中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (31): 3924-3931.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2025.0019
收稿日期:2025-03-06
修回日期:2025-06-30
出版日期:2025-11-05
发布日期:2025-09-23
通讯作者:
刘涛
作者贡献:
张骥提出主要研究目标,负责数据统计,构思并撰写论文;周婕、李凌、吴延莉、吉维负责数据收集;周婕、吴延莉协助整理数据和统计学处理;刘涛负责文章的质量控制与审查,对论文整体负责。
基金资助:
ZHANG Ji, ZHOU Jie, LI Ling, WU Yanli, JI Wei, LIU Tao*( )
)
Received:2025-03-06
Revised:2025-06-30
Published:2025-11-05
Online:2025-09-23
Contact:
LIU Tao
摘要: 背景 既往研究关于空腹血糖(FBG)和成人全因死亡和特定原因死亡的关联结论不一致,需进一步探讨。 目的 探讨FBG水平与成人全因死亡、心血管疾病死亡和恶性肿瘤死亡风险的关系,为重点疾病防控提供理论依据。 方法 本研究为前瞻性队列研究,队列于2010年11月建立,在贵州省12个县(市、区)抽取9 280名在该地每年居住≥6个月的18岁及以上居民作为研究对象开展基线调查,分别于2020年和2023年对所有参与基线调查的人员进行随访。根据基线FBG水平将研究对象分为4组:低血糖组(LFG)、正常血糖组(NFG)、血糖受损组(IFG)、糖尿病组(DM),各组人数分别为437、6 210、2 035、427名。采用COX比例风险模型分析FBG水平与成人全因死亡、特定原因死亡风险的关系,计算风险比(HR)及95%可信区间(95%CI),并利用限制性立方样条分析FBG与死因的剂量-反应关系,同时根据研究对象的不同特征进行亚组分析。 结果 共纳入9 109名研究对象,中位随访时间为11.69年,随访期间发生589例死亡。COX比例风险回归分析显示:在调整相关混杂因素后,FBG每增加1 mmol/L,全因死亡风险增加10%(HR=1.10,95%CI=1.06~1.15);与NFG比较,DM增加了全死因风险(HR=1.59,95%CI=1.18~2.17)和恶性肿瘤死亡风险(HR=2.16,95%CI=1.03~4.49)。限制性立方样条分析结果表明,FBG水平与全因死亡及恶性肿瘤死亡风险呈线性剂量-反应关系。亚组分析显示,女性(HR=2.01,95%CI=1.27~3.20)、≥45岁(HR=1.57,95%CI=1.13~2.16)、BMI<24.0 kg/m2(HR=1.45,95%CI=1.11~2.43)、BMI≥24.0 kg/m2(HR=1.67,95%CI=1.01~2.76)的DM全因死亡风险均增加,女性(HR=2.39,95%CI=1.11~5.14)、≥45岁(HR=6.62,95%CI=1.61~9.76)、BMI<24.0 kg/m2(HR=2.69,95%CI=1.11~6.52)的DM恶性肿瘤死亡风险增加。 结论 FBG水平与死亡呈线性正相关,DM增加全因死亡和恶性肿瘤死亡风险,应采取有效措施将血糖有效控制在理想水平。
| 特征 | 合计(n=9 109) | LFG(n=437) | NFG(n=6 210) | IFG(n=2 035) | DM(n=427) | F(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄( | 44.7±15.7 | 43.0±15.7 | 43.9±15.7 | 46.4±15.4 | 50.4±15.7 | 34.293 | <0.001 |
| 性别[名(%)] | 26.399a | <0.001 | |||||
| 男 | 4 356(47.82) | 210(48.05) | 2 872(46.25) | 1 032(50.71) | 242(56.67) | ||
| 女 | 4 753(52.18) | 227(51.95) | 3 338(53.75) | 1 003(49.29) | 185(43.33) | ||
| 居住地[名(%)] | 253.465a | <0.001 | |||||
| 城市 | 3 100(34.03) | 120(27.46) | 2 445(39.37) | 438(21.52) | 97(22.72) | ||
| 农村 | 6 009(65.97) | 317(72.54) | 3 765(60.63) | 1 597(78.48) | 330(77.28) | ||
