

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (05): 584-588.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.115
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical Featuresof IgG4-related Disease
Department of Gastroenterology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450052,China
*Corresponding author:ZHOU Lin,Chief physician,Professor;E-mail:ZL372@126.com
Received:2021-09-10
Revised:2021-12-15
Published:2022-02-15
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
周琳
基金资助:CLC Number:
DING Hang, LIU Yuan, ZHANG Lianfeng, ZHOU Lin.
Clinical Featuresof IgG4-related Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(05): 584-588.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.115
| 受累器官 | 总体(n=106) | 男(n=69) | 女(n=37) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淋巴结 | 71(67.0) | 48(69.6) | 23(62.2) | 0.597 | 0.440 |
| 涎腺 | 40(37.7) | 21(30.4) | 19(51.4) | 4.485 | 0.034 |
| 胰腺 | 38(35.8) | 34(49.3) | 4(10.8) | 15.495 | <0.001 |
| 肺部 | 37(34.9) | 25(36.2) | 12(32.4) | 0.153 | 0.696 |
| 泪腺 | 34(32.1) | 17(24.6) | 17(45.9) | 5.019 | 0.025 |
| 胆管 | 14(13.2) | 12(17.4) | 2(5.4) | 2.063 | 0.151 |
| 肾脏 | 14(13.2) | 9(13.0) | 5(13.5) | 0.054 | 0.816 |
| 鼻窦 | 12(11.3) | 7(10.1) | 5(13.5) | 0.040 | 0.841 |
| 腹膜后 | 8(7.5) | 5(7.2) | 3(8.1) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| 眼眶 | 5(4.7) | 2(2.9) | 3(8.1) | 0.524 | 0.468 |
| 胃肠道 | 4(3.8) | 4(5.8) | 0 | 0.918 | 0.338 |
| 动脉 | 3(2.8) | 2(2.9) | 1(2.7) | 0.310 | 0.578 |
| 硬脑膜 | 2(1.9) | 1(1.4) | 1(2.7) | - | 1.000 |
| 纵隔 | 1(0.9) | 0 | 1(2.7) | - | 0.349 |
Table 1 Sex disparities in organ involvements in IgG4-RD patients
| 受累器官 | 总体(n=106) | 男(n=69) | 女(n=37) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淋巴结 | 71(67.0) | 48(69.6) | 23(62.2) | 0.597 | 0.440 |
| 涎腺 | 40(37.7) | 21(30.4) | 19(51.4) | 4.485 | 0.034 |
| 胰腺 | 38(35.8) | 34(49.3) | 4(10.8) | 15.495 | <0.001 |
| 肺部 | 37(34.9) | 25(36.2) | 12(32.4) | 0.153 | 0.696 |
| 泪腺 | 34(32.1) | 17(24.6) | 17(45.9) | 5.019 | 0.025 |
| 胆管 | 14(13.2) | 12(17.4) | 2(5.4) | 2.063 | 0.151 |
| 肾脏 | 14(13.2) | 9(13.0) | 5(13.5) | 0.054 | 0.816 |
| 鼻窦 | 12(11.3) | 7(10.1) | 5(13.5) | 0.040 | 0.841 |
| 腹膜后 | 8(7.5) | 5(7.2) | 3(8.1) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| 眼眶 | 5(4.7) | 2(2.9) | 3(8.1) | 0.524 | 0.468 |
| 胃肠道 | 4(3.8) | 4(5.8) | 0 | 0.918 | 0.338 |
| 动脉 | 3(2.8) | 2(2.9) | 1(2.7) | 0.310 | 0.578 |
| 硬脑膜 | 2(1.9) | 1(1.4) | 1(2.7) | - | 1.000 |
| 纵隔 | 1(0.9) | 0 | 1(2.7) | - | 0.349 |
| 项目 | IgG4<2.7 g/L (n=21) | IgG4≥2.7g /L(n=82) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 10(47.6) | 57(69.5) | 3.525a | 0.060 |
发病年龄(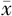 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 52.5±10.4 | 55.9±12.6 | -1.14b | 0.257 |
| 受累器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | 2(1,3) | 3(2,4) | -2.915c | 0.004 |
| IgG4相关性疾病RI | 9(6,12) | 12(9,15) | -3.143c | 0.002 |
| 嗜酸粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.13(0.07,0.24) | 0.29(0.14,0.51) | -2.743c | 0.006 |
| 球蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 30.0(26.0,39.0) | 33.9(29.3,41.5) | -1.453c | 0.150 |
| 红细胞沉降率〔M(P25,P75),mm/1h〕 | 44.5(9.1,82.3) | 26(11.0,81.5) | -0.231c | 0.817 |
| 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 | 4(19.0) | 41(50.0) | 4.163a | 0.041 |
| IgG〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 13.3(10.5,16.9) | 18.8(14.5,26.1) | -2.232c | 0.026 |
| IgA〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 2.1(1.7,2.8) | 1.8(1.3,2.7) | -0.682c | 0.495 |
| IgM〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.9(0.5,1.4) | -0.176c | 0.860 |
| IgG1〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 7.9(6.8,9.5) | 9.6(8.0,13.1) | -1.581c | 0.122 |
| IgG2〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 4.5(3.4,4.9) | 6.3(5.1,9.3) | -2.310c | 0.019 |
