

Chinese General Practice ›› 2026, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (01): 76-83.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0630
Special Issue: 社区卫生服务最新研究合辑
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-08-19
Revised:2025-10-08
Published:2026-01-05
Online:2025-12-18
Contact:
ZHANG Lijuan
通讯作者:
张丽娟
作者简介:作者贡献:
聂倩倩提出研究目标,负责研究实施与数据分析;程桂荣进行统计学处理与撰写论文;宋丹、李景耀进行数据的收集、整理;许浪负责文章质量控制;张丽娟对文章总体负责。
本文首次刊登于Chinese General Practice Journal 2025年第1期(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2950559325000069)
基金资助:CLC Number:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0630
| 组别 | 例数 | 居住地[例(%)] | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄[例(%)] | 受教育程度[例(%)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农村 | 城市 | 男 | 女 | <75岁 | ≥75岁 | <1年 | 1~6年 | 7~12年 | >12年 | ||
| 非痴呆组 | 13 621 | 6 241(45.8) | 7 380(54.2) | 6 236(45.8) | 7 385(54.2) | 9 659(70.9) | 3 962(29.1) | 2 629(19.3) | 4 368(32.1) | 5 178(38.0) | 1 446(10.6) |
| 痴呆组 | 1 111 | 867(78.0) | 244(22.0) | 335(30.2) | 776(69.8) | 480(43.2) | 631(56.8) | 727(65.4) | 277(24.9) | 95(8.6) | 12(1.1) |
| χ2(t)值 | 427.046 | 101.551 | 367.545 | 1 319.890 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 组别 | 婚姻状态[例(%)] | BMI( | 吸烟情况[例(%)]a | 饮酒情况[例(%)]a | 社交活动频率[例(%)]a | ||||||
| 无配偶 | 有配偶 | 无 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 基本没有 | 偶尔有 | 经常有 | |||
| 非痴呆组 | 3 206(23.5) | 10 415(76.5) | 23.6±3.4 | 9 821(72.1) | 3 793(27.9) | 10 037(73.8) | 3 570(26.2) | 2 058(15.3) | 6 705(50.0) | 4 656(34.7) | |
| 痴呆组 | 518(46.6) | 593(53.4) | 23.1±3.9 | 903(81.6) | 203(18.4) | 829(75.0) | 277(25.0) | 454(42.1) | 389(36.1) | 235(21.8) | |
| χ2(t)值 | 289.881 | 4.000b | 46.743 | 0.752 | 501.346 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.386 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 组别 | 疾病种类[例(%)] | 共病情况[例(%)] | |||||||||
| 高血压 | 糖尿病 | 心脏病 | 脑血管疾病 | 失眠 | 自主神经功能紊乱 | 否(0~1种疾病) | 是(≥2种疾病) | ||||
| 非痴呆组 | 7 041(51.7) | 2 181(16.0) | 2 149(15.8) | 2 205(16.2) | 5 125(37.6) | 5 729(42.1) | 6 068(44.5) | 7 553(55.5) | |||
| 痴呆组 | 745(67.1) | 195(17.6) | 258(23.2) | 257(23.1) | 432(38.9) | 527(47.4) | 371(33.4) | 740(66.6) | |||