| 吸烟[名(%)] | 1.613a | 0.656 | |||||
| 是 | 2 635(28.93) | 121(27.69) | 1 790(28.82) | 590(28.99) | 134(31.38) | ||
| 否 | 6 474(71.07) | 316(72.31) | 4 420(71.18) | 1 445(71.01) | 293(68.62) | ||
| 饮酒[名(%)] | 20.669a | <0.001 | |||||
| 是 | 2 937(32.24) | 130(29.75) | 1 933(31.13) | 705(34.64) | 169(39.58) | ||
| 否 | 6 172(67.76) | 307(70.25) | 4 277(68.87) | 1 330(65.36) | 258(60.42) | ||
| 经常锻炼[名(%)] | 13.226a | 0.004 | |||||
| 是 | 7 887(86.58) | 354(81.01) | 5 385(86.71) | 1 780(87.47) | 368(86.18) | ||
| 否 | 1 222(13.42) | 83(18.99) | 825(13.29) | 255(12.53) | 59(13.82) | ||
| 血脂异常[名(%)] | 43.387a | <0.001 | |||||
| 是 | 5 286(58.03) | 253(57.89) | 3 523(56.73) | 1 199(58.92) | 311(72.83) | ||
| 否 | 3 823(41.97) | 184(42.11) | 2 687(43.27) | 836(41.08) | 116(27.17) | ||
| 基线患CVD[名(%)] | 0.205a | 0.977 | |||||
| 是 | 9 058(99.44) | 434(99.31) | 6 175(99.44) | 2 024(99.46) | 425(99.53) | ||
| 否 | 51(0.56) | 3(0.69) | 35(0.56) | 11(0.54) | 2(0.47) | ||
| 恶性肿瘤史[名(%)] | 5.716a | 0.456 | |||||
| 是 | 9 042(145.6) | 6 164(99.26) | 436(7.02) | 2 018(32.5) | 424(6.83) | ||
| 否 | 27(0.43) | 17(0.27) | 1(0.02) | 9(0.14) | 0 | ||
| 不清楚 | 40(0.64) | 29(0.47) | 0 | 8(0.13) | 3(0.05) | ||
| BMI( | 22.8±3.3 | 22.3±2.9 | 22.6±3.2 | 23.3±3.7 | 24.2±3.6 | 52.308 | <0.001 |
| WC( | 76.5±9.5 | 76.1±8.7 | 75.7±9.4 | 77.9±9.6 | 81.0±10.3 | 57.765 | <0.001 |
| SBP( | 126±22 | 124±19 | 125±21 | 128±22 | 133±23 | 32.404 | <0.001 |
| DBP( | 78±12 | 77±11 | 78±12 | 80±13 | 81±12 | 22.953 | <0.001 |
| FBG( | 5.3±1.3 | 3.5±0.4 | 4.9±0.4 | 6.1±0.4 | 9.3±3.0 | 6 163.890 | <0.001 |
表1 不同血糖水平人群的基线特征比较
Table 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics for participants with different blood glucose levels
| 特征 | 合计(n=9 109) | LFG(n=437) | NFG(n=6 210) | IFG(n=2 035) | DM(n=427) | F(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄( | 44.7±15.7 | 43.0±15.7 | 43.9±15.7 | 46.4±15.4 | 50.4±15.7 | 34.293 | <0.001 |
| 性别[名(%)] | 26.399a | <0.001 | |||||
| 男 | 4 356(47.82) | 210(48.05) | 2 872(46.25) | 1 032(50.71) | 242(56.67) | ||