| IgG3〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.4(0.1,0.6) | 0.5(0.3,0.7) | -0.963c | 0.356 |
| IgE〔M(P25,P75),kU/L〕 | 114.5 (28.4,628.9) | 440.9 (184.8,801.1) | -1.900c | 0.060 |
Table 2 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with serum IgG4<2.7 g/L and serum IgG4≥2.7 g/L
| 项目 | IgG4<2.7 g/L (n=21) | IgG4≥2.7g /L(n=82) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 10(47.6) | 57(69.5) | 3.525a | 0.060 |
发病年龄(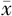 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 52.5±10.4 | 55.9±12.6 | -1.14b | 0.257 |
| 受累器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | 2(1,3) | 3(2,4) | -2.915c | 0.004 |
| IgG4相关性疾病RI | 9(6,12) | 12(9,15) | -3.143c | 0.002 |
| 嗜酸粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.13(0.07,0.24) | 0.29(0.14,0.51) | -2.743c | 0.006 |
| 球蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 30.0(26.0,39.0) | 33.9(29.3,41.5) | -1.453c | 0.150 |
| 红细胞沉降率〔M(P25,P75),mm/1h〕 | 44.5(9.1,82.3) | 26(11.0,81.5) | -0.231c | 0.817 |
| 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 | 4(19.0) | 41(50.0) | 4.163a | 0.041 |
| IgG〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 13.3(10.5,16.9) | 18.8(14.5,26.1) | -2.232c | 0.026 |
| IgA〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 2.1(1.7,2.8) | 1.8(1.3,2.7) | -0.682c | 0.495 |
| IgM〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.9(0.5,1.4) | -0.176c | 0.860 |
| IgG1〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 7.9(6.8,9.5) | 9.6(8.0,13.1) | -1.581c | 0.122 |
| IgG2〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 4.5(3.4,4.9) | 6.3(5.1,9.3) | -2.310c | 0.019 |
| IgG3〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.4(0.1,0.6) | 0.5(0.3,0.7) | -0.963c | 0.356 |
| IgE〔M(P25,P75),kU/L〕 | 114.5 (28.4,628.9) | 440.9 (184.8,801.1) | -1.900c | 0.060 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L 〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 68 | 3(2,4) | 50(76.9) | 15(22.1) | 17(36.2) |
| 受累组 | 38 | 3(3,4) | 32(84.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(66.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -0.604a | 0.785 | 0.015 | 4.302 | |
| P值 | 0.546 | 0.380 | 0.904 | 0.038 |
Table 3 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without pancreatic involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L 〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 68 | 3(2,4) | 50(76.9) | 15(22.1) | 17(36.2) |
| 受累组 | 38 | 3(3,4) | 32(84.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(66.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -0.604a | 0.785 | 0.015 | 4.302 | |
| P值 | 0.546 | 0.380 | 0.904 | 0.038 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 92 | 3(2,4) | 70(78.7) | 18(19.8) | 19(36.5) |
| 受累组 | 14 | 4(2,5) | 12(85.7) | 5(35.7) | 8(80.0) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -1.770a | 0.211 | 1.036 | 6.709 | |
| P值 | 0.070 | 0.646 | 0.309 | 0.010 |
Table 4 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without kidney involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 92 | 3(2,4) | 70(78.7) | 18(19.8) | 19(36.5) |
| 受累组 | 14 | 4(2,5) | 12(85.7) | 5(35.7) | 8(80.0) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -1.770a | 0.211 | 1.036 | 6.709 | |
| P值 | 0.070 | 0.646 | 0.309 | 0.010 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 55 | 2(1,3) | 39(73.6) | 7(12.7) | 11(40.7) |
| 受累组 | 51 | 3(3,4) | 43(86) | 16(31.4) | 16(45.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -4.266a | 2.443 | 5.415 | 0.153 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.118 | 0.020 | 0.695 |
Table 5 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without salivary gland/lacrimal gland involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 55 | 2(1,3) | 39(73.6) | 7(12.7) | 11(40.7) |
