

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (09): 1123-1129.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.079
Special Issue: 神经系统疾病最新文章合辑; 精神卫生最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
• Article·Brain Health • Previous Articles Next Articles
Brain White Matter Fiber Bundle Alterations and Severity of Depression in Patients with Post-stroke Depression
1.Department of Neurology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2.Nursing School,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
*Corresponding author:SUI Rubo,Professor,Chief physician;E-mail:srb7246@163.com
Received:2021-08-16
Revised:2021-11-29
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2022-03-01
通讯作者:
隋汝波
基金资助:CLC Number:
QI Jie, ZHANG Lei, DENG Lijun, DUAN Xiaodi, DONG Binbin, SUI Rubo.
Brain White Matter Fiber Bundle Alterations and Severity of Depression in Patients with Post-stroke Depression [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(09): 1123-1129.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.079
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(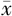 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 受教育年限(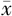 ±s,年) ±s,年) | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | LDL(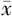 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | HDL(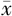 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 血糖(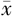 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | NIHSS评分(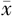 ±s,分) ±s,分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 10/10 | 53.8±8.4 | 9.3±3.2 | 10(50.0) | 3.06±1.12 | 1.13±0.34 | 7.4±1.7 | - |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 10/10 | 55.1±8.8 | 8.8±3.2 | 10(50.0) | 3.11±1.01 | 1.28±0.32 | 7.4±1.8 | 6.8±3.0 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 10/10 | 54.6±7.5 | 9.1±3.2 | 9(45.0) | 3.03±1.06 | 1.20±0.24 | 7.4±2.1 | 6.9±4.3 |
| 检验统计量值 | 0a | 0.182 | 0.130 | 0.133 | 0.033 | 1.138 | 0.012 | 0.016b | |
| P值 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
Table 1 Comparison of general information among first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with and without post-stroke depression,and healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(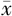 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 受教育年限(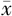 ±s,年) ±s,年) | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | LDL(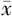 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | HDL(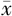 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 血糖(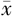 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | NIHSS评分(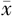 ±s,分) ±s,分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 10/10 | 53.8±8.4 | 9.3±3.2 | 10(50.0) | 3.06±1.12 | 1.13±0.34 | 7.4±1.7 | - |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 10/10 | 55.1±8.8 | 8.8±3.2 | 10(50.0) | 3.11±1.01 | 1.28±0.32 | 7.4±1.8 | 6.8±3.0 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 10/10 | 54.6±7.5 | 9.1±3.2 | 9(45.0) | 3.03±1.06 | 1.20±0.24 | 7.4±2.1 | 6.9±4.3 |
