

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (09): 1113-1118.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.128
Special Issue: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 心血管最新文章合辑
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Department of Endocrinology,Beijing Friendship Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100050,China
*Corresponding author:YUAN Mingxia,Professor,Chief physician;E-mail:mx.yuan@ccmu.edu.cn
Received:2021-10-15
Revised:2021-12-07
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2022-03-01
通讯作者:
袁明霞
CLC Number:
ZHAO Lei, LI Ruqiang, YUAN Mingxia.
Association between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(09): 1113-1118.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.128
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(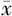 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 性别(男/女) | 糖尿病病程(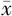 ±s,年) ±s,年) | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 高血压病史〔n(%)〕 | 血脂异常病史〔n(%)〕 | BMI(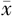 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | SBP(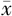 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP(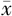 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 435 | 53.2±8.1 | 221/214 | 7.2±2.5 | 67(15.4) | 141(32.4) | 230(52.9) | 24.7±2.2 | 137±13 | 83±10 |
| DCAN组 | 129 | 54.5±7.4 | 66/63 | 9.3±1.9 | 45(34.9) | 52(40.3) | 85(65.9) | 25.0±2.2 | 136±11 | 73±13 |
| t(χ2)值 | -1.678 | 0.005a | -9.839 | 23.727a | 2.756a | 6.838a | -1.355 | 1.460 | 7.958 | |
| P值 | 0.094 | 0.943 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.097 | <0.001 | 0.176 | 0.145 | <0.001 |
Table 1 Comparison of general data and physical examination indices between type 2 diabetics with and without cardiac autonomic neuropathy
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(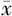 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 性别(男/女) | 糖尿病病程(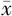 ±s,年) ±s,年) | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 高血压病史〔n(%)〕 | 血脂异常病史〔n(%)〕 | BMI(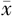 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | SBP(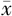 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | DBP(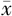 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 435 | 53.2±8.1 | 221/214 | 7.2±2.5 | 67(15.4) | 141(32.4) | 230(52.9) | 24.7±2.2 | 137±13 | 83±10 |
| DCAN组 | 129 | 54.5±7.4 | 66/63 | 9.3±1.9 | 45(34.9) | 52(40.3) | 85(65.9) | 25.0±2.2 | 136±11 | 73±13 |
| t(χ2)值 | -1.678 | 0.005a | -9.839 | 23.727a | 2.756a | 6.838a | -1.355 | 1.460 | 7.958 | |
| P值 | 0.094 | 0.943 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.097 | <0.001 | 0.176 | 0.145 | <0.001 |
| 例数 | 例数 | HbA1c(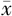 ±s,%) ±s,%) | FBG(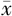 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | hs-CRP(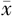 ±s,mg/L) ±s,mg/L) | TC(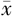 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TG(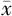 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C(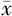 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | HDL-C〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 435 | 8.22±0.29 | 7.50±0.32 | 1.14±0.73 | 5.08±0.35 | 1.21±0.24 | 2.34±0.03 | 0.83(0.70,0.90) |
| DCAN组 | 129 | 8.91±0.41 | 9.90±0.47 | 1.29±0.70 | 5.47±0.72 | 1.18±0.30 | 2.55±0.18 | 0.82(0.70,0.90) |
| t(Z)值 | -17.363 | -54.346 | -2.114 | -5.989 | 1.045 | -13.181 | 0.806a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.035 | <0.001 | 0.297 | <0.001 | 0.420 |
Table 2 Comparison of biochemical indices between type 2 diabetics with and without cardiac autonomic neuropathy