| 受累组 | 51 | 3(3,4) | 43(86) | 16(31.4) | 16(45.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -4.266a | 2.443 | 5.415 | 0.153 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.118 | 0.020 | 0.695 |
| [1] | TAKAHASHI H, YAMAMOTO M, SUZUKI C,et al. The birthday of a new syndrome:IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity[J]. Autoimmun Rev,2010,9(9):591-594. DOI:10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.003. |
| [2] | UMEHARA H, OKAZAKI K, MASAKI Y,et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD),2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol,2012,22(1):21-30. DOI:10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z. |
| [3] | CARRUTHERS M N, STONE J H, DESHPANDE V,et al. Development of an IgG4-RD responder index[J]. Int J Rheumatol,2012,2012:259408. DOI:10.1155/2012/259408. |
| [4] | MASAMUNE A, KIKUTA K, HAMADA S,et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan in 2016[J]. J Gastroenterol,2020,55(4):462-470. DOI:10.1007/s00535-019-01658-7. |
| [5] | BLEDSOE J R, DELLA-TORRE E, ROVATI L,et al. IgG4-related disease:review of the histopathologic features,differential diagnosis,and therapeutic approach[J]. APMIS,2018,126(6):459-476. DOI:10.1111/apm.12845. |
| [6] | YAMADA K, YAMAMOTO M, SAEKI T,et al. New clues to the nature of immunoglobulin G4-related disease:a retrospective Japanese multicenter study of baseline clinical features of 334 cases[J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2017,19(1):262. DOI:10.1186/s13075-017-1467-x. |
| [7] | 张盼盼,赵继志,王木,等. IgG4相关性疾病346例临床特征分析[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(9):644-649. |
| [8] | WANG L W, ZHANG P P, ZHANG X,et al. Sex disparities in clinical characteristics and prognosis of immunoglobulin G4-related disease:a prospective study of 403 patients[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford),2019,58(5):820-830. |
| [9] | DE BUY WENNIGER L J, CULVER E L, BEUERS U. Exposure to occupational antigens might predispose to IgG4-related disease[J]. Hepatology,2014,60(4):1453-1454. |
| [10] | HAO M J, LIU M, FAN G W,et al. Diagnostic value of serum IgG4 for IgG4-related disease:a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2016,95(21):e3785. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000003785. |
| [11] | OKAZAKI K, UCHIDA K. Current perspectives on autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease[J]. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,2018,94(10):412-427. |
| [12] | WALLACE Z S, DESHPANDE V, MATTOO H,et al. IgG4-related disease:clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol,2015,67(9):2466-2475. DOI:10.1002/art.39205. |
| [13] | VARGHESE J L, FUNG A W S, MATTMAN A,et al. Clinical utility of serum IgG4 measurement[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2020,506:228-235. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.001. |
| [14] | YANG H, LI J, WANG Y,et al. Distribution characteristics of elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)and its relationship with IgG4-related disease[J]. Scand J Rheumatol,2019,48(6):497-504. DOI:10.1080/03009742.2019.1602882. |
| [15] | CULVER E L, SADLER R, SIMPSON D,et al. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in diagnosis,treatment response,organ involvement,and relapse in a prospective IgG4-related disease UK cohort[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2016,111(5):733-743. |
| [16] | ZHANG X, ZHANG P, LI J,et al. Different clinical patterns of IgG4-RD patients with and without eosinophilia[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9(1):16483. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-52847-6. |
| [17] | MOHAPATRA S, CHARILAOU P, SHARMA A,et al. Significance of peripheral eosinophilia for diagnosis of IgG4-related disease in subjects with elevated serum IgG4 levels[J]. Pancreatology,2020,20(1):74-78. |