| 检验统计量值 | 0a | 0.182 | 0.130 | 0.133 | 0.033 | 1.138 | 0.012 | 0.016b | |
| P值 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
| 组别 | 例数 | SDS标准分 | HAMD-24评分 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 26.80±7.47a | 2.45±1.50a |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 29.20±10.74a | 2.60±1.39a |
| PSD组 | 20 | 57.85±5.04 | 17.65±4.37 |
| F值 | 92.085 | 194.912 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Table 2 Comparison of standard score of SDS and HAMD-24 score among first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with and without post-stroke depression,and healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | SDS标准分 | HAMD-24评分 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 26.80±7.47a | 2.45±1.50a |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 29.20±10.74a | 2.60±1.39a |
| PSD组 | 20 | 57.85±5.04 | 17.65±4.37 |
| F值 | 92.085 | 194.912 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 下额枕束 | 皮质脊髓束 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 0.574±0.059a | 0.583±0.067 | 1.156 | 0.26 | 0.575±0.049a | 0.573±0.052 | 0.322 | 0.75 |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 0.575±0.047a | 0.578±0.049 | 0.993 | 0.33 | 0.565±0.033a | 0.571±0.039 | 1.602 | 0.13 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 0.475±0.055 | 0.572±0.071 | -8.622 | <0.01 | 0.459±0.038 | 0.576±0.077 | -6.153 | <0.01 |
| F(χ2)值 | 22.868 | 0.165 | 50.404 | 0.035 | |||||
| P值 | <0.01 | 0.85 | <0.01 | 0.97 | |||||
Table 3 Comparison of fractional anisotropy in regions of interest among first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with and without post-stroke depression,and healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 下额枕束 | 皮质脊髓束 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 0.574±0.059a | 0.583±0.067 | 1.156 | 0.26 | 0.575±0.049a | 0.573±0.052 | 0.322 | 0.75 |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 0.575±0.047a | 0.578±0.049 | 0.993 | 0.33 | 0.565±0.033a | 0.571±0.039 | 1.602 | 0.13 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 0.475±0.055 | 0.572±0.071 | -8.622 | <0.01 | 0.459±0.038 | 0.576±0.077 | -6.153 | <0.01 |
| F(χ2)值 | 22.868 | 0.165 | 50.404 | 0.035 | |||||
| P值 | <0.01 | 0.85 | <0.01 | 0.97 | |||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 下额枕束 | 皮质脊髓束 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 1 235.90±207.09a | 1 246.95±213.17 | 1.381 | 0.18 | 1 348.85±152.50a | 1 376.65±108.78 | 1.391 | 0.18 |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 1 162.00±217.06a | 1 173.25±219.02 | 1.093 | 0.29 | 1 347.15±218.66a | 1 357.15±215.53 | 1.900 | 0.07 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 888.75±144.07 | 1 297.40±157.94 | 10.812 | <0.01 | 946.15±210.66 | 1 379.65±152.42 | 8.270 | <0.01 |
