et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose,a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2010,95(7):3347-3351. DOI:10.1210/jc.2010-0288. |
| [7] | SÁNCHEZ-ÍÑIGO L, NAVARRO-GONZÁLEZ D, PASTRANA-DELGADO J,et al. Association of triglycerides and new lipid markers with the incidence of hypertension in a Spanish cohort[J]. J Hypertens,2016,34(7):1257-1265. |
| [8] | ZHENG R, MAO Y. Triglyceride and glucose(TyG) index as a predictor of incident hypertension:a 9-year longitudinal population-based study[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2017,16(1):175. |
| [9] | WANG K, HE G, ZHANG Y,et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index and its interaction with obesity on hypertension risk in Chinese:a population-based study[J]. J Hum Hypertens,2020,35(3):232-239. DOI:10.1038/s41371-020-0326-4. |
| [10] | ZHU B, WANG J, CHEN K,et al. A high triglyceride glucose index is more closely associated with hypertension than lipid or glycemic parameters in elderly individuals:a cross-sectional survey from the Reaction Study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2020,19(1):112. DOI:10.1186/s12933-020-01077-6. |
| [11] | ZENG Z Y, LIU S X, XU H,et al. Association of triglyceride glucose index and its combination of obesity indices with prehypertension in lean individuals:a cross-sectional study of Chinese adults[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2020,22(6):1025-1032. DOI:10.1111/jch.13878. |
| [12] | LIU X Z, FAN J, PAN S J. METS-IR,a novel simple insulin resistance indexes,is associated with hypertension in normal-weight Chinese adults[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2019,21(8):1075-1081. DOI:10.1111/jch.13591. |
| [13] | MORALES-GURROLA G, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA L E, CASTELLANOS-JUÁREZ F X,et al. The triglycerides and glucose index is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in metabolically obese normal-weight subjects[J]. J Endocrinol Invest,2020,43(7):995-1000. DOI:10.1007/s40618-020-01184-x. |
| [14] | BARZEGAR N, TOHIDI M, HASHEMINIA M,et al. The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on incident cardiovascular events during 16 years of follow-up:tehran lipid and glucose study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2020,19(1):155. |
| [15] | LEE S H, HAN K, YANG H K,et al. A novel criterion for identifying metabolically obese but normal weight individuals using the product of triglycerides and glucose[J]. Nutr Diabetes,2015,5(4):e149. DOI:10.1038/nutd.2014.46. |
| [16] | 汤宁,宋秋月,易东,等. 医学纵向数据建模方法及其统计分析策略[J]. 中国卫生统计,2019,36(3):441-444,447. |
| [17] | RAHMAN S, ISLAM S, HAQUE T,et al. Association between serum liver enzymes and hypertension:a cross-sectional study in Bangladeshi adults[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord,2020,20(1):128. DOI:10.1186/s12872-020-01411-6. |
| [18] | YU Z, CORESH J, QI G,et al. A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study supports causal effects of kidney function on blood pressure[J]. Kidney Int,2020,98(3):708-716. |
| [19] | 中国肥胖问题工作组. 中国成人超重和肥胖症预防与控制指南(节录)[J]. 营养学报,2004,26(1):1-4. |
| [20] | 诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001. |
| [21] | 高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科共识专家组. 中国高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(3):235-248. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.03.021. |
| [22] | 万学红,卢雪峰. 诊断学[M]. 9版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2018:343-364. |
| [23] | RIECHMANN-WOLF M, JANKOWIAK S, SCHULZ A,et al. Self-reported cardiovascular health of teachers:results from the 5-year follow-up of the Gutenberg health study cohort[J]. Int Arch Occup Environ Health,2021,94(2):251-259. |
| [24] | MINH H V, TIEN H A, SINH C T,et al. Assessment of preferred methods to measure insulin resistance in Asian patients with hypertension[J]. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich),2021,23(3):529-537. DOI:10.1111/jch.14155. |
| [25] | WANG Y, YANG W, JIANG X. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and hypertension:a meta-analysis[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med,2021,8:644035. |
| [26] | SIMONENKO V B, GORIUTSKII V N, DULIN P A. The role of insulin resistance in pathogenesis of arterial hypertension[J]. Klin Med(Mosk),2014,92(9):27-33. |