| 例数 | 例数 | HbA1c(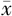 ±s,%) ±s,%) | FBG(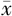 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | hs-CRP(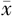 ±s,mg/L) ±s,mg/L) | TC(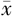 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | TG(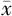 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C(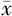 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | HDL-C〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 435 | 8.22±0.29 | 7.50±0.32 | 1.14±0.73 | 5.08±0.35 | 1.21±0.24 | 2.34±0.03 | 0.83(0.70,0.90) |
| DCAN组 | 129 | 8.91±0.41 | 9.90±0.47 | 1.29±0.70 | 5.47±0.72 | 1.18±0.30 | 2.55±0.18 | 0.82(0.70,0.90) |
| t(Z)值 | -17.363 | -54.346 | -2.114 | -5.989 | 1.045 | -13.181 | 0.806a | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.035 | <0.001 | 0.297 | <0.001 | 0.420 |
| 变量 | r(rs)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -0.059 | 0.879 |
| 糖尿病病程 | -0.222 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.031 | 0.417 |
| SBP | -0.011 | 0.561 |
| DBP | 0.227 | 0.004 |
| HbA1c | -0.437 | <0.001 |
| FBG | -0.426 | <0.001 |
| hs-CRP | -0.139 | 0.001 |
| TC | -0.165 | <0.001 |
| TG | -0.021 | 0.456 |
| LDL-C | -0.315 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C | 0.134a | 0.425 |
| TSH | -0.285a | <0.001 |
| UACR | -0.280a | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.059 | 0.429 |
Table 3 Correlation analysis of the ratio between maximum and minimum R-R intervals during the Valsalva maneuver with demographic and biochemical indices in type 2 diabetics
| 变量 | r(rs)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -0.059 | 0.879 |
| 糖尿病病程 | -0.222 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.031 | 0.417 |
| SBP | -0.011 | 0.561 |
| DBP | 0.227 | 0.004 |
| HbA1c | -0.437 | <0.001 |
| FBG | -0.426 | <0.001 |
| hs-CRP | -0.139 | 0.001 |
| TC | -0.165 | <0.001 |
| TG | -0.021 | 0.456 |
| LDL-C | -0.315 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C | 0.134a | 0.425 |
| TSH | -0.285a | <0.001 |
| UACR | -0.280a | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.059 | 0.429 |
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸烟 | 1.079 | 0.228 | 22.499 | <0.001 | 2.942 | (1.884,4.596) |
| 血脂异常病史 | 0.543 | 0.209 | 6.754 | 0.009 | 1.722 | (1.143,2.594) |
| DBP | 0.203 | 0.116 | 3.072 | 0.080 | 1.225 | (0.976,1.537) |
| LDL-C | 0.389 | 0.040 | 96.360 | <0.001 | 1.475 | (1.365,1.594) |
| hs-CRP | 0.144 | 0.072 | 3.960 | 0.047 | 1.155 | (1.002,1.331) |
| SCH | 1.140 | 0.250 | 20.857 | <0.001 | 3.126 | (1.917,5.097) |
| 常量 | -3.449 | 1.306 | 6.972 | 0.008 | 0.032 | (0.000,0.410) |
Table 4 Multivariate stepwise Logistic regression analysis results of factors possibly associated with cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸烟 | 1.079 | 0.228 | 22.499 | <0.001 | 2.942 | (1.884,4.596) |
| 血脂异常病史 | 0.543 | 0.209 | 6.754 | 0.009 | 1.722 | (1.143,2.594) |
| DBP | 0.203 | 0.116 | 3.072 | 0.080 | 1.225 | (0.976,1.537) |
| LDL-C | 0.389 | 0.040 | 96.360 | <0.001 | 1.475 | (1.365,1.594) |
| hs-CRP | 0.144 | 0.072 | 3.960 | 0.047 | 1.155 | (1.002,1.331) |
| SCH | 1.140 | 0.250 | 20.857 | <0.001 | 3.126 | (1.917,5.097) |
| 常量 | -3.449 | 1.306 | 6.972 | 0.008 | 0.032 | (0.000,0.410) |
| [1] | SPALLONE V,ZIEGLER D,FREEMAN R,et al. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes:clinical impact,assessment,diagnosis,and management[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2011,27(7):639-653. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.1239. |
| [2] | YANG W,LU J,WENG J,et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China[J]. N Engl J Med,2010,362(12):1090-1101. DOI:10.1056/nejmoa0908292. |
| [3] | VALENSI P,PARIÈS J,ATTALI J R,et al. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetic patients:influence of diabetes duration,obesity,and microangiopathic complications——the French multicenter study[J]. Metabolism,2003,52(7):815-820. DOI:10.1016/s0026-0495(03)00095-7. |
