中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 3573-3584.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0678
所属专题: 社区卫生服务最新研究合辑; 肿瘤最新文章合辑; 安宁疗护专题研究
胡婧伊1, 洪景1,*( ), 郭晓冬2, 张晓红1, 莫宁1, 周小翠2, 余钦2, 周敏华1, 孙艳1, 倪柳1, 石晓丽1, 苏小青1, 李玉倩1
), 郭晓冬2, 张晓红1, 莫宁1, 周小翠2, 余钦2, 周敏华1, 孙艳1, 倪柳1, 石晓丽1, 苏小青1, 李玉倩1
收稿日期:2022-11-16
修回日期:2023-05-16
出版日期:2023-10-05
发布日期:2023-06-26
通讯作者:
洪景
基金资助:
HU Jingyi1, HONG Jing1,*( ), GUO Xiaodong2, ZHANG Xiaohong1, MO Ning1, ZHOU Xiaocui2, YU Qin2, ZHOU Minhua1, SUN Yan1, NI Liu1, SHI Xiaoli1, SU Xiaoqing1, LI Yuqian1
), GUO Xiaodong2, ZHANG Xiaohong1, MO Ning1, ZHOU Xiaocui2, YU Qin2, ZHOU Minhua1, SUN Yan1, NI Liu1, SHI Xiaoli1, SU Xiaoqing1, LI Yuqian1
Received:2022-11-16
Revised:2023-05-16
Published:2023-10-05
Online:2023-06-26
Contact:
HONG Jing
摘要: 背景 社区干预是临终期肿瘤患者安宁疗护的重要组成部分,其在临终期肿瘤患者健康管理中的作用尚有待循证医学证据的支持。 目的 评价社区参与安宁疗护对临终期肿瘤患者的干预效果。 方法 于2022-05-22,采用Cochrane系统评价方法,以"社区""医疗模式""临终期肿瘤"等为检索词检索万方数据知识服务平台、中国知网、维普网,以"Community-based""Model of Palliative Care""Advanced Cancer""Quality of Life"等为检索词检索Cochrane Library、PubMed、Web of Science,以获取和社区参与安宁疗护干预效果相关的文献,研究类型设定为随机对照试验(RCT),检索时限设定为2007-01-01至2022-05-10。对符合纳入标准的RCT进行质量评价,提取有效信息进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入11项英文RCT(涉及患者2 356例),9项中文RCT(涉及患者1 238例)。Meta分析结果显示:与常规肿瘤护理相比,社区参与的安宁疗护能够改善临终期肿瘤患者的生活质量和症状严重程度,其可提高患者的慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表得分〔MD(95%CI)=3.77(0.83,6.71),P=0.01〕、癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分〔MD(95%CI)=12.53(2.36,22.69),P=0.02〕,降低患者的癌症治疗功能评价量表总分〔MD(95%CI)=-2.61(-3.53,-1.70),P<0.01〕、埃德蒙顿量表得分〔MD(95%CI)=-2.45(-4.70,-0.20),P=0.03〕。但是否能改善患者的抑郁症状、总体生存率存在争议,而对于入院率、住院天数/次数等经济学指标的作用有待进一步研究。 结论 社区参与的安宁疗护可以改善临终期肿瘤患者的生活质量和症状严重程度,但在改善抑郁、提高生存率、降低医疗成本方面的作用有待进一步研究。
| 第一作者 | 年份(年) | 国家(省份) | 干预措施 | 干预模式 | 参与人员 | 样本量 | 随访时间(月) | 随访频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | ||||||||
| BAKITAS[ | 2009 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 161 | 161 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| BAKITAS[ | 2015 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:①+②(晚介入)+③ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 104 | 103 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| ZIMMERMANN[ | 2014 | 加拿大 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 228 | 233 | 0~4 | 每2个月1次 |
| MCCORKLE[ | 2015 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 66 | 80 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| MALTONI[ | 2016 | 意大利 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 107 | 100 | 0~20 | NA |