| χ2(t)值 | 97.313 | 1.800 | 41.656 | 35.586 | 0.692 | 12.145 | 51.956 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.180 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.405 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
Table 1 Comparison of basic characteristics between dementia and non-dementia groups in community-dwelling older adults
| 组别 | 例数 | 居住地[例(%)] | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄[例(%)] | 受教育程度[例(%)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农村 | 城市 | 男 | 女 | <75岁 | ≥75岁 | <1年 | 1~6年 | 7~12年 | >12年 | ||
| 非痴呆组 | 13 621 | 6 241(45.8) | 7 380(54.2) | 6 236(45.8) | 7 385(54.2) | 9 659(70.9) | 3 962(29.1) | 2 629(19.3) | 4 368(32.1) | 5 178(38.0) | 1 446(10.6) |
| 痴呆组 | 1 111 | 867(78.0) | 244(22.0) | 335(30.2) | 776(69.8) | 480(43.2) | 631(56.8) | 727(65.4) | 277(24.9) | 95(8.6) | 12(1.1) |
| χ2(t)值 | 427.046 | 101.551 | 367.545 | 1 319.890 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 组别 | 婚姻状态[例(%)] | BMI( | 吸烟情况[例(%)]a | 饮酒情况[例(%)]a | 社交活动频率[例(%)]a | ||||||
| 无配偶 | 有配偶 | 无 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 基本没有 | 偶尔有 | 经常有 | |||
| 非痴呆组 | 3 206(23.5) | 10 415(76.5) | 23.6±3.4 | 9 821(72.1) | 3 793(27.9) | 10 037(73.8) | 3 570(26.2) | 2 058(15.3) | 6 705(50.0) | 4 656(34.7) | |
| 痴呆组 | 518(46.6) | 593(53.4) | 23.1±3.9 | 903(81.6) | 203(18.4) | 829(75.0) | 277(25.0) | 454(42.1) | 389(36.1) | 235(21.8) | |
| χ2(t)值 | 289.881 | 4.000b | 46.743 | 0.752 | 501.346 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.386 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 组别 | 疾病种类[例(%)] | 共病情况[例(%)] | |||||||||
| 高血压 | 糖尿病 | 心脏病 | 脑血管疾病 | 失眠 | 自主神经功能紊乱 | 否(0~1种疾病) | 是(≥2种疾病) | ||||
| 非痴呆组 | 7 041(51.7) | 2 181(16.0) | 2 149(15.8) | 2 205(16.2) | 5 125(37.6) | 5 729(42.1) | 6 068(44.5) | 7 553(55.5) | |||
| 痴呆组 | 745(67.1) | 195(17.6) | 258(23.2) | 257(23.1) | 432(38.9) | 527(47.4) | 371(33.4) | 740(66.6) | |||
| χ2(t)值 | 97.313 | 1.800 | 41.656 | 35.586 | 0.692 | 12.145 | 51.956 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.180 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.405 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 居住地 | 农村=1,城市=2 |
| 性别 | 男=1,女=2 |
| 年龄 | < 75岁=1,≥ 75岁=2 |
| 受教育程度 | < 1年=1,1 ~ 6年=2,7 ~ 12年=3,> 12年=4 |
| 婚姻状态 | 无配偶=0,有配偶=1 |
| 吸烟情况 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 饮酒情况 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 社交活动频率 | 基本没有=1,偶尔有=2,经常有=3 |