| F(χ2)值 | 18.115 | 1.976 | 27.976 | 0.110 | |||||
| P值 | <0.01 | 0.15 | <0.01 | 0.90 | |||||
Table 4 Comparison of number of fiber bundles in regions of interest among first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with and without post-stroke depression,and healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 下额枕束 | 皮质脊髓束 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | 病灶侧 | 病灶对侧 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 正常对照组 | 20 | 1 235.90±207.09a | 1 246.95±213.17 | 1.381 | 0.18 | 1 348.85±152.50a | 1 376.65±108.78 | 1.391 | 0.18 |
| 非PSD组 | 20 | 1 162.00±217.06a | 1 173.25±219.02 | 1.093 | 0.29 | 1 347.15±218.66a | 1 357.15±215.53 | 1.900 | 0.07 |
| PSD组 | 20 | 888.75±144.07 | 1 297.40±157.94 | 10.812 | <0.01 | 946.15±210.66 | 1 379.65±152.42 | 8.270 | <0.01 |
| F(χ2)值 | 18.115 | 1.976 | 27.976 | 0.110 | |||||
| P值 | <0.01 | 0.15 | <0.01 | 0.90 | |||||
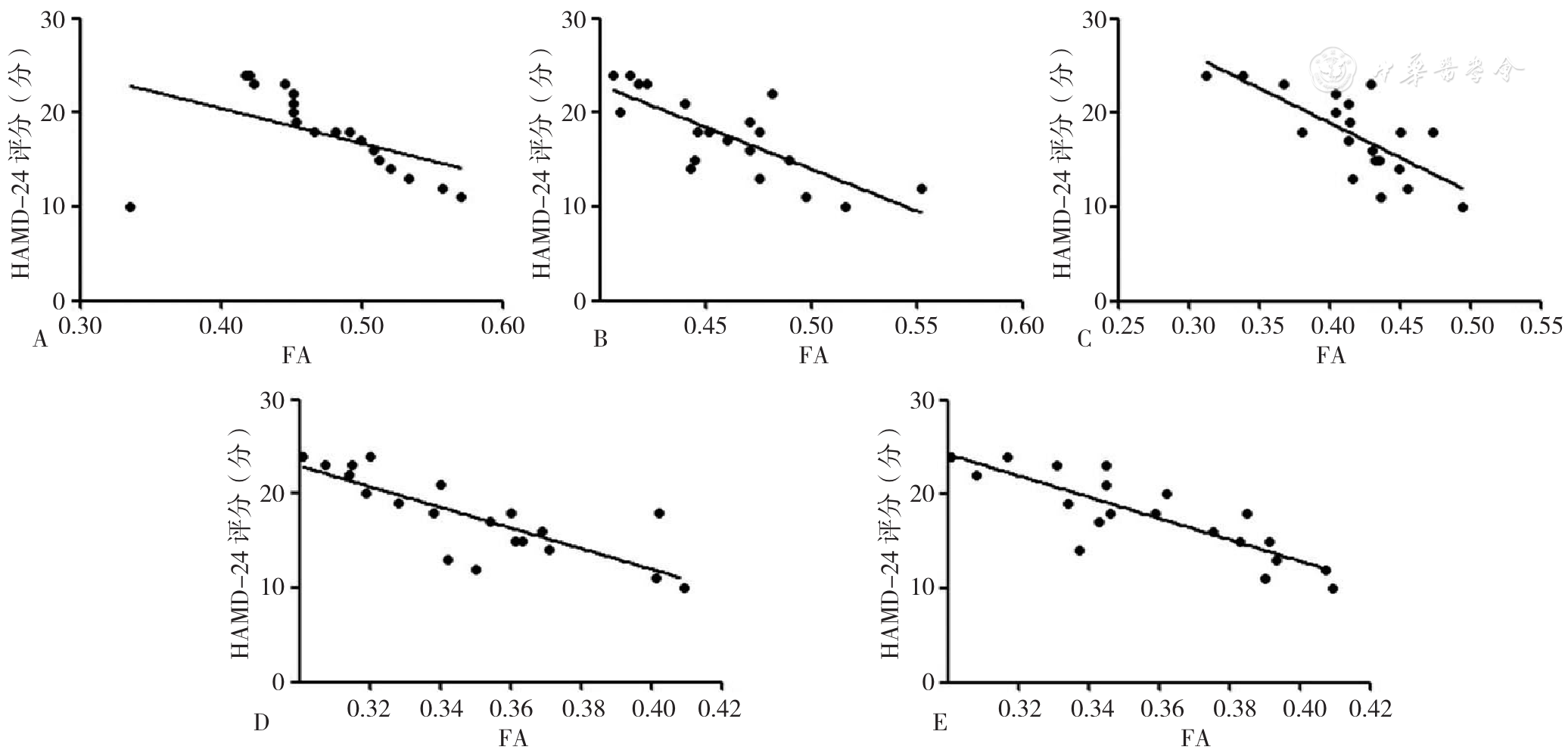
Figure 1 Correlation of fiber bundles on the side of stroke with HAMD-24 score in first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with post-stroke depression
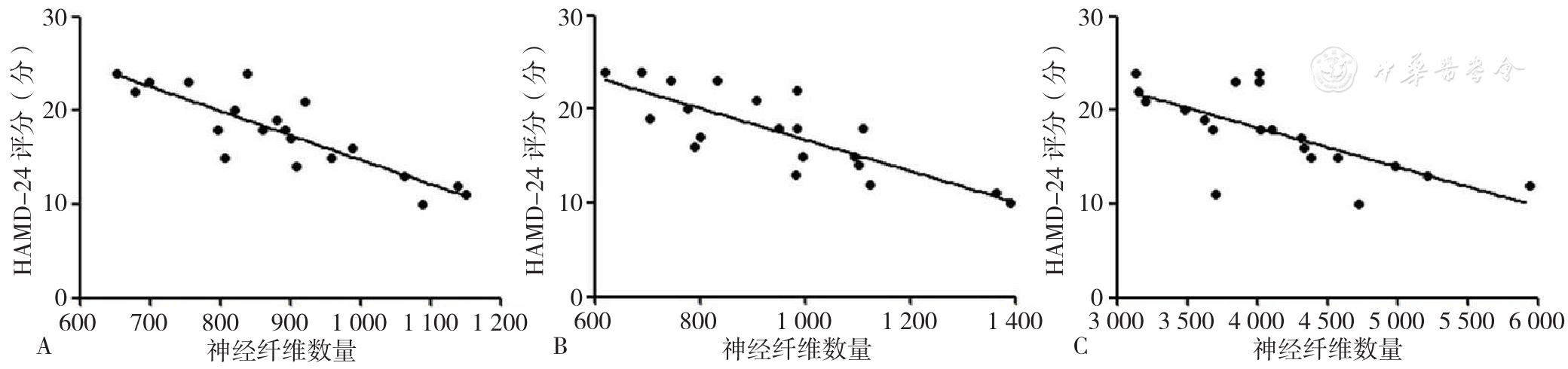
Figure 2 Correlation between number of fiber bundles on the side of stroke and HAMD-24 score in first-episode ischemic stroke inpatients with post-stroke depression
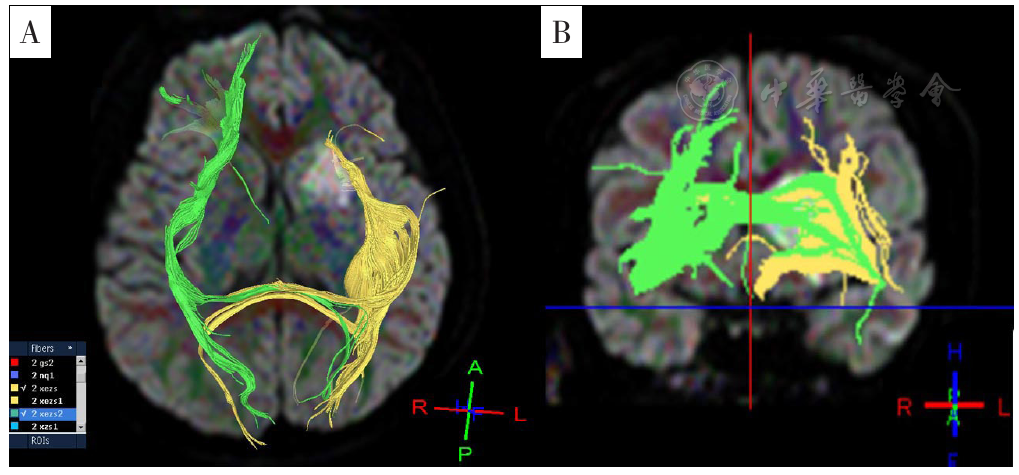
Figure 3 Diffusion tensor tractography imaging of inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus of a first-episode ischemic stroke inpatient with post-stroke depression
| [1] | MIR H,SIEMIENIUK R A C,GE L,et al. Patent foramen ovale closure,antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation in patients with patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke:a systematic review and network meta-analysis incorporating complementary external evidence[J]. BMJ Open,2018,8(7):e023761. DOI:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023761. |
| [2] | VOLZ M,LADWIG S,WERHEID K. Gender differences in post-stroke depression:a longitudinal analysis of prevalence,persistence and predictive value of known risk factors[J]. Neuropsychol Rehabil,2021,31(1):1-17. DOI:10.1080/09602011.2019.1648301. |
| [3] | SHI Y Z,XIANG Y T,YANG Y,et al. Depression after minor stroke:prevalence and predictors[J]. J Psychosom Res,2015,79(2):143-147. DOI:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2015.03.012. |
| [5] | KIM J S. Post-stroke mood and emotional disturbances:pharmacological therapy based on mechanisms[J]. J Stroke,2016,18(3):244-255. DOI:10.5853/jos.2016.01144. |
| [6] | 许孝南,吴军,陈旭辉,等. 卒中后抑郁的扩散张量成像研究进展[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2015,12(6):321-324. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2015.06.010. |