| TATTERSALL[ | 2014 | 澳大利亚 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 60 | 60 | 0~18 | 每6个月1次 |
| MATTHEW[ | 2013 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A(限NSCLC晚期辅助化疗后,三级综合医院主导)+B+C | 65 | 64 | 0~4 | 每月1次 |
| GROENVOLD[ | 2017 | 丹麦 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 145 | 152 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| VANBUTSELE[ | 2018 | 比利时 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 92 | 94 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| FRANCIOSI[ | 2019 | 意大利 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 142 | 139 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| ENRIQUE[ | 2020 | 墨西哥 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C+D(加强双向转诊流程) | 66 | 67 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 范娟宁[ | 2018 | 中国四川省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(社区-家庭一体化居家姑息照护) | 36 | 36 | 0~12 | 每月1次 |
| 宋舒娟[ | 2021 | 中国河南省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(晚期肝癌) | 41 | 41 | 0~12 | 每月1次 |
| 张建伟[ | 2012 | 中国北京市 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 92 | 88 | 0~6 | NA |
| 王君[ | 2018 | 中国江苏省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C("生物-心理-社会"干预模式,包含中医药治疗) | 32 | 32 | 0~6 | 每月1次 |
| 朱静[ | 2019 | 中国上海市 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(晚期结肠癌) | 107 | 100 | 0~6 | NA |
| 赵洁[ | 2020 | 中国湖北省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 60 | 60 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 王素平[ | 2019 | 中国安徽省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 50 | 50 | 0~6 | 每月1次 |
| 曾主平[ | 2017 | 中国广东省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 100 | 100 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 陈莉[ | 2017 | 中国四川省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 40 | 40 | 0~12 | 每3个月1次 |
| 第一作者 | 观察指标 | 结果 | 文献质量评分(分) | ||||||
| BAKITAS[ | (1)慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表;(2)埃德蒙顿症状量表;(3)流行病学研究中心抑郁量表;(4)住院天数,重症监护病房及急诊住院天数;(5)总生存率(K-P生存曲线);(6)中位生存期 | 干预组更优:(1)、(3)、(6) 两组无差异:(2)、(4)、(5) | 8 | ||||||
| BAKITAS[ | (1)流行病学研究中心抑郁量表;(2)慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表;(3)生命晚期生活质量量表;(4)总生存率(K-P生存曲线);(5)生存时间中位数;(6)住院天数,重症监护病房及急诊住院天数,急诊就诊次数,14 d内接受化疗次数的每月下降率,死亡地点 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2) 两组无差异:(3)、(4)、(5)、(6) | 7 | ||||||
| ZIMMERMANN[ | (1)慢性病功能评价量表-幸福感亚表;(2)生命晚期生活质量量表;(3)埃德蒙顿症状量表;(4)临终期肿瘤护理家庭满意度问卷-16;(5)肿瘤康复评估系统医患互动亚表 | 第3个月〔干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(4)两组无差异:(3)、(5)〕 第16周〔干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)〕 | 7 | ||||||
