中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (27): 3441-3446.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0331
收稿日期:2024-03-02
修回日期:2024-11-01
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-07-22
通讯作者:
邢彦
作者贡献:
刘振宇负责文章的构思与设计、统计学处理、结果的分析与解释、论文撰写;刘振宇、王江敏负责数据收集、整理;刘振宇、魏云鹏负责论文的修订;邢彦负责文章的质量控制及审校,对文章整体负责。
LIU Zhenyu, WEI Yunpeng, WANG Jiangmin, XING Yan*( )
)
Received:2024-03-02
Revised:2024-11-01
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-07-22
Contact:
XING Yan
摘要: 背景 睡眠时间与心力衰竭相关,但大多数研究为观察性研究,由于混杂因素过多难以进行因果关联的推断。 目的 采用两样本孟德尔随机化(MR)方法评估睡眠时间过短和睡眠时间过长与心力衰竭的因果关联。 方法 研究数据来自全基因组关联分析(GWAS)汇总数据库,其中睡眠时间过短包含106 192例样本,睡眠时间过长34 184例样本,分别选取合适的单核苷酸多态性(SNPs)作为工具变量,采用逆方差加权法(IVW)、加权中位数法和MR-Egger回归法等进行两样本MR分析,以OR值评估睡眠时间与心力衰竭之间的因果关联。采用异质性检验、水平多效性检验、leave-one-out检验等进行敏感性分析。 结果 筛选到与睡眠时间过短相关的SNPs有23个,与睡眠时间过长相关的SNPs有5个,IVW结果显示睡眠时间过短是心力衰竭发生的危险因素[OR(95%CI)=2.347(1.209~4.555),P=0.012];剔除存在水平多效性的SNP后进行敏感性分析,表明MR结果具有稳健性。 结论 睡眠时间过短与心力衰竭存在正向因果关联,即睡眠时间过短会增加心力衰竭的患病风险。
中图分类号:
| SNP | CHR | 位置 | EA | OA | EAF | β | SE | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11763750 | 7 | 2080114 | G | A | 0.814 346 | 0.007 212 | 0.001 234 | 5.10E-09 |
| rs1229762 | 7 | 114218582 | C | T | 0.335 499 | -0.007 239 | 0.001 017 | 1.00E-12 |
| rs12518468 | 5 | 7249696 | T | C | 0.671 544 | -0.005 885 | 0.001 021 | 8.50E-09 |
| rs12567114 | 1 | 98527951 | G | A | 0.724 600 | 0.006 325 | 0.001 077 | 4.10E-09 |
| rs12661667 | 6 | 41792545 | C | T | 0.736 505 | -0.006 022 | 0.001 087 | 2.80E-08 |
| rs12963463 | 18 | 53099093 | C | T | 0.299 425 | 0.007 114 | 0.001 060 | 1.90E-11 |
| rs13107325 | 4 | 103188709 | C | T | 0.925 472 | -0.013 268 | 0.001 828 | 2.50E-13 |
| rs1380703 | 2 | 57941287 | A | G | 0.616 469 | -0.006 764 | 0.001 005 | 1.60E-11 |
| rs1607227 | 11 | 28808617 | G | T | 0.704 938 | 0.006 369 | 0.001 055 | 1.50E-09 |
| rs17005118 | 4 | 82288564 | G | A | 0.735 064 | -0.006 482 | 0.001 087 | 2.50E-09 |