| [7] | NIIDA R,YAMAGATA B,NIIDA A,et al. Aberrant anterior thalamic radiation structure in bipolar disorder:a diffusion tensor tractography study[J]. Front Psychiatry,2018,9:522. DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00522. |
| [8] | JANG S H,KWON H G. Relationship between depression and dorsolateral prefronto-thalamic tract injury in patients with mild traumatic brain injury[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):19728. DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-76889-3. |
| [9] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2014[J].中华神经科杂志,2015,48(4):246-257. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2015.04.002. |
| [10] | 中华医学会精神科分会. CCMD-3中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准[M]. 3版. 济南:山东科学技术出版社,2001. |
| [11] | GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global,regional,and national life expectancy,all-cause mortality,and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death,1980—2015:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015[J]. Lancet,2016,388(10053):1459-1544. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. |
| [12] | LI L J,YAO X M,GUAN B Y,et al. Persistent depression is a predictor of quality of life in stroke survivors:results from a 5-year follow-up study of a Chinese cohort[J]. Chin Med J(Engl),2019,132(18):2206-2212. DOI:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000400. |
| [13] | WANG C X,LUO B Y,WU J,et al. Diagnosis and treatment of post-stroke depression in China:a cross-sectional survey of 350 senior clinicians in neurology,geriatrics,and rehabilitation departments[J]. Int Psychogeriatr,2020,32(1):151-153. DOI:10.1017/S1041610218001254. |
| [14] | SHI Y,YANG D,ZENG Y,et al. Risk factors for post-stroke depression:a Meta-analysis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci,2017,9:218. |
| [15] | 李晶雪,王天俊. 卒中后抑郁发病机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃,2019,34(6):572-576. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2019.06.018. |
| [16] | POLETTI S,AGGIO V,BRIOSCHI S,et al. Impact of early and recent stress on white matter microstructure in major depressive disorder[J]. J Affect Disord,2017,225:289-297. DOI:10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.017. |
| [17] | SHEN X Y,FAN Z X,WANG L,et al. Altered white matter microstructure in patients with post-stroke depression detected by diffusion kurtosis imaging[J]. Neurol Sci,2019,40(10):2097-2103. DOI:10.1007/s10072-019-03947-8. |
| [18] | 苑杰,姜伟时,刘颖,等. 卒中后抑郁与病灶分布关系的研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊),2019,19(80):103-104. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.80.047. |
| [19] | FERRIS J K,EDWARDS J D,MA J A,et al. Changes to white matter microstructure in transient ischemic attack:a longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging study[J]. Hum Brain Mapp,2017,38(11):5795-5803. DOI:10.1002/hbm.23768. |
| [20] | QIN L,GUO Z,MCCLURE M A,et al. White matter changes from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease:a meta-analysis[J]. Acta Neurol Belg,2021,121(6):1435-1447. DOI:10.1007/s13760-020-01322-5. |