| MCCORKLE[ | (1)抑郁症状自测量表;(2)抑郁症筛查量表;(3)社会依赖度量表加强版;(4)生活质量简易量表-12;(5)功能评价量表-总表;(6)医院焦虑抑郁量表;(7)患者对疾病不确定性的自我认知量表;(8)慢性病自我管理量表 | 全程〔两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3)、(5)、(6)〕 第1个月〔干预组更优:(7)、(8)〕 第3个月〔干预组更优:(4)、(7)〕 | 5 | ||||||
| MALTONI[ | (1)医院焦虑抑郁量表;(2)功能评价量表-肝癌分表;(3)疗效指数;(4)短期内死亡率;(5)就医率;(6)住院天数,死亡前就诊次数,死亡前住院天数;(7)支持治疗接受率和死亡地点 | 第3个月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(7) 干预组更优:(3)、(4)、(5)、(6) | 7 | ||||||
| TATTERSALL[ | (1)麦吉尔生活质量问卷;(2)支持治疗需求总分;(3)鹿特丹症状量表;(4)支持治疗接受率;(5)死亡地点;(6)确诊后中位生存时间 | 第1、3、6、9、12月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)、(5) 干预组更优:(6) 对照组更优:(1)疼痛和食欲不振症状 | 6 | ||||||
| MATTHEW[ | 功能评价量表-总表 | 第4周:干预组更优 第27周:两组无差异 | 6 | ||||||
| GROENVOLD[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表;(2)总生存率(K-P生存曲线) | 0~8周: 干预组更优:(1)呕吐症状 两组无差异:(1)、(2) | 7 | ||||||
| VANBUTSELE[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表;(2)麦吉尔生活质量问卷 | 第3个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2) | 7 | ||||||
| FRANCIOSI[ | (1)功能评价量表-总表;(2)预后相关因素 | 第3、6个月: 干预组更优:(1) | 6 | ||||||
| ENRIQUE[ | (1)功能评价量表-总表;(2)抑郁症筛查量表-2;(3)泛性焦虑筛查量表-2;(4)支持治疗满意度量表;(5)PC治疗就诊率 | 第3个月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3) 干预组更优:(1)、(4)、(5) | 5 | ||||||
| 范娟宁[ | 癌症患者生命质量测定量表 | 干预组更优 | 4 | ||||||
| 宋舒娟[ | (1)生活质量简易量表-36;(2)抑郁症状自测量表;(3)并发症发生率;(4)干预满意度 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4) | 5 | ||||||
| 张建伟[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)经济状况亚组以外得分 无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 6 | ||||||
| 王君[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)疼痛评分 | 干预组更优:(1);(2)躯体功能(躯体功能中疲倦、疼痛、恶心呕吐、失眠、食欲),社会功能,情绪功能;(3) 两组无差异:(2)躯体功能(其余指标)、角色功能、认知功能、经济状况 | 5 | ||||||
| 朱静[ | (1)自觉负担指数;(2)简易自测焦虑和抑郁量表;(3)干预满意度 | 第6个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 6 | ||||||
| 赵洁[ | (1)生活质量简易量表-36;(2)简易自测焦虑和抑郁量表;(3)匹兹堡睡眠质量指数 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 6 | ||||||
| 王素平[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)疼痛评分 | 干预组更优:(1)、(3) 两组无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 5 | ||||||
| 曾主平[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)干预满意度 | 第3个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)除经济状况亚组外得分、(3) 两组无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 5 | ||||||
| 陈莉[ | (1)疾病控制情况;(2)自拟生活质量;(3)住院相关事项情况(发病次数、住院天数、住院次数、医疗费用) | 第3、6个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 4 | ||||||
表1 纳入研究的基本特征和质量评价结果
Table 1 Basic characteristics and quality evaluation results of the included studies
