中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 3573-3582.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2025.0051
收稿日期:2025-03-25
修回日期:2025-07-24
出版日期:2025-10-05
发布日期:2025-08-28
通讯作者:
沈珑慧
作者贡献:
李珊珊提出概念构思,研究方法,软件应用,数据整理,文章撰写,审阅与修改;沈珑慧负责调查研究、监督指导及文章审校,对文章整体负责。
本文首次刊登于Precision Medication 2024年第2期(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prmedi.2025.100016)
基金资助:
LI Shanshan1,2, SHEN Longhui2,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Revised:2025-07-24
Published:2025-10-05
Online:2025-08-28
Contact:
SHEN Longhui
摘要: 背景 子宫内膜异位症(EMT)为妇科常见疾病,坤泰胶囊能改善EMT相关症状,但其药理和分子机制尚缺系统阐明。 目的 探讨坤泰胶囊治疗EMT中的作用机制。 方法 于2024-01-01—04-31,通过中药系统药理学分析平台(TCMSP)、中药分子机制生物信息学分析工具(BATMAN-TCM)、Pubchem和SwissTargetPrediction数据库中获取坤泰胶囊的活性成分及对应靶点。从GeneCards、DisGeNET、TTD、OMIM和Drugbank数据库中检索与EMT相关的疾病靶点,使用维恩图获得坤泰胶囊和EMT的交集靶点。运用Cytoscape构建疾病-成分-靶点网络,并使用STRING数据库构建共同靶蛋白-蛋白相互作用(PPI)网络图。采用Cytoscape对PPI网络进行拓扑分析,筛选核心靶点。利用DAVID数据库进行基因本体(GO)富集和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路分析。使用AutoDockTools进行分子对接。使用GROMACS分子动力学模拟进一步验证最佳结合能量模型的稳定性。 结果 共确定了182个共同靶点。核心成分包括谷甾醇、二甲氧基黄酮和黄芩黄酮。其中,肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH)和丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT1)在坤泰胶囊治疗EMT的生物网络中发挥重要作用,这些核心靶点主要参与凋亡途径的负调控及磷脂肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K-Akt)信号等癌症通路,在EMT治疗中发挥治疗作用。