| [21] | SHELINE Y I,PRICE J L,VAISHNAVI S N,et al. Regional white matter hyperintensity burden in automated segmentation distinguishes late-life depressed subjects from comparison subjects matched for vascular risk factors[J]. Am J Psychiatry,2008,165(4):524-532. DOI:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07010175. |
| [22] | GOZDAS E,FINGERHUT H,CHROMIK L C,et al. Focal white matter disruptions along the cingulum tract explain cognitive decline in amnestic mild cognitive impairment(aMCI)[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):10213. DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-66796-y. |
| [23] | SANTOS J P L,BRENT D,BERTOCCI M,et al. White matter correlates of suicidality in adults with bipolar disorder who have been prospectively characterized since childhood[J]. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging,2021,6(1):107-116. DOI:10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.07.007. |
| [24] | JUNG S,KIM J H,SUNG G,et al. Uncinate fasciculus white matter connectivity related to impaired social perception and cross-sectional and longitudinal symptoms in patients with schizophrenia spectrum psychosis[J]. Neurosci Lett,2020,737:135144. DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135144. |
| [25] | OESTREICH L K L,WRIGHT P,O'SULLIVAN M J. Microstructural changes in the reward system are associated with post-stroke depression[J]. Neuroimage Clin,2020,28:102360. DOI:10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102360. |
| [26] | DRESANG H C,HULA W D,YEH F C,et al. White matter neuroanatomical predictors of aphasic verb retrieval[J]. Brain Connect,2021,11(4):319-330. DOI:10.1089/brain.2020.0921. |
| [27] | KAKEDA S,WATANABE K,KATSUKI A,et al. Genetic effects on white matter integrity in drug-naive patients with major depressive disorder:a diffusion tensor imaging study of 17 genetic loci associated with depressive symptoms[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat,2019,15:375-383. DOI:10.2147/NDT.S190268. |
| [28] | 单苏民,王雁,宫本强. 以高级智能减退为首发症状的基底节区梗死1例报告[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2002,19(2):126. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-2754.2002.02.029. |
| [1] | GU Xiaolin, CHEN Junyu, CHEN Dan, HAN Guangli, CHEN Yidi, LI Chunhong, LUO Xiaoxi. Emotional Experience of Pregnant Women in Rural China: a Qualitative Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3283-3288. |
| [2] | YANG Ji, ZHANG Yao, ZHAO Yingqiang, ZHANG Qiuyue. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of TCM Three-level Prevention and Control Model in the Management of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke: a Single-center, Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2750-2761. |
| [3] | WEI Xiaoxia, CHEN Nuo, WANG Juanjuan, ZHU Jingfen. The Effects of Depression and Anxiety on Smoking Behavior among Vocational School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2826-2832. |