| 女 | 4 753(52.18) | 227(51.95) | 3 338(53.75) | 1 003(49.29) | 185(43.33) | ||
| 居住地[名(%)] | 253.465a | <0.001 | |||||
| 城市 | 3 100(34.03) | 120(27.46) | 2 445(39.37) | 438(21.52) | 97(22.72) | ||
| 农村 | 6 009(65.97) | 317(72.54) | 3 765(60.63) | 1 597(78.48) | 330(77.28) | ||
| 吸烟[名(%)] | 1.613a | 0.656 | |||||
| 是 | 2 635(28.93) | 121(27.69) | 1 790(28.82) | 590(28.99) | 134(31.38) | ||
| 否 | 6 474(71.07) | 316(72.31) | 4 420(71.18) | 1 445(71.01) | 293(68.62) | ||
| 饮酒[名(%)] | 20.669a | <0.001 | |||||
| 是 | 2 937(32.24) | 130(29.75) | 1 933(31.13) | 705(34.64) | 169(39.58) | ||
| 否 | 6 172(67.76) | 307(70.25) | 4 277(68.87) | 1 330(65.36) | 258(60.42) | ||
| 经常锻炼[名(%)] | 13.226a | 0.004 | |||||
| 是 | 7 887(86.58) | 354(81.01) | 5 385(86.71) | 1 780(87.47) | 368(86.18) | ||
| 否 | 1 222(13.42) | 83(18.99) | 825(13.29) | 255(12.53) | 59(13.82) | ||
| 血脂异常[名(%)] | 43.387a | <0.001 | |||||
| 是 | 5 286(58.03) | 253(57.89) | 3 523(56.73) | 1 199(58.92) | 311(72.83) | ||
| 否 | 3 823(41.97) | 184(42.11) | 2 687(43.27) | 836(41.08) | 116(27.17) | ||
| 基线患CVD[名(%)] | 0.205a | 0.977 | |||||
| 是 | 9 058(99.44) | 434(99.31) | 6 175(99.44) | 2 024(99.46) | 425(99.53) | ||
| 否 | 51(0.56) | 3(0.69) | 35(0.56) | 11(0.54) | 2(0.47) | ||
| 恶性肿瘤史[名(%)] | 5.716a | 0.456 | |||||
| 是 | 9 042(145.6) | 6 164(99.26) | 436(7.02) | 2 018(32.5) | 424(6.83) | ||
| 否 | 27(0.43) | 17(0.27) | 1(0.02) | 9(0.14) | 0 | ||
| 不清楚 | 40(0.64) | 29(0.47) | 0 | 8(0.13) | 3(0.05) | ||
| BMI( | 22.8±3.3 | 22.3±2.9 | 22.6±3.2 | 23.3±3.7 | 24.2±3.6 | 52.308 | <0.001 |
| WC( | 76.5±9.5 | 76.1±8.7 | 75.7±9.4 | 77.9±9.6 | 81.0±10.3 | 57.765 | <0.001 |
| SBP( | 126±22 | 124±19 | 125±21 | 128±22 | 133±23 | 32.404 | <0.001 |
| DBP( | 78±12 | 77±11 | 78±12 | 80±13 | 81±12 | 22.953 | <0.001 |
| FBG( | 5.3±1.3 | 3.5±0.4 | 4.9±0.4 | 6.1±0.4 | 9.3±3.0 | 6 163.890 | <0.001 |
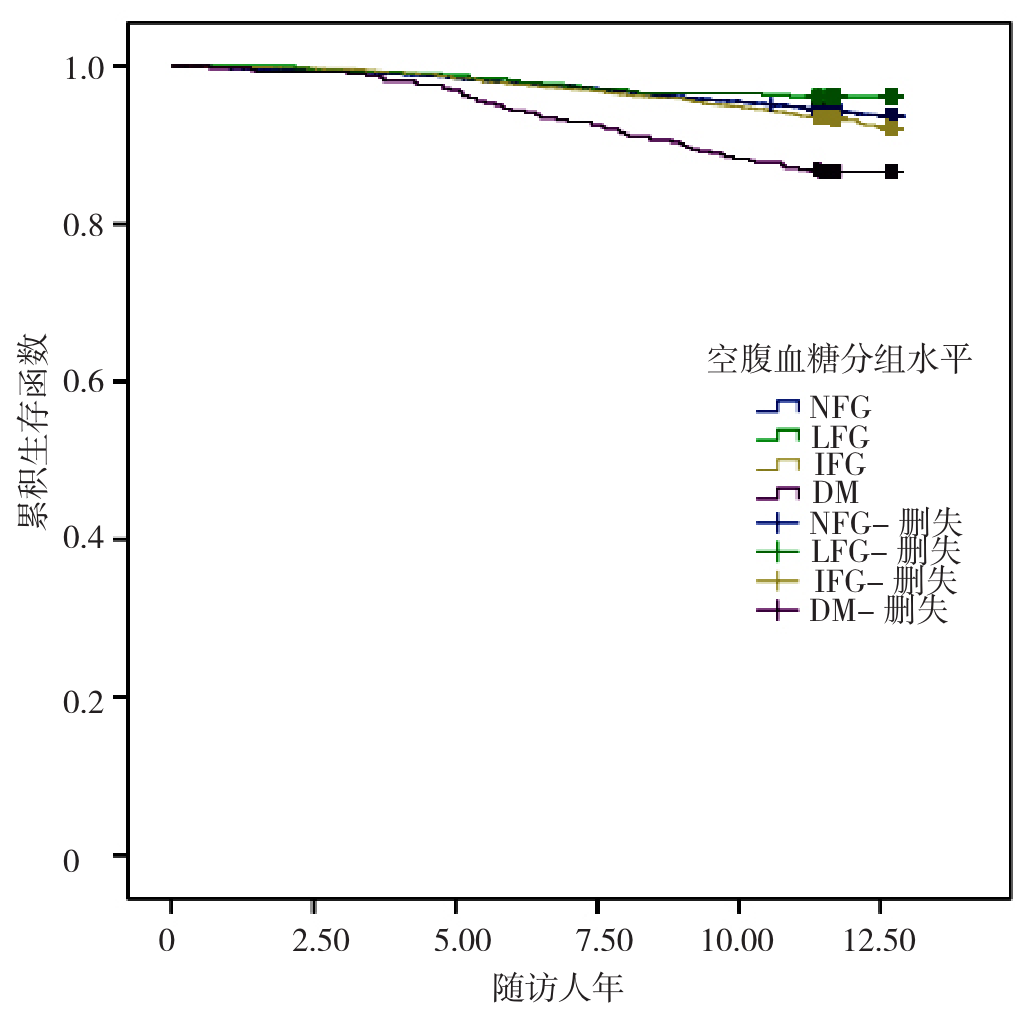
图1 不同FBG水平人群的累积生存曲线注:FBG=空腹血糖,LFG=低血糖,NFG=正常血糖,IFG=血糖受损,DM=糖尿病。
Figure 1 Cumulative survival curves for different groups of fasting blood glucose levels
| 血糖分组 | 死亡(人) | 死亡率(千人年) | 模型1 | 模型2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | |||
