

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (08): 924-929.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.410
Special Issue: 呼吸疾病文章合辑; 儿科最新文章合辑
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
The Study of the Value of High Mobility Group Protein B1 Combined with Acute Physiological Score in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Children with Severe Pneumonia
Respiratory Department,Children's Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450000,China
*Corresponding author:LI Yi,Pharmacist-in-charge;E-mail:lkyypl@163.com
Received:2021-11-11
Revised:2021-12-14
Published:2022-03-15
Online:2022-03-02
通讯作者:
李奕
基金资助:CLC Number:
KANG Ping, LI Yi, TANG Yu.
The Study of the Value of High Mobility Group Protein B1 Combined with Acute Physiological Score in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Children with Severe Pneumonia [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(08): 924-929.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.410
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄〔n(%)〕 | 发病季节〔n(%)〕 | 体温(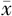 ±s,℃) ±s,℃) | 氧分压(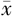 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <3岁 | ≥3岁 | 春夏 | 秋冬 | |||||||||||||||
| 转归亚组 | 41 | 25(62.0) | 16(39.0) | 24(58.5) | 17(41.5) | 12(29.27) | 29(70.73) | 37.56±0.87 | 85±12 | |||||||||||
| 预后不良亚组 | 14 | 7(50.0) | 7(50.0) | 8(57.1) | 6(42.9) | 5(35.71) | 9(64.29) | 38.12±0.84 | 79±11 | |||||||||||
| χ2(t)值 | 0.517a | 0.015a | 0.203a | 0.253 | 1.574 | |||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.472 | 0.904 | 0.652 | 0.801 | 0.121 | |||||||||||||||
Table 1 Comparison of clinical data and HMGB1 level and APS score between the children in the outcome subgroup and poor prognosis subgroup
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别〔n(%)〕 | 年龄〔n(%)〕 | 发病季节〔n(%)〕 | 体温(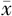 ±s,℃) ±s,℃) | 氧分压(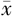 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | <3岁 | ≥3岁 | 春夏 | 秋冬 | |||||||||||||||
| 转归亚组 | 41 | 25(62.0) | 16(39.0) | 24(58.5) | 17(41.5) | 12(29.27) | 29(70.73) | 37.56±0.87 | 85±12 | |||||||||||
| 预后不良亚组 | 14 | 7(50.0) | 7(50.0) | 8(57.1) | 6(42.9) | 5(35.71) | 9(64.29) | 38.12±0.84 | 79±11 | |||||||||||
| χ2(t)值 | 0.517a | 0.015a | 0.203a | 0.253 | 1.574 | |||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.472 | 0.904 | 0.652 | 0.801 | 0.121 | |||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | HMGB1(μg/L) | APS(分) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 40 | 4.99±1.27 | 0 |
| 普通肺炎组 | 60 | 101.45±18.77a | 11.61±3.27 |
| 重症肺炎组 | 55 | 137.35±20.76ab | 20.06±5.25b |
| F值 | 287.659 | 334.188 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Comparison of serum HMGB1 levels and APS scores in the three children groups
| 组别 | 例数 | HMGB1(μg/L) | APS(分) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 40 | 4.99±1.27 | 0 |
| 普通肺炎组 | 60 | 101.45±18.77a | 11.61±3.27 |
| 重症肺炎组 | 55 | 137.35±20.76ab | 20.06±5.25b |
| F值 | 287.659 | 334.188 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 致病菌种类 | <2种=0,≥2种=1 |
| 并发症 | 有=0,无=1 |
| 机械通气 | 是=0,否=1 |
| HMGB1 | ≤126.37 μg/L=0,>126.37 μg/L=1 |
| APS评分 | <22.54分=0,≥22.54分=1 |
Table 3 Variable assignment table of prognosis index of children with severe pneumonia
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 致病菌种类 | <2种=0,≥2种=1 |
| 并发症 | 有=0,无=1 |