| BMI | 实测值 |
| 共病情况 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 认知状态 | 非痴呆=0,痴呆=1 |
Table 2 Variable assignment of multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the association between hypertension comorbidity and dementia
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 居住地 | 农村=1,城市=2 |
| 性别 | 男=1,女=2 |
| 年龄 | < 75岁=1,≥ 75岁=2 |
| 受教育程度 | < 1年=1,1 ~ 6年=2,7 ~ 12年=3,> 12年=4 |
| 婚姻状态 | 无配偶=0,有配偶=1 |
| 吸烟情况 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 饮酒情况 | 无=0,有=1 |
| 社交活动频率 | 基本没有=1,偶尔有=2,经常有=3 |
| BMI | 实测值 |
| 共病情况 | 否=0,是=1 |
| 认知状态 | 非痴呆=0,痴呆=1 |
| 患病情况 | 高血压共病数量 | 患病情况 | 高血压共单一特定疾病 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 无疾病 | 1.000 | 无疾病 | 1.000 | ||
| H | 1.516(1.014~2.267) | 0.042 | H+D | 2.128(1.066~4.249) | 0.032 |
| H+X | 1.879(1.312~2.692) | 0.001 | H+HD | 2.248(1.171~4.316) | 0.015 |
| H+2X | 2.071(1.428~3.004) | <0.001 | H+C | 2.550(1.384~4.700) | 0.003 |
| H+3X | 2.338(1.612~3.392) | <0.001 | H+I | 1.350(0.792~2.300) | 0.270 |
| H+≥4X | 2.591(1.634~4.108) | <0.001 | H+A | 1.792(1.142~2.811) | 0.011 |
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the number of hypertension comorbidities and the association between hypertension with a single specific disease and dementia in community-dwelling older adults
| 患病情况 | 高血压共病数量 | 患病情况 | 高血压共单一特定疾病 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 无疾病 | 1.000 | 无疾病 | 1.000 | ||
| H | 1.516(1.014~2.267) | 0.042 | H+D | 2.128(1.066~4.249) | 0.032 |
| H+X | 1.879(1.312~2.692) | 0.001 | H+HD | 2.248(1.171~4.316) | 0.015 |
| H+2X | 2.071(1.428~3.004) | <0.001 | H+C | 2.550(1.384~4.700) | 0.003 |
| H+3X | 2.338(1.612~3.392) | <0.001 | H+I | 1.350(0.792~2.300) | 0.270 |
| H+≥4X | 2.591(1.634~4.108) | <0.001 | H+A | 1.792(1.142~2.811) | 0.011 |
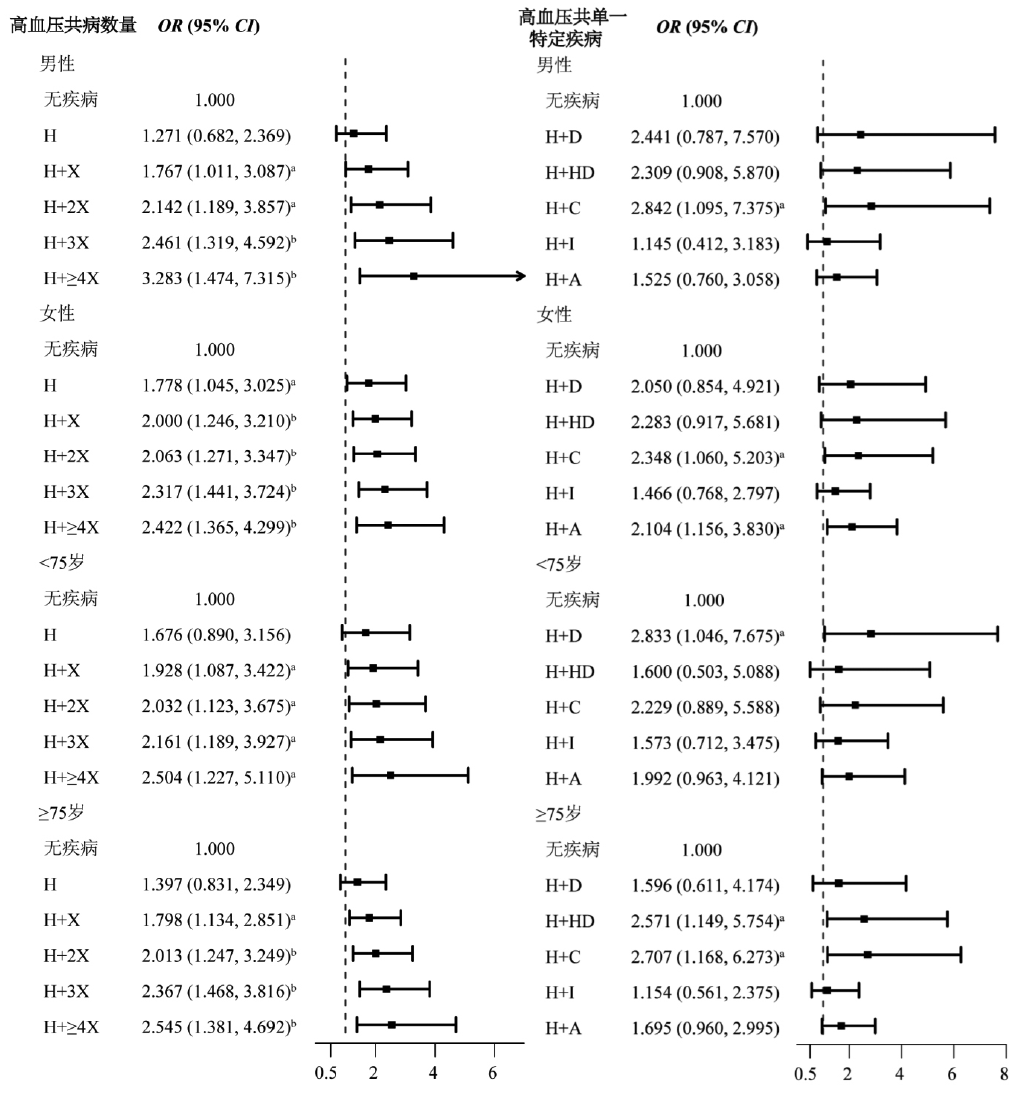
Figure 2 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the number of hypertension comorbidities and the association between hypertension with a single specific disease and dementia in community-dwelling older adults of different sex and age groups
| 高血压共多种疾病组合 | B值 | SE值 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无疾病 | 1.000 | ||||
| H+D+HD | 0.988 | 0.588 | 2.823 | 0.093 | 2.685(0.848~8.499) |
| H+D+C | 1.150 | 0.517 | 4.944 | 0.026 | 3.159(1.146~8.705) |