| 全因死亡 | 589 | 5.51 | ||||
| LFG | 17 | 3.27 | 0.65(0.40~1.05) | 0.077 | 0.72(0.44~1.17) | 0.185 |
| NFG | 372 | 5.09 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 143 | 6.01 | 1.19(0.98~1.45) | 0.074 | 1.13(0.92~1.39) | 0.243 |
| DM | 57 | 11.83 | 2.38(1.80~3.14) | <0.001 | 1.59(1.18~2.17) | 0.003 |
| P趋势值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| CVD死亡 | 224 | 2.10 | ||||
| LFG | 4 | 0.77 | 0.37(0.14~1.00) | 0.050 | 0.42(0.16~1.15) | 0.092 |
| NFG | 152 | 2.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 50 | 2.10 | 1.02(0.74~1.40) | 0.907 | 0.92(0.65~1.29) | 0.632 |
| DM | 18 | 3.74 | 1.84(1.13~3.00) | 0.015 | 1.23(0.73~2.06) | 0.427 |
| P趋势值 | 0.004 | 0.236 | ||||
| 恶性肿瘤死亡 | 90 | 0.84 | ||||
| LFG | 3 | 0.58 | 0.81(0.25~2.58) | 0.718 | 0.99(0.31~3.21) | 0.989 |
| NFG | 52 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 25 | 1.05 | 1.48(0.92~2.39) | 0.107 | 1.35(0.80~2.28) | 0.259 |
| DM | 10 | 2.08 | 2.96(1.51~5.83) | 0.002 | 2.16(1.03~4.49) | 0.041 |
| P趋势值 | 0.001 | 0.037 | ||||
表2 全人群血糖水平与死亡风险的COX比例风险模型分析
Table 2 COX regression analysis of correlation between fasting blood glucose and risk of mortality
| 血糖分组 | 死亡(人) | 死亡率(千人年) | 模型1 | 模型2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95%CI) | P值 | HR(95%CI) | P值 | |||
| 全因死亡 | 589 | 5.51 | ||||
| LFG | 17 | 3.27 | 0.65(0.40~1.05) | 0.077 | 0.72(0.44~1.17) | 0.185 |
| NFG | 372 | 5.09 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 143 | 6.01 | 1.19(0.98~1.45) | 0.074 | 1.13(0.92~1.39) | 0.243 |
| DM | 57 | 11.83 | 2.38(1.80~3.14) | <0.001 | 1.59(1.18~2.17) | 0.003 |
| P趋势值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| CVD死亡 | 224 | 2.10 | ||||
| LFG | 4 | 0.77 | 0.37(0.14~1.00) | 0.050 | 0.42(0.16~1.15) | 0.092 |
| NFG | 152 | 2.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 50 | 2.10 | 1.02(0.74~1.40) | 0.907 | 0.92(0.65~1.29) | 0.632 |
| DM | 18 | 3.74 | 1.84(1.13~3.00) | 0.015 | 1.23(0.73~2.06) | 0.427 |
| P趋势值 | 0.004 | 0.236 | ||||
| 恶性肿瘤死亡 | 90 | 0.84 | ||||