| 第一作者 | 年份(年) | 国家(省份) | 干预措施 | 干预模式 | 参与人员 | 样本量 | 随访时间(月) | 随访频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | ||||||||
| BAKITAS[ | 2009 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 161 | 161 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| BAKITAS[ | 2015 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:①+②(晚介入)+③ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 104 | 103 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| ZIMMERMANN[ | 2014 | 加拿大 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 228 | 233 | 0~4 | 每2个月1次 |
| MCCORKLE[ | 2015 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 66 | 80 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| MALTONI[ | 2016 | 意大利 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 107 | 100 | 0~20 | NA |
| TATTERSALL[ | 2014 | 澳大利亚 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 60 | 60 | 0~18 | 每6个月1次 |
| MATTHEW[ | 2013 | 美国 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A(限NSCLC晚期辅助化疗后,三级综合医院主导)+B+C | 65 | 64 | 0~4 | 每月1次 |
| GROENVOLD[ | 2017 | 丹麦 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 145 | 152 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| VANBUTSELE[ | 2018 | 比利时 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 92 | 94 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| FRANCIOSI[ | 2019 | 意大利 | 干预组:①+②(早介入)+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 142 | 139 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| ENRIQUE[ | 2020 | 墨西哥 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C+D(加强双向转诊流程) | 66 | 67 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 范娟宁[ | 2018 | 中国四川省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(社区-家庭一体化居家姑息照护) | 36 | 36 | 0~12 | 每月1次 |
| 宋舒娟[ | 2021 | 中国河南省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(晚期肝癌) | 41 | 41 | 0~12 | 每月1次 |
| 张建伟[ | 2012 | 中国北京市 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 92 | 88 | 0~6 | NA |
| 王君[ | 2018 | 中国江苏省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C("生物-心理-社会"干预模式,包含中医药治疗) | 32 | 32 | 0~6 | 每月1次 |
| 朱静[ | 2019 | 中国上海市 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C(晚期结肠癌) | 107 | 100 | 0~6 | NA |
| 赵洁[ | 2020 | 中国湖北省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 60 | 60 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 王素平[ | 2019 | 中国安徽省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 50 | 50 | 0~6 | 每月1次 |
| 曾主平[ | 2017 | 中国广东省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 医联体 | A+B+C | 100 | 100 | 0~3 | 每月1次 |
| 陈莉[ | 2017 | 中国四川省 | 干预组:①+②+③ 对照组:④ | 多机构协作 | A+B+C | 40 | 40 | 0~12 | 每3个月1次 |