| [4] | YANG J K,LIU W,SHI J,et al. An association between subclinical hypothyroidism and sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Diabetes Care,2010,33(5):1018-1020. DOI:10.2337/dc09-1784. |
| [5] | ALBERTI K G,ZIMMET P Z. Definition,diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1:diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation[J]. Diabet Med,1998,15(7):539-553. DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539:AID-DIA668>3.0.CO;2-S. |
| [6] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国),中华医学会心血管病学分会中国医师协会高血压专业委员会,等. 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002. |
| [7] | 中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001. |
| [8] | 中华医学会内分泌学分会《中国甲状腺疾病诊治指南》编写组. 甲状腺疾病诊治指南——甲状腺功能减退症[J]. 中华内科杂志,2007,46(11):967-971. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0578-1426.2007.11.032. |
| [9] | LEVEY A S,STEVENS L A,SCHMID C H,et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J]. Ann Intern Med,2009,150(9):604-612. DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006. |
| [10] | BOULTON A J M,VINIK A I,AREZZO J C,et al. Diabetic neuropathies:a statement by the American Diabetes Association[J]. Diabetes Care,2005,28(4):956-962. DOI:10.2337/diacare.28.4.956. |
| [11] | 陈崇鑫,余萌,杨征,等. 2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白指数与糖尿病心脏自主神经病变的相关性研究[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(3):238-244. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20200827-00538. |
| [12] | 张晓宇,郭杏苑,张舒婷,等. 基于Ewing试验的心率变异性分析对2型糖尿病患者心脏自主神经病变诊断的临床价值研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2021,29(3):161-167. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006?6187.2021.03.001. |
| [13] | SERHIYENKO V A,SERHIYENKO A A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy:Risk factors,diagnosis and treatment[J]. World J Diabetes,2018,9(1):1-24. DOI:10.4239/wjd.v9.i1.1. |
| [14] | OATES P J. Polyol pathway and diabetic peripheral neuropathy[J]. Int Rev Neurobiol,2002,50:325-392. DOI:10.1016/s0074-7742(02)50082-9. |
| [15] | BAYNES J W,THORPE S R. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications:a new perspective on an old paradigm[J]. Diabetes,1999,48(1):1-9. DOI:10.2337/diabetes.48.1.1. |
| [16] | EDWARDS J L,VINCENT A M,CHENG H T,et al. Diabetic neuropathy:mechanisms to management[J]. Pharmacol Ther,2008,120(1):1-34. DOI:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.05.005. |
| [17] | BRAFFETT B H,GUBITOSI-KLUG R A,ALBERS J W,et al. Risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications (DCCT/EDIC) study[J]. Diabetes,2020,69(5):1000-1010. DOI:10.2337/db19-1046. |
| [18] | SPALLONE V,ZIEGLER D,FREEMAN R,et al. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes:clinical impact,assessment,diagnosis,and management[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2011,27(7):639-653. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.1239. |
| [19] | CHEN H S,WU T E,JAP T S,et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism is a risk factor for nephropathy and cardiovascular diseases in Type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Diabet Med,2007,24(12):1336-1344. DOI:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02270.x. |
| [20] | MARATOU E,HADJIDAKIS D J,KOLLIAS A,et al. Studies of insulin resistance in patients with clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism[J]. Eur J Endocrinol,2009,160(5):785-790. DOI:10.1530/EJE-08-0797. |
| [21] | CEBECI E,ALIBAZ-ONER F,USTA M,et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress,the activities of paraoxonase and arylesterase in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism[J]. J Investig Med,2012,60(1):23-28. DOI:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31823581dd. |
| [22] | CAPPOLA A R,LADENSON P W. Hypothyroidism and atherosclerosis[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2003,88(6):2438-2444. DOI:10.1210/jc.2003-030398. |
