中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (18): 2255-2261.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.121
所属专题: 女性健康最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2021-10-25
修回日期:2021-11-20
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2021-12-09
通讯作者:
陆华
基金资助:
Qian YANG1,2, Hua LU2,*( ), Qianchen LIU2
), Qianchen LIU2
Received:2021-10-25
Revised:2021-11-20
Published:2022-06-20
Online:2021-12-09
Contact:
Hua LU
About author:摘要: 背景 桥本甲状腺炎(HT)是一种常见的自身免疫性疾病,是引起甲状腺功能减退的主要原因之一。由于该病起病隐匿,无明显的临床症状,患者常因诊断不及时而延误治疗,造成不可逆的损伤,因此早期筛查及提高诊断效能对HT的治疗具有重要意义,但目前以红外热成像技术作为HT辅助诊断工具的研究较少。 目的 探索女性HT红外热成像人体代谢热值特点。 方法 选择2019年4月至2021年6月在成都中医药大学附属医院妇科门诊就诊的HT女性患者100例作为HT组,选择同期体检健康的女性100例作为对照组。两组受试者均填写《中医体质分类与判定(ZYYXH/T157-2009)》调查问卷,检测甲状腺相关指标〔甲状腺球蛋白抗体(TGAb)、甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体(TPOAb)、促甲状腺素(TSH)、游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸(FT3)、游离甲状腺素(FT4)〕,进行红外热成像全身扫描(测量甲状腺左叶和右叶、子宫、神阙及督脉区位热值)。比较两组受试者中医体质、甲状腺相关指标及各区位热值差异性;分析HT组9种中医体质患者的5个区位热值差异性,以及5个区位热值与甲状腺相关指标的相关性;同时采用多因素Logistic回归分析各区位热值与HT合并不孕症的关系。 结果 HT患者偏颇体质分布由多至少依次为阳虚质、气郁质、湿热质及痰湿质,9种中医体质间的督脉与神阙区位热值比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与对照组相比较,HT组TGAb、TPOAb水平及TSH水平升高(P<0.05)。两组受试者FT3、FT4水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);HT组甲状腺左、右叶区位热值均高于对照组,其子宫、督脉及神阙区位热值均低于对照组(P<0.05)。HT组甲状腺左、右叶区位热值与TGAb呈正相关(rs=0.260,rs=0.198,P<0.05),子宫区位热值与TSH呈负相关(rs=-0.313,P<0.05)。子宫〔OR=0.413,95%CI(0.180,0.945)〕、督脉〔OR=0.270,95%CI(0.075,0.971)〕、神阙〔OR=0.264,95%CI(0.073,0.954)〕区位热值是HT合并不孕症的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 HT患者好发的中医体质为阳虚质、气郁质、湿热质及痰湿质,其代谢热值变化具有甲状腺左、右叶区位热值偏高,子宫、督脉及神阙区位热值偏低的特点,该特点也为HT引发不孕症提供了新的临床理论依据。同时甲状腺左、右叶区位热值可作为HT早期诊断及筛查的指标之一,因此可将红外热成像技术作为辅助诊断工具以提高HT的诊断效能。
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 手术史〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 32.0±5.8 | 2(2.0) | 1(1.0) | 21(21.0) |
| HT组 | 100 | 32.1±5.4 | 4(4.0) | 2(2.0) | 30(30.0) |
| χ2(t)值 | 0.110a | 0.687 | 0.338 | 2.132 | |
| P值 | 0.090 | 0.407 | 0.561 | 0.144 |
表1 两组受试者一般资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of general information of adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 手术史〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 32.0±5.8 | 2(2.0) | 1(1.0) | 21(21.0) |