| 机械通气 | 是=0,否=1 |
| HMGB1 | ≤126.37 μg/L=0,>126.37 μg/L=1 |
| APS评分 | <22.54分=0,≥22.54分=1 |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量 | -4.061 | 1.054 | 14.854 | - | 0.017 | - |
| 致病菌种类 | 1.665 | 0.813 | 4.193 | 0.041 | 5.283 | (1.074,26.004) |
| HMGB1 | 2.130 | 0.911 | 5.467 | 0.019 | 8.411 | (1.411,50.137) |
| APS | 1.745 | 0.838 | 4.335 | 0.037 | 5.724 | (1.108,29.572) |
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of prognosis factors of children with severe pneumonia
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量 | -4.061 | 1.054 | 14.854 | - | 0.017 | - |
| 致病菌种类 | 1.665 | 0.813 | 4.193 | 0.041 | 5.283 | (1.074,26.004) |
| HMGB1 | 2.130 | 0.911 | 5.467 | 0.019 | 8.411 | (1.411,50.137) |
| APS | 1.745 | 0.838 | 4.335 | 0.037 | 5.724 | (1.108,29.572) |
| 预测指标 | AUC | 约登指数 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 95%CI | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1 | 0.796 | 0.611 | 72.73 | 88.33 | (0.699,0.873) | <0.001 |
| APS | 0.885 | 0.632 | 78.18 | 85.00 | (0.801,0.942) | <0.001 |
| 联合指标 | 0.975 | 0.949 | 98.18 | 96.67 | (0.918,0.996) | <0.001 |
Table 5 Diagnostic value of HMGB1,APS and combined indexes in pneumonia
| 预测指标 | AUC | 约登指数 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 95%CI | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1 | 0.796 | 0.611 | 72.73 | 88.33 | (0.699,0.873) | <0.001 |
| APS | 0.885 | 0.632 | 78.18 | 85.00 | (0.801,0.942) | <0.001 |
| 联合指标 | 0.975 | 0.949 | 98.18 | 96.67 | (0.918,0.996) | <0.001 |
| 预测指标 | AUC | 约登指数 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 95%CI | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1 | 0.868 | 0.592 | 87.80 | 71.43 | (0.749,0.944) | <0.001 |
| APS | 0.887 | 0.654 | 87.80 | 78.57 | (0.772,0.956) | <0.001 |
| 联合指标 | 0.923 | 0.904 | 97.56 | 92.86 | (0.819,0.978) | <0.001 |
Table 6 The prognostic value of HMGB1 combined with APS in children with severe pneumonia
| 预测指标 | AUC | 约登指数 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 95%CI | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1 | 0.868 | 0.592 | 87.80 | 71.43 | (0.749,0.944) | <0.001 |
| APS | 0.887 | 0.654 | 87.80 | 78.57 | (0.772,0.956) | <0.001 |
| 联合指标 | 0.923 | 0.904 | 97.56 | 92.86 | (0.819,0.978) | <0.001 |
| [1] | HE C, LIU L, CHU Y,et al. National and subnational all-cause and cause-specific child mortality in China,1996-2015:a systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals[J]. Lancet Glob Health,2017,5(2):e186-197. DOI:10.1016/s2214-109x(16)30334-5. |
| [2] | GODINJAK A, IGLICA A, RAMA A,et al. Predictive value of SAPS II and APACHE II scoring systems for patient outcome in a medical intensive care unit[J]. Acta Med Acad,2016,45(2):97-103. DOI:10.5644/ama2006-124.165. |
| [3] | 张严,文小玲. 活化蛋白C、脑钠肽及APACHEⅡ评分在老年重症肺炎患者中的动态变化及与预后的相关性[J]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版),2020,14(2):157-162. |
| [4] | ESCOBAR-ARELLANO R, GURAIEB-BARRAGÁN E, MANSANARES-HERNÁNDEZ A,et al. Sensitivity,specificity and reliability of the POP score vs. APACHE II score as predictors of severe acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Cir Cir,2019,87(4):402-409. DOI:10.24875/CIRU.18000662. |
| [5] | 李成,王丽,李建红,等. 血清甘油三酯与IL-6及APACHEⅡ评分对重症急性胰腺炎患者感染及预后的预测价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2020,30(20):3125-3129. |
| [6] | 陈艳青,黄潇,孔桂青,等. HMGB1和vWF等细胞因子对脓毒症患者病情严重程度及预后评估的意义[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2020,32(8):933-937. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200428-00346. |