分子对接和分子动力学模拟进一步证实了谷甾醇与AKT1的稳定且紧密地结合。 结论 坤泰胶囊可能通过调节核心靶点如TNF,激活多条信号通路,从而在EMT中发挥治疗效果。这些发现不仅加深了对坤泰胶囊作用机制的理解,也为传统中药在EMT治疗中的潜在临床应用提供了新的见解。未来研究可以进一步探讨TCM药物如何干预EMT的病理过程。
| 来源 | MOL ID | 成分(Ingredient) | OB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白芍 | MOL001918 | 芍药苷元(paeoniflorgenone) | 87.59 | 0.37 |
| 白芍 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 黄芩 | MOL002932 | 二甲氧基黄酮(panicolin) | 76.26 | 0.29 |
| 黄芩 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 黄连 | MOL000785 | 巴马汀(palmatine) | 64.60 | 0.65 |
| 黄连 | MOL000098 | 槲皮素(quercetin) | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| 茯苓 | MOL000275 | 栓菌酸(trametenolic acid) | 38.71 | 0.80 |
| 茯苓 | MOL000283 | 过氧麦角甾醇(ergosterol peroxide) | 40.36 | 0.81 |
| 熟地黄 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 熟地黄 | MOL000449 | 豆甾醇(stigmasterol) | 43.83 | 0.76 |
| 阿胶 | MOL000054 | 精氨酸(arginine) | 47.64 | 0.03 |
| 阿胶 | MOL000055 | 赖氨酸(lysine) | 29.33 | 0.02 |
表1 坤泰胶囊部分活性成分基本信息
Table 1 Basic information on some active ingredients of Kuntai capsule
| 来源 | MOL ID | 成分(Ingredient) | OB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白芍 | MOL001918 | 芍药苷元(paeoniflorgenone) | 87.59 | 0.37 |