| 第一作者 | 观察指标 | 结果 | 文献质量评分(分) | ||||||
| BAKITAS[ | (1)慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表;(2)埃德蒙顿症状量表;(3)流行病学研究中心抑郁量表;(4)住院天数,重症监护病房及急诊住院天数;(5)总生存率(K-P生存曲线);(6)中位生存期 | 干预组更优:(1)、(3)、(6) 两组无差异:(2)、(4)、(5) | 8 | ||||||
| BAKITAS[ | (1)流行病学研究中心抑郁量表;(2)慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表;(3)生命晚期生活质量量表;(4)总生存率(K-P生存曲线);(5)生存时间中位数;(6)住院天数,重症监护病房及急诊住院天数,急诊就诊次数,14 d内接受化疗次数的每月下降率,死亡地点 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2) 两组无差异:(3)、(4)、(5)、(6) | 7 | ||||||
| ZIMMERMANN[ | (1)慢性病功能评价量表-幸福感亚表;(2)生命晚期生活质量量表;(3)埃德蒙顿症状量表;(4)临终期肿瘤护理家庭满意度问卷-16;(5)肿瘤康复评估系统医患互动亚表 | 第3个月〔干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(4)两组无差异:(3)、(5)〕 第16周〔干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)〕 | 7 | ||||||
| MCCORKLE[ | (1)抑郁症状自测量表;(2)抑郁症筛查量表;(3)社会依赖度量表加强版;(4)生活质量简易量表-12;(5)功能评价量表-总表;(6)医院焦虑抑郁量表;(7)患者对疾病不确定性的自我认知量表;(8)慢性病自我管理量表 | 全程〔两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3)、(5)、(6)〕 第1个月〔干预组更优:(7)、(8)〕 第3个月〔干预组更优:(4)、(7)〕 | 5 | ||||||
| MALTONI[ | (1)医院焦虑抑郁量表;(2)功能评价量表-肝癌分表;(3)疗效指数;(4)短期内死亡率;(5)就医率;(6)住院天数,死亡前就诊次数,死亡前住院天数;(7)支持治疗接受率和死亡地点 | 第3个月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(7) 干预组更优:(3)、(4)、(5)、(6) | 7 | ||||||
| TATTERSALL[ | (1)麦吉尔生活质量问卷;(2)支持治疗需求总分;(3)鹿特丹症状量表;(4)支持治疗接受率;(5)死亡地点;(6)确诊后中位生存时间 | 第1、3、6、9、12月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)、(5) 干预组更优:(6) 对照组更优:(1)疼痛和食欲不振症状 | 6 | ||||||
| MATTHEW[ | 功能评价量表-总表 | 第4周:干预组更优 第27周:两组无差异 | 6 | ||||||
| GROENVOLD[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表;(2)总生存率(K-P生存曲线) | 0~8周: 干预组更优:(1)呕吐症状 两组无差异:(1)、(2) | 7 | ||||||
| VANBUTSELE[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表;(2)麦吉尔生活质量问卷 | 第3个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2) | 7 | ||||||
| FRANCIOSI[ | (1)功能评价量表-总表;(2)预后相关因素 | 第3、6个月: 干预组更优:(1) | 6 | ||||||
| ENRIQUE[ | (1)功能评价量表-总表;(2)抑郁症筛查量表-2;(3)泛性焦虑筛查量表-2;(4)支持治疗满意度量表;(5)PC治疗就诊率 | 第3个月: 两组无差异:(1)、(2)、(3) 干预组更优:(1)、(4)、(5) | 5 | ||||||
| 范娟宁[ | 癌症患者生命质量测定量表 | 干预组更优 | 4 | ||||||
| 宋舒娟[ | (1)生活质量简易量表-36;(2)抑郁症状自测量表;(3)并发症发生率;(4)干预满意度 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3)、(4) | 5 | ||||||
| 张建伟[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)经济状况亚组以外得分 无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 6 | ||||||
| 王君[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)疼痛评分 | 干预组更优:(1);(2)躯体功能(躯体功能中疲倦、疼痛、恶心呕吐、失眠、食欲),社会功能,情绪功能;(3) 两组无差异:(2)躯体功能(其余指标)、角色功能、认知功能、经济状况 | 5 | ||||||
| 朱静[ | (1)自觉负担指数;(2)简易自测焦虑和抑郁量表;(3)干预满意度 | 第6个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 6 | ||||||