| H+D+I | 0.255 | 0.561 | 0.207 | 0.649 | 1.290(0.430~3.871) |
| H+D+A | 0.650 | 0.452 | 2.069 | 0.150 | 1.916(0.790~4.647) |
| H+HD+C | 1.270 | 0.499 | 6.469 | 0.011 | 3.559(1.338~9.468) |
| H+HD+I | 0.618 | 0.492 | 1.577 | 0.209 | 1.856(0.707~4.871) |
| H+HD+A | 1.119 | 0.383 | 8.527 | 0.003 | 3.062(1.445~6.490) |
| H+C+I | 0.930 | 0.404 | 5.290 | 0.021 | 2.534(1.147~5.595) |
| H+C+A | 1.033 | 0.397 | 6.778 | 0.009 | 2.809(1.291~6.111) |
| H+I+A | 0.527 | 0.242 | 4.741 | 0.029 | 1.693(1.054~2.720) |
| H+D+HD+I | 0.914 | 0.571 | 2.561 | 0.110 | 2.494(0.814~7.636) |
| H+D+HD+A | 0.804 | 0.421 | 3.649 | 0.056 | 2.234(0.979~5.098) |
| H+D+C+A | 1.106 | 0.541 | 4.183 | 0.041 | 3.024(1.047~8.730) |
| H+D+I+A | 0.881 | 0.325 | 7.352 | 0.007 | 2.413(1.277~4.562) |
| H+HD+C+I | 1.033 | 0.401 | 6.647 | 0.010 | 2.810(1.281~6.165) |
| H+HD+C+A | 1.356 | 0.411 | 10.912 | 0.001 | 3.881(1.736~8.677) |
| H+HD+I+A | 0.613 | 0.283 | 4.669 | 0.031 | 1.845(1.059~3.216) |
| H+C+I+A | 1.007 | 0.285 | 12.473 | <0.001 | 2.739(1.566~4.790) |
| H+D+HD+I+A | 0.959 | 0.445 | 4.655 | 0.031 | 2.609(1.092~6.235) |
| H+D+C+I+A | 0.789 | 0.478 | 2.721 | 0.099 | 2.200(0.862~5.614) |
| H+HD+C+I+A | 1.047 | 0.339 | 9.553 | 0.002 | 2.850(1.467~5.536) |
| H+D+HD+C+I+A | 1.184 | 0.462 | 6.555 | 0.010 | 3.266(1.320~8.084) |
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the association between hypertension≥ 2 specific diseases and dementia in community-dwelling older adults
| 高血压共多种疾病组合 | B值 | SE值 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无疾病 | 1.000 | ||||
| H+D+HD | 0.988 | 0.588 | 2.823 | 0.093 | 2.685(0.848~8.499) |
| H+D+C | 1.150 | 0.517 | 4.944 | 0.026 | 3.159(1.146~8.705) |
| H+D+I | 0.255 | 0.561 | 0.207 | 0.649 | 1.290(0.430~3.871) |
| H+D+A | 0.650 | 0.452 | 2.069 | 0.150 | 1.916(0.790~4.647) |
| H+HD+C | 1.270 | 0.499 | 6.469 | 0.011 | 3.559(1.338~9.468) |
| H+HD+I | 0.618 | 0.492 | 1.577 | 0.209 | 1.856(0.707~4.871) |
| H+HD+A | 1.119 | 0.383 | 8.527 | 0.003 | 3.062(1.445~6.490) |
| H+C+I | 0.930 | 0.404 | 5.290 | 0.021 | 2.534(1.147~5.595) |
| H+C+A | 1.033 | 0.397 | 6.778 | 0.009 | 2.809(1.291~6.111) |
| H+I+A | 0.527 | 0.242 | 4.741 | 0.029 | 1.693(1.054~2.720) |
| H+D+HD+I | 0.914 | 0.571 | 2.561 | 0.110 | 2.494(0.814~7.636) |