| rs17388803 | 15 | 48027204 | A | C | 0.894 352 | -0.009 826 | 0.001 587 | 6.50E-10 |
| rs2014830 | 3 | 50172397 | C | T | 0.698 128 | 0.005 786 | 0.001 050 | 2.70E-08 |
| rs205024 | 17 | 11227352 | C | T | 0.616 724 | 0.005 510 | 0.000 986 | 2.70E-08 |
| rs2186122* | 1 | 66470206 | A | T | 0.438 434 | -0.005 670 | 0.000 972 | 4.80E-09 |
| rs2517827 | 6 | 29832846 | C | A | 0.688 933 | -0.005 929 | 0.001 036 | 5.70E-09 |
| rs2820313 | 1 | 201870221 | A | G | 0.658 888 | -0.006 006 | 0.001 010 | 2.30E-09 |
| rs2863957 | 2 | 114089551 | C | A | 0.781 508 | 0.010 190 | 0.001 161 | 2.60E-18 |
| rs3776864 | 5 | 102327868 | A | C | 0.667 210 | 0.005 724 | 0.001 019 | 1.70E-08 |
| rs4585442 | 5 | 135508381 | A | G | 0.688 977 | -0.006 347 | 0.001 036 | 8.10E-10 |
| rs5757675 | 22 | 39838892 | G | T | 0.259 528 | 0.006 455 | 0.001 099 | 2.70E-09 |
| rs59779556 | 16 | 56227965 | T | G | 0.553 827 | 0.005 491 | 0.000 966 | 2.00E-08 |
| rs60882754* | 8 | 52886619 | A | T | 0.938 985 | 0.011 304 | 0.002 001 | 1.80E-08 |
| rs7524118 | 1 | 34736052 | T | C | 0.291 624 | -0.005 762 | 0.001 054 | 4.90E-08 |
| rs7939345 | 11 | 47980568 | T | G | 0.207 569 | 0.006 498 | 0.001 182 | 4.00E-08 |
| rs9321171 | 6 | 129848635 | C | T | 0.540 122 | 0.005 354 | 0.000 966 | 4.20E-08 |
| rs9367621* | 6 | 55040290 | T | A | 0.431 040 | 0.005 445 | 0.000 970 | 1.60E-08 |
表1 与睡眠时间不足相关联的SNPs的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of SNPs associated with insufficient sleep duration
| SNP | CHR | 位置 | EA | OA | EAF | β | SE | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11763750 | 7 | 2080114 | G | A | 0.814 346 | 0.007 212 | 0.001 234 | 5.10E-09 |
| rs1229762 | 7 | 114218582 | C | T | 0.335 499 | -0.007 239 | 0.001 017 | 1.00E-12 |
| rs12518468 | 5 | 7249696 | T | C | 0.671 544 | -0.005 885 | 0.001 021 | 8.50E-09 |
| rs12567114 | 1 | 98527951 | G | A | 0.724 600 | 0.006 325 | 0.001 077 | 4.10E-09 |
