

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (06): 742-749.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.119
Special Issue: 老年人群健康最新文章合辑; 衰弱最新文章合辑; 胰腺炎最新文章合辑; 老年问题最新文章合辑
• Geriatric Health Problems • Previous Articles Next Articles
Developmental Trajectory of Frailty in Chinese Elderly People:an Analysis Based on the Latent Growth Model
1.Physical Education College of Hunan University of Technology,Zhuzhou 412007,China
2.Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Physical Health and Sports Fitness,Zhuzhou 412007,China
*Corresponding author:WANG Shiqiang,Associate professor;E-mail:suswsq@163.com
Received:2021-08-15
Revised:2021-11-05
Published:2022-02-20
Online:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
王世强
基金资助:CLC Number:
GUO Kailin, WANG Shiqiang, LI Dan, WANG Yijie, WANG Shaokun, XU Zhihan.
Developmental Trajectory of Frailty in Chinese Elderly People:an Analysis Based on the Latent Growth Model [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(06): 742-749.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.119
| 项目 | 2011年 | 2013年 | 2015年 | 2018年 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 慢性疾病〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 高血压 | 614(27.0) | 703(30.9) | 801(35.2) | 1 146(50.4) | |
| 血脂异常 | 214(9.4) | 291(12.8) | 337(14.8) | 430(19.0) | |
| 糖尿病 | 125(5.5) | 169(7.4) | 213(9.4) | 229(10.1) | |
| 肺部疾病 | 275(12.1) | 317(13.9) | 362(15.9) | 386(17.0) | |
| 肝脏疾病 | 82(3.6) | 86(3.7) | 90(4.0) | 96(4.2) | |
| 心脏病 | 313(13.8) | 368(16.2) | 421(18.5) | 521(22.9) | |
| 卒中 | 50(2.2) | 56(2.5) | 75(3.3) | 93(4.1) | |
| 肾脏疾病 | 142(6.2) | 149(6.5) | 174(7.6) | 254(11.2) | |
| 消化系统疾病 | 469(20.6) | 527(23.2) | 521(22.9) | 612(26.9) | |
| 精神疾病 | 23(0.1) | 20(0.08) | 35(1.5) | 25(1.1) | |
| 与记忆相关疾病 | 21(0.09) | 34(1.5) | 54(2.4) | 65(2.9) | |
| 关节炎或风湿 | 778(34.2) | 851(37.4) | 870(38.2) | 966(42.4) | |
| 哮喘 | 98(4.3) | 123(5.4) | 156(6.9) | 179(7.9) | |
| 残疾〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 躯体残疾 | 81(3.6) | 129(5.7) | 172(7.6) | 188(8.3) | |
| 大脑受损 | 37(1.6) | 83(3.6) | 146(6.4) | 178(7.8) | |
| 视觉障碍〔n(%)〕 | 137(6.0) | 246(10.8) | 374(16.4) | 252(11.1) | |
| 听觉障碍〔n(%)〕 | 186(8.2) | 309(13.6) | 464(20.4) | 525(23.1) | |
| 健康变化〔n(%)〕 | 591(25.9) | 522(22.9) | 581(25.5) | 431(18.9) | |
| BADL〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 穿衣 | 81(3.6) | 88(3.9) | 126(5.7) | 138(6.1) | |
| 吃饭 | 47(2.1) | 33(1.4) | 49(2.2) | 61(2.9) | |
| 洗澡 | 100(4.4) | 122(5.4) | 165(7.2) | 186(8.2) | |
| 起床 | 88(3.9) | 108(4.7) | 167(7.3) | 200(8.8) | |
| 上厕所 | 271(11.9) | 285(12.5) | 327(14.4) | 365(16.0) | |
| 控制大小便 | 91(4.0) | 92(4.0) | 112(4.9) | 150(6.6) | |
| IADL〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 做家务 | 159(7.0) | 195(8.6) | 291(12.8) | 421(18.4) | |
| 做饭 | 145(6.4) | 154(6.8) | 200(8.8) | 253(11.1) | |
| 购物 | 141(6.2) | 121(5.3) | 163(7.2) | 168(7.4) | |
| 理财 | 207(9.1) | 169(7.4) | 196(8.6) | 265(11.6) | |
| 服药 | 104(4.6) | 71(3.1) | 89(3.9) | 93(4.1) | |
| 移动能力〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 跑或慢跑1 km | 1 177(51.7) | 1 184(52.0) | 1 255(55.1) | 2 500(26.0) | |
| 走1 km | 288(12.7) | 352(15.5) | 446(19.6) | 517(22.7) | |
| 爬楼 | 922(40.5) | 902(39.6) | 976(42.9) | 1 011(44.4) | |
| 肌肉能力〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 久坐再站立 | 600(26.4) | 640(28.0) | 679(29.8) | 719(31.6) | |
| 弯腰屈膝下蹲 | 658(28.9) | 731(32.1) | 798(35.1) | 851(37.4) | |
| 手臂向上伸展 | 191(8.4) | 208(9.1) | 242(10.6) | 284(12.5) | |
| 提5 kg重物 | 223(9.8) | 293(12.9) | 326(14.3) | 369(16.2) | |
| 从桌上拾起硬币 | 62(2.7) | 63(2.8) | 120(5.3) | 189(8.3) | |
| 抑郁〔n(%)〕 | 706(31.0) | 551(24.2) | 633(27.8) | 841(37.0) | |
认知( ±s,分) ±s,分) | 0.50±0.19 | 0.48±0.19 | 0.69±0.78 | 0.71±0.26 | |
Table 1 Frailty index and the distribution of health defects in participants by the wave of CHARLS