| 白芍 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 黄芩 | MOL002932 | 二甲氧基黄酮(panicolin) | 76.26 | 0.29 |
| 黄芩 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 黄连 | MOL000785 | 巴马汀(palmatine) | 64.60 | 0.65 |
| 黄连 | MOL000098 | 槲皮素(quercetin) | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| 茯苓 | MOL000275 | 栓菌酸(trametenolic acid) | 38.71 | 0.80 |
| 茯苓 | MOL000283 | 过氧麦角甾醇(ergosterol peroxide) | 40.36 | 0.81 |
| 熟地黄 | MOL000359 | 谷甾醇(sitosterol) | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| 熟地黄 | MOL000449 | 豆甾醇(stigmasterol) | 43.83 | 0.76 |
| 阿胶 | MOL000054 | 精氨酸(arginine) | 47.64 | 0.03 |
| 阿胶 | MOL000055 | 赖氨酸(lysine) | 29.33 | 0.02 |
| 来源 | MOL ID | 编号 |
|---|---|---|
| 白芍、黄芩 | MOL000358 | A |
| 黄芩、熟地黄、白芍 | MOL000359 | B |
| 黄芩、熟地黄 | MOL000449 | C |
| 黄连、黄芩 | MOL001458 | D1 |
| 黄连、黄芩 | MOL002897 | D2 |
表2 坤泰胶囊重复活性成分
Table 2 Repetitive active ingredients of Kuntai capsule
| 来源 | MOL ID | 编号 |
|---|---|---|
| 白芍、黄芩 | MOL000358 | A |
| 黄芩、熟地黄、白芍 | MOL000359 | B |
| 黄芩、熟地黄 | MOL000449 | C |
| 黄连、黄芩 | MOL001458 | D1 |
| 黄连、黄芩 | MOL002897 | D2 |
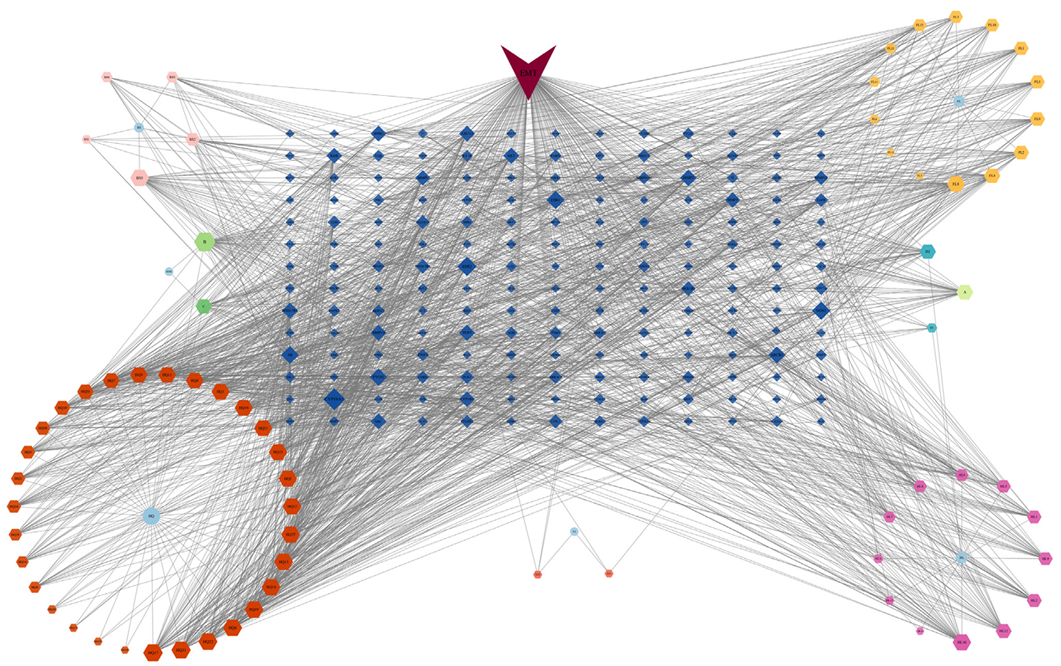
图2 活性成分预测靶点网络注:六边形节点代表活性成分,菱形节点代表活性成分靶点。图形面积大小与活性成分及其相应靶点的相对重要性成比例。HQ=黄芩,HL=黄连,FL=茯苓,BC=白芍,EJ=阿胶,SDH=熟地黄;表示活性成分靶点;表示黄芩、黄连、茯苓、白芍、阿胶、熟地黄中药;表示黄芩活性成分;表示黄连活性成分;表示茯苓活性成分;表示白芍性成分,表示阿胶活性成分;表示白芍和黄芩重复活性成分;表示黄芩、熟地黄、白芍重复活性成分;表示黄芩、熟地黄重复活性成分;表示黄连、黄芩重复活性成分;表示EMT。