| rs12661667 | 6 | 41792545 | C | T | 0.736 505 | -0.006 022 | 0.001 087 | 2.80E-08 |
| rs12963463 | 18 | 53099093 | C | T | 0.299 425 | 0.007 114 | 0.001 060 | 1.90E-11 |
| rs13107325 | 4 | 103188709 | C | T | 0.925 472 | -0.013 268 | 0.001 828 | 2.50E-13 |
| rs1380703 | 2 | 57941287 | A | G | 0.616 469 | -0.006 764 | 0.001 005 | 1.60E-11 |
| rs1607227 | 11 | 28808617 | G | T | 0.704 938 | 0.006 369 | 0.001 055 | 1.50E-09 |
| rs17005118 | 4 | 82288564 | G | A | 0.735 064 | -0.006 482 | 0.001 087 | 2.50E-09 |
| rs17388803 | 15 | 48027204 | A | C | 0.894 352 | -0.009 826 | 0.001 587 | 6.50E-10 |
| rs2014830 | 3 | 50172397 | C | T | 0.698 128 | 0.005 786 | 0.001 050 | 2.70E-08 |
| rs205024 | 17 | 11227352 | C | T | 0.616 724 | 0.005 510 | 0.000 986 | 2.70E-08 |
| rs2186122* | 1 | 66470206 | A | T | 0.438 434 | -0.005 670 | 0.000 972 | 4.80E-09 |
| rs2517827 | 6 | 29832846 | C | A | 0.688 933 | -0.005 929 | 0.001 036 | 5.70E-09 |
| rs2820313 | 1 | 201870221 | A | G | 0.658 888 | -0.006 006 | 0.001 010 | 2.30E-09 |
| rs2863957 | 2 | 114089551 | C | A | 0.781 508 | 0.010 190 | 0.001 161 | 2.60E-18 |
| rs3776864 | 5 | 102327868 | A | C | 0.667 210 | 0.005 724 | 0.001 019 | 1.70E-08 |
| rs4585442 | 5 | 135508381 | A | G | 0.688 977 | -0.006 347 | 0.001 036 | 8.10E-10 |
| rs5757675 | 22 | 39838892 | G | T | 0.259 528 | 0.006 455 | 0.001 099 | 2.70E-09 |
| rs59779556 | 16 | 56227965 | T | G | 0.553 827 | 0.005 491 | 0.000 966 | 2.00E-08 |
| rs60882754* | 8 | 52886619 | A | T | 0.938 985 | 0.011 304 | 0.002 001 | 1.80E-08 |
| rs7524118 | 1 | 34736052 | T | C | 0.291 624 | -0.005 762 | 0.001 054 | 4.90E-08 |
| rs7939345 | 11 | 47980568 | T | G | 0.207 569 | 0.006 498 | 0.001 182 | 4.00E-08 |
| rs9321171 | 6 | 129848635 | C | T | 0.540 122 | 0.005 354 | 0.000 966 | 4.20E-08 |
| rs9367621* | 6 | 55040290 | T | A | 0.431 040 | 0.005 445 | 0.000 970 | 1.60E-08 |