| 项目 | 2011年 | 2013年 | 2015年 | 2018年 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 慢性疾病〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 高血压 | 614(27.0) | 703(30.9) | 801(35.2) | 1 146(50.4) | |
| 血脂异常 | 214(9.4) | 291(12.8) | 337(14.8) | 430(19.0) | |
| 糖尿病 | 125(5.5) | 169(7.4) | 213(9.4) | 229(10.1) | |
| 肺部疾病 | 275(12.1) | 317(13.9) | 362(15.9) | 386(17.0) | |
| 肝脏疾病 | 82(3.6) | 86(3.7) | 90(4.0) | 96(4.2) | |
| 心脏病 | 313(13.8) | 368(16.2) | 421(18.5) | 521(22.9) | |
| 卒中 | 50(2.2) | 56(2.5) | 75(3.3) | 93(4.1) | |
| 肾脏疾病 | 142(6.2) | 149(6.5) | 174(7.6) | 254(11.2) | |
| 消化系统疾病 | 469(20.6) | 527(23.2) | 521(22.9) | 612(26.9) | |
| 精神疾病 | 23(0.1) | 20(0.08) | 35(1.5) | 25(1.1) | |
| 与记忆相关疾病 | 21(0.09) | 34(1.5) | 54(2.4) | 65(2.9) | |
| 关节炎或风湿 | 778(34.2) | 851(37.4) | 870(38.2) | 966(42.4) | |
| 哮喘 | 98(4.3) | 123(5.4) | 156(6.9) | 179(7.9) | |
| 残疾〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 躯体残疾 | 81(3.6) | 129(5.7) | 172(7.6) | 188(8.3) | |
| 大脑受损 | 37(1.6) | 83(3.6) | 146(6.4) | 178(7.8) | |
| 视觉障碍〔n(%)〕 | 137(6.0) | 246(10.8) | 374(16.4) | 252(11.1) | |
| 听觉障碍〔n(%)〕 | 186(8.2) | 309(13.6) | 464(20.4) | 525(23.1) | |
| 健康变化〔n(%)〕 | 591(25.9) | 522(22.9) | 581(25.5) | 431(18.9) | |
| BADL〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 穿衣 | 81(3.6) | 88(3.9) | 126(5.7) | 138(6.1) | |
| 吃饭 | 47(2.1) | 33(1.4) | 49(2.2) | 61(2.9) | |
| 洗澡 | 100(4.4) | 122(5.4) | 165(7.2) | 186(8.2) | |
| 起床 | 88(3.9) | 108(4.7) | 167(7.3) | 200(8.8) | |
| 上厕所 | 271(11.9) | 285(12.5) | 327(14.4) | 365(16.0) | |
| 控制大小便 | 91(4.0) | 92(4.0) | 112(4.9) | 150(6.6) | |
| IADL〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 做家务 | 159(7.0) | 195(8.6) | 291(12.8) | 421(18.4) | |
| 做饭 | 145(6.4) | 154(6.8) | 200(8.8) | 253(11.1) | |
| 购物 | 141(6.2) | 121(5.3) | 163(7.2) | 168(7.4) | |
| 理财 | 207(9.1) | 169(7.4) | 196(8.6) | 265(11.6) | |
| 服药 | 104(4.6) | 71(3.1) | 89(3.9) | 93(4.1) | |
| 移动能力〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 跑或慢跑1 km | 1 177(51.7) | 1 184(52.0) | 1 255(55.1) | 2 500(26.0) | |
| 走1 km | 288(12.7) | 352(15.5) | 446(19.6) | 517(22.7) | |
| 爬楼 | 922(40.5) | 902(39.6) | 976(42.9) | 1 011(44.4) | |
| 肌肉能力〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 久坐再站立 | 600(26.4) | 640(28.0) | 679(29.8) | 719(31.6) | |
| 弯腰屈膝下蹲 | 658(28.9) | 731(32.1) | 798(35.1) | 851(37.4) | |
| 手臂向上伸展 | 191(8.4) | 208(9.1) | 242(10.6) | 284(12.5) | |
| 提5 kg重物 | 223(9.8) | 293(12.9) | 326(14.3) | 369(16.2) | |
| 从桌上拾起硬币 | 62(2.7) | 63(2.8) | 120(5.3) | 189(8.3) | |
| 抑郁〔n(%)〕 | 706(31.0) | 551(24.2) | 633(27.8) | 841(37.0) | |
认知( ±s,分) ±s,分) | 0.50±0.19 | 0.48±0.19 | 0.69±0.78 | 0.71±0.26 | |
| 变量 | FI2011 | FI2013 | FI2015 | FI2018 | PA2011 | PA2013 | PA2015 | PA2018 | 吸烟2011 | 吸烟2013 | 吸烟2015 | 吸烟2018 | 饮酒2011 | 饮酒2013 | 饮酒2015 | 饮酒2018 | 睡眠2011 | 睡眠2013 | 睡眠2015 | 睡眠2018 | 性别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI2011 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FI2013 | 0.73a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| FI2015 | 0.65a | 0.76a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FI2018 | 0.30a | 0.31a | 0.36a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2011 | -0.03a | -0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2013 | -0.04 | -0.03a | <0.01 | -0.01 | 0.74a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2015 | -0.05a | -0.06a | -0.08a | 0.02 | 0.04a | 0.05a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2018 | -0.16a | -0.17a | -0.20a | -0.14a | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2011 | 0.13a | 0.14a | 0.14a | 0.06a | -0.02 | -0.03 | -0.01 | 0.02 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2013 | 0.11a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.03 | -0.04 | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.92a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2015 | 0.10a | 0.12a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.01 | -0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.79a | 0.82a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2018 | 0.10a | 0.12a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.03 | -0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.74a | 0.75a | 0.82a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2011 | 0.13a | 0.17a | 0.15a | 0.09a | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.01 | 0.06a | 0.27a | 0.28a | 0.24a | 0.24a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2013 | 0.13a | 0.16a | 0.14a | 0.10a | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07a | 0.25a | 0.26a | 0.24a | 0.23a | 0.63a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2015 | 0.12a | 0.17a | 0.15a | 0.10a | <0.01 | -0.03 | 0.01 | 0.08a | 0.23a | 0.24a | 0.24a | 0.23a | 0.64a | 0.66a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2018 | 0.15a | 0.19a | 0.17a | 0.09a | -0.01 | -0.04a | 0.02 | 0.08a | 0.23a | 0.24a | 0.22a | 0.22a | 0.60a | 0.62a | 0.65a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2011 | -0.21a | -0.18a | -0.17a | -0.70a | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0.03 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2013 | -0.17a | -0.22a | -0.17a | -0.08a | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.05a | 0.06a | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05a | 0.35a | 1.00 | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2015 | -0.21a | -0.21a | -0.22a | -0.09a | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04a | 0.11a | 0.11a | 0.10a | 0.09a | 0.05a | 0.08a | 0.06a | 0.05a | 0.36a | 0.41a | 1.00 | - | - |
| 睡眠2018 | -0.20a | -0.23a | -0.20a | -0.10a | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.07a | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.06a | 0.02 | 0.05a | 0.06a | 0.05a | 0.35a | 0.38a | 0.40a | 1.00 | - |
| 性别 | -0.20a | -0.21a | -0.22a | -0.17a | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07a | 0.50a | 0.51a | 0.44a | 0.41a | 0.37a | 0.38a | 0.34a | 0.35a | 0.10a | 0.11a | 0.14a | 0.15a | 1.00 |
| 教育程度 | -0.22a | -0.20a | -0.20a | -0.21a | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10a | 0.14a | 0.15a | 0.14a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.15a | 0.09a | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.10a | 0.39a |
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of frailty index with PA,smoking,alcohol consumption,sleep,gender,and education level in Chinese older people
| 变量 | FI2011 | FI2013 | FI2015 | FI2018 | PA2011 | PA2013 | PA2015 | PA2018 | 吸烟2011 | 吸烟2013 | 吸烟2015 | 吸烟2018 | 饮酒2011 | 饮酒2013 | 饮酒2015 | 饮酒2018 | 睡眠2011 | 睡眠2013 | 睡眠2015 | 睡眠2018 | 性别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI2011 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FI2013 | 0.73a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| FI2015 | 0.65a | 0.76a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FI2018 | 0.30a | 0.31a | 0.36a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2011 | -0.03a | -0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2013 | -0.04 | -0.03a | <0.01 | -0.01 | 0.74a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2015 | -0.05a | -0.06a | -0.08a | 0.02 | 0.04a | 0.05a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PA2018 | -0.16a | -0.17a | -0.20a | -0.14a | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2011 | 0.13a | 0.14a | 0.14a | 0.06a | -0.02 | -0.03 | -0.01 | 0.02 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2013 | 0.11a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.03 | -0.04 | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.92a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2015 | 0.10a | 0.12a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.01 | -0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.79a | 0.82a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 