| HT组 | 100 | 32.1±5.4 | 4(4.0) | 2(2.0) | 30(30.0) |
| χ2(t)值 | 0.110a | 0.687 | 0.338 | 2.132 | |
| P值 | 0.090 | 0.407 | 0.561 | 0.144 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 平和质 | 阳虚质 | 气郁质 | 湿热质 | 痰湿质 | 阴虚质 | 血瘀质 | 气虚质 | 特禀质 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 67(67.0) | 11(11.0) | 6(6.0) | 3(3.0) | 2(2.0) | 2(2.0) | 4(4.0) | 4(4.0) | 1(1.0) |
| HT组 | 100 | 7(7.0) | 34(34.0) | 26(26.0) | 11(11.0) | 8(8.0) | 5(5.0) | 4(4.0) | 3(3.0) | 2(2.0) |
| χ2值 | 77.220 | 15.168 | 14.881 | 4.916 | 3.789 | 1.332 | 0 | 0.148 | 0.338 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.027 | 0.052 | 0.248 | 1.000 | 0.700 | 0.561 |
表2 两组受试者9种体质分布〔n(%)〕
Table 2 Distribution of 9 types of constitution in TCM in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 平和质 | 阳虚质 | 气郁质 | 湿热质 | 痰湿质 | 阴虚质 | 血瘀质 | 气虚质 | 特禀质 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 67(67.0) | 11(11.0) | 6(6.0) | 3(3.0) | 2(2.0) | 2(2.0) | 4(4.0) | 4(4.0) | 1(1.0) |
| HT组 | 100 | 7(7.0) | 34(34.0) | 26(26.0) | 11(11.0) | 8(8.0) | 5(5.0) | 4(4.0) | 3(3.0) | 2(2.0) |
| χ2值 | 77.220 | 15.168 | 14.881 | 4.916 | 3.789 | 1.332 | 0 | 0.148 | 0.338 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.027 | 0.052 | 0.248 | 1.000 | 0.700 | 0.561 |
| 组别 | 例数 | TGAb | TPOAb(U/ml) | TSH(μU/ml) | FT3(pmol/L) | FT4(pmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 1.23(1.08,2.09) | 19.00(16.00,23.00) | 3.23(1.78,3.95) | 4.62(3.78,5.12) | 17.90(15.80,29.30) |
| HT组 | 100 | 5.11(3.95,5.94) | 27.30(18.11,46.16) | 4.19(3.23,4.68) | 4.11(3.51,4.68) | 17.50(16.40,18.94) |
| Z值 | -11.015 | -4.425 | -2.468 | -0.229 | -0.259 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.819 | 0.795 |
表3 两组受试者甲状腺相关指标〔M(P25,P75)〕
Table 3 Thyroid function parameters in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | TGAb | TPOAb(U/ml) | TSH(μU/ml) | FT3(pmol/L) | FT4(pmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 1.23(1.08,2.09) | 19.00(16.00,23.00) | 3.23(1.78,3.95) | 4.62(3.78,5.12) | 17.90(15.80,29.30) |
| HT组 | 100 | 5.11(3.95,5.94) | 27.30(18.11,46.16) | 4.19(3.23,4.68) | 4.11(3.51,4.68) | 17.50(16.40,18.94) |