| SNP | CHR | 位置 | EA | OA | EAF | β | SE | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10899257 | 11 | 76415209 | G | A | 0.855 527 | -0.005 638 | 0.001 031 | 4.60E-08 |
| rs147114641 | 17 | 43748492 | C | A | 0.774 030 | 0.005 689 | 0.000 868 | 4.90E-11 |
| rs17817288# | 16 | 53807764 | A | G | 0.518 127 | 0.004 188 | 0.000 727 | 8.90E-09 |
| rs3751046 | 11 | 122828342 | A | G | 0.852 658 | -0.005 775 | 0.001 027 | 2.00E-08 |
| rs6737318 | 2 | 114083120 | A | G | 0.778 159 | -0.006 380 | 0.000 877 | 3.40E-13 |
| rs7534398* | 1 | 7767464 | T | A | 0.798 618 | -0.005 079 | 0.000 908 | 2.10E-08 |
| rs75458655 | 11 | 118115331 | C | T | 0.977 027 | -0.016 731 | 0.002 423 | 5.40E-12 |
表2 与睡眠时间过长相关联的SNPs的基本信息
Table 2 Basic information of SNPs associated with excessive sleep duration
| SNP | CHR | 位置 | EA | OA | EAF | β | SE | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10899257 | 11 | 76415209 | G | A | 0.855 527 | -0.005 638 | 0.001 031 | 4.60E-08 |
| rs147114641 | 17 | 43748492 | C | A | 0.774 030 | 0.005 689 | 0.000 868 | 4.90E-11 |
| rs17817288# | 16 | 53807764 | A | G | 0.518 127 | 0.004 188 | 0.000 727 | 8.90E-09 |
| rs3751046 | 11 | 122828342 | A | G | 0.852 658 | -0.005 775 | 0.001 027 | 2.00E-08 |
| rs6737318 | 2 | 114083120 | A | G | 0.778 159 | -0.006 380 | 0.000 877 | 3.40E-13 |
| rs7534398* | 1 | 7767464 | T | A | 0.798 618 | -0.005 079 | 0.000 908 | 2.10E-08 |
| rs75458655 | 11 | 118115331 | C | T | 0.977 027 | -0.016 731 | 0.002 423 | 5.40E-12 |
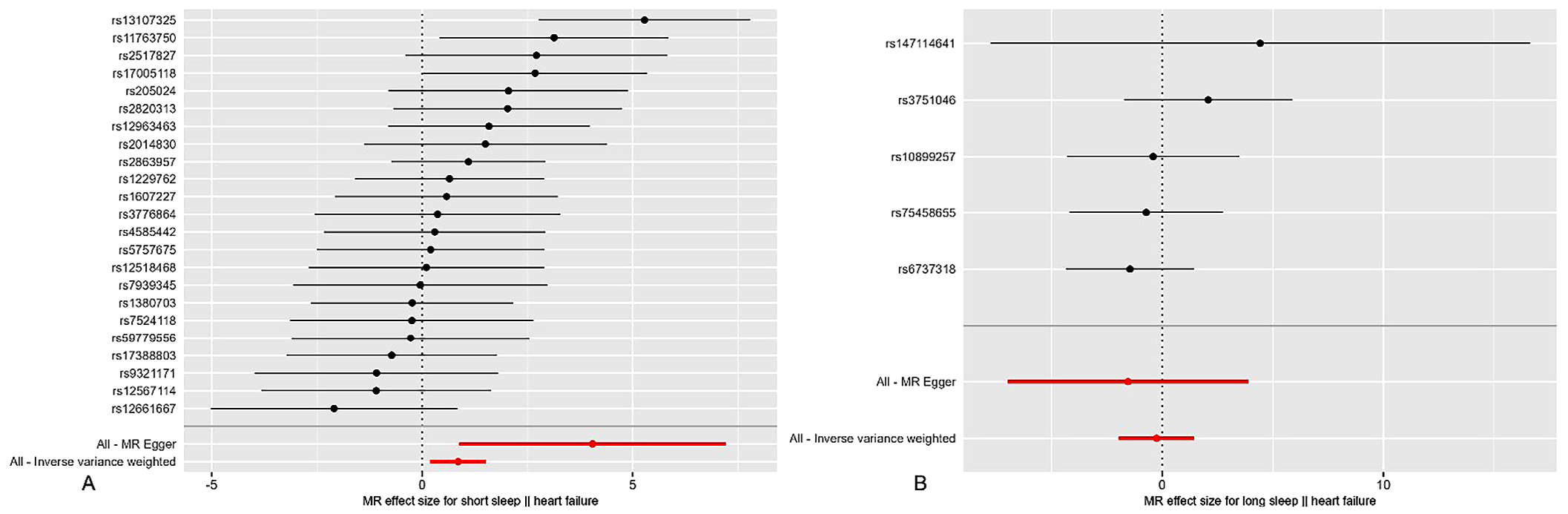
图1 睡眠时间与心力衰竭MR结果的森林图注:A表示睡眠不足与心力衰竭之间MR分析的森林图,B表示睡眠过长与心力衰竭之间MR分析的森林图。
Figure 1 Forest plot of MR results for the relationship between sleep duration and heart failure
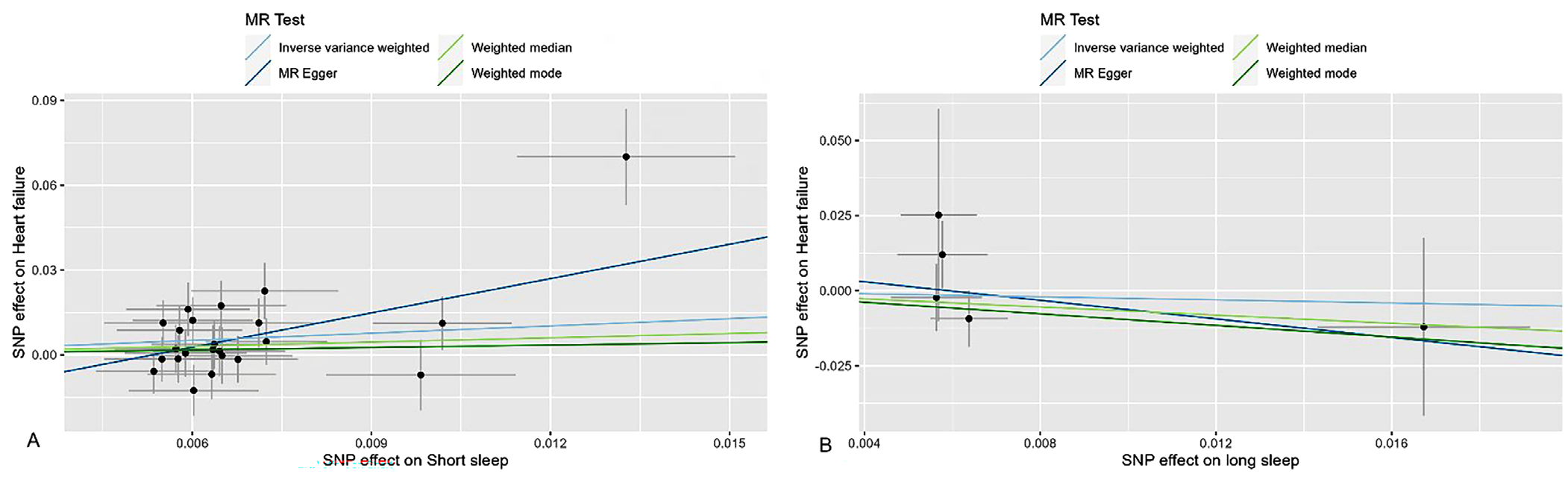
图2 睡眠时间与心力衰竭MR结果的散点图注:SNP effect on Short sleep=SNP对睡眠时间不足的影响,SNP effect on Heart failure=SNP对心力衰竭的影响;MR Test=孟德尔随机化检验Inverse variance weighted=逆方差加权,Weighted median=加权中位数,MR Egger=MR Egger回归,Weighted mode=加权众数;A表示睡眠不足与心力衰竭之间MR分析的散点图、B表示睡眠过长与心力衰竭之间MR分析的散点图。