吸烟2018 | 0.10a | 0.12a | 0.13a | 0.06a | -0.03 | -0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.74a | 0.75a | 0.82a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2011 | 0.13a | 0.17a | 0.15a | 0.09a | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.01 | 0.06a | 0.27a | 0.28a | 0.24a | 0.24a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2013 | 0.13a | 0.16a | 0.14a | 0.10a | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07a | 0.25a | 0.26a | 0.24a | 0.23a | 0.63a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2015 | 0.12a | 0.17a | 0.15a | 0.10a | <0.01 | -0.03 | 0.01 | 0.08a | 0.23a | 0.24a | 0.24a | 0.23a | 0.64a | 0.66a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 饮酒2018 | 0.15a | 0.19a | 0.17a | 0.09a | -0.01 | -0.04a | 0.02 | 0.08a | 0.23a | 0.24a | 0.22a | 0.22a | 0.60a | 0.62a | 0.65a | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2011 | -0.21a | -0.18a | -0.17a | -0.70a | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0.03 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2013 | -0.17a | -0.22a | -0.17a | -0.08a | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.05a | 0.06a | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05a | 0.35a | 1.00 | - | - | - |
| 睡眠2015 | -0.21a | -0.21a | -0.22a | -0.09a | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04a | 0.11a | 0.11a | 0.10a | 0.09a | 0.05a | 0.08a | 0.06a | 0.05a | 0.36a | 0.41a | 1.00 | - | - |
| 睡眠2018 | -0.20a | -0.23a | -0.20a | -0.10a | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.07a | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.06a | 0.02 | 0.05a | 0.06a | 0.05a | 0.35a | 0.38a | 0.40a | 1.00 | - |
| 性别 | -0.20a | -0.21a | -0.22a | -0.17a | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07a | 0.50a | 0.51a | 0.44a | 0.41a | 0.37a | 0.38a | 0.34a | 0.35a | 0.10a | 0.11a | 0.14a | 0.15a | 1.00 |
| 教育程度 | -0.22a | -0.20a | -0.20a | -0.21a | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10a | 0.14a | 0.15a | 0.14a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.13a | 0.15a | 0.09a | 0.08a | 0.07a | 0.10a | 0.39a |
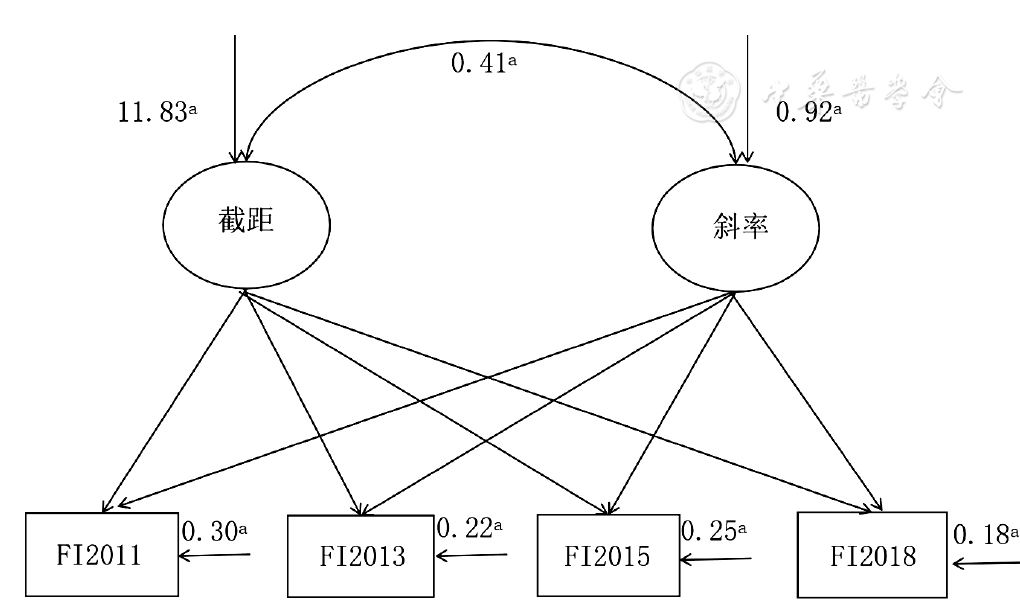
Figure 1 Unconditional latent growth model with undefined curve for analyzing the developmental trajectory and associated factors of frailty in Chinese older people
| 模型 | χ2(df) | P值 | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | 系数 | 变异 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 斜率 | 截距 | 斜率 | |||||||
| 线性无条件LGM | 97.87(5) | <0.01 | 0.977 | 0.973 | 0.090 | 0.053 | 11.87 | 0.79 | 58.52 | 1.87 |
| 二次函数无条件LGM | 51.05(1) | <0.01 | 0.988 | 0.927 | 0.148 | 0.033 | 11.82 | 0.51 | 85.02 | 9.85 |
| 不定义曲线无条件LGM | 36.16(3) | <0.01 | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.070 | 0.022 | 11.83 | 0.92 | 53.16 | 1.13 |
Table 3 Fitting indices of the unconditional latent growth model for analyzing the developmental trajectory of frailty in Chinese older people
| 模型 | χ2(df) | P值 | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | 系数 | 变异 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 斜率 | 截距 | 斜率 | |||||||
| 线性无条件LGM | 97.87(5) | <0.01 | 0.977 | 0.973 | 0.090 | 0.053 | 11.87 | 0.79 | 58.52 | 1.87 |
| 二次函数无条件LGM | 51.05(1) | <0.01 | 0.988 | 0.927 | 0.148 | 0.033 | 11.82 | 0.51 | 85.02 | 9.85 |
| 不定义曲线无条件LGM | 36.16(3) | <0.01 | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.070 | 0.022 | 11.83 | 0.92 | 53.16 | 1.13 |
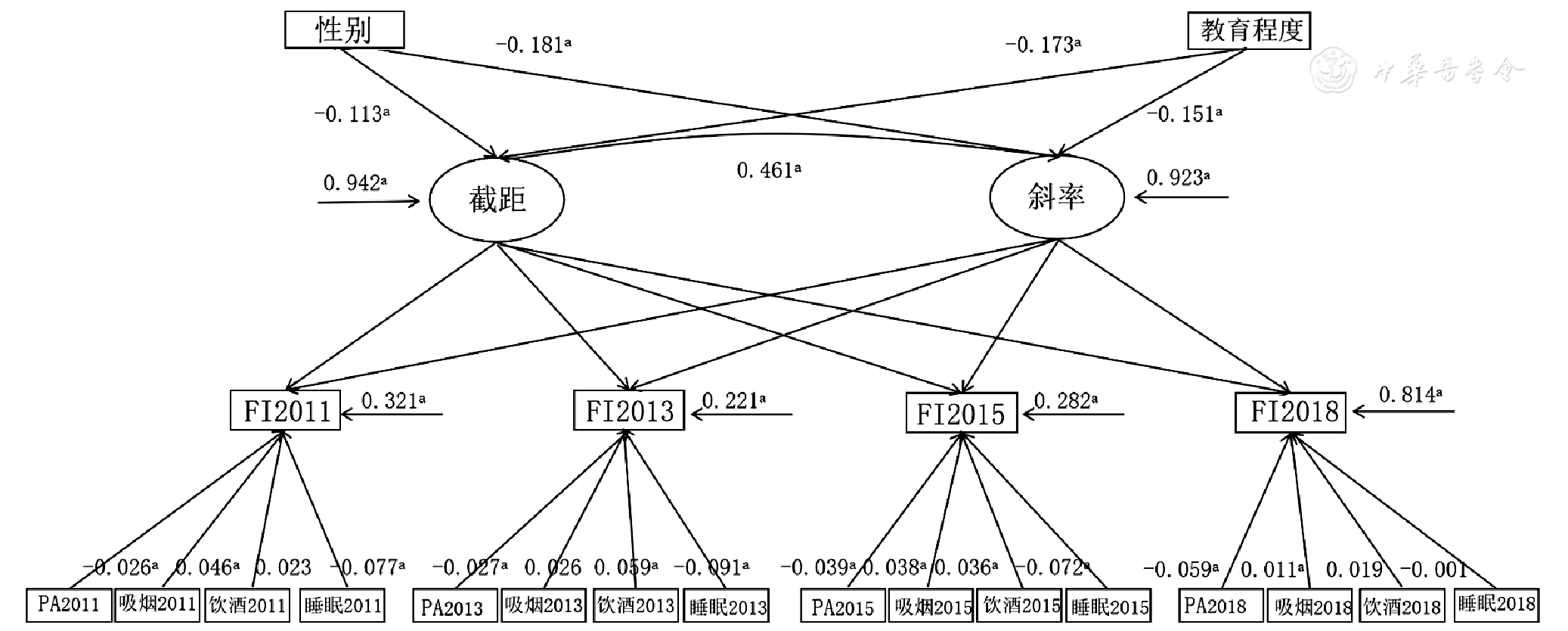
Figure 2 Conditional latent growth model with undefined curve for analyzing the developmental trajectory and associated factors of frailty in Chinese older people
| [1] | United Nations.World Population Prospects 2019-Highlights[EB/OL]. (2019-12-31)[2021-02-15]. . |
| [2] | CLEGG A, YOUNG J, ILIFFE S,et al. Frailty in elderly people[J]. Lancet,2013,381(9868):752-762. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)62167-9. |