| [4] | LI Xinyue, WU Minmin, ZHU Luwen. Exploration of the Association and Mechanism between Abnormal Lipid Metabolism and Depressive Development [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2562-2569. |
| [5] | TAN Yi, ZHU Lihong, YIN Zengwei, HOU Shunan, YU Houming. A Real-world Study of MRI-guided Intravenous Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2508-2515. |
| [6] | FU Rong, SHI Lei, HE Feiying. Comorbidity of Diabetes and Depression in Middle-aged and Elderly People: the Impact of Sleep, Exercise, and Social Activities [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2491-2500. |
| [7] | CHU Tianyu, GU Yan. Carotid Artery Calcification Features in Plaque Stability and Clinical Events [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2247-2252. |
| [8] | TAN Wenbin, LI Jia, LIU Mingyu, LU Yongxin, CHENG Yaxin. Research Progress on the Influence of Nervous System Diseases and Related Therapeutic Drugs on Osteoporosis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2092-2100. |
| [9] | FAN Yu, LI Rong, GONG Shuangying, YANG Xiaojuan, LI Rui. Meta-analysis of the Incidence of Postpartum Depression among Maternal Spouses in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2179-2185. |
| [10] | XIA Yuwen, SHI Huifeng, LI Mengshi, ZHANG Jingxu, WANG Xiaoli. Analysis of the Influencing Factors for Depression of Female Caregivers of Left-behind Children in Rural Area in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1717-1722. |
| [11] | WU Dadong, LIU Huimin, ZHANG Jiayi, LIU Siyuan, ZHAO Guanglin, JIN Shuyan, JIANG Lei. Application and Evaluation of the Mobile Platform for Perinatal Depression Screening and Intervention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1773-1780. |
| [12] | LI Mei, JIANG Dongsheng, ZHAO Jingjing, CAO Yajing, ZHANG Fan, TANG Lijuan, LIU Xiaoli. Correlation Analysis of Homocysteine and Stroke in People over 40 Years Old [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1723-1729. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ying, JIANG Xintong, WANG Pingyu. The Influencing Factors of Depression Symptoms in the Chinese Female Elderly Population Based on Health Ecology Models [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(13): 1595-1600. |
| [14] | ZHAO Lili, LIU Lewei, GENG Feng, MO Daming, LIU Huanzhong. The Relationship between Suicidal Ideation and Childhood Trauma in Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: the Dual Mediating Effects of Depressive Symptom Severity and Low Vitamin D Levels [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(13): 1614-1621. |
| [15] | WEI Xuan, WANG Ning, WEI Ying, CHEN Qilin, ZHAO Yang. Analysis of Depression Status and Influencing Factors in Middle-aged and Elderly Patients with Chronic Diseases in China: an Empirical Analysis Based on CHARLS Data [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(11): 1303-1308. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||