

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (05): 584-588.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.115
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical Featuresof IgG4-related Disease
Department of Gastroenterology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450052,China
*Corresponding author:ZHOU Lin,Chief physician,Professor;E-mail:ZL372@126.com
Received:2021-09-10
Revised:2021-12-15
Published:2022-02-15
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
周琳
基金资助:CLC Number:
DING Hang, LIU Yuan, ZHANG Lianfeng, ZHOU Lin.
Clinical Featuresof IgG4-related Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(05): 584-588.
| 受累器官 | 总体(n=106) | 男(n=69) | 女(n=37) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淋巴结 | 71(67.0) | 48(69.6) | 23(62.2) | 0.597 | 0.440 |
| 涎腺 | 40(37.7) | 21(30.4) | 19(51.4) | 4.485 | 0.034 |
| 胰腺 | 38(35.8) | 34(49.3) | 4(10.8) | 15.495 | <0.001 |
| 肺部 | 37(34.9) | 25(36.2) | 12(32.4) | 0.153 | 0.696 |
| 泪腺 | 34(32.1) | 17(24.6) | 17(45.9) | 5.019 | 0.025 |
| 胆管 | 14(13.2) | 12(17.4) | 2(5.4) | 2.063 | 0.151 |
| 肾脏 | 14(13.2) | 9(13.0) | 5(13.5) | 0.054 | 0.816 |
| 鼻窦 | 12(11.3) | 7(10.1) | 5(13.5) | 0.040 | 0.841 |
| 腹膜后 | 8(7.5) | 5(7.2) | 3(8.1) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| 眼眶 | 5(4.7) | 2(2.9) | 3(8.1) | 0.524 | 0.468 |
| 胃肠道 | 4(3.8) | 4(5.8) | 0 | 0.918 | 0.338 |
| 动脉 | 3(2.8) | 2(2.9) | 1(2.7) | 0.310 | 0.578 |
| 硬脑膜 | 2(1.9) | 1(1.4) | 1(2.7) | - | 1.000 |
| 纵隔 | 1(0.9) | 0 | 1(2.7) | - | 0.349 |
Table 1 Sex disparities in organ involvements in IgG4-RD patients
| 受累器官 | 总体(n=106) | 男(n=69) | 女(n=37) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淋巴结 | 71(67.0) | 48(69.6) | 23(62.2) | 0.597 | 0.440 |
| 涎腺 | 40(37.7) | 21(30.4) | 19(51.4) | 4.485 | 0.034 |
| 胰腺 | 38(35.8) | 34(49.3) | 4(10.8) | 15.495 | <0.001 |
| 肺部 | 37(34.9) | 25(36.2) | 12(32.4) | 0.153 | 0.696 |
| 泪腺 | 34(32.1) | 17(24.6) | 17(45.9) | 5.019 | 0.025 |
| 胆管 | 14(13.2) | 12(17.4) | 2(5.4) | 2.063 | 0.151 |
| 肾脏 | 14(13.2) | 9(13.0) | 5(13.5) | 0.054 | 0.816 |
| 鼻窦 | 12(11.3) | 7(10.1) | 5(13.5) | 0.040 | 0.841 |
| 腹膜后 | 8(7.5) | 5(7.2) | 3(8.1) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| 眼眶 | 5(4.7) | 2(2.9) | 3(8.1) | 0.524 | 0.468 |
| 胃肠道 | 4(3.8) | 4(5.8) | 0 | 0.918 | 0.338 |
| 动脉 | 3(2.8) | 2(2.9) | 1(2.7) | 0.310 | 0.578 |
| 硬脑膜 | 2(1.9) | 1(1.4) | 1(2.7) | - | 1.000 |
| 纵隔 | 1(0.9) | 0 | 1(2.7) | - | 0.349 |
| 项目 | IgG4<2.7 g/L (n=21) | IgG4≥2.7g /L(n=82) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 10(47.6) | 57(69.5) | 3.525a | 0.060 |
发病年龄(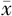 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 52.5±10.4 | 55.9±12.6 | -1.14b | 0.257 |
| 受累器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | 2(1,3) | 3(2,4) | -2.915c | 0.004 |
| IgG4相关性疾病RI | 9(6,12) | 12(9,15) | -3.143c | 0.002 |
| 嗜酸粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.13(0.07,0.24) | 0.29(0.14,0.51) | -2.743c | 0.006 |
| 球蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 30.0(26.0,39.0) | 33.9(29.3,41.5) | -1.453c | 0.150 |
| 红细胞沉降率〔M(P25,P75),mm/1h〕 | 44.5(9.1,82.3) | 26(11.0,81.5) | -0.231c | 0.817 |
| 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 | 4(19.0) | 41(50.0) | 4.163a | 0.041 |
| IgG〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 13.3(10.5,16.9) | 18.8(14.5,26.1) | -2.232c | 0.026 |
| IgA〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 2.1(1.7,2.8) | 1.8(1.3,2.7) | -0.682c | 0.495 |
| IgM〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.9(0.5,1.4) | -0.176c | 0.860 |
| IgG1〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 7.9(6.8,9.5) | 9.6(8.0,13.1) | -1.581c | 0.122 |
| IgG2〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 4.5(3.4,4.9) | 6.3(5.1,9.3) | -2.310c | 0.019 |
| IgG3〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.4(0.1,0.6) | 0.5(0.3,0.7) | -0.963c | 0.356 |