| [3] | VERMEIREN S, VELLA-AZZOPARDI R, BECKWÉE D,et al. Frailty and the prediction of negative health outcomes:a meta-analysis[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc,2016,17(12):1163.e1-1161163.e17. DOI:10.1016/j.jamda.2016.09.010. |
| [4] | BOCK J O, KÖNIG H H, BRENNER H,et al. Associations of frailty with health care costs——results of the ESTHER cohort study[J]. BMC Health Serv Res,2016,16:128. DOI:10.1186/s12913-016-1360-3. |
| [5] | O'BRIEN T D, ROBERTS J, BRACKENRIDGE G R,et al. Some aspects of community care of the frail and elderly:the need for assessment[J]. Gerontol Clin (Basel),1968,10(4):215-227. DOI:10.1159/000245187. |
| [6] | ROCKWOOD K, SONG X W, MACKNIGHT C,et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people[J]. J De L'association Med Can,2005,173(5):489-495. DOI:10.1503/cmaj.050051. |
| [7] | ROGERS N T, FANCOURT D. Cultural engagement is a risk-reducing factor for frailty incidence and progression[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci,2020,75(3):571-576. DOI:10.1093/geronb/gbz004. |
| [8] | STOLZ E, MAYERL H, WAXENEGGER A,et al. Impact of socioeconomic position on frailty trajectories in 10 European countries:evidence from the Survey of Health,Ageing and Retirement in Europe (2004—2013)[J]. J Epidemiol Community Health,2017,71(1):73-80. DOI:10.1136/jech-2016-207712. |
| [9] | 尹佳慧,曾雁冰,周鼒,等. 中国老年人衰弱状况及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2018,39(9):1244-1248. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.09.019. |
| [10] | 王志燕,高欢玲,宋歌. 山西省农村老年人衰弱现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学杂志,2021,36(5):88-91. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.05.088. |
| [11] | 余静雅,高静,柏丁兮,等. 成都市社区老年人衰弱现状与影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2021,41(9):1972-1977. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.09.052. |
| [12] | 田鹏,杨宁,郝秋奎,等. 中国老年衰弱患病率的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2019,19(6):656-664. DOI:10.7507/1672-2531.201901056. |
| [13] | HSU H C, CHANG W C. Trajectories of frailty and related factors of the older people in Taiwan[J]. Exp Aging Res,2015,41(1):104-114. DOI:10.1080/0361073X.2015.978219. |
| [14] | STOW D, MATTHEWS F E, HANRATTY B. Frailty trajectories to identify end of life:a longitudinal population-based study[J]. BMC Med,2018,16(1):171. DOI:10.1186/s12916-018-1148-x. |
| [15] | 王宇宸,马腾,蒋晓燕,等. 老年人衰弱与睡眠障碍的关联探究[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(15):1766-1771. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.113. |
| [16] | 崔光辉,李少杰,尹永田,等. 济南市社区老年人中医体质类型与衰弱综合征的关联性分析[J]. 中医药导报,2021,27(1):178-181. DOI:10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2021.01.042. |
| [17] | 中国健康与养老追踪调查[EB/OL]. (2019-09-13)[2021-02-10]. . |
| [18] | CRAIG C L, MARSHALL A L, SJÖSTRÖM M,et al. International physical activity questionnaire:12-country reliability and validity[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc,2003,35(8):1381-1395. DOI:10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB. |
| [19] | 乔玉成. 身体活动水平:等级划分、度量方法和能耗估算[J]. 体育研究与教育,2017,32(3):1-12,113. DOI:10.16207/j.cnki.2095-235x.2017.03.001. |
| [20] | 樊萌语,吕筠,何平平. 国际体力活动问卷中体力活动水平的计算方法[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2014,35(8):961-964. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.08.019. |
| [21] | APÓSTOLO J, COOKE R, BOBROWICZ-CAMPOS E,et al. Predicting risk and outcomes for frail older adults:an umbrella review of frailty screening tools[J]. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep,2017,15(4):1154-1208. DOI:10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003018. |
| [22] | KOJIMA G, ILIFFE S, WALTERS K. Frailty index as a predictor of mortality:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Age Ageing,2018,47(2):193-200. DOI:10.1093/ageing/afx162. |