| 赵洁[ | (1)生活质量简易量表-36;(2)简易自测焦虑和抑郁量表;(3)匹兹堡睡眠质量指数 | 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 6 | ||||||
| 王素平[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)疼痛评分 | 干预组更优:(1)、(3) 两组无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 5 | ||||||
| 曾主平[ | (1)癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分;(2)癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能、角色功能、情绪功能、认知功能、社会功能、经济状况亚组得分;(3)干预满意度 | 第3个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)除经济状况亚组外得分、(3) 两组无差异:(2)经济状况亚组得分 | 5 | ||||||
| 陈莉[ | (1)疾病控制情况;(2)自拟生活质量;(3)住院相关事项情况(发病次数、住院天数、住院次数、医疗费用) | 第3、6个月: 干预组更优:(1)、(2)、(3) | 4 | ||||||
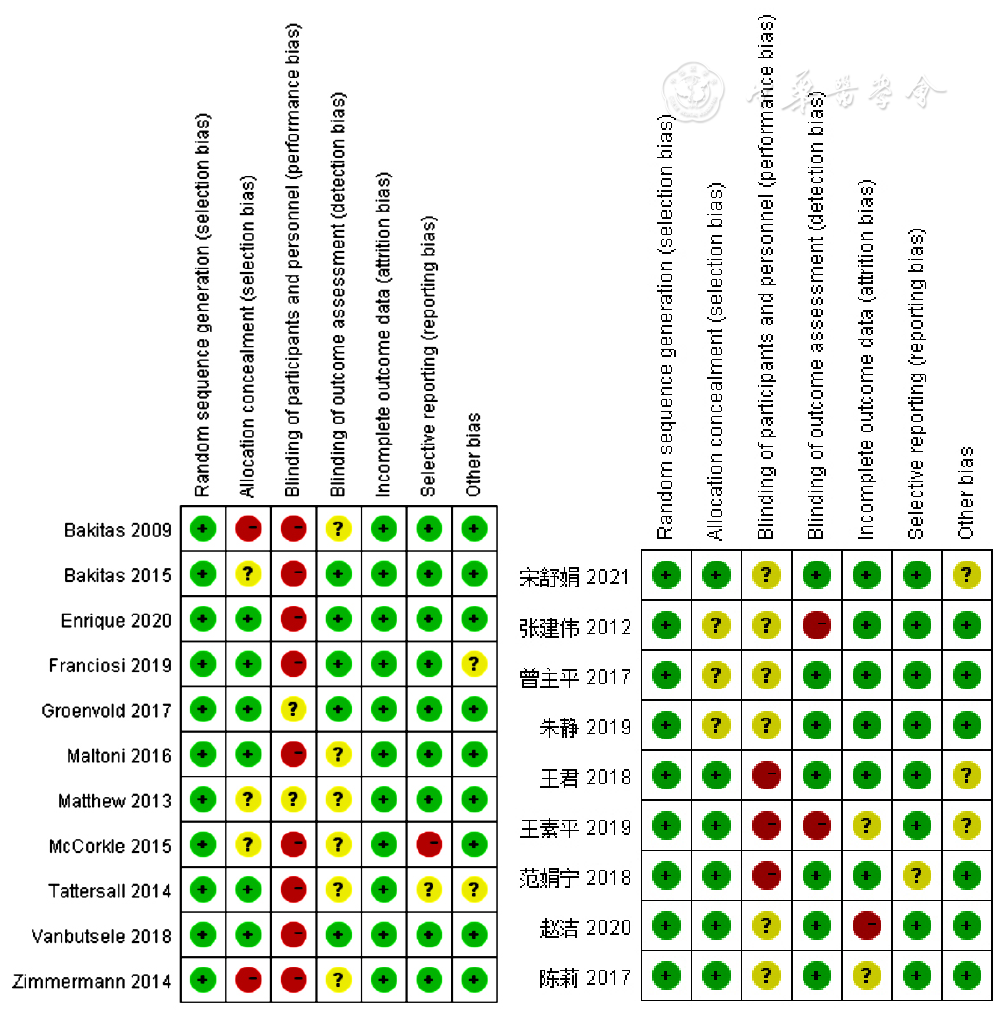
图2 21篇RCT的偏倚风险注:Random sequence generation(selection bias)=随机序列生成(选择偏倚),Allocation concealment(selection bias)=分组保密性(选择偏倚),Blinding of participants and personnel(performance bias)=受试者和工作人员盲法(操作偏倚),Blinding of outcome assessment(detection bias)=结果分析盲法(检测偏倚),Incomplete outcome data(attrition bias)=结果数据不完整(损耗偏倚),Selective reporting(reporting bias)=选择性报道(报告偏倚),Other bisa=其他偏倚;-表示high risk(高风险),+表示low risk(低风险),?表示unclear risk(风险不详)。
Figure 2 Risk of bias in 21 RCTs
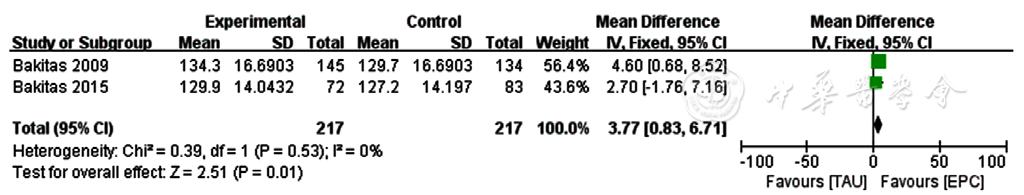
图3 两组患者慢性病支持治疗功能评价量表得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 3 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Palliative Care scale scores between the two groups
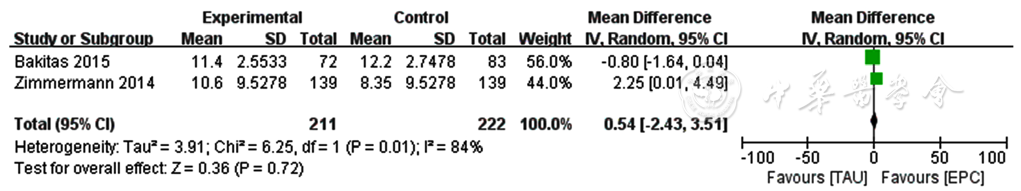
图4 两组患者生命晚期生活质量量表得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 4 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
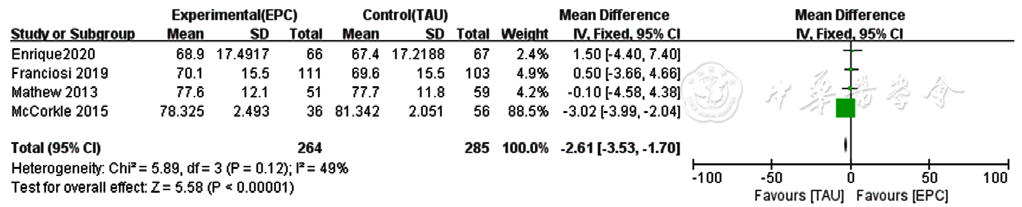
图5 两组患者癌症治疗功能评价量表-总表得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 5 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale total scores between the two groups
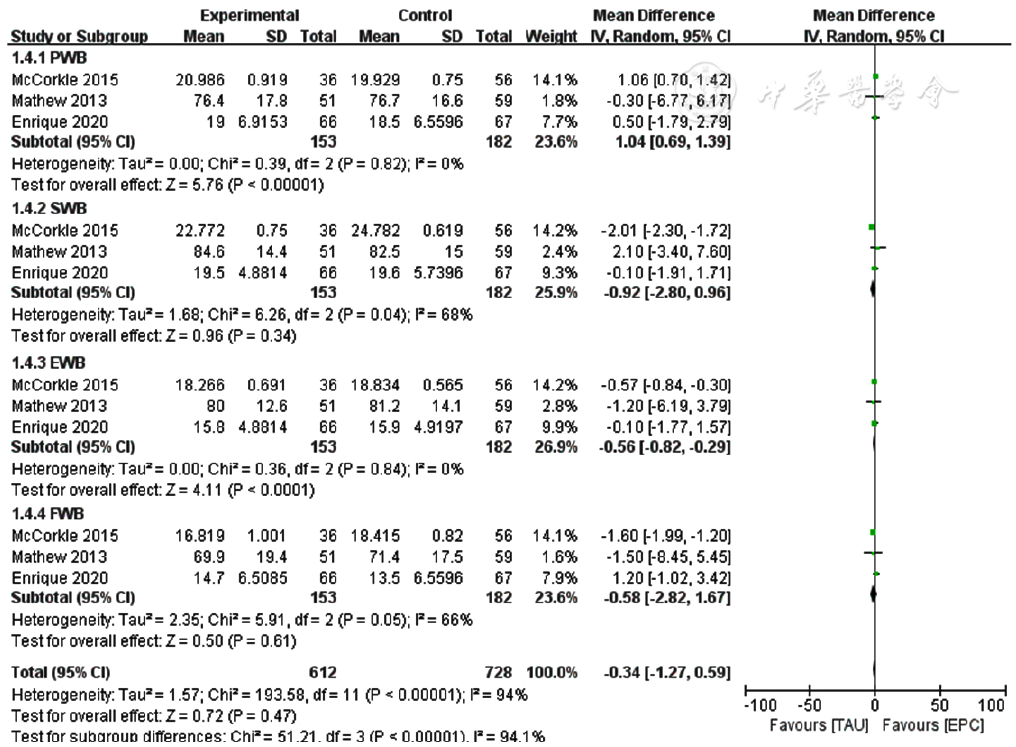
图6 两组患者癌症治疗功能评价量表-维度得分比较的Meta分析森林图注:PWB=躯体状况维度,SWB=社会家庭状况维度,EWB=情感状况维度,FWB=功能状况维度。
Figure 6 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale-subgroup analysis scores between the two groups
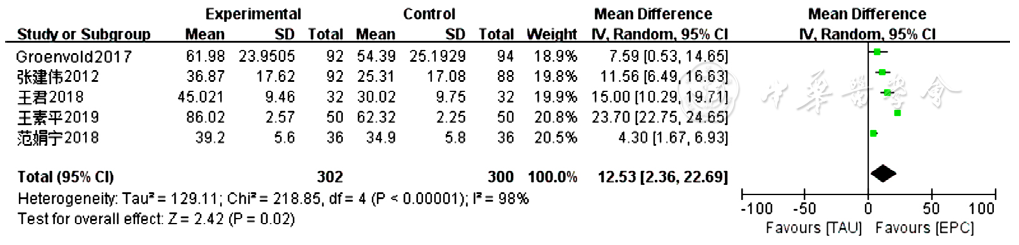
图8 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表总分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 8 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing total score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
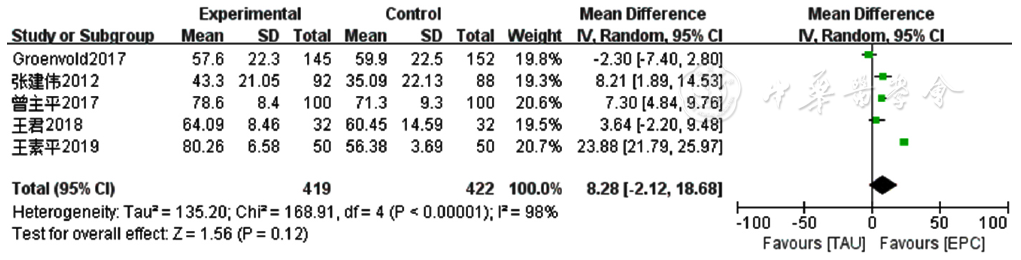
图9 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表躯体功能评分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 9 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing physical function score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