| Z值 | -11.015 | -4.425 | -2.468 | -0.229 | -0.259 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.819 | 0.795 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 甲状腺左叶 | 甲状腺右叶 | 子宫 | 督脉 | 神阙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 30.69±0.79 | 30.64±0.80 | 31.45±0.39 | 32.17±0.40 | 32.02±0.35 |
| HT组 | 100 | 31.58±0.69 | 31.45±0.69 | 29.08±0.70 | 30.75±0.53 | 30.59±0.64 |
| t值 | 8.413 | 7.614 | -29.247 | -21.557 | -19.573 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表4 两组受试者相关区位热值比较(±s,℃)
Table 4 Calorific values of thyroid left and right lobes,the uterus,the Shenque acupoint and the Governor vessel measured by infrared thermal imaging in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
| 组别 | 例数 | 甲状腺左叶 | 甲状腺右叶 | 子宫 | 督脉 | 神阙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 100 | 30.69±0.79 | 30.64±0.80 | 31.45±0.39 | 32.17±0.40 | 32.02±0.35 |
| HT组 | 100 | 31.58±0.69 | 31.45±0.69 | 29.08±0.70 | 30.75±0.53 | 30.59±0.64 |
| t值 | 8.413 | 7.614 | -29.247 | -21.557 | -19.573 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
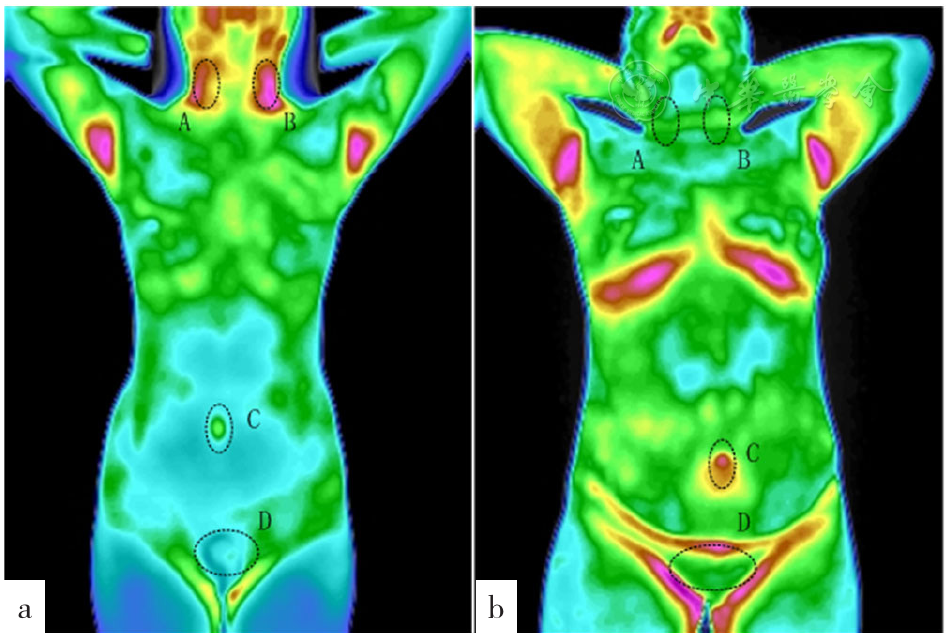
图1 HT患者与对照者正位图注:a为桥本甲状腺炎患者正位图,b为对照者正位图,A表示甲状腺右叶,B表示甲状腺左叶,C表示神阙,D表示子宫
Figure 1 Front view of the metabolic calorific values of thyroid left and right lobes,the uterus,the Shenque acupoint and the Governor vessel measured by infrared thermal imaging in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
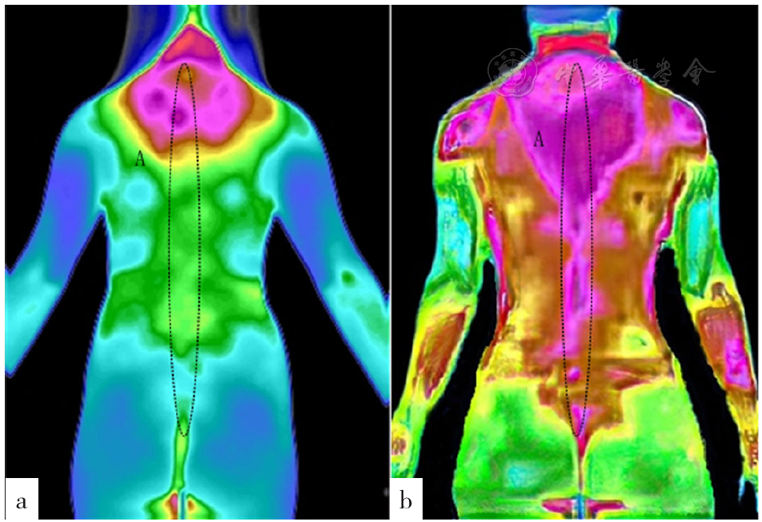
图2 HT患者与对照者胸后位图注:a为桥本甲状腺炎患者胸后位图,b为对照者胸后位图,A表示督脉
Figure 2 Post-thoracic view of the metabolic calorific values of the Governor vessel measured by infrared thermal imaging in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients and adult female healthy physical examinees
| 中医体质类型 | 例数 | 甲状腺左叶 | 甲状腺右叶 | 子宫 | 督脉 | 神阙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平和质 | 7 | 31.21±0.33 | 31.11±0.36 | 29.25±0.67 | 31.16±0.23 | 30.48±0.23 |
| 阳虚质 | 34 | 31.55±0.73 | 31.44±0.74 | 29.03±0.93 | 30.27±0.34 | 30.16±0.35 |
| 气郁质 | 26 | 31.48±0.69 | 31.41±0.65 | 28.94±0.56 | 30.93±0.24 | 30.64±0.32 |
| 湿热质 | 11 | 31.91±0.74 | 31.62±0.88 | 29.30±0.55 | 31.14±0.48 | 30.71±0.41 |
| 痰湿质 | 8 | 31.54±0.80 | 31.49±0.78 | 29.28±0.22 | 30.52±0.24 | 30.62±0.31 |
| 阴虚质 | 5 | 31.78±0.47 | 31.53±0.66 | 29.41±0.43 | 31.76±0.39 | 32.38±1.03 |
| 血瘀质 | 4 | 31.78±0.69 | 31.53±0.49 | 28.95±0.99 | 30.79±0.53 | 31.12±1.05 |