| IgE〔M(P25,P75),kU/L〕 | 114.5 (28.4,628.9) | 440.9 (184.8,801.1) | -1.900c | 0.060 |
Table 2 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with serum IgG4<2.7 g/L and serum IgG4≥2.7 g/L
| 项目 | IgG4<2.7 g/L (n=21) | IgG4≥2.7g /L(n=82) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 10(47.6) | 57(69.5) | 3.525a | 0.060 |
发病年龄(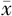 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 52.5±10.4 | 55.9±12.6 | -1.14b | 0.257 |
| 受累器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | 2(1,3) | 3(2,4) | -2.915c | 0.004 |
| IgG4相关性疾病RI | 9(6,12) | 12(9,15) | -3.143c | 0.002 |
| 嗜酸粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.13(0.07,0.24) | 0.29(0.14,0.51) | -2.743c | 0.006 |
| 球蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 30.0(26.0,39.0) | 33.9(29.3,41.5) | -1.453c | 0.150 |
| 红细胞沉降率〔M(P25,P75),mm/1h〕 | 44.5(9.1,82.3) | 26(11.0,81.5) | -0.231c | 0.817 |
| 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 | 4(19.0) | 41(50.0) | 4.163a | 0.041 |
| IgG〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 13.3(10.5,16.9) | 18.8(14.5,26.1) | -2.232c | 0.026 |
| IgA〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 2.1(1.7,2.8) | 1.8(1.3,2.7) | -0.682c | 0.495 |
| IgM〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.9(0.5,1.4) | -0.176c | 0.860 |
| IgG1〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 7.9(6.8,9.5) | 9.6(8.0,13.1) | -1.581c | 0.122 |
| IgG2〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 4.5(3.4,4.9) | 6.3(5.1,9.3) | -2.310c | 0.019 |
| IgG3〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 0.4(0.1,0.6) | 0.5(0.3,0.7) | -0.963c | 0.356 |
| IgE〔M(P25,P75),kU/L〕 | 114.5 (28.4,628.9) | 440.9 (184.8,801.1) | -1.900c | 0.060 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L 〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 68 | 3(2,4) | 50(76.9) | 15(22.1) | 17(36.2) |
| 受累组 | 38 | 3(3,4) | 32(84.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(66.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -0.604a | 0.785 | 0.015 | 4.302 | |
| P值 | 0.546 | 0.380 | 0.904 | 0.038 |
Table 3 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without pancreatic involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L 〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 68 | 3(2,4) | 50(76.9) | 15(22.1) | 17(36.2) |
| 受累组 | 38 | 3(3,4) | 32(84.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(66.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -0.604a | 0.785 | 0.015 | 4.302 | |
| P值 | 0.546 | 0.380 | 0.904 | 0.038 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 92 | 3(2,4) | 70(78.7) | 18(19.8) | 19(36.5) |
| 受累组 | 14 | 4(2,5) | 12(85.7) | 5(35.7) | 8(80.0) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -1.770a | 0.211 | 1.036 | 6.709 | |
| P值 | 0.070 | 0.646 | 0.309 | 0.010 |
Table 4 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without kidney involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 92 | 3(2,4) | 70(78.7) | 18(19.8) | 19(36.5) |
| 受累组 | 14 | 4(2,5) | 12(85.7) | 5(35.7) | 8(80.0) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -1.770a | 0.211 | 1.036 | 6.709 | |
| P值 | 0.070 | 0.646 | 0.309 | 0.010 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 55 | 2(1,3) | 39(73.6) | 7(12.7) | 11(40.7) |
| 受累组 | 51 | 3(3,4) | 43(86) | 16(31.4) | 16(45.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -4.266a | 2.443 | 5.415 | 0.153 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.118 | 0.020 | 0.695 |
Table 5 Comparison of clinical characteristics between IgG4-RD patients with and without salivary gland/lacrimal gland involvement
| 组别 | 例数 | 累及器官数目〔M(P25,P75),个〕 | IgG4≥2.7 g/L〔n(%)〕 | 嗜酸粒细胞增多症〔n(%)〕 | 低补体血症〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未受累组 | 55 | 2(1,3) | 39(73.6) | 7(12.7) | 11(40.7) |
| 受累组 | 51 | 3(3,4) | 43(86) | 16(31.4) | 16(45.7) |