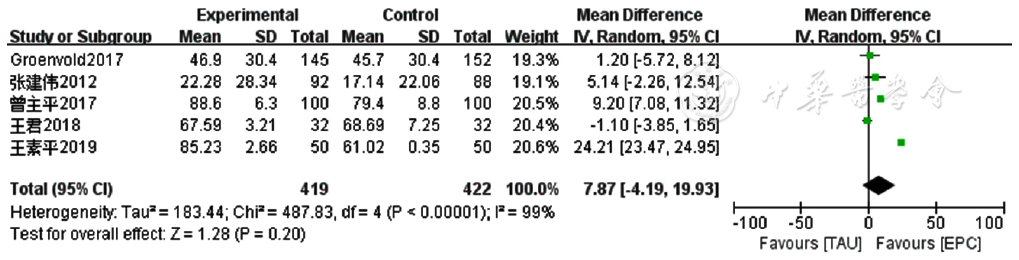
图10 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表角色功能评分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 10 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing role function score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
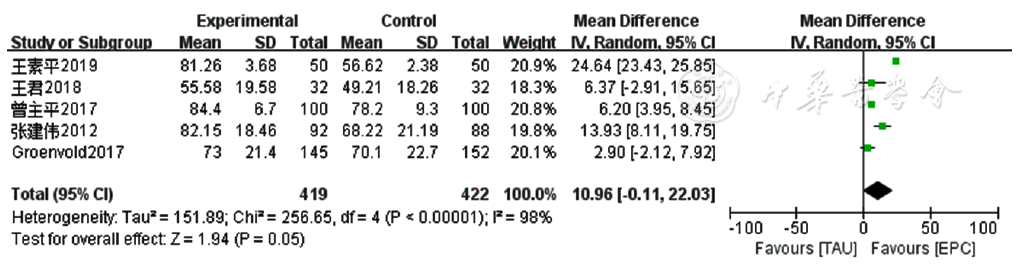
图11 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表情绪功能评分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 11 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing emotional function score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
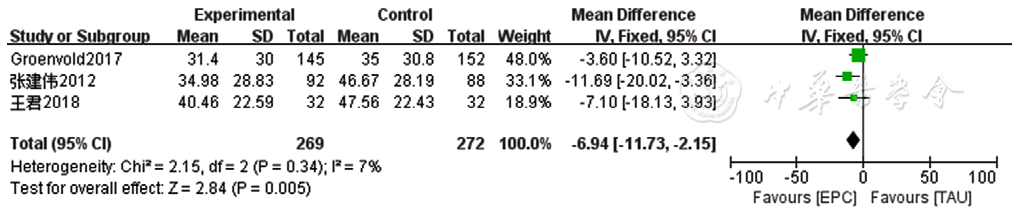
图12 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表疼痛症状得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 12 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing severity of pain score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
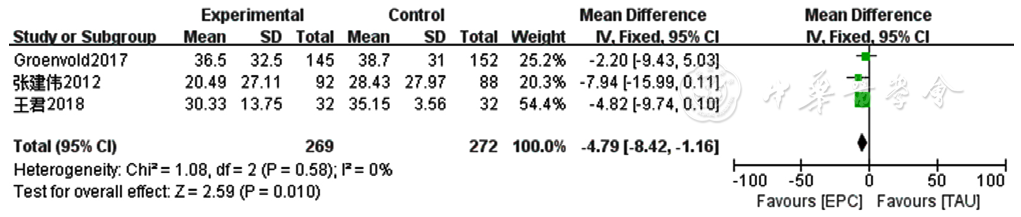
图13 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表气促症状得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 13 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing shortness of breath score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale
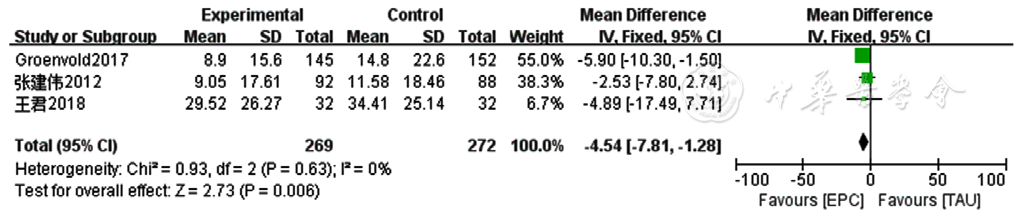
图14 两组患者癌症患者生命质量测定量表恶心症状得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 14 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing severity of nausea score of Quality of Life at the End of Life-Cancer Scale scores between the two groups
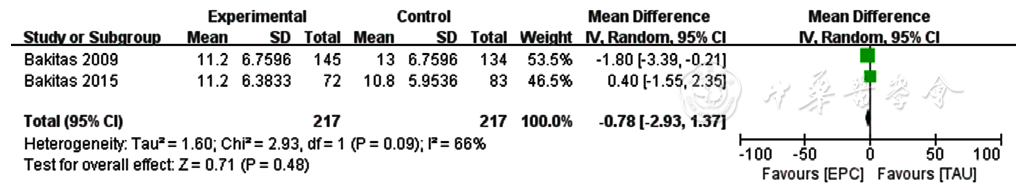
图17 两组患者流行病学研究中心抑郁量表得分比较的Meta分析森林图
Figure 17 Meta-analysis forest plot comparing Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale scores between the two groups
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
何小梅,樊晋川,朱昌明,等. 恶性肿瘤患者生存质量的调查研究[J]. 中华医院管理杂志,2006,22(3):192-196.
|
| [4] |
National Cancer Institution Dictionary. Definition of advanced cancer[EB/OL].(2015-12-04)[2022-05-16].
|
| [5] |
World Health Organization. Definition of palliative care[EB/OL].(2020-08-06)[2022-05-16].
|
| [6] |
卢培培,张楠,王家林. 中国恶性肿瘤健康管理现状研究[J]. 中国公共卫生管理,2019,35(6):760-763.
|
| [7] |
史晓晓,宋徽江,葛许华,等. 基于双向转诊的城郊社区卫生服务中心差异性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(1):30-35. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.269.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
马捷,刘莹,钟来平,等. Jadad量表与Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照试验质量评价中的应用与比较[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(5):417-422.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
何寒青,陈坤. Meta分析中的异质性检验方法[J]. 中国卫生统计,2006,23(6):486-487,490.