| [23] | SEARLE S D, MITNITSKI A, GAHBAUER E A,et al. A standard procedure for creating a frailty index[J]. BMC Geriatr,2008,8(1):24-33. DOI:10.1186/1471-2318-8-24. |
| [24] | ROCKWOOD K, SONG X W, MACKNIGHT C,et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people[J]. J De L'association Med Can,2005,173(5):489-495. DOI:10.1503/cmaj.050051. |
| [25] | 石婧,石冰,陶永康,等. 基于衰弱指数评估的老年人衰弱状况与死亡风险的相关性分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2020,41(11):1824-1830. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200506-00691. |
| [26] | GU D N, DUPRE M E, SAUTTER J,et al. Frailty and mortality among Chinese at advanced ages[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci,2009,64(2):279-289. DOI:10.1093/geronb/gbn009. |
| [27] | 黄庆波,王晓华,陈功. 10项流调中心抑郁自评量表在中国中老人群中的信效度[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志,2015,23(7):1036-1041. DOI:10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2015.07.023. |
| [28] | KULMINSKI A M, UKRAINTSEVA S V, KULMINSKAYA I V,et al. Cumulative deficits better characterize susceptibility to death in elderly people than phenotypic frailty:lessons from the Cardiovascular Health Study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc,2008,56(5):898-903. DOI:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01656.x. |
| [29] | DEMIRTAS H, FREELS S A, YUCEL R M. Plausibility of multivariate normality assumption when multiply imputing non-Gaussian continuous outcomes:a simulation assessment[J]. J Stat Comput Simul,2008,78(1):69-84. DOI:10.1080/10629360600903866. |
| [30] | 张文娟,付敏. 长期护理保险制度中老年人的失能风险和照料时间——基于Barthel指数的分析[J]. 保险研究,2020(5):80-93. DOI:10.13497/j.cnki.is.2020.05.006. |
| [31] | TEO T, KHINE M S. Structural equation modeling in educational research:concepts and applications[M]. Rotterdam:Sense Publishers,2009. |
| [32] | ETMAN A, BURDORF A, VAN DER CAMMEN T J,et al. Socio-demographic determinants of worsening in frailty among community-dwelling older people in 11 European countries[J]. J Epidemiol Community Health,2012,66(12):1116-1121. DOI:10.1136/jech-2011-200027. |
| [33] | RODRIGUEZ-MAÑAS L, FRIED L P. Frailty in the clinical scenario[J]. Lancet,2015,385(9968):e7-9. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(14)61595-6. |
| [34] | BRAY N W, SMART R R, JAKOBI J M,et al. Exercise prescription to reverse frailty[J]. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab,2016,41(10):1112-1116. DOI:10.1139/apnm-2016-0226. |
| [35] | STOLZ E, MAYERL H, RÁSKY É,et al. Does sample attrition affect the assessment of frailty trajectories among older adults? A joint model approach[J]. Gerontology,2018,64(5):430-439. DOI:10.1159/000489335. |
| [36] | STOW D, MATTHEWS F E, HANRATTY B. Frailty trajectories to identify end of life:a longitudinal population-based study[J]. BMC Med,2018,16(1):171. DOI:10.1186/s12916-018-1148-x. |
| [37] | AGUAYO G A, HULMAN A, VAILLANT M T,et al. Prospective association among diabetes diagnosis,HbA1c,glycemia,and frailty trajectories in an elderly population[J]. Diabetes Care,2019,42(10):1903-1911. DOI:10.2337/dc19-0497. |
| [38] | GALE C R, COOPER C, SAYER A A. Prevalence of frailty and disability:findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing[J]. Age Ageing,2015,44(1):162-165. DOI:10.1093/ageing/afu148. |
| [39] | HARTTGEN K, KOWAL P, STRULIK H,et al. Patterns of frailty in older adults:comparing results from higher and lower income countries using the Survey of Health,Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) and the Study on Global Ageing and Adult Health (SAGE)[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(10):e75847. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0075847. |
| [40] | PEL-LITTEL R E, SCHUURMANS M J, EMMELOT-VONK M H,et al. Frailty:defining and measuring of a concept[J]. J Nutr Health Aging,2009,13(4):390-394. DOI:10.1007/s12603-009-0051-8. |