| χ2(Z)值 | -4.266a | 2.443 | 5.415 | 0.153 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.118 | 0.020 | 0.695 |
| [1] | TAKAHASHI H, YAMAMOTO M, SUZUKI C,et al. The birthday of a new syndrome:IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity[J]. Autoimmun Rev,2010,9(9):591-594. DOI:10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.003. |
| [2] | UMEHARA H, OKAZAKI K, MASAKI Y,et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD),2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol,2012,22(1):21-30. DOI:10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z. |
| [3] | CARRUTHERS M N, STONE J H, DESHPANDE V,et al. Development of an IgG4-RD responder index[J]. Int J Rheumatol,2012,2012:259408. DOI:10.1155/2012/259408. |
| [4] | MASAMUNE A, KIKUTA K, HAMADA S,et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan in 2016[J]. J Gastroenterol,2020,55(4):462-470. DOI:10.1007/s00535-019-01658-7. |
| [5] | BLEDSOE J R, DELLA-TORRE E, ROVATI L,et al. IgG4-related disease:review of the histopathologic features,differential diagnosis,and therapeutic approach[J]. APMIS,2018,126(6):459-476. DOI:10.1111/apm.12845. |
| [6] | YAMADA K, YAMAMOTO M, SAEKI T,et al. New clues to the nature of immunoglobulin G4-related disease:a retrospective Japanese multicenter study of baseline clinical features of 334 cases[J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2017,19(1):262. DOI:10.1186/s13075-017-1467-x. |
| [7] | 张盼盼,赵继志,王木,等. IgG4相关性疾病346例临床特征分析[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(9):644-649. |
| [8] | WANG L W, ZHANG P P, ZHANG X,et al. Sex disparities in clinical characteristics and prognosis of immunoglobulin G4-related disease:a prospective study of 403 patients[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford),2019,58(5):820-830. |
| [9] | DE BUY WENNIGER L J, CULVER E L, BEUERS U. Exposure to occupational antigens might predispose to IgG4-related disease[J]. Hepatology,2014,60(4):1453-1454. |
| [10] | HAO M J, LIU M, FAN G W,et al. Diagnostic value of serum IgG4 for IgG4-related disease:a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2016,95(21):e3785. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000003785. |
| [11] | OKAZAKI K, UCHIDA K. Current perspectives on autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease[J]. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,2018,94(10):412-427. |
| [12] | WALLACE Z S, DESHPANDE V, MATTOO H,et al. IgG4-related disease:clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol,2015,67(9):2466-2475. DOI:10.1002/art.39205. |
| [13] | VARGHESE J L, FUNG A W S, MATTMAN A,et al. Clinical utility of serum IgG4 measurement[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2020,506:228-235. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.001. |
| [14] | YANG H, LI J, WANG Y,et al. Distribution characteristics of elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)and its relationship with IgG4-related disease[J]. Scand J Rheumatol,2019,48(6):497-504. DOI:10.1080/03009742.2019.1602882. |
| [15] | CULVER E L, SADLER R, SIMPSON D,et al. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in diagnosis,treatment response,organ involvement,and relapse in a prospective IgG4-related disease UK cohort[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2016,111(5):733-743. |
| [16] | ZHANG X, ZHANG P, LI J,et al. Different clinical patterns of IgG4-RD patients with and without eosinophilia[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9(1):16483. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-52847-6. |
| [17] | MOHAPATRA S, CHARILAOU P, SHARMA A,et al. Significance of peripheral eosinophilia for diagnosis of IgG4-related disease in subjects with elevated serum IgG4 levels[J]. Pancreatology,2020,20(1):74-78. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 859
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 998
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||