| [23] | GORSKA-CIEBIADA M,CIEBIADA M. Association of hsCRP and vitamin D levels with mild cognitive impairment in elderly type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Exp Gerontol,2020,135:110926. DOI:10.1016/j.exger.2020.110926. |
| [1] | HU Jieman, TAN Feixiang, YUAN Anxin, CHEN Shiyu, TANG Chulei, YIN Yueheng, BA Lei, XU Qin. Analysis of the Trajectory of Postoperative Frailty and Influencing Factors in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [2] | CHOU Xintong, PENG Hanyu, MA Hui, ZHANG Zhen, SU Xian, QIU Hongyan. Maternal Preferences in Contraceptive Decision-making: an Analysis of Influencing Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [3] | WEI Jiaohua, PENG Huiru, PENG Jianye, TAN Wenting, HUANG Jine, FANG Li. Expression of the Serum MOTS-c and Its Correlation with Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [4] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [5] | FAN Boyang, ZHANG Yu, SUN Wenning, ZHANG Huifang, WANG Yingjie, ZHANG Ao, ZHAO Yang, WANG Haipeng. Study of Behavioral Intention and Influencing Factors of Integrated Medical and Preventive Care Provided by Grassroots Doctors for Patients with Chronic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [6] | WANG Rupeng, NAN Jing, HU Yiran, YANG Shenghua, JIN Zening. Predictive Value of the Triglyceride-Glucose Body Mass Index for Slow Flow/No-reflow Phenomenon in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Acute Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [7] | WU Yue, WANG Xuetong, KE Bilian. Evaluation of Vision-related Quality of Life in Myopic Macular Degeneration Patients with Low Vision and Associated Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [8] | DING Zijun, ZHOU Nannan, LUO Xing, LUO Jieyu, HAO Wenjuan, ZHANG Chunjiang, JIN Xin, ZHAO Dan. Cognitive Impairment in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis and Its Influencing Factors: a Multicenter Cross-sectional Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2885-2893. |
| [9] | WEI Xiaoxia, CHEN Nuo, WANG Juanjuan, ZHU Jingfen. The Effects of Depression and Anxiety on Smoking Behavior among Vocational School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2826-2832. |
| [10] | ZHAO Xiaoqing, GUO Tongtong, ZHANG Xinyi, LI Linhong, ZHANG Ya, JI Lihong, DONG Zhiwei, GAO Qianqian, CAI Weiqing, ZHENG Wengui, JING Qi. Construction and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Cognitive Impairment in Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [11] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Ziying, JIN Aiqiong, TANG Lingling, ZHENG Zique, MA Jingtai, ZHAO Jianguo, ZENG Weilin, XIAO Jianpeng, NIE Hui, YANG Ying. Analysis of Factors Influencing Avoidable Hospitalization for Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [12] | JING Tao, DAI Yongmei, LUO Jianying, LUO Wei, JI Yelinfan, PENG Chi, ZHANG Cuijun, CAO Yanjun, ZHENG Qing, HUANG Yu, SHEN Hejun. The Body Mass Index, Dietary Knowledge Acquisition Level, Sedentary Time and Influencing Factors among Chinese High School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2025-2032. |
| [13] | HUANG Zhijie, MAI Zhihua, WANG Haoxiang, HE Yuming, DENG Qiaoyan, DAI Ranran, ZHOU Zhiheng. Multimorbidity of Hypertension, Diabetes, and Dyslipidemia and Influencing Factors of Family Function among the Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2001-2010. |
| [14] | ZHAO Can, SHEN Ying, XI Qian, PENG Houxuan, QIN Jinqiong, WANG Xuan, ZHENG Yanping, QIN Li, ZUO Yanli. The Hospitalization Spending and Associated Factors in Inpatients with Multimorbidity in Township Health Centers in Guangxi [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2039-2049. |
| [15] | SHENG Jingyu, LIU Fanfan, MA Mei, TIAN Lin, LIU Yutong, LIU Fengmin, GAO Shan, YU Chunquan. Association between Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(15): 1831-1839. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||