| [7] | WANG J, LI R T, PENG Z Y,et al. HMGB1 participates in LPS induced acute lung injury by activating the AIM2 inflammasome in macrophages and inducing polarization of M1 macrophages via TLR2,TLR4,and RAGE/NF κB signaling pathways[J]. Int J Mol Med,2020,45(1):61-80. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4402. |
| [8] | 陈敏,徐慧,王琦,等. 重症肺炎患儿支气管肺泡灌洗液中IL-6、IL-10、IL-17、HMGB1的水平变化及意义[J]. 中国急救医学,2017,37(1):171-172. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2017.z1.131. |
| [9] | 中华医学会儿科学分会呼吸学组,《中华儿科杂志》编辑委员会. 儿童社区获得性肺炎管理指南(2013修订)(下)[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2013,51(11):856-862. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2013.11.012. |
| [10] | 王卫平. 儿科学[M]. 北京:北京大学医学出版社,2013. |
| [11] | LEGALL J R, LOIRAT P, ALPÉROVITCH A. APACHE II--a severity of disease classification system[J]. Crit Care Med,1986,14(8):754-755. DOI:10.1097/00003246-198608000-00027. |
| [12] | MIZGERD J P. Pathogenesis of severe pneumonia:advances and knowledge gaps[J]. Curr Opin Pulm Med,2017,23(3):193-197. DOI:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000365. |
| [13] | 付红敏,聂文莎. 儿童重症肺炎的早期识别[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志,2018,33(9):691-695. DOI:10.19538/j.ek2018090608. |
| [14] | 陈莉,邓立普,赵红梅,等. NEWS、REMS和APACHEⅡ评分对急诊危重患者预后评估的对比研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2017,29(12):1092-1096. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.12.008. |
| [15] | 江蓉,刘建华,徐内卫. 血清S-ChE PAB Apo A1及APACHEⅡ评分对重症肺炎预后的评估[J]. 河北医学,2018,24(4):540-544. |
| [16] | 陈亮,卓越,曾宗鼎,等. NT-ProBNP、sTREM-1及APACHEⅡ评分对老年重症肺炎患者预后评估的价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志,2019,20(6):454-460. DOI:10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2019.06.008. |
| [17] | 刘纪,张生雷,茅一萍,等. ASIS和APACHEⅡ评分对重症患者病情严重程度评估作用的研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2018,28(8):1195-1198. |
| [18] | 孔庆华,白久武,王晓如,等. 三种评分系统在老年社区获得性肺炎危险度分层及病情评估中的应用[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2018,17(2):138-143. |
| [19] | ANDERSSON U, YANG H, HARRIS H. High-mobility group box 1 protein(HMGB1)operates as an alarmin outside as well as inside cells[J]. Semin Immunol,2018,38:40-48. DOI:10.1016/j.smim.2018.02.011. |
| [20] | DENG M H, SCOTT M J, FAN J,et al. Location is the key to function:HMGB1 in Sepsis and trauma-induced inflammation[J]. J Leukoc Biol,2019,106(1):161-169. DOI:10.1002/JLB.3MIR1218-497R. |
| [21] | 龚曼芹,王宇静,王庆秋,等. 脉冲高容量血液滤过对重症急性胰腺炎患者血清HMGB1的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2018,28(13):45-51. |
| [22] | 陈金妮,李大伟,林秋玉,等. 难治性肺炎患儿感染病原学及HMGB1、TLR2、TLR4表达[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2020,30(18):2847-2850. |
| [23] | 张林娇,张明,于思筠. HMGB1水平与重症肺炎伴ARDS的相关性分析[J]. 实验与检验医学,2019,37(2):276-278. |
| [24] | 黄洪婕,李宁秀. 呼吸机相关性肺炎患者病原菌分布及血清sTREM-1和HMGB1的变化[J]. 中国微生态学杂志,2020,32(4):435-438. DOI:10.13381/j.cnki.cjm.202004013. |
| [25] | 彭艳,王学虎,刘琼. 血清高迁移率族蛋白B1与APACHE-Ⅱ评分对急性胰腺炎患者严重程度及预后的评估价值[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(17):2350-2352. |
| [26] | 黄一桂,陈钰,符征高,等. 血浆单核细胞趋化蛋白1、可溶性髓系细胞触发受体1及高迁移率族蛋白B1水平对急性肺损伤患者病情及预后的评估价值[J]. 中华危重症医学杂志(电子版),2021,14(1):25-29. |
| [1] | LYU Juan, LI Yuchuan, CAI Siyu, WANG Chen. Reasons for Seeking Medical Treatment in Endocrinology Department and the Need for Non-medical Intervention in Children with Normal Height: a Qualitative Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3766-3772. |