| LFG | 3 | 0.58 | 0.81(0.25~2.58) | 0.718 | 0.99(0.31~3.21) | 0.989 |
| NFG | 52 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| IFG | 25 | 1.05 | 1.48(0.92~2.39) | 0.107 | 1.35(0.80~2.28) | 0.259 |
| DM | 10 | 2.08 | 2.96(1.51~5.83) | 0.002 | 2.16(1.03~4.49) | 0.041 |
| P趋势值 | 0.001 | 0.037 | ||||
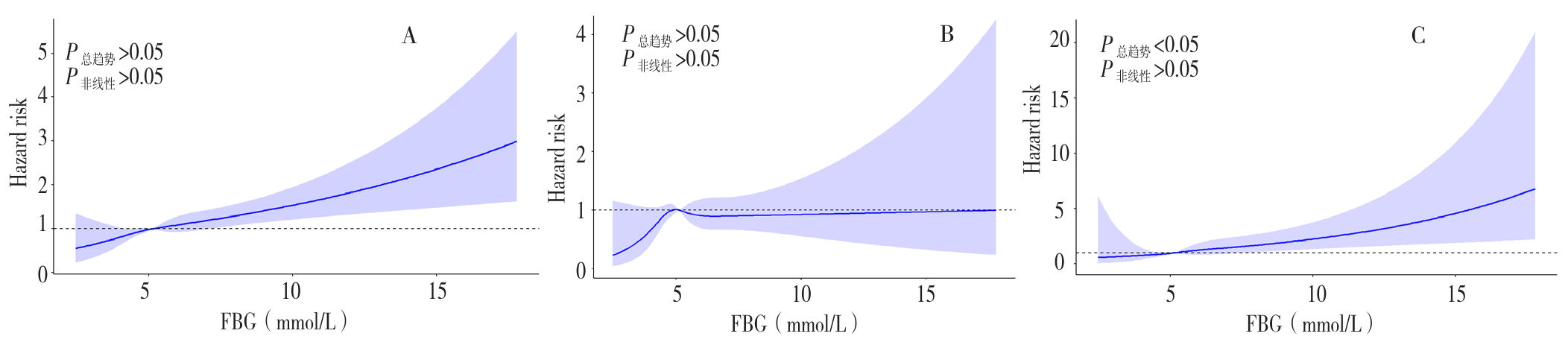
图2 FBG水平与成人死亡风险的剂量反应关系注:图A为FBG水平与全因死亡风险的COX分析,图B为FBG水平与CVD死亡风险的COX分析,图C为FBG水平与恶性肿瘤死亡风险的COX分析。
Figure 2 Dose-response relationship between fasting blood glucose and risk of mortality
| 血糖分组 | 性别 | 年龄 | BMI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <45岁 | ≥45岁 | <24.0 kg/m2 | ≥24.0 kg/m2 | |
| 全因死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 0.87(0.48~1.56) | 0.50(0.21~1.23) | 2.06(0.92~4.60) | 0.49(0.26~0.92) | 0.63(0.35~1.13) | 1.15(0.46~2.87) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 1.06(0.81~1.39) | 1.21(0.88~1.65) | 0.73(0.36~1.47) | 1.19(0.96~1.47) | 1.02(0.80~1.31) | 1.42(0.98~2.06) |
| DM | 1.39(0.92~2.09) | 2.01(1.27~3.20) | 2.41(0.93~6.29) | 1.57(1.13~2.16) | 1.45(1.11~2.43) | 1.67(1.01~2.76) |
| P趋势值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.945 | <0.001 | 0.027 | 0.034 |
| CVD死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 0.41(0.10~1.67) | 0.45(0.11~1.85) | 0.84(0.11~6.39) | 0.37(0.12~1.15) | 0.39(0.12~1.23) | 0.54(0.07~3.99) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 1.08(0.70~1.66) | 0.77(0.44~1.35) | 0.58(0.17~2.03) | 0.96(0.68~1.38) | 0.76(0.49~1.17) | 1.37(0.77~2.44) |
| DM | 0.94(0.44~1.98) | 1.73(0.84~3.55) | 1.34(0.17~4.51) | 1.24(0.73~2.11) | 1.27(0.65~2.46) | 1.14(0.50~2.62) |
| P趋势值 | 0.631 | 0.188 | 0.836 | 0.185 | 0.455 | 0.467 |
| 肿瘤死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 1.03(0.25~4.36) | 0.95(0.12~7.19) | 3.34(0.69~16.13) | 0.42(0.06~3.05) | 0.84(0.20~3.51) | 1.96(0.24~5.97) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 0.84(0.39~1.80) | 2.31(0.67~8.17) | 0.36(0.04~3.00) | 1.51(0.87~2.61) | 1.23(0.64~2.36) | 1.63(0.64~4.13) |
| DM | 2.07(0.83~5.13) | 2.39(1.11~5.14) | 1.67(0.66~3.89) | 6.62(1.61~9.76) | 2.69(1.11~6.52) | 1.95(0.52~7.30) |