|
| [13] |
贾博颖,周双,周颖,等. 居家药学服务在多重用药老年患者中效果的系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(2):189-195. DOI:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.02.15.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
赵洁. 临终关怀与家庭延续护理对肺癌晚期患者生活质量及睡眠质量的影响[J]. 当代护士,2020,27(9):69-71. DOI:10.19791/j.cnki.1006-6411.2020.25.031.
|
| [27] |
陈莉. 晚期癌症患者社区-家庭一体化居家姑息照护的健康教育效果[J]. 医学信息,2017,30(3):211-212.
|
| [28] |
范娟宁,冯延延,李钰,等. 对晚期癌症患者实施社区-家庭一体化居家姑息照护的健康教育效果[J]. 当代护士,2018,25(1):143-145. DOI:10.11876/mimt201606032.
|
| [29] |
宋舒娟,周方园,刘建敏. 医院—社区—家庭一体化护理模式对肝癌介入治疗患者生活质量的影响[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复,2021,28(5):631-634. DOI:10.13455/j.cnki.cjcor.2021.05.29.
|
| [30] |
王君,徐力. 社区管理模式对中晚期肺癌癌痛患者生活质量的研究[J]. 中医临床研究,2018,10(5):24-26. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2018.05.008.
|
| [31] |
王素平. 医联体协助社区管理模式对中晚期肺癌癌痛患者生活质量及生存质量的影响[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(s2):13-15.
|
| [32] |
朱静,黄中正,吉守艳. 居家宁养全科团队服务在晚期结肠癌患者中初步应用效果评估[J]. 山西医药杂志,2019,48(3):378-380. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2019.03.046.
|
| [33] |
曾主平,江卫群,陈碧. 基于社区给予癌症晚期患者社区干预对患者满意度及生活质量提高[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2017,17(4):128-130. DOI:10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2017.04.082.
|
| [34] |
张建伟,亢玺刚,张宏艳,等. 社区肿瘤患者姑息治疗效果观察[J]. 河北医学,2012,18(11):1570-1572. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2012.11.019.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
常伟,孙亮,陈旻洁,等. 晚期肿瘤患者生活质量的影响比较:基于舒缓病房与居家舒缓医疗两种模式的研究[J]. 中国医学伦理学,2018,31(3):352-355.
|
| [39] |
张莉,邵志坚,陈琼英,等. IKAP护理模式对提高晚期肿瘤患者生活质量的研究[J]. 国际医药卫生导报,2013,19(14):2106-2109. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-1245.2013.14.011.
|
| [40] |
顾益玮,章璞,刘文娟,等. 结合微信群的团体认知行为干预对社区癌症患者生活质量的影响[J]. 上海预防医学,2018,30(6):487-492. DOI:10.19428/j.cnki.sjpm.2018.18629.
|
| [41] |
沙磊. 中医音乐疗法在临终关怀肿瘤病人郁证中的应用研究进展[J]. 中文科技期刊数据库(全文版)医药卫生,2017,2(1):153.
|
| [42] |
袁珺,郁文恺,毛懿雯. 中药贴敷法治疗肝肺癌晚期疼痛的临床观察[J]. 中国中医药科技,2020,27(6):932-933.
|
| [43] |
宁创霞. 含毒性中药材对肿瘤患者抗肿瘤及免疫调节作用的影响[J]. 社区医学杂志,2015,13(22):34-36.
|
| [44] |
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [3] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [4] | 韩笑, 李奇遇, 葛蒲, 范思园, 刘迪玥, 吴一波, 张清霜. 高血压患者行为生活方式对生命质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [5] | 纪冰, 姜嘟嘟, 陈晨, 郑艳玲, 石建伟, 方力争, 杜雪平. 分级诊疗背景下带状疱疹社区全科诊疗路径构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3110-3118. |
| [6] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [7] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [8] | 吴越, 王雪彤, 柯碧莲. 近视性黄斑病变低视力患者视觉相关生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [9] | 王笑林, 李秋月, 周彦君, 张金辉, 梁涛. 转移性结直肠癌患者呋喹替尼治疗相关心血管毒性发生率和风险的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [10] | 石佳瑞, 王梓力, 张薛晴, 宋玉磊, 徐桂华, 柏亚妹. 南京市社区认知症服务中心认知初步筛查服务开展现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [11] | 陈友兰, 蓝彦琦, 吴阿华, 张海霞, 黄健康, 郭志南. "三师共管"家庭医生签约服务对老年高血压患者的健康管理效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2769-2775. |
| [12] | 文敏, 周永玲, 刘静静, 蒋苛晴, 刘娟, 朱晓丹. 基于移动医疗APP的认知补偿训练对稳定期精神分裂症患者的干预效果与机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2819-2825. |
| [13] | 马盼盼, 王思静, 游娜, 丁大法, 鲁一兵. Danuglipron与Orforglipron治疗2型糖尿病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [14] | 胡婉琴, 余深艳, 曹学华, 向凤, 贾钰. 中国儿童性早熟影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2661-2671. |
| [15] | 阿迪力·吐尔孙, 程刚. 非奈利酮治疗2型糖尿病肾病有效性和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2686-2691. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