| [2] | LI Hao, LI Peijin, LIU Tingting, CUI Yiyuan, LI Sicong, LIU Lixing, FENG Li, Working Group on Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines for Cancer Pain. Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer Pain by Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3729-3740. |
| [3] | BAI Jiaxin, CHEN Yu, ZHOU Yiheng, LIU Lidi, YANG Rong, YAO Yi, YUAN Bo, ZHANG Yonggang, LEI Yi, ZENG Rui, JIA Yu, LIAO Xiaoyang. Assessment and Treatment of Early-onset Hypertension: Position Statement of the British and Irish Hypertension Association and Its Implications for Clinical Management of Early-onset Hypertension in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3741-3746. |
| [4] | XU Yanpeng, HUANG Pe, ZHANG Pingping, LUO Yan, SHI Xiaoqi, WU Liusong, CHEN Yan, HE Zhixu. Expression of β-Adrenergic Receptors in Acute T-cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Clinical Significance [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3391-3398. |
| [5] | SHAO Xiaoying, SHAO Jie, ZHU Yan, SHAO Jinling, SHANG Ling, WU Zhenlian, ZHAO Yu, ZHANG Jiacai. Analysis of the Current Status of Iron Deficiency and Factors Affecting Iron Deficiency Anemia among Children Aged 6-36 Months in Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3368-3374. |
| [6] | QUAN Jialin, ZHU Lin, SU Yu, CHEN Zekai, CHEN Ziqi, ZHANG Zhuofan. Research on the Improvement Effect of Exercise Modes on the Executive Function of Overweight or Obese Children or Adolescents: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [7] | YIN Jiahui, YANG Xinhui, WANG Jingjing, ZHANG Yajing, WANG Lijuan, FU Zuodi, KONG Xiangshuang, GUO Guangxia, LI Yufeng. Predictive Value Waist-to-height Ratio, Waist-to-hip Ratio and Body Mass Index for Metabolic Syndrome [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3258-3263. |
| [8] | WEI Jiaohua, PENG Huiru, PENG Jianye, TAN Wenting, HUANG Jine, FANG Li. Expression of the Serum MOTS-c and Its Correlation with Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [9] | ZHI Congcong, LI Xue, CHENG Yicheng, WANG Xiaolong, ZHENG Lihua. Guidelines for Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemorrhoids (2025 Edition) [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3217-3228. |
| [10] | HU Jieman, TAN Feixiang, YUAN Anxin, CHEN Shiyu, TANG Chulei, YIN Yueheng, BA Lei, XU Qin. Analysis of the Trajectory of Postoperative Frailty and Influencing Factors in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [11] | CHOU Xintong, PENG Hanyu, MA Hui, ZHANG Zhen, SU Xian, QIU Hongyan. Maternal Preferences in Contraceptive Decision-making: an Analysis of Influencing Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [12] | FAN Boyang, ZHANG Yu, SUN Wenning, ZHANG Huifang, WANG Yingjie, ZHANG Ao, ZHAO Yang, WANG Haipeng. Study of Behavioral Intention and Influencing Factors of Integrated Medical and Preventive Care Provided by Grassroots Doctors for Patients with Chronic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [13] | PAN Qi, REN Jingjing, MA Fanghui, HU Mengjie. Survey of General Practitioners' Cognition and Needs for AI Assisted Diagnosis and Treatment Systems [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [14] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [15] | YANG Chen, CHEN Tong, ZHANG Lifang, ZHANG Hongxu, LI Pengfei, ZHANG Xuejuan. Prognostic Impact of Dapagliflozin in Elderly Breast Cancer Survivors with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||