| P趋势值 | 0.238 | 0.035 | 0.257 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.351 |
表3 不同性别、年龄、BMI人群血糖水平与死亡关系的COX比例风险模型分析[HR(95%CI)]
Table 3 COX regression analysis of correlation between fasting blood glucose and hypertension in different age,sex and BMI population
| 血糖分组 | 性别 | 年龄 | BMI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <45岁 | ≥45岁 | <24.0 kg/m2 | ≥24.0 kg/m2 | |
| 全因死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 0.87(0.48~1.56) | 0.50(0.21~1.23) | 2.06(0.92~4.60) | 0.49(0.26~0.92) | 0.63(0.35~1.13) | 1.15(0.46~2.87) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 1.06(0.81~1.39) | 1.21(0.88~1.65) | 0.73(0.36~1.47) | 1.19(0.96~1.47) | 1.02(0.80~1.31) | 1.42(0.98~2.06) |
| DM | 1.39(0.92~2.09) | 2.01(1.27~3.20) | 2.41(0.93~6.29) | 1.57(1.13~2.16) | 1.45(1.11~2.43) | 1.67(1.01~2.76) |
| P趋势值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.945 | <0.001 | 0.027 | 0.034 |
| CVD死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 0.41(0.10~1.67) | 0.45(0.11~1.85) | 0.84(0.11~6.39) | 0.37(0.12~1.15) | 0.39(0.12~1.23) | 0.54(0.07~3.99) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 1.08(0.70~1.66) | 0.77(0.44~1.35) | 0.58(0.17~2.03) | 0.96(0.68~1.38) | 0.76(0.49~1.17) | 1.37(0.77~2.44) |
| DM | 0.94(0.44~1.98) | 1.73(0.84~3.55) | 1.34(0.17~4.51) | 1.24(0.73~2.11) | 1.27(0.65~2.46) | 1.14(0.50~2.62) |
| P趋势值 | 0.631 | 0.188 | 0.836 | 0.185 | 0.455 | 0.467 |
| 肿瘤死亡 | ||||||
| LFG | 1.03(0.25~4.36) | 0.95(0.12~7.19) | 3.34(0.69~16.13) | 0.42(0.06~3.05) | 0.84(0.20~3.51) | 1.96(0.24~5.97) |
| NFG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| IFG | 0.84(0.39~1.80) | 2.31(0.67~8.17) | 0.36(0.04~3.00) | 1.51(0.87~2.61) | 1.23(0.64~2.36) | 1.63(0.64~4.13) |
| DM | 2.07(0.83~5.13) | 2.39(1.11~5.14) | 1.67(0.66~3.89) | 6.62(1.61~9.76) | 2.69(1.11~6.52) | 1.95(0.52~7.30) |
| P趋势值 | 0.238 | 0.035 | 0.257 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.351 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition 2021[EB/OL]. (2021-12-06)[2024-12-30].