| 气虚质 | 3 | 31.95±0.74 | 31.67±0.96 | 28.72±0.38 | 30.74±0.56 | 30.94±0.09 |
| 特禀质 | 2 | 31.50±0.16 | 31.50±0.18 | 29.20±0.82 | 30.54±0.45 | 30.52±0.41 |
| F值 | 0.817 | 0.334 | 0.632 | 18.139 | 15.797 | |
| P值 | 0.590 | 0.951 | 0.749 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表5 HT组不同中医体质患者各区位热值比较(±s,℃)
Table 5 Calorific values of thyroid left and right lobes,the uterus,the Shenque acupoint and the Governor vessel measured by infrared thermal imaging in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients by the type of constitution in TCM
| 中医体质类型 | 例数 | 甲状腺左叶 | 甲状腺右叶 | 子宫 | 督脉 | 神阙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平和质 | 7 | 31.21±0.33 | 31.11±0.36 | 29.25±0.67 | 31.16±0.23 | 30.48±0.23 |
| 阳虚质 | 34 | 31.55±0.73 | 31.44±0.74 | 29.03±0.93 | 30.27±0.34 | 30.16±0.35 |
| 气郁质 | 26 | 31.48±0.69 | 31.41±0.65 | 28.94±0.56 | 30.93±0.24 | 30.64±0.32 |
| 湿热质 | 11 | 31.91±0.74 | 31.62±0.88 | 29.30±0.55 | 31.14±0.48 | 30.71±0.41 |
| 痰湿质 | 8 | 31.54±0.80 | 31.49±0.78 | 29.28±0.22 | 30.52±0.24 | 30.62±0.31 |
| 阴虚质 | 5 | 31.78±0.47 | 31.53±0.66 | 29.41±0.43 | 31.76±0.39 | 32.38±1.03 |
| 血瘀质 | 4 | 31.78±0.69 | 31.53±0.49 | 28.95±0.99 | 30.79±0.53 | 31.12±1.05 |
| 气虚质 | 3 | 31.95±0.74 | 31.67±0.96 | 28.72±0.38 | 30.74±0.56 | 30.94±0.09 |
| 特禀质 | 2 | 31.50±0.16 | 31.50±0.18 | 29.20±0.82 | 30.54±0.45 | 30.52±0.41 |
| F值 | 0.817 | 0.334 | 0.632 | 18.139 | 15.797 | |
| P值 | 0.590 | 0.951 | 0.749 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 区位热值 | 例数 | TGAb | TPOAb(U/ml) | TSH(μU/ml) | FT3(pmol/L) | FT4(pmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | ||
| 甲状腺左叶 | 100 | 0.260 | 0.009 | 0.066 | 0.516 | 0.172 | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.435 | 0.051 | 0.613 |
| 甲状腺右叶 | 100 | 0.198 | 0.049 | 0.033 | 0.747 | 0.083 | 0.411 | 0.091 | 0.366 | 0.012 | 0.906 |
| 子宫 | 100 | 0.144 | 0.152 | 0.044 | 0.666 | -0.313 | 0.002 | 0.174 | 0.084 | 0.177 | 0.079 |
| 督脉 | 100 | -0.025 | 0.804 | -0.059 | 0.557 | -0.024 | 0.809 | 0.045 | 0.657 | -0.004 | 0.969 |
| 神阙 | 100 | 0.030 | 0.764 | -0.089 | 0.380 | -0.040 | 0.695 | -0.050 | 0.620 | -0.004 | 0.965 |