| [1] | LI Hao, LI Peijin, LIU Tingting, CUI Yiyuan, LI Sicong, LIU Lixing, FENG Li, Working Group on Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines for Cancer Pain. Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer Pain by Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3729-3740. |
| [2] | ZHI Congcong, LI Xue, CHENG Yicheng, WANG Xiaolong, ZHENG Lihua. Guidelines for Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemorrhoids (2025 Edition) [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3217-3228. |
| [3] | PAN Qi, REN Jingjing, MA Fanghui, HU Mengjie. Survey of General Practitioners' Cognition and Needs for AI Assisted Diagnosis and Treatment Systems [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [4] | Chinese Geriatrics Society, General Practice Branch of Zhejiang Medical Association, the Expert Collaboration Group on Medically Unspecified Disease in General Practice. Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management of Emaciation (2025) [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(21): 2577-2594. |
| [5] | LIU Hongya, YU Dehua. Construction and Practice of Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Technology Combining General Practice and Specialist in Shanghai Community [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2390-2397. |
| [6] | BIAN Ying, YIN Gang, ZHANG Zixun, TAO Hongbing. The Mechanism of Information Construction Enabling High-quality Development of Compact County-level Medical Consortium [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2426-2432. |
| [7] | DENG Yaqian, CAO Chunli, MA Jinmei, LI Wenxiao, XU Zelin, CHENG Jing, LI Jun. Predictive Value of S-Detect Combined with Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging Quantification in Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis of Breast Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2149-2155. |
| [8] | LI Jie, DU Yue, SHAO Shen, PAN Dong, ZHANG Yaxin. The Operational Efficiency of Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment Services in Primary Medical Institutions in Tianjin Based on DEA and SFA [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 1980-1986. |
| [9] | GU Jie, HUANG Yanyan. Diagnosis and Comprehensive Management of Rare Diseases: the Indispensable Role of General Practitioners [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 1955-1960. |
| [10] | Chinese Academy Society of Sleep Medicine, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Sleep Medicine Group, China Neurologist Association. Chinese Guideline for Diagnosis and Treatment of Co-morbid Insomnia and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (2024) [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(11): 1289-1303. |
| [11] | HUANG Lujie, ZHANG Xiaoying, YU Shasha. Risk Factors, Prognosis and Rapid Screening in Patients with Acute Aortic Dissection Complicated with Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(09): 1100-1105. |
| [12] | MA Xiaoxuan, WANG Rongqi. Research Progress in Metabolomics for HCC Diagnosis and Treatment [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 1017-1022. |
| [13] | MA Hongyang, YUE Anna, SUN Kangyun. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Diagnostic Differences between Domestic and Foreign Guidelines [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(06): 655-665. |
| [14] | DAI Yao, XUE Liping, ZHANG Shiqi, XU Min, ZHANG Qiu, HU Honglin. Congential Adrenal Hyperplasia Associated with CYP17A1 Gene Mutation: a Case Report and Literature Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(06): 771-776. |
| [15] | LI Lingqi, GAO Yinyan, ZHANG Yuqin, SUN Dingkui, WU Xinyin, ZHANG Weiru. Survey on the Status and Training Demands of Capabilities for Diagnosing and Treating Common Diseases of Primary Care General Practitioners in Hunan Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(04): 443-449. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||