Figure 2 The potential targets network of active components
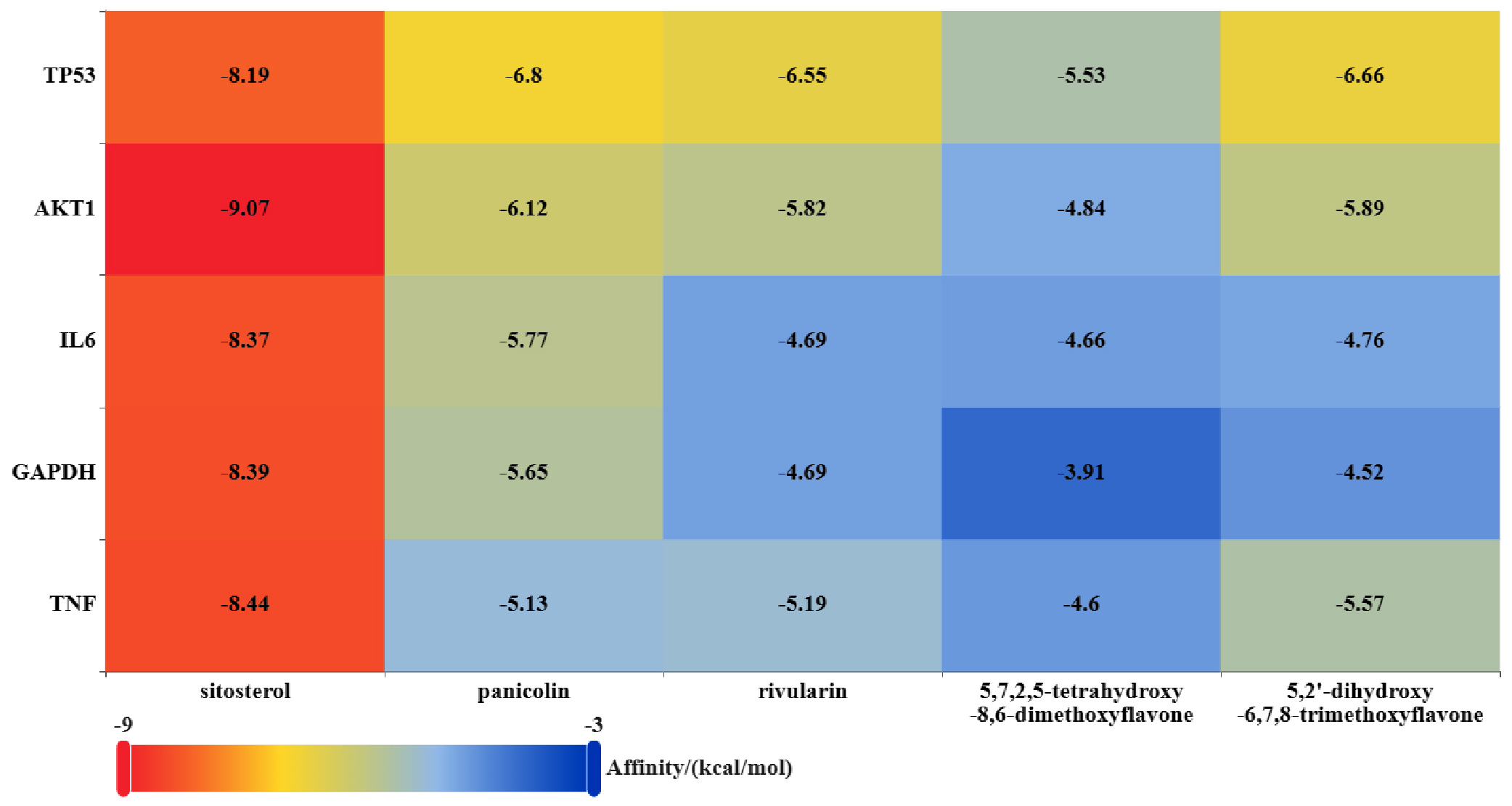
图7 分子对接热图注:TNF=肿瘤坏死因子,GAPDH=甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶,IL-6白介素6,AKT1=丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,TP53=肿瘤蛋白P53;sitosterol=谷甾醇,panicolin=二甲氧基黄酮,rivularin=黄芩黄酮,5,7,2,5-tetrahydroxy-8,6-dimethoxyflavone=5,7,2,5-四羟基-8,6-二甲氧基黄酮,5,2'-dihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone=5,2'-二羟基-6,7,8-三甲氧基异黄酮。
Figure 7 Molecular docking heatmap
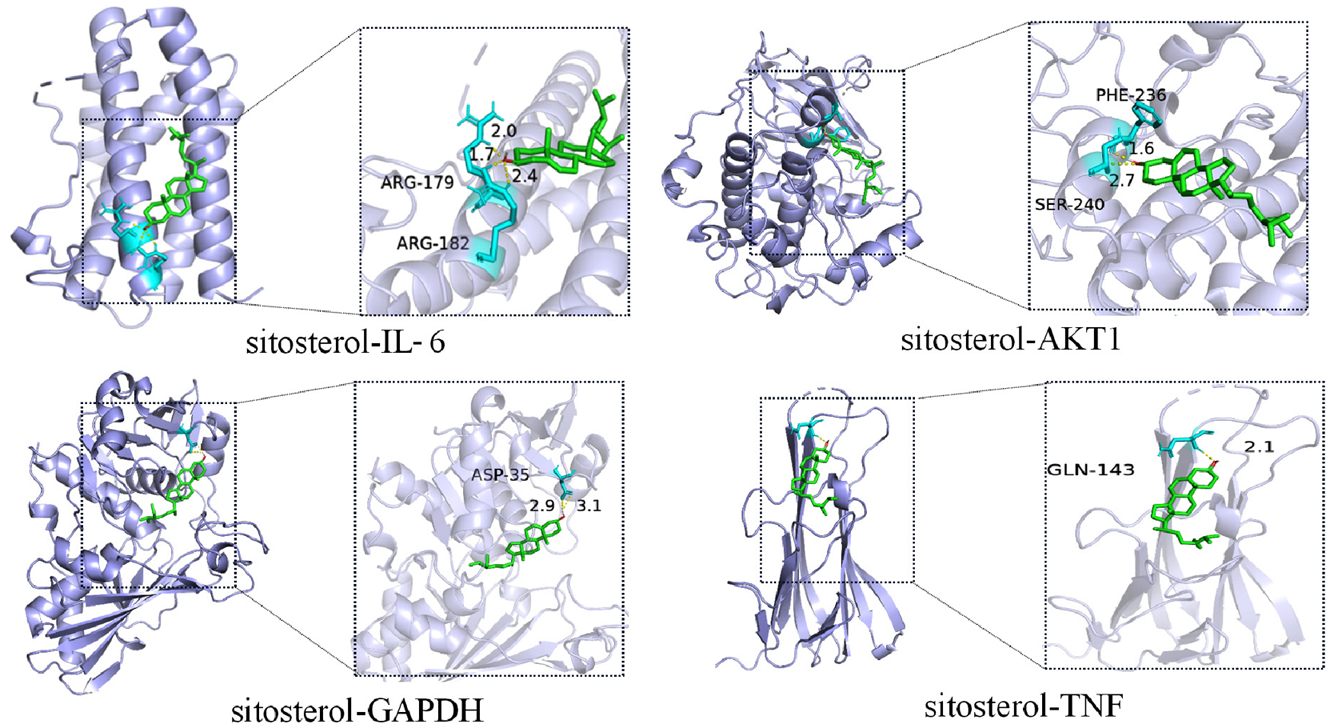
图8 分子对接结果可视化图注:sitosterol-IL-6=谷甾醇-白介素6,sitosterol-AKT1=谷甾醇-丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,sitosterol-GAPDH=谷甾醇-甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶,sitosterol-TNF=谷甾醇-肿瘤坏死因子。
Figure 8 Visualization diagram of molecular docking
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
中国医师协会妇产科医师分会,中华医学会妇产科学分会子宫内膜异位症协作组,冷金花. 子宫内膜异位症诊治指南(第三版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志,2021,56(12):812-824.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
中国中西医结合学会妇产科专业委员会. 子宫内膜异位症中西医结合诊治指南[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2019,39(10):1169-1176. DOI:10.7661/j.cjim.20190923.288.