表6 HT组各区位热值与甲状腺相关指标的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analyses of calorific values of thyroid left and right lobes,the uterus,the Shenque acupoint and the Governor vessel measured by infrared thermal imaging with thyroid function parameters in adult female Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients
| 区位热值 | 例数 | TGAb | TPOAb(U/ml) | TSH(μU/ml) | FT3(pmol/L) | FT4(pmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | rs值 | P值 | ||
| 甲状腺左叶 | 100 | 0.260 | 0.009 | 0.066 | 0.516 | 0.172 | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.435 | 0.051 | 0.613 |
| 甲状腺右叶 | 100 | 0.198 | 0.049 | 0.033 | 0.747 | 0.083 | 0.411 | 0.091 | 0.366 | 0.012 | 0.906 |
| 子宫 | 100 | 0.144 | 0.152 | 0.044 | 0.666 | -0.313 | 0.002 | 0.174 | 0.084 | 0.177 | 0.079 |
| 督脉 | 100 | -0.025 | 0.804 | -0.059 | 0.557 | -0.024 | 0.809 | 0.045 | 0.657 | -0.004 | 0.969 |
| 神阙 | 100 | 0.030 | 0.764 | -0.089 | 0.380 | -0.040 | 0.695 | -0.050 | 0.620 | -0.004 | 0.965 |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲状腺左叶 | 0.553 | 0.645 | 0.736 | 0.391 | 0.575(0.162,2.036) |
| 甲状腺右叶 | 1.324 | 0.679 | 3.804 | 0.051 | 3.758(0.993,14.219) |
| 子宫 | -0.885 | 0.422 | 4.388 | 0.036 | 0.413(0.180,0.945) |
| 督脉 | -1.310 | 0.653 | 4.023 | 0.045 | 0.270(0.075,0.971) |
| 神阙 | -1.332 | 0.655 | 4.131 | 0.042 | 0.264(0.073,0.954) |
表7 HT组患者不孕症影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 7 Binary Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors of infertility in Hashimoto's thyroiditis
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲状腺左叶 | 0.553 | 0.645 | 0.736 | 0.391 | 0.575(0.162,2.036) |
| 甲状腺右叶 | 1.324 | 0.679 | 3.804 | 0.051 | 3.758(0.993,14.219) |
| 子宫 | -0.885 | 0.422 | 4.388 | 0.036 | 0.413(0.180,0.945) |
| 督脉 | -1.310 | 0.653 | 4.023 | 0.045 | 0.270(0.075,0.971) |
| 神阙 | -1.332 | 0.655 | 4.131 | 0.042 | 0.264(0.073,0.954) |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
葛均波,徐永健.内科学[M]. 8版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:697.
|
| [5] |
赵霞,唐婕,吴韶清,等.妊娠期碘营养状态与甲状腺功能的关系研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2017,38(11):3. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.11.018.
|
| [6] |
周国威,马丙娥,夏天卫,等. 温阳法治疗桥本甲状腺炎伴甲减的研究进展[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2020,26(8):1223-1226.
|
| [7] | |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会,《中国甲状腺疾病诊治指南》编写组.中国甲状腺疾病诊治指南[J]. 中华内科杂志,2008,47(10):867-868.