| [41] | XUE Q L. The frailty syndrome:definition and natural history[J]. Clin Geriatr Med,2011,27(1):1-15. DOI:10.1016/j.cger.2010.08.009. |
| [42] | YANG Y, LEE L C. Sex and race disparities in health:cohort variations in life course patterns[J]. Soc Forces,2009,87(4):2093-2124. DOI:10.1353/sof.0.0183. |
| [43] | ETMAN A, KAMPHUIS C B, VAN DER CAMMEN T J,et al. Do lifestyle,health and social participation mediate educational inequalities in frailty worsening?[J]. Eur J Public Health,2015,25(2):345-350. DOI:10.1093/eurpub/cku093. |
| [44] | BAKKER C J, KOFFEL J B, THEIS-MAHON N R. Measuring the health literacy of the Upper Midwest[J]. J Med Libr Assoc,2017,105(1):34-43. DOI:10.5195/jmla.2017.105. |
| [45] | 侯桂云,黎光明,谢晋艳,等. 老年人认知功能的变化轨迹:基于潜变量增长模型的分析[J]. 心理科学,2018,41(4):835-841. DOI:10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20180411. |
| [46] | 解瑞宁,李英娥. 社区老年人认知功能及影响因素[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志,2015,23(8):1222-1224. DOI:10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2015.08.029. |
| [47] | 王会会,王君俏,谢博钦,等. 养老机构非卧床老年人衰弱影响因素的路径分析[J]. 护理学杂志,2018,33(13):76-80. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2018.13.076. |
| [48] | DENT E, MORLEY J E, CRUZ-JENTOFT A J,et al. Physical frailty:ICFSR international clinical practice guidelines for identification and management[J]. J Nutr Health Aging,2019,23(9):771-787. DOI:10.1007/s12603-019-1273-z. |
| [49] | PAULO T R S, TRIBESS S, SASAKI J E,et al. A cross-sectional study of the relationship of physical activity with depression and cognitive deficit in older adults[J]. J Aging Phys Act,2016,24 (2):311-321. DOI:10.1123/japa.2014-0253. |
| [50] | VIRTUOSO JÚNIOR J S, TRIBESS S, PAULO T R,et al. Physical activity as an indicator of predictive functional disability in elderly[J]. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem,2012,20(2):259-265. DOI:10.1590/s0104-11692012000200007. |
| [51] | TRIBESS S, VIRTUOSO JÚNIOR J S, OLIVEIRA R J. Physical activity as a predictor of absence of frailty in the elderly[J]. Rev Assoc Med Bras:1992,2012,58(3):341-347. DOI:10.1590/s0104-42302012000300015. |
| [52] | ROBERTS C K, HEVENER A L, BARNARD R J. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance:underlying causes and modification by exercise training[J]. Compr Physiol,2013,3(1):1-58. DOI:10.1002/cphy.c110062. |
| [53] | LAUTENSCHLAGER N T, COX K L, FLICKER L,et al. Effect of physical activity on cognitive function in older adults at risk for Alzheimer disease:a randomized trial[J]. JAMA,2008,300(9):1027-1037. DOI:10.1001/jama.300.9.1027. |
| [54] | POWER G A, DALTON B H, BEHM D G,et al. Motor unit survival in lifelong runners is muscle dependent[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc,2012,44(7):1235-1242. DOI:10.1249/mss.0b013e318249953c. |
| [55] | GILLESPIE L D, ROBERTSON M C, GILLESPIE W J,et al. Interventions for preventing Falls in older people living in the community[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2012(9):CD007146. DOI:10.1002/14651858.cd007146.pub3. |
| [56] | IRELAND A, MADEN-WILKINSON T, GANSE B,et al. Effects of age and starting age upon side asymmetry in the arms of veteran tennis players:a cross-sectional study[J]. Osteoporos Int,2014,25(4):1389-1400. DOI:10.1007/s00198-014-2617-5. |
| [57] | WALSTON J, MCBURNIE M A, NEWMAN A,et al. Frailty and activation of the inflammation and coagulation systems with and without clinical comorbidities:results from the Cardiovascular Health Study[J]. Arch Intern Med,2002,162(20):2333-2341. DOI:10.1001/archinte.162.20.2333. |
| [58] | KOJIMA G, ILIFFE S, TANIGUCHI Y,et al. Prevalence of frailty in Japan:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Epidemiol,2017,27(8):347-353. DOI:10.1016/j.je.2016.09.008. |