Figure 2 Scatter plot of MR results for the relationship between sleep duration and heart failure
| 暴露因素 | 方法 | SNPs | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 睡眠时间不足 | ||||
| MR Egger | 23 | 57.304(2.415~1 359.486) | 0.021 | |
| Weighted median | 23 | 1.655(0.710~3.857) | 0.244 | |
| Inverse variance weighted | 23 | 2.347(1.209~4.555) | 0.012 | |
| Weighted mode | 23 | 1.334(0.349~5.102) | 0.677 | |
| 睡眠时间过长 | ||||
| MR Egger | 5 | 0.213(0.001~49.025) | 0.616 | |
| Weighted median | 5 | 0.508(0.066~3.901) | 0.515 | |
| Inverse variance weighted | 5 | 0.774(0.141~4.249) | 0.768 | |
| Weighted mode | 5 | 0.381(0.033~4.415) | 0.484 |
表3 睡眠时间与心力衰竭的孟德尔随机化分析结果
Table 3 Mendelian randomization analysis results for the relationship between sleep duration and heart failure
| 暴露因素 | 方法 | SNPs | OR(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 睡眠时间不足 | ||||
| MR Egger | 23 | 57.304(2.415~1 359.486) | 0.021 | |
| Weighted median | 23 | 1.655(0.710~3.857) | 0.244 | |
| Inverse variance weighted | 23 | 2.347(1.209~4.555) | 0.012 | |
| Weighted mode | 23 | 1.334(0.349~5.102) | 0.677 | |
| 睡眠时间过长 | ||||
| MR Egger | 5 | 0.213(0.001~49.025) | 0.616 | |
| Weighted median | 5 | 0.508(0.066~3.901) | 0.515 | |
| Inverse variance weighted | 5 | 0.774(0.141~4.249) | 0.768 | |
| Weighted mode | 5 | 0.381(0.033~4.415) | 0.484 |
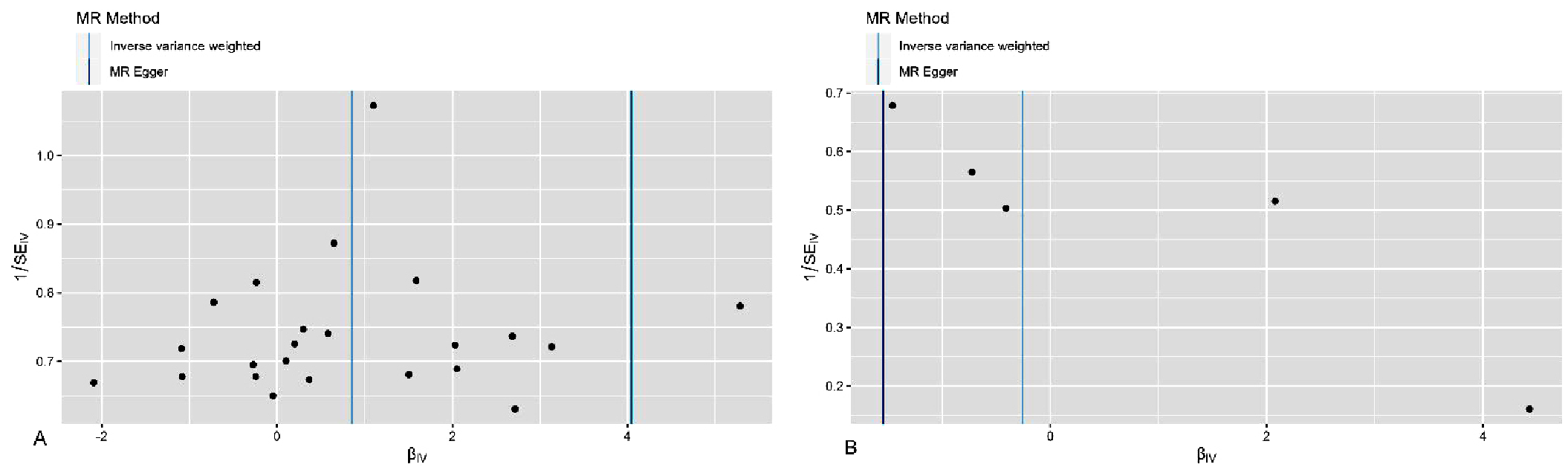
图4 睡眠时间与心力衰竭MR分析的漏斗图注:MR Method =孟德尔随机化方法;A表示睡眠不足与心力衰竭之间MR分析的漏斗图,B表示睡眠过长与心力衰竭之间MR分析的漏斗图。
Figure 4 Funnel plot for the MR analysis of sleep duration and heart failure
| [4] |
刘振宇,王江敏,魏云鹏,等. 北京市海淀区居民睡眠时间与糖尿病患病的相关性研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2022,49(18):3451-3456. DOI:10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202203360.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [1] | 马双双, 邢岩江, 张佳玮, 王婧. 心力衰竭中心脏能量代谢变化研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3831-3840. |