| [27] | NAKAGOMI A, SUNAMI Y, KAWASAKI Y,et al. Sex difference in the association between surrogate markers of insulin resistance and arterial stiffness[J]. J Diabetes Complications,2020,34(6):107442. DOI:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.107442. |
| [28] | COLANGELO L A, VU T H, SZKLO M,et al. Is the association of hypertension with cardiovascular events stronger among the lean and normal weight than among the overweight and obese? The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis[J]. Hypertension,2015,66(2):286-293. DOI:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04863. |
| [1] | ZHANG Shuai, LI Qin, LI Dongfeng, XIAO Jinping, LI Yunpeng. A Prospective Cohort Study of Solid Fuels Use and Risk of Hypertension in Chinese Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4001-4006. |
| [2] | CHEN Xi, ZHANG Juan, LI Lin, ZHANG Jiaqi, WU Yaoli, GUO Hui, WANG Chaoqun. Association between Physical Activity and Risk of All-cause Mortality in Middle-aged and Elderly People in China: a Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3890-3895. |
| [3] | ZHANG Peng, GAO Ying, YANG Hongxi, WAN Chunxiao. Association between Serum Uric Acid Level and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease among the Elderly in Longevity Areas of China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3884-3889. |
| [4] | HE Yingmei, JIA Xue, ZHU Guojun, LIU Bing. Effect of Serum Uric Acid Longitudinal Trajectory on New-onset Hypertriglyceridemia: a Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3636-3639. |
| [5] | XIAO Liqi, YANG Li, CUI Saixian, ZHANG Yayuan, WANG Yulu, HE Yan. Advances in the Association of High Salt-induced Gut Microbiota Disturbances with Salt-sensitive Blood Pressure [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3704-3709. |
| [6] | CHENG Xiaoran, ZHANG Xiaotian, LI Mingyue, CHENG Haozhe, TANG Haoqing, ZHENG Huixian, ZHANG Baisong, LIU Xiaoyun. Impact of Chronic Diseases Follow-up on Health Behaviors and Blood Pressure/Glucose Control of Patients with Hypertension and Diabetes in the Context of Treatment-prevention Integration [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(28): 3482-3488. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yunsheng, ZHANG Peng, JIN Yujing, GAO Ying. Association of Blood Pressure Level with the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease among the Elderly in Longevity Areas of China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(28): 3502-3506. |
| [8] | BIAN Lili, LI Xiaoxiao, DU Xueping, DAI Qinfang, WU Lin, SONG Beibei. Risk Stratification of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Lipid Goal Attainment in Hypertensive Patients Registered in Community [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(27): 3388-3391. |
| [9] | ZHAO Wei, TANG Rongjie, YANG Shanshan, YANG Fang, SUN Feng, LIAN Qiufang. The Role and Molecules Mechanism of Klotho in Renal Injury in Salt-sensitive Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(24): 3042-3049. |
| [10] | ZUO Xu, HUANG Zhaolan, LU Biao. Differences between the First and Another 3-day Blood Pressure Levels and Associated Factors in a Self-reported Non-hypertensive Population Aged 35-64 Years [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(22): 2771-2777. |
| [11] | FENG Jia, WANG Jie, YU Dan, LIU Yongheng, ZHAO Weidong, TIAN Hongyuan. Analysis of Research Hotspots of Multiple Chronic Conditions in the Elderly in 2010-2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(21): 2574-2580. |
| [12] | YU Tong, YANG Yi, DU Shihong, DING Zihao, HONG Xiuqin. Correlation of Shearing Force and Estradiol with Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(20): 2469-2475,2495. |
| [13] | FEI Min, LEI Si, XU Yan, YE Yun, ZHUO Hui, ZHANG Hui, LUO Yingquan. Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea-hypopnea Syndrome with Blood Pressure Variability and Heart Rate Variability in Patients with Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(20): 2459-2468. |
| [14] | TIAN Meixiang, ZHANG Zhengyi. Standard Management of Hypertension During the Preparation for Pregnancy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(18): 2190-2194. |
| [15] | LIU Hai, HUANG Guanhua. The Significance of High Normal Blood Pressure for Children and Adolescents [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(18): 2183-2189. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||