| H+D+HD+A | 0.804 | 0.421 | 3.649 | 0.056 | 2.234(0.979~5.098) |
| H+D+C+A | 1.106 | 0.541 | 4.183 | 0.041 | 3.024(1.047~8.730) |
| H+D+I+A | 0.881 | 0.325 | 7.352 | 0.007 | 2.413(1.277~4.562) |
| H+HD+C+I | 1.033 | 0.401 | 6.647 | 0.010 | 2.810(1.281~6.165) |
| H+HD+C+A | 1.356 | 0.411 | 10.912 | 0.001 | 3.881(1.736~8.677) |
| H+HD+I+A | 0.613 | 0.283 | 4.669 | 0.031 | 1.845(1.059~3.216) |
| H+C+I+A | 1.007 | 0.285 | 12.473 | <0.001 | 2.739(1.566~4.790) |
| H+D+HD+I+A | 0.959 | 0.445 | 4.655 | 0.031 | 2.609(1.092~6.235) |
| H+D+C+I+A | 0.789 | 0.478 | 2.721 | 0.099 | 2.200(0.862~5.614) |
| H+HD+C+I+A | 1.047 | 0.339 | 9.553 | 0.002 | 2.850(1.467~5.536) |
| H+D+HD+C+I+A | 1.184 | 0.462 | 6.555 | 0.010 | 3.266(1.320~8.084) |
| [1] |
2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2023, 19(4): 1598-1695. DOI: 10.1002/alz.13016.
|
| [2] |
GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2022, 7(2): e105-125.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
刘通达,郝志梅. 基于CHARLS 2020的我国中老年人慢性病及共病现状分析[J]. 老年医学研究, 2025, 6(4): 17-22.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
张知音,马瑜瑾,付留俊,等. 复合自主神经症状评分-31在糖尿病心血管自主神经病变中的诊断价值[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27(2): 229-234.
|
| [15] |
郭起浩,洪震. 神经心理评估[M]. 2版. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2016.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍指南写作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(一):痴呆及其分类诊断标准[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(13): 965-970.
|
| [20] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(五):轻度认知障碍的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(17): 1294-1301.
|
| [21] |
道日敖,田园,陈焕,等. 术后返回ICU患者亚急性和慢性疼痛发生率及影响因素分析[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2024, 15(3): 598-603.
|
| [22] |
黎艳娜,王艺桥. 我国老年人慢性病共病现状及模式研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(31): 3955-3962, 3978.
|
| [23] |
王梅杰,周翔,李亚杰,等. 2010—2019年中国中老年人慢性病共病患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(16): 2085-2091.
|
| [24] |
章轶立,黄馨懿,齐保玉,等. 老年人群共病问题现状挑战与应对策略[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(35): 4363-4368.
|
| [25] |
杨曦,杨星,杨敬源,等. 贵州省农村老年人睡眠障碍对认知功能损害影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2021, 37(8): 1233-1236.
|
| [26] |
韩利知. 老年人失眠现况及相关因素的临床研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2016.