| [1] | XU Jialan, YAN Hong, WEN Jun, ZHOU Zitong, WANG Siyu. Prevalence of Potentially Inappropriate Medication in Older Adults with Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | LI Ling, LI Yaping, QIAN Shixing, NIE Jing, LU Chunhua, LI Xia. Research on Influencing Factors and Risk Prediction of Cognitive Function in Community-dwelling Middle-aged and Elderly People [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | CHENG Yuxin, FANG Jiamin, LIANG Hao, WANG Zhiling, WEI Li, LIAO Huilian, XU Mingming, CHEN Yumei, LI Yanfen, DONG Lijuan, GUO Yingui. Preoperative Platelet-to-albumin Ratio in Elective Geriatric Surgery Patients and Its Correlation with Postoperative Incidental Frailty: a Multicenter Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3359-3367. |
| [4] | HU Jieman, TAN Feixiang, YUAN Anxin, CHEN Shiyu, TANG Chulei, YIN Yueheng, BA Lei, XU Qin. Analysis of the Trajectory of Postoperative Frailty and Influencing Factors in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [5] | YU Wenhua, LI Jianguo, DUAN Wenyan, GAO Xuyan, LI Xiaxia, ZHANG Zilong, ZHANG Li, MA Lina. Reliability and Validity of the Function Impairment Screening Tool among Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [6] | YANG Chen, CHEN Tong, ZHANG Lifang, ZHANG Hongxu, LI Pengfei, ZHANG Xuejuan. Prognostic Impact of Dapagliflozin in Elderly Breast Cancer Survivors with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [7] | LI Jiaxin, LIU Zhonghui, XIE Shuo, FU Zhifang, SUN Dan, JIAO Hongmei. Trajectory in Biomarkers of Metabolic and Inflammatory States as Early Predictors of Chronic Critical Illness in Aging Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2993-2999. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xiaoqing, GUO Tongtong, ZHANG Xinyi, LI Linhong, ZHANG Ya, JI Lihong, DONG Zhiwei, GAO Qianqian, CAI Weiqing, ZHENG Wengui, JING Qi. Construction and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Cognitive Impairment in Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [9] | SHI Xiaotian, WANG Shan, YANG Huayu, YANG Yifan, LI Xu, MA Qing. Association between Body Mass Index and Mortality among Older Chinese: a Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2791-2797. |
| [10] | LIU Meixia, YIN Jinnian, WU Mei, YANG Xing, ZHOU Quanxiang, YANG Jingyuan. Impact of Body Mass Index on the Association of Triglyceride Glucose Index with Cognitive Function: a Cross-sectional Study in Rural Older Adults in Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2806-2812. |
| [11] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Ziying, JIN Aiqiong, TANG Lingling, ZHENG Zique, MA Jingtai, ZHAO Jianguo, ZENG Weilin, XIAO Jianpeng, NIE Hui, YANG Ying. Analysis of Factors Influencing Avoidable Hospitalization for Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [12] | CHEN Qiaoqiao, SU Ping, ZHAO Yingying, PANG Jinhong, SHI Jie, WANG Yaqian, LI Qiuchun, HE Ruiyan, WANG Yue, CHEN Xueyu, QIAO Junpeng, CHI Weiwei. Association between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Incident Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity in the Elderly: a Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2270-2277. |
| [13] | JIANG Xiaoman, XU Xinyi, DING Lingyu, GUO Yinning, MIAO Xueyi, CHEN Li, XU Qin. Clinical Characteristics and Correlation between Preoperative Frailty and Metabolic Syndrome among Older Patients with Gastric Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2134-2141. |
| [14] | WANG Biqing, ZHANG Ping, YANG Hongxia, WANG Qian, JU Chunxiao, ZHAO Junnan, MEI Jun, ZHANG Ying, XU Fengqin. Meta-analysis of Prevalence and Development Trend of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hypertensive Patients in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2186-2192. |
| [15] | LIU Yuting, QIU Lixia, LI Yuling. Impact of Frailty on Cognitive Function in Chinese Older Adults: a Moderated Chain-mediated Effect [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2119-2126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||