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations,1990-2021:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet,2024,403(10440):2162-2203. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00933-4.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
田园梦,井丽,阎涵,等. 辽宁省2017—2019年60岁及以上老年人群糖尿病患病况及其与死亡风险的相关性分析[J].中华流行病学杂志,2024,45(7):941-946. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20240111-00012.
|
| [11] |
张骥,周婕,吴延莉,等. 体质指数动态变化与代谢综合征发病关系前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国公共卫生,2023,39(7):851-856.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
中国血脂管理指南修订联合专家委员会. 中国血脂管理指南(2023年)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2023,38(3):237-271. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.03.001.
|
| [14] |
World Health Organization. ICD-10:international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems:tenth revision[M]. 2nd ed. Geneva:World Health Organization,2004.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
孙中明,梅冬蒙,缪丹丹,等. 2型糖尿病患者血糖控制与全因死亡风险的相关性分析[J]. 现代预学,2023,50(10):1729-1735. DOI:10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202207428.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] | |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [1] | 张磊, 张环宇, 陈凯悦, 励晓红, 郭莺. 空腹血糖与糖化血红蛋白对2型糖尿病与糖尿病前期的筛查效果及筛查策略研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4055-4061. |
| [2] | 陈慧龙, 廖芸楚, 刘育伟, 孔政辉, 黄兴辉, 徐嘉辉, 漆娜, 王远平, 梁文坚. 相对脂肪量与中老年人群心血管疾病之间的关联:一项基于CHARLS的横断面与纵向研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4047-4054. |
| [3] | 廖姣姣, 王照宇, 李兆基, 赵威, 詹思延, 王鹏, 陶立元. 非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇动态变化对颈动脉内中膜增厚的预测价值:一项双向性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(31): 3932-3941. |
| [4] | 苏晴, 徐曜, 李一航, 汪丽燕, 蔡业峰, 倪小佳. 脑卒中及其风险人群中医证候演变规律研究的方法学质量评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3694-3702. |
| [5] | 邓洁, 齐祺, 吴欣雨, 韩全乐, 李雷, 蒋越, 郁静, 吴若洁, 吴寿岭, 李康博. 血浆致动脉硬化指数与体检人群新发心力衰竭风险的队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(29): 3645-3652. |
| [6] | 丁香, 刘健, 陈晓露, 张先恒. 中草药降低类风湿关节炎合并链球菌感染患者再入院的风险:一项匹配队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3005-3012. |
| [7] | 杨继, 张垚, 赵英强, 张秋月. 中医三级防控模式对冠心病与脑卒中患者的管理效能评价:一项单中心前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2750-2761. |
| [8] | 梁恒妙, 黄锶哲, 陈玉婷, 刘策, 王慧君, 杜庆锋. 健康体检人群血尿酸水平与胰岛素抵抗程度关系的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2635-2642. |
| [9] | 陈巧巧, 苏萍, 赵颖颖, 逄锦宏, 施婕, 王雅倩, 李秋春, 何蕊言, 王玥, 陈学禹, 乔俊鹏, 迟蔚蔚. 三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与老年人群新发心脏代谢性共病的相关性:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2270-2277. |
| [10] | 梅景雁, 陈敏, 张列强, 潘昀熙, 王鑫, 赵小登, 詹玮, 刘涛, 王艺颖. 累积脂质蓄积指数与高血压发病相关性:一项前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2205-2211. |
| [11] | 安芹彧, 王艺颖, 张小丹, 张畑霖, 詹清清, 张福艳, 刘涛, 吴延莉. 社会经济地位、健康生活方式对心血管疾病影响的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2017-2024. |
| [12] | 张欣, 朱晴, 李南方. 脂质蓄积指数与高血压伴糖代谢异常患者发生慢性肾脏病风险的关系:一项回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(15): 1840-1846. |
| [13] | 张树静, 孙立新, 曹雨晴. 人乳头瘤病毒相关宫颈腺癌与非人乳头瘤相关宫颈腺癌的临床病理特征比较及预后研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1758-1764. |
| [14] | 倪雪桐, 阿合叶尔克·哈冷别克, 汤建敏, 曹腾瑞, 陶丽新, 郑德强, 李强, 韩玉梅, 杨兴华. 血糖异常与非酒精性脂肪肝病的双向因果关联研究:基于北京市健康管理队列[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1607-1613. |
| [15] | 李东幸, 牛紫敏, 王皓翔. 广州市黄埔区老年人群健康体检的回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1635-1641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