|
| [27] |
张芮仙,张善东,齐涵,等. 老年人睡眠障碍的影响因素及对机体免疫状态、认知功能和生活质量的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2022, 22(21): 4071-4075.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
杨萌柳,曾燕,许浪,等. 老年人失眠及其类型对认知障碍患病影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2023, 39(6): 734-739.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [1] | ZHENG Huatao, WANG Shiqiang, LI Dan, YANG E, LUO Dan, LAI Yu, MA Rentao. Association between Physical Activity Changes Trajectories and Frailty in Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(03): 316-324. |
| [2] | ZHOU Wenchao, LIANG Jiaqi, YAO Shangman, XUE Zhao, LIU Long, GUO Xiangjie. Identification of Shared Loci between Hypertension and Parkinson's Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(02): 201-206. |
| [3] | CHENG Zhuozhuo, ZHANG Rui, HU Jiao, PAN Xuanda, XU Haofeng, HUANG Junting, YAN Ping, LIANG Zijing. Study on the Association between Multiple Chronic Conditions and Impaired Activities of Daily Living in the Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(02): 219-225. |
| [4] | MA Yuping, QIAO Mengyuan, HE Yanyun, XU Manru, CHEN Chongli, WU Wenbin. Study on the Current Status and Influencing Factors of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus from the Perspective of "Physical Disease-related Adjustable Constitution": a Case Study in Sichuan Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(02): 188-194. |
| [5] | REN Panpan, JIA Changli, JIA Jingjing, XU Jinglin, CHEN Mengyao, ZHANG Xiang. The Impact of Livelihood Capitals on the Quality of Life of Rural Older Adults: a Study Based on Different Chronic Disease Conditions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(01): 129-136. |
| [6] | HU Zhetao, PAN Xiaoyi. A Quantitative Research on Effectiveness of China's Community-dwelling Integrated Medical and Elderly Care Policy from the Perspective of Health Service Continuity [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(01): 42-49. |
| [7] | CHEN Yufei, ZHAO Qian, XIEYIRE· Hamulati, CAI Liting, LI Xiaomei, YANG Yining, LIU Fen. Association between Life's Essential 8 Score and Hypertension Risk: a Cross-Sectional Study in the Rural and Pastoral Population of Altay Prefecture, Xinjiang [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(01): 91-99. |
| [8] | ZHAO Lingyu, HAO Xiaoning, FENG Zhiqiang. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation of Implementation Effect of Medical and Prevention Integration Based on Residents' Perception [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2026, 29(01): 115-121. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ying, LIAO Xiaoyang, YANG Hanfei, YU Yongjun, LIU Lidi, JIA Yu, SHEN Can, LI Xiao, HUANG Chuanying, YANG Rong. Interpretation of the 2024 International Society of Hypertension Position Paper on Innovations in Blood Pressure Measurement and Reporting Technology and Its Implications for China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(36): 4541-4549. |
| [10] | YU Xinyan, YANG Jianyun, JIANG Qingru, CHEN Tao, SU Peng, WANG Siyang, LUO Zhanwu, ZHANG Haicheng. Study on the Correlation between the Course of Hypertension and Autonomic Nervous System Damage in Elderly Patients in Primary Care Institutions in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Based on Single Lead Wearable Electrocardiogram Device [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(34): 4359-4370. |
| [11] | MA Nian, WANG Ziyun, TENG Xiaoyan, CHEN Yun, SUN Zhengyong. Study on the Current Situation and Influencing Factors of Comorbidities among Urban-rural Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(34): 4344-4350. |
| [12] | YIN Jiajia, YAO Li, ZHOU Zihan, LI Qinqin, WANG Tingrui, LIU Yan. Meta-analysis of Factors Influencing the Prevalence of Multimorbidity among the Elderly in Different Regions of China: a Comparative Study between the North and the South [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(34): 4326-4336. |
| [13] | Expert Panel of the National Key R&D Program "Research on the Effects and Mechanisms of Multiple Types of Physical Stimulation on Body Function", Brain Function Detection and Regulation Rehabilitation Professional Committee of Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine, Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Professional Committee of Beijing Neurology Association. Expert Consensus on the Effects and Efficacy Evaluation of Non-invasive Neuromodulation in Elders with Disability and Dementia [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(34): 4258-4281. |
| [14] | XU Chunyan, HE Ling, GUO Canhui, LAI Hurong, LIAO Caifeng, TU Huaijun. Associations of Lipid Levels and the Risk of Sarcopenic Obesity in Middle-aged and Elderly Chinese: a Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(33): 4125-4131. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xi, GUAN Chengguo, WANG Jing, XU Dingxin, ZHANG Bo. Advances in Intervention Strategies for Advance Care Planning in Dementia Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(32): 4109-4116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||