|
| [12] |
中华中医药学会. 中医体质分类与判定(ZYYXH/T157-2009)[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2009,4(4):303-304.
|
| [13] |
崔慧先,李瑞锡. 局部解剖学[M]. 9版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2018.
|
| [14] |
石学敏. 针灸学[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社,2017:32-45.
|
| [15] |
李洪娟. 红外成像检测与中医[M]. 北京:中医古籍出版社,2015.
|
| [16] |
谢幸,孔北华,段涛. 妇产科学[M]. 9版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2018.
|
| [17] |
廖结英,王天芳,李站,等. 红外热成像技术用于疾病诊断及中医辨证研究进展[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(4):698-702. DOI:10.19945/j.cnki.issn.1006-3250.2021.04.042.
|
| [18] |
周鑫,王平. 医用红外热成像技术在中医学研究中的应用[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2018,24(2):258-260.
|
| [19] |
张冀东,何清湖,孙涛. 红外热成像技术在中医学研究中的问题探讨[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2016,31(7):2669-2671.
|
| [20] |
牛聪,李妙媛. 痛经与中医体质相关性分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(12):2888-2893.
|
| [21] |
魏绍斌,黄玲,王烨,等. 四川湿热气候与妇科疾病证治特色[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(4):1308-1310.
|
| [22] |
刘婧,杨凯,董佳妮,等. 张兰中西结合治疗桥本氏病经验总结[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2019,25(9):1319-1321.
|
| [23] |
王小龙,高天舒. 甲状腺功能正常桥本甲状腺炎患者中医体质特征调查[J]. 北京中医药,2016,35(6):557-559. DOI:10.16025/j.1674-1307.2016.06.014.
|
| [24] |
陈岳祺,范源,阮凌玉,等. 桥本甲状腺炎中医体质分布特征与甲状腺激素相关性研究[J]. 西部中医药,2020,33(2):66-68.
|
| [25] | |
| [26] |
方琴琴,黄泳,蔡晓雯,等. 不同体质人群穴位特异性分析与辨体调质的临床应用概述[J]. 河北中医,2019,41(9):1431-1436.
|
| [27] |
王雨婷,邓品,李洪娟. 红外热成像技术在中医领域的研究综述[J]. 红外技术,2017,39(1):14-21.
|
| [28] |
杜恒,高全彩,苏振丽,等. 二仙消瘿汤对桥本甲状腺炎患者免疫性抗体、Th1/Th2相关细胞因子的影响[J]. 中医学报,2020,35(12):2682-2686. DOI:10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2020.12.590.
|
| [29] |
张文娟. 孕晚期不同滴度过氧化物酶抗体与新生儿甲减关系[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2017.
|
| [30] |
崔云华,雷菲,赵继梦,等. 艾灸对EAT大鼠甲状腺功能及其IL-17、IL-23表达影响的研究[J]. 世界中医药,2016,11(12):2558-2565,2570.
|
| [31] |
刘安国. 基于红外热成像技术的针刺"三阴穴"治疗慢性前列腺炎的临床评价[D]. 兰州:甘肃中医学院,2014.
|
| [32] |
刘维,李梦,刘雪珂,等. 基于红外热成像对刺络放血结合艾灸治疗腰背肌筋膜炎的临床研究[J]. 中国中医急症,2020,29(8):1400-1402.
|
| [33] |
陈丁山,何六元,杨建安,等. 彩色多普勒超声联合医用红外热像仪在甲状腺疾病诊断中的应用[J]. 现代医用影像学,2017,26(2):315-316.
|
| [34] |
杨丽丽,马会民,田微芳. TTM技术在甲状腺功能异常患者早期筛查中的应用价值[J]. 河南医学研究,2020,29(14):2639-2641.
|
| [35] |
王瑜,国春英,杨芸,等. 热断层成像系统早期筛查甲状腺疾病41例分析[J]. 医疗装备,2012,25(1):31-32.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
贺帅,张力. TGAb、TMAb和TPOAb诊断在桥本甲状腺炎诊断中的价值[J]. 西南国防医药,2017,27(8):822-824.