| [2] | 张红石, 曲子涵, 孙雪峰, 王宇峰, 丛德毓, 张野. 基于蛋白质组学技术分析腹部推拿对失眠大鼠下丘脑的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3399-3409. |
| [3] | 刘文洁, 孙煌, 罗薇, 陈旋, 彭云珠, 李锐洁, 马米尔. 可穿戴式心音心电远程监测设备用于心力衰竭的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3104-3109. |
| [4] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [5] | 韩冰, 杜淑珍, 孟晓雪, 张璐, 陈梓娴, 滕凤玲. 心力衰竭患者血浆骨膜蛋白水平与心肌纤维化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2979-2984. |
| [6] | 杨涵单, 乔雯, 何姝, 陈易, 童云梅. 接纳承诺疗法联合舍曲林对抑郁症青少年抑郁情绪、自杀意念及睡眠质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2813-2818. |
| [7] | 王爽, 吴树法, 令垚, 谭茜蔚, 曹汝岱, 曾慧婷, 孔丹莉, 丁元林, 于海兵. 基于代谢组学探究非脂质代谢物在肥胖与糖尿病视网膜病变间的中介作用:孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2625-2634. |
| [8] | 董浩铖, 郝潇, 安东, 李浩翰, 李树仁. 射血分数超常的心力衰竭的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2692-2696. |
| [9] | 扶蓉, 石磊, 何飞英. 中老年人糖尿病与抑郁状态共病:睡眠和运动及社交活动的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2491-2500. |
| [10] | 方莹莹, 林伟权, 孙敏英, 利耀辉, 刘览, 杨韵鸥, 陈嘉敏, 罗丽楹, 石磊, 刘慧. 屏幕时间对35岁及以上多重慢病患者睡眠质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2501-2507. |
| [11] | 何燕, 崔赛仙, 胡阳, 倪晴, 甘露路, 刘茜, 代安妮, 刘师节, 杨莉. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停相关高血压患者尿钠排泄及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2222-2227. |
| [12] | 宋小玲, 郑利, 金菊珍, 卯光艳, 商元昊, 胡瑾, 汪俊华, 王子云. 40~65岁人群睡眠质量与动脉硬化的关联性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2113-2118. |
| [13] | 贺婷, 李佳, 谭文彬. 循环系统疾病与继发性骨质疏松症的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2101-2112. |
| [14] | 汪蝶, 吴帮云, 谭存瑶, 谌世晖, 李游, 蒙玥, 王大珊, 胡瑾, 王子云, 汪俊华. 40~65岁人群睡眠效率与血脂异常关联性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1601-1606. |
| [15] | 黄传应, 廖晓阳, 杨荣, 李东泽, 张鹏, 贾禹, 刘力滴. 2024年《女性心脏急症管理》临床声明解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1427-1432. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