|
| [7] |
杨蔚. 坤泰胶囊治疗妇科疾病的临床应用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究,2015,38(4):453-458.
|
| [8] |
吴翠杰. 坤泰胶囊对排卵障碍性不孕症患者卵泡发育、子宫内膜及排卵的影响[J]. 中国实用医药,2015,10(18):10-12.
|
| [9] |
钟伟青,钱红燕. 中重度子宫内膜异位症患者应用坤泰胶囊联合GnRH-a疗效及预后分析[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2016,34(12):3069-3072. DOI:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2016.12.072.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
赵秀萍,马小娜,郭亚楠. 基于网络药理学及实验研究探究坤泰胶囊异病同治卵巢早衰及绝经综合征作用机制[J]. 世界中医药,2023,18(14):1945-1951.
|
| [24] |
郑勇凤,王佳婧,傅超美,等. 黄芩的化学成分与药理作用研究进展[J]. 中成药,2016,38(1):141-147. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2016.01.032.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
刘敏娟,邓月秀,马颖. miR-34a-5p靶向AKT1基因对子宫内膜异位症子宫内膜基质细胞侵袭及自噬的调控[J]. 中国医科大学学报,2020,49(9):776-782.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 张可兴, 张博, 吴琼, 朱珊珊, 王迪, 张春男. 基于代谢组学四妙勇安汤治疗糖尿病足的作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3796-3805. |
| [2] | 杨安银, 刘红丽, 陈妙洋, 郑玉凤, 徐志远, 杨永峰. 基于网络药理学方法探析汉黄芩素治疗肝细胞癌作用机制和体外实验研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4040-4049. |
| [3] | 张林, 高锦, 吴明华, 王广梅. 通脑饮治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效及作用机制研究:基于网络药理学和分子对接技术[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2904-2912. |
| [4] | 刁翯, 白文佩, 赵立东. 左慈丸的化学成分及治疗围绝经期听力损失的作用机制研究:基于网络药理学与分子对接技术[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1493-1503. |
| [5] | 张康, 赵婷婷, 张波, 高梦琦, 李昱熹, 王邵鹏, 赵文景. 基于网络药理学探究布地奈德治疗IgA肾病的作用机制[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4453-4458. |
| [6] | 叶坤, 雷敏, 谢欣, 郑晖, 陈敏, 余曙光. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探讨黄芪建中汤治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征的作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(15): 1814-1824. |
| [7] | 孙凯,朱立国,魏戌,银河,李秋月,秦晓宽,杨博文. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS结合网络药理学的壮腰通络方延缓腰椎间盘退行性病变的化学成分及作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(35): 4437-4446. |
| [8] | 王礼贤,李琰,康山. 谷胱甘肽硫转移酶mu1基因启动子区异常甲基化与卵巢子宫内膜异位症的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(24): 3082-3086. |
| [9] | 樊霞,安冬,李琰,康山. E-钙黏蛋白基因启动子区甲基化在卵巢子宫内膜异位症中作用的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(24): 2948-2951. |
| [10] | 赵健,梁玉丹,王小寅,罗海丽,马碧茹,周思英,郭端英,奎瑜,韦丽芬. 基于数据挖掘的针灸综合疗法治疗子宫内膜异位症的应用规律研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(1): 104-108. |
| [11] | 杨眉1,2,蒋春樊3,哈春芳4*. 白介素5/TNFRSF13B在深部浸润型子宫内膜异位症微环境中的表达及其意义研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017, 20(29): 3628-3632. |
| [12] | 伍佰秀*,谢红英. 红细胞分布宽度诊断子宫内膜异位症的价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017, 20(27): 3391-3395. |
| [13] | 周赞华1,董海娜1*,卫哲1,施倩2,周丽红3,毛雪梅3. 子宫内膜异位症早期综合评分临床诊断模型研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017, 20(21): 2665-2671. |
| [14] | 白治苗,姚卫卫,李望舒,卢玉凤,杨眉,哈春芳. 骨桥蛋白在子宫内膜异位症中介导细胞迁移与依赖核转录因子κB通路促进基质金属蛋白酶及尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物表达中的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2016, 19(24): 2930-2934. |
| [15] | 杨眉,蒋春樊,哈春芳. 米非司酮对子宫内膜异位症子宫内膜腺上皮细胞骨桥蛋白和基质金属蛋白酶9表达的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2016, 19(24): 2925-2929. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