|
| [39] |
程士德. 内经讲义[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,1984:68-78,83-84,142.
|
| [40] |
计烨,李云楚,左舒颖,等. 甲状腺为奇恒之府的探析及其证治规律[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017,32(7):2977-2979.
|
| [41] |
陈士铎. 外经微言[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社,2011:48.
|
| [42] |
陈士铎. 石室秘录[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社,2009:205-206.
|
| [43] |
陈惠华. 岭南中医妇科医家诊治卵巢早衰病证文献资料及学术经验整理研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2017:1-141.
|
| [44] |
| [1] | 蒋琪霞, 朱玉玲, 祝文君, 李秀芸, 谢郝婷, 王华军, 袁斯明. "五点"皮瓣温度和"单点"皮瓣温度预测血管危象的准确性及临界值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3013-3018. |
| [2] | 杨佳诺, 王冠理, 杨佳夫, 何嘉豪, 陈舒敏, 沈毅, 李娟, 任妮, 刘春丽, 邓方阁. 红外热成像在肺部疾病应用的新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(08): 1012-1016. |
| [3] | 黄帆, 郑贝思, 黄嘉莹, 黄芊莹, 李涛, 吴山, 林嬿钊, 范志勇. 基于红外线热成像技术探索"按之则热气至"的按压次数-热效应机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(26): 3264-3272. |
| [4] | 葛亚雪, 丁治国, 陈晓珩, 李会龙, 祁烁, 户蕊. 桥本甲状腺炎并发甲状腺毒症人群临床症状及证型分布规律研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(21): 2630-2638. |
| [5] | 冯晓玲, 尹文卿, 王颖, 侯丽辉. 多囊卵巢综合征患者游离睾酮指数水平与临床指标的相关性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 3005-3009. |
| [6] | 胡春燕, 李雅婧, 耿同会, 张东雪. HITH-4远红外线治疗仪联合多磺酸粘多糖乳膏对糖尿病血液透析患者动静脉内瘘功能的保护效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(08): 951-954. |
| [7] | 赵伟, 杨珊珊, 唐荣杰, 杨芳, 孙锋, 廉秋芳. 甲状腺功能正常的高血压患者血清甲状腺激素水平与高尿酸血症的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(35): 4394-4398. |
| [8] | 万会娜, 张国玉, 万红, 符宇, 王泽瑾, 燕树勋, 王颖. 营养因素对桥本甲状腺炎患者甲状腺自身抗体滴度的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(17): 2152-2158. |
| [9] | 柳怡莹,程筱玲,邓偲婕,郝鑫琳,蒋玥芾,万沁. 女性2型糖尿病患者高三酰甘油腰围表型与甲状腺激素的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(33): 4172-4177. |
| [10] | 张亚军,郭小敏,蒋玉凤. 原发性胆汁性胆管炎患者甲状腺激素及抗体的临床意义研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(33): 4064-4068. |
| [11] | 范尧夫,曹雯,狄红杰,张会峰,孙洪平,曹琳,褚晓秋. 甲状腺功能正常和甲状腺功能减退患者游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸与游离甲状腺素比值与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(32): 3915-3920. |
| [12] | 路娜,冉晓丹,李永伟,杨玉莲. 甲状腺球蛋白及游离甲状腺素/游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸联合甲状腺激素抗体在亚急性甲状腺炎诊断中的应用价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(3): 361-365. |
| [13] | 刘奕婷,王巍. 正常甲状腺功能人群甲状腺激素水平与非酒精性脂肪肝的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(25): 3088-3093. |
| [14] | 张乐,白宇,翟晓丹. 妊娠期碘缺乏及补碘干预对后代神经智力发育的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(24): 2962-2966. |
| [15] | 熊斌,周云,詹俊锋,黄晶晶,李凯,王永召,荆珏华,吴建贤. 红外线联合气压治疗在跟骨骨折切开复位内固定术患者围术期的应用效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(17): 2125-2129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





